Psychedelics are a class of substances known to produce alterations in consciousness and perception. In the last 2 decades, psychedelic research has garnered increasing attention from scientists, therapists, entrepreneurs, and the public. While many of these compounds remain illegal in the United States and in many parts of the world (Box1), a recent resurrection of psychedelic research has motivated the FDA to designate multiple psychedelic compounds as “breakthrough therapies,” thereby expediting the investigation, development, and review of psychedelic treatments.
Box
The legal landscape of psychedelics is rapidly evolving. Psilocybin use has been decriminalized in many cities in the United States (such as Denver), and some states (such as Oregon) have legalized it for therapeutic use.
It is important to understand the difference between decriminalization and legalization. Decriminalization means the substance is still prohibited under existing laws, but the legal system will choose not to enforce the prohibition. Legalization is the rescinding of laws prohibiting the use of the substance. In the United States, these laws may be state or federal. Despite psilocybin legalization for therapeutic use in Oregon and decriminalization in various cities, psychedelics currently remain illegal under federal law.
Source: Reference 1
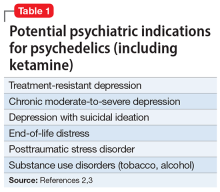
There is growing evidence that psychedelics may be efficacious for treating a range of psychiatric disorders. Potential clinical indications for psychedelics include some forms of depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and substance use disorders (Table 12,3). In most instances, the clinical use of psychedelics is being investigated and offered in the context of psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy, though ketamine is a prominent exception. Ketamine and esketamine are already being used to treat depression, and FDA approval is anticipated for other psychedelics. An examination of the safety considerations of psychedelics for the treatment of psychiatric disorders is therefore highly relevant and timely.
This article examines the adverse effect profile of classical (psilocybin [“mushrooms”], lysergic acid diethylamide [LSD], and N,N-dimethyltryptamine [DMT]/ayahuasca) and nonclassical (the entactogen 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine [MDMA, known as “ecstasy”] and the dissociative anesthetic ketamine) psychedelics.
Psilocybin
Psilocybin is typically administered as a single dose of 10 to 30 mg and used in conjunction with preintegration and postintegration psychotherapy. Administration of psilocybin typically produces perceptual distortions and mind-altering effects, which are mediated through 5-HT2A brain receptor agonistic action.4 The acute effects last approximately 6 hours.5 While psilocybin has generated promising results in early clinical trials,3 the adverse effects of these agents have received less attention.
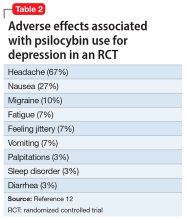
The adverse effect profile of psilocybin in adults appears promising but its powerful psychoactive effects necessitate cautious use.6 It has a very wide therapeutic index, and in a recent meta-analysis of psilocybin for depression, no serious adverse effects were reported in any of the 7 included studies.7 Common adverse effects in the context of clinical use include anxiety, dysphoria, confusion, and an increase in blood pressure and heart rate.6 Due to potential cardiac effects, psilocybin is contraindicated in individuals with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease.8 In recreational/nonclinical use, reactions such as suicidality, violence, convulsions, panic attacks, paranoia, confusion, prolonged dissociation, and mania have been reported.9,10 Animal and human studies indicate the risk of abuse and physical dependence is low. Major national surveys indicate low rates of abuse, treatment-seeking, and harm.11 In a recent 6-week randomized controlled trial (RCT) of psilocybin vs escitalopram for depression,12 no serious adverse events were reported. Adverse events reported in the psilocybin group in this trial are listed in Table 2.12
A recent phase 2 double-blind trial of single-dose psilocybin (1 mg, 10 mg, and 25 mg) for treatment-resistant depression (N = 233) sheds more light on the risk of adverse effects.13 The percentage of individuals experiencing adverse effects on Day 1 of administration was high: 61% in the 25 mg psilocybin group. Headache, nausea, fatigue, and dizziness were the most common effects. The incidence of any adverse event in the 25 mg group was 56% from Day 2 to Week 3, and 29% from Week 3 to Week 12. Suicidal ideation, suicidal behavior, or self-injury occurred in all 3 dose groups. Overall, 14% in the 25 mg group, 17% in the 10 mg group, and 9% in the 1 mg group showed worsening of suicidality from baseline to Week 3. Suicidal behavior was reported by 3 individuals in the 25 mg group after Week 3. The new-onset or worsening of preexisting suicidality with psilocybin reported in this study requires further investigation.
Lysergic acid diethylamide
LSD is similar to psilocybin in its agonistic action at the 5-HT2A brain receptors.4 It is typically administered as a single 100 to 200 μg dose and is used in conjunction with preintegration and postintegration psychotherapy.14 Its acute effects last approximately 12 hours.15
Continue to: Like psilocybin...