The prevalence of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) in the general population is estimated at 23.1%.1 While FAI is often bilateral,2 patients usually present with unilateral symptoms.3 Young, highly active individuals are most commonly affected.3 Despite significant improvement in our understanding of FAI in recent years, it remains a poorly recognized cause of hip pain among orthopedic providers. Clohisy and colleagues3 found that the average time to diagnosis was 3.1 years (range, 3-15 years) and the average number of providers seen before correct diagnosis was 4.2 (range, 1-16) with nearly half those providers being orthopedic specialists. This is likely attributed to limited training and lack of appropriate imaging. Multiple comprehensive radiographic approaches have been described, including plain films, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging.2,4 The objective of this article is to present a simple 3-view plain film approach for young adults with hip pain. While history and physical examination remain key to FAI diagnosis, a basic knowledge of the common sites of impingement with appropriate radiographic views to visualize these sites may help eliminate unnecessary imaging and delayed diagnosis.
STANDING ANTEROPOSTERIOR VIEW OF THE PELVIS
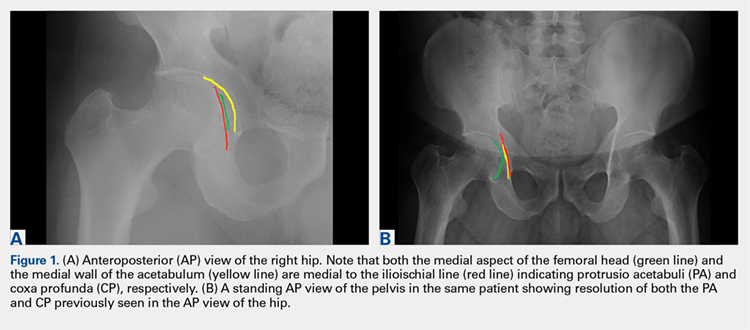
An anteroposterior (AP) view of the pelvis, as opposed to an AP view of the hip, is an important first radiograph in the evaluation of young patients presenting with hip pain. Not only does it permit visualization of the contralateral hip for comparison, but it also allows more accurate measurements of several radiographic parameters (Table). An AP view of the hip often gives the false impression of global over coverage, such as coxa profunda2 and protrusio acetabuli (Figures 1A, 1B), and may overestimate the amount of acetabular anteversion.2
Table. Summary of Common Radiographic Parameters When Assessing Young Adults with Hip Pain2,4
Sign | Best Radiographic View | Measurement | Quoted Normal Valuesa | Clinical Relevance of Abnormal Values |
Acetabular depth | AP pelvis | Medial wall of the acetabulum (MWA) relative to the ilioischial line (IIL) | MWA is lateral to IIL | Global overcoverage (ie, coxa profunda) |
Femoral depth | AP pelvis | Medial surface of the femoral head (MFH) relative to the IIL | MFH is lateral and within 10 mm of the IIL | >10 mm may indicate undercoverage (ie, dysplasia) MFH medial to IIL may indicate overcoverage (ie, protrusio acetabuli) |
Tonnis angle | AP pelvis | Angle between the weight-bearing surface of the acetabulum and a line parallel to the horizontal axis of the pelvis (eg, inter-teardrop line) | 0°-10° | >10° may indicate undercoverage (ie, dysplasia) <0° may indicate overcoverage (ie, pincer-type FAI) |
Lateral center edge angle | AP pelvis | Angle between a line perpendicular to the horizontal axis of the pelvis through the center of the femoral head and a line connecting the center of the femoral head to the lateral most edge of the acetabular weight-bearing surface | 25°-40° | >40° may indicate overcoverage (ie, pincer-type FAI) <25° may indicate undercoverage (ie, dysplasia) |
Crossover sign | AP pelvis | Intersection between the anterior and posterior rims of the acetabulum | Crossover occurs at the lateral most aspect of the acetabular weight-bearing surface | Crossover occurring distal to the lateral most aspect of the acetabular weight-bearing surface may indicate acetabular retroversion |
Femoral neck-shaft angle | AP pelvis | Angle between the femoral shaft and the longitudinal axis of the neck | 135° ± 5° | >140° may indicate coxa valga <130° may indicate coxa vara |
Alpha angle | Cross-table lateral | Angle between a line connecting the center of the femoral neck to the center of the femoral head and a line connecting the center of the head to a point on the anterolateral aspect of the head-neck junction where the head sphericity ends | >55° | Decreased head-neck offset (ie, cam-type impingement) |
Anterior head-neck offset | Cross-table lateral | Distance between 2 lines parallel to the longitudinal axis of the femoral neck: 1 line tangent to the anterior most aspect of the neck and 1 line tangent to the anterior surface of the femoral head | >10 mm | Decreased head-neck offset (ie, cam-type impingement) |
Anterior head-neck offset ratio | Cross-table lateral | Anterior head-neck offset divided by the diameter of the femoral head | >0.14 | Decreased head-neck offset (ie, cam-type impingement) |
Femoral version | Cross-table lateral | Angle between the longitudinal axis of the femoral neck and the longitudinal axis of the femoral shaft | 15° ± 5° | Developmental disorders (eg, dysplasia, slipped capital femoral epiphysis) |
Anterior center edge angle | False profile view | Angle between a vertical line through the center of the femoral head and a line connecting the center of the femoral head to the anterior most edge of the acetabular weight-bearing surface | >20° | Undercoverage (ie, dysplasia) |
aNormal values are provided for reference only and should not be solely relied on for diagnosis.
Abbreviations: AP, anteroposterior; FAI, femoroacetabular impingement.
A good quality radiograph is important for accurate assessment. The X-ray beam should be perpendicular to the coronal plane of the pelvis. Neutral rotation of the pelvis is a prerequisite and can be confirmed by the presence of symmetric obturator foramina, iliac wings, and coccyx vertically in line with the pubic symphysis. Deviations from this configuration can significantly affect the ability to accurately assess the acetabular version. This is because the rotational profile of the acetabulum is sensitive to pelvic rotation.5,6
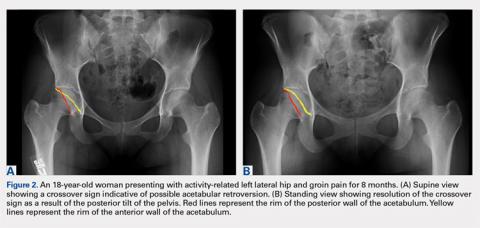
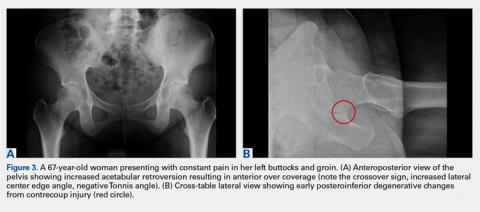
While the AP view of the pelvis can be obtained in either supine or standing positions, the standing position is recommended. A supine view tends to increase the likelihood of finding a crossover sign that often disappears in the standing position (Figures 2A, 2B). This is attributed to the posterior tilt of the pelvis in the sagittal plane with standing, which functionally increases acetabular anteversion, eliminating the crossover sign.5,6 In contrast, a crossover sign that persists in the standing position combined with other abnormal radiographic parameters, such as a negative Tonnis angle and/or increased lateral center edge angle, are concerning for pincer-type FAI (Figures 3A, 3B). An isolated crossover sign may be a normal variant in young asymptomatic patients7 and is not a reliable indicator of acetabular retroversion.5
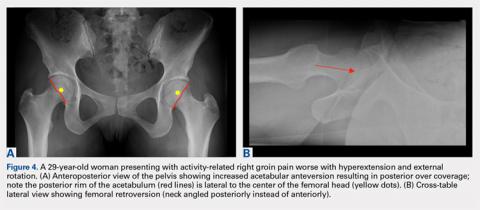
In addition to assessing the acetabular coverage and version (Figures 1A, 1B, 3A, 3B, and 4A, 4B), the AP view of the pelvis can provide valuable information regarding the proximal femur. One should pay attention to the sphericity of the head (pistol grip cam lesions are most obvious on this view), congruency between the femoral head and the acetabulum, femoral offset, and neck-shaft angle. While we tend to traditionally classify FAI into cam and pincer osseous bumps, alterations in hip dynamics (i.e., coxa vara and coxa breva) can result in functional impingement even in the absence of the osseous bumps.
Continue to: CROSS-TABLE LATERAL...