Descriptive statistics were used to characterize the patient demographic information. Chi-square analyses were performed to evaluate the difference between presence of organisms before and after solution application, and the data were also layered with reported Hibiclens cleanser use. In addition, binary logistic regression was used to determine if demographic variables could predict presence of organism isolates before and after solution application. Data analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics Version 20.
Results
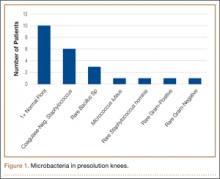
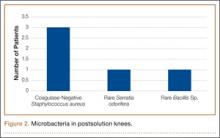
No patient had a postoperative infection. Culture isolates grew in 20 (20%) of the 99 patients before solution application and in 5 (5%) of the 99 after application. Of the 20 patients with presolution culture isolates, 16 (80%) had 1 bacterial isolate, and 4 (20%) had 2 or more species. Presolution isolates included normal flora (10, 50%), coagulase-negative Staphylococcus aureus (6, 30%), rare Bacillus (3, 15%), Micrococcus luteus (1, 5%), rare gram-negative (1, 5%), rare gram-positive (1, 5%), and Staphylococcus hominis (1, 5%) (Figure 1). Postsolution isolates included coagulase-negative S aureus (3, 60%), rare Bacillus (1, 20%), and rare Serratia odorifera (1, 20%) (Figure 2). Two postsolution isolates did not have an associated presolution isolate. Presolution organism isolation was an important predictor of postsolution organism isolation (P < .046).
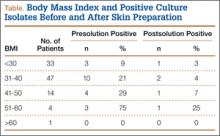
BMI was recorded for all patients. Mean BMI was 35 (range, 20-63). Distribution was as follows: BMI under 20 (3 patients), under 30 (30 patients), under 40 (47 patients), under 50 (14 patients), under 60 (4 patients), and over 60 (1 patient). Mean presolution BMI was significantly (P < .03) higher for patients with bacterial isolates than for patients without isolates (38 and 34, respectively). Mean postsolution BMI was 40 for patients with bacterial isolates and 35 for patients without isolates (Figure 3). Of the 33 patients with BMI under 30, 3 (9%) had presolution isolates and 1 (3%) had postsolution isolates. Of the 66 patients with BMI over 30, 17 (26%) had presolution isolates and 4 (6%) had postsolution isolates (Table).
Of the 99 patients, 30 (30%) had diabetes. Of these 30 patients, 9 (30%) had presolution isolates (45% of all presolution isolates) and 3 (10%) had postsolution isolates (60% of all postsolution isolates.) Although neither pre- nor postsolution results were statistically significant (P = .172) for increasing organism isolation in patients with diabetes, the odds ratio for these patients was 3.6 when the focus was on the likelihood of postsolution organism isolation.
Mean age was 57 years (range, 29-87 years). Results were not statistically significant for age being a likely factor for organism isolate prediction.
There were 81 women and 18 men in the study. Of the 81 women, 16 (20%) had positive presolution cultures and 5 (6%) had positive postsolution cultures. Of the 18 men, 4 (22%) had positive presolution cultures and none had a positive postsolution culture.
Race was recorded. Forty-nine patients were white, 27 black, 18 Hispanic, and 5 unknown. Presolution, 12 whites (24%), 5 blacks (19%), and 3 Hispanics (17%) had positive cultures. Postsolution, 1 white (2%), 1 black (4%), 3 Hispanics (17%), and 1 patient of unknown race (20%) had positive cultures.
ASA classifications were recorded and analyzed. Of the 99 patients, 38 were classified ASA-2, 60 were ASA-3, and 1 was ASA-4. Presolution, 9 (24%) of the 38 ASA-2 patients and 11 (18%) of the 60 ASA-3 patients had positive cultures; postsolution, 2 (5%) of the 38 ASA-2 patients and 3 (5%) of the 60 ASA-3 patients had positive cultures. The 1 ASA-4 patient had neither presolution nor postsolution positive cultures.
Types of TKA (bilateral, unilateral) were recorded. Of the 99 patients, 89 had unilateral TKAs and 10 had bilateral TKAs. Presolution, 19 (21%) of the 89 unilaterals and 1 (10%) of the 10 bilaterals had positive cultures. Postsolution, 5 (6%) of the 89 unilaterals and none of the 10 bilaterals had positive cultures.
Patients were also verbally asked how many cleanser baths they had taken before surgery. Of the 99 patients, 88 reported having taken 1 or more cleanser baths, and 1 reported no baths; 10 patients’ responses were not available. The 88 patients who had taken at least 1 cleanser bath were divided into 3 groups: 1 bath (35 patients), 2 baths (49 patients), and 3 or more baths (4 patients). Presolution, positive cultures were found for 18 (20%) of the 88 patients; for 7 (20%) of the 35 patients with 1 bath; for 10 (20%) of the 49 patients with 2 baths; and for 1 (25%) of the 4 patients with 3 or more baths. Postsolution, positive cultures were found for 5 (6%) of the 88 patients; for 2 (6%) of the 35 patients with 1 bath; for 3 (6%) of the 49 patients with 2 baths; and for 0 (0%) of the 4 patients with 3 or more baths. The 1 patient with no baths did not have a positive culture. Of the 10 patients whose responses were unavailable, 2 patients had positive presolution cultures and no patients had a positive postsolution culture.