PALM BEACH, FLA. – Administering a brief oral antibiotic regimen preoperatively to colorectal surgery patients cut the average postoperative hospitalization by more than a day and reduced 30-day readmissions by about 3% compared with no presurgical bowel preparation, a review of more than 8,000 patients found.
The primary driver of these beneficial effects was a reduced rate of surgical site infections, Dr. Mary T. Hawn said at the annual meeting of the Southern Surgical Association.
"Efforts to improve adherence with the use of oral antibiotic preparation may improve the efficiency of care for colorectal surgery," said Dr. Hawn, chief of gastrointestinal surgery at the University of Alabama, Birmingham. "Further research is needed to determine the best protocol for bowel prep prior to colorectal surgery, and to prospectively monitor the rate of Clostridium difficile infection."
The findings by Dr. Hawn’s group also showed that oral antibiotic bowel preparation (OABP) led to a small but statistically significant increase in the rate of hospital readmissions among patients with a principal diagnostic code of colitis caused by C. difficile infection. The OABP patients had a 0.5% readmission rate, compared with a 0.1% rate among patients who received no presurgical bowel preparation.
The value of OABP as shown in this study is particularly important because the use of OABP before colorectal surgery has declined in the United States over the past 20 years, Dr. Hawn added.
Using data collected as part of the VA Surgical Quality Improvement Program, Dr. Hawn and her colleagues analyzed results for 8,180 patients who underwent elective colorectal resection at any of 112 participating VA hospitals during 2005-2009. Patients who had a partial or total colectomy, a rectal resection, or an ostomy were included. Patients were excluded if they had a preoperative stay of more than 2 days, a postoperative stay of more than 30 days, or an American Surgical Association 5 classification, or if they died before hospital discharge.
Most of the patients (83%) underwent surgery for neoplasms; the next most common reason for surgery was diverticulitis, in 6%. OABP was the most common form of presurgical preparation, used on 44% of patients; mechanical preparation only was used on 39%, and no preparation was done in 17%. Ninety percent of the OABP patients also underwent mechanical preparation, while the other 10% had OABP only.
The average postoperative length of stay was 9.1 days among those who received no preparation, 8.6 days for those who got mechanical preparation only, and 7.9 days for those who had OABP – a statistically significant advantage for OABP. In a multivariate regression analysis that controlled for indication, age, and wound class, OABP cut length of stay by an average of 12% compared with no preparation, a statistically significant reduction. In the same analysis, mechanical preparation cut length of stay by only 4% compared with no preparation, also a significant effect.
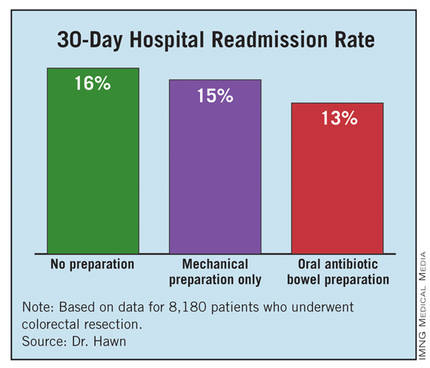
The hospital readmission rate was 16% with no preparation, 15% with mechanical preparation only, and 13% with OABP. In the multivariate regression analysis with adjustment for procedure, age, and wound class, OABP cut the readmission rate by 19% compared with no preparation, a statistically significant reduction. Mechanical preparation only did not have a statistically significant effect.
Further analyses showed that the most common reason for readmission among all patients studied was postoperative infection, in 18%, followed by digestive-system complications, in 10%. C. difficile infection caused 3% of readmissions.
In addition, infections were responsible for readmissions among 6% of patients who underwent no presurgical preparation and in 4% of those who underwent OABP, a statistically significant difference. In contrast, use of OABP produced no statistically significant decline in noninfectious causes of readmission. This rate ran 10% among patients with no preparation, and 9% in patients who underwent OABP.
Dr. Hawn said that she had no disclosures.