New targets
Spironolactone reduced alcohol intake in mice drinking a sweetened alcohol solution; a 2-way ANOVA revealed a main effect of dose (F 4,52 = 9.09; P < .0001) and sex, with female mice drinking more alcohol, compared to male mice (F 1,13 = 6.05; P = .02).
Post hoc comparisons showed that spironolactone at doses of 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg significantly reduced alcohol intake (P values = .007, .002, and .0001, respectively).
In mice drinking an unsweetened alcohol solution, the 2-way repeated measures ANOVA similarly found a main effect of dose (F 4,52 = 5.77; P = .0006), but not of sex (F 1,13 = 1.41; P = .25).
Spironolactone had no effect on the mice’s intake of a sweet solution without alcohol and had no impact on the consumption of food and water or on locomotion and coordination.
In rats, a 2-way ANOVA revealed a significant spironolactone effect of dose (F 3,66 = 43.95; P < .001), with a post hoc test indicating that spironolactone at 25, 50, and 75 mg/kg reduced alcohol self-administration in alcohol-dependent and nondependent rats (all P values = .0001).
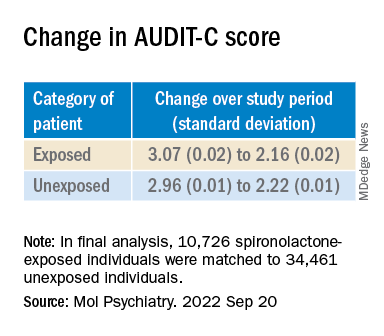
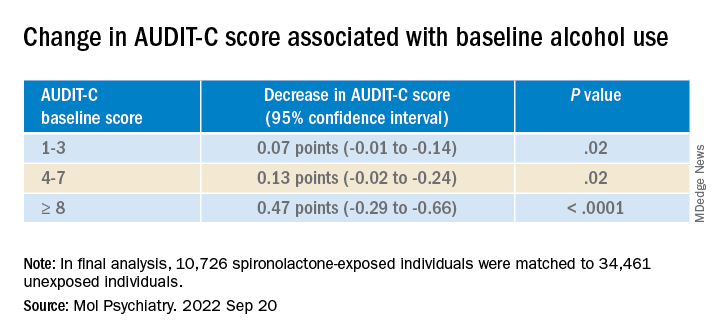
In humans, among the exposed individuals in the matched cohort, 25%, 57%, and 18% received daily doses of spironolactone of less than 25 mg/day, 25-49 mg/day, and 50 mg/day or higher, respectively, with a median follow-up time of 542 (interquartile range, 337-730) days.
The AUDIT-C scores decreased during the study period in both treatment groups, with a larger decrease in average AUDIT-C scores among the exposed vs. unexposed individuals.
“These are very exciting times because, thanks to the progress in the addiction biomedical research field, we are increasing our understanding of the mechanisms how some people develop AUD; hence we can use this knowledge to identify new targets.” The current study “is an example of these ongoing efforts,” said Dr. Leggio.
“It is important to note that [these results] are important but preliminary.” At this juncture, “it would be too premature to think about prescribing spironolactone to treat AUD,” he added.
Exciting findings
Commenting on the study, Joyce Besheer, PhD, professor, department of psychiatry and Bowles Center for Alcohol Studies, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, called the study an “elegant demonstration of translational science.”
“While clinical trials will be needed to determine whether this medication is effective at reducing drinking in patients with AUD, these findings are exciting as they suggest that spironolactone may be a promising compound and new treatment options for AUD are much needed,” said Dr. Besheer, who was not involved with the current study.
Dr. Leggio agreed. “We now need prospective, placebo-controlled studies to assess the potential safety and efficacy of spironolactone in people with AUD,” he said.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the NIAAA. Dr. Leggio, study coauthors, and Dr. Besheer declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.