Age-adjusted suicide rate rose from 10.5 per 100,000 to 14.2 from 1999 to 2018, according to trends reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in a data brief.
Holly Hedegaard, MD, and colleagues from the National Center for Health Statistics within the CDC analyzed final mortality data from the National Vital Statistics System. As the second most common cause of death among Americans aged 10-34 years and the fourth most common among those aged 35-54 years, suicide is a major contributer to premature mortality.
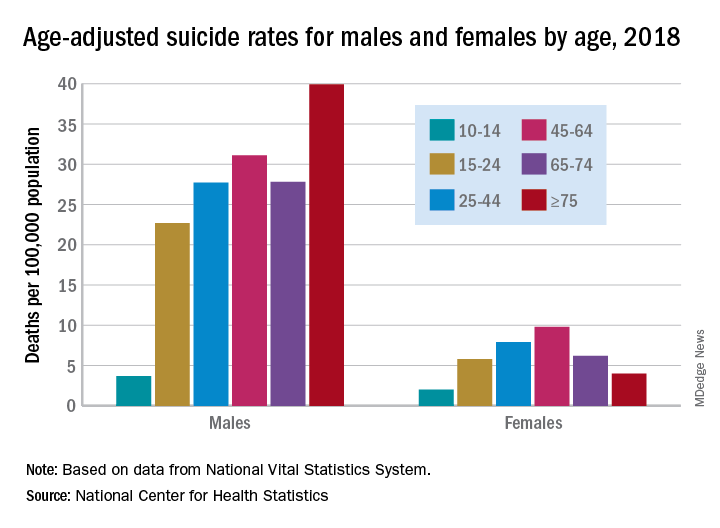
at 22.8 and 6.2 per 100,000, respectively. Young people aged 10-14 years among both genders had the lowest rates of completing suicide, but it was men aged 75 years and older and women aged 45-64 years who had the highest rates. All of these trends were consistent throughout the study period.
Drawing from the 2013 National Center for Health Statistics Urban-Rural Classification Scheme for Counties, the researchers found that rural counties had significantly higher rates of suicide than did urban counties in 2018, and this was true for men and women. That said, suicide rates were still 3.5-3.9 times higher among men than among women regardless of urbanicity or rurality that year.
The full data brief can be found on the CDC website.