Risk factors
Authors of a retrospective cohort study found that patients with prior diagnosis of a chronic pain syndrome, low back pain, headaches, or fibromyalgia were 5 to 6 times more likely to report acute and chronic pain after hysteroscopic sterilization with Essure.11 Since chronic pain is often thought to be driven by a hyperalgesic state of the central nervous system, as previously shown in patients with conditions such as vulvodynia, interstitial cystitis, and fibromyalgia,12 a hyperalgesic state can potentially explain why some patients are more susceptible to developing worsening pain.
Van Limburg and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study with prospective follow-up on 284 women who underwent Essure sterilization. Among these patients, 48% reported negative AEs; risk factors included young age at placement, increasing gravidity, and no prior abdominal surgery.13
Onset of pain
The timing and onset of pelvic pain vary widely, suggesting there is no particular time frame for this AE after device placement.2,6,14-18 A case series by Arjona and colleagues analyzed the incidence of chronic pelvic pain in 4,274 patients after Essure sterilization. Seven patients (0.16%) reported chronic pelvic pain that necessitated device removal. In 6 of the women, the pelvic pain began within 1 week of device placement. In 3 of the 6 cases, the surgeon reported the removal procedures as “difficult.” In all 6 cases, the level of pelvic pain increased with time and was not alleviated with standard analgesic medications.6
In another case series of 26 patients, the authors evaluated patients undergoing laparoscopic removal of Essure secondary to pelvic pain and reported that the time range for symptom presentation was immediate to 85 months. Thirteen of 26 patients (50%) reported pain onset within less than 1 month of device placement, 5 of 26 patients (19.2%) reported pain between 1 and 12 months after device placement, and 8 of 26 patients (30.8%) reported pain onset more than 12 months after microinsert placement.2 In this study, 17.2% of operative reports indicated difficulty with device placement. It is unclear whether difficulty with placement was associated with development of subsequent abdominal or pelvic pain; however, the relevance of initial insertion difficulty diminished with longer follow-up.
Workup and evaluation
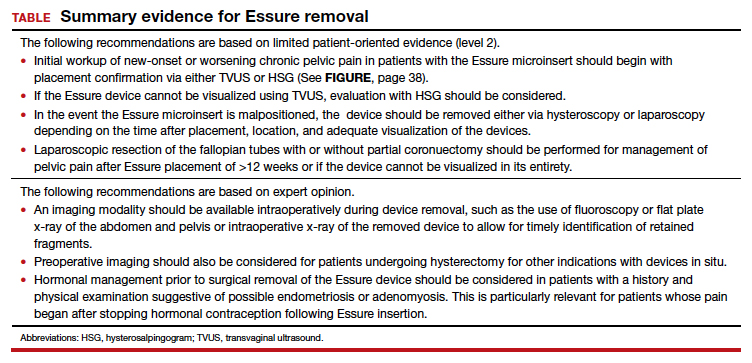
We found 5 studies that provided some framework for evaluating a patient with new-onset or worsening pelvic pain after microinsert placement. Overall, correct placement and functionality of the device should be confirmed by either hysterosalpingogram (HSG) or transvaginal ultrasonography (TVUS). The gold standard to determine tubal occlusion is the HSG. However, TVUS may be a dependable alternative, and either test can accurately demonstrate Essure location.19 Patients often prefer TVUS over HSG due to the low cost, minimal discomfort, and short examination time.1 TVUS is a noninvasive and reasonable test to start the initial assessment. The Essure devices are highly echogenic on pelvic ultrasound and easily identifiable by the proximity of the device to the uterotubal junction and its relationship with the surrounding soft tissue. If the device perforates the peritoneal cavity, then the echogenic bowel can impede adequate visualization of the Essure microinsert. If the Essure insert is not visualized on TVUS, an HSG will not only confirm placement but also test insert functionality. After confirming correct placement of the device, the provider can proceed with standard workup for chronic pelvic pain.
If one or more of the devices are malpositioned, the devices are generally presumed to be the etiology of the new pain. Multiple case reports demonstrate pain due to Essure misconfiguration or perforation with subsequent resolution of symptoms after device removal.18,20,21 A case study by Alcantara and colleagues described a patient with chronic pelvic pain and an Essure coil that was curved in an elliptical shape, not adhering to the anatomic course of the fallopian tube. The patient reported pain resolution after laparoscopic removal of the device.20 Another case report by Mahmoud et al described a subserosal malpositioned device that caused acute pelvic pain 4 months after sterilization. The patient reported resolution of pain after the microinsert was removed via laparoscopy.21 These reports highlight the importance of considering malpositioned devices as the etiology of new pelvic pain after Essure placement.
Continue to: Device removal and patient outcomes...