User login
ISCHEMIA substudy data don’t add up, cardiac surgeons say
A recent ISCHEMIA trial substudy is under scrutiny from surgeons for a data discrepancy, rekindling concerns about reliance on the landmark trial data in the latest coronary revascularization guidelines.
As previously reported, the main ISCHEMIA findings showed no significant benefit for an initial strategy of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass graft surgery (CABG) over medical therapy in patients with stable moderate to severe ischemic heart disease.
The 2021 substudy by Reynolds et al. showed that coronary artery disease (CAD) severity, classified using the modified Duke Prognostic Index score, predicted 4-year mortality and myocardial infarction in the trial, whereas ischemia severity did not.
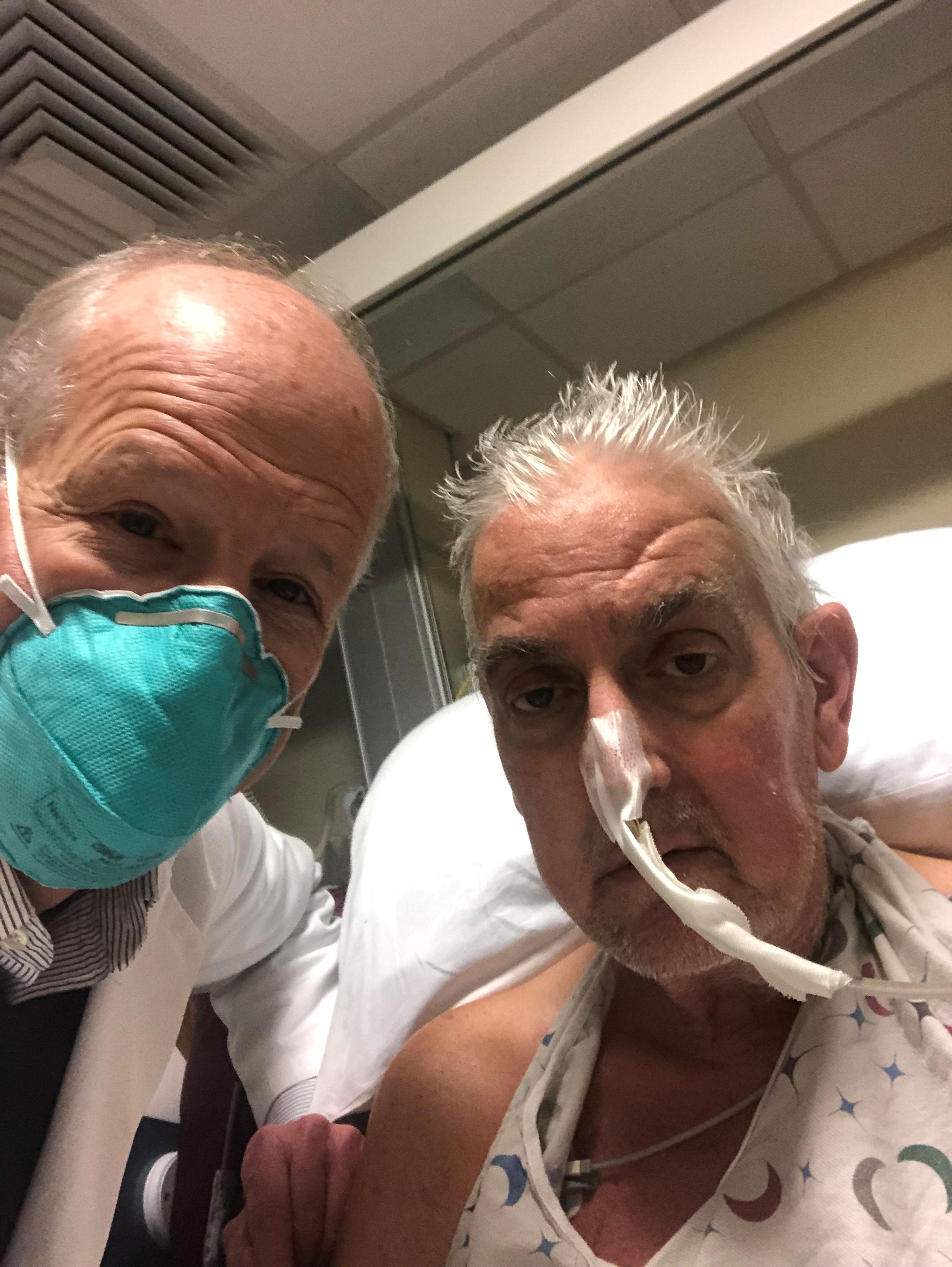
Cardiac surgeons Joseph F. Sabik III, MD, and Faisal Bakaeen, MD, however, spotted that only 40 patients are in the Duke category 6 group (three-vessel severe stenosis of at least 70% or two-vessel severe stenosis with a proximal left anterior descending lesion) in Supplemental tables 1 and 2, whereas 659 are in the main paper.
In addition, the Supplemental tables list the following:
- 659 patients in Duke group 5, not 894 as in the paper.
- 894 patients in Duke group 4, not 743 as in the paper.
- 743 patients in Duke group 3, not 179 as in the paper.
The surgeons penned a letter to Circulation early in April flagging the discrepancies, but say it was rejected April 15 because it was submitted outside the journal’s 6-week window for letters. They posted a public comment on the Remarq research platform, as advised by Circulation’s editorial office, and reached out directly to the authors and ISCHEMIA leadership.
“They just keep saying it’s a simple formatting error. Well, if it is a simple formatting error, then fix it,” Dr. Sabik, chair of surgery at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, said in an interview. “But here we are now, a month later, and they still haven’t published our letter. Why? We’re the ones who identified the problem.”
Dr. Sabik said the accuracy of the data has important implications because the recent AHA/ACC/SCAI coronary revascularization guidelines used the ISCHEMIA data to downgrade the CABG recommendation for complex multivessel disease from class 1 to class 2B. Patients with a Duke 6 score are also typically the ones referred for CABG by today’s heart teams.
Several surgical societies have contested the guidelines, questioning whether the ISCHEMIA patients are truly reflective of those seen in clinical practice and questioning the decision to treat PCI and surgery as equivalent strategies to decrease ischemic events.
Dr. Bakaeen, from the Cleveland Clinic, told this news organization they don’t want a public battle over the data like the one that befell the EXCEL trial, and that it’s entirely possible the investigators might have inadvertently upgraded all the Duke score assignments by 1.
A systematic error, however, is more plausible than a formatting error, he said, because Supplemental tables 1 and 2 correspond exactly to the Duke 1 to Duke 7 sequence, suggesting the tables are correct and that the error might have occurred downstream, including in the manuscript.
The numbers should be consistent across all the ISCHEMIA manuscripts, Dr. Bakaeen added, but currently “don’t add up,” even after adjustment for different denominators, and especially for participants with left main disease.
They hope that publication of their letter, he said, will convince the authors to publicly share the data for patients in each of the seven modified Duke categories.
Lead author of the ISCHEMIA substudy, Harmony Reynolds, MD, New York (N.Y.) University Langone Health, told this news organization via email that as a result of a “formatting error in the transfer of data from the statistical output file to a Word document, data in Supplemental tables 1 and 2 were incorrect.”
She explained that they planned to present six, not seven, rows for the Duke score in the tables, collapsing the first two categories of nonobstructive disease (Duke 1-2), as they were in all other tables and figures. However, the Supplemental tables had incorrect row headings and because the Word program is designed to fill all available rows, it inserted the data from the output file into a seven-row table shell, duplicating the values for row 1 in the last row for left main disease of at least 50%.
“The data were correctly presented in the main manuscript tables and figures and in the remainder of the supplement, with a total of 659 patients in the subset with modified Duke prognostic index category 6 on coronary CT angiography,” Dr. Reynolds said.
She noted that Circulation will issue a correction. In addition, “we are in the process of preparing the data for public sharing soon. The data will include the Duke prognostic score at all levels.”
Circulation editor-in-chief Joseph A. Hill, MD, PhD, chief of cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, declined to be interviewed but confirmed via email that Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik’s letter and the correction will be published the week of May 16.
As for the delay, he said, “I received their reach-out just over 1 week ago, and per protocol, we conducted an internal evaluation of their allegations, which took a bit of time.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent ISCHEMIA trial substudy is under scrutiny from surgeons for a data discrepancy, rekindling concerns about reliance on the landmark trial data in the latest coronary revascularization guidelines.
As previously reported, the main ISCHEMIA findings showed no significant benefit for an initial strategy of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass graft surgery (CABG) over medical therapy in patients with stable moderate to severe ischemic heart disease.
The 2021 substudy by Reynolds et al. showed that coronary artery disease (CAD) severity, classified using the modified Duke Prognostic Index score, predicted 4-year mortality and myocardial infarction in the trial, whereas ischemia severity did not.
Cardiac surgeons Joseph F. Sabik III, MD, and Faisal Bakaeen, MD, however, spotted that only 40 patients are in the Duke category 6 group (three-vessel severe stenosis of at least 70% or two-vessel severe stenosis with a proximal left anterior descending lesion) in Supplemental tables 1 and 2, whereas 659 are in the main paper.
In addition, the Supplemental tables list the following:
- 659 patients in Duke group 5, not 894 as in the paper.
- 894 patients in Duke group 4, not 743 as in the paper.
- 743 patients in Duke group 3, not 179 as in the paper.
The surgeons penned a letter to Circulation early in April flagging the discrepancies, but say it was rejected April 15 because it was submitted outside the journal’s 6-week window for letters. They posted a public comment on the Remarq research platform, as advised by Circulation’s editorial office, and reached out directly to the authors and ISCHEMIA leadership.
“They just keep saying it’s a simple formatting error. Well, if it is a simple formatting error, then fix it,” Dr. Sabik, chair of surgery at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, said in an interview. “But here we are now, a month later, and they still haven’t published our letter. Why? We’re the ones who identified the problem.”
Dr. Sabik said the accuracy of the data has important implications because the recent AHA/ACC/SCAI coronary revascularization guidelines used the ISCHEMIA data to downgrade the CABG recommendation for complex multivessel disease from class 1 to class 2B. Patients with a Duke 6 score are also typically the ones referred for CABG by today’s heart teams.
Several surgical societies have contested the guidelines, questioning whether the ISCHEMIA patients are truly reflective of those seen in clinical practice and questioning the decision to treat PCI and surgery as equivalent strategies to decrease ischemic events.
Dr. Bakaeen, from the Cleveland Clinic, told this news organization they don’t want a public battle over the data like the one that befell the EXCEL trial, and that it’s entirely possible the investigators might have inadvertently upgraded all the Duke score assignments by 1.
A systematic error, however, is more plausible than a formatting error, he said, because Supplemental tables 1 and 2 correspond exactly to the Duke 1 to Duke 7 sequence, suggesting the tables are correct and that the error might have occurred downstream, including in the manuscript.
The numbers should be consistent across all the ISCHEMIA manuscripts, Dr. Bakaeen added, but currently “don’t add up,” even after adjustment for different denominators, and especially for participants with left main disease.
They hope that publication of their letter, he said, will convince the authors to publicly share the data for patients in each of the seven modified Duke categories.
Lead author of the ISCHEMIA substudy, Harmony Reynolds, MD, New York (N.Y.) University Langone Health, told this news organization via email that as a result of a “formatting error in the transfer of data from the statistical output file to a Word document, data in Supplemental tables 1 and 2 were incorrect.”
She explained that they planned to present six, not seven, rows for the Duke score in the tables, collapsing the first two categories of nonobstructive disease (Duke 1-2), as they were in all other tables and figures. However, the Supplemental tables had incorrect row headings and because the Word program is designed to fill all available rows, it inserted the data from the output file into a seven-row table shell, duplicating the values for row 1 in the last row for left main disease of at least 50%.
“The data were correctly presented in the main manuscript tables and figures and in the remainder of the supplement, with a total of 659 patients in the subset with modified Duke prognostic index category 6 on coronary CT angiography,” Dr. Reynolds said.
She noted that Circulation will issue a correction. In addition, “we are in the process of preparing the data for public sharing soon. The data will include the Duke prognostic score at all levels.”
Circulation editor-in-chief Joseph A. Hill, MD, PhD, chief of cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, declined to be interviewed but confirmed via email that Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik’s letter and the correction will be published the week of May 16.
As for the delay, he said, “I received their reach-out just over 1 week ago, and per protocol, we conducted an internal evaluation of their allegations, which took a bit of time.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent ISCHEMIA trial substudy is under scrutiny from surgeons for a data discrepancy, rekindling concerns about reliance on the landmark trial data in the latest coronary revascularization guidelines.
As previously reported, the main ISCHEMIA findings showed no significant benefit for an initial strategy of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass graft surgery (CABG) over medical therapy in patients with stable moderate to severe ischemic heart disease.
The 2021 substudy by Reynolds et al. showed that coronary artery disease (CAD) severity, classified using the modified Duke Prognostic Index score, predicted 4-year mortality and myocardial infarction in the trial, whereas ischemia severity did not.
Cardiac surgeons Joseph F. Sabik III, MD, and Faisal Bakaeen, MD, however, spotted that only 40 patients are in the Duke category 6 group (three-vessel severe stenosis of at least 70% or two-vessel severe stenosis with a proximal left anterior descending lesion) in Supplemental tables 1 and 2, whereas 659 are in the main paper.
In addition, the Supplemental tables list the following:
- 659 patients in Duke group 5, not 894 as in the paper.
- 894 patients in Duke group 4, not 743 as in the paper.
- 743 patients in Duke group 3, not 179 as in the paper.
The surgeons penned a letter to Circulation early in April flagging the discrepancies, but say it was rejected April 15 because it was submitted outside the journal’s 6-week window for letters. They posted a public comment on the Remarq research platform, as advised by Circulation’s editorial office, and reached out directly to the authors and ISCHEMIA leadership.
“They just keep saying it’s a simple formatting error. Well, if it is a simple formatting error, then fix it,” Dr. Sabik, chair of surgery at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, said in an interview. “But here we are now, a month later, and they still haven’t published our letter. Why? We’re the ones who identified the problem.”
Dr. Sabik said the accuracy of the data has important implications because the recent AHA/ACC/SCAI coronary revascularization guidelines used the ISCHEMIA data to downgrade the CABG recommendation for complex multivessel disease from class 1 to class 2B. Patients with a Duke 6 score are also typically the ones referred for CABG by today’s heart teams.
Several surgical societies have contested the guidelines, questioning whether the ISCHEMIA patients are truly reflective of those seen in clinical practice and questioning the decision to treat PCI and surgery as equivalent strategies to decrease ischemic events.
Dr. Bakaeen, from the Cleveland Clinic, told this news organization they don’t want a public battle over the data like the one that befell the EXCEL trial, and that it’s entirely possible the investigators might have inadvertently upgraded all the Duke score assignments by 1.
A systematic error, however, is more plausible than a formatting error, he said, because Supplemental tables 1 and 2 correspond exactly to the Duke 1 to Duke 7 sequence, suggesting the tables are correct and that the error might have occurred downstream, including in the manuscript.
The numbers should be consistent across all the ISCHEMIA manuscripts, Dr. Bakaeen added, but currently “don’t add up,” even after adjustment for different denominators, and especially for participants with left main disease.
They hope that publication of their letter, he said, will convince the authors to publicly share the data for patients in each of the seven modified Duke categories.
Lead author of the ISCHEMIA substudy, Harmony Reynolds, MD, New York (N.Y.) University Langone Health, told this news organization via email that as a result of a “formatting error in the transfer of data from the statistical output file to a Word document, data in Supplemental tables 1 and 2 were incorrect.”
She explained that they planned to present six, not seven, rows for the Duke score in the tables, collapsing the first two categories of nonobstructive disease (Duke 1-2), as they were in all other tables and figures. However, the Supplemental tables had incorrect row headings and because the Word program is designed to fill all available rows, it inserted the data from the output file into a seven-row table shell, duplicating the values for row 1 in the last row for left main disease of at least 50%.
“The data were correctly presented in the main manuscript tables and figures and in the remainder of the supplement, with a total of 659 patients in the subset with modified Duke prognostic index category 6 on coronary CT angiography,” Dr. Reynolds said.
She noted that Circulation will issue a correction. In addition, “we are in the process of preparing the data for public sharing soon. The data will include the Duke prognostic score at all levels.”
Circulation editor-in-chief Joseph A. Hill, MD, PhD, chief of cardiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, declined to be interviewed but confirmed via email that Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik’s letter and the correction will be published the week of May 16.
As for the delay, he said, “I received their reach-out just over 1 week ago, and per protocol, we conducted an internal evaluation of their allegations, which took a bit of time.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves Medtronic’s Onyx Frontier drug-eluting stent
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the Onyx Frontier drug-eluting stent (DES) to treat patients with coronary artery disease, the device manufacturer, Medtronic, announced today.
The Onyx Frontier shares the same stent platform and clinical indications as the previous-generation Resolute Onyx zotarolimus-eluting stent, including the most recent approval for patients at high risk of bleeding who may benefit from just 1 month dual-antiplatelet therapy.
“Meaningful design changes, including increased catheter flexibility, an innovative dual-layer balloon technology and a lower crossing profile led to a 16% improvement in deliverability with Onyx Frontier vs. the previous generation Resolute Onyx DES,” Medtronic said in a news release.
Onyx Frontier also offers a broad size matrix to treat more patients, and joins the Resolute Onyx as the only 2-mm DES available in the United States, the company noted. The stent is available in 4.5- to 5-mm sizes that can be expanded to 6 mm, specifically designed to support extra-large vessels.
The Onyx Frontier DES is pending CE Mark in Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the Onyx Frontier drug-eluting stent (DES) to treat patients with coronary artery disease, the device manufacturer, Medtronic, announced today.
The Onyx Frontier shares the same stent platform and clinical indications as the previous-generation Resolute Onyx zotarolimus-eluting stent, including the most recent approval for patients at high risk of bleeding who may benefit from just 1 month dual-antiplatelet therapy.
“Meaningful design changes, including increased catheter flexibility, an innovative dual-layer balloon technology and a lower crossing profile led to a 16% improvement in deliverability with Onyx Frontier vs. the previous generation Resolute Onyx DES,” Medtronic said in a news release.
Onyx Frontier also offers a broad size matrix to treat more patients, and joins the Resolute Onyx as the only 2-mm DES available in the United States, the company noted. The stent is available in 4.5- to 5-mm sizes that can be expanded to 6 mm, specifically designed to support extra-large vessels.
The Onyx Frontier DES is pending CE Mark in Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the Onyx Frontier drug-eluting stent (DES) to treat patients with coronary artery disease, the device manufacturer, Medtronic, announced today.
The Onyx Frontier shares the same stent platform and clinical indications as the previous-generation Resolute Onyx zotarolimus-eluting stent, including the most recent approval for patients at high risk of bleeding who may benefit from just 1 month dual-antiplatelet therapy.
“Meaningful design changes, including increased catheter flexibility, an innovative dual-layer balloon technology and a lower crossing profile led to a 16% improvement in deliverability with Onyx Frontier vs. the previous generation Resolute Onyx DES,” Medtronic said in a news release.
Onyx Frontier also offers a broad size matrix to treat more patients, and joins the Resolute Onyx as the only 2-mm DES available in the United States, the company noted. The stent is available in 4.5- to 5-mm sizes that can be expanded to 6 mm, specifically designed to support extra-large vessels.
The Onyx Frontier DES is pending CE Mark in Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Endovascular benefit finally confirmed for basilar artery stroke
The benefit of endovascular therapy in the treatment of stroke caused by an occlusion of the basilar artery has finally been confirmed in the ATTENTION randomized trial.
The study, conducted in China, showed that endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion is associated with higher rates of favorable and independent outcomes, as well as lower overall disability and lower mortality at 90 days, than best medical management alone.
The results were presented by Raul Nogueira, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) 2022, where they were greeted with applause from the audience.
“We can finally say that we have conquered the basilar artery territory. It is about time. We can finally confirm that the benefit of endovascular therapy persists in the posterior circulation,” Dr. Nogueira said.
“The disability reduction benefit of endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion appears to be within the same range as that observed in the anterior circulation. However, in contrast to most anterior circulation endovascular trials, the ATTENTION trial also demonstrated a potential benefit in terms of mortality,” he added.
Dr. Nogueira explained that the first series of endovascular treatment for stroke in the modern era was published in 1988, and this was in the basilar artery occlusion territory, but almost 35 years later, although there has been overwhelming proof of benefit of endovascular treatment in the antiterror circulation, it remains unknown whether endovascular treatment is beneficial to treat acute basilar artery occlusion. This is despite efforts in conducting two trials – the BEST and BASICS trials – which showed a direction of benefit but failed to show real significance.
“Having said that, these trials paved the way for the current trial, specifically by demonstrating the importance of consecutive recruitment, fast enrollment, and the minimalization of crossover. They also confirmed the ideal target population for this procedure in an individual patient level meta-analysis of these two trials,” he said.
In addition, there have also been two large Chinese registries suggesting significant benefits.
The ATTENTION trial was conducted to evaluate the hypothesis that endovascular therapy is superior to best medical management alone in achieving more favorable outcomes (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days in subjects presenting with acute basilar artery stroke within 12 hours of the estimated time of onset.
The study enrolled 342 patients at 36 comprehensive stroke centers in China. All patients had occlusion of the basilar artery confirmed on vascular imaging within 12 hours of stroke onset, and they had severe symptoms at presentation, with an NIHSS score of at least 10. They were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to endovascular treatment or best medical management alone.
“It took us less than a year to enroll 342 patients,” Dr. Nogueira noted. “To put this into perspective, it took the BASICS trial over 8 years to enroll 300 patients, so these are very high-volume centers.”
He reported that two patients withdrew consent, and there were three patient crossovers on each side, comparing favorably with BASICS, leaving 226 patients in the intervention group and 114 in the control group.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups: median age was 67 years, median NIHSS score was 24, about 25% received thrombolysis, and median time from stroke onset to randomization was 5 hours.
Results showed that the primary outcome – a favorable functional outcome (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days – was achieved in 22.8% of the control group and in 46% of the endovascular group, giving an adjusted risk ratio of 2.1 (P < .001).
The number needed to treat was just four.
“There were no surprises with secondary endpoints; everything was highly statistically significant,” Dr. Nogueira said.
Specifically, there was a lower rate of overall disability in the shift analysis, with a common odds ratio of 2.8 favoring the intervention.
Safety results showed an increased risk for symptomatic ICH in the endovascular group (5.3% vs. 0.0%) but, despite that, 90-day mortality was significantly lower in the endovascular group (36.7% vs. 55.3%).
Dr. Nogueira noted a limitation of the study was that it was conducted in China.
“This was a Chinese study and, as Asians are known to have higher rates of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, the overall degree of generalizability of our findings to Western countries needs to be considered,” he commented.
However, subgroup analysis showed no treatment effect modification based on the presence of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, he noted.
Also, the proportion of comorbidities in the ATTENTION trial was similar to that in the BASICS trial, with the same degree of diabetes and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Nogueira concluded that, in contrast to previous randomized trials of endovascular treatment for basilar artery occlusion, the ATTENTION trial was able to reinforce consecutive enrollment, resulting in a fast recruitment while minimizing crossovers.
Furthermore, he pointed out that the overall results are consistent with modern era observational studies, large registries, and meta-analysis.
Commenting on the study, Joanna Wardlaw, MD, professor of applied neuroimaging at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland), and chair of the ESOC Planning Group, said: “This is a very important result, since it provides confirmation beyond doubt the benefit of thrombectomy versus medical therapy for basilar artery occlusion stroke up to 12 hours after onset.”
Dr. Wardlaw added: “The trial was large enough to provide clear results and to enable subgroup analyses; no subgroup did not benefit from thrombectomy.”
In a discussion after the presentation, Urs Fischer, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University Hospital Basel, Switzerland, said he was not surprised by the results of the ATTENTION trial.
“We have been doing thrombectomy in patients with basilar artery occlusion now for 20 years, although trials are extremely important to answer these questions, so now we have some clear evidence,” Dr. Fischer said. “Nevertheless, there are some caveats, as this is an Asian population, but this is a proof of concept, and it is going in the right direction.”
The ATTENTION trial was sponsored by the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefit of endovascular therapy in the treatment of stroke caused by an occlusion of the basilar artery has finally been confirmed in the ATTENTION randomized trial.
The study, conducted in China, showed that endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion is associated with higher rates of favorable and independent outcomes, as well as lower overall disability and lower mortality at 90 days, than best medical management alone.
The results were presented by Raul Nogueira, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) 2022, where they were greeted with applause from the audience.
“We can finally say that we have conquered the basilar artery territory. It is about time. We can finally confirm that the benefit of endovascular therapy persists in the posterior circulation,” Dr. Nogueira said.
“The disability reduction benefit of endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion appears to be within the same range as that observed in the anterior circulation. However, in contrast to most anterior circulation endovascular trials, the ATTENTION trial also demonstrated a potential benefit in terms of mortality,” he added.
Dr. Nogueira explained that the first series of endovascular treatment for stroke in the modern era was published in 1988, and this was in the basilar artery occlusion territory, but almost 35 years later, although there has been overwhelming proof of benefit of endovascular treatment in the antiterror circulation, it remains unknown whether endovascular treatment is beneficial to treat acute basilar artery occlusion. This is despite efforts in conducting two trials – the BEST and BASICS trials – which showed a direction of benefit but failed to show real significance.
“Having said that, these trials paved the way for the current trial, specifically by demonstrating the importance of consecutive recruitment, fast enrollment, and the minimalization of crossover. They also confirmed the ideal target population for this procedure in an individual patient level meta-analysis of these two trials,” he said.
In addition, there have also been two large Chinese registries suggesting significant benefits.
The ATTENTION trial was conducted to evaluate the hypothesis that endovascular therapy is superior to best medical management alone in achieving more favorable outcomes (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days in subjects presenting with acute basilar artery stroke within 12 hours of the estimated time of onset.
The study enrolled 342 patients at 36 comprehensive stroke centers in China. All patients had occlusion of the basilar artery confirmed on vascular imaging within 12 hours of stroke onset, and they had severe symptoms at presentation, with an NIHSS score of at least 10. They were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to endovascular treatment or best medical management alone.
“It took us less than a year to enroll 342 patients,” Dr. Nogueira noted. “To put this into perspective, it took the BASICS trial over 8 years to enroll 300 patients, so these are very high-volume centers.”
He reported that two patients withdrew consent, and there were three patient crossovers on each side, comparing favorably with BASICS, leaving 226 patients in the intervention group and 114 in the control group.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups: median age was 67 years, median NIHSS score was 24, about 25% received thrombolysis, and median time from stroke onset to randomization was 5 hours.
Results showed that the primary outcome – a favorable functional outcome (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days – was achieved in 22.8% of the control group and in 46% of the endovascular group, giving an adjusted risk ratio of 2.1 (P < .001).
The number needed to treat was just four.
“There were no surprises with secondary endpoints; everything was highly statistically significant,” Dr. Nogueira said.
Specifically, there was a lower rate of overall disability in the shift analysis, with a common odds ratio of 2.8 favoring the intervention.
Safety results showed an increased risk for symptomatic ICH in the endovascular group (5.3% vs. 0.0%) but, despite that, 90-day mortality was significantly lower in the endovascular group (36.7% vs. 55.3%).
Dr. Nogueira noted a limitation of the study was that it was conducted in China.
“This was a Chinese study and, as Asians are known to have higher rates of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, the overall degree of generalizability of our findings to Western countries needs to be considered,” he commented.
However, subgroup analysis showed no treatment effect modification based on the presence of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, he noted.
Also, the proportion of comorbidities in the ATTENTION trial was similar to that in the BASICS trial, with the same degree of diabetes and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Nogueira concluded that, in contrast to previous randomized trials of endovascular treatment for basilar artery occlusion, the ATTENTION trial was able to reinforce consecutive enrollment, resulting in a fast recruitment while minimizing crossovers.
Furthermore, he pointed out that the overall results are consistent with modern era observational studies, large registries, and meta-analysis.
Commenting on the study, Joanna Wardlaw, MD, professor of applied neuroimaging at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland), and chair of the ESOC Planning Group, said: “This is a very important result, since it provides confirmation beyond doubt the benefit of thrombectomy versus medical therapy for basilar artery occlusion stroke up to 12 hours after onset.”
Dr. Wardlaw added: “The trial was large enough to provide clear results and to enable subgroup analyses; no subgroup did not benefit from thrombectomy.”
In a discussion after the presentation, Urs Fischer, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University Hospital Basel, Switzerland, said he was not surprised by the results of the ATTENTION trial.
“We have been doing thrombectomy in patients with basilar artery occlusion now for 20 years, although trials are extremely important to answer these questions, so now we have some clear evidence,” Dr. Fischer said. “Nevertheless, there are some caveats, as this is an Asian population, but this is a proof of concept, and it is going in the right direction.”
The ATTENTION trial was sponsored by the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefit of endovascular therapy in the treatment of stroke caused by an occlusion of the basilar artery has finally been confirmed in the ATTENTION randomized trial.
The study, conducted in China, showed that endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion is associated with higher rates of favorable and independent outcomes, as well as lower overall disability and lower mortality at 90 days, than best medical management alone.
The results were presented by Raul Nogueira, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) 2022, where they were greeted with applause from the audience.
“We can finally say that we have conquered the basilar artery territory. It is about time. We can finally confirm that the benefit of endovascular therapy persists in the posterior circulation,” Dr. Nogueira said.
“The disability reduction benefit of endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion appears to be within the same range as that observed in the anterior circulation. However, in contrast to most anterior circulation endovascular trials, the ATTENTION trial also demonstrated a potential benefit in terms of mortality,” he added.
Dr. Nogueira explained that the first series of endovascular treatment for stroke in the modern era was published in 1988, and this was in the basilar artery occlusion territory, but almost 35 years later, although there has been overwhelming proof of benefit of endovascular treatment in the antiterror circulation, it remains unknown whether endovascular treatment is beneficial to treat acute basilar artery occlusion. This is despite efforts in conducting two trials – the BEST and BASICS trials – which showed a direction of benefit but failed to show real significance.
“Having said that, these trials paved the way for the current trial, specifically by demonstrating the importance of consecutive recruitment, fast enrollment, and the minimalization of crossover. They also confirmed the ideal target population for this procedure in an individual patient level meta-analysis of these two trials,” he said.
In addition, there have also been two large Chinese registries suggesting significant benefits.
The ATTENTION trial was conducted to evaluate the hypothesis that endovascular therapy is superior to best medical management alone in achieving more favorable outcomes (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days in subjects presenting with acute basilar artery stroke within 12 hours of the estimated time of onset.
The study enrolled 342 patients at 36 comprehensive stroke centers in China. All patients had occlusion of the basilar artery confirmed on vascular imaging within 12 hours of stroke onset, and they had severe symptoms at presentation, with an NIHSS score of at least 10. They were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to endovascular treatment or best medical management alone.
“It took us less than a year to enroll 342 patients,” Dr. Nogueira noted. “To put this into perspective, it took the BASICS trial over 8 years to enroll 300 patients, so these are very high-volume centers.”
He reported that two patients withdrew consent, and there were three patient crossovers on each side, comparing favorably with BASICS, leaving 226 patients in the intervention group and 114 in the control group.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups: median age was 67 years, median NIHSS score was 24, about 25% received thrombolysis, and median time from stroke onset to randomization was 5 hours.
Results showed that the primary outcome – a favorable functional outcome (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days – was achieved in 22.8% of the control group and in 46% of the endovascular group, giving an adjusted risk ratio of 2.1 (P < .001).
The number needed to treat was just four.
“There were no surprises with secondary endpoints; everything was highly statistically significant,” Dr. Nogueira said.
Specifically, there was a lower rate of overall disability in the shift analysis, with a common odds ratio of 2.8 favoring the intervention.
Safety results showed an increased risk for symptomatic ICH in the endovascular group (5.3% vs. 0.0%) but, despite that, 90-day mortality was significantly lower in the endovascular group (36.7% vs. 55.3%).
Dr. Nogueira noted a limitation of the study was that it was conducted in China.
“This was a Chinese study and, as Asians are known to have higher rates of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, the overall degree of generalizability of our findings to Western countries needs to be considered,” he commented.
However, subgroup analysis showed no treatment effect modification based on the presence of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, he noted.
Also, the proportion of comorbidities in the ATTENTION trial was similar to that in the BASICS trial, with the same degree of diabetes and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Nogueira concluded that, in contrast to previous randomized trials of endovascular treatment for basilar artery occlusion, the ATTENTION trial was able to reinforce consecutive enrollment, resulting in a fast recruitment while minimizing crossovers.
Furthermore, he pointed out that the overall results are consistent with modern era observational studies, large registries, and meta-analysis.
Commenting on the study, Joanna Wardlaw, MD, professor of applied neuroimaging at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland), and chair of the ESOC Planning Group, said: “This is a very important result, since it provides confirmation beyond doubt the benefit of thrombectomy versus medical therapy for basilar artery occlusion stroke up to 12 hours after onset.”
Dr. Wardlaw added: “The trial was large enough to provide clear results and to enable subgroup analyses; no subgroup did not benefit from thrombectomy.”
In a discussion after the presentation, Urs Fischer, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University Hospital Basel, Switzerland, said he was not surprised by the results of the ATTENTION trial.
“We have been doing thrombectomy in patients with basilar artery occlusion now for 20 years, although trials are extremely important to answer these questions, so now we have some clear evidence,” Dr. Fischer said. “Nevertheless, there are some caveats, as this is an Asian population, but this is a proof of concept, and it is going in the right direction.”
The ATTENTION trial was sponsored by the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antithrombotic therapies shifting for Watchman LAA occlusion
A new study finds clinicians are shifting away from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved combination of warfarin and aspirin after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device and that adverse events, particularly bleeding, are lower when aspirin is dropped.
Of 31,994 patients successfully implanted with the Watchman 2.5 device in the 3 years after its March 2015 approval, only 1 in 10 received the full postprocedure protocol studied in pivotal trials and codified into the FDA-device approval.
The protocol consisted of aspirin (81-325 mg) indefinitely and warfarin for 45 days. Following transesophageal echocardiography, patients were then maintained on warfarin and aspirin if there was a peridevice leak greater than 5 mm or switched to clopidogrel 75 mg for 6 months if a peridevice leak was ruled out or was 5 mm or less.
Based on the results, drawn from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry, the most common discharge medications were warfarin and aspirin in 36.9% of patients, followed by a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and aspirin (20.8%), warfarin alone (13.5%), DOAC only (12.3%), and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (5%).
“There’s a little bit of practice leading the science in this space,” lead author James V. Freeman, MD, MPH, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., told this news organization.
Patients who couldn’t tolerate long-term anticoagulation were excluded from the pivotal trials but are now the patients in whom the device is most often used, because of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid reimbursement mandate for a relative or absolute contraindication to long-term anticoagulation, he noted.
Not surprisingly, 70% of patients in the registry had history of clinically relevant bleeding, the mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.6, and mean HAS-BLED score was 3. At an average age of 76, they were also older, by years, than those in the clinical trials.
Secular trends at the time also saw the ascendancy of the DOACs relative to warfarin, observed Dr. Freeman. “So I think it’s pretty reasonable for physicians to be considering DOACs rather than warfarin in this context.”
Aspirin takes another hit
Results, published May 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed that any adverse event occurred at 45 days in 5.7% of patients discharged on warfarin and aspirin, 4% on warfarin alone, 5.2% on DOAC and aspirin, 3.8% on DOAC only, and 5.5% on DAPT.
Rates of any major adverse event were 4.4%, 3.3%, 4.3%, 3.1%, and 4.2% respectively, and for major bleeding were 3%, 1.8%, 2.8%, 1.7%, and 2.2% respectively. Although patients were similar across treatment groups, those treated with DAPT were slightly older and had more comorbidities, Dr. Freeman said.
In Cox frailty regression, the adjusted risk of any adverse event at 45 days was significantly lower when patients were discharged on warfarin alone (hazard ratio, 0.692; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.84) and a DOAC alone (HR, 0.731; 95% CI, 0.57-0.93), compared with warfarin and aspirin. There were no differences among the other groups.
The risk of any major adverse event was also significantly lower with warfarin alone (HR, 0.658; 95% CI, 0.53-0.80) and DOAC alone (HR, 0.767; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98).
At 6 months, rates of any adverse event (HR, 0.814; 95% CI, 0.72-0.93) and any major adverse event (HR, 0.840; 95% CI, 0.73-0.95) were significantly lower only in patients treated with warfarin alone.
“I think if there’s a take-home [message] here, it’s that for a lot of patients there’s good data now to suggest getting rid of the aspirin is a very reasonable thing to do,” Dr. Freeman said.
Further studies are needed in the space, but the results are consistent with those from transcatheter aortic valve replacement studies showing discharge on warfarin or DOAC anticoagulation alone reduces major adverse events without increasing thrombotic events, he said.
“I do think if there’s a strong indication for aspirin – someone has terrible coronary disease – there may be a role for using it,” Dr. Freeman said. But for a lot of these patients, anticoagulation alone without aspirin “may present a big opportunity to mitigate morbidity associated with this procedure.”
Dr. Freeman said he doesn’t expect the findings would be dramatically different with the second-generation Watchman FLX device but noted that randomized data will be forthcoming, as Boston Scientific changed the CHAMPION-AF trial protocol to include DOAC alone without aspirin.
Commenting for this news organization, Domenico Della Rocca, MD, Texas Cardiac Arrhythmia Institute at St. David’s Medical Center, Austin, said the study is a useful overview of post-LAAO therapies in a large population – but not surprising.
“Practice has changed over the years. More and more we are adopting and trusting the DOACs,” he said. “And, we are realizing that dual antiplatelet therapy is so aggressive and antiplatelet therapy alone maybe is not the best choice based on data on activation of coagulation.”
Commenting further, he said “I think it’s too early to suggest being too keen to completely drop aspirin,” noting that 20%-25% of patients have clopidogrel resistance and that the combination of two antiplatelets may be too aggressive a strategy for others.
Dr. Della Rocca and colleagues recently reported favorable long-term results with half-dose DOAC therapy after Watchman implantation and said the team is launching a randomized trial in more than 500 LAAO patients in the United States and Europe later this year. The trial will be comparing a DOAC-based strategy with low-dose apixaban long-term versus clopidogrel and aspirin initially and then switching to 100 mg aspirin long-term.
“We hope that in the next 2-3 years we will have some better answers, but at this point I would say that clopidogrel is kind of an obsolete strategy for appendage closure,” Dr. Della Rocca said.
In an accompanying editorial, David R. Holmes Jr., MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., says “the cornucopia of these specific strategies can be expected to change as practices evolve, as instructions for use broaden and, hopefully, with the results of well-done, scientifically performed trials. This current LAAO Registry report, however, serves as a useful benchmark.”
He cautioned that this is an observational cohort study and that unmeasured imbalances still may affect the ability to identify an unbiased treatment signal. The use of DAPT was also infrequent during the study and “conclusions based on this information are soft.”
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR), and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) grants. Dr. Freeman has received salary support from the ACC NCDR and the NHLBI and has received consulting/advisory board fees from Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Biosense Webster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study finds clinicians are shifting away from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved combination of warfarin and aspirin after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device and that adverse events, particularly bleeding, are lower when aspirin is dropped.
Of 31,994 patients successfully implanted with the Watchman 2.5 device in the 3 years after its March 2015 approval, only 1 in 10 received the full postprocedure protocol studied in pivotal trials and codified into the FDA-device approval.
The protocol consisted of aspirin (81-325 mg) indefinitely and warfarin for 45 days. Following transesophageal echocardiography, patients were then maintained on warfarin and aspirin if there was a peridevice leak greater than 5 mm or switched to clopidogrel 75 mg for 6 months if a peridevice leak was ruled out or was 5 mm or less.
Based on the results, drawn from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry, the most common discharge medications were warfarin and aspirin in 36.9% of patients, followed by a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and aspirin (20.8%), warfarin alone (13.5%), DOAC only (12.3%), and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (5%).
“There’s a little bit of practice leading the science in this space,” lead author James V. Freeman, MD, MPH, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., told this news organization.
Patients who couldn’t tolerate long-term anticoagulation were excluded from the pivotal trials but are now the patients in whom the device is most often used, because of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid reimbursement mandate for a relative or absolute contraindication to long-term anticoagulation, he noted.
Not surprisingly, 70% of patients in the registry had history of clinically relevant bleeding, the mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.6, and mean HAS-BLED score was 3. At an average age of 76, they were also older, by years, than those in the clinical trials.
Secular trends at the time also saw the ascendancy of the DOACs relative to warfarin, observed Dr. Freeman. “So I think it’s pretty reasonable for physicians to be considering DOACs rather than warfarin in this context.”
Aspirin takes another hit
Results, published May 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed that any adverse event occurred at 45 days in 5.7% of patients discharged on warfarin and aspirin, 4% on warfarin alone, 5.2% on DOAC and aspirin, 3.8% on DOAC only, and 5.5% on DAPT.
Rates of any major adverse event were 4.4%, 3.3%, 4.3%, 3.1%, and 4.2% respectively, and for major bleeding were 3%, 1.8%, 2.8%, 1.7%, and 2.2% respectively. Although patients were similar across treatment groups, those treated with DAPT were slightly older and had more comorbidities, Dr. Freeman said.
In Cox frailty regression, the adjusted risk of any adverse event at 45 days was significantly lower when patients were discharged on warfarin alone (hazard ratio, 0.692; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.84) and a DOAC alone (HR, 0.731; 95% CI, 0.57-0.93), compared with warfarin and aspirin. There were no differences among the other groups.
The risk of any major adverse event was also significantly lower with warfarin alone (HR, 0.658; 95% CI, 0.53-0.80) and DOAC alone (HR, 0.767; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98).
At 6 months, rates of any adverse event (HR, 0.814; 95% CI, 0.72-0.93) and any major adverse event (HR, 0.840; 95% CI, 0.73-0.95) were significantly lower only in patients treated with warfarin alone.
“I think if there’s a take-home [message] here, it’s that for a lot of patients there’s good data now to suggest getting rid of the aspirin is a very reasonable thing to do,” Dr. Freeman said.
Further studies are needed in the space, but the results are consistent with those from transcatheter aortic valve replacement studies showing discharge on warfarin or DOAC anticoagulation alone reduces major adverse events without increasing thrombotic events, he said.
“I do think if there’s a strong indication for aspirin – someone has terrible coronary disease – there may be a role for using it,” Dr. Freeman said. But for a lot of these patients, anticoagulation alone without aspirin “may present a big opportunity to mitigate morbidity associated with this procedure.”
Dr. Freeman said he doesn’t expect the findings would be dramatically different with the second-generation Watchman FLX device but noted that randomized data will be forthcoming, as Boston Scientific changed the CHAMPION-AF trial protocol to include DOAC alone without aspirin.
Commenting for this news organization, Domenico Della Rocca, MD, Texas Cardiac Arrhythmia Institute at St. David’s Medical Center, Austin, said the study is a useful overview of post-LAAO therapies in a large population – but not surprising.
“Practice has changed over the years. More and more we are adopting and trusting the DOACs,” he said. “And, we are realizing that dual antiplatelet therapy is so aggressive and antiplatelet therapy alone maybe is not the best choice based on data on activation of coagulation.”
Commenting further, he said “I think it’s too early to suggest being too keen to completely drop aspirin,” noting that 20%-25% of patients have clopidogrel resistance and that the combination of two antiplatelets may be too aggressive a strategy for others.
Dr. Della Rocca and colleagues recently reported favorable long-term results with half-dose DOAC therapy after Watchman implantation and said the team is launching a randomized trial in more than 500 LAAO patients in the United States and Europe later this year. The trial will be comparing a DOAC-based strategy with low-dose apixaban long-term versus clopidogrel and aspirin initially and then switching to 100 mg aspirin long-term.
“We hope that in the next 2-3 years we will have some better answers, but at this point I would say that clopidogrel is kind of an obsolete strategy for appendage closure,” Dr. Della Rocca said.
In an accompanying editorial, David R. Holmes Jr., MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., says “the cornucopia of these specific strategies can be expected to change as practices evolve, as instructions for use broaden and, hopefully, with the results of well-done, scientifically performed trials. This current LAAO Registry report, however, serves as a useful benchmark.”
He cautioned that this is an observational cohort study and that unmeasured imbalances still may affect the ability to identify an unbiased treatment signal. The use of DAPT was also infrequent during the study and “conclusions based on this information are soft.”
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR), and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) grants. Dr. Freeman has received salary support from the ACC NCDR and the NHLBI and has received consulting/advisory board fees from Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Biosense Webster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study finds clinicians are shifting away from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved combination of warfarin and aspirin after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device and that adverse events, particularly bleeding, are lower when aspirin is dropped.
Of 31,994 patients successfully implanted with the Watchman 2.5 device in the 3 years after its March 2015 approval, only 1 in 10 received the full postprocedure protocol studied in pivotal trials and codified into the FDA-device approval.
The protocol consisted of aspirin (81-325 mg) indefinitely and warfarin for 45 days. Following transesophageal echocardiography, patients were then maintained on warfarin and aspirin if there was a peridevice leak greater than 5 mm or switched to clopidogrel 75 mg for 6 months if a peridevice leak was ruled out or was 5 mm or less.
Based on the results, drawn from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry, the most common discharge medications were warfarin and aspirin in 36.9% of patients, followed by a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and aspirin (20.8%), warfarin alone (13.5%), DOAC only (12.3%), and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (5%).
“There’s a little bit of practice leading the science in this space,” lead author James V. Freeman, MD, MPH, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., told this news organization.
Patients who couldn’t tolerate long-term anticoagulation were excluded from the pivotal trials but are now the patients in whom the device is most often used, because of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid reimbursement mandate for a relative or absolute contraindication to long-term anticoagulation, he noted.
Not surprisingly, 70% of patients in the registry had history of clinically relevant bleeding, the mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.6, and mean HAS-BLED score was 3. At an average age of 76, they were also older, by years, than those in the clinical trials.
Secular trends at the time also saw the ascendancy of the DOACs relative to warfarin, observed Dr. Freeman. “So I think it’s pretty reasonable for physicians to be considering DOACs rather than warfarin in this context.”
Aspirin takes another hit
Results, published May 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed that any adverse event occurred at 45 days in 5.7% of patients discharged on warfarin and aspirin, 4% on warfarin alone, 5.2% on DOAC and aspirin, 3.8% on DOAC only, and 5.5% on DAPT.
Rates of any major adverse event were 4.4%, 3.3%, 4.3%, 3.1%, and 4.2% respectively, and for major bleeding were 3%, 1.8%, 2.8%, 1.7%, and 2.2% respectively. Although patients were similar across treatment groups, those treated with DAPT were slightly older and had more comorbidities, Dr. Freeman said.
In Cox frailty regression, the adjusted risk of any adverse event at 45 days was significantly lower when patients were discharged on warfarin alone (hazard ratio, 0.692; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.84) and a DOAC alone (HR, 0.731; 95% CI, 0.57-0.93), compared with warfarin and aspirin. There were no differences among the other groups.
The risk of any major adverse event was also significantly lower with warfarin alone (HR, 0.658; 95% CI, 0.53-0.80) and DOAC alone (HR, 0.767; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98).
At 6 months, rates of any adverse event (HR, 0.814; 95% CI, 0.72-0.93) and any major adverse event (HR, 0.840; 95% CI, 0.73-0.95) were significantly lower only in patients treated with warfarin alone.
“I think if there’s a take-home [message] here, it’s that for a lot of patients there’s good data now to suggest getting rid of the aspirin is a very reasonable thing to do,” Dr. Freeman said.
Further studies are needed in the space, but the results are consistent with those from transcatheter aortic valve replacement studies showing discharge on warfarin or DOAC anticoagulation alone reduces major adverse events without increasing thrombotic events, he said.
“I do think if there’s a strong indication for aspirin – someone has terrible coronary disease – there may be a role for using it,” Dr. Freeman said. But for a lot of these patients, anticoagulation alone without aspirin “may present a big opportunity to mitigate morbidity associated with this procedure.”
Dr. Freeman said he doesn’t expect the findings would be dramatically different with the second-generation Watchman FLX device but noted that randomized data will be forthcoming, as Boston Scientific changed the CHAMPION-AF trial protocol to include DOAC alone without aspirin.
Commenting for this news organization, Domenico Della Rocca, MD, Texas Cardiac Arrhythmia Institute at St. David’s Medical Center, Austin, said the study is a useful overview of post-LAAO therapies in a large population – but not surprising.
“Practice has changed over the years. More and more we are adopting and trusting the DOACs,” he said. “And, we are realizing that dual antiplatelet therapy is so aggressive and antiplatelet therapy alone maybe is not the best choice based on data on activation of coagulation.”
Commenting further, he said “I think it’s too early to suggest being too keen to completely drop aspirin,” noting that 20%-25% of patients have clopidogrel resistance and that the combination of two antiplatelets may be too aggressive a strategy for others.
Dr. Della Rocca and colleagues recently reported favorable long-term results with half-dose DOAC therapy after Watchman implantation and said the team is launching a randomized trial in more than 500 LAAO patients in the United States and Europe later this year. The trial will be comparing a DOAC-based strategy with low-dose apixaban long-term versus clopidogrel and aspirin initially and then switching to 100 mg aspirin long-term.
“We hope that in the next 2-3 years we will have some better answers, but at this point I would say that clopidogrel is kind of an obsolete strategy for appendage closure,” Dr. Della Rocca said.
In an accompanying editorial, David R. Holmes Jr., MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., says “the cornucopia of these specific strategies can be expected to change as practices evolve, as instructions for use broaden and, hopefully, with the results of well-done, scientifically performed trials. This current LAAO Registry report, however, serves as a useful benchmark.”
He cautioned that this is an observational cohort study and that unmeasured imbalances still may affect the ability to identify an unbiased treatment signal. The use of DAPT was also infrequent during the study and “conclusions based on this information are soft.”
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR), and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) grants. Dr. Freeman has received salary support from the ACC NCDR and the NHLBI and has received consulting/advisory board fees from Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Biosense Webster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Porcine virus a suspect in man’s death after pig heart transplant
A porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV) in the heart had gone undetected before the operation and may or may not have been instrumental in David Bennett’s death 2 months later, according to a report published in MIT Technology Review.
“The issue is now a subject of wide discussion among specialists, who think the infection was a potential contributor to Mr. Bennett’s death and a possible reason why the heart did not last longer,” states the article, written by staff journalist Antonio Regalado.
As described in the story, the xenotransplant saga’s new twist comes from the surgeon who performed the operation, Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, Baltimore, who related the PCMV finding in an April 20 online presentation hosted by the American Society of Transplantation.
Mr. Bennett’s initially promising but later turbulent clinical course, described by his surgeons and widely reported upon his death, included repeated skirmishes with infection and retaliatory adjustments to his immunosuppressant regimen. Those episodes were thought to have contributed to his death, the actual cause of which is undetermined or at least not yet reported.
“We are beginning to learn why he passed on,” Dr. Griffith said in Mr. Regalado’s article, acknowledging further that the porcine virus “maybe was the actor, or could be the actor,” that set off the events leading to Bennett’s death.
Xenotransplant specialists know that PCMV is a potential problem with pig organs and know to test for it before attempting the procedure in animal models, notes the article. It refers to a published series of pig-heart transplants to baboons in Germany. The hearts “lasted only a couple of weeks if the virus was present, while organs free from the infection could survive more than half a year.”
The heart Mr. Bennett received had been extensively screened for bacteria, viruses, and other issues that could have threatened the organ and Mr. Bennett, but the effort apparently fell short. In the MIT Technology Review story, the first author of the German baboon series speculates on how the University of Maryland team might have missed PCMV.
“The U.S. team appears to have tested the pig’s snout for the virus, but often it is lurking deeper in the tissues,” Joachim Denner, PhD, Institute of Virology, Free University of Berlin, said in the article. The virus, he contended, “can be detected and easily removed from pig populations, but unfortunately they didn’t use a good assay and didn’t detect the virus.”
That PCMV escaped detection before the operation “could now factor into some people’s questions over whether the experiment should have taken place at all,” the MIT Technology Review article proposes. “It’s a big red flag,” bioethicist Arthur Caplan, PhD, New York University, said in a quote, adding: “If doctors can’t prevent or control infection, ‘then such experiments are tough to justify.’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV) in the heart had gone undetected before the operation and may or may not have been instrumental in David Bennett’s death 2 months later, according to a report published in MIT Technology Review.
“The issue is now a subject of wide discussion among specialists, who think the infection was a potential contributor to Mr. Bennett’s death and a possible reason why the heart did not last longer,” states the article, written by staff journalist Antonio Regalado.
As described in the story, the xenotransplant saga’s new twist comes from the surgeon who performed the operation, Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, Baltimore, who related the PCMV finding in an April 20 online presentation hosted by the American Society of Transplantation.
Mr. Bennett’s initially promising but later turbulent clinical course, described by his surgeons and widely reported upon his death, included repeated skirmishes with infection and retaliatory adjustments to his immunosuppressant regimen. Those episodes were thought to have contributed to his death, the actual cause of which is undetermined or at least not yet reported.
“We are beginning to learn why he passed on,” Dr. Griffith said in Mr. Regalado’s article, acknowledging further that the porcine virus “maybe was the actor, or could be the actor,” that set off the events leading to Bennett’s death.
Xenotransplant specialists know that PCMV is a potential problem with pig organs and know to test for it before attempting the procedure in animal models, notes the article. It refers to a published series of pig-heart transplants to baboons in Germany. The hearts “lasted only a couple of weeks if the virus was present, while organs free from the infection could survive more than half a year.”
The heart Mr. Bennett received had been extensively screened for bacteria, viruses, and other issues that could have threatened the organ and Mr. Bennett, but the effort apparently fell short. In the MIT Technology Review story, the first author of the German baboon series speculates on how the University of Maryland team might have missed PCMV.
“The U.S. team appears to have tested the pig’s snout for the virus, but often it is lurking deeper in the tissues,” Joachim Denner, PhD, Institute of Virology, Free University of Berlin, said in the article. The virus, he contended, “can be detected and easily removed from pig populations, but unfortunately they didn’t use a good assay and didn’t detect the virus.”
That PCMV escaped detection before the operation “could now factor into some people’s questions over whether the experiment should have taken place at all,” the MIT Technology Review article proposes. “It’s a big red flag,” bioethicist Arthur Caplan, PhD, New York University, said in a quote, adding: “If doctors can’t prevent or control infection, ‘then such experiments are tough to justify.’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV) in the heart had gone undetected before the operation and may or may not have been instrumental in David Bennett’s death 2 months later, according to a report published in MIT Technology Review.
“The issue is now a subject of wide discussion among specialists, who think the infection was a potential contributor to Mr. Bennett’s death and a possible reason why the heart did not last longer,” states the article, written by staff journalist Antonio Regalado.
As described in the story, the xenotransplant saga’s new twist comes from the surgeon who performed the operation, Bartley P. Griffith, MD, University of Maryland, Baltimore, who related the PCMV finding in an April 20 online presentation hosted by the American Society of Transplantation.
Mr. Bennett’s initially promising but later turbulent clinical course, described by his surgeons and widely reported upon his death, included repeated skirmishes with infection and retaliatory adjustments to his immunosuppressant regimen. Those episodes were thought to have contributed to his death, the actual cause of which is undetermined or at least not yet reported.
“We are beginning to learn why he passed on,” Dr. Griffith said in Mr. Regalado’s article, acknowledging further that the porcine virus “maybe was the actor, or could be the actor,” that set off the events leading to Bennett’s death.
Xenotransplant specialists know that PCMV is a potential problem with pig organs and know to test for it before attempting the procedure in animal models, notes the article. It refers to a published series of pig-heart transplants to baboons in Germany. The hearts “lasted only a couple of weeks if the virus was present, while organs free from the infection could survive more than half a year.”
The heart Mr. Bennett received had been extensively screened for bacteria, viruses, and other issues that could have threatened the organ and Mr. Bennett, but the effort apparently fell short. In the MIT Technology Review story, the first author of the German baboon series speculates on how the University of Maryland team might have missed PCMV.
“The U.S. team appears to have tested the pig’s snout for the virus, but often it is lurking deeper in the tissues,” Joachim Denner, PhD, Institute of Virology, Free University of Berlin, said in the article. The virus, he contended, “can be detected and easily removed from pig populations, but unfortunately they didn’t use a good assay and didn’t detect the virus.”
That PCMV escaped detection before the operation “could now factor into some people’s questions over whether the experiment should have taken place at all,” the MIT Technology Review article proposes. “It’s a big red flag,” bioethicist Arthur Caplan, PhD, New York University, said in a quote, adding: “If doctors can’t prevent or control infection, ‘then such experiments are tough to justify.’ ”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM MIT TECHNOLOGY REVIEW
Cutting dementia risk in AFib: Does rhythm control strategy matter?
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. However, a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD-only at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, New Hampshire, told this news organization. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings April 30 at the Heart Rhythm Society 2022 Scientific Sessions, conducted virtually and live in San Francisco.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin-system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler discloses consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. However, a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD-only at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, New Hampshire, told this news organization. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings April 30 at the Heart Rhythm Society 2022 Scientific Sessions, conducted virtually and live in San Francisco.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin-system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler discloses consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk for dementia goes up in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), but some evidence suggests that risk can be blunted with therapies that restore sinus rhythm. However, a new cohort study suggests that the treatment effect’s magnitude might depend on the rhythm control strategy. It hinted that AFib catheter ablation might be more effective than pharmacologic rhythm control alone at cutting the risk for dementia.
The case-matched study of more than 38,000 adults with AFib saw a 41% reduction (P < .0001) in risk for dementia among those who underwent catheter ablation after attempted rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs (AAD), compared with those managed with pharmacologic rhythm control therapy alone.
The observational study comprising 20 years of data comes with big limitations and can’t say for sure whether catheter ablation is better than AAD-only at cutting the dementia risk in AFib. But it and other evidence support the idea, which has yet to be explored in a randomized fashion.
In a secondary finding, the analysis showed a similar reduction in dementia risk from catheter ablation, compared with AAD, in women and in men by 40% and 45%, respectively (P < .0001 for both). The findings are particularly relevant “given the higher life-long risk of dementia among women and the lower likelihood that women will be offered ablation, which has been demonstrated repeatedly,” Emily P. Zeitler, MD, MHS, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, New Hampshire, told this news organization. “I think this is another reason to try to be more generous in offering ablation to women.”
Management of AFib certainly evolved in important ways from 2000 to 2021, the period covered by the study. But a sensitivity analysis based on data from 2010 to 2021 showed “no meaningful differences” in the results, said Dr. Zeitler, who is slated to present the findings April 30 at the Heart Rhythm Society 2022 Scientific Sessions, conducted virtually and live in San Francisco.
Dr. Zeitler acknowledged that the observational study, even with its propensity-matched ablation and AAD cohorts, can only hint at a preference for ablation over AAD for lowering risk for AFib-associated dementia. “We know there’s unmeasured and unfixable confounding between those two groups, so we see this really as hypothesis-generating.”
It was “a well-done analysis,” and the conclusion that the dementia risk was lower with catheter ablation is “absolutely correct,” but only as far as the study and its limitations allow, agreed David Conen, MD, MPH, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, who is not a coauthor.
“Even with propensity matching, you can get rid of some sorts of confounding, but you can never get rid of all selection bias issues.” That, he said when interviewed, takes randomized trials.
Dr. Conen, who is studying cognitive decline in AFib as a SWISS-AF trial principal investigator, pointed to a secondary finding of the analysis as evidence for such confounding. He said the ablation group’s nearly 50% drop (P < .0001) in competing risk for death, compared with patients managed with AAD, isn’t plausible.
The finding “strongly suggests these people were healthier and that there’s some sort of selection bias. They were at lower risk of death, they were at lower risk of dementia, and they were probably also at lower risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and cancer because they were just probably a little healthier than the others,” Dr. Conen said. The ablation and AAD groups “were two very different populations from the get-go.”
The analysis was based on U.S. insurance and Medicare claims data from AFib patients who either underwent catheter ablation after at least one AAD trial or filled prescriptions for at least two different antiarrhythmic agents in the year after AFib diagnosis. Patients with history of dementia, catheter or surgical AFib ablation, or a valve procedure were excluded.
The ablation and AAD-only groups each consisted of 19,066 patients after propensity matching, and the groups were balanced with respect to age, sex, type of insurance, CHA2DS2-VASc scores, and use of renin-angiotensin-system inhibitors, oral anticoagulants, and antiplatelets.
The overall risk for dementia was 1.9% for the ablation group and 3.3% for AAD-only patients (hazard ratio, 0.59; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.67). Corresponding HRs by sex were 0.55 (95% CI, 0.46-0.66) for men and 0.60 (95% CI, 0.50-0.72) for women.
The competing risk for death was also significantly decreased in the ablation group (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.46-0.55).
Dr. Zeitler pointed to a randomized trial now in the early stages called Neurocognition and Greater Maintenance of Sinus Rhythm in Atrial Fibrillation, or NOGGIN-AF, which will explore relationships between rhythm control therapy and dementia in patients with AFib, whether catheter ablation or AAD can mitigate that risk, and whether either strategy works better than the other, among other goals.
“I’m optimistic,” she said, “and I think it’s going to add to the growing motivations to get patients ablated more quickly and more broadly.”
The analysis was funded by Biosense-Webster. Dr. Zeitler discloses consulting for Biosense-Webster and Arena Pharmaceuticals (now Pfizer); fees for speaking from Medtronic; and receiving research support from Boston Scientific, Sanofi, and Biosense-Webster. Dr. Conen has previously reported receiving speaker fees from Servier Canada.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
First-ever best practices for percutaneous axillary access
The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) has issued the first statement on best practices for percutaneous axillary arterial access and training.
The position statement helps fill a gap amid increasing use of transaxillary access as an alternative to the femoral route for large-bore transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), endovascular aortic repair (EVAR), and mechanical circulatory support.
“The need for alternative access has increased as we are using more and more TAVR for our elderly population, and EVAR has also increased,” writing committee chair Arnold H. Seto, MD, Long Beach VA Health Care System (California) said in an interview. “There’s also a set of patients who require balloon pumps for a prolonged period, and people were using balloon pumps from the axillary approach, which were not custom-designed for that purpose.”
He noted that the evidence base leans heavily on case reports and case series, and that they were approached for guidance by a vendor developing a balloon pump specific to axillary access. “So that helped spur all of us to get together and decide to write up something on this topic, which was developing, but was certainly picking up steam rapidly.”
The statement was published in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and it reflects the consensus of experts in heart failure, interventional cardiology and radiology, and cardiothoracic and vascular surgery. It reviews anatomic considerations and risks for percutaneous axillary access and suggests techniques for insertion, closure, and complication management.
Although the femoral artery is the most frequent access site for percutaneous large-bore procedures, the document notes that this approach may be limited in 13%-20% of patients because of prior surgeries or severe aortoiliac and/or iliofemoral atherosclerotic disease, tortuosity, or calcification.
“Absolutely, the femoral should be the predominant access site,” Dr. Seto said. Whenever there is a compromised femoral artery, “the axillary artery, which is rarely involved with atherosclerosis, makes for the most optimal alternative access. Other forms of alternative access, including transcaval and transcarotid, are possible but have their own issues and difficulties.”
Axillary access has traditionally been done through an open surgical approach, which allows for direct puncture, primary arterial repair, or placement of a sidearm conduit. Percutaneous transaxillary access avoids a surgical incision and general anesthesia and, theoretically, reduces the risk of infection, he said. It also allows for better mobility for patients, for example, who may have a balloon pump in place for weeks or even a month when waiting for a bridge to transplant.
In terms of technique, key recommendations include:
- Gaining access preferably through the left axillary
- Inserting the needle directly through the pectoralis minor into the second segment of the axillary artery
- Using a shallow-needle angle of 25-30 degrees to improve access success and decrease sheath malformation, kinking, bleeding, or vessel perforation
- Using micropuncture needles to minimize trauma to adjacent tissues
- Abducting the patient’s arm to 45-90 degrees to reduce tortuosity
- Using angiographic and ultrasound techniques to optimize vascular access
The latter point was the one area of debate among the writing committee, Dr. Seto observed. “That is one of the controversies: Should we make ultrasound mandatory? ... Everybody agreed that it can be quite useful and was likely to be useful because of its success in every other access area,” he said. “But in the absence of randomized evidence, we couldn’t make it mandatory or a strong recommendation. We just had to make it one of several options for the operator.”
The document highlights the need for familiarity with potential axillary artery complications and their management, noting that the axillary is more fragile than the femoral artery and, thus, potentially more prone to complications during instrumentation.
Data from the ARMS study in 102 patients undergoing transaxillary access for mechanical hemodynamic support reported 17 procedural complications, including 10 minor access site bleeding events, one stroke, and one pseudoaneurysm. A small study of 25 complex EVAR procedures reported a perioperative access complication rate of 8%, including one axillary artery dissection and one stenosis.
“Despite the brachial plexus being around there, there’s actually rare reports of neurologic injury and certainly none that have been permanent,” Dr. Seto said. “Also, stroke risk is probably more related to your device size and type of device rather than the approach itself.”
A significant amount of the paper is also devoted to training and privileging suggestions with an emphasis on a multidisciplinary team. The writing group recommends graduate medical education programs develop training curricula in percutaneous axillary artery access.
Those already in practice should participate in a formal training program that focuses on axillary artery anatomy, training in large bore access and closure devices, and didactic training in imaging modalities as applied to the axillary artery. Training can occur hands-on or using online simulations.
They also recommend outlining the potential need or role for proctoring and call for ongoing formal professional monitoring programs to evaluate operator outcomes using local or registry data.
“From a privileging standpoint, it was important for hospitals to be equally fair, regardless of the specialty that a requesting practitioner came from,” Dr. Seto said. “In other words, treat the vascular surgeons and interventional cardiologists and radiologists equally in terms of who has the privilege to do transaxillary access.”
The SCAI position statement has been endorsed by the American College of Cardiology, the Heart Failure Society of America, the Society of Interventional Radiology, and the Vascular & Endovascular Surgery Society.
Dr. Seto reported receiving honoraria from Getinge prior to initiation of the document. Disclosures for the rest of the writing group are available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) has issued the first statement on best practices for percutaneous axillary arterial access and training.
The position statement helps fill a gap amid increasing use of transaxillary access as an alternative to the femoral route for large-bore transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), endovascular aortic repair (EVAR), and mechanical circulatory support.
“The need for alternative access has increased as we are using more and more TAVR for our elderly population, and EVAR has also increased,” writing committee chair Arnold H. Seto, MD, Long Beach VA Health Care System (California) said in an interview. “There’s also a set of patients who require balloon pumps for a prolonged period, and people were using balloon pumps from the axillary approach, which were not custom-designed for that purpose.”
He noted that the evidence base leans heavily on case reports and case series, and that they were approached for guidance by a vendor developing a balloon pump specific to axillary access. “So that helped spur all of us to get together and decide to write up something on this topic, which was developing, but was certainly picking up steam rapidly.”
The statement was published in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and it reflects the consensus of experts in heart failure, interventional cardiology and radiology, and cardiothoracic and vascular surgery. It reviews anatomic considerations and risks for percutaneous axillary access and suggests techniques for insertion, closure, and complication management.
Although the femoral artery is the most frequent access site for percutaneous large-bore procedures, the document notes that this approach may be limited in 13%-20% of patients because of prior surgeries or severe aortoiliac and/or iliofemoral atherosclerotic disease, tortuosity, or calcification.
“Absolutely, the femoral should be the predominant access site,” Dr. Seto said. Whenever there is a compromised femoral artery, “the axillary artery, which is rarely involved with atherosclerosis, makes for the most optimal alternative access. Other forms of alternative access, including transcaval and transcarotid, are possible but have their own issues and difficulties.”
Axillary access has traditionally been done through an open surgical approach, which allows for direct puncture, primary arterial repair, or placement of a sidearm conduit. Percutaneous transaxillary access avoids a surgical incision and general anesthesia and, theoretically, reduces the risk of infection, he said. It also allows for better mobility for patients, for example, who may have a balloon pump in place for weeks or even a month when waiting for a bridge to transplant.
In terms of technique, key recommendations include:
- Gaining access preferably through the left axillary
- Inserting the needle directly through the pectoralis minor into the second segment of the axillary artery
- Using a shallow-needle angle of 25-30 degrees to improve access success and decrease sheath malformation, kinking, bleeding, or vessel perforation
- Using micropuncture needles to minimize trauma to adjacent tissues
- Abducting the patient’s arm to 45-90 degrees to reduce tortuosity
- Using angiographic and ultrasound techniques to optimize vascular access
The latter point was the one area of debate among the writing committee, Dr. Seto observed. “That is one of the controversies: Should we make ultrasound mandatory? ... Everybody agreed that it can be quite useful and was likely to be useful because of its success in every other access area,” he said. “But in the absence of randomized evidence, we couldn’t make it mandatory or a strong recommendation. We just had to make it one of several options for the operator.”
The document highlights the need for familiarity with potential axillary artery complications and their management, noting that the axillary is more fragile than the femoral artery and, thus, potentially more prone to complications during instrumentation.
Data from the ARMS study in 102 patients undergoing transaxillary access for mechanical hemodynamic support reported 17 procedural complications, including 10 minor access site bleeding events, one stroke, and one pseudoaneurysm. A small study of 25 complex EVAR procedures reported a perioperative access complication rate of 8%, including one axillary artery dissection and one stenosis.
“Despite the brachial plexus being around there, there’s actually rare reports of neurologic injury and certainly none that have been permanent,” Dr. Seto said. “Also, stroke risk is probably more related to your device size and type of device rather than the approach itself.”
A significant amount of the paper is also devoted to training and privileging suggestions with an emphasis on a multidisciplinary team. The writing group recommends graduate medical education programs develop training curricula in percutaneous axillary artery access.
Those already in practice should participate in a formal training program that focuses on axillary artery anatomy, training in large bore access and closure devices, and didactic training in imaging modalities as applied to the axillary artery. Training can occur hands-on or using online simulations.
They also recommend outlining the potential need or role for proctoring and call for ongoing formal professional monitoring programs to evaluate operator outcomes using local or registry data.
“From a privileging standpoint, it was important for hospitals to be equally fair, regardless of the specialty that a requesting practitioner came from,” Dr. Seto said. “In other words, treat the vascular surgeons and interventional cardiologists and radiologists equally in terms of who has the privilege to do transaxillary access.”
The SCAI position statement has been endorsed by the American College of Cardiology, the Heart Failure Society of America, the Society of Interventional Radiology, and the Vascular & Endovascular Surgery Society.
Dr. Seto reported receiving honoraria from Getinge prior to initiation of the document. Disclosures for the rest of the writing group are available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) has issued the first statement on best practices for percutaneous axillary arterial access and training.
The position statement helps fill a gap amid increasing use of transaxillary access as an alternative to the femoral route for large-bore transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), endovascular aortic repair (EVAR), and mechanical circulatory support.
“The need for alternative access has increased as we are using more and more TAVR for our elderly population, and EVAR has also increased,” writing committee chair Arnold H. Seto, MD, Long Beach VA Health Care System (California) said in an interview. “There’s also a set of patients who require balloon pumps for a prolonged period, and people were using balloon pumps from the axillary approach, which were not custom-designed for that purpose.”
He noted that the evidence base leans heavily on case reports and case series, and that they were approached for guidance by a vendor developing a balloon pump specific to axillary access. “So that helped spur all of us to get together and decide to write up something on this topic, which was developing, but was certainly picking up steam rapidly.”
The statement was published in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and it reflects the consensus of experts in heart failure, interventional cardiology and radiology, and cardiothoracic and vascular surgery. It reviews anatomic considerations and risks for percutaneous axillary access and suggests techniques for insertion, closure, and complication management.
Although the femoral artery is the most frequent access site for percutaneous large-bore procedures, the document notes that this approach may be limited in 13%-20% of patients because of prior surgeries or severe aortoiliac and/or iliofemoral atherosclerotic disease, tortuosity, or calcification.
“Absolutely, the femoral should be the predominant access site,” Dr. Seto said. Whenever there is a compromised femoral artery, “the axillary artery, which is rarely involved with atherosclerosis, makes for the most optimal alternative access. Other forms of alternative access, including transcaval and transcarotid, are possible but have their own issues and difficulties.”
Axillary access has traditionally been done through an open surgical approach, which allows for direct puncture, primary arterial repair, or placement of a sidearm conduit. Percutaneous transaxillary access avoids a surgical incision and general anesthesia and, theoretically, reduces the risk of infection, he said. It also allows for better mobility for patients, for example, who may have a balloon pump in place for weeks or even a month when waiting for a bridge to transplant.
In terms of technique, key recommendations include:
- Gaining access preferably through the left axillary
- Inserting the needle directly through the pectoralis minor into the second segment of the axillary artery
- Using a shallow-needle angle of 25-30 degrees to improve access success and decrease sheath malformation, kinking, bleeding, or vessel perforation
- Using micropuncture needles to minimize trauma to adjacent tissues
- Abducting the patient’s arm to 45-90 degrees to reduce tortuosity
- Using angiographic and ultrasound techniques to optimize vascular access
The latter point was the one area of debate among the writing committee, Dr. Seto observed. “That is one of the controversies: Should we make ultrasound mandatory? ... Everybody agreed that it can be quite useful and was likely to be useful because of its success in every other access area,” he said. “But in the absence of randomized evidence, we couldn’t make it mandatory or a strong recommendation. We just had to make it one of several options for the operator.”
The document highlights the need for familiarity with potential axillary artery complications and their management, noting that the axillary is more fragile than the femoral artery and, thus, potentially more prone to complications during instrumentation.
Data from the ARMS study in 102 patients undergoing transaxillary access for mechanical hemodynamic support reported 17 procedural complications, including 10 minor access site bleeding events, one stroke, and one pseudoaneurysm. A small study of 25 complex EVAR procedures reported a perioperative access complication rate of 8%, including one axillary artery dissection and one stenosis.
“Despite the brachial plexus being around there, there’s actually rare reports of neurologic injury and certainly none that have been permanent,” Dr. Seto said. “Also, stroke risk is probably more related to your device size and type of device rather than the approach itself.”
A significant amount of the paper is also devoted to training and privileging suggestions with an emphasis on a multidisciplinary team. The writing group recommends graduate medical education programs develop training curricula in percutaneous axillary artery access.
Those already in practice should participate in a formal training program that focuses on axillary artery anatomy, training in large bore access and closure devices, and didactic training in imaging modalities as applied to the axillary artery. Training can occur hands-on or using online simulations.
They also recommend outlining the potential need or role for proctoring and call for ongoing formal professional monitoring programs to evaluate operator outcomes using local or registry data.
“From a privileging standpoint, it was important for hospitals to be equally fair, regardless of the specialty that a requesting practitioner came from,” Dr. Seto said. “In other words, treat the vascular surgeons and interventional cardiologists and radiologists equally in terms of who has the privilege to do transaxillary access.”
The SCAI position statement has been endorsed by the American College of Cardiology, the Heart Failure Society of America, the Society of Interventional Radiology, and the Vascular & Endovascular Surgery Society.
Dr. Seto reported receiving honoraria from Getinge prior to initiation of the document. Disclosures for the rest of the writing group are available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY FOR CARDIOVASCULAR ANGIOGRAPHY AND INTERVENTIONS
FDA clears mavacamten (Camzyos) for obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved mavacamten (Camzyos, Bristol Myers Squibb) to improve functional capacity and symptoms in adults with symptomatic New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II-III obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM).
Mavacamten is the first FDA-approved allosteric and reversible inhibitor selective for cardiac myosin that targets the underlying pathophysiology of the genetic disorder. It’s available in 2.5-mg, 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg capsules.
“The approval of Camzyos represents a significant milestone for appropriate symptomatic obstructive HCM patients and their families, who have long awaited a new treatment option for this chronic and progressive disease,” Anjali T. Owens, MD, medical director of the Center for Inherited Cardiac Disease and assistant professor of medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a news release.
‘Revolutionary’ change
The approval of mavacamten was based on data from the pivotal EXPLORER-HCM and EXPLORER-LTE (long-term extension) trial of adults with symptomatic NYHA class II-III oHCM.
In EXPLORER-HCM, treatment with mavacamten over 30 weeks led to significant improvement in exercise capacity, left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction, NYHA functional class, and health status, as reported by this news organization.
The safety and efficacy findings seen at the end of the blinded, randomized, initial 30-week phase of EXPLORER-LTE were maintained in patients who continued treatment for a median of about 62 weeks.
Mavacamten represents “an almost revolutionary change” for the treatment of oHCM, Maya E. Guglin, MD, professor of clinical medicine and an advanced heart failure physician at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said during a press briefing earlier this month at the American College of Cardiology 2022 Scientific Session earlier this month.
“Until now, there was no good medical treatment for symptomatic oHCM. This will change the landscape, and without question it will change guidelines for treating oHCM,” Dr. Guglin said.
The product information for mavacamten includes a boxed warning citing a risk for heart failure.
Echocardiogram assessments of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) are required before and during treatment.
Starting mavacamten in patients with LVEF below 55% is not recommended and the drug should be interrupted if LVEF falls below 50% at any visit or if the patient experiences heart failure symptoms or worsening clinical status.
Concomitant use of mavacamten with certain cytochrome P450 inhibitors or discontinuation of certain cytochrome P450 inducers can increase the risk for heart failure attributable to systolic dysfunction. Therefore, its use is contraindicated in patients using moderate to strong CYP2C19 inhibitors or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, and moderate to strong CYP2C19 inducers or moderate to strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Because of the risk for heart failure attributable to systolic dysfunction, mavacamten is only available through the Camzyos Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved mavacamten (Camzyos, Bristol Myers Squibb) to improve functional capacity and symptoms in adults with symptomatic New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II-III obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM).
Mavacamten is the first FDA-approved allosteric and reversible inhibitor selective for cardiac myosin that targets the underlying pathophysiology of the genetic disorder. It’s available in 2.5-mg, 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg capsules.
“The approval of Camzyos represents a significant milestone for appropriate symptomatic obstructive HCM patients and their families, who have long awaited a new treatment option for this chronic and progressive disease,” Anjali T. Owens, MD, medical director of the Center for Inherited Cardiac Disease and assistant professor of medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a news release.
‘Revolutionary’ change
The approval of mavacamten was based on data from the pivotal EXPLORER-HCM and EXPLORER-LTE (long-term extension) trial of adults with symptomatic NYHA class II-III oHCM.
In EXPLORER-HCM, treatment with mavacamten over 30 weeks led to significant improvement in exercise capacity, left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction, NYHA functional class, and health status, as reported by this news organization.
The safety and efficacy findings seen at the end of the blinded, randomized, initial 30-week phase of EXPLORER-LTE were maintained in patients who continued treatment for a median of about 62 weeks.
Mavacamten represents “an almost revolutionary change” for the treatment of oHCM, Maya E. Guglin, MD, professor of clinical medicine and an advanced heart failure physician at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said during a press briefing earlier this month at the American College of Cardiology 2022 Scientific Session earlier this month.
“Until now, there was no good medical treatment for symptomatic oHCM. This will change the landscape, and without question it will change guidelines for treating oHCM,” Dr. Guglin said.
The product information for mavacamten includes a boxed warning citing a risk for heart failure.
Echocardiogram assessments of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) are required before and during treatment.
Starting mavacamten in patients with LVEF below 55% is not recommended and the drug should be interrupted if LVEF falls below 50% at any visit or if the patient experiences heart failure symptoms or worsening clinical status.
Concomitant use of mavacamten with certain cytochrome P450 inhibitors or discontinuation of certain cytochrome P450 inducers can increase the risk for heart failure attributable to systolic dysfunction. Therefore, its use is contraindicated in patients using moderate to strong CYP2C19 inhibitors or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, and moderate to strong CYP2C19 inducers or moderate to strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Because of the risk for heart failure attributable to systolic dysfunction, mavacamten is only available through the Camzyos Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved mavacamten (Camzyos, Bristol Myers Squibb) to improve functional capacity and symptoms in adults with symptomatic New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II-III obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (oHCM).
Mavacamten is the first FDA-approved allosteric and reversible inhibitor selective for cardiac myosin that targets the underlying pathophysiology of the genetic disorder. It’s available in 2.5-mg, 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg capsules.
“The approval of Camzyos represents a significant milestone for appropriate symptomatic obstructive HCM patients and their families, who have long awaited a new treatment option for this chronic and progressive disease,” Anjali T. Owens, MD, medical director of the Center for Inherited Cardiac Disease and assistant professor of medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a news release.
‘Revolutionary’ change
The approval of mavacamten was based on data from the pivotal EXPLORER-HCM and EXPLORER-LTE (long-term extension) trial of adults with symptomatic NYHA class II-III oHCM.
In EXPLORER-HCM, treatment with mavacamten over 30 weeks led to significant improvement in exercise capacity, left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction, NYHA functional class, and health status, as reported by this news organization.
The safety and efficacy findings seen at the end of the blinded, randomized, initial 30-week phase of EXPLORER-LTE were maintained in patients who continued treatment for a median of about 62 weeks.
Mavacamten represents “an almost revolutionary change” for the treatment of oHCM, Maya E. Guglin, MD, professor of clinical medicine and an advanced heart failure physician at Indiana University, Indianapolis, said during a press briefing earlier this month at the American College of Cardiology 2022 Scientific Session earlier this month.
“Until now, there was no good medical treatment for symptomatic oHCM. This will change the landscape, and without question it will change guidelines for treating oHCM,” Dr. Guglin said.
The product information for mavacamten includes a boxed warning citing a risk for heart failure.
Echocardiogram assessments of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) are required before and during treatment.
Starting mavacamten in patients with LVEF below 55% is not recommended and the drug should be interrupted if LVEF falls below 50% at any visit or if the patient experiences heart failure symptoms or worsening clinical status.
Concomitant use of mavacamten with certain cytochrome P450 inhibitors or discontinuation of certain cytochrome P450 inducers can increase the risk for heart failure attributable to systolic dysfunction. Therefore, its use is contraindicated in patients using moderate to strong CYP2C19 inhibitors or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, and moderate to strong CYP2C19 inducers or moderate to strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Because of the risk for heart failure attributable to systolic dysfunction, mavacamten is only available through the Camzyos Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program.
Full prescribing information is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA warns of pump defect with Medtronic HVAD system
Patients implanted with the Medtronic HeartWare ventricular assist device (HVAD) System who develop pump thrombosis could have a welding defect in the internal pump causing the pump to malfunction, the Food and Drug Administration said in a letter to health care professionals.
Medtronic has sent providers an urgent medical device notice about the pump weld defect and is trying to identify which HVAD pumps are affected.
The Medtronic HVAD System was approved as a bridge to heart transplantation in 2012. Since then, it has been fraught with problems.
This past June, the company announced it was stopping all sales of the device and advised physicians to stop implanting it, as reported by this news organization.
Pump thrombosis
Medtronic has received complaints of suspected pump thrombosis in three patients with the HVAD System.
All three patients presented with one or more of the following signs or symptoms: grinding sound, transient power spikes on log files and high watt alarms, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, and low motor speed resulting in low perfusion or dizziness or lightheadedness.
Inspection of the returned pumps in these three cases identified a malfunction of the internal pump. The pumps were exchanged in all three patients. Two patients died after the pump exchange.
The FDA does not recommend the elective removal of properly functioning systems.
“Decisions about removing or exchanging the Medtronic HVAD System should be made by health care providers and patients on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient’s clinical status and surgical risks,” the agency advised.
Patients who present with one or more of the signs or symptoms of pump thrombosis should be first treated for pump thrombosis.
If symptoms fail to resolve, providers may consider whether the patient is a candidate for pump exchange, heart transplant, or pump explant for recovery, taking into account the patient’s clinical condition and surgical risks.
For patients with any of the signs and symptoms of pump thrombosis, logfiles from the controller should be uploaded to Medtronic.
The FDA is working with Medtronic to monitor for any adverse events related to pump weld defects and ensure patients with the HVAD implant continue to receive appropriate follow-up monitoring.
Problems related to the Medtronic HVAD System should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients implanted with the Medtronic HeartWare ventricular assist device (HVAD) System who develop pump thrombosis could have a welding defect in the internal pump causing the pump to malfunction, the Food and Drug Administration said in a letter to health care professionals.
Medtronic has sent providers an urgent medical device notice about the pump weld defect and is trying to identify which HVAD pumps are affected.
The Medtronic HVAD System was approved as a bridge to heart transplantation in 2012. Since then, it has been fraught with problems.
This past June, the company announced it was stopping all sales of the device and advised physicians to stop implanting it, as reported by this news organization.
Pump thrombosis
Medtronic has received complaints of suspected pump thrombosis in three patients with the HVAD System.
All three patients presented with one or more of the following signs or symptoms: grinding sound, transient power spikes on log files and high watt alarms, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, and low motor speed resulting in low perfusion or dizziness or lightheadedness.
Inspection of the returned pumps in these three cases identified a malfunction of the internal pump. The pumps were exchanged in all three patients. Two patients died after the pump exchange.
The FDA does not recommend the elective removal of properly functioning systems.
“Decisions about removing or exchanging the Medtronic HVAD System should be made by health care providers and patients on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient’s clinical status and surgical risks,” the agency advised.
Patients who present with one or more of the signs or symptoms of pump thrombosis should be first treated for pump thrombosis.
If symptoms fail to resolve, providers may consider whether the patient is a candidate for pump exchange, heart transplant, or pump explant for recovery, taking into account the patient’s clinical condition and surgical risks.
For patients with any of the signs and symptoms of pump thrombosis, logfiles from the controller should be uploaded to Medtronic.
The FDA is working with Medtronic to monitor for any adverse events related to pump weld defects and ensure patients with the HVAD implant continue to receive appropriate follow-up monitoring.
Problems related to the Medtronic HVAD System should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients implanted with the Medtronic HeartWare ventricular assist device (HVAD) System who develop pump thrombosis could have a welding defect in the internal pump causing the pump to malfunction, the Food and Drug Administration said in a letter to health care professionals.
Medtronic has sent providers an urgent medical device notice about the pump weld defect and is trying to identify which HVAD pumps are affected.
The Medtronic HVAD System was approved as a bridge to heart transplantation in 2012. Since then, it has been fraught with problems.
This past June, the company announced it was stopping all sales of the device and advised physicians to stop implanting it, as reported by this news organization.
Pump thrombosis
Medtronic has received complaints of suspected pump thrombosis in three patients with the HVAD System.
All three patients presented with one or more of the following signs or symptoms: grinding sound, transient power spikes on log files and high watt alarms, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, and low motor speed resulting in low perfusion or dizziness or lightheadedness.
Inspection of the returned pumps in these three cases identified a malfunction of the internal pump. The pumps were exchanged in all three patients. Two patients died after the pump exchange.
The FDA does not recommend the elective removal of properly functioning systems.
“Decisions about removing or exchanging the Medtronic HVAD System should be made by health care providers and patients on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient’s clinical status and surgical risks,” the agency advised.
Patients who present with one or more of the signs or symptoms of pump thrombosis should be first treated for pump thrombosis.
If symptoms fail to resolve, providers may consider whether the patient is a candidate for pump exchange, heart transplant, or pump explant for recovery, taking into account the patient’s clinical condition and surgical risks.
For patients with any of the signs and symptoms of pump thrombosis, logfiles from the controller should be uploaded to Medtronic.
The FDA is working with Medtronic to monitor for any adverse events related to pump weld defects and ensure patients with the HVAD implant continue to receive appropriate follow-up monitoring.
Problems related to the Medtronic HVAD System should be reported to the FDA’s MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Will you have cardiac arrest? New tech may predict if and when
Deaths from COVID-19 may have caught more attention lately, but heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the United States.
More than 300,000 Americans will die this year of sudden cardiac arrest (also called sudden cardiac death, or SCD), when the heart abruptly stops working.
These events happen suddenly and often without warning, making them nearly impossible to predict. But that may be changing, thanks to 3D imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) technology under study at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
There, researchers are working to create more accurate and personalized models of the heart – and not just any heart, your heart, if you have heart disease.
“Right now, a clinician can only say whether a patient is at risk or not at risk for sudden death,” says Dan Popescu, PhD, a Johns Hopkins research scientist and first author of a new study on AI’s ability to predict sudden cardiac arrest. “With this new technology, you can have much more nuanced predictions of probability of an event over time.”
Put another way: With AI, clinicians may be able not only to predict if someone is at risk for sudden cardiac arrest, but also when it is most likely to happen. They can do this using a much clearer and more personalized look at the electrical “wiring” of your heart.
Your heart, the conductor
Your heart isn’t just a metronome responsible for keeping a steady stream of blood pumping to tissues with every beat. It’s also a conductor through which vital energy flows.
To make the heart beat, electrical impulses flow from the top to the bottom of the organ. Healthy heart cells relay this electricity seamlessly. But in a heart damaged by inflammation or a past heart attack, scar tissue will block the energy flow.
When an electrical impulse encounters a scarred area, the signal can become erratic, disrupting the set top-to-bottom path and causing irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), which increase someone’s danger of sudden cardiac death.
Seeing the heart in 3D
Today’s tests offer some insights into the heart’s makeup. For example, MRI scans can reveal damaged areas. PET scans can show inflammation. And EKGs can record the heart’s electrical signals from beat to beat.
But all these technologies offer only a snapshot, showing heart health at a moment in time. They can’t predict the future. That’s why scientists at Johns Hopkins are going further to develop 3D digital replicas of a person’s heart, known as computational heart models.
Computational models are computer-simulated replicas that combine mathematics, physics, and computer science. These models have been around for a long time and are used in many fields, ranging from manufacturing to economics.
In heart medicine, these models are populated with digital “cells,” which imitate living cells and can be programmed with different electrical properties, depending on whether they are healthy or diseased.
“Currently available imaging and testing (MRIs, PETs, EKGs) give some representation of the scarring, but you cannot translate that to what is going to happen over time,” says Natalia Trayanova, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins department of biomedical engineering.
“With computational heart models, we create a dynamic digital image of the heart. We can then give the digital image an electrical stimulus and assess how the heart is able to respond. Then you can better predict what is going to happen.”
The computerized 3D models also mean better, more accurate treatment for heart conditions.
For example, a common treatment for a type of arrhythmia known as atrial fibrillation is ablation, or burning some heart tissue. Ablation stops the erratic electrical impulses causing the arrhythmia, but it can also damage otherwise healthy heart cells.
A personalized computational heart model could allow doctors to see more accurately what areas should and shouldn’t be treated for a specific patient.
Using deep learning AI to predict health outcomes
Dr. Trayanova’s colleague Dr. Popescu is applying deep learning and AI to do more with computerized heart models to predict the future.
In a recent paper in Nature Cardiovascular Research, the research team showed their algorithm assessed the health of 269 patients and was able to predict the chance of sudden cardiac arrest up to 10 years in advance.
“This is really the first time ever, as far as we know, where deep learning technology has been proven to analyze scarring of the heart in a successful way,” Dr. Popescu says.
Dr. Popescu and Dr. Trayanova say the AI algorithm gathers information from the 3D computational heart models with patient data like MRIs, ethnicity, age, lifestyle, and other clinical information. Analyzing all these data can produce accurate and consistent estimates about how long patients might live if they are at risk for sudden death.
“You can’t afford to be wrong. If you are wrong, you can actually impact a patient’s quality of life dramatically,” Dr. Popescu says. “Having clinicians use this technology in the decision-making process will provide confidence in a better diagnosis and prognosis.”
While the current study was specifically about patients with a particular type of heart disease, Dr. Popescu says his algorithm can also be trained to assess other health conditions.
So when might you see this being used outside of a research study? Dr. Trayanova predicts 3D imaging of heart models could be available in 2 years, but first the technique must be tested in more clinical trials – some of which are happening right now.
Adding AI to the heart models will require more studies and Food and Drug Administration approval, so the timeline is less clear. But perhaps the biggest hurdle is that after approval the technologies would need to be adopted and used by clinicians and caregivers.
“The much harder question to answer is, ‘When will doctors be perfectly comfortable with AI tools?’ And I don’t know the answer,” Dr. Popescu says. “How to use AI as an aid in the decision-making process is something that’s not currently taught.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Deaths from COVID-19 may have caught more attention lately, but heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the United States.
More than 300,000 Americans will die this year of sudden cardiac arrest (also called sudden cardiac death, or SCD), when the heart abruptly stops working.
These events happen suddenly and often without warning, making them nearly impossible to predict. But that may be changing, thanks to 3D imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) technology under study at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
There, researchers are working to create more accurate and personalized models of the heart – and not just any heart, your heart, if you have heart disease.
“Right now, a clinician can only say whether a patient is at risk or not at risk for sudden death,” says Dan Popescu, PhD, a Johns Hopkins research scientist and first author of a new study on AI’s ability to predict sudden cardiac arrest. “With this new technology, you can have much more nuanced predictions of probability of an event over time.”
Put another way: With AI, clinicians may be able not only to predict if someone is at risk for sudden cardiac arrest, but also when it is most likely to happen. They can do this using a much clearer and more personalized look at the electrical “wiring” of your heart.
Your heart, the conductor
Your heart isn’t just a metronome responsible for keeping a steady stream of blood pumping to tissues with every beat. It’s also a conductor through which vital energy flows.
To make the heart beat, electrical impulses flow from the top to the bottom of the organ. Healthy heart cells relay this electricity seamlessly. But in a heart damaged by inflammation or a past heart attack, scar tissue will block the energy flow.
When an electrical impulse encounters a scarred area, the signal can become erratic, disrupting the set top-to-bottom path and causing irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), which increase someone’s danger of sudden cardiac death.
Seeing the heart in 3D
Today’s tests offer some insights into the heart’s makeup. For example, MRI scans can reveal damaged areas. PET scans can show inflammation. And EKGs can record the heart’s electrical signals from beat to beat.
But all these technologies offer only a snapshot, showing heart health at a moment in time. They can’t predict the future. That’s why scientists at Johns Hopkins are going further to develop 3D digital replicas of a person’s heart, known as computational heart models.
Computational models are computer-simulated replicas that combine mathematics, physics, and computer science. These models have been around for a long time and are used in many fields, ranging from manufacturing to economics.
In heart medicine, these models are populated with digital “cells,” which imitate living cells and can be programmed with different electrical properties, depending on whether they are healthy or diseased.
“Currently available imaging and testing (MRIs, PETs, EKGs) give some representation of the scarring, but you cannot translate that to what is going to happen over time,” says Natalia Trayanova, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins department of biomedical engineering.
“With computational heart models, we create a dynamic digital image of the heart. We can then give the digital image an electrical stimulus and assess how the heart is able to respond. Then you can better predict what is going to happen.”
The computerized 3D models also mean better, more accurate treatment for heart conditions.
For example, a common treatment for a type of arrhythmia known as atrial fibrillation is ablation, or burning some heart tissue. Ablation stops the erratic electrical impulses causing the arrhythmia, but it can also damage otherwise healthy heart cells.
A personalized computational heart model could allow doctors to see more accurately what areas should and shouldn’t be treated for a specific patient.
Using deep learning AI to predict health outcomes
Dr. Trayanova’s colleague Dr. Popescu is applying deep learning and AI to do more with computerized heart models to predict the future.
In a recent paper in Nature Cardiovascular Research, the research team showed their algorithm assessed the health of 269 patients and was able to predict the chance of sudden cardiac arrest up to 10 years in advance.
“This is really the first time ever, as far as we know, where deep learning technology has been proven to analyze scarring of the heart in a successful way,” Dr. Popescu says.
Dr. Popescu and Dr. Trayanova say the AI algorithm gathers information from the 3D computational heart models with patient data like MRIs, ethnicity, age, lifestyle, and other clinical information. Analyzing all these data can produce accurate and consistent estimates about how long patients might live if they are at risk for sudden death.
“You can’t afford to be wrong. If you are wrong, you can actually impact a patient’s quality of life dramatically,” Dr. Popescu says. “Having clinicians use this technology in the decision-making process will provide confidence in a better diagnosis and prognosis.”
While the current study was specifically about patients with a particular type of heart disease, Dr. Popescu says his algorithm can also be trained to assess other health conditions.
So when might you see this being used outside of a research study? Dr. Trayanova predicts 3D imaging of heart models could be available in 2 years, but first the technique must be tested in more clinical trials – some of which are happening right now.
Adding AI to the heart models will require more studies and Food and Drug Administration approval, so the timeline is less clear. But perhaps the biggest hurdle is that after approval the technologies would need to be adopted and used by clinicians and caregivers.
“The much harder question to answer is, ‘When will doctors be perfectly comfortable with AI tools?’ And I don’t know the answer,” Dr. Popescu says. “How to use AI as an aid in the decision-making process is something that’s not currently taught.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Deaths from COVID-19 may have caught more attention lately, but heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the United States.
More than 300,000 Americans will die this year of sudden cardiac arrest (also called sudden cardiac death, or SCD), when the heart abruptly stops working.
These events happen suddenly and often without warning, making them nearly impossible to predict. But that may be changing, thanks to 3D imaging and artificial intelligence (AI) technology under study at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
There, researchers are working to create more accurate and personalized models of the heart – and not just any heart, your heart, if you have heart disease.
“Right now, a clinician can only say whether a patient is at risk or not at risk for sudden death,” says Dan Popescu, PhD, a Johns Hopkins research scientist and first author of a new study on AI’s ability to predict sudden cardiac arrest. “With this new technology, you can have much more nuanced predictions of probability of an event over time.”
Put another way: With AI, clinicians may be able not only to predict if someone is at risk for sudden cardiac arrest, but also when it is most likely to happen. They can do this using a much clearer and more personalized look at the electrical “wiring” of your heart.
Your heart, the conductor
Your heart isn’t just a metronome responsible for keeping a steady stream of blood pumping to tissues with every beat. It’s also a conductor through which vital energy flows.
To make the heart beat, electrical impulses flow from the top to the bottom of the organ. Healthy heart cells relay this electricity seamlessly. But in a heart damaged by inflammation or a past heart attack, scar tissue will block the energy flow.
When an electrical impulse encounters a scarred area, the signal can become erratic, disrupting the set top-to-bottom path and causing irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), which increase someone’s danger of sudden cardiac death.
Seeing the heart in 3D
Today’s tests offer some insights into the heart’s makeup. For example, MRI scans can reveal damaged areas. PET scans can show inflammation. And EKGs can record the heart’s electrical signals from beat to beat.
But all these technologies offer only a snapshot, showing heart health at a moment in time. They can’t predict the future. That’s why scientists at Johns Hopkins are going further to develop 3D digital replicas of a person’s heart, known as computational heart models.
Computational models are computer-simulated replicas that combine mathematics, physics, and computer science. These models have been around for a long time and are used in many fields, ranging from manufacturing to economics.
In heart medicine, these models are populated with digital “cells,” which imitate living cells and can be programmed with different electrical properties, depending on whether they are healthy or diseased.
“Currently available imaging and testing (MRIs, PETs, EKGs) give some representation of the scarring, but you cannot translate that to what is going to happen over time,” says Natalia Trayanova, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins department of biomedical engineering.
“With computational heart models, we create a dynamic digital image of the heart. We can then give the digital image an electrical stimulus and assess how the heart is able to respond. Then you can better predict what is going to happen.”
The computerized 3D models also mean better, more accurate treatment for heart conditions.
For example, a common treatment for a type of arrhythmia known as atrial fibrillation is ablation, or burning some heart tissue. Ablation stops the erratic electrical impulses causing the arrhythmia, but it can also damage otherwise healthy heart cells.
A personalized computational heart model could allow doctors to see more accurately what areas should and shouldn’t be treated for a specific patient.
Using deep learning AI to predict health outcomes
Dr. Trayanova’s colleague Dr. Popescu is applying deep learning and AI to do more with computerized heart models to predict the future.
In a recent paper in Nature Cardiovascular Research, the research team showed their algorithm assessed the health of 269 patients and was able to predict the chance of sudden cardiac arrest up to 10 years in advance.
“This is really the first time ever, as far as we know, where deep learning technology has been proven to analyze scarring of the heart in a successful way,” Dr. Popescu says.
Dr. Popescu and Dr. Trayanova say the AI algorithm gathers information from the 3D computational heart models with patient data like MRIs, ethnicity, age, lifestyle, and other clinical information. Analyzing all these data can produce accurate and consistent estimates about how long patients might live if they are at risk for sudden death.
“You can’t afford to be wrong. If you are wrong, you can actually impact a patient’s quality of life dramatically,” Dr. Popescu says. “Having clinicians use this technology in the decision-making process will provide confidence in a better diagnosis and prognosis.”
While the current study was specifically about patients with a particular type of heart disease, Dr. Popescu says his algorithm can also be trained to assess other health conditions.
So when might you see this being used outside of a research study? Dr. Trayanova predicts 3D imaging of heart models could be available in 2 years, but first the technique must be tested in more clinical trials – some of which are happening right now.
Adding AI to the heart models will require more studies and Food and Drug Administration approval, so the timeline is less clear. But perhaps the biggest hurdle is that after approval the technologies would need to be adopted and used by clinicians and caregivers.
“The much harder question to answer is, ‘When will doctors be perfectly comfortable with AI tools?’ And I don’t know the answer,” Dr. Popescu says. “How to use AI as an aid in the decision-making process is something that’s not currently taught.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.