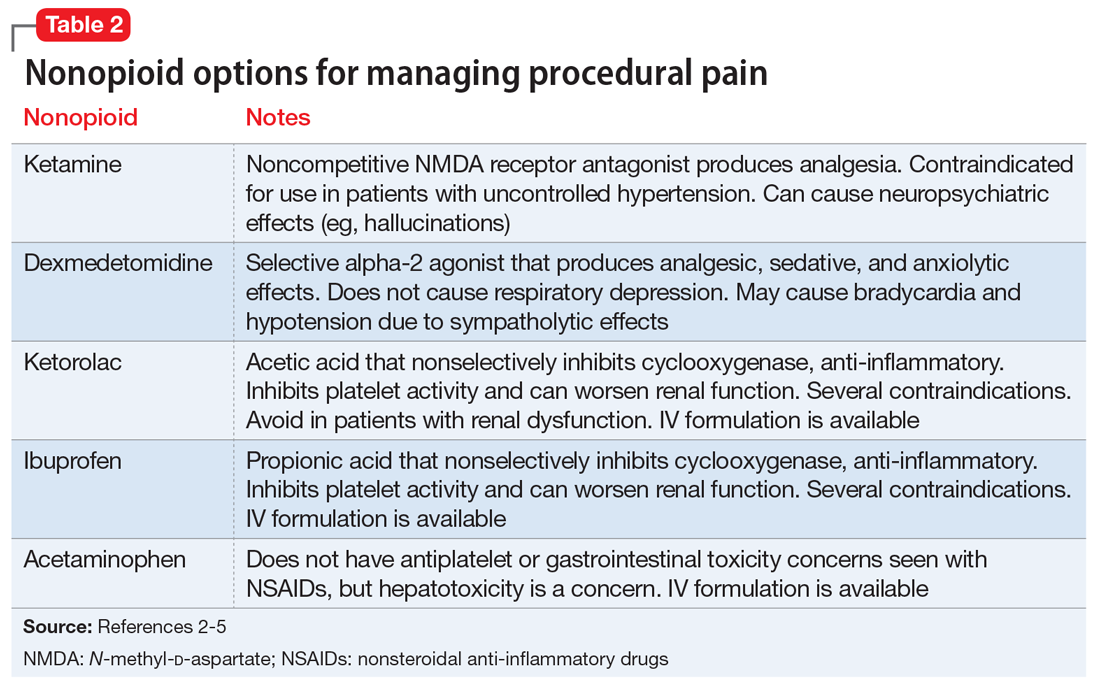
Nonopioid analgesic agents
For a patient receiving naltrexone who needs to undergo a procedure, a multidisciplinary consultation between the patient’s psychiatrist and other clinicians is key for providing a regimen that is safe and effective. A nonopioid analgesic agent may be considered to avoid the problematic interactions possible in these patients (Table 23-5). Nonopioid regimens can be utilized alone or in combination, and may include the following3-5:
Ketamine is a non-competitive antagonist at the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor that can provide sedation and analgesia with a rapid onset and short duration of action. However, analgesics should still be used for patients undergoing procedures that might cause visceral pain. Ketamine is contraindicated for patients with uncontrolled hypertension.
Dexmedetomidine is an alpha-2 agonist that can provide sedative and analgesic effects. It can cause procedural hypotension and bradycardia, so caution is advised in patients with cardiac disease and hepatic and/or renal insufficiencies.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or ketorolac, inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes and can be considered in analgesic regimens. However, for most surgical procedures, the increased risk of bleeding due to platelet inhibition is a concern.
Continue to: Acetaminophen