Almost three-quarters of primary care physicians believe that their patients will take their controlled medications as prescribed, but more than half of drug-monitoring lab tests show signs of misuse, according to a new report from Quest Diagnostics.
“ and may miss some of the drug misuse risks affecting their patients,” report coauthor Harvey W. Kaufman, MD, Quest’s senior medical director, said in a written statement.
Analysis of more than 4.4 million drug-monitoring tests showed that 51% involved an inconsistent result, such as detection of a nonprescribed drug or nondetection of a drug that was prescribed. The report also included a survey of 500 primary care physicians, of whom 72% said they trusted their patents to properly use opioids and other controlled substances.
“The intersection of these two data sets reveals, for the first time, the contrast between physician expectations about patient drug use and the evolution of the drug epidemic and actual patient behavior, as revealed by objective lab data, amid a national drug crisis that claimed an estimated 68,500 lives last year,” the report said.
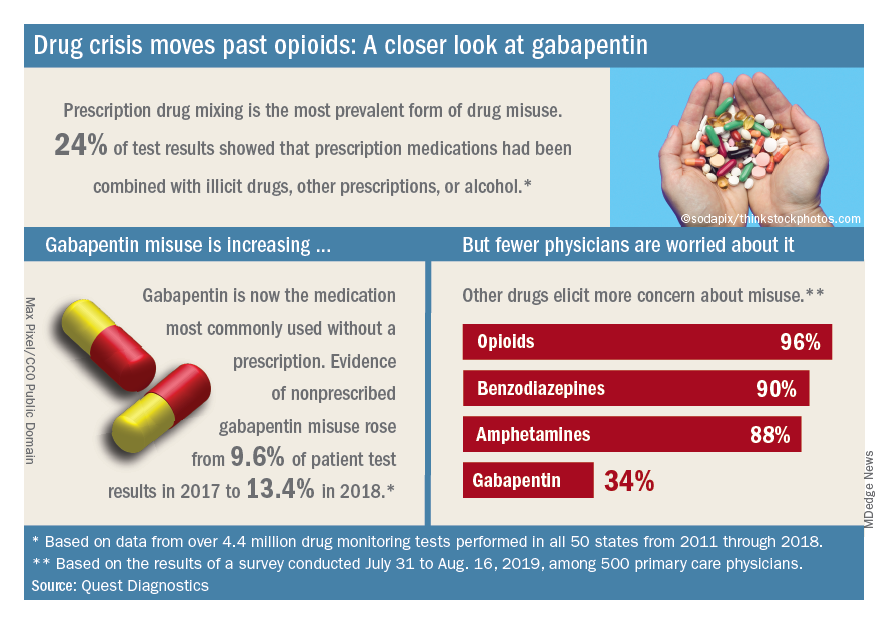
A majority (62%) of the physicians surveyed also said that the opioid crisis will evolve into a new prescription drug crisis, and even more (72%) think that patients with chronic pain will use illicit drugs if they cannot get prescription opioids. Evidence from the drug test dataset suggests that “misuse of nonprescribed fentanyl and nonprescribed gabapentin warrant[s] a closer look,” the report said. In the survey, 78% of respondents reported prescribing gabapentin as an alternative to opioids for patients with chronic pain.
Those two drugs, along with alcohol, are the only three drug groups for which misuse increased from 2017 to 2018, and both are frequently involved in drug mixing, which is the most common form of misuse. Gabapentin went from 9.6% of all nonprescribed misuse in 2017 to 13.4% in 2018, an increase of 40%. Nonprescribed fentanyl was found in 64% of test results that were positive for heroin and 24% that were positive for cocaine, the Quest data showed.
The survey results, however, suggest that gabapentin is not on physicians’ radar, as only 34% said that they were concerned about its misuse, compared with 96% for opioids and 90% for benzodiazepines, according to the report.
“While gabapentin may not have opioids’ addictive potential, it can exaggerate euphoric effects when combined with opioids or anxiety medications. This drug mixing is dangerous,” said report coauthor Jeffrey Gudin, MD, senior medical advisor, prescription drug monitoring, for Quest Diagnostics.
The survey was conducted online among family physicians, general practitioners, and internists from July 31 to Aug. 16, 2019, by the Harris Poll on behalf of Quest and Center for Addiction. The test result data were collected in all 50 states and Washington, D.C., from 2011 to 2018, and results from drug rehabilitation clinics and addiction specialists were excluded from the analysis, so actual misuse rates are probably higher than reported.