Mr. J, age 23, presents to an outpatient mental health clinic for treatment of anxiety. He has no psychiatric history, is dressed neatly, and recently finished graduate school with a degree in accounting. Mr. J is reserved during the initial psychiatric evaluation and provides only basic facts about his developmental history.
Mr. J comes from a middle-class household with no history of trauma or substance use. He does not report any symptoms consistent with anxiety, but discloses a history of sexual preoccupations. Mr. J says that during adolescence he developed a predilection for observing others engage in sexual activity. In his late teens, he began following couples to their homes in the hope of witnessing sexual intimacy. In the rare instance that his voyeuristic fantasy comes to fruition, he masturbates and achieves sexual gratification he is incapable of experiencing otherwise. Mr. J notes that he has not yet been caught, but he expresses concern and embarrassment related to his actions. He concludes by noting that he seeks help because the frequency of this behavior has steadily increased.
How would you treat Mr. J? Where does the line exist between a normophilic sexual interest, fantasy or urge, and a paraphilia? Does Mr. J qualify as a sexually violent predator?
From The Rocky Horror Picture Show to Fifty Shades of Grey, sensationalized portrayals of sexual deviancy have long been present in popular culture. The continued popularity of serial killers years after their crimes seems in part related to the extreme sexual torture their victims often endure. However, a sexual offense does not always qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1 In fact, many individuals with paraphilic disorders never engage in illegal activity. Additionally, experiencing sexually deviant thoughts alone does not qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1
A thorough psychiatric evaluation should include a discussion of the patient’s sexual history, including the potential of sexual dysfunction and abnormal desires or behaviors. Most individuals with sexual dysfunction do not have a paraphilic disorder.2 DSM-5 and ICD-11 classify sexual dysfunction and paraphilic disorders in different categories. However, previous editions grouped them together under sexual and gender identity disorders. Individuals with paraphilic disorders may not originally present to the outpatient setting for a paraphilic disorder, but instead may first seek treatment for a more common comorbid disorder, such as a mood disorder, personality disorder, or substance use disorder.3
Diagnostically speaking, if individuals do not experience distress or issues with functionality and lack legal charges (suggesting that they have not violated the rights of others), they are categorized as having an atypical sexual interest but do not necessarily meet the criteria for a disorder.4 This article provides an overview of paraphilic disorders as well as forensic considerations when examining individuals with sexually deviant behaviors.
Overview of paraphilic disorders
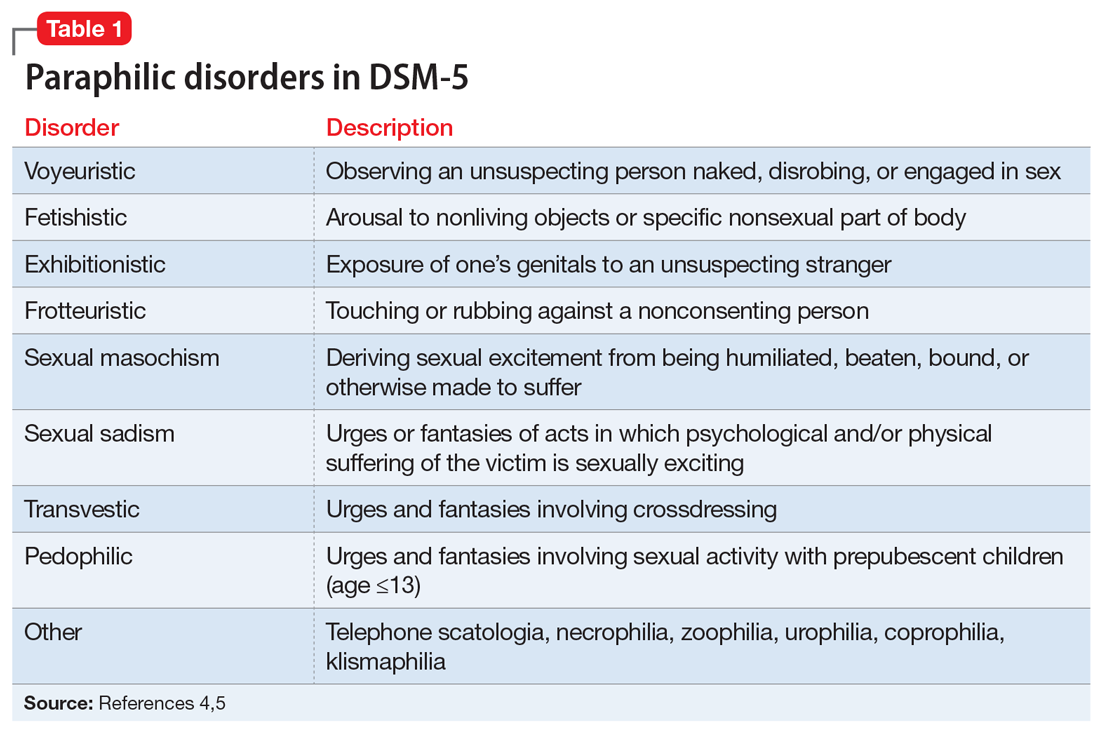
DSM-5 characterizes a paraphilic disorder as “recurrent, intense sexually arousing fantasies, sexual urges, or behaviors generally involving nonhuman objects or nonconsenting partners for at least 6 months. The individual must have acted on the thought and/or it caused clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.” DSM-5 outlines 9 categories of paraphilic disorders, which are described in Table 1.4,5
Continue to: Paraphilic disorders are more common...