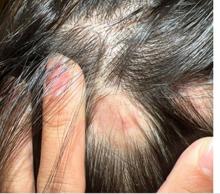
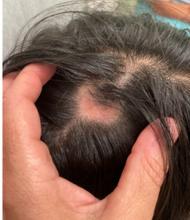
KOH analysis of the scales from the scalp areas revealed no fungal elements. Given the observed erythema and scaling, a punch biopsy was conducted. Histopathological examination of the biopsy sample displayed interface inflammation affecting both the infundibular and lower portions of hair follicles. The presence of folliculosebaceous units transitioning from intermediate to terminal size follicles was noted. A perifollicular, peri eccrine, superficial, and deep perivascular lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate was identified, alongside increased dermal mucin, findings consistent with a diagnosis of discoid lupus erythematosus.
Subsequent laboratory investigations were largely unremarkable, except for an elevated ANA titer (1:320, with a speckled pattern). The patient was initiated on a treatment regimen comprising intralesional triamcinolone and oral hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil).
Discussion
It predominantly affects adults, yet pediatric cases account for 5%-7% of DLE diagnoses, with a significant predominance in females. Pediatric scalp DLE is particularly concerning due to its potential for causing scarring and permanent hair loss, which can significantly impact the psychological wellbeing of affected children.
The pathogenesis of DLE is multifactorial, involving genetic predispositions, environmental factors like UV light exposure, and immunological mechanisms leading to skin damage.
In children, DLE typically presents as well-demarcated, erythematous plaques with scale and follicular plugging, primarily affecting the scalp. Lesions may also exhibit changes in pigmentation, atrophy, and telangiectasia. The scalp involvement often leads to scarring alopecia, which can be distressing for pediatric patients. Unlike systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), DLE is usually limited to the skin without systemic involvement. The progression of DLE to systemic lupus erythematosus in children has been previously described to be 22.2%. In a recent report of 201 pediatric cases of DLE, 12% of the cases progressed to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and 14.5% had concurrent SLE. The onset of symptoms before the age of 10 years was the only statistically significant predictor for progression to SLE. Pruritus is a common symptom and may be correlated with disease activity.
The differential diagnosis for this patient encompassed a variety of conditions, including tinea capitis, alopecia areata, trichotillomania, and lichen planopilaris, each considered based on clinical presentation but ultimately excluded through clinical, microscopic, and biopsy findings.
Management strategies for pediatric scalp DLE aim at preventing disease progression, minimizing scarring, and addressing aesthetic concerns. These include the use of topical and intralesional corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antimalarial agents like hydroxychloroquine, alongside stringent photoprotection to mitigate UV-triggered exacerbations.
Conclusion
The prognosis for pediatric scalp DLE can be favorable with timely and appropriate management, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis and intervention to prevent scarring and hair loss. However, ongoing surveillance is crucial for monitoring potential progression to systemic lupus erythematosus, albeit a low-risk transformation.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
1. George PM and Tunnessen WW. Childhood discoid lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129(5):613-617.
2. Hawat T et al. Pediatric discoid lupus erythematosus: Short report. Dermatol Ther. 2022 Jan;35(1):e15170. doi: 10.1111/dth.15170.
3. Arkin LM et al. Practice-based differences in paediatric discoid lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2019 Oct;181(4):805-810. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17780.