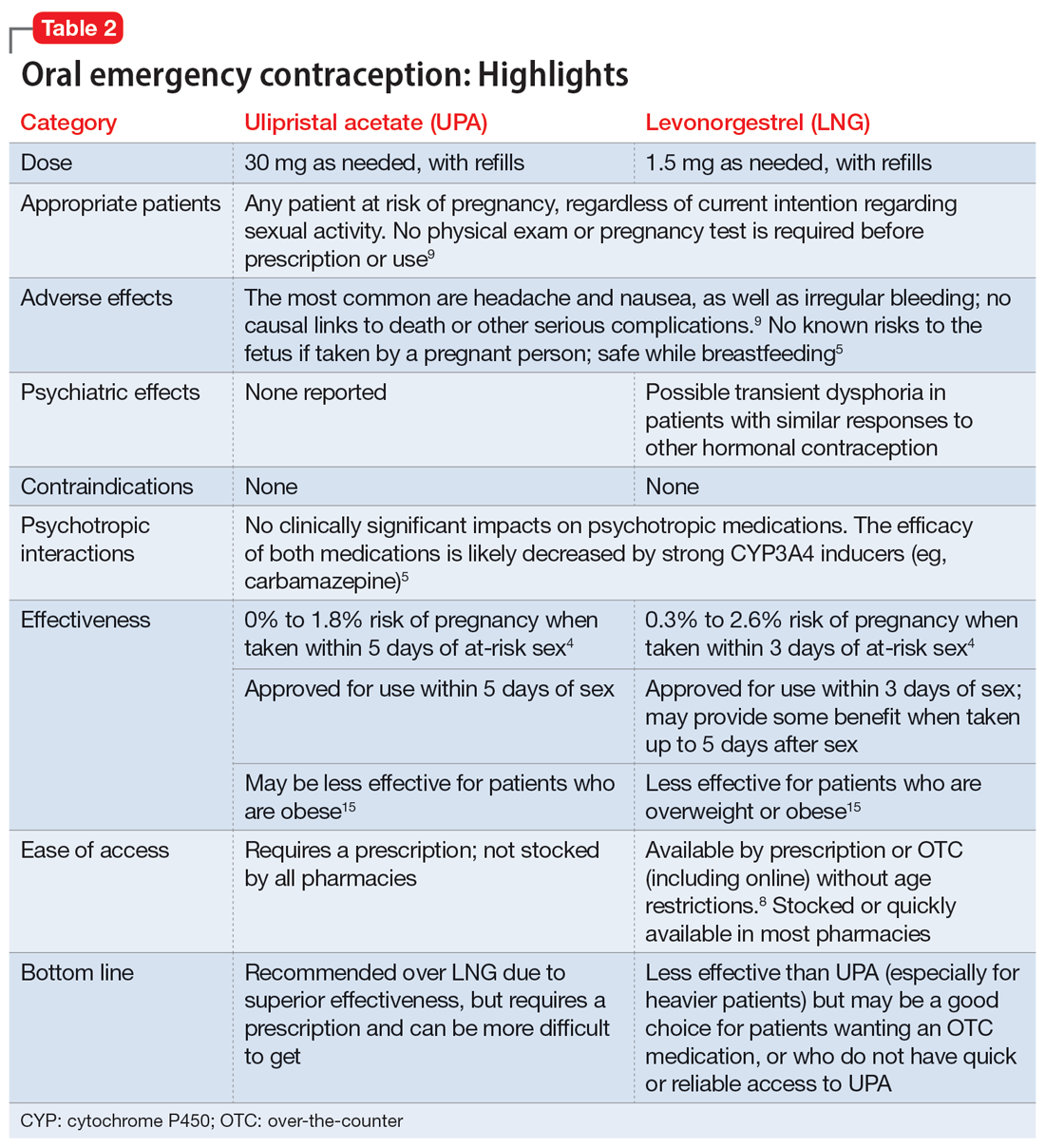
Which to prescribe. UPA is more effective in preventing pregnancy than LNG at all time points up to 120 hours after sex, including for women who are overweight or obese.15 As such, it is recommended as the first-line choice. However, because LNG is available without prescription and is more readily available (including via online order), it may be a good choice for patients who need rapid EC or who prefer a medication that does not require a prescription (Table 24,5,8,9,15).
What to tell patients. Patients should be instructed to fill their prescription before they expect to use it, to ensure ready availability when desired (Table 35,9). Oral EC is shelf stable for at least 3 years when stored in a cool, dry environment. Patients should take the medication as soon as possible following at-risk sexual intercourse (Table 4). Tell them that if they vomit within 3 hours of taking the medication, they should take a second dose. Remind patients that EC does not protect against sexually transmitted infections, or from sex that occurs after the medication is taken (in fact, they can increase the possibility of pregnancy later in that menstrual cycle due to delayed ovulation).9 Counsel patients to abstain from sex or to use barrier contraception for 7 days after use. Those who take birth control pills can resume use immediately after using LNG; they should wait 5 days after taking UPA.
No routine follow-up is needed after taking UPA or LNG. However, patients should get a pregnancy test if their period does not start within 3 weeks, and should seek medical evaluation if they experience significant lower abdominal pain or persistent irregular bleeding in order to rule out pregnancy-related complications. Patients who use EC repeatedly should be recommended to pursue routine contraceptive care.
Billing. Counseling your patients about contraception can increase the reimbursement you receive by adding to the complexity of the encounter (regardless of whether you prescribe a medication) through use of the ICD-10 code Z30.0.
Emergency contraception for special populations
Some patients face additional challenges to effective EC that should be considered when counseling and prescribing. Table 54,5,7,15,17-21 discusses the use of EC in these special populations. Of particular importance for psychiatrists, LNG is less effective at preventing undesired pregnancy among patients who are overweight or obese,15,17,18 and strong CYP3A4-inducing agents may decrease the effectiveness of both LNG and UPA.5 Keep in mind, however, that the advantages of using either UPA or LNG outweigh the risks for all populations.5 Patients must be aware of appropriate information in order to make informed decisions, but should not be discouraged from using EC.
Continue to: Other groups of patients...