Medicolegal Issues

Eight tools for improving obstetric patient safety and unit performance
Building a comprehensive obstetric patient safety program for your unit
Deborah Reale, Managing Editor

Researchers also ask, “Can a state birth injury fund reduce malpractice rates?”
Over the last 20 years, litigation rates, malpractice coverage costs, and the number of cesarean deliveries have increased significantly. In fact, many ObGyns have dropped their obstetric practices because of the increased cost of malpractice insurance, say researchers from Johns Hopkins and Brown, and three states (New York, Florida, and Virginia) now have birth injury funds to help deflect the burden of malpractice insurance and litigation costs.1
What is the existing state-level relationship between malpractice rates and the mode of delivery, including cesarean delivery (CD) and vaginal delivery (VD), as well as operative vaginal delivery (OVD)? And how do the state-run injury funds affect this relationship, asked Clark T. Johnson, MD, MPH, and Erika F. Werner, MD.
To answer their question, the investigators collected 8 years of data on mode of delivery (from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Vital Statistics System) and malpractice rates for ObGyns in each US state (from the 2011 Medical Liability Monitor Rate Survey). The researchers used linear regression modeling to analyze their 2003−2010 data.1
They found that states with higher malpractice rates had higher CD delivery rates and lower VD rates than states with lower malpractice rates, and that higher malpractice rates also correlated with lower rates of OVD, including the use of forceps and vacuum extraction. Overall, the change in malpractice rates between 2003 and 2010 did not correlate with the rates of OVD.1
Those states with the highest average annual malpractice insurance rate (> $120,000) to cover claims with a cap of $1 million/$3 million in 2010, were Florida, New York, and Connecticut. Illinois, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Maryland had an average annual rate of $100,000 to $120,000.
Those states with the lowest average annual malpractice insurance rate (0$ to $40,000) were North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Minnesota, Iowa, and Wisconsin.
In the 1980s, medical malpractice insurance rates soared and insurance companies were faced with eliminating coverage to obstetricians. In 1987, the Virginia General Assembly developed the Virginia Birth-Related Neurological Injury Compensation Program. This no-fault system ensures lifetime care to eligible participants, and has successfully stabilized the malpractice environment in the state.2 Birth-related neurologic injury funds were also created in Florida in 19883 and in New York in 2011.4
The three states with birth injury funds showed a decrease in malpractice rates, a slower rate of CD-rate increase, and an OVD-rate decrease. However, the researchers note that while developing a state birth injury fund is seen as a trend that might reduce malpractice rates, there were not enough data to demonstrate significance.1

Building a comprehensive obstetric patient safety program for your unit
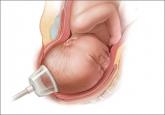
New data confirm that the combination of forceps and vacuum extraction should be avoided and demonstrate that use of midcavity rotational forceps...
A communication–trust–shared responsibility triad established at the first prenatal visit is your best hedge against allegation of malpractice...
