The authors’ observations
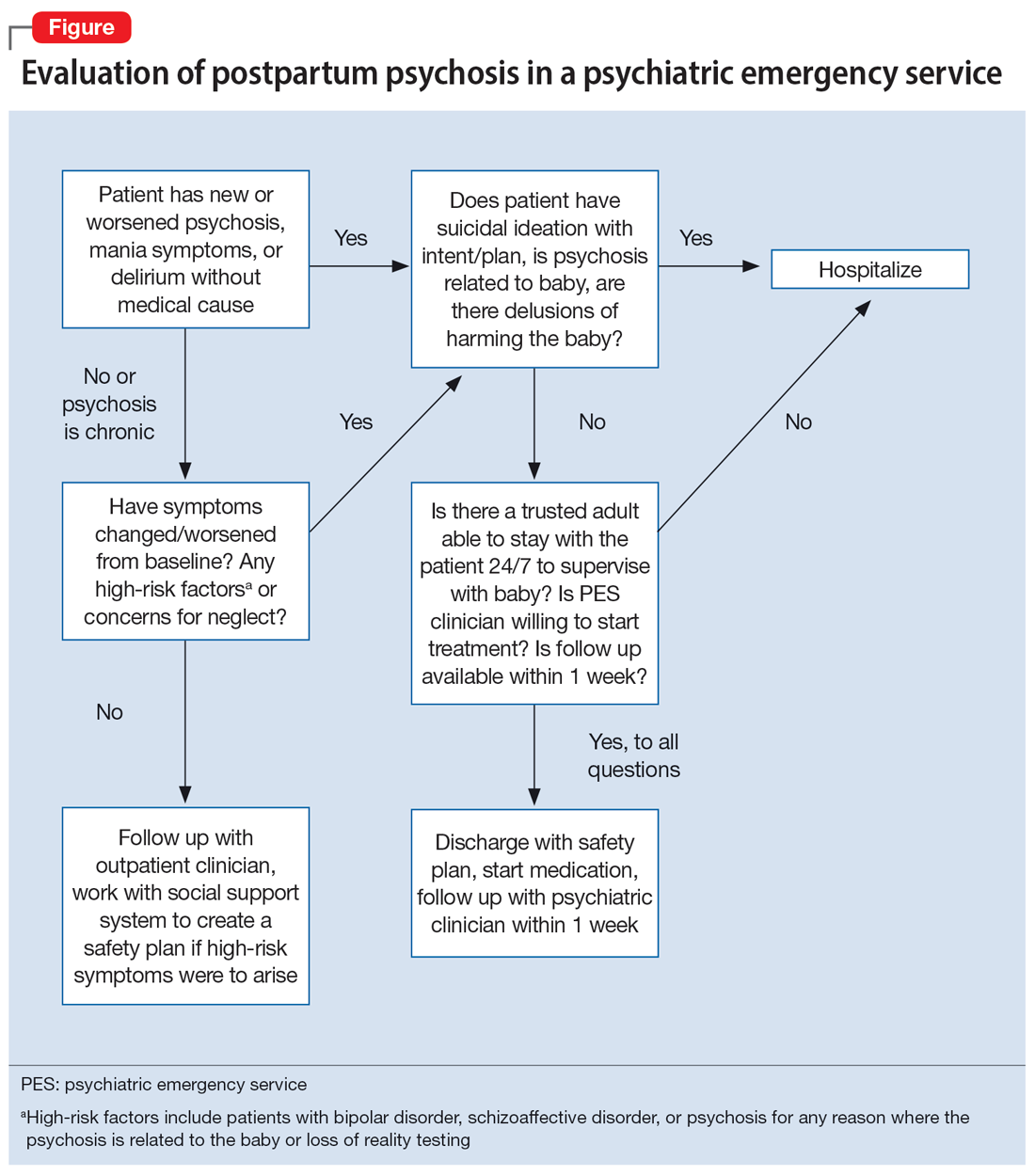
Due to an elevated acute risk of suicide and infanticide, postpartum psychosis represents a psychiatric emergency and often requires hospitalization. The Figure outlines steps in evaluating a patient with concerns for postpartum psychosis in a psychiatric emergency service setting. Due to the waxing and waning nature of symptoms, patients may appear psychiatrically stable at any time but remain at an overall elevated acute risk of harm to self and/or their baby.
If a patient is being considered for discharge based on yes answers to all questions in Step 2 of the Figure, the emergency psychiatric clinician must initiate appropriate psychotropic medications and complete robust safety planning with the patient and a trusted adult who will provide direct supervision. Safety planning may include (but is not limited to) strict return precautions, education on concerning symptoms and behaviors, psychotropic education and agreement of compliance, and detailed instructions on outpatient follow-up within 1 week. Ideally—and as was the case for Ms. A—a reproductive psychiatrist should be consulted in the emergency setting for shared decision-making on admission vs discharge, medication management, and outpatient follow-up considerations.
Because postpartum psychosis carries significant risks and hospitalization generally results in separating the patient from their baby, initiating psychotropics should not be delayed. Clinicians must consider the patient’s psychiatric history, allergies, and breastfeeding status.
Based on current evidence, first-line treatment for postpartum psychosis includes a mood stabilizer, an antipsychotic, and possibly a benzodiazepine.6 Thus, an appropriate initial treatment regimen would be a benzodiazepine (particularly lorazepam due to its relatively shorter half-life) and an antipsychotic (eg, haloperidol, olanzapine, or quetiapine) for acute psychosis, plus lithium for mood stabilization.1,5
If the postpartum psychosis represents an episode of BD, use of a long-term mood stabilizer may be required. In contrast, for isolated postpartum psychosis, clinicians may consider initiating psychotropics only in the immediate postpartum period, with an eventual slow taper. In future pregnancies, psychotropics may be reintroduced postpartum, which will avoid peripartum fetal exposure.8 If the patient is breastfeeding, lithium may be deferred in an acute care setting. For patients with evidence of catatonia, severe suicidality, refusal of oral intake with compromised nutrition, severe agitation, or treatment resistance, electroconvulsive therapy remains a safe and effective treatment option.6 Additionally, the safety of continued breastfeeding in acute psychosis must be considered, with the potential for recommending discontinuation, which would decrease sleep disruptions at night and increase the ability of others to feed the baby. Comprehensive care requires nonpharmacologic interventions, including psychoeducation for the patient and their family, individual psychotherapy, and expansion of psychosocial supports.
Continue to: Patients who have experienced...