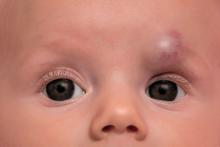
according to a study published in Pediatric Dermatology.
Diana B. Mannschreck, BSN, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues performed a retrospective chart review of 559 patients with infantile hemangioma seen in the dermatology clinic at Johns Hopkins between December 2008 and January 2018. Patients received any of five courses of treatment, including oral propranolol followed by topical timolol, propranolol only, and timolol only. Of the courses evaluated, propranolol followed by timolol had the shortest duration of propranolol therapy – a median of 2.2 months shorter than propranolol-only therapy (P = .0006). This sequential regimen also was associated with no reinitiations of propranolol therapy following tapering, whereas 13% of those receiving propranolol alone had to reinitiate it after tapering.
This is of interest because oral beta-blockers, including propranolol, have been associated with rare but serious adverse events, such as bronchospasm, hypotension, and hypoglycemia.
Limitations of the study include its retrospective and single-center nature. There was no funding or disclosure information given.
SOURCE: Mannschreck DB et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Apr 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.13816.