, according to an analysis of national survey data from 2011 to 2014.
“The adult prevalence rate of 3.0% continues to place psoriasis as one of the most common immune-mediated diseases affecting adults” in the United States, April W. Armstrong, MD, MPH, and associates said in a report published in JAMA Dermatology. At that rate, approximately 7,560,000 Americans aged 20 years or older have psoriasis.
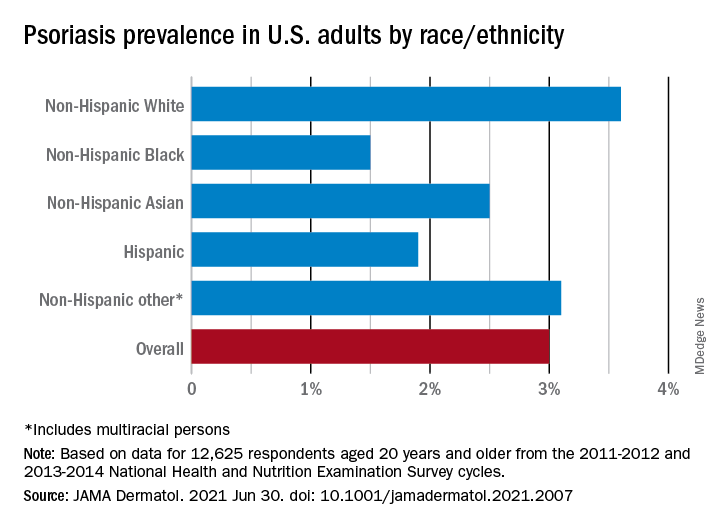
That overall rate among adults aged 20 years and older, based on data from the 2011-2012 and 2013-2014 cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), did not change significantly when compared with the 2003-2004 NHANES, when it was 3.15% among those aged 20-59, said Dr. Armstrong, professor of dermatology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and associates.
For the 2011-2014 period, psoriasis prevalence was similar between women (3.2%) and men (2.8%) but was significantly associated with older age and White/non-White status. Those aged 50-59 years had the highest prevalence of any age group at 4.3% and those aged 70 and older had a rate of 3.9%, while those aged 20-29 were the lowest at 1.6%, the investigators reported.
The prevalence in non-Hispanic Whites in the United States was 3.6% over the study period, and their odds ratio for having psoriasis was 1.92, compared with non-White individuals. Asian respondents had a prevalence of 2.5%, with the Hispanic population at 1.9%, non-Hispanic Black respondents at 1.5%, and those identifying as other (including multiracial persons) at 3.1%, they said.
The NHANES sample consisted of 12,638 people who had participated in the question that asked if they had ever been diagnosed with psoriasis by a physician or other health care professional, of whom 12,625 gave a definitive yes or no answer, the investigators noted.
A much smaller number, 329, also answered a question about the severity of their disease: Fifty-six percent had little or no psoriasis, almost 22% reported 1-2 palms of involvement, 16% had 3-10 palms of involvement, and 5.5% said the coverage was more than 10 palms. Since the survey did not distinguish between treated and untreated patients, however, some “of those reporting low body surface area involvement may be receiving treatments that are controlling their otherwise more extensive disease,” they wrote.
Dr. Armstrong and another investigator said that they have received grants, personal fees, and honoraria from a number of pharmaceutical companies; two other investigators are employees of the National Psoriasis Foundation.