User login
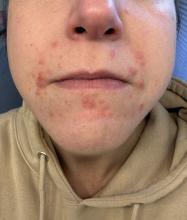
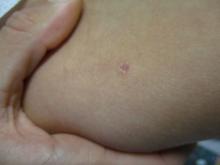
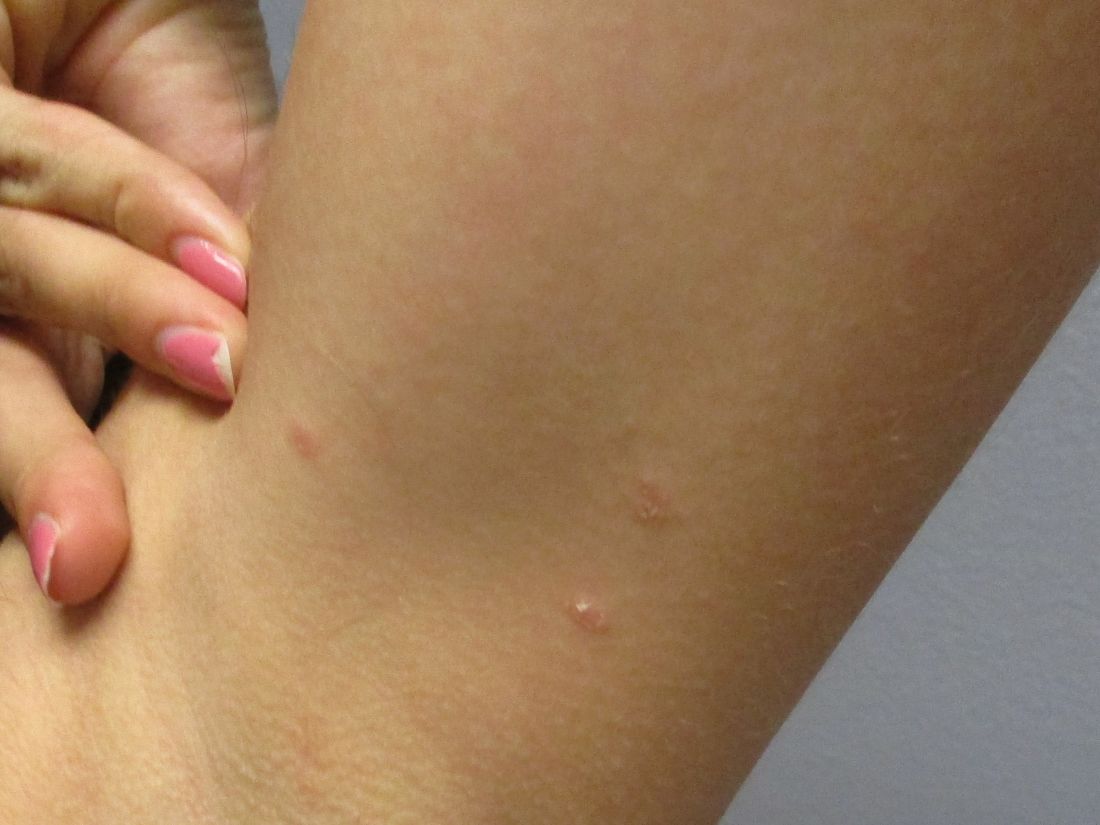
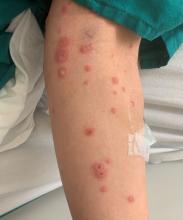
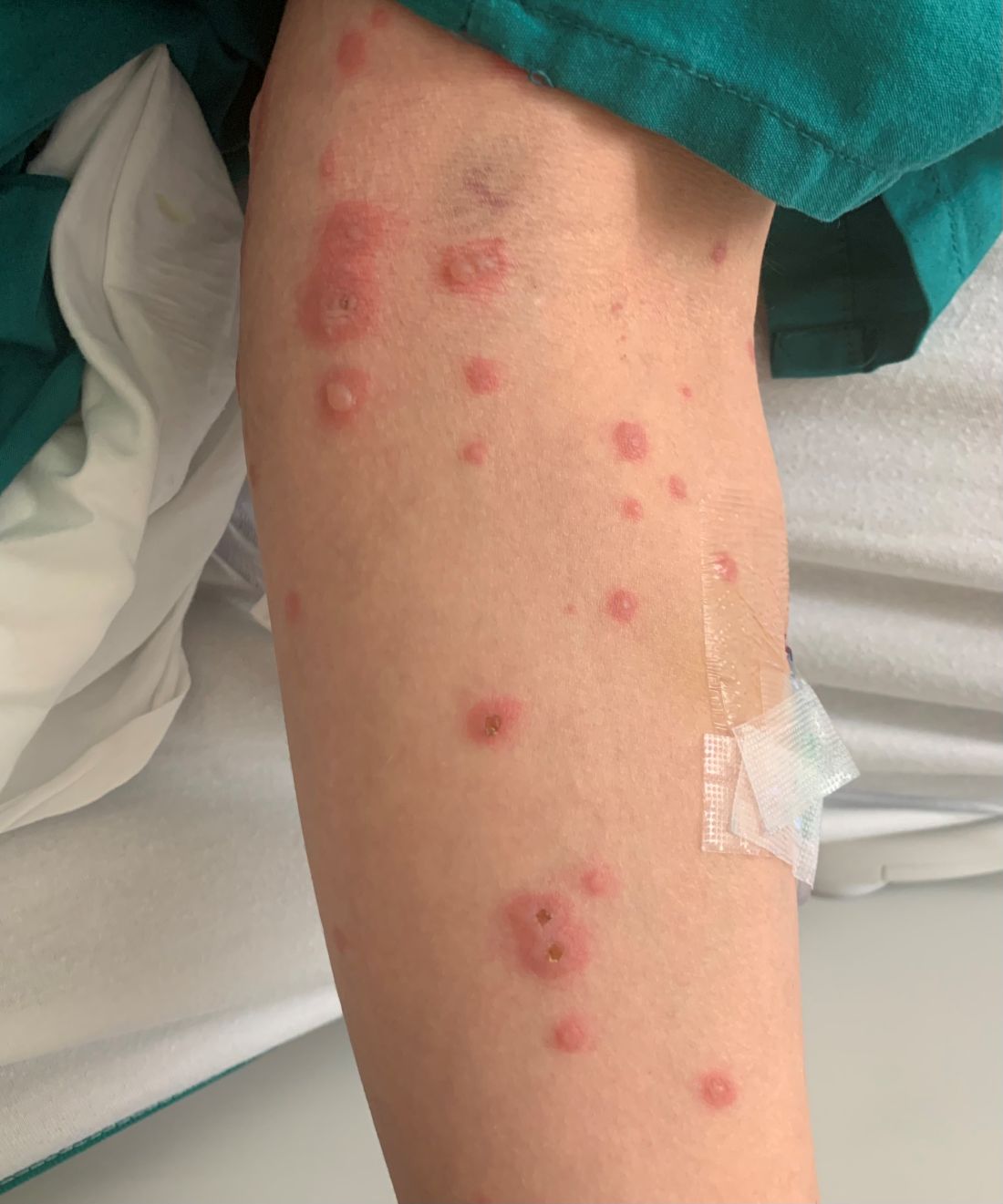
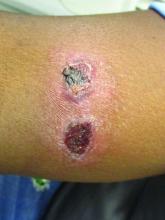
A 35-year-old female presented with a 1-day history of eroded papules and vesicles distributed periorally
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
.1 While it predominantly affects children, it is important to note that it can also affect adults. Although it is not a life threatening infection, it can cause a painful rash and is highly contagious. The infection is easily spread in multiple ways, including via respiratory droplets, contact with vesicular or nasal secretions, or through fecal-oral transmission. Most cases occur during the summer and fall seasons but individuals can be infected at any time of the year.
HFMD typically starts with a few days of non-specific viral symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, and fatigue. It is then followed by an eruption of intraoral macules and vesicles and a widespread distribution of oval shaped macules that predominantly involve the hands and feet.1 Both children and adults can present atypically. Atypical presentations include vesicles and bullae on extensor surfaces such as the forearms, as well as eruptions on the face or buttocks.2 Other atypical morphologies include eczema herpeticum-like, Gianotti-Crosti-like, and purpuric/petechiae.3 Atypical hand, food, and mouth disease cases are often caused by coxsackievirus A6, however other strains of coxsackievirus can also cause atypical symptoms.2,3
Our 35-year-old female patient presented with eroded papules and vesicles around the mouth. A diagnosis of atypical HFMD was made clinically in the following days when the patient developed the more classic intraoral and acral macules and vesicles.
Similar to our case, HFMD is most often diagnosed clinically. PCR testing from an active vesicle or nasopharyngeal swab can be obtained. Treatment for HFMD is supportive and symptoms generally resolve over 7-10 days. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as oral analgesics that contain lidocaine or diphenhydramine are often helpful3. In this case, our patient improved over the course of seven days without needing therapy.
This case and the photos were submitted by Vanessa Ortega, BS, University of California, San Diego; Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, and Justin Gordon, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, June 20). Symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
2. Drago F et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 Aug;77(2):e51-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.03.046.
3. Starkey SY et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jan-Feb;41(1):23-7. doi: 10.1111/pde.15461.
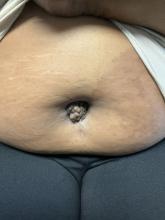
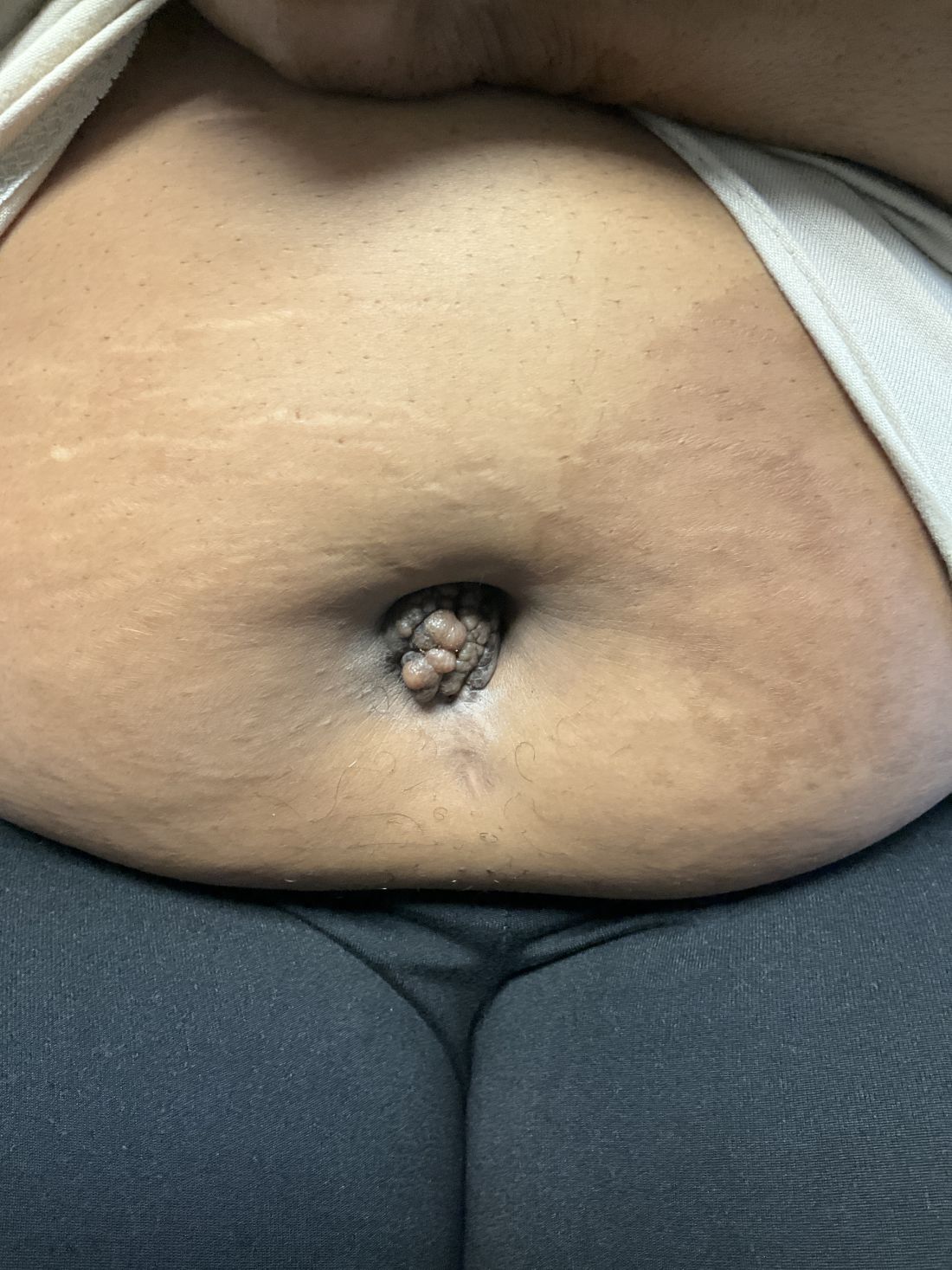
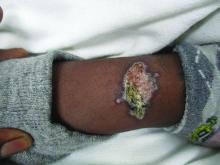
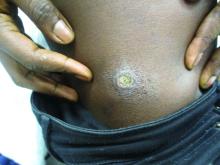
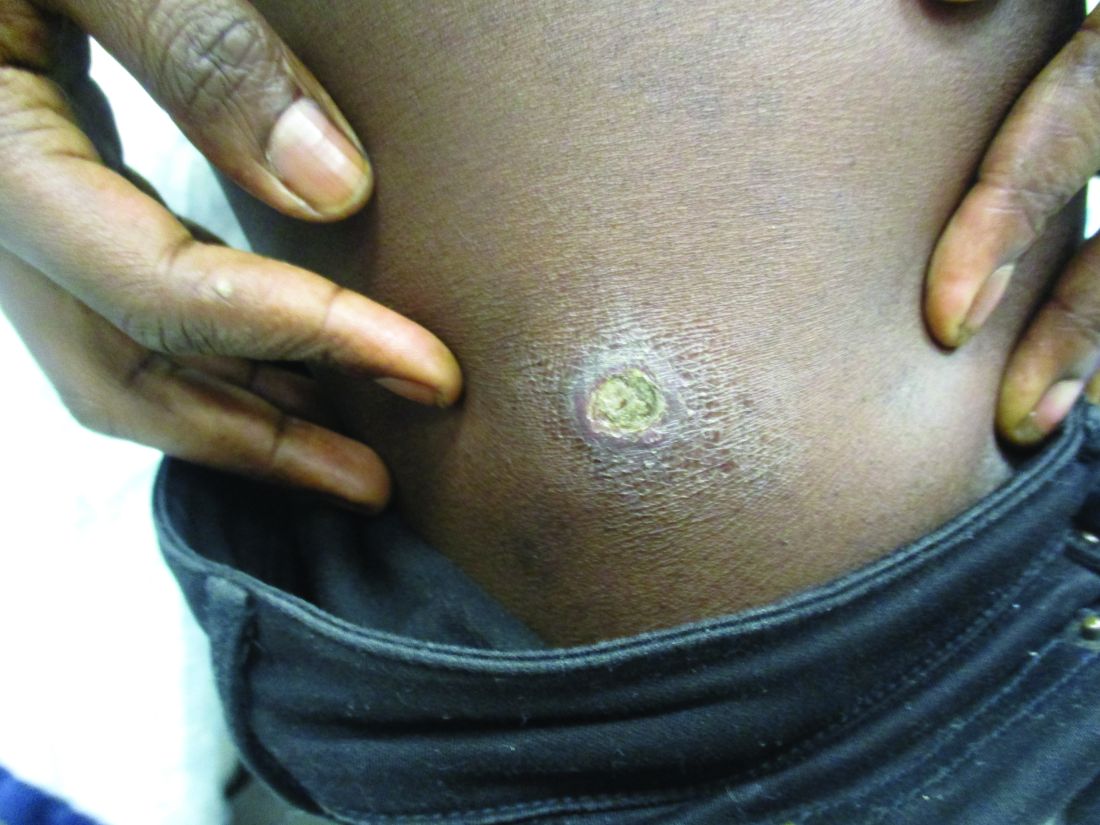
A 27-year-old Haitian woman presented with a painful umbilical mass which had been growing in size for 5 months
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
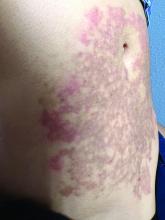
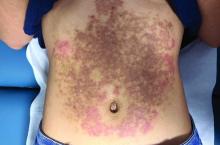
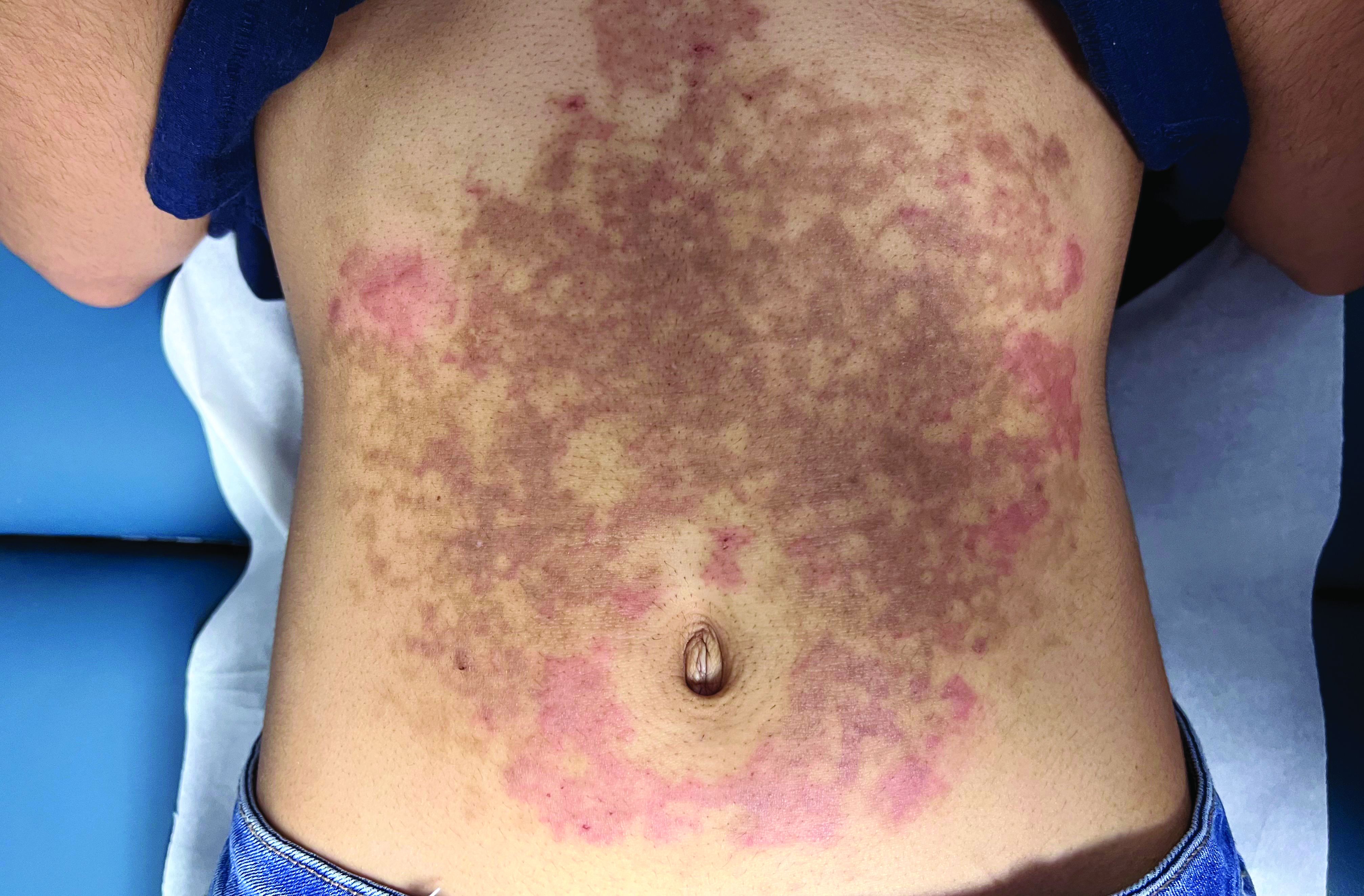
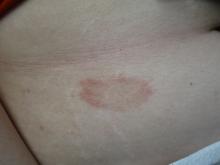
A White female presented with pruritic, reticulated, erythematous plaques on the abdomen
It is characterized by pruritic, erythematous papules, papulovesicles, and vesicles that appear in a reticular pattern, most commonly on the trunk. The lesions are typically followed by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Although PP has been described in people of all races, ages, and sexes, it is predominantly observed in Japan, often in female young adults. Triggers may include a ketogenic diet, diabetes mellitus, and pregnancy. Friction and contact allergic reactions to chrome or nickel have been proposed as exogenous trigger factors. Individual cases of Sjögren’s syndrome, Helicobacter pylori infections, and adult Still syndrome have also been associated with recurrent eruptions.
The diagnosis of PP is made both clinically and by biopsy. The histological features vary according to the stage of the disease. In early-stage disease, superficial and perivascular infiltration of neutrophils are prominent. Later stages are characterized by spongiosis and necrotic keratinocytes.
The first-line therapy for prurigo pigmentosa is oral minocycline. However, for some patients, doxycycline, macrolide antibiotics, or dapsone may be indicated. Adding carbohydrates to a keto diet may be helpful. In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed an interface dermatitis with eosinophils and neutrophils, consistent with prurigo pigmentosa. The cause of her PP remains idiopathic. She was treated with 100 mg doxycycline twice a day, which resulted in a resolution of active lesions. The patient did have postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
This case and photo were submitted by Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California, and Mina Zulal, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Hamburg, Germany. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Beutler et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015 Dec;16(6):533-43.
2. Kim et al. J Dermatol. 2012 Nov;39(11):891-7.
3. Mufti et al. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10;3:79-87.
It is characterized by pruritic, erythematous papules, papulovesicles, and vesicles that appear in a reticular pattern, most commonly on the trunk. The lesions are typically followed by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Although PP has been described in people of all races, ages, and sexes, it is predominantly observed in Japan, often in female young adults. Triggers may include a ketogenic diet, diabetes mellitus, and pregnancy. Friction and contact allergic reactions to chrome or nickel have been proposed as exogenous trigger factors. Individual cases of Sjögren’s syndrome, Helicobacter pylori infections, and adult Still syndrome have also been associated with recurrent eruptions.
The diagnosis of PP is made both clinically and by biopsy. The histological features vary according to the stage of the disease. In early-stage disease, superficial and perivascular infiltration of neutrophils are prominent. Later stages are characterized by spongiosis and necrotic keratinocytes.
The first-line therapy for prurigo pigmentosa is oral minocycline. However, for some patients, doxycycline, macrolide antibiotics, or dapsone may be indicated. Adding carbohydrates to a keto diet may be helpful. In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed an interface dermatitis with eosinophils and neutrophils, consistent with prurigo pigmentosa. The cause of her PP remains idiopathic. She was treated with 100 mg doxycycline twice a day, which resulted in a resolution of active lesions. The patient did have postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
This case and photo were submitted by Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California, and Mina Zulal, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Hamburg, Germany. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Beutler et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015 Dec;16(6):533-43.
2. Kim et al. J Dermatol. 2012 Nov;39(11):891-7.
3. Mufti et al. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10;3:79-87.
It is characterized by pruritic, erythematous papules, papulovesicles, and vesicles that appear in a reticular pattern, most commonly on the trunk. The lesions are typically followed by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Although PP has been described in people of all races, ages, and sexes, it is predominantly observed in Japan, often in female young adults. Triggers may include a ketogenic diet, diabetes mellitus, and pregnancy. Friction and contact allergic reactions to chrome or nickel have been proposed as exogenous trigger factors. Individual cases of Sjögren’s syndrome, Helicobacter pylori infections, and adult Still syndrome have also been associated with recurrent eruptions.
The diagnosis of PP is made both clinically and by biopsy. The histological features vary according to the stage of the disease. In early-stage disease, superficial and perivascular infiltration of neutrophils are prominent. Later stages are characterized by spongiosis and necrotic keratinocytes.
The first-line therapy for prurigo pigmentosa is oral minocycline. However, for some patients, doxycycline, macrolide antibiotics, or dapsone may be indicated. Adding carbohydrates to a keto diet may be helpful. In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed an interface dermatitis with eosinophils and neutrophils, consistent with prurigo pigmentosa. The cause of her PP remains idiopathic. She was treated with 100 mg doxycycline twice a day, which resulted in a resolution of active lesions. The patient did have postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
This case and photo were submitted by Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California, and Mina Zulal, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Hamburg, Germany. Dr. Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Beutler et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015 Dec;16(6):533-43.
2. Kim et al. J Dermatol. 2012 Nov;39(11):891-7.
3. Mufti et al. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10;3:79-87.
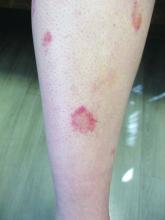
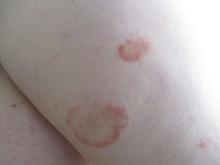
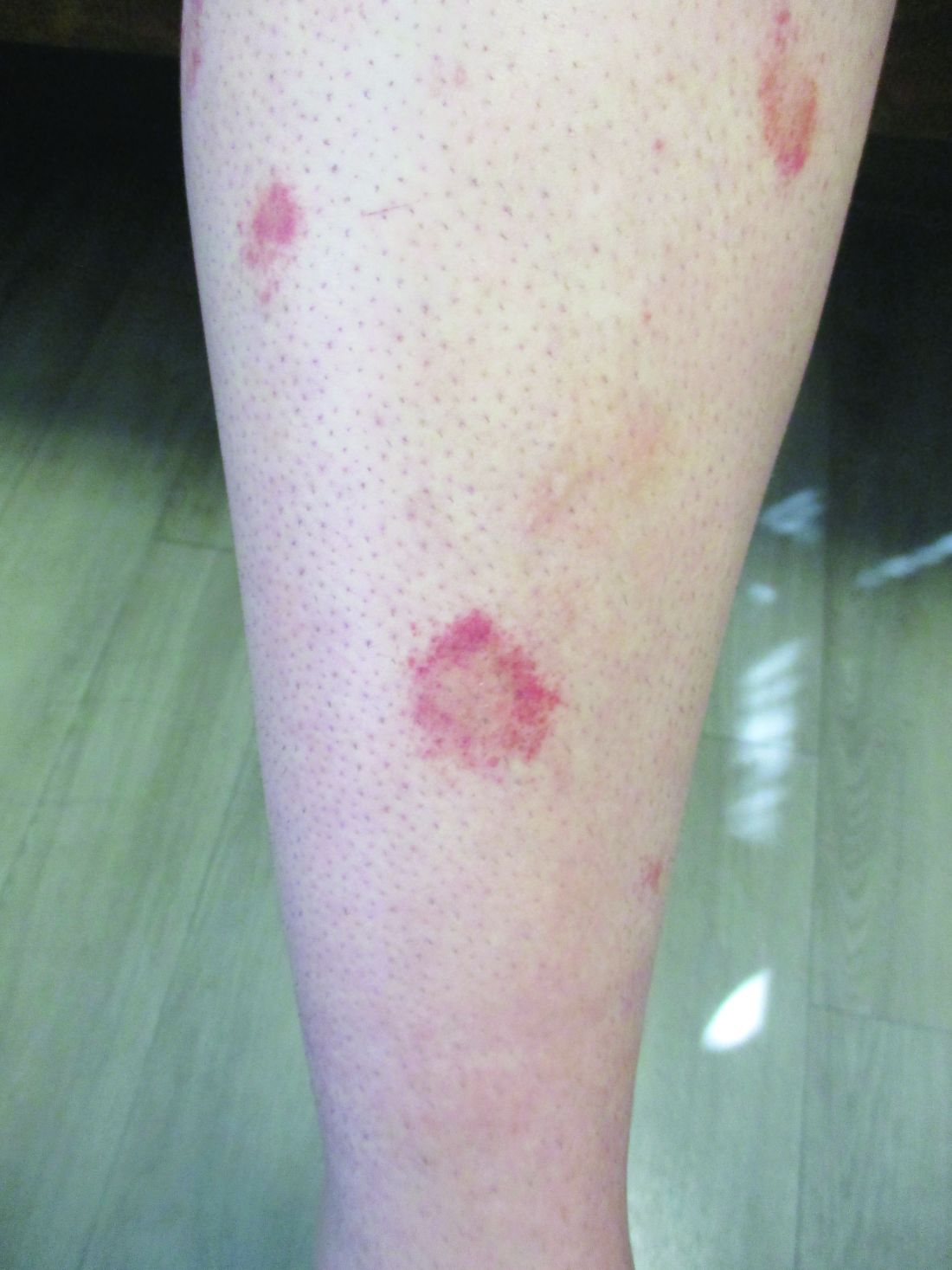
24-year-old female presents with a 3-month history of nonpruritic rash
, typically characterized by symmetrical, nonblanching, purpuric, telangiectatic, and atrophic patches with a predilection for the lower extremities and buttocks.
Plaques are usually 1-3 cm in diameter and annular with punctate telangiectasias and cayenne pepper petechiae in the border. The annular patches may form concentric rings. It is most commonly seen in children and young females.
The etiology of Majocchi’s disease is largely unknown and idiopathic.
Triggers are not always detected but may be associated with viral infections, chronic comorbidities, and medications. Levofloxacin and isotretinoin have been described in as reports as causing PATM. Other medications reported to cause PPD include sedatives, stimulants, antibiotics, NSAIDS, and cardiovascular drugs.
Diagnosis of PATM is clinical and histopathologic. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) may show fibrinogen, IgM, and/or C3 deposition in superficial dermal vessels. Histopathologic findings show lymphocytic infiltrate involving the superficial small vessels, extravasated red blood cells, and hemosiderin-laden macrophages.
There is no consensus regarding treatment with variable responses to proposed treatment based on reports and case studies. The first line of treatment is topical corticosteroids and compression hose. Additional treatments, including narrowband UVB phototherapy (NBUVB), griseofulvin, pentoxifylline, cyclosporine, colchicine, rutoside with ascorbic acid, and methotrexate, have been used with varying success.
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed lymphocytes and extravasated erythrocytes and siderophages in the dermis. She was treated with topical steroids with improvement. She started NBUVB, a short course of griseofulvin, and vitamin C supplements.
This case and the photos were photo submitted by Ms. Xu, of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology. Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Garcez A et al. An Bras Dermatol. Sep-Oct 2020;95(5):664-6. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2020.02.007.
2. Asadbeigi S, Momtahen S. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis. PathologyOutlines.com website.
3. Martínez P et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020 Apr;111(3):196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2019.02.013.
4. Hoesly FJ et al. Int J Dermatol. 2009 Oct;48(10):1129-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04160.x.
, typically characterized by symmetrical, nonblanching, purpuric, telangiectatic, and atrophic patches with a predilection for the lower extremities and buttocks.
Plaques are usually 1-3 cm in diameter and annular with punctate telangiectasias and cayenne pepper petechiae in the border. The annular patches may form concentric rings. It is most commonly seen in children and young females.
The etiology of Majocchi’s disease is largely unknown and idiopathic.
Triggers are not always detected but may be associated with viral infections, chronic comorbidities, and medications. Levofloxacin and isotretinoin have been described in as reports as causing PATM. Other medications reported to cause PPD include sedatives, stimulants, antibiotics, NSAIDS, and cardiovascular drugs.
Diagnosis of PATM is clinical and histopathologic. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) may show fibrinogen, IgM, and/or C3 deposition in superficial dermal vessels. Histopathologic findings show lymphocytic infiltrate involving the superficial small vessels, extravasated red blood cells, and hemosiderin-laden macrophages.
There is no consensus regarding treatment with variable responses to proposed treatment based on reports and case studies. The first line of treatment is topical corticosteroids and compression hose. Additional treatments, including narrowband UVB phototherapy (NBUVB), griseofulvin, pentoxifylline, cyclosporine, colchicine, rutoside with ascorbic acid, and methotrexate, have been used with varying success.
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed lymphocytes and extravasated erythrocytes and siderophages in the dermis. She was treated with topical steroids with improvement. She started NBUVB, a short course of griseofulvin, and vitamin C supplements.
This case and the photos were photo submitted by Ms. Xu, of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology. Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Garcez A et al. An Bras Dermatol. Sep-Oct 2020;95(5):664-6. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2020.02.007.
2. Asadbeigi S, Momtahen S. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis. PathologyOutlines.com website.
3. Martínez P et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020 Apr;111(3):196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2019.02.013.
4. Hoesly FJ et al. Int J Dermatol. 2009 Oct;48(10):1129-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04160.x.
, typically characterized by symmetrical, nonblanching, purpuric, telangiectatic, and atrophic patches with a predilection for the lower extremities and buttocks.
Plaques are usually 1-3 cm in diameter and annular with punctate telangiectasias and cayenne pepper petechiae in the border. The annular patches may form concentric rings. It is most commonly seen in children and young females.
The etiology of Majocchi’s disease is largely unknown and idiopathic.
Triggers are not always detected but may be associated with viral infections, chronic comorbidities, and medications. Levofloxacin and isotretinoin have been described in as reports as causing PATM. Other medications reported to cause PPD include sedatives, stimulants, antibiotics, NSAIDS, and cardiovascular drugs.
Diagnosis of PATM is clinical and histopathologic. Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) may show fibrinogen, IgM, and/or C3 deposition in superficial dermal vessels. Histopathologic findings show lymphocytic infiltrate involving the superficial small vessels, extravasated red blood cells, and hemosiderin-laden macrophages.
There is no consensus regarding treatment with variable responses to proposed treatment based on reports and case studies. The first line of treatment is topical corticosteroids and compression hose. Additional treatments, including narrowband UVB phototherapy (NBUVB), griseofulvin, pentoxifylline, cyclosporine, colchicine, rutoside with ascorbic acid, and methotrexate, have been used with varying success.
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, which revealed lymphocytes and extravasated erythrocytes and siderophages in the dermis. She was treated with topical steroids with improvement. She started NBUVB, a short course of griseofulvin, and vitamin C supplements.
This case and the photos were photo submitted by Ms. Xu, of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology. Dr. Donna Bilu Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Garcez A et al. An Bras Dermatol. Sep-Oct 2020;95(5):664-6. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2020.02.007.
2. Asadbeigi S, Momtahen S. Pigmented purpuric dermatosis. PathologyOutlines.com website.
3. Martínez P et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2020 Apr;111(3):196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2019.02.013.
4. Hoesly FJ et al. Int J Dermatol. 2009 Oct;48(10):1129-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04160.x.
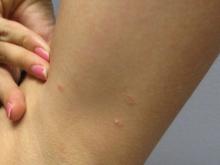
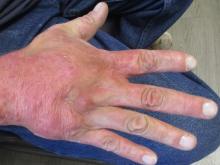
A 31-year-old female presented with a burning rash on upper arms, groin, and axillae
The exact cause is unknown, but possible causes include medications, dental amalgam fillings, or an autoimmune reaction. Drugs implicated in causing LP include beta-blockers, methyldopa, penicillamine, quinidine, and quinine. A meta-analysis of case-control studies show a statistically significant association between hepatitis C infection and LP patients; thus, all patients presenting with LP should be screened for hepatitis.1 Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by LP, but it is predominantly observed in middle-aged adults. Women are also twice as likely to get oral lichen planus.2
Atrophic lichen planus, the least common form of LP, presents as flat, violaceous papules with an atrophic, pale center. Although these papules can be found anywhere on the body, they most commonly affect the trunk and/or legs on areas of the skin previously affected by classical lichen planus.3 In most cases, LP is diagnosed by observing its clinical features. A biopsy is recommended to confirm the diagnosis for more atypical cases.
Histopathology reveals thinning of the epidermis with flattening of the rete ridges, vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer, and a lichenoid mononuclear infiltrate in the papillary dermis.
If the patient is diagnosed with LP but experiences no symptoms, treatment is not needed as LP may resolve spontaneously within 1-2 years. Recurrences are common, however. Lesions may heal with hyperpigmentation. Possible treatments that can help relieve symptoms of pruritus are high potency topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antihistamines. In more severe and widespread cases, lesions may respond well to systemic corticosteroids or intralesional steroid injections.4 Phototherapy is reported to be effective as well. Acitretin, isotretinoin, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and mycophenolate mofetil are all described in the literature. It is important to note that LP on mucous membranes may be more persistent and resistant to treatment.1
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. The patient was treated with topical and intralesional steroids, as well as a course of prednisone, and her lesions improved with treatment. Hepatitis serologies were negative.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Erras of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology, and edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Usatine R, Tinitigan M. Am Fam Physician. 2011 Jul 1;84(1):53-602.
2. Lichen planus, Johns Hopkins Medicine. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
3. Atrophic lichen planus, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
4. ”Atrophic lichen planus,” Medscape, 2004 Feb 1. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
The exact cause is unknown, but possible causes include medications, dental amalgam fillings, or an autoimmune reaction. Drugs implicated in causing LP include beta-blockers, methyldopa, penicillamine, quinidine, and quinine. A meta-analysis of case-control studies show a statistically significant association between hepatitis C infection and LP patients; thus, all patients presenting with LP should be screened for hepatitis.1 Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by LP, but it is predominantly observed in middle-aged adults. Women are also twice as likely to get oral lichen planus.2
Atrophic lichen planus, the least common form of LP, presents as flat, violaceous papules with an atrophic, pale center. Although these papules can be found anywhere on the body, they most commonly affect the trunk and/or legs on areas of the skin previously affected by classical lichen planus.3 In most cases, LP is diagnosed by observing its clinical features. A biopsy is recommended to confirm the diagnosis for more atypical cases.
Histopathology reveals thinning of the epidermis with flattening of the rete ridges, vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer, and a lichenoid mononuclear infiltrate in the papillary dermis.
If the patient is diagnosed with LP but experiences no symptoms, treatment is not needed as LP may resolve spontaneously within 1-2 years. Recurrences are common, however. Lesions may heal with hyperpigmentation. Possible treatments that can help relieve symptoms of pruritus are high potency topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antihistamines. In more severe and widespread cases, lesions may respond well to systemic corticosteroids or intralesional steroid injections.4 Phototherapy is reported to be effective as well. Acitretin, isotretinoin, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and mycophenolate mofetil are all described in the literature. It is important to note that LP on mucous membranes may be more persistent and resistant to treatment.1
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. The patient was treated with topical and intralesional steroids, as well as a course of prednisone, and her lesions improved with treatment. Hepatitis serologies were negative.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Erras of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology, and edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Usatine R, Tinitigan M. Am Fam Physician. 2011 Jul 1;84(1):53-602.
2. Lichen planus, Johns Hopkins Medicine. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
3. Atrophic lichen planus, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
4. ”Atrophic lichen planus,” Medscape, 2004 Feb 1. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
The exact cause is unknown, but possible causes include medications, dental amalgam fillings, or an autoimmune reaction. Drugs implicated in causing LP include beta-blockers, methyldopa, penicillamine, quinidine, and quinine. A meta-analysis of case-control studies show a statistically significant association between hepatitis C infection and LP patients; thus, all patients presenting with LP should be screened for hepatitis.1 Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by LP, but it is predominantly observed in middle-aged adults. Women are also twice as likely to get oral lichen planus.2
Atrophic lichen planus, the least common form of LP, presents as flat, violaceous papules with an atrophic, pale center. Although these papules can be found anywhere on the body, they most commonly affect the trunk and/or legs on areas of the skin previously affected by classical lichen planus.3 In most cases, LP is diagnosed by observing its clinical features. A biopsy is recommended to confirm the diagnosis for more atypical cases.
Histopathology reveals thinning of the epidermis with flattening of the rete ridges, vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer, and a lichenoid mononuclear infiltrate in the papillary dermis.
If the patient is diagnosed with LP but experiences no symptoms, treatment is not needed as LP may resolve spontaneously within 1-2 years. Recurrences are common, however. Lesions may heal with hyperpigmentation. Possible treatments that can help relieve symptoms of pruritus are high potency topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and antihistamines. In more severe and widespread cases, lesions may respond well to systemic corticosteroids or intralesional steroid injections.4 Phototherapy is reported to be effective as well. Acitretin, isotretinoin, methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, and mycophenolate mofetil are all described in the literature. It is important to note that LP on mucous membranes may be more persistent and resistant to treatment.1
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. The patient was treated with topical and intralesional steroids, as well as a course of prednisone, and her lesions improved with treatment. Hepatitis serologies were negative.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Erras of the University of California, San Diego, and Dr. Sateesh, of San Diego Family Dermatology, and edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Usatine R, Tinitigan M. Am Fam Physician. 2011 Jul 1;84(1):53-602.
2. Lichen planus, Johns Hopkins Medicine. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
3. Atrophic lichen planus, Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
4. ”Atrophic lichen planus,” Medscape, 2004 Feb 1. [Cited 2022 Mar 13.]
Betamethasone cream did not alleviate symptoms.
A 34-year-old male presented with 10 days of a pruritic rash
Less frequently observable infectious agents associated with EM are Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Histoplasma capsulatum, and parapoxvirus (orf). Rarely, EM is triggered by drug eruption or systemic disease. Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by EM. However, it is predominantly observed in young adult patients (20-40 years of age), and there is a male predominance.
Patients typically present with the abrupt onset of symmetrical red papules that evolve into typical and atypical targetoid lesions. Lesions evolve in 48-72 hours, favoring acrofacial sites that then spread down towards the trunk. Systemic symptoms such as fever and arthralgia may accompany the skin lesions.1-3
Erythema multiforme is recognized in two forms: EM minor and EM major. Both forms share the same characteristic of target lesions. However, the presence of mucosal involvement distinguishes the two. Mucosal involvement is absent or mild in EM minor, while mucosal involvement in EM major is often severe.2,3 Painful bullous lesions are commonly present in the mouth, genital, and ocular mucous membranes. Severe symptoms can often result in difficulty eating and drinking.
Diagnosis is largely clinical. Further histologic study may accompany diagnoses to exclude differential diagnosis. In EM, direct immunofluorescence (DIF) is negative. Histopathology reveals apoptosis of individual keratinocytes.1,2
Therapeutic treatment for painful bullous lesions in the mouth involve antiseptic rinses and anesthetic solutions. Preventive treatment for patients with HSV-associated EM recurrence includes oral acyclovir or valacyclovir.2
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. A DIF was negative, and a chest x-ray was negative. Treatment was initiated with oral acyclovir, doxycycline, and a prednisone taper. In addition, topical clobetasol propionate and magic mouthwash (Maalox/lidocaine/nystatin) was prescribed. The patient was placed on daily suppressive valacyclovir to prevent frequent recurrence of EM.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Pham, the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Sateesh, San Diego Family Dermatology. Dr. Bilu-Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Hafsi W and Badri T. Erythema Multiforme, in “StatPearls [Internet].” Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology. St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008.
3. Oakley A. Erythema Multiforme. DermNet NZ. 2015 Oct.
Less frequently observable infectious agents associated with EM are Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Histoplasma capsulatum, and parapoxvirus (orf). Rarely, EM is triggered by drug eruption or systemic disease. Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by EM. However, it is predominantly observed in young adult patients (20-40 years of age), and there is a male predominance.
Patients typically present with the abrupt onset of symmetrical red papules that evolve into typical and atypical targetoid lesions. Lesions evolve in 48-72 hours, favoring acrofacial sites that then spread down towards the trunk. Systemic symptoms such as fever and arthralgia may accompany the skin lesions.1-3
Erythema multiforme is recognized in two forms: EM minor and EM major. Both forms share the same characteristic of target lesions. However, the presence of mucosal involvement distinguishes the two. Mucosal involvement is absent or mild in EM minor, while mucosal involvement in EM major is often severe.2,3 Painful bullous lesions are commonly present in the mouth, genital, and ocular mucous membranes. Severe symptoms can often result in difficulty eating and drinking.
Diagnosis is largely clinical. Further histologic study may accompany diagnoses to exclude differential diagnosis. In EM, direct immunofluorescence (DIF) is negative. Histopathology reveals apoptosis of individual keratinocytes.1,2
Therapeutic treatment for painful bullous lesions in the mouth involve antiseptic rinses and anesthetic solutions. Preventive treatment for patients with HSV-associated EM recurrence includes oral acyclovir or valacyclovir.2
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. A DIF was negative, and a chest x-ray was negative. Treatment was initiated with oral acyclovir, doxycycline, and a prednisone taper. In addition, topical clobetasol propionate and magic mouthwash (Maalox/lidocaine/nystatin) was prescribed. The patient was placed on daily suppressive valacyclovir to prevent frequent recurrence of EM.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Pham, the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Sateesh, San Diego Family Dermatology. Dr. Bilu-Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Hafsi W and Badri T. Erythema Multiforme, in “StatPearls [Internet].” Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology. St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008.
3. Oakley A. Erythema Multiforme. DermNet NZ. 2015 Oct.
Less frequently observable infectious agents associated with EM are Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Histoplasma capsulatum, and parapoxvirus (orf). Rarely, EM is triggered by drug eruption or systemic disease. Individuals of all age groups and races can be affected by EM. However, it is predominantly observed in young adult patients (20-40 years of age), and there is a male predominance.
Patients typically present with the abrupt onset of symmetrical red papules that evolve into typical and atypical targetoid lesions. Lesions evolve in 48-72 hours, favoring acrofacial sites that then spread down towards the trunk. Systemic symptoms such as fever and arthralgia may accompany the skin lesions.1-3
Erythema multiforme is recognized in two forms: EM minor and EM major. Both forms share the same characteristic of target lesions. However, the presence of mucosal involvement distinguishes the two. Mucosal involvement is absent or mild in EM minor, while mucosal involvement in EM major is often severe.2,3 Painful bullous lesions are commonly present in the mouth, genital, and ocular mucous membranes. Severe symptoms can often result in difficulty eating and drinking.
Diagnosis is largely clinical. Further histologic study may accompany diagnoses to exclude differential diagnosis. In EM, direct immunofluorescence (DIF) is negative. Histopathology reveals apoptosis of individual keratinocytes.1,2
Therapeutic treatment for painful bullous lesions in the mouth involve antiseptic rinses and anesthetic solutions. Preventive treatment for patients with HSV-associated EM recurrence includes oral acyclovir or valacyclovir.2
In this patient, a punch biopsy was performed, confirming the diagnosis. A DIF was negative, and a chest x-ray was negative. Treatment was initiated with oral acyclovir, doxycycline, and a prednisone taper. In addition, topical clobetasol propionate and magic mouthwash (Maalox/lidocaine/nystatin) was prescribed. The patient was placed on daily suppressive valacyclovir to prevent frequent recurrence of EM.
This case and photo were submitted by Ms. Pham, the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Sateesh, San Diego Family Dermatology. Dr. Bilu-Martin edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Hafsi W and Badri T. Erythema Multiforme, in “StatPearls [Internet].” Treasure Island, Fla.: StatPearls Publishing, 2022 Jan.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology. St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008.
3. Oakley A. Erythema Multiforme. DermNet NZ. 2015 Oct.
A healthy family who had been living in Brazil presented with crusted plaques on their extremities
Trypanosomatidae
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoa of the family Trypanosomatidae, called Leishmania. The vector is a sandfly infected with the protozoa.1
The three main forms of leishmaniasis – cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral – varies with the species of organism involved, the geographic distribution, and the immune response of the patient. A majority of the cases seen in the United States are from patients who contracted the disease elsewhere, particularly from Peru and Brazil.2
Lesions can vary from asymptomatic to severe. The initial lesion typically develops within weeks or months, and presents as an erythematous papule that is seen at the bite site.3 The papule evolves into a nodule or plaque that may ulcerate and crust.3 The ulcer can be distinguished by a raised and distinct border. In older stages, atrophic scarring may be seen. In some cases, the lesions may present years after exposure, because of immunosuppression or trauma.
Histology of CL reveals tuberculoid granulomas with parasitized histiocytes present. Amastigotes with distinct nuclei and kinetoplasts characterize Leishmania.2 In addition to histology, the biopsy may be sent for the press-imprint-smear method (PIS). In a study of 75 patients, the PIS method showed a higher sensitivity, as well as being a less costly and more rapid option for diagnosis.5
The treatment depends on the severity of the lesion and the species of the Leishmania genus. Mild lesions may resolve spontaneously. Topical imiquimod, cryotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and heat therapy may aid in the healing process.5 Systemic azole antifungal medications, miltefosine, and amphotericin B, and pentamidine may be used for more persistent lesions. In very severe cases, pentavalent antimonials (sodium stibogluconate, Pentostam) may be administered intravenously, although there is a high occurrence of recorded side effects.2
This case and the photos were submitted by Sabrina Liao, BS, University of California, San Diego; and Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
References
1. Leishmaniasis – Resources for Health Professionals. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Jun 3.
2. Stark CG. Leishmaniasis. Medscape. 2020 Feb 18.
3. Markle WH and Makhoul K. Am Fam Physician. 2004 Mar 15;69(6):1455-604.
4. Ngan V. Leishmaniasis. DermNet NZ. 2017 Jan. 7.
5. Sousa AQ et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014 Nov;91(5):905-7.
Trypanosomatidae
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoa of the family Trypanosomatidae, called Leishmania. The vector is a sandfly infected with the protozoa.1
The three main forms of leishmaniasis – cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral – varies with the species of organism involved, the geographic distribution, and the immune response of the patient. A majority of the cases seen in the United States are from patients who contracted the disease elsewhere, particularly from Peru and Brazil.2
Lesions can vary from asymptomatic to severe. The initial lesion typically develops within weeks or months, and presents as an erythematous papule that is seen at the bite site.3 The papule evolves into a nodule or plaque that may ulcerate and crust.3 The ulcer can be distinguished by a raised and distinct border. In older stages, atrophic scarring may be seen. In some cases, the lesions may present years after exposure, because of immunosuppression or trauma.
Histology of CL reveals tuberculoid granulomas with parasitized histiocytes present. Amastigotes with distinct nuclei and kinetoplasts characterize Leishmania.2 In addition to histology, the biopsy may be sent for the press-imprint-smear method (PIS). In a study of 75 patients, the PIS method showed a higher sensitivity, as well as being a less costly and more rapid option for diagnosis.5
The treatment depends on the severity of the lesion and the species of the Leishmania genus. Mild lesions may resolve spontaneously. Topical imiquimod, cryotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and heat therapy may aid in the healing process.5 Systemic azole antifungal medications, miltefosine, and amphotericin B, and pentamidine may be used for more persistent lesions. In very severe cases, pentavalent antimonials (sodium stibogluconate, Pentostam) may be administered intravenously, although there is a high occurrence of recorded side effects.2
This case and the photos were submitted by Sabrina Liao, BS, University of California, San Diego; and Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
References
1. Leishmaniasis – Resources for Health Professionals. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Jun 3.
2. Stark CG. Leishmaniasis. Medscape. 2020 Feb 18.
3. Markle WH and Makhoul K. Am Fam Physician. 2004 Mar 15;69(6):1455-604.
4. Ngan V. Leishmaniasis. DermNet NZ. 2017 Jan. 7.
5. Sousa AQ et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014 Nov;91(5):905-7.
Trypanosomatidae
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoa of the family Trypanosomatidae, called Leishmania. The vector is a sandfly infected with the protozoa.1
The three main forms of leishmaniasis – cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral – varies with the species of organism involved, the geographic distribution, and the immune response of the patient. A majority of the cases seen in the United States are from patients who contracted the disease elsewhere, particularly from Peru and Brazil.2
Lesions can vary from asymptomatic to severe. The initial lesion typically develops within weeks or months, and presents as an erythematous papule that is seen at the bite site.3 The papule evolves into a nodule or plaque that may ulcerate and crust.3 The ulcer can be distinguished by a raised and distinct border. In older stages, atrophic scarring may be seen. In some cases, the lesions may present years after exposure, because of immunosuppression or trauma.
Histology of CL reveals tuberculoid granulomas with parasitized histiocytes present. Amastigotes with distinct nuclei and kinetoplasts characterize Leishmania.2 In addition to histology, the biopsy may be sent for the press-imprint-smear method (PIS). In a study of 75 patients, the PIS method showed a higher sensitivity, as well as being a less costly and more rapid option for diagnosis.5
The treatment depends on the severity of the lesion and the species of the Leishmania genus. Mild lesions may resolve spontaneously. Topical imiquimod, cryotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and heat therapy may aid in the healing process.5 Systemic azole antifungal medications, miltefosine, and amphotericin B, and pentamidine may be used for more persistent lesions. In very severe cases, pentavalent antimonials (sodium stibogluconate, Pentostam) may be administered intravenously, although there is a high occurrence of recorded side effects.2
This case and the photos were submitted by Sabrina Liao, BS, University of California, San Diego; and Brooke Resh Sateesh, MD, San Diego Family Dermatology The case was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
References
1. Leishmaniasis – Resources for Health Professionals. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2021 Jun 3.
2. Stark CG. Leishmaniasis. Medscape. 2020 Feb 18.
3. Markle WH and Makhoul K. Am Fam Physician. 2004 Mar 15;69(6):1455-604.
4. Ngan V. Leishmaniasis. DermNet NZ. 2017 Jan. 7.
5. Sousa AQ et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014 Nov;91(5):905-7.
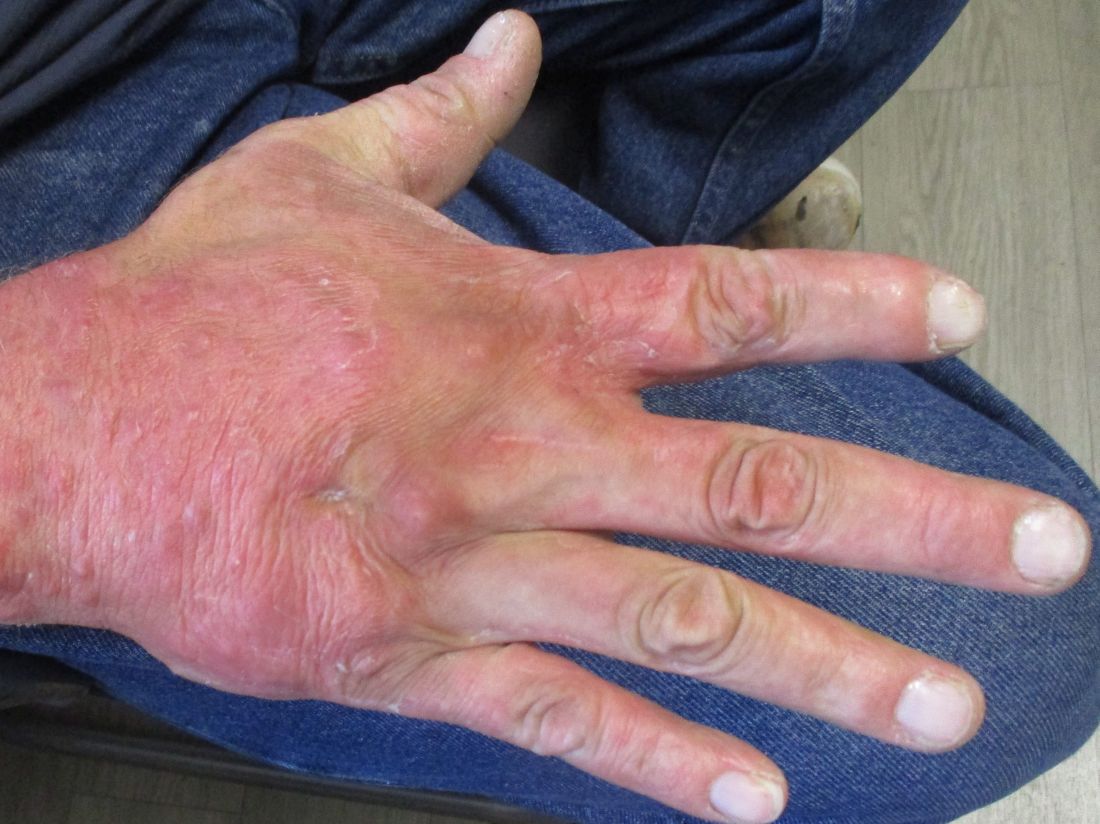
A 36-year-old presents with a mildly pruritic rash consisting of pink papules on his hand
. MG is a dermatophytic folliculitis that classically presents as folliculocentric plaque, in which there are papules, pustules, and nodules, usually found on the lower leg and almost exclusively in adults.1 Wrists are commonly affected as well.
MG is typically caused by mechanical disruption of hair follicles that allows fungi to penetrate deep into dermal tissue.2 Quite often, the source of infection is typically the patient’s skin or nails. Associated risk factors include longstanding fungal infection, shaving or other cutaneous trauma, topical steroids, and immunosuppressive therapy.3,4 Although MG can be caused by other fungal species, it is most often caused by Trichophyton rubrum or Trichophyton tonsurans.1 There are two types of MG, the perifollicular papular form, which is localized and typically occurs in healthy individuals, and the deep subcutaneous plaque or nodular forms that usually occur in immunocompromised individuals.5
MG is an important clinical manifestation to be familiar with because of the increase in the numbers of solid-organ transplants and patients on immunosuppressive therapies. These patients are highly predisposed to opportunistic infections with aggressive clinical courses and will usually require prolonged treatment as relapses are common.3,5
Tissue culture and skin biopsy are often needed to establish the diagnosis. If a topical antifungal has been used, KOH (potassium hydroxide) and culture may be negative. This patient’s tissue culture was positive for T. rubrum. The histopathology revealed hyperkeratosis and acanthosis with focal parakeratosis and a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the dermis. On PAS (Periodic acid–Schiff ) stain, PAS-positive hyphae were identified in the keratin layer, confirming a diagnosis of tinea infection.
First line treatment includes systemic antifungals such as griseofulvin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, and terbinafine. Duration of therapy is typically 4-8 weeks or until all lesions are cleared.3,5
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Hakimi of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Dr. Sateesh of San Diego Family Dermatology. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1.“Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine” (New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2012).
2. Bonifaz A et al. Gac Med Mex. Sep-Oct 2008;144(5):427-33.
3. Romero FA et al. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011 Aug;13(4):424-3. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3062.2010.00596.x
4. Chou WY, Hsu CJ. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(2):e2245. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002245.
5. Ilkit M et al. Med Mycol. 2102 Jul;50(5):449-57.
. MG is a dermatophytic folliculitis that classically presents as folliculocentric plaque, in which there are papules, pustules, and nodules, usually found on the lower leg and almost exclusively in adults.1 Wrists are commonly affected as well.
MG is typically caused by mechanical disruption of hair follicles that allows fungi to penetrate deep into dermal tissue.2 Quite often, the source of infection is typically the patient’s skin or nails. Associated risk factors include longstanding fungal infection, shaving or other cutaneous trauma, topical steroids, and immunosuppressive therapy.3,4 Although MG can be caused by other fungal species, it is most often caused by Trichophyton rubrum or Trichophyton tonsurans.1 There are two types of MG, the perifollicular papular form, which is localized and typically occurs in healthy individuals, and the deep subcutaneous plaque or nodular forms that usually occur in immunocompromised individuals.5
MG is an important clinical manifestation to be familiar with because of the increase in the numbers of solid-organ transplants and patients on immunosuppressive therapies. These patients are highly predisposed to opportunistic infections with aggressive clinical courses and will usually require prolonged treatment as relapses are common.3,5
Tissue culture and skin biopsy are often needed to establish the diagnosis. If a topical antifungal has been used, KOH (potassium hydroxide) and culture may be negative. This patient’s tissue culture was positive for T. rubrum. The histopathology revealed hyperkeratosis and acanthosis with focal parakeratosis and a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the dermis. On PAS (Periodic acid–Schiff ) stain, PAS-positive hyphae were identified in the keratin layer, confirming a diagnosis of tinea infection.
First line treatment includes systemic antifungals such as griseofulvin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, and terbinafine. Duration of therapy is typically 4-8 weeks or until all lesions are cleared.3,5
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Hakimi of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Dr. Sateesh of San Diego Family Dermatology. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1.“Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine” (New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2012).
2. Bonifaz A et al. Gac Med Mex. Sep-Oct 2008;144(5):427-33.
3. Romero FA et al. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011 Aug;13(4):424-3. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3062.2010.00596.x
4. Chou WY, Hsu CJ. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(2):e2245. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002245.
5. Ilkit M et al. Med Mycol. 2102 Jul;50(5):449-57.
. MG is a dermatophytic folliculitis that classically presents as folliculocentric plaque, in which there are papules, pustules, and nodules, usually found on the lower leg and almost exclusively in adults.1 Wrists are commonly affected as well.
MG is typically caused by mechanical disruption of hair follicles that allows fungi to penetrate deep into dermal tissue.2 Quite often, the source of infection is typically the patient’s skin or nails. Associated risk factors include longstanding fungal infection, shaving or other cutaneous trauma, topical steroids, and immunosuppressive therapy.3,4 Although MG can be caused by other fungal species, it is most often caused by Trichophyton rubrum or Trichophyton tonsurans.1 There are two types of MG, the perifollicular papular form, which is localized and typically occurs in healthy individuals, and the deep subcutaneous plaque or nodular forms that usually occur in immunocompromised individuals.5
MG is an important clinical manifestation to be familiar with because of the increase in the numbers of solid-organ transplants and patients on immunosuppressive therapies. These patients are highly predisposed to opportunistic infections with aggressive clinical courses and will usually require prolonged treatment as relapses are common.3,5
Tissue culture and skin biopsy are often needed to establish the diagnosis. If a topical antifungal has been used, KOH (potassium hydroxide) and culture may be negative. This patient’s tissue culture was positive for T. rubrum. The histopathology revealed hyperkeratosis and acanthosis with focal parakeratosis and a lymphohistiocytic infiltrate in the dermis. On PAS (Periodic acid–Schiff ) stain, PAS-positive hyphae were identified in the keratin layer, confirming a diagnosis of tinea infection.
First line treatment includes systemic antifungals such as griseofulvin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, and terbinafine. Duration of therapy is typically 4-8 weeks or until all lesions are cleared.3,5
This case and photo were submitted by Mr. Hakimi of University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Dr. Sateesh of San Diego Family Dermatology. Donna Bilu Martin, MD, edited the column.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1.“Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine” (New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2012).
2. Bonifaz A et al. Gac Med Mex. Sep-Oct 2008;144(5):427-33.
3. Romero FA et al. Transpl Infect Dis. 2011 Aug;13(4):424-3. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3062.2010.00596.x
4. Chou WY, Hsu CJ. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jan;95(2):e2245. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002245.
5. Ilkit M et al. Med Mycol. 2102 Jul;50(5):449-57.