User login
FDA OKs new agent to block chemotherapy-induced neutropenia
Efbemalenograstim joins other agents already on the U.S. market, including pegfilgrastim (Neulasta), that aim to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia.
The approval of efbemalenograstim was based on two randomized trials. The first included 122 women with either metastatic or nonmetastatic breast cancer who were receiving doxorubicin and docetaxel. These patients were randomly assigned to receive either one subcutaneous injection of efbemalenograstim or placebo on the second day of their first chemotherapy cycle. All patients received efbemalenograstim on the second day of cycles two through four.
The mean duration of grade 4 neutropenia in the first cycle was 1.4 days with efbemalenograstim versus 4.3 days with placebo. Only 4.8% of patients who received efbemalenograstim experienced chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia, compared with 25.6% who received the placebo.
The new agent went up against pegfilgrastim in the second trial, which included 393 women who received docetaxel and cyclophosphamide as treatment for nonmetastatic breast cancer. These patients were randomly assigned to receive either a single subcutaneous injection of efbemalenograstim or pegfilgrastim on the second day of each cycle.
During the first cycle, patients in both arms of the trial experienced a mean of 0.2 days of grade 4 neutropenia.
The most common side effects associated with efbemalenograstim were nausea, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. Similar to pegfilgrastim’s label, efbemalenograstim’s label warns of possible splenic rupture, respiratory distress syndrome, sickle cell crisis, and other serious adverse events.
The FDA recommends a dose of 20 mg subcutaneous once per chemotherapy cycle.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Efbemalenograstim joins other agents already on the U.S. market, including pegfilgrastim (Neulasta), that aim to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia.
The approval of efbemalenograstim was based on two randomized trials. The first included 122 women with either metastatic or nonmetastatic breast cancer who were receiving doxorubicin and docetaxel. These patients were randomly assigned to receive either one subcutaneous injection of efbemalenograstim or placebo on the second day of their first chemotherapy cycle. All patients received efbemalenograstim on the second day of cycles two through four.
The mean duration of grade 4 neutropenia in the first cycle was 1.4 days with efbemalenograstim versus 4.3 days with placebo. Only 4.8% of patients who received efbemalenograstim experienced chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia, compared with 25.6% who received the placebo.
The new agent went up against pegfilgrastim in the second trial, which included 393 women who received docetaxel and cyclophosphamide as treatment for nonmetastatic breast cancer. These patients were randomly assigned to receive either a single subcutaneous injection of efbemalenograstim or pegfilgrastim on the second day of each cycle.
During the first cycle, patients in both arms of the trial experienced a mean of 0.2 days of grade 4 neutropenia.
The most common side effects associated with efbemalenograstim were nausea, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. Similar to pegfilgrastim’s label, efbemalenograstim’s label warns of possible splenic rupture, respiratory distress syndrome, sickle cell crisis, and other serious adverse events.
The FDA recommends a dose of 20 mg subcutaneous once per chemotherapy cycle.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Efbemalenograstim joins other agents already on the U.S. market, including pegfilgrastim (Neulasta), that aim to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia.
The approval of efbemalenograstim was based on two randomized trials. The first included 122 women with either metastatic or nonmetastatic breast cancer who were receiving doxorubicin and docetaxel. These patients were randomly assigned to receive either one subcutaneous injection of efbemalenograstim or placebo on the second day of their first chemotherapy cycle. All patients received efbemalenograstim on the second day of cycles two through four.
The mean duration of grade 4 neutropenia in the first cycle was 1.4 days with efbemalenograstim versus 4.3 days with placebo. Only 4.8% of patients who received efbemalenograstim experienced chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia, compared with 25.6% who received the placebo.
The new agent went up against pegfilgrastim in the second trial, which included 393 women who received docetaxel and cyclophosphamide as treatment for nonmetastatic breast cancer. These patients were randomly assigned to receive either a single subcutaneous injection of efbemalenograstim or pegfilgrastim on the second day of each cycle.
During the first cycle, patients in both arms of the trial experienced a mean of 0.2 days of grade 4 neutropenia.
The most common side effects associated with efbemalenograstim were nausea, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. Similar to pegfilgrastim’s label, efbemalenograstim’s label warns of possible splenic rupture, respiratory distress syndrome, sickle cell crisis, and other serious adverse events.
The FDA recommends a dose of 20 mg subcutaneous once per chemotherapy cycle.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA panel voices concerns over 2 lymphoma accelerated approvals
At a Nov. 16 meeting, the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee of the Food and Drug Administration reviewed the reasons for delays in confirmatory trials for pralatrexate (Folotyn) and belinostat (Beleodaq), both now owned by East Windsor, N.J.–based Acrotech. The FDA granted accelerated approval for pralatrexate in 2009 and belinostat in 2014.
“The consensus of the advisory committee is that we have significant concerns about the very prolonged delay and getting these confirmatory studies underway,” said Andy Chen, MD, PhD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who served as acting ODAC chair for the meeting.
Corporate ownership changes were among the reasons Acrotech cited for the long delays in producing the confirmatory research on pralatrexate and belinostat. Allos Therapeutics won the FDA approval of pralatrexate in 2009. In 2012, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals acquired Acrotech. Spectrum won approval of belinostat in 2014. Acrotech acquired Spectrum in 2019.
The FDA didn’t ask ODAC to take votes on any questions at the meeting. Instead, the FDA sought its expert feedback about how to address the prolonged delays with pralatrexate and belinostat research and, in general, how to promote more timely completion of confirmatory trials for drugs cleared by accelerated approval.
Pralatrexate and belinostat are both used to treat relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma, a rare and aggressive disease affecting about 10,000-15,000 people annually in the United States.
Through the accelerated approval process, the FDA seeks to speed medicines to people with fatal and serious conditions based on promising signs in clinical testing.
The initial pralatrexate and belinostat were based on phase 2, single-arm, monotherapy studies, with about 109 evaluable patients in the key pralatrexate study and 120 evaluable patients in the belinostat study. As is common, these phase 2 tests used measurements of cancer progression, known as the overall response rate.
The FDA then expects companies to show through more extensive testing that medicines cleared with accelerated approvals can deliver significant benefits, such as extending lives. When there are delays in confirmatory trials, patients can be exposed to medicines, often with significant side effects, that are unlikely to benefit them.
For example, the FDA granted an accelerated approval in 2011 for romidepsin for this use for peripheral T-cell lymphoma, the same condition for which pralatrexate and belinostat are used. But in 2021, Bristol-Myers Squibb withdrew the approval for that use of romidepsin when a confirmatory trial failed to meet the primary efficacy endpoint of progression free survival.
At the meeting, Richard Pazdur, MD, who leads oncology medicine at the FDA, urged Acrotech to shorten the time needed to determine whether its medicines deliver significant benefits to patients and thus merit full approval, or whether they too may fall short.
“We’re really in a situation where patients are caught in the middle here,” Dr. Pazdur said. “I feel very bad for that situation and very bad for the patients that they don’t have this information.”
‘Dangerous precedent’
The FDA in recent years has stepped up its efforts to get companies to complete their required studies on drugs cleared by accelerated approvals. The FDA has granted a total of 187 accelerated approvals for cancer drugs. Many of these cover new uses of established drugs and others serve to allow the introduction of new medicines.
For more than half of these cases, 96 of 187, the FDA already has learned that it made the right call in allowing early access to medicines. Companies have presented study results that confirmed the benefit of drugs and thus been able to convert accelerated approvals to traditional approvals.
But 27 of the 187 oncology accelerated approvals have been withdrawn. In these cases, subsequent research failed to establish the expected benefits of these cancer drugs.
And in 95 cases, the FDA and companies are still waiting for the results of studies to confirm the expected benefit of drugs granted accelerated approvals. The FDA classifies these as ongoing accelerated approvals. About 85% of these ongoing approvals were granted in the past 5 years, in contrast to 14 years for pralatrexate and 9 for belinostat.
“It sets a dangerous precedent for the other sponsors and drug companies to have such outliers from the same company,” said ODAC member Toni K. Choueiri, MD, of Harvard Medical School and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston.
The current agreement between the FDA and Acrotech focuses on a phase 3 trial, SPI-BEL-301 as the confirmatory study. Acrotech’s plan is to start with dose optimization studies in part 1 of the trial, with part 2 meant to see if its medicines provide a significant benefit as measured by progression-free survival.
The plan is to compare treatments. One group of patients would get belinostat plus a common cancer regimen known as CHOP, another group would get pralatrexate plus the COP cancer regimen, which is CHOP without doxorubicin, and a third group would get CHOP.
Acrotech’s current time line is for part 1, which began in October, to finish by December 2025. Then the part 2 timeline would run from 2026 to 2030, with interim progression-free survival possible by 2028.
ODAC member Ashley Rosko, MD, a hematologist from Ohio State University, Columbus, asked Acrotech what steps it will take to try to speed recruitment for the study.
“We are going to implement many strategies,” including what’s called digital amplification, replied Ashish Anvekar, president of Acrotech. This will help identify patients and channel them toward participating clinical sites.
Alexander A. Vinks, PhD, PharmD, who served as a temporary member of ODAC for the Nov. 16 meeting, said many clinicians will not be excited about enrolling patients in this kind of large, traditionally designed study.
Dr. Vinks, who is professor emeritus at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati, now works with consultant group NDA, a firm that advises companies on developing drugs.
Dr. Vinks advised Acrotech should try “to pin down what is most likely a smaller study that could be simpler, but still give robust, informative data.”
At a Nov. 16 meeting, the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee of the Food and Drug Administration reviewed the reasons for delays in confirmatory trials for pralatrexate (Folotyn) and belinostat (Beleodaq), both now owned by East Windsor, N.J.–based Acrotech. The FDA granted accelerated approval for pralatrexate in 2009 and belinostat in 2014.
“The consensus of the advisory committee is that we have significant concerns about the very prolonged delay and getting these confirmatory studies underway,” said Andy Chen, MD, PhD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who served as acting ODAC chair for the meeting.
Corporate ownership changes were among the reasons Acrotech cited for the long delays in producing the confirmatory research on pralatrexate and belinostat. Allos Therapeutics won the FDA approval of pralatrexate in 2009. In 2012, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals acquired Acrotech. Spectrum won approval of belinostat in 2014. Acrotech acquired Spectrum in 2019.
The FDA didn’t ask ODAC to take votes on any questions at the meeting. Instead, the FDA sought its expert feedback about how to address the prolonged delays with pralatrexate and belinostat research and, in general, how to promote more timely completion of confirmatory trials for drugs cleared by accelerated approval.
Pralatrexate and belinostat are both used to treat relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma, a rare and aggressive disease affecting about 10,000-15,000 people annually in the United States.
Through the accelerated approval process, the FDA seeks to speed medicines to people with fatal and serious conditions based on promising signs in clinical testing.
The initial pralatrexate and belinostat were based on phase 2, single-arm, monotherapy studies, with about 109 evaluable patients in the key pralatrexate study and 120 evaluable patients in the belinostat study. As is common, these phase 2 tests used measurements of cancer progression, known as the overall response rate.
The FDA then expects companies to show through more extensive testing that medicines cleared with accelerated approvals can deliver significant benefits, such as extending lives. When there are delays in confirmatory trials, patients can be exposed to medicines, often with significant side effects, that are unlikely to benefit them.
For example, the FDA granted an accelerated approval in 2011 for romidepsin for this use for peripheral T-cell lymphoma, the same condition for which pralatrexate and belinostat are used. But in 2021, Bristol-Myers Squibb withdrew the approval for that use of romidepsin when a confirmatory trial failed to meet the primary efficacy endpoint of progression free survival.
At the meeting, Richard Pazdur, MD, who leads oncology medicine at the FDA, urged Acrotech to shorten the time needed to determine whether its medicines deliver significant benefits to patients and thus merit full approval, or whether they too may fall short.
“We’re really in a situation where patients are caught in the middle here,” Dr. Pazdur said. “I feel very bad for that situation and very bad for the patients that they don’t have this information.”
‘Dangerous precedent’
The FDA in recent years has stepped up its efforts to get companies to complete their required studies on drugs cleared by accelerated approvals. The FDA has granted a total of 187 accelerated approvals for cancer drugs. Many of these cover new uses of established drugs and others serve to allow the introduction of new medicines.
For more than half of these cases, 96 of 187, the FDA already has learned that it made the right call in allowing early access to medicines. Companies have presented study results that confirmed the benefit of drugs and thus been able to convert accelerated approvals to traditional approvals.
But 27 of the 187 oncology accelerated approvals have been withdrawn. In these cases, subsequent research failed to establish the expected benefits of these cancer drugs.
And in 95 cases, the FDA and companies are still waiting for the results of studies to confirm the expected benefit of drugs granted accelerated approvals. The FDA classifies these as ongoing accelerated approvals. About 85% of these ongoing approvals were granted in the past 5 years, in contrast to 14 years for pralatrexate and 9 for belinostat.
“It sets a dangerous precedent for the other sponsors and drug companies to have such outliers from the same company,” said ODAC member Toni K. Choueiri, MD, of Harvard Medical School and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston.
The current agreement between the FDA and Acrotech focuses on a phase 3 trial, SPI-BEL-301 as the confirmatory study. Acrotech’s plan is to start with dose optimization studies in part 1 of the trial, with part 2 meant to see if its medicines provide a significant benefit as measured by progression-free survival.
The plan is to compare treatments. One group of patients would get belinostat plus a common cancer regimen known as CHOP, another group would get pralatrexate plus the COP cancer regimen, which is CHOP without doxorubicin, and a third group would get CHOP.
Acrotech’s current time line is for part 1, which began in October, to finish by December 2025. Then the part 2 timeline would run from 2026 to 2030, with interim progression-free survival possible by 2028.
ODAC member Ashley Rosko, MD, a hematologist from Ohio State University, Columbus, asked Acrotech what steps it will take to try to speed recruitment for the study.
“We are going to implement many strategies,” including what’s called digital amplification, replied Ashish Anvekar, president of Acrotech. This will help identify patients and channel them toward participating clinical sites.
Alexander A. Vinks, PhD, PharmD, who served as a temporary member of ODAC for the Nov. 16 meeting, said many clinicians will not be excited about enrolling patients in this kind of large, traditionally designed study.
Dr. Vinks, who is professor emeritus at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati, now works with consultant group NDA, a firm that advises companies on developing drugs.
Dr. Vinks advised Acrotech should try “to pin down what is most likely a smaller study that could be simpler, but still give robust, informative data.”
At a Nov. 16 meeting, the Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee of the Food and Drug Administration reviewed the reasons for delays in confirmatory trials for pralatrexate (Folotyn) and belinostat (Beleodaq), both now owned by East Windsor, N.J.–based Acrotech. The FDA granted accelerated approval for pralatrexate in 2009 and belinostat in 2014.
“The consensus of the advisory committee is that we have significant concerns about the very prolonged delay and getting these confirmatory studies underway,” said Andy Chen, MD, PhD, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who served as acting ODAC chair for the meeting.
Corporate ownership changes were among the reasons Acrotech cited for the long delays in producing the confirmatory research on pralatrexate and belinostat. Allos Therapeutics won the FDA approval of pralatrexate in 2009. In 2012, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals acquired Acrotech. Spectrum won approval of belinostat in 2014. Acrotech acquired Spectrum in 2019.
The FDA didn’t ask ODAC to take votes on any questions at the meeting. Instead, the FDA sought its expert feedback about how to address the prolonged delays with pralatrexate and belinostat research and, in general, how to promote more timely completion of confirmatory trials for drugs cleared by accelerated approval.
Pralatrexate and belinostat are both used to treat relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma, a rare and aggressive disease affecting about 10,000-15,000 people annually in the United States.
Through the accelerated approval process, the FDA seeks to speed medicines to people with fatal and serious conditions based on promising signs in clinical testing.
The initial pralatrexate and belinostat were based on phase 2, single-arm, monotherapy studies, with about 109 evaluable patients in the key pralatrexate study and 120 evaluable patients in the belinostat study. As is common, these phase 2 tests used measurements of cancer progression, known as the overall response rate.
The FDA then expects companies to show through more extensive testing that medicines cleared with accelerated approvals can deliver significant benefits, such as extending lives. When there are delays in confirmatory trials, patients can be exposed to medicines, often with significant side effects, that are unlikely to benefit them.
For example, the FDA granted an accelerated approval in 2011 for romidepsin for this use for peripheral T-cell lymphoma, the same condition for which pralatrexate and belinostat are used. But in 2021, Bristol-Myers Squibb withdrew the approval for that use of romidepsin when a confirmatory trial failed to meet the primary efficacy endpoint of progression free survival.
At the meeting, Richard Pazdur, MD, who leads oncology medicine at the FDA, urged Acrotech to shorten the time needed to determine whether its medicines deliver significant benefits to patients and thus merit full approval, or whether they too may fall short.
“We’re really in a situation where patients are caught in the middle here,” Dr. Pazdur said. “I feel very bad for that situation and very bad for the patients that they don’t have this information.”
‘Dangerous precedent’
The FDA in recent years has stepped up its efforts to get companies to complete their required studies on drugs cleared by accelerated approvals. The FDA has granted a total of 187 accelerated approvals for cancer drugs. Many of these cover new uses of established drugs and others serve to allow the introduction of new medicines.
For more than half of these cases, 96 of 187, the FDA already has learned that it made the right call in allowing early access to medicines. Companies have presented study results that confirmed the benefit of drugs and thus been able to convert accelerated approvals to traditional approvals.
But 27 of the 187 oncology accelerated approvals have been withdrawn. In these cases, subsequent research failed to establish the expected benefits of these cancer drugs.
And in 95 cases, the FDA and companies are still waiting for the results of studies to confirm the expected benefit of drugs granted accelerated approvals. The FDA classifies these as ongoing accelerated approvals. About 85% of these ongoing approvals were granted in the past 5 years, in contrast to 14 years for pralatrexate and 9 for belinostat.
“It sets a dangerous precedent for the other sponsors and drug companies to have such outliers from the same company,” said ODAC member Toni K. Choueiri, MD, of Harvard Medical School and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, both in Boston.
The current agreement between the FDA and Acrotech focuses on a phase 3 trial, SPI-BEL-301 as the confirmatory study. Acrotech’s plan is to start with dose optimization studies in part 1 of the trial, with part 2 meant to see if its medicines provide a significant benefit as measured by progression-free survival.
The plan is to compare treatments. One group of patients would get belinostat plus a common cancer regimen known as CHOP, another group would get pralatrexate plus the COP cancer regimen, which is CHOP without doxorubicin, and a third group would get CHOP.
Acrotech’s current time line is for part 1, which began in October, to finish by December 2025. Then the part 2 timeline would run from 2026 to 2030, with interim progression-free survival possible by 2028.
ODAC member Ashley Rosko, MD, a hematologist from Ohio State University, Columbus, asked Acrotech what steps it will take to try to speed recruitment for the study.
“We are going to implement many strategies,” including what’s called digital amplification, replied Ashish Anvekar, president of Acrotech. This will help identify patients and channel them toward participating clinical sites.
Alexander A. Vinks, PhD, PharmD, who served as a temporary member of ODAC for the Nov. 16 meeting, said many clinicians will not be excited about enrolling patients in this kind of large, traditionally designed study.
Dr. Vinks, who is professor emeritus at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center and University of Cincinnati, now works with consultant group NDA, a firm that advises companies on developing drugs.
Dr. Vinks advised Acrotech should try “to pin down what is most likely a smaller study that could be simpler, but still give robust, informative data.”
Fatigue and night sweats
Given the patient's presentation of generalized lymphadenopathy, B symptoms, fatigue (probably from anemia), hepatosplenomegaly, immunophenotyping results of flow cell cytometry, and central nervous system (CNS) involvement, blastoid mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is the most likely diagnosis. Although small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)/chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) most often occur in men 60-70 years old with similar clinical findings, an initial presentation with a stage IV involvement is rare; moreover, SLL/CLL and DLBCL are typically CD23 positive. Pleomorphic MCL displays larger and more pleomorphic cells with irregular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and pale cytoplasm, resembling DLBCL.
MCL is a rare type of mature B-cell lymphoma that was first described in 1992 and was recognized by World Health Organization in 2001. MCL represents 3%-10% of all non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases, with an incidence between 0.50 and 1.0 per 100,000 population. Men are more likely than women to present with MCL by a ratio of 3:1, with a median age at presentation of 67 years. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. MCL usually affects the lymph nodes, with the spleen and bone marrow being significant sites of the disease. Stage IV disease is present in 70% of patients; the gastrointestinal tract, lung, pleura, and CNS are also frequently affected.
Besides classic MCL, several variants have been described that exhibit specific morphologic features, including small cell variant mimicking SLL marginal zone-like MCL (resembling marginal zone lymphoma), in situ mantle cell neoplasia (associated with indolent course), and two aggressive variants, including blastoid and pleomorphic MCL. These blastoid and pleomorphic variants are defined by cytomorphologic features; the criteria are somewhat subjective, but both are characterized by highly aggressive features and a dismal clinical course. In clinical cohorts, the frequency of these subsets varies widely but probably represents ∼10% of all cases.
Diagnosing MCL requires a multipronged approach. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveal monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin, immunoglobulin M, or immunoglobulin D that are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy are used more for staging than diagnosis. Blood studies commonly reveal anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with 20%-40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000 cells/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and elevated lactate dehydrogenase when tumor burden is high. The term "blastoid mantle cell lymphoma" describes a morphologic subgroup of lymphomas with blastic features that morphologically resemble the lymphoblasts found in lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia (roundish nuclei, a narrow rim of cytoplasm, and finely dispersed chromatin).
MCL is associated with a poor prognosis; patients generally experience disease progression after chemotherapy, even with initial treatment response rates ranging from 50% to 70%. The 5-year survival rate is about 50% in the overall population, 75% in persons younger than 50 years, and 36% in those aged 75 years or older. A poorer prognosis is also associated with the presence of the blastoid variant, commonly associated with TP53 mutations. Median survival can vary by as much as 5 years, depending on the expression of cyclin D1 and other proliferation signature genes.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given the patient's presentation of generalized lymphadenopathy, B symptoms, fatigue (probably from anemia), hepatosplenomegaly, immunophenotyping results of flow cell cytometry, and central nervous system (CNS) involvement, blastoid mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is the most likely diagnosis. Although small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)/chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) most often occur in men 60-70 years old with similar clinical findings, an initial presentation with a stage IV involvement is rare; moreover, SLL/CLL and DLBCL are typically CD23 positive. Pleomorphic MCL displays larger and more pleomorphic cells with irregular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and pale cytoplasm, resembling DLBCL.
MCL is a rare type of mature B-cell lymphoma that was first described in 1992 and was recognized by World Health Organization in 2001. MCL represents 3%-10% of all non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases, with an incidence between 0.50 and 1.0 per 100,000 population. Men are more likely than women to present with MCL by a ratio of 3:1, with a median age at presentation of 67 years. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. MCL usually affects the lymph nodes, with the spleen and bone marrow being significant sites of the disease. Stage IV disease is present in 70% of patients; the gastrointestinal tract, lung, pleura, and CNS are also frequently affected.
Besides classic MCL, several variants have been described that exhibit specific morphologic features, including small cell variant mimicking SLL marginal zone-like MCL (resembling marginal zone lymphoma), in situ mantle cell neoplasia (associated with indolent course), and two aggressive variants, including blastoid and pleomorphic MCL. These blastoid and pleomorphic variants are defined by cytomorphologic features; the criteria are somewhat subjective, but both are characterized by highly aggressive features and a dismal clinical course. In clinical cohorts, the frequency of these subsets varies widely but probably represents ∼10% of all cases.
Diagnosing MCL requires a multipronged approach. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveal monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin, immunoglobulin M, or immunoglobulin D that are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy are used more for staging than diagnosis. Blood studies commonly reveal anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with 20%-40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000 cells/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and elevated lactate dehydrogenase when tumor burden is high. The term "blastoid mantle cell lymphoma" describes a morphologic subgroup of lymphomas with blastic features that morphologically resemble the lymphoblasts found in lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia (roundish nuclei, a narrow rim of cytoplasm, and finely dispersed chromatin).
MCL is associated with a poor prognosis; patients generally experience disease progression after chemotherapy, even with initial treatment response rates ranging from 50% to 70%. The 5-year survival rate is about 50% in the overall population, 75% in persons younger than 50 years, and 36% in those aged 75 years or older. A poorer prognosis is also associated with the presence of the blastoid variant, commonly associated with TP53 mutations. Median survival can vary by as much as 5 years, depending on the expression of cyclin D1 and other proliferation signature genes.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given the patient's presentation of generalized lymphadenopathy, B symptoms, fatigue (probably from anemia), hepatosplenomegaly, immunophenotyping results of flow cell cytometry, and central nervous system (CNS) involvement, blastoid mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is the most likely diagnosis. Although small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL)/chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) most often occur in men 60-70 years old with similar clinical findings, an initial presentation with a stage IV involvement is rare; moreover, SLL/CLL and DLBCL are typically CD23 positive. Pleomorphic MCL displays larger and more pleomorphic cells with irregular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and pale cytoplasm, resembling DLBCL.
MCL is a rare type of mature B-cell lymphoma that was first described in 1992 and was recognized by World Health Organization in 2001. MCL represents 3%-10% of all non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases, with an incidence between 0.50 and 1.0 per 100,000 population. Men are more likely than women to present with MCL by a ratio of 3:1, with a median age at presentation of 67 years. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. MCL usually affects the lymph nodes, with the spleen and bone marrow being significant sites of the disease. Stage IV disease is present in 70% of patients; the gastrointestinal tract, lung, pleura, and CNS are also frequently affected.
Besides classic MCL, several variants have been described that exhibit specific morphologic features, including small cell variant mimicking SLL marginal zone-like MCL (resembling marginal zone lymphoma), in situ mantle cell neoplasia (associated with indolent course), and two aggressive variants, including blastoid and pleomorphic MCL. These blastoid and pleomorphic variants are defined by cytomorphologic features; the criteria are somewhat subjective, but both are characterized by highly aggressive features and a dismal clinical course. In clinical cohorts, the frequency of these subsets varies widely but probably represents ∼10% of all cases.
Diagnosing MCL requires a multipronged approach. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveal monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin, immunoglobulin M, or immunoglobulin D that are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy are used more for staging than diagnosis. Blood studies commonly reveal anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with 20%-40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000 cells/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and elevated lactate dehydrogenase when tumor burden is high. The term "blastoid mantle cell lymphoma" describes a morphologic subgroup of lymphomas with blastic features that morphologically resemble the lymphoblasts found in lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia (roundish nuclei, a narrow rim of cytoplasm, and finely dispersed chromatin).
MCL is associated with a poor prognosis; patients generally experience disease progression after chemotherapy, even with initial treatment response rates ranging from 50% to 70%. The 5-year survival rate is about 50% in the overall population, 75% in persons younger than 50 years, and 36% in those aged 75 years or older. A poorer prognosis is also associated with the presence of the blastoid variant, commonly associated with TP53 mutations. Median survival can vary by as much as 5 years, depending on the expression of cyclin D1 and other proliferation signature genes.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston; Medical Director, Department of Oncology and Hematology, Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Peabody, Massachusetts.
Karl J. D'Silva, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 65-year-old man presents to the oncology clinic with a 6-week history of fatigue, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss of 15 lb. He reports occasional fevers and generalized discomfort in his abdomen and has recently been experiencing painful headaches that are not relieved with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. His medical history is otherwise unremarkable except for mild hypertension, for which he takes medication. His family history is unremarkable.
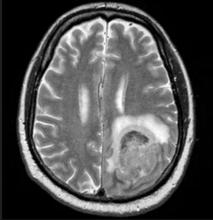
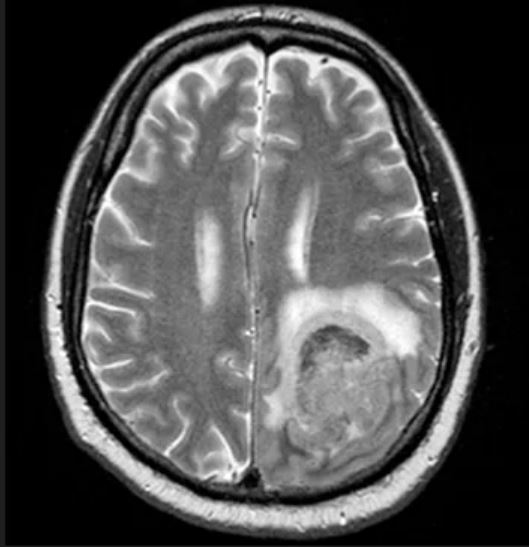
Physical examination reveals palpable lymph nodes in the neck, axilla, and inguinal regions; the spleen is palpable 3 cm below the left costal margin. A complete blood count shows anemia (hemoglobin level, 9.1g/dL) thrombocytopenia (platelet count, 90,000 cells/μL), and lymphocytosis (total leukocyte count, 5000 cells/μL); peripheral blood smear shows small, monomorphic lymphoid cells with oval-shaped nuclei and high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio. Flow cytometry of lymph node biopsy is CD5-positive and pan B-cell antigen positive (eg, CD19, CD20, and CD22) but lacks expression of CD10 and CD23. A T2-weighted MRI is ordered.
MCL Guidelines
CAR T-Cell Therapy: Promising Treatments in Development for DLBCL
There have been several recent developments in the treatment of B-cell lymphoma; however, one of the most significant advances has been the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. CAR T-cell therapy is a type of personalized immunotherapy that can help cure some people with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common form of aggressive NHL. CAR T-cell therapy has revolutionized the treatment of hematologic malignancies over the past 5 years, with impressive response rates and durable remissions for patients who previously had no viable options. This strategy is highly effective in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, as well as mantle cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and multiple myeloma, as evidenced by recent regulatory approvals.
In 2021, the FDA also approved lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), a new CAR T-cell therapy for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory (nonresponsive) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) have been treated with at least 2 prior lines of therapy. These products have design differences, including differences in the costimulatory domain, mechanism of gene/transgene delivery, ability for cryopreservation, and need for T-cell selection.
The CAR T-cell therapy axi-cel demonstrated superior results in the ZUMA-7 clinical trial, which compared CAR T-cell therapy directly to traditional chemotherapy with intended autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). About 55% of patients were still alive 4 years after receiving axi-cel, compared with 46% of those who initially received the standard treatment for relapsed disease. Based on these results, axi-cel is now the preferred treatment for people whose DLBCL has recurred with 12 months of front-line treatment or who are resistant to standard initial treatment.
Additionally, the BELINDA trial was a randomized phase 3 trial that compared CAR T-cell therapy with liso-cel with second-line chemotherapy with planned ASCT. Like ZUMA-7, this study also demonstrated an improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to standard treatment. As such, CAR T-cell therapy represents the new standard of care for second-line treatment in appropriate patients with refractory or early relapsing LBCL.
There have been several other recent studies on the use of CAR T-cell therapy for B-cell lymphoma. One study, published in Blood Advances (2023), found that receiving a greater number of therapies prior to CAR T-cell therapy is associated with poorer outcomes in patients with aggressive relapsed/refractory B-cell NHL. The study, which included 514 patients from 13 centers treated with CAR-T for aggressive B-cell NHL between 2015 and 2021, found that a greater number of lines of therapy before CAR-T apheresis and bridging therapy were predictive of inferior PFS and overall survival.
Another study compared 2 CD19-targeting CAR T-cell treatments, axi-cel and tisa-cel, with ASCT in the second line setting for LBCL. The study found that axi-cel was superior to ASCT, with longer median event-free survival and a higher response rate. However, tisa-cel was not found to be superior to ASCT. Further studies will be needed to definitively characterize the relative benefits of CAR-T cell therapies and standard second-line treatments for different subgroups of patients with LBCL.
An increasing number of effective targeted agents for DLBCL, including novel monoclonal antibodies (tafasitamab) and antibody-drug conjugates (polatuzumab vedotin and loncastuximab teserine), are being used in earlier lines of therapy. Additionally, 2 anti-CD20 bispecific antibodies (epcoritamab and glofitamab) have gained approval for relapsed/refractory DLBCL due to high response rates. Future studies will be needed to determine if treatment with these agents can produce durable remissions like that of CAR-T cell therapy.
There have been several recent developments in the treatment of B-cell lymphoma; however, one of the most significant advances has been the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. CAR T-cell therapy is a type of personalized immunotherapy that can help cure some people with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common form of aggressive NHL. CAR T-cell therapy has revolutionized the treatment of hematologic malignancies over the past 5 years, with impressive response rates and durable remissions for patients who previously had no viable options. This strategy is highly effective in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, as well as mantle cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and multiple myeloma, as evidenced by recent regulatory approvals.
In 2021, the FDA also approved lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), a new CAR T-cell therapy for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory (nonresponsive) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) have been treated with at least 2 prior lines of therapy. These products have design differences, including differences in the costimulatory domain, mechanism of gene/transgene delivery, ability for cryopreservation, and need for T-cell selection.
The CAR T-cell therapy axi-cel demonstrated superior results in the ZUMA-7 clinical trial, which compared CAR T-cell therapy directly to traditional chemotherapy with intended autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). About 55% of patients were still alive 4 years after receiving axi-cel, compared with 46% of those who initially received the standard treatment for relapsed disease. Based on these results, axi-cel is now the preferred treatment for people whose DLBCL has recurred with 12 months of front-line treatment or who are resistant to standard initial treatment.
Additionally, the BELINDA trial was a randomized phase 3 trial that compared CAR T-cell therapy with liso-cel with second-line chemotherapy with planned ASCT. Like ZUMA-7, this study also demonstrated an improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to standard treatment. As such, CAR T-cell therapy represents the new standard of care for second-line treatment in appropriate patients with refractory or early relapsing LBCL.
There have been several other recent studies on the use of CAR T-cell therapy for B-cell lymphoma. One study, published in Blood Advances (2023), found that receiving a greater number of therapies prior to CAR T-cell therapy is associated with poorer outcomes in patients with aggressive relapsed/refractory B-cell NHL. The study, which included 514 patients from 13 centers treated with CAR-T for aggressive B-cell NHL between 2015 and 2021, found that a greater number of lines of therapy before CAR-T apheresis and bridging therapy were predictive of inferior PFS and overall survival.
Another study compared 2 CD19-targeting CAR T-cell treatments, axi-cel and tisa-cel, with ASCT in the second line setting for LBCL. The study found that axi-cel was superior to ASCT, with longer median event-free survival and a higher response rate. However, tisa-cel was not found to be superior to ASCT. Further studies will be needed to definitively characterize the relative benefits of CAR-T cell therapies and standard second-line treatments for different subgroups of patients with LBCL.
An increasing number of effective targeted agents for DLBCL, including novel monoclonal antibodies (tafasitamab) and antibody-drug conjugates (polatuzumab vedotin and loncastuximab teserine), are being used in earlier lines of therapy. Additionally, 2 anti-CD20 bispecific antibodies (epcoritamab and glofitamab) have gained approval for relapsed/refractory DLBCL due to high response rates. Future studies will be needed to determine if treatment with these agents can produce durable remissions like that of CAR-T cell therapy.
There have been several recent developments in the treatment of B-cell lymphoma; however, one of the most significant advances has been the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. CAR T-cell therapy is a type of personalized immunotherapy that can help cure some people with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common form of aggressive NHL. CAR T-cell therapy has revolutionized the treatment of hematologic malignancies over the past 5 years, with impressive response rates and durable remissions for patients who previously had no viable options. This strategy is highly effective in patients with relapsed/refractory DLBCL, as well as mantle cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and multiple myeloma, as evidenced by recent regulatory approvals.
In 2021, the FDA also approved lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), a new CAR T-cell therapy for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory (nonresponsive) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) have been treated with at least 2 prior lines of therapy. These products have design differences, including differences in the costimulatory domain, mechanism of gene/transgene delivery, ability for cryopreservation, and need for T-cell selection.
The CAR T-cell therapy axi-cel demonstrated superior results in the ZUMA-7 clinical trial, which compared CAR T-cell therapy directly to traditional chemotherapy with intended autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). About 55% of patients were still alive 4 years after receiving axi-cel, compared with 46% of those who initially received the standard treatment for relapsed disease. Based on these results, axi-cel is now the preferred treatment for people whose DLBCL has recurred with 12 months of front-line treatment or who are resistant to standard initial treatment.
Additionally, the BELINDA trial was a randomized phase 3 trial that compared CAR T-cell therapy with liso-cel with second-line chemotherapy with planned ASCT. Like ZUMA-7, this study also demonstrated an improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to standard treatment. As such, CAR T-cell therapy represents the new standard of care for second-line treatment in appropriate patients with refractory or early relapsing LBCL.
There have been several other recent studies on the use of CAR T-cell therapy for B-cell lymphoma. One study, published in Blood Advances (2023), found that receiving a greater number of therapies prior to CAR T-cell therapy is associated with poorer outcomes in patients with aggressive relapsed/refractory B-cell NHL. The study, which included 514 patients from 13 centers treated with CAR-T for aggressive B-cell NHL between 2015 and 2021, found that a greater number of lines of therapy before CAR-T apheresis and bridging therapy were predictive of inferior PFS and overall survival.
Another study compared 2 CD19-targeting CAR T-cell treatments, axi-cel and tisa-cel, with ASCT in the second line setting for LBCL. The study found that axi-cel was superior to ASCT, with longer median event-free survival and a higher response rate. However, tisa-cel was not found to be superior to ASCT. Further studies will be needed to definitively characterize the relative benefits of CAR-T cell therapies and standard second-line treatments for different subgroups of patients with LBCL.
An increasing number of effective targeted agents for DLBCL, including novel monoclonal antibodies (tafasitamab) and antibody-drug conjugates (polatuzumab vedotin and loncastuximab teserine), are being used in earlier lines of therapy. Additionally, 2 anti-CD20 bispecific antibodies (epcoritamab and glofitamab) have gained approval for relapsed/refractory DLBCL due to high response rates. Future studies will be needed to determine if treatment with these agents can produce durable remissions like that of CAR-T cell therapy.
What’s New in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma?
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most diagnosed non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), accounting for up to one-third of cases. For many decades, R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) has been the standard first-line treatment approach for eligible patients in the first-line setting, resulting in long-term remissions in about two-thirds of patients. However, as our understanding of the biologic heterogeneity of this disease has advanced with the ability to perform more sophisticated molecular testing at diagnosis, researchers have been able to identify high-risk patient subtypes with suboptimal outcomes. While survival outcomes among low-risk patient subgroups are favorable with first-line immunochemotherapy, the majority of high-risk patients will experience relapse and often succumb to their disease.
Given the poor outcomes among patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) DLBCL, there has been a massive research effort over the last decade to improve survival in this setting. Many experts agree that the approval of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was the first major victory in this uphill battle. First approved in October of 2017, axicabtagene ciloleucel was the first of the 3 currently available commercial CAR T-cell therapy constructs to be approved in the third-line setting for DLBCL. Compared to historical controls, CAR T-cell therapy is associated with significant improvement in patient survival with complete response (CR) rates of 40%-50% compared to <20% with standard salvage immunochemotherapy.
Following approval in the third-line setting, these agents were quickly expedited to second-line therapy with pivotal trials demonstrating superiority with CAR T-cell therapy in the second line compared to salvage immunochemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant. In 2022 the ZUMA-7 study reported a 24-month event-free survival (EFS) of 41% with axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to 16% with standard of care, and the TRANSFORM study documented a median EFS not yet reached with lisocabtagene ciloleucel compared to 2.3 months with standard of care. Despite these drastic improvements in patient outcomes, more than half of patients will still fail CAR T-cell therapy and require further systemic therapy.
Thankfully, this year has seen even more advancement in the treatment landscape of R/R DLBCL with two new commercially approved agents in yet another novel therapeutic category: bispecific antibodies. The following is a description of the newest data leading to the latest approvals by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are an off-the-shelf product that activate endogenous immune cells by cotargeting both tumor antigens as well as host T cells or natural killer cells. Several different experimental agents with varying constructs are under active observation in a wide variety of both hematologic and solid malignancies. Specifically within the realm of B-cell NHL, however, this class of agents is extremely promising and possibly represents the next significant milestone in the treatment of lymphoma.
The toxicity profile of these agents has been reliably predictable in most early phase clinical studies and is related predominantly to T-cell overactivation. The most commonly reported adverse events consist of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) as well as neutropenia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia. While neurologic toxicity has been reported, the incidence is low, and the mechanism is thought to be different than that reported with CAR T-cell therapy given that BsAbs are not likely to cross the blood–brain barrier.
Epcoritamab is a subcutaneously administered bispecific antibody that targets CD3 and CD20 in a 1:1 ratio and activates T cells to destroy CD20-expressing malignant cells. The recent EPCORE NHL-1 clinical trial investigated epcoritamab monotherapy in R/R mature B-cell lymphomas. This agent is administered with a step-up dosing strategy seen consistently across the BsAb drug class. Patients receive a first priming dose of 0.16 mg on cycle 1 day 1, followed by an intermediate dose of 0.8 mg on cycle 1 day 8, followed by the first full dose of 48 mg on cycle 1 day 15. Subsequent doses are administered once weekly for cycles 1-3 followed by every 2 weeks for cycles 4-9, and every 4 weeks starting with cycle 10.
The study enrolled 157 patients globally with median age of 64 and 3 median prior lines of antilymphoma therapy. Nearly 40% of patients had received at least 4 prior lines of therapy, and 83% of patients were refractory to last systemic therapy. Thirty-nine percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy; 75% of these patients developed progressive disease within 6 months of CAR T-cell therapy.
Among patients treated in the study, the results were as follows:
CR rate 39% with an overall response rate (ORR) of 63%
Duration of response 12 months; duration of objective response not reached in patients with CR
Duration of CR 12 months
Median PFS 4.4 months; median OS not reached
Time to CR of 2.7 months
Toxicity profile was notable for the following:
Any grade CRS in 50%, grade ≥3 in 2.5%
Most CRS occurs with first full dose on cycle 1 day 15 with median time to onset of 20 hours and median time to resolution of 48 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 22%, grade ≥3 in 15%, febrile neutropenia in 2.5%
Any grade anemia in 18%, grade ≥3 in 10%
Injection site reaction, any grade, in 20%
Any grade neurotoxicity in 6%, grade ≥3 in 1 patient (0.6%)
Epcoritamab was granted accelerated approval on May 19, 2023, for use in patients with R/R DLBCL who have received at least 2 prior lines of systemic therapy.
Glofitamab is the more recently approved BsAb for DLBCL. This agent is distinguished by its 2:1 binding configuration that confers bivalency for the CD20 binding site. Glofitamab is delivered intravenously and requires pretreatment with obinutuzumab 1000 mg 7 days before the first dose. With a similar step-up dosing strategy, patients receive a priming dose of 2.5mg on cycle 1 day 8, an intermediate dose of 10mg on cycle 1 day 15, and a first full dose of 30mg on cycle 2 day 1. Subsequent treatments are administered every 21 days for up to 12 cycles.
The open-label phase 1-2 clinical trial of glofitamab monotherapy enrolled 155 patients with a median age of 66 and 3 median prior lines of therapy. Thirty-three percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy, and 86% were refractory to last line of therapy with 30% refractory to CAR T-cell therapy.
Results were as follows:
CR rate of 39%, ORR 52%
Median duration of CR not reached, median duration of objective response 18.4 months
Median PFS 4.9 months, median OS not reached
Toxicity profile demonstrated the following:
Any grade CRS 66%, grade ≥ 2 in 18%
Median time to onset 13.5 hours from cycle 1 day 8, median duration 30.5 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 38%, grade ≥ 3 in 27%
Grade ≥ 2 neurologic event in 15%
Glofitamab received accelerated approval from the FDA on June 15, 2023, with an identical indication to epcoritamab.
The introduction of BsAbs in DLBCL has highlighted some important issues. Will BsAbs supplant CAR T-cell therapy in DLBCL? Experts can be found on both sides of this debate. BsAbs circumvent the logistics surrounding the production of CAR T-cell therapy products and can, for the large part, be administered in the outpatient setting. However, CAR T-cell therapy has significantly longer follow-up times, which speaks to the curative potential of these agents even in the third-line setting. BsAbs, some may argue, seem to carry a more favorable toxicity profile with the CRS mitigation strategies. However, we still have much to learn about the downstream side effects with prolonged T-cell activation and the potential for T-cell exhaustion.
Finally, with the continued development of new agents in this arena, the art of sequencing therapies will become ever more important. What is the efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy after BsAb exposure? Can BsAbs be used as bridging therapy to a curative option with CAR T-cell therapy? With longer-term follow-up in several years, will we see late relapses after CR with BsAbs? Ongoing clinical trials investigating combination strategies and CAR T-cell therapy consolidation with BsAbs will hopefully eventually clarify some of these questions.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most diagnosed non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), accounting for up to one-third of cases. For many decades, R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) has been the standard first-line treatment approach for eligible patients in the first-line setting, resulting in long-term remissions in about two-thirds of patients. However, as our understanding of the biologic heterogeneity of this disease has advanced with the ability to perform more sophisticated molecular testing at diagnosis, researchers have been able to identify high-risk patient subtypes with suboptimal outcomes. While survival outcomes among low-risk patient subgroups are favorable with first-line immunochemotherapy, the majority of high-risk patients will experience relapse and often succumb to their disease.
Given the poor outcomes among patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) DLBCL, there has been a massive research effort over the last decade to improve survival in this setting. Many experts agree that the approval of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was the first major victory in this uphill battle. First approved in October of 2017, axicabtagene ciloleucel was the first of the 3 currently available commercial CAR T-cell therapy constructs to be approved in the third-line setting for DLBCL. Compared to historical controls, CAR T-cell therapy is associated with significant improvement in patient survival with complete response (CR) rates of 40%-50% compared to <20% with standard salvage immunochemotherapy.
Following approval in the third-line setting, these agents were quickly expedited to second-line therapy with pivotal trials demonstrating superiority with CAR T-cell therapy in the second line compared to salvage immunochemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant. In 2022 the ZUMA-7 study reported a 24-month event-free survival (EFS) of 41% with axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to 16% with standard of care, and the TRANSFORM study documented a median EFS not yet reached with lisocabtagene ciloleucel compared to 2.3 months with standard of care. Despite these drastic improvements in patient outcomes, more than half of patients will still fail CAR T-cell therapy and require further systemic therapy.
Thankfully, this year has seen even more advancement in the treatment landscape of R/R DLBCL with two new commercially approved agents in yet another novel therapeutic category: bispecific antibodies. The following is a description of the newest data leading to the latest approvals by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are an off-the-shelf product that activate endogenous immune cells by cotargeting both tumor antigens as well as host T cells or natural killer cells. Several different experimental agents with varying constructs are under active observation in a wide variety of both hematologic and solid malignancies. Specifically within the realm of B-cell NHL, however, this class of agents is extremely promising and possibly represents the next significant milestone in the treatment of lymphoma.
The toxicity profile of these agents has been reliably predictable in most early phase clinical studies and is related predominantly to T-cell overactivation. The most commonly reported adverse events consist of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) as well as neutropenia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia. While neurologic toxicity has been reported, the incidence is low, and the mechanism is thought to be different than that reported with CAR T-cell therapy given that BsAbs are not likely to cross the blood–brain barrier.
Epcoritamab is a subcutaneously administered bispecific antibody that targets CD3 and CD20 in a 1:1 ratio and activates T cells to destroy CD20-expressing malignant cells. The recent EPCORE NHL-1 clinical trial investigated epcoritamab monotherapy in R/R mature B-cell lymphomas. This agent is administered with a step-up dosing strategy seen consistently across the BsAb drug class. Patients receive a first priming dose of 0.16 mg on cycle 1 day 1, followed by an intermediate dose of 0.8 mg on cycle 1 day 8, followed by the first full dose of 48 mg on cycle 1 day 15. Subsequent doses are administered once weekly for cycles 1-3 followed by every 2 weeks for cycles 4-9, and every 4 weeks starting with cycle 10.
The study enrolled 157 patients globally with median age of 64 and 3 median prior lines of antilymphoma therapy. Nearly 40% of patients had received at least 4 prior lines of therapy, and 83% of patients were refractory to last systemic therapy. Thirty-nine percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy; 75% of these patients developed progressive disease within 6 months of CAR T-cell therapy.
Among patients treated in the study, the results were as follows:
CR rate 39% with an overall response rate (ORR) of 63%
Duration of response 12 months; duration of objective response not reached in patients with CR
Duration of CR 12 months
Median PFS 4.4 months; median OS not reached
Time to CR of 2.7 months
Toxicity profile was notable for the following:
Any grade CRS in 50%, grade ≥3 in 2.5%
Most CRS occurs with first full dose on cycle 1 day 15 with median time to onset of 20 hours and median time to resolution of 48 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 22%, grade ≥3 in 15%, febrile neutropenia in 2.5%
Any grade anemia in 18%, grade ≥3 in 10%
Injection site reaction, any grade, in 20%
Any grade neurotoxicity in 6%, grade ≥3 in 1 patient (0.6%)
Epcoritamab was granted accelerated approval on May 19, 2023, for use in patients with R/R DLBCL who have received at least 2 prior lines of systemic therapy.
Glofitamab is the more recently approved BsAb for DLBCL. This agent is distinguished by its 2:1 binding configuration that confers bivalency for the CD20 binding site. Glofitamab is delivered intravenously and requires pretreatment with obinutuzumab 1000 mg 7 days before the first dose. With a similar step-up dosing strategy, patients receive a priming dose of 2.5mg on cycle 1 day 8, an intermediate dose of 10mg on cycle 1 day 15, and a first full dose of 30mg on cycle 2 day 1. Subsequent treatments are administered every 21 days for up to 12 cycles.
The open-label phase 1-2 clinical trial of glofitamab monotherapy enrolled 155 patients with a median age of 66 and 3 median prior lines of therapy. Thirty-three percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy, and 86% were refractory to last line of therapy with 30% refractory to CAR T-cell therapy.
Results were as follows:
CR rate of 39%, ORR 52%
Median duration of CR not reached, median duration of objective response 18.4 months
Median PFS 4.9 months, median OS not reached
Toxicity profile demonstrated the following:
Any grade CRS 66%, grade ≥ 2 in 18%
Median time to onset 13.5 hours from cycle 1 day 8, median duration 30.5 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 38%, grade ≥ 3 in 27%
Grade ≥ 2 neurologic event in 15%
Glofitamab received accelerated approval from the FDA on June 15, 2023, with an identical indication to epcoritamab.
The introduction of BsAbs in DLBCL has highlighted some important issues. Will BsAbs supplant CAR T-cell therapy in DLBCL? Experts can be found on both sides of this debate. BsAbs circumvent the logistics surrounding the production of CAR T-cell therapy products and can, for the large part, be administered in the outpatient setting. However, CAR T-cell therapy has significantly longer follow-up times, which speaks to the curative potential of these agents even in the third-line setting. BsAbs, some may argue, seem to carry a more favorable toxicity profile with the CRS mitigation strategies. However, we still have much to learn about the downstream side effects with prolonged T-cell activation and the potential for T-cell exhaustion.
Finally, with the continued development of new agents in this arena, the art of sequencing therapies will become ever more important. What is the efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy after BsAb exposure? Can BsAbs be used as bridging therapy to a curative option with CAR T-cell therapy? With longer-term follow-up in several years, will we see late relapses after CR with BsAbs? Ongoing clinical trials investigating combination strategies and CAR T-cell therapy consolidation with BsAbs will hopefully eventually clarify some of these questions.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most diagnosed non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), accounting for up to one-third of cases. For many decades, R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) has been the standard first-line treatment approach for eligible patients in the first-line setting, resulting in long-term remissions in about two-thirds of patients. However, as our understanding of the biologic heterogeneity of this disease has advanced with the ability to perform more sophisticated molecular testing at diagnosis, researchers have been able to identify high-risk patient subtypes with suboptimal outcomes. While survival outcomes among low-risk patient subgroups are favorable with first-line immunochemotherapy, the majority of high-risk patients will experience relapse and often succumb to their disease.
Given the poor outcomes among patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) DLBCL, there has been a massive research effort over the last decade to improve survival in this setting. Many experts agree that the approval of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy was the first major victory in this uphill battle. First approved in October of 2017, axicabtagene ciloleucel was the first of the 3 currently available commercial CAR T-cell therapy constructs to be approved in the third-line setting for DLBCL. Compared to historical controls, CAR T-cell therapy is associated with significant improvement in patient survival with complete response (CR) rates of 40%-50% compared to <20% with standard salvage immunochemotherapy.
Following approval in the third-line setting, these agents were quickly expedited to second-line therapy with pivotal trials demonstrating superiority with CAR T-cell therapy in the second line compared to salvage immunochemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant. In 2022 the ZUMA-7 study reported a 24-month event-free survival (EFS) of 41% with axicabtagene ciloleucel compared to 16% with standard of care, and the TRANSFORM study documented a median EFS not yet reached with lisocabtagene ciloleucel compared to 2.3 months with standard of care. Despite these drastic improvements in patient outcomes, more than half of patients will still fail CAR T-cell therapy and require further systemic therapy.
Thankfully, this year has seen even more advancement in the treatment landscape of R/R DLBCL with two new commercially approved agents in yet another novel therapeutic category: bispecific antibodies. The following is a description of the newest data leading to the latest approvals by the US Food and Drug Administration.
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are an off-the-shelf product that activate endogenous immune cells by cotargeting both tumor antigens as well as host T cells or natural killer cells. Several different experimental agents with varying constructs are under active observation in a wide variety of both hematologic and solid malignancies. Specifically within the realm of B-cell NHL, however, this class of agents is extremely promising and possibly represents the next significant milestone in the treatment of lymphoma.
The toxicity profile of these agents has been reliably predictable in most early phase clinical studies and is related predominantly to T-cell overactivation. The most commonly reported adverse events consist of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) as well as neutropenia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia. While neurologic toxicity has been reported, the incidence is low, and the mechanism is thought to be different than that reported with CAR T-cell therapy given that BsAbs are not likely to cross the blood–brain barrier.
Epcoritamab is a subcutaneously administered bispecific antibody that targets CD3 and CD20 in a 1:1 ratio and activates T cells to destroy CD20-expressing malignant cells. The recent EPCORE NHL-1 clinical trial investigated epcoritamab monotherapy in R/R mature B-cell lymphomas. This agent is administered with a step-up dosing strategy seen consistently across the BsAb drug class. Patients receive a first priming dose of 0.16 mg on cycle 1 day 1, followed by an intermediate dose of 0.8 mg on cycle 1 day 8, followed by the first full dose of 48 mg on cycle 1 day 15. Subsequent doses are administered once weekly for cycles 1-3 followed by every 2 weeks for cycles 4-9, and every 4 weeks starting with cycle 10.
The study enrolled 157 patients globally with median age of 64 and 3 median prior lines of antilymphoma therapy. Nearly 40% of patients had received at least 4 prior lines of therapy, and 83% of patients were refractory to last systemic therapy. Thirty-nine percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy; 75% of these patients developed progressive disease within 6 months of CAR T-cell therapy.
Among patients treated in the study, the results were as follows:
CR rate 39% with an overall response rate (ORR) of 63%
Duration of response 12 months; duration of objective response not reached in patients with CR
Duration of CR 12 months
Median PFS 4.4 months; median OS not reached
Time to CR of 2.7 months
Toxicity profile was notable for the following:
Any grade CRS in 50%, grade ≥3 in 2.5%
Most CRS occurs with first full dose on cycle 1 day 15 with median time to onset of 20 hours and median time to resolution of 48 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 22%, grade ≥3 in 15%, febrile neutropenia in 2.5%
Any grade anemia in 18%, grade ≥3 in 10%
Injection site reaction, any grade, in 20%
Any grade neurotoxicity in 6%, grade ≥3 in 1 patient (0.6%)
Epcoritamab was granted accelerated approval on May 19, 2023, for use in patients with R/R DLBCL who have received at least 2 prior lines of systemic therapy.
Glofitamab is the more recently approved BsAb for DLBCL. This agent is distinguished by its 2:1 binding configuration that confers bivalency for the CD20 binding site. Glofitamab is delivered intravenously and requires pretreatment with obinutuzumab 1000 mg 7 days before the first dose. With a similar step-up dosing strategy, patients receive a priming dose of 2.5mg on cycle 1 day 8, an intermediate dose of 10mg on cycle 1 day 15, and a first full dose of 30mg on cycle 2 day 1. Subsequent treatments are administered every 21 days for up to 12 cycles.
The open-label phase 1-2 clinical trial of glofitamab monotherapy enrolled 155 patients with a median age of 66 and 3 median prior lines of therapy. Thirty-three percent of patients had received prior CAR T-cell therapy, and 86% were refractory to last line of therapy with 30% refractory to CAR T-cell therapy.
Results were as follows:
CR rate of 39%, ORR 52%
Median duration of CR not reached, median duration of objective response 18.4 months
Median PFS 4.9 months, median OS not reached
Toxicity profile demonstrated the following:
Any grade CRS 66%, grade ≥ 2 in 18%
Median time to onset 13.5 hours from cycle 1 day 8, median duration 30.5 hours
Any grade neutropenia in 38%, grade ≥ 3 in 27%
Grade ≥ 2 neurologic event in 15%
Glofitamab received accelerated approval from the FDA on June 15, 2023, with an identical indication to epcoritamab.
The introduction of BsAbs in DLBCL has highlighted some important issues. Will BsAbs supplant CAR T-cell therapy in DLBCL? Experts can be found on both sides of this debate. BsAbs circumvent the logistics surrounding the production of CAR T-cell therapy products and can, for the large part, be administered in the outpatient setting. However, CAR T-cell therapy has significantly longer follow-up times, which speaks to the curative potential of these agents even in the third-line setting. BsAbs, some may argue, seem to carry a more favorable toxicity profile with the CRS mitigation strategies. However, we still have much to learn about the downstream side effects with prolonged T-cell activation and the potential for T-cell exhaustion.
Finally, with the continued development of new agents in this arena, the art of sequencing therapies will become ever more important. What is the efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy after BsAb exposure? Can BsAbs be used as bridging therapy to a curative option with CAR T-cell therapy? With longer-term follow-up in several years, will we see late relapses after CR with BsAbs? Ongoing clinical trials investigating combination strategies and CAR T-cell therapy consolidation with BsAbs will hopefully eventually clarify some of these questions.
Lymphoma specialist to lead MD Anderson’s cancer medicine division
“My research uncovered a series of physicians who served as ‘clinical champions’ and dramatically sped the process of drug development,” Dr. Flowers recalled in an interview. “This early career research inspired me to become the type of clinical champion that I uncovered.”
Over his career, hematologist-oncologist Dr. Flowers has developed lifesaving therapies for lymphoma, which has transformed into a highly treatable and even curable disease. He’s listed as a coauthor of hundreds of peer-reviewed cancer studies, reports, and medical society guidelines. And he’s revealed stark disparities in blood cancer care: His research shows that non-White patients suffer from worse outcomes, regardless of factors like income and insurance coverage.
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, recently named physician-scientist Dr. Flowers as division head of cancer medicine, a position he’s held on an interim basis. As of Sept. 1, he will permanently oversee 300 faculty and more than 2,000 staff members.
A running start in Seattle
For Dr. Flowers, track and field is a sport that runs in the family. His grandfather was a top runner in both high school and college, and both Dr. Flowers and his brother ran competitively in Seattle, where they grew up. But Dr. Flowers chose a career in oncology, earning a medical degree at Stanford and master’s degrees at both Stanford and the University of Washington, Seattle.
The late Kenneth Melmon, MD, a groundbreaking pharmacologist, was a major influence. “He was one of the first people that I met when I began as an undergraduate at Stanford. We grew to be long-standing friends, and he demonstrated what outstanding mentorship looks like. In our research collaboration, we investigated the work of Dr. Gertrude Elion and Dr. George Hitchings involving the translation of pharmacological data from cellular and animal models to clinically useful drugs including 6-mercaptopurine, allopurinol, azathioprine, acyclovir, and zidovudine.”
The late Oliver Press, MD, a blood cancer specialist, inspired Dr. Flower’s interest in lymphoma. “I began work with him during an internship at the University of Washington. Ollie was a great inspiration and a key leader in the development of innovative therapies for lymphoma. He embodied the role of a clinical champion translating work in radioimmunotherapy to new therapeutics for patients with lymphomas. Working with him ultimately led me to pursue a career in hematology and oncology with a focus on the care for patients with lymphomas.”
Career blooms as lymphoma care advances
Dr. Flowers went on to Emory University, Atlanta, where he served as scientific director of the Research Informatics Shared Resource and a faculty member in the department of biomedical informatics. “I applied my training in informatics and my clinical expertise to support active grants from the Burroughs Wellcome Fund for Innovation in Regulatory Science and from the National Cancer Institute to develop informatics tools for pathology image analysis and prognostic modeling.”
For 13 years, he also served the Winship Cancer Institute as director of the Emory Healthcare lymphoma program (where his patients included Kansas City Chiefs football star Eric Berry), and for 4 years as scientific director of research informatics. Meanwhile, Dr. Flowers helped develop national practice guidelines for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the American Cancer Society, and the American College of Radiology. He also chaired the ASCO guideline on management of febrile neutropenia.
In 2019, MD Anderson hired Dr. Flowers as chair of the department of lymphoma/myeloma. A year later, he was appointed division head ad interim for cancer medicine.
“Chris is a unique leader who expertly combines mentorship, sponsorship, and bidirectional open, honest communication,” said Sairah Ahmed, MD, associate professor of lymphoma at MD Anderson. “He doesn’t just empower his team to reach their goals. He also inspires those around him to turn vision into reality.”
As Dr. Flowers noted, many patients with lymphoma are now able to recover and live normal lives. He himself played a direct role himself in boosting lifespans.
“I have been fortunate to play a role in the development of several treatments that have led to advances in first-line therapy for patients with aggressive lymphomas. I partnered with others at MD Anderson, including Dr. Sattva Neelapu and Dr. Jason Westin, who have developed novel therapies like chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for patients with relapse lymphomas,” he said. “Leaders in the field at MD Anderson like Dr. Michael Wang have developed new oral treatments for patients with rare lymphoma subtypes like mantle cell lymphoma. Other colleagues such as Dr. Nathan Fowler and Dr. Loretta Nastoupil have focused on the care for patients with indolent lymphomas and developed less-toxic therapies that are now in common use.”
Exposing the disparities in blood cancer care
Dr. Flowers, who’s African American, has also been a leader in health disparity research. In 2016, for example, he was coauthor of a study into non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that revealed that Blacks in the United States have dramatically lower survival rates than Whites. The 10-year survival rate for Black women with chronic lymphocytic leukemia was just 47%, for example, compared with 66% for White females. “Although incidence rates of lymphoid neoplasms are generally higher among Whites, Black men tend to have poorer survival,” Dr. Flowers and colleagues wrote.
In a 2021 report for the ASCO Educational Book, Dr. Flowers and hematologist-oncologist Demetria Smith-Graziani, MD, now with Emory University, explored disparities across blood cancers and barriers to minority enrollment in clinical trials. “Some approaches that clinicians can apply to address these disparities include increasing systems-level awareness, improving access to care, and reducing biases in clinical setting,” the authors wrote.
Luis Malpica Castillo, MD, assistant professor of lymphoma at MD Anderson Cancer Center, lauded the work of Dr. Flowers in expanding opportunities for minority patients with the disease.
“During the past years, Dr. Flowers’ work has not only had a positive impact on the Texan community, but minority populations living with cancer in the United States and abroad,” he said. “Currently, we are implementing cancer care networks aimed to increase diversity in clinical trials by enrolling a larger number of Hispanic and African American patients, who otherwise may not have benefited from novel therapies. The ultimate goal is to provide high-quality care to all patients living with cancer.”
In addition to his research work, Dr. Flowers is an advocate for diversity within the hematology community. He’s a founding member and former chair of the American Society of Hematology’s Committee on Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (formerly the Committee on Promoting Diversity), and he helped develop the society’s Minority Recruitment Initiative.
What’s next for Dr. Flowers? For one, he plans to continue working as a mentor; he received the ASH Mentor Award in honor of his service in 2022. “I am strongly committed to increasing the number of tenure-track investigators trained in clinical and translational cancer research and to promote their career development.”
And he looks forward to helping develop MD Anderson’s recently announced $2.5 billion hospital in Austin. “This will extend the exceptional care that we provide as the No. 1 cancer center in the United States,” he said. “It will also create new opportunities for research and collaboration with experts at UT Austin.”
When he’s not in clinic, Dr. Flowers embraces his lifelong love of speeding through life on his own two feet. He’s even inspired his children to share his passion. “I run most days of the week,” he said. “Running provides a great opportunity to think and process new research ideas, work through leadership challenges, and sometimes just to relax and let go of the day.”
“My research uncovered a series of physicians who served as ‘clinical champions’ and dramatically sped the process of drug development,” Dr. Flowers recalled in an interview. “This early career research inspired me to become the type of clinical champion that I uncovered.”
Over his career, hematologist-oncologist Dr. Flowers has developed lifesaving therapies for lymphoma, which has transformed into a highly treatable and even curable disease. He’s listed as a coauthor of hundreds of peer-reviewed cancer studies, reports, and medical society guidelines. And he’s revealed stark disparities in blood cancer care: His research shows that non-White patients suffer from worse outcomes, regardless of factors like income and insurance coverage.
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, recently named physician-scientist Dr. Flowers as division head of cancer medicine, a position he’s held on an interim basis. As of Sept. 1, he will permanently oversee 300 faculty and more than 2,000 staff members.
A running start in Seattle
For Dr. Flowers, track and field is a sport that runs in the family. His grandfather was a top runner in both high school and college, and both Dr. Flowers and his brother ran competitively in Seattle, where they grew up. But Dr. Flowers chose a career in oncology, earning a medical degree at Stanford and master’s degrees at both Stanford and the University of Washington, Seattle.
The late Kenneth Melmon, MD, a groundbreaking pharmacologist, was a major influence. “He was one of the first people that I met when I began as an undergraduate at Stanford. We grew to be long-standing friends, and he demonstrated what outstanding mentorship looks like. In our research collaboration, we investigated the work of Dr. Gertrude Elion and Dr. George Hitchings involving the translation of pharmacological data from cellular and animal models to clinically useful drugs including 6-mercaptopurine, allopurinol, azathioprine, acyclovir, and zidovudine.”
The late Oliver Press, MD, a blood cancer specialist, inspired Dr. Flower’s interest in lymphoma. “I began work with him during an internship at the University of Washington. Ollie was a great inspiration and a key leader in the development of innovative therapies for lymphoma. He embodied the role of a clinical champion translating work in radioimmunotherapy to new therapeutics for patients with lymphomas. Working with him ultimately led me to pursue a career in hematology and oncology with a focus on the care for patients with lymphomas.”
Career blooms as lymphoma care advances
Dr. Flowers went on to Emory University, Atlanta, where he served as scientific director of the Research Informatics Shared Resource and a faculty member in the department of biomedical informatics. “I applied my training in informatics and my clinical expertise to support active grants from the Burroughs Wellcome Fund for Innovation in Regulatory Science and from the National Cancer Institute to develop informatics tools for pathology image analysis and prognostic modeling.”
For 13 years, he also served the Winship Cancer Institute as director of the Emory Healthcare lymphoma program (where his patients included Kansas City Chiefs football star Eric Berry), and for 4 years as scientific director of research informatics. Meanwhile, Dr. Flowers helped develop national practice guidelines for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the American Cancer Society, and the American College of Radiology. He also chaired the ASCO guideline on management of febrile neutropenia.
In 2019, MD Anderson hired Dr. Flowers as chair of the department of lymphoma/myeloma. A year later, he was appointed division head ad interim for cancer medicine.
“Chris is a unique leader who expertly combines mentorship, sponsorship, and bidirectional open, honest communication,” said Sairah Ahmed, MD, associate professor of lymphoma at MD Anderson. “He doesn’t just empower his team to reach their goals. He also inspires those around him to turn vision into reality.”
As Dr. Flowers noted, many patients with lymphoma are now able to recover and live normal lives. He himself played a direct role himself in boosting lifespans.
“I have been fortunate to play a role in the development of several treatments that have led to advances in first-line therapy for patients with aggressive lymphomas. I partnered with others at MD Anderson, including Dr. Sattva Neelapu and Dr. Jason Westin, who have developed novel therapies like chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for patients with relapse lymphomas,” he said. “Leaders in the field at MD Anderson like Dr. Michael Wang have developed new oral treatments for patients with rare lymphoma subtypes like mantle cell lymphoma. Other colleagues such as Dr. Nathan Fowler and Dr. Loretta Nastoupil have focused on the care for patients with indolent lymphomas and developed less-toxic therapies that are now in common use.”
Exposing the disparities in blood cancer care
Dr. Flowers, who’s African American, has also been a leader in health disparity research. In 2016, for example, he was coauthor of a study into non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that revealed that Blacks in the United States have dramatically lower survival rates than Whites. The 10-year survival rate for Black women with chronic lymphocytic leukemia was just 47%, for example, compared with 66% for White females. “Although incidence rates of lymphoid neoplasms are generally higher among Whites, Black men tend to have poorer survival,” Dr. Flowers and colleagues wrote.
In a 2021 report for the ASCO Educational Book, Dr. Flowers and hematologist-oncologist Demetria Smith-Graziani, MD, now with Emory University, explored disparities across blood cancers and barriers to minority enrollment in clinical trials. “Some approaches that clinicians can apply to address these disparities include increasing systems-level awareness, improving access to care, and reducing biases in clinical setting,” the authors wrote.
Luis Malpica Castillo, MD, assistant professor of lymphoma at MD Anderson Cancer Center, lauded the work of Dr. Flowers in expanding opportunities for minority patients with the disease.
“During the past years, Dr. Flowers’ work has not only had a positive impact on the Texan community, but minority populations living with cancer in the United States and abroad,” he said. “Currently, we are implementing cancer care networks aimed to increase diversity in clinical trials by enrolling a larger number of Hispanic and African American patients, who otherwise may not have benefited from novel therapies. The ultimate goal is to provide high-quality care to all patients living with cancer.”
In addition to his research work, Dr. Flowers is an advocate for diversity within the hematology community. He’s a founding member and former chair of the American Society of Hematology’s Committee on Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (formerly the Committee on Promoting Diversity), and he helped develop the society’s Minority Recruitment Initiative.
What’s next for Dr. Flowers? For one, he plans to continue working as a mentor; he received the ASH Mentor Award in honor of his service in 2022. “I am strongly committed to increasing the number of tenure-track investigators trained in clinical and translational cancer research and to promote their career development.”
And he looks forward to helping develop MD Anderson’s recently announced $2.5 billion hospital in Austin. “This will extend the exceptional care that we provide as the No. 1 cancer center in the United States,” he said. “It will also create new opportunities for research and collaboration with experts at UT Austin.”
When he’s not in clinic, Dr. Flowers embraces his lifelong love of speeding through life on his own two feet. He’s even inspired his children to share his passion. “I run most days of the week,” he said. “Running provides a great opportunity to think and process new research ideas, work through leadership challenges, and sometimes just to relax and let go of the day.”
“My research uncovered a series of physicians who served as ‘clinical champions’ and dramatically sped the process of drug development,” Dr. Flowers recalled in an interview. “This early career research inspired me to become the type of clinical champion that I uncovered.”
Over his career, hematologist-oncologist Dr. Flowers has developed lifesaving therapies for lymphoma, which has transformed into a highly treatable and even curable disease. He’s listed as a coauthor of hundreds of peer-reviewed cancer studies, reports, and medical society guidelines. And he’s revealed stark disparities in blood cancer care: His research shows that non-White patients suffer from worse outcomes, regardless of factors like income and insurance coverage.
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, recently named physician-scientist Dr. Flowers as division head of cancer medicine, a position he’s held on an interim basis. As of Sept. 1, he will permanently oversee 300 faculty and more than 2,000 staff members.
A running start in Seattle
For Dr. Flowers, track and field is a sport that runs in the family. His grandfather was a top runner in both high school and college, and both Dr. Flowers and his brother ran competitively in Seattle, where they grew up. But Dr. Flowers chose a career in oncology, earning a medical degree at Stanford and master’s degrees at both Stanford and the University of Washington, Seattle.
The late Kenneth Melmon, MD, a groundbreaking pharmacologist, was a major influence. “He was one of the first people that I met when I began as an undergraduate at Stanford. We grew to be long-standing friends, and he demonstrated what outstanding mentorship looks like. In our research collaboration, we investigated the work of Dr. Gertrude Elion and Dr. George Hitchings involving the translation of pharmacological data from cellular and animal models to clinically useful drugs including 6-mercaptopurine, allopurinol, azathioprine, acyclovir, and zidovudine.”
The late Oliver Press, MD, a blood cancer specialist, inspired Dr. Flower’s interest in lymphoma. “I began work with him during an internship at the University of Washington. Ollie was a great inspiration and a key leader in the development of innovative therapies for lymphoma. He embodied the role of a clinical champion translating work in radioimmunotherapy to new therapeutics for patients with lymphomas. Working with him ultimately led me to pursue a career in hematology and oncology with a focus on the care for patients with lymphomas.”
Career blooms as lymphoma care advances
Dr. Flowers went on to Emory University, Atlanta, where he served as scientific director of the Research Informatics Shared Resource and a faculty member in the department of biomedical informatics. “I applied my training in informatics and my clinical expertise to support active grants from the Burroughs Wellcome Fund for Innovation in Regulatory Science and from the National Cancer Institute to develop informatics tools for pathology image analysis and prognostic modeling.”
For 13 years, he also served the Winship Cancer Institute as director of the Emory Healthcare lymphoma program (where his patients included Kansas City Chiefs football star Eric Berry), and for 4 years as scientific director of research informatics. Meanwhile, Dr. Flowers helped develop national practice guidelines for the American Society of Clinical Oncology, the American Cancer Society, and the American College of Radiology. He also chaired the ASCO guideline on management of febrile neutropenia.
In 2019, MD Anderson hired Dr. Flowers as chair of the department of lymphoma/myeloma. A year later, he was appointed division head ad interim for cancer medicine.
“Chris is a unique leader who expertly combines mentorship, sponsorship, and bidirectional open, honest communication,” said Sairah Ahmed, MD, associate professor of lymphoma at MD Anderson. “He doesn’t just empower his team to reach their goals. He also inspires those around him to turn vision into reality.”
As Dr. Flowers noted, many patients with lymphoma are now able to recover and live normal lives. He himself played a direct role himself in boosting lifespans.
“I have been fortunate to play a role in the development of several treatments that have led to advances in first-line therapy for patients with aggressive lymphomas. I partnered with others at MD Anderson, including Dr. Sattva Neelapu and Dr. Jason Westin, who have developed novel therapies like chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for patients with relapse lymphomas,” he said. “Leaders in the field at MD Anderson like Dr. Michael Wang have developed new oral treatments for patients with rare lymphoma subtypes like mantle cell lymphoma. Other colleagues such as Dr. Nathan Fowler and Dr. Loretta Nastoupil have focused on the care for patients with indolent lymphomas and developed less-toxic therapies that are now in common use.”
Exposing the disparities in blood cancer care
Dr. Flowers, who’s African American, has also been a leader in health disparity research. In 2016, for example, he was coauthor of a study into non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that revealed that Blacks in the United States have dramatically lower survival rates than Whites. The 10-year survival rate for Black women with chronic lymphocytic leukemia was just 47%, for example, compared with 66% for White females. “Although incidence rates of lymphoid neoplasms are generally higher among Whites, Black men tend to have poorer survival,” Dr. Flowers and colleagues wrote.
In a 2021 report for the ASCO Educational Book, Dr. Flowers and hematologist-oncologist Demetria Smith-Graziani, MD, now with Emory University, explored disparities across blood cancers and barriers to minority enrollment in clinical trials. “Some approaches that clinicians can apply to address these disparities include increasing systems-level awareness, improving access to care, and reducing biases in clinical setting,” the authors wrote.
Luis Malpica Castillo, MD, assistant professor of lymphoma at MD Anderson Cancer Center, lauded the work of Dr. Flowers in expanding opportunities for minority patients with the disease.
“During the past years, Dr. Flowers’ work has not only had a positive impact on the Texan community, but minority populations living with cancer in the United States and abroad,” he said. “Currently, we are implementing cancer care networks aimed to increase diversity in clinical trials by enrolling a larger number of Hispanic and African American patients, who otherwise may not have benefited from novel therapies. The ultimate goal is to provide high-quality care to all patients living with cancer.”
In addition to his research work, Dr. Flowers is an advocate for diversity within the hematology community. He’s a founding member and former chair of the American Society of Hematology’s Committee on Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (formerly the Committee on Promoting Diversity), and he helped develop the society’s Minority Recruitment Initiative.
What’s next for Dr. Flowers? For one, he plans to continue working as a mentor; he received the ASH Mentor Award in honor of his service in 2022. “I am strongly committed to increasing the number of tenure-track investigators trained in clinical and translational cancer research and to promote their career development.”
And he looks forward to helping develop MD Anderson’s recently announced $2.5 billion hospital in Austin. “This will extend the exceptional care that we provide as the No. 1 cancer center in the United States,” he said. “It will also create new opportunities for research and collaboration with experts at UT Austin.”
When he’s not in clinic, Dr. Flowers embraces his lifelong love of speeding through life on his own two feet. He’s even inspired his children to share his passion. “I run most days of the week,” he said. “Running provides a great opportunity to think and process new research ideas, work through leadership challenges, and sometimes just to relax and let go of the day.”
MCL: Pathophysiology and Epidemiology
Red nodules on legs
Given the patient's diagnosis of stage IV MCL, the presentation of diffuse skin lesions, and the histopathologic and immunophenotyping results of those lesions, this patient is diagnosed with secondary cutaneous MCL. The hematologist-oncologist discusses the findings with the patient and presents potential next steps and treatment options.
MCL is a type of B-cell neoplasm that, with advancements in the understanding of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in the past 30 years, has been defined as its own clinicopathologic entity by the Revised European-American Lymphoma and World Health Organization classifications. Up to 10% of all NHLs are MCL. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. Skin manifestations are not as common as other extranodal manifestations. Primary cutaneous MCL occurs in up to 6% of patients with MCL; secondary cutaneous involvement is slightly more common, occurring in 17% of patients with MCL. Secondary cutaneous MCL usually presents in late-stage disease. Men are more likely to present with MCL than are women by a ratio of 3:1. Median age at presentation is 67 years.
Diagnosing MCL is a multipronged approach. Physical examination may reveal lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveals monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin (Ig), IgM, or IgD, that are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen–positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate/biopsy are used more for staging than for diagnosis. Blood studies, including anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with up to 40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and a negative Coombs test also help diagnose MCL. Secondary cutaneous MCL is diagnosed on the basis of an MCL diagnosis along with diffuse infiltration of the skin, with multiple erythematous papules and nodules coalescing to form plaques; skin biopsy and immunohistopathology showing monotonous proliferation of small- to medium-sized lymphoid cells with scant cytoplasm; irregular cleaved nuclei with coarse chromatin; and inconspicuous nucleoli as well as a spared papillary dermis.
Pathogenesis of MCL involves disordered lymphoproliferation in a subset of naive pregerminal center cells in primary follicles or in the mantle region of secondary follicles. Most cases are linked with translocation of chromosome 14 and 11, which induces overexpression of protein cyclin D1. Viral infection (Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1, human herpes virus 6), environmental factors, and primary and secondary immunodeficiency are also associated with the development of NHL.
Patient education should include detailed information about clinical trials, available treatment options, and associated adverse events as well as psychosocial and nutrition counseling.
Chemoimmunotherapy is standard initial treatment for MCL, but relapse is expected. Chemotherapy-free regimens with biologic targets, which were once used in second-line treatment, have increasingly become an important first-line treatment given their efficacy in the relapsed/refractory setting. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is also a second-line treatment option. In patients with MCL and a TP53 mutation, clinical trial participation is encouraged because of poor prognosis.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grants from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given the patient's diagnosis of stage IV MCL, the presentation of diffuse skin lesions, and the histopathologic and immunophenotyping results of those lesions, this patient is diagnosed with secondary cutaneous MCL. The hematologist-oncologist discusses the findings with the patient and presents potential next steps and treatment options.
MCL is a type of B-cell neoplasm that, with advancements in the understanding of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in the past 30 years, has been defined as its own clinicopathologic entity by the Revised European-American Lymphoma and World Health Organization classifications. Up to 10% of all NHLs are MCL. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. Skin manifestations are not as common as other extranodal manifestations. Primary cutaneous MCL occurs in up to 6% of patients with MCL; secondary cutaneous involvement is slightly more common, occurring in 17% of patients with MCL. Secondary cutaneous MCL usually presents in late-stage disease. Men are more likely to present with MCL than are women by a ratio of 3:1. Median age at presentation is 67 years.
Diagnosing MCL is a multipronged approach. Physical examination may reveal lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveals monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin (Ig), IgM, or IgD, that are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen–positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate/biopsy are used more for staging than for diagnosis. Blood studies, including anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with up to 40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and a negative Coombs test also help diagnose MCL. Secondary cutaneous MCL is diagnosed on the basis of an MCL diagnosis along with diffuse infiltration of the skin, with multiple erythematous papules and nodules coalescing to form plaques; skin biopsy and immunohistopathology showing monotonous proliferation of small- to medium-sized lymphoid cells with scant cytoplasm; irregular cleaved nuclei with coarse chromatin; and inconspicuous nucleoli as well as a spared papillary dermis.
Pathogenesis of MCL involves disordered lymphoproliferation in a subset of naive pregerminal center cells in primary follicles or in the mantle region of secondary follicles. Most cases are linked with translocation of chromosome 14 and 11, which induces overexpression of protein cyclin D1. Viral infection (Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1, human herpes virus 6), environmental factors, and primary and secondary immunodeficiency are also associated with the development of NHL.
Patient education should include detailed information about clinical trials, available treatment options, and associated adverse events as well as psychosocial and nutrition counseling.
Chemoimmunotherapy is standard initial treatment for MCL, but relapse is expected. Chemotherapy-free regimens with biologic targets, which were once used in second-line treatment, have increasingly become an important first-line treatment given their efficacy in the relapsed/refractory setting. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is also a second-line treatment option. In patients with MCL and a TP53 mutation, clinical trial participation is encouraged because of poor prognosis.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grants from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given the patient's diagnosis of stage IV MCL, the presentation of diffuse skin lesions, and the histopathologic and immunophenotyping results of those lesions, this patient is diagnosed with secondary cutaneous MCL. The hematologist-oncologist discusses the findings with the patient and presents potential next steps and treatment options.
MCL is a type of B-cell neoplasm that, with advancements in the understanding of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in the past 30 years, has been defined as its own clinicopathologic entity by the Revised European-American Lymphoma and World Health Organization classifications. Up to 10% of all NHLs are MCL. Clinical presentation includes advanced disease with B symptoms (eg, night sweats, fever, weight loss), generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal distention associated with hepatosplenomegaly, and fatigue. Skin manifestations are not as common as other extranodal manifestations. Primary cutaneous MCL occurs in up to 6% of patients with MCL; secondary cutaneous involvement is slightly more common, occurring in 17% of patients with MCL. Secondary cutaneous MCL usually presents in late-stage disease. Men are more likely to present with MCL than are women by a ratio of 3:1. Median age at presentation is 67 years.
Diagnosing MCL is a multipronged approach. Physical examination may reveal lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Lymph node biopsy and aspiration with immunophenotyping in MCL reveals monoclonal B cells expressing surface immunoglobulin (Ig), IgM, or IgD, that are characteristically CD5+ and pan B-cell antigen–positive (eg, CD19, CD20, CD22) but lack expression of CD10 and CD23 and overexpress cyclin D1. Bone marrow aspirate/biopsy are used more for staging than for diagnosis. Blood studies, including anemia and cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration (with up to 40% of cases showing lymphocytosis > 4000/μL), abnormal liver function tests, and a negative Coombs test also help diagnose MCL. Secondary cutaneous MCL is diagnosed on the basis of an MCL diagnosis along with diffuse infiltration of the skin, with multiple erythematous papules and nodules coalescing to form plaques; skin biopsy and immunohistopathology showing monotonous proliferation of small- to medium-sized lymphoid cells with scant cytoplasm; irregular cleaved nuclei with coarse chromatin; and inconspicuous nucleoli as well as a spared papillary dermis.
Pathogenesis of MCL involves disordered lymphoproliferation in a subset of naive pregerminal center cells in primary follicles or in the mantle region of secondary follicles. Most cases are linked with translocation of chromosome 14 and 11, which induces overexpression of protein cyclin D1. Viral infection (Epstein-Barr virus, HIV, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1, human herpes virus 6), environmental factors, and primary and secondary immunodeficiency are also associated with the development of NHL.
Patient education should include detailed information about clinical trials, available treatment options, and associated adverse events as well as psychosocial and nutrition counseling.
Chemoimmunotherapy is standard initial treatment for MCL, but relapse is expected. Chemotherapy-free regimens with biologic targets, which were once used in second-line treatment, have increasingly become an important first-line treatment given their efficacy in the relapsed/refractory setting. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is also a second-line treatment option. In patients with MCL and a TP53 mutation, clinical trial participation is encouraged because of poor prognosis.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine - Clinical, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University James Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbus, OH.
Timothy J. Voorhees, MD, MSCR, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grants from: AstraZeneca; Morphosys; Incyte; Recordati.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 72-year-old man presents to his hematologist-oncologist with red ulcerative nodules on both legs. Six months before, the patient was diagnosed with stage IV mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and began chemotherapy with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP). Initial patient reports at diagnosis were abdominal distention, generalized lymphadenopathy, night sweats, and fatigue; he received a referral to hematology-oncology after his complete blood count with differential revealed anemia and cytopenias. Additional blood studies showed lymphocytosis > 4000/μL, elevated lactate dehydrogenase levels, abnormal liver function tests, and a negative result on the Coombs test. Ultrasound of the abdomen revealed hepatosplenomegaly and abdominal lymphadenopathy. The hematologist-oncologist ordered a lymph node biopsy and aspiration. Immunophenotyping showed CD5 and CD20 expression but a lack of CD23 and CD10 expression; cyclin D1 was overexpressed. Bone marrow biopsy revealed hypercellular marrow spaces showing infiltration by sheets of atypical lymphoid cells.
Because the patient presents with red ulcerative nodules on both legs, the hematologist-oncologist orders a skin biopsy of the lesions. Histopathologic evaluation shows monotonous proliferation of small- to medium-sized lymphoid cells with scant cytoplasm, irregular cleaved nuclei with coarse chromatin, and inconspicuous nucleoli as well as a spared papillary dermis. Immunophenotyping shows CD5 and CD20 expression but a lack of CD23 and CD10 expression; cyclin D1 is overexpressed.
ESMO helps hematologists assess new cancer drugs
It consists of 11 2- to 3-page forms with checklists to grade treatment trials on the extent to which they meet efficacy and safety thresholds. Each of the 11 forms covers a specific trial scenario, such as a randomized controlled trial with curative intent or a trial of a therapy that is not likely to be curative with a primary endpoint of overall survival.
Treatments with curative intent are graded A, B, or C, while treatments in the noncurative setting are graded on a descending scale from 5 to 1. Scores of A and B in the curative setting and 5 and 4 in the noncurative setting represent substantial benefit.
On the form for RCTs with curative intent, for instance, a survival improvement of 5% or more garners an A but an improvement of less than 3% gets a C. Scores are also annotated for serious acute and/or persistent toxicity if present.
The tool, dubbed the ESMO-MCBS:H (European Society for Medical Oncology Magnitude of Clinical Benefit Scale: Hematology), is explained in an article published in Annals of Oncology. The evaluation forms are available online.
The idea behind the work is to help health care professionals and others to more “accurately assess the value of and prioritise therapies for patients with blood cancers. For clinicians, ESMO-MCBS:H will aid in their clinical decision-making and in the development of evidence-based practice and guidelines,” ESMO said in a press release.
To develop ESMO-MCBS:H, the group tailored its tool for evaluating solid tumor therapies, the ESMO-MCBS, to account for the sometimes different endpoints used in hematologic malignancy trials and the very indolent nature of some blood cancers, such as follicular lymphoma, which hampers development of mature data.
Specific changes include adding a new evaluation form to grade single-arm trials with curative intent, such as those used for CAR-T-cell therapies; incorporating molecular surrogate endpoints used in CML trials; and adding a way to grade outcomes for indolent cancers, among others.
The development process included applying the solid tumor tool to 80 blood cancer studies to identify shortcomings and improve its applicability. The final tool was field tested with 51 international experts from EHA and ESMO who largely agreed on the reasonableness of the trial scores.
ESMO said it expects ESMO-MCBS:H will be useful. The solid tumor tool, first published in 2015, is used by the World Health Organization to screen medications for its essential medicines list as well as by ESMO to generate guidelines and oncology centers across Europe to help with resource allocation decisions.
It consists of 11 2- to 3-page forms with checklists to grade treatment trials on the extent to which they meet efficacy and safety thresholds. Each of the 11 forms covers a specific trial scenario, such as a randomized controlled trial with curative intent or a trial of a therapy that is not likely to be curative with a primary endpoint of overall survival.
Treatments with curative intent are graded A, B, or C, while treatments in the noncurative setting are graded on a descending scale from 5 to 1. Scores of A and B in the curative setting and 5 and 4 in the noncurative setting represent substantial benefit.
On the form for RCTs with curative intent, for instance, a survival improvement of 5% or more garners an A but an improvement of less than 3% gets a C. Scores are also annotated for serious acute and/or persistent toxicity if present.
The tool, dubbed the ESMO-MCBS:H (European Society for Medical Oncology Magnitude of Clinical Benefit Scale: Hematology), is explained in an article published in Annals of Oncology. The evaluation forms are available online.
The idea behind the work is to help health care professionals and others to more “accurately assess the value of and prioritise therapies for patients with blood cancers. For clinicians, ESMO-MCBS:H will aid in their clinical decision-making and in the development of evidence-based practice and guidelines,” ESMO said in a press release.
To develop ESMO-MCBS:H, the group tailored its tool for evaluating solid tumor therapies, the ESMO-MCBS, to account for the sometimes different endpoints used in hematologic malignancy trials and the very indolent nature of some blood cancers, such as follicular lymphoma, which hampers development of mature data.
Specific changes include adding a new evaluation form to grade single-arm trials with curative intent, such as those used for CAR-T-cell therapies; incorporating molecular surrogate endpoints used in CML trials; and adding a way to grade outcomes for indolent cancers, among others.
The development process included applying the solid tumor tool to 80 blood cancer studies to identify shortcomings and improve its applicability. The final tool was field tested with 51 international experts from EHA and ESMO who largely agreed on the reasonableness of the trial scores.
ESMO said it expects ESMO-MCBS:H will be useful. The solid tumor tool, first published in 2015, is used by the World Health Organization to screen medications for its essential medicines list as well as by ESMO to generate guidelines and oncology centers across Europe to help with resource allocation decisions.
It consists of 11 2- to 3-page forms with checklists to grade treatment trials on the extent to which they meet efficacy and safety thresholds. Each of the 11 forms covers a specific trial scenario, such as a randomized controlled trial with curative intent or a trial of a therapy that is not likely to be curative with a primary endpoint of overall survival.
Treatments with curative intent are graded A, B, or C, while treatments in the noncurative setting are graded on a descending scale from 5 to 1. Scores of A and B in the curative setting and 5 and 4 in the noncurative setting represent substantial benefit.
On the form for RCTs with curative intent, for instance, a survival improvement of 5% or more garners an A but an improvement of less than 3% gets a C. Scores are also annotated for serious acute and/or persistent toxicity if present.
The tool, dubbed the ESMO-MCBS:H (European Society for Medical Oncology Magnitude of Clinical Benefit Scale: Hematology), is explained in an article published in Annals of Oncology. The evaluation forms are available online.
The idea behind the work is to help health care professionals and others to more “accurately assess the value of and prioritise therapies for patients with blood cancers. For clinicians, ESMO-MCBS:H will aid in their clinical decision-making and in the development of evidence-based practice and guidelines,” ESMO said in a press release.
To develop ESMO-MCBS:H, the group tailored its tool for evaluating solid tumor therapies, the ESMO-MCBS, to account for the sometimes different endpoints used in hematologic malignancy trials and the very indolent nature of some blood cancers, such as follicular lymphoma, which hampers development of mature data.
Specific changes include adding a new evaluation form to grade single-arm trials with curative intent, such as those used for CAR-T-cell therapies; incorporating molecular surrogate endpoints used in CML trials; and adding a way to grade outcomes for indolent cancers, among others.
The development process included applying the solid tumor tool to 80 blood cancer studies to identify shortcomings and improve its applicability. The final tool was field tested with 51 international experts from EHA and ESMO who largely agreed on the reasonableness of the trial scores.
ESMO said it expects ESMO-MCBS:H will be useful. The solid tumor tool, first published in 2015, is used by the World Health Organization to screen medications for its essential medicines list as well as by ESMO to generate guidelines and oncology centers across Europe to help with resource allocation decisions.
FROM ANNALS OF ONCOLOGY