- cognition
- global performance
- attention
- activities of daily living.2
Based on my clinical experience, these improvements reflect small but clinically meaningful changes that are noted by patients and caregivers.
Figure
Efficacy of transdermal rivastigmine for Alzheimer’s symptoms
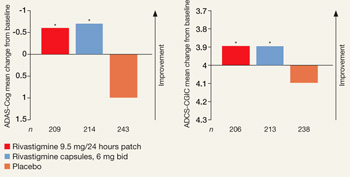
*P<0.05 vs placebo
ADAS-Cog: Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale; ADCS-CGIC: Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study-Clinical Global Impression of Change
Source: Adapted from reference 2
In a 24-week study, transdermal rivastigmine, 9.5 mg/24 hours, and the highest recommended dose of oral rivastigmine (6 mg bid) showed comparable efficacy as measured by mean change in score on scales commonly used in Alzheimer’s disease clinical trials. ADAS-Cog assesses orientation, memory, language, praxis, and visuospatial functions. ADCS-CGIC provides a single global rating of change from baseline based on interviews with the patient and caregiver.
Safety and tolerability
Adverse events associated with rivastigmine are predominantly cholinergic; GI side effects—nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea—are observed most frequently.2 These events occur less frequently with the patch than with capsules. In the efficacy trial, patients in the 9.5 mg/24 hours rivastigmine patch group had one-third as many reports of nausea (7.2% vs 23.1%) and vomiting (6.2% vs 17.0%) compared with the 6 mg bid capsule group.2
Diarrhea was reported by 6% of subjects receiving the 9.5 mg/24 hours patch, 5% of those taking 6-mg capsule bid, and 3% receiving placebo. Fewer subjects in the 9.5 mg/24 hours patch group (3%) experienced decreased weight compared with those in the capsule group (5%). The rate of decreased weight with placebo was 1%.
Dizziness affected 2% of those in the 9.5 mg/24 hours patch and placebo groups; incidence in the capsule group was significantly higher at 8%. Headache was similar with the 9.5 mg/24 hours patch (3%) and placebo (2%), with the capsule significantly higher at 6%.2
The proportion of patients who experienced no, slight, or mild skin irritation ranged from 90% to 98%.2 The most commonly reported moderate or severe skin irritations were erythema (8% rivastigmine patch vs 4% placebo) and pruritus (7% rivastigmine patch vs 3% placebo). Two percent of patients using active patch discontinued the trial because of skin irritation.
Rivastigmine appears not to produce adverse effects on cardiac function as assessed by ECG. In clinical trials of 2,791 patients, pooled 12-lead ECG data comparing oral rivastigmine and placebo groups did not differ significantly in heart rate or PR, QRS, and QTc intervals.10
Dosing
The rivastigmine patch is administered once daily, and the recommended maintenance dose is the 9.5 mg/24 hours patch. Start patients on a 4.6 mg/24 hours patch for at least 4 weeks and then increase to the 9.5 mg/24 hours target dose if the lower dose is well tolerated.
Dosage adjustment of rivastigmine is not necessary in patients with hepatic or renal disease because of minimal liver metabolism and the acetylcholinesterase-mediated hydrolysis of rivastigmine to the inactive decarbamylated metabolite NAP 226-90, which is excreted in the urine.11
Instruct patients or caregivers to apply the patch to clean, dry, hairless skin that is free of cuts, rashes, or irritation on the upper or lower back or upper arm or chest.1 The patch has shown good adhesive properties over 24 hours, remaining attached in a range of situations, including bathing and hot weather.2 In the 9.5 mg/24 hours group of the efficacy study, 96% of patches remained attached or had slight lifting of the edges (1,336 total patch evaluations).
Transitioning to rivastigmine patch
The efficacy study included an open-label extension, during which blinding was maintained. This provided information on patients beginning rivastigmine patch therapy directly from placebo2 or transitioning from rivastigmine capsules to the target dose 9.5 mg/24 hours patch.12 Based on these results, transition patients as follows:
- Patients taking oral rivastigmine, <6 mg/d: Switch to a 4.6 mg/24 hours patch for ≥4 weeks before increasing to a 9.5 mg/24 hours patch.
- Patients taking oral rivastigmine, 6 to 12 mg/d: Switch directly to a 9.5 mg/24 hours patch.
Apply the first patch the day after the last oral dose.
Related resource
- Rivastigmine transdermal system prescribing information. www.pharma.us.novartis.com/product/pi/pdf/exelonpatch.pdf.
Drug brand names
- Digoxin • Lanoxin
- Rivastigmine • Exelon
- Rivastigmine transdermal
- system • Exelon Patch
Disclosure
Dr. Sadowsky is a consultant to and speaker for Forest Pharmaceuticals and Novartis Pharmaceuticals.
Acknowledgment
The author thanks Christina Mackins, PhD, a medical writer for Alpha-Plus Medical Communications Ltd, for her editorial assistance with this article. Funding for her work was provided by Novartis Pharmaceuticals.

