“I did not like those patients… They made me angry and I found myself irritated to experience them as they seemed so distant from myself and from all that is human. This is an astonishing intolerance which brands me a poor psychiatrist.”
Sigmund Freud, Letter to István Hollós (1928)
While Freud was referring to psychotic patients,1 his evident frustration shows that difficult and challenging patients have vexed even the best of us. All physicians and other clinicians will experience patient encounters that lead to anger or frustration, or even challenge their sense of equanimity and professional identity. In short, difficult and challenging patient interactions are unavoidable, regardless of the physician’s discipline.2-5 At times, physicians might struggle with demanding, unpleasant, ungrateful, and possibly dangerous patients, while sometimes the struggle is with the patient’s family members. No physician is immune to the problem, which makes it crucial to learn to anticipate and manage difficult patient interactions, skills which are generally not taught in medical schools or residency programs.
One prospective study of clinic patients found that up to 15% of patient encounters are deemed “difficult.”6 Common scenarios include patients (or their relatives) who seek certain tests after researching symptoms online, threats of legal or social media action in response to feeling that the physician is not listening to them, demands for a second opinion after disagreeing with the physician’s diagnosis, and mistrust of doctors after presenting with symptoms and not receiving a diagnosis. It is also common to care for patients who focus on negative outcomes or fail to adhere to treatment recommendations. These encounters can make physicians feel stressed out, disrespected, abused, or even fearful if threatened. Some physicians may come to feel they are trapped in a hostile work environment with little support from their supervisors or administrators. Patients often have a complaint office or department to turn to, but there is no equivalent for physicians, who are expected to soldier on regardless.
This article highlights a model that describes poor physician-patient encounters, factors contributing to these issues, how to manage these difficult interactions, and what to do if the relationship cannot be remediated.
Describing the ‘difficult’ patient
In a landmark 1978 paper, Groves7 provided one of the first descriptions of “difficult” patients. His colorful observations continue to provide useful insights. Groves emphasized that most medical texts ignore the issue of difficult patients and provide little or no guidance—which is still true 43 years later. He observed that physicians cannot avoid occasional negative feelings toward some patients. Further, Groves suggested that countertransference is often at the root of hateful reactions, a process he defines as “conscious or unconscious unbidden and unwanted hostile or sexual feelings toward the patient.”7Table 17 outlines how Groves divided “hateful” patients into several categories, and how physicians might respond to such patients.
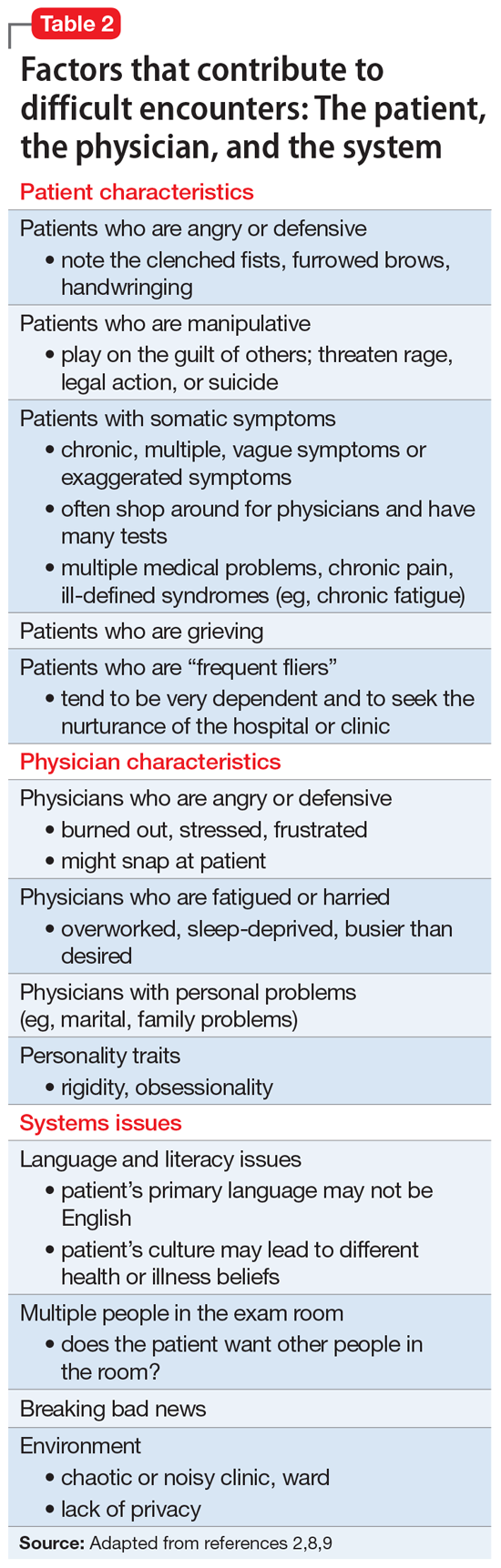
A model for understanding difficult patient encounters
Adams and Murray2 created a model to help explain interactions with difficult or challenging patients that consists of 3 elements: the patient, the physician, and the system (ie, situation or environment). Hull and Broquet8 and Hardavella et al9 later adapted the model and described its components (Table 22,8,9).
Continue to: When considering...