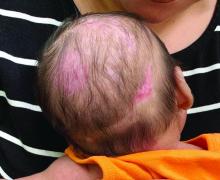
With the perinatal history of prolonged labor and prolonged rupture of membranes, the diagnosis of halo scalp ring was made. This occurs secondary to prolonged pressure of the baby’s scalp with the mother’s pelvic bones, uterus, or cervical area, which causes decreased blood flow to the area, secondary ischemic damage, and in some cases scarring and hair loss.1
The degree of involvement is variable as some babies have mild alopecia and others have severe full-thickness necrosis and scarring. These lesions also can present with associated caput succedaneum and scalp molding, but these were not seen in our patient. Predisposing factors for halo scalp ring include caput succedaneum, prolonged or difficult labor, premature or prolonged rupture of membranes, vaginal delivery, vertex presentation, first delivery, as well as prematurity.2 On physical examination, a semicircular patch of alopecia with associated scarring, crusting, or erythema can be seen in some more severe cases.
The differential diagnosis includes aplasia cutis. In aplasia cutis, there is congenital loss of skin on the affected areas. The scalp usually is affected, but these lesions can occur in any other part of the body. Most patients with aplasia cutis have no other findings, but there are cases that can be associated with other cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, or central nervous system abnormalities. Neonatal lupus also can present with scarring lesions on the scalp, but they usually present a little after birth, mainly affecting the face. The mothers of this children usually have a diagnosis of connective tissue disease and may have positive antibodies to Sjögren’s syndrome antibody A, Sjögren’s syndrome antibody B, or antiribonucleoprotein antibody. Seborrheic dermatitis does not cause scarring alopecia. The lesions present as waxy scaly plaques on the scalp, erythematous waxy plaques behind the ears, face, and folds. Some patients can have hair loss secondary to the inflammation, but the hair grows back once the inflammation is controlled. Dissecting cellulitis is a type of scarring alopecia seen in pubescent and adult individuals. No cases of neonatal dissecting cellulitis have been described.
Halo scalp ring is not associated with any other systemic symptoms or syndromes. Extensive imaging and systemic work-up are not required unless the baby presents with other neurologic symptoms. The areas can be treated with petrolatum and observation as most lesions resolve.
In cases of extensive areas of scarring alopecia, referral to a plastic surgeon can be made to consider tissue expanders or scar revision prior to the child starting school if the lesions are causing psychological stressors.
The true prevalence of this condition is unknown. We believe halo ring alopecia is sometimes not diagnosed, and as lesions tend to resolve, most cases go unreported.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010;164(7):673.
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2009 Nov-Dec;26(6):706-8.
3. Dermatol Online J. 2016 Nov 15;22(11).pii:13030/qt7rt592tz.