User login
Verbal working memory deterioration predicts relapse in remitted psychosis
Previous research has suggested that cognitive impairments may predict recurrent psychotic episodes, but data on the association between specific cognitive deficits and relapse of psychosis over time are limited, wrote Tiffany J. Tao, MPhil, a PhD candidate at the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues.
In a naturalistic 1-year follow-up study published in Psychiatry Research , the researchers recruited psychosis patients with full remission for a least 6 months from two outpatient psychiatric clinics. The study population included adults aged 18-55 years, with an average age of 29.2 years; 62% were women. Relapse, defined as a recurrence of psychotic symptoms measured by the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and the Clinical Global Impression Scale, was assessed monthly via phone interviews with the use of a smartphone app. Cognitive decline was based on working memory deterioration, assessed monthly via the Visual Patterns Test (VPT) and the Letter-Number Sequencing (LNS) test, respectively, for visual and verbal working memory.
Overall, 18 patients (16%) experienced a relapse at 1 year. One-third of these (six patients) required hospitalization, with a median hospital stay of 23 days.
In a multivariate analysis, independent and significant predictors of relapse were verbal working memory deterioration 2 months prior to relapse (P = .029), worse medication adherence (P = .018), and less resilience (P = .014) with odds ratios of 9.445, 0.051, and 0.769, respectively.
“Specifically, declines in verbal working memory were observed beginning at 2 months prior to the relapse episode in both the univariate and multivariate models after controlling for other significant predictors,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The mechanism of action for the association remains unclear, but cognitive impairment might reflect dopamine dysregulation or other processes in the prefrontal cortex that could contribute to psychotic relapse, they said.
Other factors include the associations between cognitive impairment and medication nonadherence, and the impact of cognitive impairment on a patient’s ability to manage the stresses of daily living that could trigger a psychotic relapse, they added.
Notably, the current study identified verbal working memory, but not visual working memory, as a predictor of relapse, which is important given the different neurobiological bases for visual and verbal tasks, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to identify weaker predictors of relapse given the low relapse rate, and potential lack of generalizability to other less homogeneous populations, and the exclusion of patients with illicit drug use, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the prospective measurements that prevented recall bias, and the inclusion of other objective predictors of relapse. The findings highlight the potential for early intervention to prevent relapse based on cognitive assessment, which can be measured objectively in the clinical setting or remotely from home using digital technology, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Tao had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous research has suggested that cognitive impairments may predict recurrent psychotic episodes, but data on the association between specific cognitive deficits and relapse of psychosis over time are limited, wrote Tiffany J. Tao, MPhil, a PhD candidate at the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues.
In a naturalistic 1-year follow-up study published in Psychiatry Research , the researchers recruited psychosis patients with full remission for a least 6 months from two outpatient psychiatric clinics. The study population included adults aged 18-55 years, with an average age of 29.2 years; 62% were women. Relapse, defined as a recurrence of psychotic symptoms measured by the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and the Clinical Global Impression Scale, was assessed monthly via phone interviews with the use of a smartphone app. Cognitive decline was based on working memory deterioration, assessed monthly via the Visual Patterns Test (VPT) and the Letter-Number Sequencing (LNS) test, respectively, for visual and verbal working memory.
Overall, 18 patients (16%) experienced a relapse at 1 year. One-third of these (six patients) required hospitalization, with a median hospital stay of 23 days.
In a multivariate analysis, independent and significant predictors of relapse were verbal working memory deterioration 2 months prior to relapse (P = .029), worse medication adherence (P = .018), and less resilience (P = .014) with odds ratios of 9.445, 0.051, and 0.769, respectively.
“Specifically, declines in verbal working memory were observed beginning at 2 months prior to the relapse episode in both the univariate and multivariate models after controlling for other significant predictors,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The mechanism of action for the association remains unclear, but cognitive impairment might reflect dopamine dysregulation or other processes in the prefrontal cortex that could contribute to psychotic relapse, they said.
Other factors include the associations between cognitive impairment and medication nonadherence, and the impact of cognitive impairment on a patient’s ability to manage the stresses of daily living that could trigger a psychotic relapse, they added.
Notably, the current study identified verbal working memory, but not visual working memory, as a predictor of relapse, which is important given the different neurobiological bases for visual and verbal tasks, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to identify weaker predictors of relapse given the low relapse rate, and potential lack of generalizability to other less homogeneous populations, and the exclusion of patients with illicit drug use, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the prospective measurements that prevented recall bias, and the inclusion of other objective predictors of relapse. The findings highlight the potential for early intervention to prevent relapse based on cognitive assessment, which can be measured objectively in the clinical setting or remotely from home using digital technology, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Tao had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Previous research has suggested that cognitive impairments may predict recurrent psychotic episodes, but data on the association between specific cognitive deficits and relapse of psychosis over time are limited, wrote Tiffany J. Tao, MPhil, a PhD candidate at the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues.
In a naturalistic 1-year follow-up study published in Psychiatry Research , the researchers recruited psychosis patients with full remission for a least 6 months from two outpatient psychiatric clinics. The study population included adults aged 18-55 years, with an average age of 29.2 years; 62% were women. Relapse, defined as a recurrence of psychotic symptoms measured by the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and the Clinical Global Impression Scale, was assessed monthly via phone interviews with the use of a smartphone app. Cognitive decline was based on working memory deterioration, assessed monthly via the Visual Patterns Test (VPT) and the Letter-Number Sequencing (LNS) test, respectively, for visual and verbal working memory.
Overall, 18 patients (16%) experienced a relapse at 1 year. One-third of these (six patients) required hospitalization, with a median hospital stay of 23 days.
In a multivariate analysis, independent and significant predictors of relapse were verbal working memory deterioration 2 months prior to relapse (P = .029), worse medication adherence (P = .018), and less resilience (P = .014) with odds ratios of 9.445, 0.051, and 0.769, respectively.
“Specifically, declines in verbal working memory were observed beginning at 2 months prior to the relapse episode in both the univariate and multivariate models after controlling for other significant predictors,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The mechanism of action for the association remains unclear, but cognitive impairment might reflect dopamine dysregulation or other processes in the prefrontal cortex that could contribute to psychotic relapse, they said.
Other factors include the associations between cognitive impairment and medication nonadherence, and the impact of cognitive impairment on a patient’s ability to manage the stresses of daily living that could trigger a psychotic relapse, they added.
Notably, the current study identified verbal working memory, but not visual working memory, as a predictor of relapse, which is important given the different neurobiological bases for visual and verbal tasks, the researchers wrote.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the inability to identify weaker predictors of relapse given the low relapse rate, and potential lack of generalizability to other less homogeneous populations, and the exclusion of patients with illicit drug use, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the prospective measurements that prevented recall bias, and the inclusion of other objective predictors of relapse. The findings highlight the potential for early intervention to prevent relapse based on cognitive assessment, which can be measured objectively in the clinical setting or remotely from home using digital technology, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. Ms. Tao had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PSYCHIATRY RESEARCH
Opioid initiation in dementia tied to an 11-fold increased risk of death
Opioid initiation for older adults with dementia is linked to a significantly increased risk of death, especially in the first 2 weeks, when the risk is elevated 11-fold, new research shows.
“We expected that opioids would be associated with an increased risk of death, but we are surprised by the magnitude,” study investigator Christina Jensen-Dahm, MD, PhD, with the Danish Dementia Research Centre, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet, Denmark, told this news organization.
“It’s important that physicians carefully evaluate the risk and benefits if considering initiating an opioid, and this is particularly important in elderly with dementia,” Dr. Jensen-Dahm added.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Risky business
Using Danish nationwide registries, the researchers analyzed data on all 75,471 adults in Denmark who were aged 65 and older and had been diagnosed with dementia between 2008 and 2018. A total of 31,619 individuals (42%) filled a prescription for an opioid. These “exposed” individuals were matched to 63,235 unexposed individuals.
Among the exposed group, 10,474 (33%) died within 180 days after starting opioid therapy, compared with 3,980 (6.4%) in the unexposed group.
After adjusting for potential differences between groups, new use of an opioid was associated with a greater than fourfold excess mortality risk (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.16; 95% confidence interval, 4.00-4.33).
New use of a strong opioid – defined as morphine, oxycodone, ketobemidone, hydromorphone, pethidine, buprenorphine, and fentanyl – was associated with a greater than sixfold increase in mortality risk (aHR, 6.42; 95% CI, 6.08-6.79).
Among those who used fentanyl patches as their first opioid, 65% died within the first 180 days, compared with 6.7% in the unexposed – an eightfold increased mortality risk (aHR, 8.04; 95% CI, 7.01-9.22).
For all opioids, the risk was greatest in the first 14 days, with a nearly 11-fold increased risk of mortality (aHR, 10.8; 95% CI, 9.74-11.99). However, there remained a twofold increase in risk after taking opioids for 90 days (aHR, 2.32; 95% CI, 2.17-2.48).
“Opioids are associated with severe and well-known side effects, such as sedation, confusion, respiratory depression, falls, and in the most severe cases, death. In the general population, opioids have been associated with an increased risk of death, and similar to ours, greatest in the first 14 days,” said Dr. Jensen-Dahm.
Need to weigh risks, benefits
Commenting on the study, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement at the Alzheimer’s Association, told this news organization that the use of strong opioids has “increased considerably over the past decade among older people with dementia. Opioid therapy should only be considered for pain if the benefits are anticipated to outweigh the risks in individuals who are living with dementia.”
“Opioids are very powerful drugs, and while we need to see additional research in more diverse populations, these initial findings indicate they may put older adults with dementia at much higher risk of death,” Nicole Purcell, DO, neurologist and senior director of clinical practice at the Alzheimer’s Association, added in a conference statement.
“Pain should not go undiagnosed or untreated, in particular in people living with dementia, who may not be able to effectively articulate the location and severity of the pain,” Dr. Purcell added.
These new findings further emphasize the need for discussion between patient, family, and physician. Decisions about prescribing pain medication should be thought through carefully, and if used, there needs to be careful monitoring of the patient, said Dr. Purcell.
The study was supported by a grant from the Capital Region of Denmark. Dr. Jensen-Dahm, Dr. Griffin, and Dr. Purcell have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid initiation for older adults with dementia is linked to a significantly increased risk of death, especially in the first 2 weeks, when the risk is elevated 11-fold, new research shows.
“We expected that opioids would be associated with an increased risk of death, but we are surprised by the magnitude,” study investigator Christina Jensen-Dahm, MD, PhD, with the Danish Dementia Research Centre, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet, Denmark, told this news organization.
“It’s important that physicians carefully evaluate the risk and benefits if considering initiating an opioid, and this is particularly important in elderly with dementia,” Dr. Jensen-Dahm added.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Risky business
Using Danish nationwide registries, the researchers analyzed data on all 75,471 adults in Denmark who were aged 65 and older and had been diagnosed with dementia between 2008 and 2018. A total of 31,619 individuals (42%) filled a prescription for an opioid. These “exposed” individuals were matched to 63,235 unexposed individuals.
Among the exposed group, 10,474 (33%) died within 180 days after starting opioid therapy, compared with 3,980 (6.4%) in the unexposed group.
After adjusting for potential differences between groups, new use of an opioid was associated with a greater than fourfold excess mortality risk (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.16; 95% confidence interval, 4.00-4.33).
New use of a strong opioid – defined as morphine, oxycodone, ketobemidone, hydromorphone, pethidine, buprenorphine, and fentanyl – was associated with a greater than sixfold increase in mortality risk (aHR, 6.42; 95% CI, 6.08-6.79).
Among those who used fentanyl patches as their first opioid, 65% died within the first 180 days, compared with 6.7% in the unexposed – an eightfold increased mortality risk (aHR, 8.04; 95% CI, 7.01-9.22).
For all opioids, the risk was greatest in the first 14 days, with a nearly 11-fold increased risk of mortality (aHR, 10.8; 95% CI, 9.74-11.99). However, there remained a twofold increase in risk after taking opioids for 90 days (aHR, 2.32; 95% CI, 2.17-2.48).
“Opioids are associated with severe and well-known side effects, such as sedation, confusion, respiratory depression, falls, and in the most severe cases, death. In the general population, opioids have been associated with an increased risk of death, and similar to ours, greatest in the first 14 days,” said Dr. Jensen-Dahm.
Need to weigh risks, benefits
Commenting on the study, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement at the Alzheimer’s Association, told this news organization that the use of strong opioids has “increased considerably over the past decade among older people with dementia. Opioid therapy should only be considered for pain if the benefits are anticipated to outweigh the risks in individuals who are living with dementia.”
“Opioids are very powerful drugs, and while we need to see additional research in more diverse populations, these initial findings indicate they may put older adults with dementia at much higher risk of death,” Nicole Purcell, DO, neurologist and senior director of clinical practice at the Alzheimer’s Association, added in a conference statement.
“Pain should not go undiagnosed or untreated, in particular in people living with dementia, who may not be able to effectively articulate the location and severity of the pain,” Dr. Purcell added.
These new findings further emphasize the need for discussion between patient, family, and physician. Decisions about prescribing pain medication should be thought through carefully, and if used, there needs to be careful monitoring of the patient, said Dr. Purcell.
The study was supported by a grant from the Capital Region of Denmark. Dr. Jensen-Dahm, Dr. Griffin, and Dr. Purcell have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Opioid initiation for older adults with dementia is linked to a significantly increased risk of death, especially in the first 2 weeks, when the risk is elevated 11-fold, new research shows.
“We expected that opioids would be associated with an increased risk of death, but we are surprised by the magnitude,” study investigator Christina Jensen-Dahm, MD, PhD, with the Danish Dementia Research Centre, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet, Denmark, told this news organization.
“It’s important that physicians carefully evaluate the risk and benefits if considering initiating an opioid, and this is particularly important in elderly with dementia,” Dr. Jensen-Dahm added.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Risky business
Using Danish nationwide registries, the researchers analyzed data on all 75,471 adults in Denmark who were aged 65 and older and had been diagnosed with dementia between 2008 and 2018. A total of 31,619 individuals (42%) filled a prescription for an opioid. These “exposed” individuals were matched to 63,235 unexposed individuals.
Among the exposed group, 10,474 (33%) died within 180 days after starting opioid therapy, compared with 3,980 (6.4%) in the unexposed group.
After adjusting for potential differences between groups, new use of an opioid was associated with a greater than fourfold excess mortality risk (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.16; 95% confidence interval, 4.00-4.33).
New use of a strong opioid – defined as morphine, oxycodone, ketobemidone, hydromorphone, pethidine, buprenorphine, and fentanyl – was associated with a greater than sixfold increase in mortality risk (aHR, 6.42; 95% CI, 6.08-6.79).
Among those who used fentanyl patches as their first opioid, 65% died within the first 180 days, compared with 6.7% in the unexposed – an eightfold increased mortality risk (aHR, 8.04; 95% CI, 7.01-9.22).
For all opioids, the risk was greatest in the first 14 days, with a nearly 11-fold increased risk of mortality (aHR, 10.8; 95% CI, 9.74-11.99). However, there remained a twofold increase in risk after taking opioids for 90 days (aHR, 2.32; 95% CI, 2.17-2.48).
“Opioids are associated with severe and well-known side effects, such as sedation, confusion, respiratory depression, falls, and in the most severe cases, death. In the general population, opioids have been associated with an increased risk of death, and similar to ours, greatest in the first 14 days,” said Dr. Jensen-Dahm.
Need to weigh risks, benefits
Commenting on the study, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement at the Alzheimer’s Association, told this news organization that the use of strong opioids has “increased considerably over the past decade among older people with dementia. Opioid therapy should only be considered for pain if the benefits are anticipated to outweigh the risks in individuals who are living with dementia.”
“Opioids are very powerful drugs, and while we need to see additional research in more diverse populations, these initial findings indicate they may put older adults with dementia at much higher risk of death,” Nicole Purcell, DO, neurologist and senior director of clinical practice at the Alzheimer’s Association, added in a conference statement.
“Pain should not go undiagnosed or untreated, in particular in people living with dementia, who may not be able to effectively articulate the location and severity of the pain,” Dr. Purcell added.
These new findings further emphasize the need for discussion between patient, family, and physician. Decisions about prescribing pain medication should be thought through carefully, and if used, there needs to be careful monitoring of the patient, said Dr. Purcell.
The study was supported by a grant from the Capital Region of Denmark. Dr. Jensen-Dahm, Dr. Griffin, and Dr. Purcell have no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
From AAIC 2023
‘Brain fitness program’ may aid memory loss, concussion, ADHD
new research shows.
The program, which consists of targeted cognitive training and EEG-based neurofeedback, coupled with meditation and diet/lifestyle coaching, led to improvements in memory, attention, mood, alertness, and sleep.
The program promotes “neuroplasticity and was equally effective for patients with all three conditions,” program creator Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Patients with mild to moderate cognitive symptoms often see “remarkable” results within 3 months of consistently following the program, said Dr. Fotuhi, adjunct professor of neuroscience at George Washington University, Washington, and medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center, McLean, Va.
“It actually makes intuitive sense that a healthier and stronger brain would function better and that patients of all ages with various cognitive or emotional symptoms would all benefit from improving the biology of their brain,” Dr. Fotuhi added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Personalized program
The findings are based on 223 children and adults who completed the 12-week NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Program (NeuroGrow BFP), including 71 with ADHD, 88 with PCS, and 64 with memory loss, defined as diagnosed mild cognitive impairment or subjective cognitive decline.
As part of the program, participants undergo a complete neurocognitive evaluation, including tests for verbal memory, complex attention, processing speed, executive functioning, and the Neurocognitive Index.
They also complete questionnaires regarding sleep, mood, diet, exercise, and anxiety/depression, and they undergo quantitative EEG at the beginning and end of the program.
A comparison of before and after neurocognitive test scores showed that all three patient subgroups experienced statistically significant improvements on most measures, the study team reports.
After completing the program, 60%-90% of patients scored higher on cognitive tests and reported having fewer cognitive, sleep, and emotional symptoms.
In all subgroups, the most significant improvement was observed in executive functioning.
“These preliminary findings appear to show that multimodal interventions which are known to increase neuroplasticity in the brain, when personalized, can have benefits for patients with cognitive symptoms from a variety of neurological conditions,” the investigators wrote.
The study’s strengths include a large, community-based sample of patients of different ages who had disruptive symptoms and abnormalities as determined using objective cognitive tests whose progress was monitored by objective and subjective measures.
The chief limitation is the lack of a control or placebo group.
“Though it is difficult to find a comparable group of patients with the exact same profile of cognitive deficits and brain-related symptoms, studying a larger group of patients – and comparing them with a wait-list group – may make it possible to do a more definitive assessment of the NeuroGrow BFP,” the researchers noted.
Dr. Fotuhi said the “secret to the success” of the program is that it involves a full assessment of all cognitive and neurobehavioral symptoms for each patient. This allows for individualized and targeted interventions for specific concerns and symptoms.
He said there is a need to recognize that patients who present to a neurology practice with a single complaint, such as a problem with memory or attention, often have other problems, such as anxiety/depression, stress, insomnia, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes, sleep apnea, or alcohol overuse.
“Each of these factors can affect their cognitive abilities and need a multimodal set of interventions in order to see full resolution of their cognitive symptoms,” Dr. Fotuhi said.
He has created a series of educational videos to demonstrate the program’s benefits.
The self-pay cost for the NeuroGrow BFP assessment and treatment sessions is approximately $7,000.
Dr. Fotuhi said all of the interventions included in the program are readily available at low cost.
He suggested that health care professionals who lack time or staff for conducting a comprehensive neurocognitive assessment for their patients can provide them with a copy of the Brain Health Index.
“Patients can then be instructed to work on the individual components of their brain health on their own – and measure their brain health index on a weekly basis,” Dr. Fotuhi said. “Private practices or academic centers can use the detailed information I have provided in my paper to develop their own brain fitness program.”
Not ready for prime time
Commenting on the study, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that “nonpharmacologic interventions can help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with dementia.
“The current study investigates nonpharmacologic interventions in a small number of patients with ADHD, postconcussion syndrome, or memory loss. The researchers found improvements on most measures following the brain rehabilitation program.
“While this is interesting, more work is needed in larger, more diverse cohorts before these programs can be applied broadly. Nonpharmacologic interventions are a helpful tool that need to be studied further in future studies,” Dr. Griffin added.
Funding for the study was provided by the NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center. Dr. Fotuhi, the owner of NeuroGrow, was involved in data analysis, writing, editing, approval, and decision to publish. Dr. Griffin reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
The program, which consists of targeted cognitive training and EEG-based neurofeedback, coupled with meditation and diet/lifestyle coaching, led to improvements in memory, attention, mood, alertness, and sleep.
The program promotes “neuroplasticity and was equally effective for patients with all three conditions,” program creator Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Patients with mild to moderate cognitive symptoms often see “remarkable” results within 3 months of consistently following the program, said Dr. Fotuhi, adjunct professor of neuroscience at George Washington University, Washington, and medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center, McLean, Va.
“It actually makes intuitive sense that a healthier and stronger brain would function better and that patients of all ages with various cognitive or emotional symptoms would all benefit from improving the biology of their brain,” Dr. Fotuhi added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Personalized program
The findings are based on 223 children and adults who completed the 12-week NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Program (NeuroGrow BFP), including 71 with ADHD, 88 with PCS, and 64 with memory loss, defined as diagnosed mild cognitive impairment or subjective cognitive decline.
As part of the program, participants undergo a complete neurocognitive evaluation, including tests for verbal memory, complex attention, processing speed, executive functioning, and the Neurocognitive Index.
They also complete questionnaires regarding sleep, mood, diet, exercise, and anxiety/depression, and they undergo quantitative EEG at the beginning and end of the program.
A comparison of before and after neurocognitive test scores showed that all three patient subgroups experienced statistically significant improvements on most measures, the study team reports.
After completing the program, 60%-90% of patients scored higher on cognitive tests and reported having fewer cognitive, sleep, and emotional symptoms.
In all subgroups, the most significant improvement was observed in executive functioning.
“These preliminary findings appear to show that multimodal interventions which are known to increase neuroplasticity in the brain, when personalized, can have benefits for patients with cognitive symptoms from a variety of neurological conditions,” the investigators wrote.
The study’s strengths include a large, community-based sample of patients of different ages who had disruptive symptoms and abnormalities as determined using objective cognitive tests whose progress was monitored by objective and subjective measures.
The chief limitation is the lack of a control or placebo group.
“Though it is difficult to find a comparable group of patients with the exact same profile of cognitive deficits and brain-related symptoms, studying a larger group of patients – and comparing them with a wait-list group – may make it possible to do a more definitive assessment of the NeuroGrow BFP,” the researchers noted.
Dr. Fotuhi said the “secret to the success” of the program is that it involves a full assessment of all cognitive and neurobehavioral symptoms for each patient. This allows for individualized and targeted interventions for specific concerns and symptoms.
He said there is a need to recognize that patients who present to a neurology practice with a single complaint, such as a problem with memory or attention, often have other problems, such as anxiety/depression, stress, insomnia, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes, sleep apnea, or alcohol overuse.
“Each of these factors can affect their cognitive abilities and need a multimodal set of interventions in order to see full resolution of their cognitive symptoms,” Dr. Fotuhi said.
He has created a series of educational videos to demonstrate the program’s benefits.
The self-pay cost for the NeuroGrow BFP assessment and treatment sessions is approximately $7,000.
Dr. Fotuhi said all of the interventions included in the program are readily available at low cost.
He suggested that health care professionals who lack time or staff for conducting a comprehensive neurocognitive assessment for their patients can provide them with a copy of the Brain Health Index.
“Patients can then be instructed to work on the individual components of their brain health on their own – and measure their brain health index on a weekly basis,” Dr. Fotuhi said. “Private practices or academic centers can use the detailed information I have provided in my paper to develop their own brain fitness program.”
Not ready for prime time
Commenting on the study, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that “nonpharmacologic interventions can help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with dementia.
“The current study investigates nonpharmacologic interventions in a small number of patients with ADHD, postconcussion syndrome, or memory loss. The researchers found improvements on most measures following the brain rehabilitation program.
“While this is interesting, more work is needed in larger, more diverse cohorts before these programs can be applied broadly. Nonpharmacologic interventions are a helpful tool that need to be studied further in future studies,” Dr. Griffin added.
Funding for the study was provided by the NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center. Dr. Fotuhi, the owner of NeuroGrow, was involved in data analysis, writing, editing, approval, and decision to publish. Dr. Griffin reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
The program, which consists of targeted cognitive training and EEG-based neurofeedback, coupled with meditation and diet/lifestyle coaching, led to improvements in memory, attention, mood, alertness, and sleep.
The program promotes “neuroplasticity and was equally effective for patients with all three conditions,” program creator Majid Fotuhi, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
Patients with mild to moderate cognitive symptoms often see “remarkable” results within 3 months of consistently following the program, said Dr. Fotuhi, adjunct professor of neuroscience at George Washington University, Washington, and medical director of NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center, McLean, Va.
“It actually makes intuitive sense that a healthier and stronger brain would function better and that patients of all ages with various cognitive or emotional symptoms would all benefit from improving the biology of their brain,” Dr. Fotuhi added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Personalized program
The findings are based on 223 children and adults who completed the 12-week NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Program (NeuroGrow BFP), including 71 with ADHD, 88 with PCS, and 64 with memory loss, defined as diagnosed mild cognitive impairment or subjective cognitive decline.
As part of the program, participants undergo a complete neurocognitive evaluation, including tests for verbal memory, complex attention, processing speed, executive functioning, and the Neurocognitive Index.
They also complete questionnaires regarding sleep, mood, diet, exercise, and anxiety/depression, and they undergo quantitative EEG at the beginning and end of the program.
A comparison of before and after neurocognitive test scores showed that all three patient subgroups experienced statistically significant improvements on most measures, the study team reports.
After completing the program, 60%-90% of patients scored higher on cognitive tests and reported having fewer cognitive, sleep, and emotional symptoms.
In all subgroups, the most significant improvement was observed in executive functioning.
“These preliminary findings appear to show that multimodal interventions which are known to increase neuroplasticity in the brain, when personalized, can have benefits for patients with cognitive symptoms from a variety of neurological conditions,” the investigators wrote.
The study’s strengths include a large, community-based sample of patients of different ages who had disruptive symptoms and abnormalities as determined using objective cognitive tests whose progress was monitored by objective and subjective measures.
The chief limitation is the lack of a control or placebo group.
“Though it is difficult to find a comparable group of patients with the exact same profile of cognitive deficits and brain-related symptoms, studying a larger group of patients – and comparing them with a wait-list group – may make it possible to do a more definitive assessment of the NeuroGrow BFP,” the researchers noted.
Dr. Fotuhi said the “secret to the success” of the program is that it involves a full assessment of all cognitive and neurobehavioral symptoms for each patient. This allows for individualized and targeted interventions for specific concerns and symptoms.
He said there is a need to recognize that patients who present to a neurology practice with a single complaint, such as a problem with memory or attention, often have other problems, such as anxiety/depression, stress, insomnia, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes, sleep apnea, or alcohol overuse.
“Each of these factors can affect their cognitive abilities and need a multimodal set of interventions in order to see full resolution of their cognitive symptoms,” Dr. Fotuhi said.
He has created a series of educational videos to demonstrate the program’s benefits.
The self-pay cost for the NeuroGrow BFP assessment and treatment sessions is approximately $7,000.
Dr. Fotuhi said all of the interventions included in the program are readily available at low cost.
He suggested that health care professionals who lack time or staff for conducting a comprehensive neurocognitive assessment for their patients can provide them with a copy of the Brain Health Index.
“Patients can then be instructed to work on the individual components of their brain health on their own – and measure their brain health index on a weekly basis,” Dr. Fotuhi said. “Private practices or academic centers can use the detailed information I have provided in my paper to develop their own brain fitness program.”
Not ready for prime time
Commenting on the study, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted that “nonpharmacologic interventions can help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with dementia.
“The current study investigates nonpharmacologic interventions in a small number of patients with ADHD, postconcussion syndrome, or memory loss. The researchers found improvements on most measures following the brain rehabilitation program.
“While this is interesting, more work is needed in larger, more diverse cohorts before these programs can be applied broadly. Nonpharmacologic interventions are a helpful tool that need to be studied further in future studies,” Dr. Griffin added.
Funding for the study was provided by the NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center. Dr. Fotuhi, the owner of NeuroGrow, was involved in data analysis, writing, editing, approval, and decision to publish. Dr. Griffin reported no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE REPORTS
Promising phase 3 results for Alzheimer’s drug donanemab
results of a phase 3 study showed.
“This trial demonstrates that an antiamyloid drug significantly slows the disease and provides meaningful benefit to patients, and we’re hoping that with approval, we will be able to make that drug available,” said Mark Mintun, MD, VP, pain and neurodegeneration research, Eli Lilly.
At a press briefing highlighting the new results, Maria Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer, Alzheimer’s Association, noted the “palpable excitement” surrounding this new study, which follows on the heels of other promising antiamyloid research. “This is the decade of Alzheimer’s disease, and it will get better from here,” she said.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and were published online in JAMA.
Primary, secondary endpoints met
The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 study included 1,736 patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia for whom PET showed evidence of amyloid and tau pathology. The mean age of the participants was 73 years, and most of the participants were White.
Participants were randomly assigned to receive either placebo or donanemab, an investigational IgG1 monoclonal antibody directed against an insoluble, modified, N-terminal, truncated form of beta-amyloid. Donanemab was administered at a dose of 700 mg for the first three doses and 1,400 mg thereafter. The drug was administered intravenously every 4 weeks for up to 72 weeks.
Researchers stratified patients on the basis of the amount of tau, a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease progression, into a low/medium tau group and a combined tau group (low/medium and high tau).
The primary endpoint was change from baseline to 76 weeks on the integrated Alzheimer’s Disease Rating Scale (iADRS), which measures cognition and activities of daily living.
In those with low/medium tau levels, the least squares mean (LSM) change in iADRS score was −6.02 (95% confidence interval, −7.01 to −5.03) in the donanemab group and −9.27 (95% CI, −10.23 to −8.31) in the placebo group (difference, 3.25; 95% CI, 1.88 – 4.62; P < .001), representing a 35.1% slowing of disease progression.
In the combined (tau) population, LSM change in iADRS was −10.19 (95% CI, −11.22 to −9.16) in the donanemab group and −13.11 (95% CI, −14.10 to −12.13) in the placebo group (difference, 2.92; 95% CI, 1.51 – 4.33; P < .001), representing a 22.3% slowing of disease progression.
The study also met all secondary endpoints regarding measurements of cognitive and functional decline, including the Clinical Dementia Rating–Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB), which showed 36% slowing of decline (P < .0001) over 18 months.
The authors noted that the changes on these scales were clinically meaningful (considered to be > 20% slowing of clinical progression) for both the low/medium tau and combined populations.
Greater benefit with lower tau
However, patients with low/medium tau generally demonstrated effect size estimates that were larger than those of the overall population, which suggests there’s greater benefit when amyloid-lowering therapies are initiated at an earlier disease stage, the investigators noted.
Additional support for clinical relevance was a 38.6% risk reduction of disease progression, as measured on the CDR–Global Score.
In addition, participants who received the active drug benefited in terms of activities of daily living, as demonstrated by 40% less decline (P < .0001) on the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study–Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Inventory.
Donanemab significantly reduced brain amyloid plaque: 80% (low/medium tau population) and 76% (combined population) of participants achieved amyloid clearance at 76 weeks. The intervention was also associated with a greater decrease in whole-brain volume.
The treatment effect continued to widen after patients were switched to placebo, as evidenced on PET scan at 6 or 12 months, said Dr. Mintun.
The effects of the drug were similar among men and women but were especially pronounced among younger participants, with a 48% slowing on iADRS and a 45% slowing on CDR-SB in those younger than 75 years.
Safety issues
However, the drug is not without some safety concerns. Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIAs) occurred in 36.8% of the treatment group versus 14.9% of the placebo group, and in 40.6% of patients who were homozygous for apo E4 and received the drug. Microhemorrhage occurred in 26.8% in the donanemab group versus 12.5% in the placebo group.
Most ARIA cases were mild to moderate and resolved or stabilized with appropriate management. However, three deaths were determined to be drug related among participants who developed serious ARIAs or brain bleeding and swelling.
An important study limitation was that it enrolled primarily White patients (91.5%), which may limit generalizability to other populations, and the age limit was 85 years, which some believe is an inadequate representation of older adults. In addition, the 18-month treatment window limits the long-term understanding of donanemab’s benefits and side effects.
Eli Lilly has filed a submission to the Food and Drug Administration. If approved, donanemab will be the third antiamyloid monoclonal antibody to receive this status, following aducanumab (Aduhelm) and lecanemab (Leqembi).
Strongest data yet
Commenting on the study findings, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association, said these new results are “very, very exciting” and represent “the strongest data to-date” for antiamyloid monoclonal antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease.
“A good percentage of individuals on the drug actually saw a complete clearance of amyloid, and some had to be taken off the drug, because if you’re on an antiamyloid drug and there’s no amyloid, what are you going for?”
He noted that the study had some unique aspects, including using tau-PET “to see whether or not the drug is more effective in subpopulations.”
Access to this and other antiamyloid therapies should be a priority, said Dr. Griffin. “We have to make sure people who have the potential to benefit from these treatments do.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is calling for Medicare beneficiaries who are living with the disease to receive the same coverage afforded to those with other diseases.
“The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services policy to block Medicare access to FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease treatments is in stark contrast to scientific evidence, is unprecedented and must be reversed immediately,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and CEO of the Alzheimer’s Association, said in a press release.
Also important is tracking the longitudinal performance of these drugs outside of clinical trials, said Dr. Griffin. “Not everyone is going to be in that Goldilocks zone of being able to see a doctor whenever they want and have access to these PET and MRI tools and other things used in clinical trials.”
He noted that the Alzheimer’s Association is leading a network for diagnostics and therapeutics (ALZ-NET) that will track the performance of novel FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease therapies “in the real world.”
While these are exciting findings for antiamyloid therapy, “we can’t take our foot off the gas, we need more therapies that target different aspects of the disease biology,” said Dr. Griffin.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
results of a phase 3 study showed.
“This trial demonstrates that an antiamyloid drug significantly slows the disease and provides meaningful benefit to patients, and we’re hoping that with approval, we will be able to make that drug available,” said Mark Mintun, MD, VP, pain and neurodegeneration research, Eli Lilly.
At a press briefing highlighting the new results, Maria Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer, Alzheimer’s Association, noted the “palpable excitement” surrounding this new study, which follows on the heels of other promising antiamyloid research. “This is the decade of Alzheimer’s disease, and it will get better from here,” she said.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and were published online in JAMA.
Primary, secondary endpoints met
The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 study included 1,736 patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia for whom PET showed evidence of amyloid and tau pathology. The mean age of the participants was 73 years, and most of the participants were White.
Participants were randomly assigned to receive either placebo or donanemab, an investigational IgG1 monoclonal antibody directed against an insoluble, modified, N-terminal, truncated form of beta-amyloid. Donanemab was administered at a dose of 700 mg for the first three doses and 1,400 mg thereafter. The drug was administered intravenously every 4 weeks for up to 72 weeks.
Researchers stratified patients on the basis of the amount of tau, a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease progression, into a low/medium tau group and a combined tau group (low/medium and high tau).
The primary endpoint was change from baseline to 76 weeks on the integrated Alzheimer’s Disease Rating Scale (iADRS), which measures cognition and activities of daily living.
In those with low/medium tau levels, the least squares mean (LSM) change in iADRS score was −6.02 (95% confidence interval, −7.01 to −5.03) in the donanemab group and −9.27 (95% CI, −10.23 to −8.31) in the placebo group (difference, 3.25; 95% CI, 1.88 – 4.62; P < .001), representing a 35.1% slowing of disease progression.
In the combined (tau) population, LSM change in iADRS was −10.19 (95% CI, −11.22 to −9.16) in the donanemab group and −13.11 (95% CI, −14.10 to −12.13) in the placebo group (difference, 2.92; 95% CI, 1.51 – 4.33; P < .001), representing a 22.3% slowing of disease progression.
The study also met all secondary endpoints regarding measurements of cognitive and functional decline, including the Clinical Dementia Rating–Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB), which showed 36% slowing of decline (P < .0001) over 18 months.
The authors noted that the changes on these scales were clinically meaningful (considered to be > 20% slowing of clinical progression) for both the low/medium tau and combined populations.
Greater benefit with lower tau
However, patients with low/medium tau generally demonstrated effect size estimates that were larger than those of the overall population, which suggests there’s greater benefit when amyloid-lowering therapies are initiated at an earlier disease stage, the investigators noted.
Additional support for clinical relevance was a 38.6% risk reduction of disease progression, as measured on the CDR–Global Score.
In addition, participants who received the active drug benefited in terms of activities of daily living, as demonstrated by 40% less decline (P < .0001) on the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study–Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Inventory.
Donanemab significantly reduced brain amyloid plaque: 80% (low/medium tau population) and 76% (combined population) of participants achieved amyloid clearance at 76 weeks. The intervention was also associated with a greater decrease in whole-brain volume.
The treatment effect continued to widen after patients were switched to placebo, as evidenced on PET scan at 6 or 12 months, said Dr. Mintun.
The effects of the drug were similar among men and women but were especially pronounced among younger participants, with a 48% slowing on iADRS and a 45% slowing on CDR-SB in those younger than 75 years.
Safety issues
However, the drug is not without some safety concerns. Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIAs) occurred in 36.8% of the treatment group versus 14.9% of the placebo group, and in 40.6% of patients who were homozygous for apo E4 and received the drug. Microhemorrhage occurred in 26.8% in the donanemab group versus 12.5% in the placebo group.
Most ARIA cases were mild to moderate and resolved or stabilized with appropriate management. However, three deaths were determined to be drug related among participants who developed serious ARIAs or brain bleeding and swelling.
An important study limitation was that it enrolled primarily White patients (91.5%), which may limit generalizability to other populations, and the age limit was 85 years, which some believe is an inadequate representation of older adults. In addition, the 18-month treatment window limits the long-term understanding of donanemab’s benefits and side effects.
Eli Lilly has filed a submission to the Food and Drug Administration. If approved, donanemab will be the third antiamyloid monoclonal antibody to receive this status, following aducanumab (Aduhelm) and lecanemab (Leqembi).
Strongest data yet
Commenting on the study findings, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association, said these new results are “very, very exciting” and represent “the strongest data to-date” for antiamyloid monoclonal antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease.
“A good percentage of individuals on the drug actually saw a complete clearance of amyloid, and some had to be taken off the drug, because if you’re on an antiamyloid drug and there’s no amyloid, what are you going for?”
He noted that the study had some unique aspects, including using tau-PET “to see whether or not the drug is more effective in subpopulations.”
Access to this and other antiamyloid therapies should be a priority, said Dr. Griffin. “We have to make sure people who have the potential to benefit from these treatments do.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is calling for Medicare beneficiaries who are living with the disease to receive the same coverage afforded to those with other diseases.
“The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services policy to block Medicare access to FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease treatments is in stark contrast to scientific evidence, is unprecedented and must be reversed immediately,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and CEO of the Alzheimer’s Association, said in a press release.
Also important is tracking the longitudinal performance of these drugs outside of clinical trials, said Dr. Griffin. “Not everyone is going to be in that Goldilocks zone of being able to see a doctor whenever they want and have access to these PET and MRI tools and other things used in clinical trials.”
He noted that the Alzheimer’s Association is leading a network for diagnostics and therapeutics (ALZ-NET) that will track the performance of novel FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease therapies “in the real world.”
While these are exciting findings for antiamyloid therapy, “we can’t take our foot off the gas, we need more therapies that target different aspects of the disease biology,” said Dr. Griffin.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
results of a phase 3 study showed.
“This trial demonstrates that an antiamyloid drug significantly slows the disease and provides meaningful benefit to patients, and we’re hoping that with approval, we will be able to make that drug available,” said Mark Mintun, MD, VP, pain and neurodegeneration research, Eli Lilly.
At a press briefing highlighting the new results, Maria Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer, Alzheimer’s Association, noted the “palpable excitement” surrounding this new study, which follows on the heels of other promising antiamyloid research. “This is the decade of Alzheimer’s disease, and it will get better from here,” she said.
The findings were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference and were published online in JAMA.
Primary, secondary endpoints met
The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 study included 1,736 patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia for whom PET showed evidence of amyloid and tau pathology. The mean age of the participants was 73 years, and most of the participants were White.
Participants were randomly assigned to receive either placebo or donanemab, an investigational IgG1 monoclonal antibody directed against an insoluble, modified, N-terminal, truncated form of beta-amyloid. Donanemab was administered at a dose of 700 mg for the first three doses and 1,400 mg thereafter. The drug was administered intravenously every 4 weeks for up to 72 weeks.
Researchers stratified patients on the basis of the amount of tau, a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease progression, into a low/medium tau group and a combined tau group (low/medium and high tau).
The primary endpoint was change from baseline to 76 weeks on the integrated Alzheimer’s Disease Rating Scale (iADRS), which measures cognition and activities of daily living.
In those with low/medium tau levels, the least squares mean (LSM) change in iADRS score was −6.02 (95% confidence interval, −7.01 to −5.03) in the donanemab group and −9.27 (95% CI, −10.23 to −8.31) in the placebo group (difference, 3.25; 95% CI, 1.88 – 4.62; P < .001), representing a 35.1% slowing of disease progression.
In the combined (tau) population, LSM change in iADRS was −10.19 (95% CI, −11.22 to −9.16) in the donanemab group and −13.11 (95% CI, −14.10 to −12.13) in the placebo group (difference, 2.92; 95% CI, 1.51 – 4.33; P < .001), representing a 22.3% slowing of disease progression.
The study also met all secondary endpoints regarding measurements of cognitive and functional decline, including the Clinical Dementia Rating–Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB), which showed 36% slowing of decline (P < .0001) over 18 months.
The authors noted that the changes on these scales were clinically meaningful (considered to be > 20% slowing of clinical progression) for both the low/medium tau and combined populations.
Greater benefit with lower tau
However, patients with low/medium tau generally demonstrated effect size estimates that were larger than those of the overall population, which suggests there’s greater benefit when amyloid-lowering therapies are initiated at an earlier disease stage, the investigators noted.
Additional support for clinical relevance was a 38.6% risk reduction of disease progression, as measured on the CDR–Global Score.
In addition, participants who received the active drug benefited in terms of activities of daily living, as demonstrated by 40% less decline (P < .0001) on the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study–Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Inventory.
Donanemab significantly reduced brain amyloid plaque: 80% (low/medium tau population) and 76% (combined population) of participants achieved amyloid clearance at 76 weeks. The intervention was also associated with a greater decrease in whole-brain volume.
The treatment effect continued to widen after patients were switched to placebo, as evidenced on PET scan at 6 or 12 months, said Dr. Mintun.
The effects of the drug were similar among men and women but were especially pronounced among younger participants, with a 48% slowing on iADRS and a 45% slowing on CDR-SB in those younger than 75 years.
Safety issues
However, the drug is not without some safety concerns. Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIAs) occurred in 36.8% of the treatment group versus 14.9% of the placebo group, and in 40.6% of patients who were homozygous for apo E4 and received the drug. Microhemorrhage occurred in 26.8% in the donanemab group versus 12.5% in the placebo group.
Most ARIA cases were mild to moderate and resolved or stabilized with appropriate management. However, three deaths were determined to be drug related among participants who developed serious ARIAs or brain bleeding and swelling.
An important study limitation was that it enrolled primarily White patients (91.5%), which may limit generalizability to other populations, and the age limit was 85 years, which some believe is an inadequate representation of older adults. In addition, the 18-month treatment window limits the long-term understanding of donanemab’s benefits and side effects.
Eli Lilly has filed a submission to the Food and Drug Administration. If approved, donanemab will be the third antiamyloid monoclonal antibody to receive this status, following aducanumab (Aduhelm) and lecanemab (Leqembi).
Strongest data yet
Commenting on the study findings, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association, said these new results are “very, very exciting” and represent “the strongest data to-date” for antiamyloid monoclonal antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease.
“A good percentage of individuals on the drug actually saw a complete clearance of amyloid, and some had to be taken off the drug, because if you’re on an antiamyloid drug and there’s no amyloid, what are you going for?”
He noted that the study had some unique aspects, including using tau-PET “to see whether or not the drug is more effective in subpopulations.”
Access to this and other antiamyloid therapies should be a priority, said Dr. Griffin. “We have to make sure people who have the potential to benefit from these treatments do.”
The Alzheimer’s Association is calling for Medicare beneficiaries who are living with the disease to receive the same coverage afforded to those with other diseases.
“The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services policy to block Medicare access to FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease treatments is in stark contrast to scientific evidence, is unprecedented and must be reversed immediately,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and CEO of the Alzheimer’s Association, said in a press release.
Also important is tracking the longitudinal performance of these drugs outside of clinical trials, said Dr. Griffin. “Not everyone is going to be in that Goldilocks zone of being able to see a doctor whenever they want and have access to these PET and MRI tools and other things used in clinical trials.”
He noted that the Alzheimer’s Association is leading a network for diagnostics and therapeutics (ALZ-NET) that will track the performance of novel FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease therapies “in the real world.”
While these are exciting findings for antiamyloid therapy, “we can’t take our foot off the gas, we need more therapies that target different aspects of the disease biology,” said Dr. Griffin.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2023
U.S. states, counties with highest Alzheimer’s prevalence rates identified
Investigators at Rush University in Chicago found AD prevalence was highest in Maryland, New York, Mississippi, and Florida. At the county level, Miami-Dade in Florida, Baltimore city, and Bronx County in New York were among the U.S. counties with the highest prevalence of the disease.
Such geographical variations may be caused by the unique make-up of regional populations, study investigator Kumar Rajan, PhD, professor of medicine and director of Rush Institute for Healthy Aging, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said in an interview.
Dr. Rajan presented the research at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
High-impact research
An estimated 6.7 million Americans are living with AD, a figure that’s expected to double by 2050. Estimating the prevalence of Alzheimer’s across states’ counties can provide a better understanding of region-specific disease burden and have policy implications for resource allocation, Dr. Rajan noted.
To determine the state- and county-specific prevalence of AD, the researchers applied AD data from the Chicago Health and Aging Project, a population-based study that’s about 60% African American, to county- and state-level data from the National Center for Health Statistics.
“We used estimates in our study in Chicago, which began in the 1990s and has approximately 10,800 people, and projected those estimates to county-level populations to see what the variations look like,” said Dr. Rajan.
Of 3,142 counties in 50 states, the East and Southeastern regions of the United States had the highest AD prevalence. For states, the highest rates were in Maryland (12.9%), New York (12.7%), Mississippi (12.5%), and Florida (12.5%).
California and Illinois were also among the top 10 states with the highest prevalence of Alzheimer’s.
California had the highest number of residents, with 719,000 (95% confidence interval, 665,000-774,400), followed by Florida with 579,000 (95% CI, 539,900 to 620,000), and Texas with 459,000 (95% CI, 422,700 to 496,000).
The three counties with the highest prevalence, all with 16.6%, were Miami-Dade County, Baltimore city, and Bronx County.
One county in the top 10 for AD prevalence was El Paso, Tex., which Dr. Rajan found “a bit surprising,” as Texas was not among the top four states with the highest prevalence.
In addition to older age, what’s likely driving elevated AD prevalence in these areas is the substantially larger proportion of minority populations who are at higher risk for AD, possibly due to health disparities, said Dr. Rajan.
Determining local-level estimates of AD should have “a very high impact” on public health programs aimed at AD prevention, detection, and treatment, he said. In addition, as more AD drugs are approved, there will likely be county-level and even state-level implications for Medicare coverage.
In addition, these new findings could help physicians treating or caring for minority populations “understand the landscape of what the disease looks like,” said Dr. Rajan.
A limitation of the study was that it was based on data from a single study, he noted.
The next step is to expand this research. Dr. Rajan and others are establishing the Regional and Ethnic Variations in Alzheimer’s and Cognitive Health Consortium, with the goal of gaining a better understanding of AD prevalence across six U.S. regions.
Optimal resource distribution
In a comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association, said the research provides useful information about AD prevalence at the local level.
“We need to understand how specific demographics and characteristics can help explain some of the high prevalence in certain areas.”
Compared with White Americans, Dr. Griffin noted that Black Americans are twice as likely to have AD, and older Hispanic Americans are 1.5 times as likely.
This new data will help pinpoint areas of high risk and high need so that funding, staffing, and other resources for those with AD and other dementias can be optimally distributed, he said.
“It gives us that kind of geographic specificity in terms of the prevalence so we can dig deeper and better allocate resources on a county level,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association “is fully committed to working with local agencies and being in the communities to assist them in their efforts to intervene in this disease.”
The study also highlights the need for more research to determine what factors other than age and race – such as potential environmental factors – might affect regional AD prevalence, he said.
The study received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Rajan and Dr. Griffin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators at Rush University in Chicago found AD prevalence was highest in Maryland, New York, Mississippi, and Florida. At the county level, Miami-Dade in Florida, Baltimore city, and Bronx County in New York were among the U.S. counties with the highest prevalence of the disease.
Such geographical variations may be caused by the unique make-up of regional populations, study investigator Kumar Rajan, PhD, professor of medicine and director of Rush Institute for Healthy Aging, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said in an interview.
Dr. Rajan presented the research at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
High-impact research
An estimated 6.7 million Americans are living with AD, a figure that’s expected to double by 2050. Estimating the prevalence of Alzheimer’s across states’ counties can provide a better understanding of region-specific disease burden and have policy implications for resource allocation, Dr. Rajan noted.
To determine the state- and county-specific prevalence of AD, the researchers applied AD data from the Chicago Health and Aging Project, a population-based study that’s about 60% African American, to county- and state-level data from the National Center for Health Statistics.
“We used estimates in our study in Chicago, which began in the 1990s and has approximately 10,800 people, and projected those estimates to county-level populations to see what the variations look like,” said Dr. Rajan.
Of 3,142 counties in 50 states, the East and Southeastern regions of the United States had the highest AD prevalence. For states, the highest rates were in Maryland (12.9%), New York (12.7%), Mississippi (12.5%), and Florida (12.5%).
California and Illinois were also among the top 10 states with the highest prevalence of Alzheimer’s.
California had the highest number of residents, with 719,000 (95% confidence interval, 665,000-774,400), followed by Florida with 579,000 (95% CI, 539,900 to 620,000), and Texas with 459,000 (95% CI, 422,700 to 496,000).
The three counties with the highest prevalence, all with 16.6%, were Miami-Dade County, Baltimore city, and Bronx County.
One county in the top 10 for AD prevalence was El Paso, Tex., which Dr. Rajan found “a bit surprising,” as Texas was not among the top four states with the highest prevalence.
In addition to older age, what’s likely driving elevated AD prevalence in these areas is the substantially larger proportion of minority populations who are at higher risk for AD, possibly due to health disparities, said Dr. Rajan.
Determining local-level estimates of AD should have “a very high impact” on public health programs aimed at AD prevention, detection, and treatment, he said. In addition, as more AD drugs are approved, there will likely be county-level and even state-level implications for Medicare coverage.
In addition, these new findings could help physicians treating or caring for minority populations “understand the landscape of what the disease looks like,” said Dr. Rajan.
A limitation of the study was that it was based on data from a single study, he noted.
The next step is to expand this research. Dr. Rajan and others are establishing the Regional and Ethnic Variations in Alzheimer’s and Cognitive Health Consortium, with the goal of gaining a better understanding of AD prevalence across six U.S. regions.
Optimal resource distribution
In a comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association, said the research provides useful information about AD prevalence at the local level.
“We need to understand how specific demographics and characteristics can help explain some of the high prevalence in certain areas.”
Compared with White Americans, Dr. Griffin noted that Black Americans are twice as likely to have AD, and older Hispanic Americans are 1.5 times as likely.
This new data will help pinpoint areas of high risk and high need so that funding, staffing, and other resources for those with AD and other dementias can be optimally distributed, he said.
“It gives us that kind of geographic specificity in terms of the prevalence so we can dig deeper and better allocate resources on a county level,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association “is fully committed to working with local agencies and being in the communities to assist them in their efforts to intervene in this disease.”
The study also highlights the need for more research to determine what factors other than age and race – such as potential environmental factors – might affect regional AD prevalence, he said.
The study received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Rajan and Dr. Griffin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators at Rush University in Chicago found AD prevalence was highest in Maryland, New York, Mississippi, and Florida. At the county level, Miami-Dade in Florida, Baltimore city, and Bronx County in New York were among the U.S. counties with the highest prevalence of the disease.
Such geographical variations may be caused by the unique make-up of regional populations, study investigator Kumar Rajan, PhD, professor of medicine and director of Rush Institute for Healthy Aging, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, said in an interview.
Dr. Rajan presented the research at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
High-impact research
An estimated 6.7 million Americans are living with AD, a figure that’s expected to double by 2050. Estimating the prevalence of Alzheimer’s across states’ counties can provide a better understanding of region-specific disease burden and have policy implications for resource allocation, Dr. Rajan noted.
To determine the state- and county-specific prevalence of AD, the researchers applied AD data from the Chicago Health and Aging Project, a population-based study that’s about 60% African American, to county- and state-level data from the National Center for Health Statistics.
“We used estimates in our study in Chicago, which began in the 1990s and has approximately 10,800 people, and projected those estimates to county-level populations to see what the variations look like,” said Dr. Rajan.
Of 3,142 counties in 50 states, the East and Southeastern regions of the United States had the highest AD prevalence. For states, the highest rates were in Maryland (12.9%), New York (12.7%), Mississippi (12.5%), and Florida (12.5%).
California and Illinois were also among the top 10 states with the highest prevalence of Alzheimer’s.
California had the highest number of residents, with 719,000 (95% confidence interval, 665,000-774,400), followed by Florida with 579,000 (95% CI, 539,900 to 620,000), and Texas with 459,000 (95% CI, 422,700 to 496,000).
The three counties with the highest prevalence, all with 16.6%, were Miami-Dade County, Baltimore city, and Bronx County.
One county in the top 10 for AD prevalence was El Paso, Tex., which Dr. Rajan found “a bit surprising,” as Texas was not among the top four states with the highest prevalence.
In addition to older age, what’s likely driving elevated AD prevalence in these areas is the substantially larger proportion of minority populations who are at higher risk for AD, possibly due to health disparities, said Dr. Rajan.
Determining local-level estimates of AD should have “a very high impact” on public health programs aimed at AD prevention, detection, and treatment, he said. In addition, as more AD drugs are approved, there will likely be county-level and even state-level implications for Medicare coverage.
In addition, these new findings could help physicians treating or caring for minority populations “understand the landscape of what the disease looks like,” said Dr. Rajan.
A limitation of the study was that it was based on data from a single study, he noted.
The next step is to expand this research. Dr. Rajan and others are establishing the Regional and Ethnic Variations in Alzheimer’s and Cognitive Health Consortium, with the goal of gaining a better understanding of AD prevalence across six U.S. regions.
Optimal resource distribution
In a comment, Percy Griffin, PhD, director of scientific engagement, Alzheimer’s Association, said the research provides useful information about AD prevalence at the local level.
“We need to understand how specific demographics and characteristics can help explain some of the high prevalence in certain areas.”
Compared with White Americans, Dr. Griffin noted that Black Americans are twice as likely to have AD, and older Hispanic Americans are 1.5 times as likely.
This new data will help pinpoint areas of high risk and high need so that funding, staffing, and other resources for those with AD and other dementias can be optimally distributed, he said.
“It gives us that kind of geographic specificity in terms of the prevalence so we can dig deeper and better allocate resources on a county level,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association “is fully committed to working with local agencies and being in the communities to assist them in their efforts to intervene in this disease.”
The study also highlights the need for more research to determine what factors other than age and race – such as potential environmental factors – might affect regional AD prevalence, he said.
The study received funding from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Rajan and Dr. Griffin reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAIC 2023
Forgetfulness and confusion
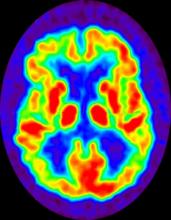
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of late-onset familial AD (onset after age 65 years).
AD is a common neurodegenerative disease associated with progressive impairment of behavioral and cognitive functions, including memory, comprehension, language, attention, reasoning, and judgment. In 2020, 5.8 million Americans were living with AD. By 2050, this number is projected to increase to 13.9 million people, or almost 3.3% of the US population. Globally, 152 million people are projected to have AD and other dementias by 2050. The worldwide increase in incidence and prevalence of AD is at least partially explained by an aging population and increased life expectancy.
The cause of AD remains unclear, but there is substantial evidence that AD is a highly heritable disorder. Familial AD is characterized by having more than one member in more than one generation with AD. The autosomal-dominant form of AD is linked to mutations in three genes: AAP on chromosome 21, PSEN1 on chromosome 14, and PSEN2 on chromosome 1. APP mutations may cause increased generation and aggregation of beta-amyloid peptide, whereas PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations result in aggregation of beta-amyloid by interfering with the processing of gamma-secretase.
APOE is another genetic marker that increases the risk for AD. Isoform e4 of the APOE gene (located on chromosome 19) has been associated with more sporadic and familial forms of AD that present after age 65 years. Approximately 50% of individuals carrying one APOEe4 develop AD, and 90% of individuals who have two alleles develop AD. Variants in the gene for the sortilin receptor, SORT1, have also been found in familial and sporadic forms of AD.
The cognitive and behavioral impairment associated with AD significantly affects a patient's social and occupational functioning. Insidiously progressive memory loss is a characteristic symptoms seen in patients presenting with AD. As the disease advances over the course of several years, other areas of cognition are impaired. Patients may develop language disorders (eg, anomic aphasia or anomia) and impairment in visuospatial skills and executive functions. A slow progression of behavioral changes may also occur in individuals with AD.
Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of AD (eg, insidious onset of cognitive impairment, clear history of worsening symptoms) have been developed and are often used to diagnose patients. In addition, biomarker evidence may help to increase the diagnostic certainty. Several cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers have shown excellent diagnostic ability by identifying tau pathology and cerebral amyloid-beta for AD.
Neuroimaging is becoming increasingly important for identifying the underlying causes of cognitive impairment. Currently, MRI is considered the preferred neuroimaging modality for AD because it allows for accurate measurement of the three-dimensional volume of brain structures, particularly the size of the hippocampus and related regions. CT can be used when MRI is not available or is contraindicated, such as in a patient with a pacemaker. PET is another noninvasive method for depicting tau pathology deposition and distribution in patients with cognitive impairment. In 2020, US Food and Drug Administration approved the first tau PET tracer, 18F-flortaucipir, which marked a significant achievement to improve AD diagnosis.
At present, the only therapies available for AD are symptomatic therapies. Cholinesterase inhibitors and a partial N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist are the standard medical treatments for AD. Antiamyloid therapies are also available for patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia. These include aducanumab, a first-in-class amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2021, and lecanemab, another amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2023. Both aducanumab and lecanemab are recommended for the treatment of patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which the safety and efficacy of these newer agents were demonstrated in clinical trials.
Secondary symptoms of AD, such as depression, agitation, aggression, hallucinations, delusions, and/or sleep disorders, can be treated with psychotropic agents. Behavioral interventions including patient-centered approaches and caregiver training can also be helpful for managing the cognitive and behavioral manifestations of AD, often in combination with pharmacologic interventions (eg, anxiolytics for anxiety and agitation, neuroleptics for delusions or hallucinations, and antidepressants or mood stabilizers for mood disorders). Regular physical activity and exercise may also play a role in delaying AD progression and possibly conferring a protective effect on brain health.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, Professor of Neurology, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood; Director, Clinical Neurophysiology Lab, Department of Neurology, Hines VA Hospital, Hines, IL.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of late-onset familial AD (onset after age 65 years).
AD is a common neurodegenerative disease associated with progressive impairment of behavioral and cognitive functions, including memory, comprehension, language, attention, reasoning, and judgment. In 2020, 5.8 million Americans were living with AD. By 2050, this number is projected to increase to 13.9 million people, or almost 3.3% of the US population. Globally, 152 million people are projected to have AD and other dementias by 2050. The worldwide increase in incidence and prevalence of AD is at least partially explained by an aging population and increased life expectancy.
The cause of AD remains unclear, but there is substantial evidence that AD is a highly heritable disorder. Familial AD is characterized by having more than one member in more than one generation with AD. The autosomal-dominant form of AD is linked to mutations in three genes: AAP on chromosome 21, PSEN1 on chromosome 14, and PSEN2 on chromosome 1. APP mutations may cause increased generation and aggregation of beta-amyloid peptide, whereas PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations result in aggregation of beta-amyloid by interfering with the processing of gamma-secretase.
APOE is another genetic marker that increases the risk for AD. Isoform e4 of the APOE gene (located on chromosome 19) has been associated with more sporadic and familial forms of AD that present after age 65 years. Approximately 50% of individuals carrying one APOEe4 develop AD, and 90% of individuals who have two alleles develop AD. Variants in the gene for the sortilin receptor, SORT1, have also been found in familial and sporadic forms of AD.
The cognitive and behavioral impairment associated with AD significantly affects a patient's social and occupational functioning. Insidiously progressive memory loss is a characteristic symptoms seen in patients presenting with AD. As the disease advances over the course of several years, other areas of cognition are impaired. Patients may develop language disorders (eg, anomic aphasia or anomia) and impairment in visuospatial skills and executive functions. A slow progression of behavioral changes may also occur in individuals with AD.
Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of AD (eg, insidious onset of cognitive impairment, clear history of worsening symptoms) have been developed and are often used to diagnose patients. In addition, biomarker evidence may help to increase the diagnostic certainty. Several cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers have shown excellent diagnostic ability by identifying tau pathology and cerebral amyloid-beta for AD.
Neuroimaging is becoming increasingly important for identifying the underlying causes of cognitive impairment. Currently, MRI is considered the preferred neuroimaging modality for AD because it allows for accurate measurement of the three-dimensional volume of brain structures, particularly the size of the hippocampus and related regions. CT can be used when MRI is not available or is contraindicated, such as in a patient with a pacemaker. PET is another noninvasive method for depicting tau pathology deposition and distribution in patients with cognitive impairment. In 2020, US Food and Drug Administration approved the first tau PET tracer, 18F-flortaucipir, which marked a significant achievement to improve AD diagnosis.
At present, the only therapies available for AD are symptomatic therapies. Cholinesterase inhibitors and a partial N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist are the standard medical treatments for AD. Antiamyloid therapies are also available for patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia. These include aducanumab, a first-in-class amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2021, and lecanemab, another amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2023. Both aducanumab and lecanemab are recommended for the treatment of patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which the safety and efficacy of these newer agents were demonstrated in clinical trials.
Secondary symptoms of AD, such as depression, agitation, aggression, hallucinations, delusions, and/or sleep disorders, can be treated with psychotropic agents. Behavioral interventions including patient-centered approaches and caregiver training can also be helpful for managing the cognitive and behavioral manifestations of AD, often in combination with pharmacologic interventions (eg, anxiolytics for anxiety and agitation, neuroleptics for delusions or hallucinations, and antidepressants or mood stabilizers for mood disorders). Regular physical activity and exercise may also play a role in delaying AD progression and possibly conferring a protective effect on brain health.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, Professor of Neurology, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood; Director, Clinical Neurophysiology Lab, Department of Neurology, Hines VA Hospital, Hines, IL.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
The history and findings in this case are suggestive of late-onset familial AD (onset after age 65 years).
AD is a common neurodegenerative disease associated with progressive impairment of behavioral and cognitive functions, including memory, comprehension, language, attention, reasoning, and judgment. In 2020, 5.8 million Americans were living with AD. By 2050, this number is projected to increase to 13.9 million people, or almost 3.3% of the US population. Globally, 152 million people are projected to have AD and other dementias by 2050. The worldwide increase in incidence and prevalence of AD is at least partially explained by an aging population and increased life expectancy.
The cause of AD remains unclear, but there is substantial evidence that AD is a highly heritable disorder. Familial AD is characterized by having more than one member in more than one generation with AD. The autosomal-dominant form of AD is linked to mutations in three genes: AAP on chromosome 21, PSEN1 on chromosome 14, and PSEN2 on chromosome 1. APP mutations may cause increased generation and aggregation of beta-amyloid peptide, whereas PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations result in aggregation of beta-amyloid by interfering with the processing of gamma-secretase.
APOE is another genetic marker that increases the risk for AD. Isoform e4 of the APOE gene (located on chromosome 19) has been associated with more sporadic and familial forms of AD that present after age 65 years. Approximately 50% of individuals carrying one APOEe4 develop AD, and 90% of individuals who have two alleles develop AD. Variants in the gene for the sortilin receptor, SORT1, have also been found in familial and sporadic forms of AD.
The cognitive and behavioral impairment associated with AD significantly affects a patient's social and occupational functioning. Insidiously progressive memory loss is a characteristic symptoms seen in patients presenting with AD. As the disease advances over the course of several years, other areas of cognition are impaired. Patients may develop language disorders (eg, anomic aphasia or anomia) and impairment in visuospatial skills and executive functions. A slow progression of behavioral changes may also occur in individuals with AD.
Clinical criteria for the diagnosis of AD (eg, insidious onset of cognitive impairment, clear history of worsening symptoms) have been developed and are often used to diagnose patients. In addition, biomarker evidence may help to increase the diagnostic certainty. Several cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers have shown excellent diagnostic ability by identifying tau pathology and cerebral amyloid-beta for AD.
Neuroimaging is becoming increasingly important for identifying the underlying causes of cognitive impairment. Currently, MRI is considered the preferred neuroimaging modality for AD because it allows for accurate measurement of the three-dimensional volume of brain structures, particularly the size of the hippocampus and related regions. CT can be used when MRI is not available or is contraindicated, such as in a patient with a pacemaker. PET is another noninvasive method for depicting tau pathology deposition and distribution in patients with cognitive impairment. In 2020, US Food and Drug Administration approved the first tau PET tracer, 18F-flortaucipir, which marked a significant achievement to improve AD diagnosis.
At present, the only therapies available for AD are symptomatic therapies. Cholinesterase inhibitors and a partial N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist are the standard medical treatments for AD. Antiamyloid therapies are also available for patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia. These include aducanumab, a first-in-class amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2021, and lecanemab, another amyloid-beta–directed antibody that was approved in 2023. Both aducanumab and lecanemab are recommended for the treatment of patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which the safety and efficacy of these newer agents were demonstrated in clinical trials.
Secondary symptoms of AD, such as depression, agitation, aggression, hallucinations, delusions, and/or sleep disorders, can be treated with psychotropic agents. Behavioral interventions including patient-centered approaches and caregiver training can also be helpful for managing the cognitive and behavioral manifestations of AD, often in combination with pharmacologic interventions (eg, anxiolytics for anxiety and agitation, neuroleptics for delusions or hallucinations, and antidepressants or mood stabilizers for mood disorders). Regular physical activity and exercise may also play a role in delaying AD progression and possibly conferring a protective effect on brain health.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, Professor of Neurology, Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood; Director, Clinical Neurophysiology Lab, Department of Neurology, Hines VA Hospital, Hines, IL.
Jasvinder Chawla, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 72-year-old woman presents with a 12-month history of short-term memory loss. The patient is accompanied by her husband, who states her symptoms have become increasingly frequent and severe. The patient can no longer drive familiar routes after becoming lost on several occasions. She frequently misplaces items; recently, she placed her husband's car keys in the refrigerator. The patient admits to increasing bouts of forgetfulness and confusion and states that she has been feeling very down. She has not been able to watch her grandchildren over the past few months, which makes her feel sad and old. She also reports trouble sleeping at night due to generalized anxiety.
The patient's past medical history is significant for hypertension and dyslipidemia. There is no history of neurotoxic exposure, head injuries, strokes, or seizures. Her family history is positive for dementia. Her older brother was diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease (AD) at age 68 years, and her mother died from AD at age 82 years. Current medications include rosuvastatin 20 mg/d and lisinopril 20 mg/d. The patient's current height and weight are 5 ft 5 in and 163 lb, respectively (BMI is 27.1).
No abnormalities are noted on physical examination; the patient's blood pressure, pulse oximetry, and heart rate are within normal ranges. Laboratory tests are within normal ranges. The patient scores 18 on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment test. The patient's clinician orders a brain fluorodeoxyglucose-PET, which reveals areas of decreased glucose metabolism involving the posterior cingulate cortex, precuneus, inferior parietal lobule, and middle temporal gyrus.
Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
Global burden of brain disorders surpasses cardiovascular disease and cancer
– at huge cost to health care systems and society, an analysis of data from the most recent Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study shows.
“The burden of brain conditions will increase as populations continue to grow and age,” said study presenter Shayla Smith, MPH, an epidemiologist at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, the University of Washington, Seattle, in a press release.
“By 2050, more than 50 million people will be aged 65-79,” she explained, adding that the COVID-19 pandemic “has also influenced the prevalence of mental disorders globally, as people were forced to isolate and social networks broke down.”
Other factors related to brain disorders, she noted, include education level, obesity, and smoking.
“There’s still research to be done on what is the most effective way to maintain brain health, but some literature suggests a healthy brain can be achieved through a healthy lifestyle of managing conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, limiting alcohol consumption and smoking, prioritizing sleep, eating healthy, and staying physically and mentally active,” said Ms. Smith.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology.
An ‘ambitious exercise’
Coinvestigator Xaviera Steele, also from the IHME, told press conference attendees that the institute was established at the University of Washington in 2007 with the aim of “standardizing the measurement of health outcomes around the world and for all health conditions.”
A central part of that is the GBD study, “which is a very ambitious exercise in descriptive epidemiology in an effort to systematically quantify health loss” due to disease, injury, and risk factors over time, stratified by country, region, age, and sex. In addition, researchers are mapping and projecting trends over the next century and are estimating disease expenditure by country, by type of expense, and by condition “to derive a health care access and quality score for each health system in the world,” Ms. Steele said.
They are also estimating exposure to risk factors, how those risk factors contribute to health burden, and associated health outcomes by race and ethnicity to reflect the “disparities that we know are very prevalent in countries such as the United States.” From that work, Ms. Steele said that brain health and related conditions “do emerge as one of the more pressing challenges of the 21st century.”
Increase in dementia, mental health conditions
The data, which were gathered from 200,000 sources by the IHME, indicate that the number of individuals aged 65 years or older will increase by 350% by 2100. Ms. Steele underlined that “policy action will be needed to help families, who will struggle to provide high-quality care for their loved ones with dementia at a reasonable cost.”
The IHME calculates that in Europe health care spending on Alzheimer’s disease will increase by 226% between 2015 and 2040.
Turning to other conditions, Ms. Steele showed that since 1990, the number of individuals living with anxiety in the European region has increased by 14%, while the number living with depressive disorders has gone up by 13%.
Worldwide, the figures are even starker. Depression is estimated to affect 300 million people across the globe, which represents a 71% increase since 1990. The number of strokes increased by 95% over the same period.
Nevertheless, the “impact of brain conditions such as stroke has decreased since the 1990s due to improved treatments available,” Ms. Smith noted in the press release.
To estimate the toll caused by brain conditions, including neurologic disorders, mental disorders, cerebrovascular disease, brain cancer, brain injuries, and select infectious conditions, the researchers calculated disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
This, Ms. Smith explained in her presentation, “captures the morbidity and mortality associated with brain conditions” and is adjusted for patient location, age, and sex.
The investigators found that, globally, brain conditions accounted for more than 15% of all health loss in 2021, at 406 DALYs – more than the 206 million DALYs that were associated with cancer, and the 402 million that were linked to cardiovascular disease.
This health loss is associated with a $1.22 trillion loss in income for people living with health disorders worldwide and accounts for $1.14 trillion in direct health care costs.
The burden of mental disorders, neurologic conditions, and stroke is expected to increase dramatically between now and 2050, said Ms. Smith, who noted that health loss linked to brain conditions is higher in younger patients. This will create “new challenges for health systems, employers, patients, and families,” she said in the press release.
“Our goal is to see an improved prevention and treatment landscape for other brain conditions and reverse the growing health loss that we are currently forecasting.”
Worrying increase in stroke
Jurgita Valaikiene, MD, PhD, center of neurology, clinic of neurology and neurosurgery, Vilnius (Lithuania) University Faculty of Medicine, who chaired the session, was taken aback by the findings, particularly by the worldwide increase in stroke cases.
“I work in stroke,” she said, and “we spend a lot of time on the diagnosis of stroke” and its prevention. “We try to be faster, to catch asymptomatic stenosis in the neck or head, and to apply the best medical treatment to avoid a stroke. But despite that, the numbers are increasing. I understand the population is getting older ... but still it’s a huge number.”
Dr. Valaikiene pointed out that stroke is not necessarily a condition of aging, insofar as increasing age “is not related directly to stenosis in the neck. “For example, we can have healthier vessels in older age and unhealthy vessels, with high-grade stenosis, in someone aged 30 or 40 years.”
“There are a lot of risk factors, such as smoking, physical activity, and so on. It depends on the individual,” she added.
The study was funded by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– at huge cost to health care systems and society, an analysis of data from the most recent Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study shows.
“The burden of brain conditions will increase as populations continue to grow and age,” said study presenter Shayla Smith, MPH, an epidemiologist at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, the University of Washington, Seattle, in a press release.
“By 2050, more than 50 million people will be aged 65-79,” she explained, adding that the COVID-19 pandemic “has also influenced the prevalence of mental disorders globally, as people were forced to isolate and social networks broke down.”
Other factors related to brain disorders, she noted, include education level, obesity, and smoking.
“There’s still research to be done on what is the most effective way to maintain brain health, but some literature suggests a healthy brain can be achieved through a healthy lifestyle of managing conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, limiting alcohol consumption and smoking, prioritizing sleep, eating healthy, and staying physically and mentally active,” said Ms. Smith.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology.
An ‘ambitious exercise’
Coinvestigator Xaviera Steele, also from the IHME, told press conference attendees that the institute was established at the University of Washington in 2007 with the aim of “standardizing the measurement of health outcomes around the world and for all health conditions.”
A central part of that is the GBD study, “which is a very ambitious exercise in descriptive epidemiology in an effort to systematically quantify health loss” due to disease, injury, and risk factors over time, stratified by country, region, age, and sex. In addition, researchers are mapping and projecting trends over the next century and are estimating disease expenditure by country, by type of expense, and by condition “to derive a health care access and quality score for each health system in the world,” Ms. Steele said.
They are also estimating exposure to risk factors, how those risk factors contribute to health burden, and associated health outcomes by race and ethnicity to reflect the “disparities that we know are very prevalent in countries such as the United States.” From that work, Ms. Steele said that brain health and related conditions “do emerge as one of the more pressing challenges of the 21st century.”
Increase in dementia, mental health conditions
The data, which were gathered from 200,000 sources by the IHME, indicate that the number of individuals aged 65 years or older will increase by 350% by 2100. Ms. Steele underlined that “policy action will be needed to help families, who will struggle to provide high-quality care for their loved ones with dementia at a reasonable cost.”
The IHME calculates that in Europe health care spending on Alzheimer’s disease will increase by 226% between 2015 and 2040.
Turning to other conditions, Ms. Steele showed that since 1990, the number of individuals living with anxiety in the European region has increased by 14%, while the number living with depressive disorders has gone up by 13%.
Worldwide, the figures are even starker. Depression is estimated to affect 300 million people across the globe, which represents a 71% increase since 1990. The number of strokes increased by 95% over the same period.
Nevertheless, the “impact of brain conditions such as stroke has decreased since the 1990s due to improved treatments available,” Ms. Smith noted in the press release.
To estimate the toll caused by brain conditions, including neurologic disorders, mental disorders, cerebrovascular disease, brain cancer, brain injuries, and select infectious conditions, the researchers calculated disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
This, Ms. Smith explained in her presentation, “captures the morbidity and mortality associated with brain conditions” and is adjusted for patient location, age, and sex.
The investigators found that, globally, brain conditions accounted for more than 15% of all health loss in 2021, at 406 DALYs – more than the 206 million DALYs that were associated with cancer, and the 402 million that were linked to cardiovascular disease.
This health loss is associated with a $1.22 trillion loss in income for people living with health disorders worldwide and accounts for $1.14 trillion in direct health care costs.
The burden of mental disorders, neurologic conditions, and stroke is expected to increase dramatically between now and 2050, said Ms. Smith, who noted that health loss linked to brain conditions is higher in younger patients. This will create “new challenges for health systems, employers, patients, and families,” she said in the press release.
“Our goal is to see an improved prevention and treatment landscape for other brain conditions and reverse the growing health loss that we are currently forecasting.”
Worrying increase in stroke
Jurgita Valaikiene, MD, PhD, center of neurology, clinic of neurology and neurosurgery, Vilnius (Lithuania) University Faculty of Medicine, who chaired the session, was taken aback by the findings, particularly by the worldwide increase in stroke cases.
“I work in stroke,” she said, and “we spend a lot of time on the diagnosis of stroke” and its prevention. “We try to be faster, to catch asymptomatic stenosis in the neck or head, and to apply the best medical treatment to avoid a stroke. But despite that, the numbers are increasing. I understand the population is getting older ... but still it’s a huge number.”
Dr. Valaikiene pointed out that stroke is not necessarily a condition of aging, insofar as increasing age “is not related directly to stenosis in the neck. “For example, we can have healthier vessels in older age and unhealthy vessels, with high-grade stenosis, in someone aged 30 or 40 years.”
“There are a lot of risk factors, such as smoking, physical activity, and so on. It depends on the individual,” she added.
The study was funded by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
– at huge cost to health care systems and society, an analysis of data from the most recent Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study shows.
“The burden of brain conditions will increase as populations continue to grow and age,” said study presenter Shayla Smith, MPH, an epidemiologist at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, the University of Washington, Seattle, in a press release.
“By 2050, more than 50 million people will be aged 65-79,” she explained, adding that the COVID-19 pandemic “has also influenced the prevalence of mental disorders globally, as people were forced to isolate and social networks broke down.”
Other factors related to brain disorders, she noted, include education level, obesity, and smoking.
“There’s still research to be done on what is the most effective way to maintain brain health, but some literature suggests a healthy brain can be achieved through a healthy lifestyle of managing conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, limiting alcohol consumption and smoking, prioritizing sleep, eating healthy, and staying physically and mentally active,” said Ms. Smith.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Congress of the European Academy of Neurology.
An ‘ambitious exercise’
Coinvestigator Xaviera Steele, also from the IHME, told press conference attendees that the institute was established at the University of Washington in 2007 with the aim of “standardizing the measurement of health outcomes around the world and for all health conditions.”
A central part of that is the GBD study, “which is a very ambitious exercise in descriptive epidemiology in an effort to systematically quantify health loss” due to disease, injury, and risk factors over time, stratified by country, region, age, and sex. In addition, researchers are mapping and projecting trends over the next century and are estimating disease expenditure by country, by type of expense, and by condition “to derive a health care access and quality score for each health system in the world,” Ms. Steele said.
They are also estimating exposure to risk factors, how those risk factors contribute to health burden, and associated health outcomes by race and ethnicity to reflect the “disparities that we know are very prevalent in countries such as the United States.” From that work, Ms. Steele said that brain health and related conditions “do emerge as one of the more pressing challenges of the 21st century.”
Increase in dementia, mental health conditions
The data, which were gathered from 200,000 sources by the IHME, indicate that the number of individuals aged 65 years or older will increase by 350% by 2100. Ms. Steele underlined that “policy action will be needed to help families, who will struggle to provide high-quality care for their loved ones with dementia at a reasonable cost.”
The IHME calculates that in Europe health care spending on Alzheimer’s disease will increase by 226% between 2015 and 2040.
Turning to other conditions, Ms. Steele showed that since 1990, the number of individuals living with anxiety in the European region has increased by 14%, while the number living with depressive disorders has gone up by 13%.
Worldwide, the figures are even starker. Depression is estimated to affect 300 million people across the globe, which represents a 71% increase since 1990. The number of strokes increased by 95% over the same period.
Nevertheless, the “impact of brain conditions such as stroke has decreased since the 1990s due to improved treatments available,” Ms. Smith noted in the press release.
To estimate the toll caused by brain conditions, including neurologic disorders, mental disorders, cerebrovascular disease, brain cancer, brain injuries, and select infectious conditions, the researchers calculated disability-adjusted life years (DALYs).
This, Ms. Smith explained in her presentation, “captures the morbidity and mortality associated with brain conditions” and is adjusted for patient location, age, and sex.
The investigators found that, globally, brain conditions accounted for more than 15% of all health loss in 2021, at 406 DALYs – more than the 206 million DALYs that were associated with cancer, and the 402 million that were linked to cardiovascular disease.
This health loss is associated with a $1.22 trillion loss in income for people living with health disorders worldwide and accounts for $1.14 trillion in direct health care costs.
The burden of mental disorders, neurologic conditions, and stroke is expected to increase dramatically between now and 2050, said Ms. Smith, who noted that health loss linked to brain conditions is higher in younger patients. This will create “new challenges for health systems, employers, patients, and families,” she said in the press release.
“Our goal is to see an improved prevention and treatment landscape for other brain conditions and reverse the growing health loss that we are currently forecasting.”
Worrying increase in stroke
Jurgita Valaikiene, MD, PhD, center of neurology, clinic of neurology and neurosurgery, Vilnius (Lithuania) University Faculty of Medicine, who chaired the session, was taken aback by the findings, particularly by the worldwide increase in stroke cases.
“I work in stroke,” she said, and “we spend a lot of time on the diagnosis of stroke” and its prevention. “We try to be faster, to catch asymptomatic stenosis in the neck or head, and to apply the best medical treatment to avoid a stroke. But despite that, the numbers are increasing. I understand the population is getting older ... but still it’s a huge number.”
Dr. Valaikiene pointed out that stroke is not necessarily a condition of aging, insofar as increasing age “is not related directly to stenosis in the neck. “For example, we can have healthier vessels in older age and unhealthy vessels, with high-grade stenosis, in someone aged 30 or 40 years.”
“There are a lot of risk factors, such as smoking, physical activity, and so on. It depends on the individual,” she added.
The study was funded by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hearing loss tied to more fatigue in middle and older age
Like many stressful chronic conditions, hearing loss appears to foster fatigue, according to an analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Study data published in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, examined NHANES data from 2015 to 2016 and 2017 to 2018, including findings on more than 3,000 participants aged 40 and older. Based on the audiometry subset of NHANES data, hearing loss was associated with a higher frequency of fatigue – even after adjustment for demographics, comorbidities, and lifestyle variables such as smoking, alcohol, and body mass index, in a nationally representative sample of adults in middle and older age.
“We wanted to get away from small clinical data and take a look at the population level to see if hearing loss was related to fatigue and, further perhaps, to cognitive decline,” said coauthor Nicholas S. Reed, AuD, PhD, an assistant professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, in an interview. “We found people with hearing loss had twice the risk of reporting fatigue nearly every day versus those not reporting fatigue.” This cross-sectional study provides needed population-based evidence from a nationally representative sample, according to Dr. Reed and associates, who have been researching the possible connection between age-related hearing loss, physical activity levels, and cognitive decline.
Study details
The 3,031 age-eligible participants had a mean age of 58 years; 48% were male, and 10% were Black. Some hearing loss was reported by 24%.
They responded to the following question: “Over the last 2 weeks, how often have you been bothered by feeling tired or having little energy?” Response categories were “not at all,” “several days,” “more than half the days,” and “nearly every day.” Those with hearing loss were more likely to report fatigue for more than half the days (relative risk ratio, 2.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.27-3.67) and nearly every day (RRR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.16-3.65), compared with not having fatigue. Additional adjustment for comorbidities and depressive symptoms showed similar results.
Hearing loss was defined as > 25 decibels hearing level (dB HL) versus normal hearing of ≤ 25 dB HL, and continuously by every 10 dB HL poorer. Each 10-dB HL of audiometric hearing loss was associated with a higher likelihood of reporting fatigue nearly every day (RRR, 1.24; 95% CI,1.04-1.47), but not for more than half the days.
The association tended to be stronger in younger, non-Hispanic White, and female participants, but statistical testing did not support differential associations by age, sex, race, or ethnicity.
While some might intuitively expect hearing loss to cause noticeably more fatigue in middle-aged people who may be straining to hear during hours in the daily workplace or at home, Dr. Reed said older people probably feel more hearing-related fatigue owing to age and comorbidities. “And higher physical activity levels of middle-aged adults can be protective.”
Dr. Reed advised primary care physicians to be sure to ask about fatigue and hearing status during wellness exams and take appropriate steps to diagnose and correct hearing problems. “Make sure hearing is part of the health equation because hearing loss can be part of the culprit. And it’s very possible that hearing loss is also contributing to cognitive decline.”
Dr. Reed’s group will soon release data on a clinical trial on hearing loss and cognitive decline.
The authors called for studies incorporating fatigue assessments in order to clarify how hearing loss might contribute to physical and mental fatigue and how it could be associated with downstream outcomes such as fatigue-related physical impairment. Dr. Reed reported grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and stock compensation from the Neosensory Advisory Board outside of the submitted work. Several coauthors reported academic or government research funding as well as fees and honoraria from various private-sector companies.
Like many stressful chronic conditions, hearing loss appears to foster fatigue, according to an analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Study data published in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, examined NHANES data from 2015 to 2016 and 2017 to 2018, including findings on more than 3,000 participants aged 40 and older. Based on the audiometry subset of NHANES data, hearing loss was associated with a higher frequency of fatigue – even after adjustment for demographics, comorbidities, and lifestyle variables such as smoking, alcohol, and body mass index, in a nationally representative sample of adults in middle and older age.
“We wanted to get away from small clinical data and take a look at the population level to see if hearing loss was related to fatigue and, further perhaps, to cognitive decline,” said coauthor Nicholas S. Reed, AuD, PhD, an assistant professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, in an interview. “We found people with hearing loss had twice the risk of reporting fatigue nearly every day versus those not reporting fatigue.” This cross-sectional study provides needed population-based evidence from a nationally representative sample, according to Dr. Reed and associates, who have been researching the possible connection between age-related hearing loss, physical activity levels, and cognitive decline.
Study details
The 3,031 age-eligible participants had a mean age of 58 years; 48% were male, and 10% were Black. Some hearing loss was reported by 24%.
They responded to the following question: “Over the last 2 weeks, how often have you been bothered by feeling tired or having little energy?” Response categories were “not at all,” “several days,” “more than half the days,” and “nearly every day.” Those with hearing loss were more likely to report fatigue for more than half the days (relative risk ratio, 2.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.27-3.67) and nearly every day (RRR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.16-3.65), compared with not having fatigue. Additional adjustment for comorbidities and depressive symptoms showed similar results.
Hearing loss was defined as > 25 decibels hearing level (dB HL) versus normal hearing of ≤ 25 dB HL, and continuously by every 10 dB HL poorer. Each 10-dB HL of audiometric hearing loss was associated with a higher likelihood of reporting fatigue nearly every day (RRR, 1.24; 95% CI,1.04-1.47), but not for more than half the days.
The association tended to be stronger in younger, non-Hispanic White, and female participants, but statistical testing did not support differential associations by age, sex, race, or ethnicity.
While some might intuitively expect hearing loss to cause noticeably more fatigue in middle-aged people who may be straining to hear during hours in the daily workplace or at home, Dr. Reed said older people probably feel more hearing-related fatigue owing to age and comorbidities. “And higher physical activity levels of middle-aged adults can be protective.”
Dr. Reed advised primary care physicians to be sure to ask about fatigue and hearing status during wellness exams and take appropriate steps to diagnose and correct hearing problems. “Make sure hearing is part of the health equation because hearing loss can be part of the culprit. And it’s very possible that hearing loss is also contributing to cognitive decline.”
Dr. Reed’s group will soon release data on a clinical trial on hearing loss and cognitive decline.
The authors called for studies incorporating fatigue assessments in order to clarify how hearing loss might contribute to physical and mental fatigue and how it could be associated with downstream outcomes such as fatigue-related physical impairment. Dr. Reed reported grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and stock compensation from the Neosensory Advisory Board outside of the submitted work. Several coauthors reported academic or government research funding as well as fees and honoraria from various private-sector companies.
Like many stressful chronic conditions, hearing loss appears to foster fatigue, according to an analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Study data published in JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, examined NHANES data from 2015 to 2016 and 2017 to 2018, including findings on more than 3,000 participants aged 40 and older. Based on the audiometry subset of NHANES data, hearing loss was associated with a higher frequency of fatigue – even after adjustment for demographics, comorbidities, and lifestyle variables such as smoking, alcohol, and body mass index, in a nationally representative sample of adults in middle and older age.
“We wanted to get away from small clinical data and take a look at the population level to see if hearing loss was related to fatigue and, further perhaps, to cognitive decline,” said coauthor Nicholas S. Reed, AuD, PhD, an assistant professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, in an interview. “We found people with hearing loss had twice the risk of reporting fatigue nearly every day versus those not reporting fatigue.” This cross-sectional study provides needed population-based evidence from a nationally representative sample, according to Dr. Reed and associates, who have been researching the possible connection between age-related hearing loss, physical activity levels, and cognitive decline.
Study details
The 3,031 age-eligible participants had a mean age of 58 years; 48% were male, and 10% were Black. Some hearing loss was reported by 24%.
They responded to the following question: “Over the last 2 weeks, how often have you been bothered by feeling tired or having little energy?” Response categories were “not at all,” “several days,” “more than half the days,” and “nearly every day.” Those with hearing loss were more likely to report fatigue for more than half the days (relative risk ratio, 2.16; 95% confidence interval, 1.27-3.67) and nearly every day (RRR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.16-3.65), compared with not having fatigue. Additional adjustment for comorbidities and depressive symptoms showed similar results.
Hearing loss was defined as > 25 decibels hearing level (dB HL) versus normal hearing of ≤ 25 dB HL, and continuously by every 10 dB HL poorer. Each 10-dB HL of audiometric hearing loss was associated with a higher likelihood of reporting fatigue nearly every day (RRR, 1.24; 95% CI,1.04-1.47), but not for more than half the days.
The association tended to be stronger in younger, non-Hispanic White, and female participants, but statistical testing did not support differential associations by age, sex, race, or ethnicity.
While some might intuitively expect hearing loss to cause noticeably more fatigue in middle-aged people who may be straining to hear during hours in the daily workplace or at home, Dr. Reed said older people probably feel more hearing-related fatigue owing to age and comorbidities. “And higher physical activity levels of middle-aged adults can be protective.”
Dr. Reed advised primary care physicians to be sure to ask about fatigue and hearing status during wellness exams and take appropriate steps to diagnose and correct hearing problems. “Make sure hearing is part of the health equation because hearing loss can be part of the culprit. And it’s very possible that hearing loss is also contributing to cognitive decline.”
Dr. Reed’s group will soon release data on a clinical trial on hearing loss and cognitive decline.
The authors called for studies incorporating fatigue assessments in order to clarify how hearing loss might contribute to physical and mental fatigue and how it could be associated with downstream outcomes such as fatigue-related physical impairment. Dr. Reed reported grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and stock compensation from the Neosensory Advisory Board outside of the submitted work. Several coauthors reported academic or government research funding as well as fees and honoraria from various private-sector companies.
FROM JAMA OTOLARYNGOLOGY – HEAD & NECK SURGERY
Alzheimer’s disease: To treat or not?
Mr. Jones has Alzheimer’s disease, recently diagnosed.
His wife is a retired hospice nurse, who’s seen plenty of patients and families deal with the illness over the years.
She came in recently, just herself, to go over his treatment options and what can be reasonably expected with them. So we went through the usual suspects, new and old.
I intermittently stopped to ask if she had any questions. At one such break she suddenly said:
“I’d rather he die now than be treated with any of these.”
I tried to address her safety concerns with the different medications, but that wasn’t the issue. Her real, and understandable, point is that none of them are cures. They don’t even stop the disease. Realistically, all we’re doing is slowing things down for maybe a year at most.
Families are different, and no one can really know how they’ll react in this situation until it happens.
Some will want me to do a full-court press, because another year of time is more family gatherings and independence, maybe a grandchild’s birth or wedding, or just being able to keep someone at home longer before starting to look into the cost of memory care.
Others, like Mrs. Jones, don’t see a point. The disease is incurable. Why bother to prolong it when the end is the same? Is it worth adding another year of medications, adult diapers, and the occasional 911 call if they wander off?
That’s a valid view, too. She wasn’t advocating a cause, such as euthanasia, but she did have legitimate concerns.
For all the marketing hype over Leqembi today or Cognex (remember that?) in 1989, the issue is the same. We have new and shinier toys, but still no cures. Whether it’s worth it to prolong life (or suffering) is a glass half-full or half-empty question that only patients and their families can answer.
It ain’t easy.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Mr. Jones has Alzheimer’s disease, recently diagnosed.
His wife is a retired hospice nurse, who’s seen plenty of patients and families deal with the illness over the years.
She came in recently, just herself, to go over his treatment options and what can be reasonably expected with them. So we went through the usual suspects, new and old.
I intermittently stopped to ask if she had any questions. At one such break she suddenly said:
“I’d rather he die now than be treated with any of these.”
I tried to address her safety concerns with the different medications, but that wasn’t the issue. Her real, and understandable, point is that none of them are cures. They don’t even stop the disease. Realistically, all we’re doing is slowing things down for maybe a year at most.
Families are different, and no one can really know how they’ll react in this situation until it happens.
Some will want me to do a full-court press, because another year of time is more family gatherings and independence, maybe a grandchild’s birth or wedding, or just being able to keep someone at home longer before starting to look into the cost of memory care.
Others, like Mrs. Jones, don’t see a point. The disease is incurable. Why bother to prolong it when the end is the same? Is it worth adding another year of medications, adult diapers, and the occasional 911 call if they wander off?
That’s a valid view, too. She wasn’t advocating a cause, such as euthanasia, but she did have legitimate concerns.
For all the marketing hype over Leqembi today or Cognex (remember that?) in 1989, the issue is the same. We have new and shinier toys, but still no cures. Whether it’s worth it to prolong life (or suffering) is a glass half-full or half-empty question that only patients and their families can answer.
It ain’t easy.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Mr. Jones has Alzheimer’s disease, recently diagnosed.
His wife is a retired hospice nurse, who’s seen plenty of patients and families deal with the illness over the years.
She came in recently, just herself, to go over his treatment options and what can be reasonably expected with them. So we went through the usual suspects, new and old.
I intermittently stopped to ask if she had any questions. At one such break she suddenly said:
“I’d rather he die now than be treated with any of these.”
I tried to address her safety concerns with the different medications, but that wasn’t the issue. Her real, and understandable, point is that none of them are cures. They don’t even stop the disease. Realistically, all we’re doing is slowing things down for maybe a year at most.
Families are different, and no one can really know how they’ll react in this situation until it happens.
Some will want me to do a full-court press, because another year of time is more family gatherings and independence, maybe a grandchild’s birth or wedding, or just being able to keep someone at home longer before starting to look into the cost of memory care.
Others, like Mrs. Jones, don’t see a point. The disease is incurable. Why bother to prolong it when the end is the same? Is it worth adding another year of medications, adult diapers, and the occasional 911 call if they wander off?
That’s a valid view, too. She wasn’t advocating a cause, such as euthanasia, but she did have legitimate concerns.
For all the marketing hype over Leqembi today or Cognex (remember that?) in 1989, the issue is the same. We have new and shinier toys, but still no cures. Whether it’s worth it to prolong life (or suffering) is a glass half-full or half-empty question that only patients and their families can answer.
It ain’t easy.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.