Growth of URiM physicians in ObGyn
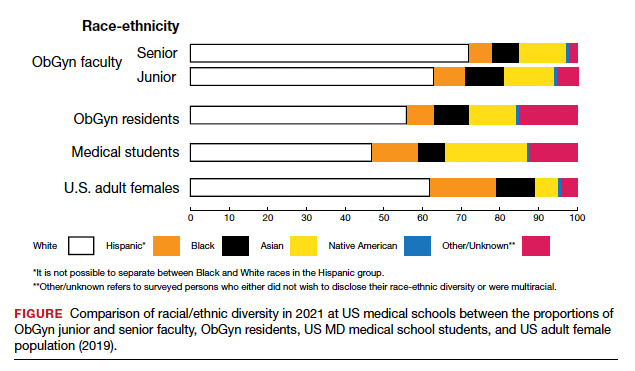
The distribution of racial/ethnic groups in 2021 were compared between senior and junior ObGyn faculty and residents with the US adult female population.9 As shown in the FIGURE, the proportion of ObGyn faculty who are White approximates the White US adult female population. The most rapidly growing racial/ethnic group in the US population is Hispanic. Although Hispanic is the best represented ethnicity among junior faculty, the proportions of Hispanics among faculty and residents lag well behind the US population. The proportion of ObGyn faculty who are Black has consistently been less than in the US adult female population. ObGyns who are Asian constitute higher proportions of faculty and residents than in the US adult female population. This finding about Asians is consistent across all clinical specialties.7
Recruiting URiM students into ObGyn is important. Racial and ethnic representation in surgical and nonsurgical residency programs has not substantially improved in the past decade and continues to lag the changing demographics of the US population.10 More students than residents and faculty are Hispanic, which represents a much-needed opportunity for recruitment. By contrast, junior ObGyn faculty are more likely to be Black than residents and students. Native Americans constitute less than 1% of all faculty, residents, students, and US adult females.9 Lastly, race/ethnicity being self-reported as “other” or “unknown” is most common among students and residents, which perhaps represents greater diversity.
Looking back
Increasing diversity in medicine and in ObGyn has not happened by accident. Transformational change requires rectifying any factors that detrimentally affect the racial/ethnic diversity of our medical students, residents, and faculty. For example, biases inherent in key residency application metrics are being recognized, and use of holistic review is increasing. Change is also accelerated by an explicit and public commitment from national organizations. In 2009, the Liaison Committee of Medical Education (LCME) mandated that medical schools engage in practices that focus on recruitment and retention of a diverse workforce. Increases in Black and Hispanic medical students were noted after implementation of this new mandate.16 The ACGME followed suit with similar guidelines in 2019.10
Diversity is one of the foundational strengths of the ObGyn specialty. Important aspects of the specialty are built upon the contributions of women of color, some voluntary and some not. One example is the knowledge of gynecology that was gained through the involuntary and nonanesthetized surgeries performed on Anarcha Westcott.17 Beyond that painful legacy, several Black physicians re-shaped our specialty, including Helen Octavia Dickens, MD, the first Black woman to receive ObGyn board certification, and Georgia Rooks Dwelled, MD, who established the first obstetrical “lying-in” hospital for African American women in Atlanta.18 Similarly, Helen Rodriguez-Trias, MD, was one of the most important advocates for the passage of the 1973 national guideline that established the requirement for a woman’s written consent for sterilization.18 Guarding and enhancing the legacy of diversity in ObGyn will require intentionality on all our parts.
Moving forward
Advancing diversity in ObGyn offers advantages: better representation of patient populations, improving public health by better access to care, enhancing learning in medical education, building more comprehensive research agendas, and driving institutional excellence. While progress has been made, significant work is still to be done. We must continue to critically examine the role of biases and structural racism that are embedded in evaluating medical students, screening of residency applicants, and selecting and retaining faculty. In future work, we should explore the hypothesis that continued change in racial/ethnic diversity of faculty will only occur once more URiM students, especially the growing number of Hispanics, are admitted into medical schools and recruited for residency positions. We should also examine whether further diversity improves patient outcomes.
It is encouraging to realize that ObGyn departments are leaders in racial/ethnic diversity at US medical schools. It is also critical that the specialty commits to the progress that still needs to be made, including increasing diversity among faculty and institutional leadership. To maintain diversity that mirrors the US adult female population, the specialty of ObGyn will require active surveillance and continued recruitment of Black and, especially Hispanic, faculty and residents.19 The national strategies aimed at building medical student and residency diversity are beginning to yield results. For those gains to help faculty diversity, institutional and departmental leaders will need to implement best practices for recruiting, retaining, and advancing URiM faculty.19 Those practices would include making workforce diversity an explicit priority, building diverse applicant pools, and establishing infrastructure and mentorship to advance URiM faculty to senior leadership positions.20
In conclusion
Building a physician workforce that is more representative of the US population should aid in addressing inequalities in health and health care. Significant strides have been made in racial/ethnic diversity in ObGyn. This has resulted in a specialty that is among the most diverse in academic medicine. At the same time, there is more work to be done. For example, the specialty is far from reaching racial equity for Hispanic physicians. Also, continued efforts are necessary to advance URiM faculty to leadership positions. The legacy of racial/ethnic diversity in ObGyn did not happen by accident and will not be maintained without intention. ●