User login
Erythematous Plaques on a Tattoo
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
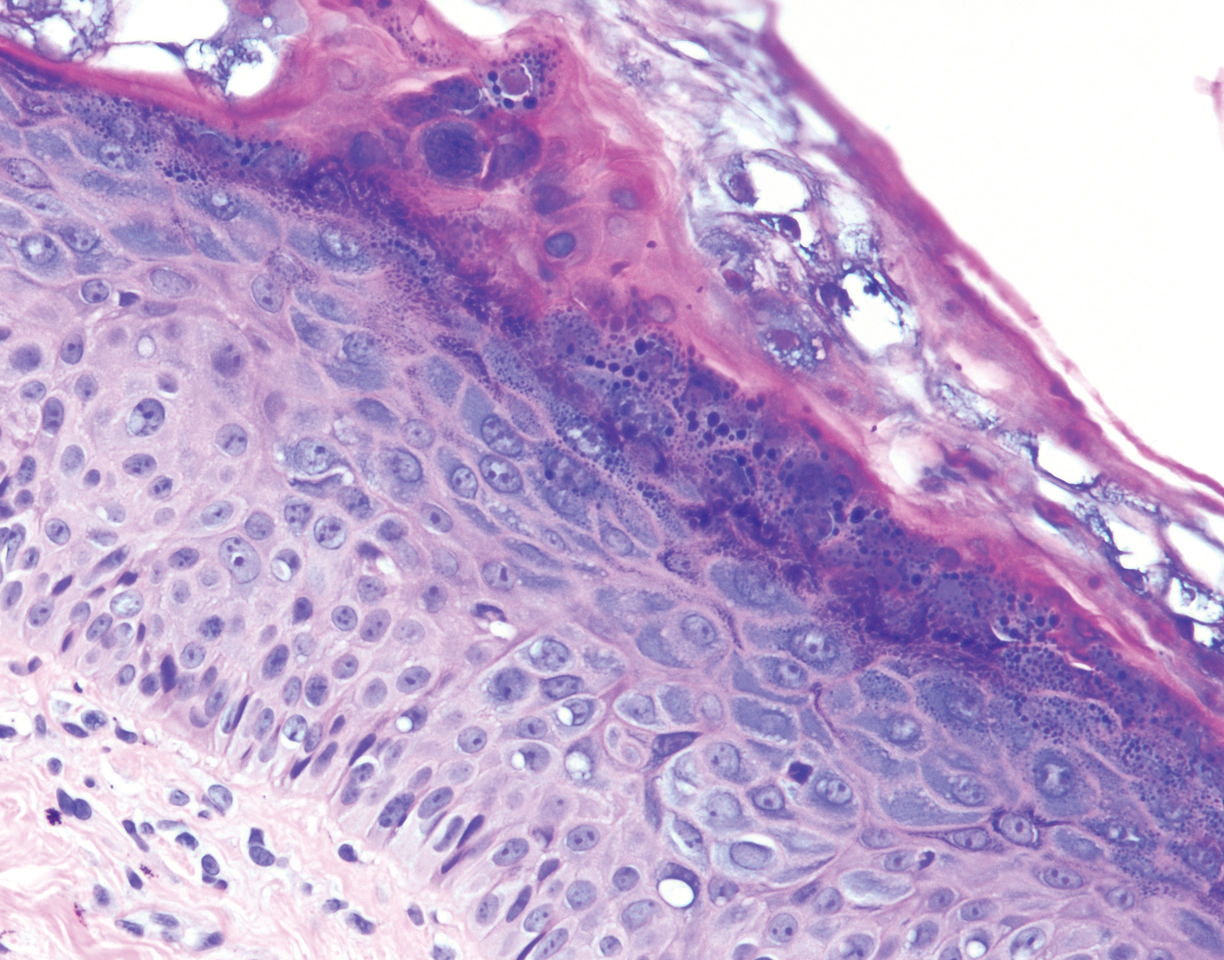
Histopathologic examination demonstrated acanthosis and coarse hypergranulosis with enlarged keratinocytes exhibiting blue cytoplasmic discoloration (Figure), which was suggestive of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV).
Acquired EV is a rare dermatologic condition associated with specific human papillomavirus (HPV) types that presents with recalcitrant lesions most commonly in the setting of immunosuppression.1 The most common HPV types associated with EV are HPV-5 and -8, but associations with HPV-3, -9, -10, -12, -14, -15, -17, -19 to -25, -36 to -38, -47, and -50 also have been reported.1,2 Acquired EV has been identified in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus, as well as in immunosuppressed patients with organ transplantation, Hodgkin lymphoma, systemic lupus erythematosus, and IgM deficiency, and in patients taking immunosuppressive medications such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.1,3 The diagnosis is clinicopathological with potential polymerase chain reaction studies to identify underlying HPV types.
Acquired EV presents as hypopigmented to red, tinea versicolor-like macules or as verrucous, flat-topped papules on the trunk, arms, and/or legs.4 Histopathology reveals viral epidermal cytopathic changes, blue cytoplasm, and coarse hypogranulosis.4
There is no standardized treatment regimen for acquired EV, and no single approach has proven to yield an efficacious clinical outcome. Topical treatment options include steroids, retinoids, immunomodulators, cryotherapy, and electrosurgery, whereas retinoids or interferon alfa have been used as oral systemic therapy. Photodynamic therapy also has been shown to improve symptoms.3 Combination therapy such as interferon alfa with zidovudine or imiquimod with oral isotretinoin has shown better results than any single treatment.4 Due to the underlying HPV infection and its role in promotion of skin cancer development, lesions can characteristically undergo malignant transformations into Bowen disease but most commonly invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), with initial lesions preferentially affecting sun-exposed areas due to the synergistic effect of UV light with EV-HPV lesions. The EV-HPV strains 5, 8, and 41 carry the highest oncogenic potential.5 Little is known of the true incidence of oncogenicity for acquired EV. Regardless, consistent sun protection and lifelong clinical examinations are critical for prognosis.5
The differential diagnosis of EV presenting in a tattoo includes allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous sarcoidosis, pityriasis versicolor, and SCC. The pathology is critical to differentiate between these entities. The most frequently reported skin reactions to tattoo ink include inflammatory diseases (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, granulomatous reaction) or infectious diseases (eg, bacterial, viral, fungal).6 Allergic contact dermatitis, typically red pigment, is a common tattoo reaction. The most common histologic feature, however, is spongiosis, which results from intercellular edema. It often is limited to the lower epidermis but may affect the upper layers if the reaction is severe.7 Cutaneous sarcoidosis is a great masquerader that can present in various ways; however, its salient features on pathology are noncaseating granuloma involving the basal cell layer and epithelioid granuloma consisting of Langerhans giant cells.8 Although pityriasis versicolor can present in young immunocompromised adults, histologically salient features are the presence of both spores and hyphae in the stratum corneum.9 Although immunosuppression is a known risk factor for SCC, it is characterized histologically by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis with thickened and elongated rete ridges. Scattered atypical cells and frequent mitoses are present.10
- Schultz B, Nguyen CV, Jacobson-Dunlop E. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in setting of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol Case Rep. 2018;4:805-807.
- DeVilliers EM, Fauquet C, Brocker TR, et al. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology. 2004;324:17-27.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Berk DR, Bruckner AL, Lu D. Epidermodysplasia verruciform-like lesions in an HIV patient. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:1.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Cappello M, et al. Skin diseases and tattoos: a five-year experience. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:644-648.
- Nixon RL, Mowad CM, Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:242-259.
- Ferringer T. Granulomatous and histiocytic diseases. In: Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko C, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. China: Elsevier; 2019:175-176.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1329-1346.
- Soyer HP, Rigel DS, McMeniman E. Actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1887-1884.
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
Histopathologic examination demonstrated acanthosis and coarse hypergranulosis with enlarged keratinocytes exhibiting blue cytoplasmic discoloration (Figure), which was suggestive of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV).

Acquired EV is a rare dermatologic condition associated with specific human papillomavirus (HPV) types that presents with recalcitrant lesions most commonly in the setting of immunosuppression.1 The most common HPV types associated with EV are HPV-5 and -8, but associations with HPV-3, -9, -10, -12, -14, -15, -17, -19 to -25, -36 to -38, -47, and -50 also have been reported.1,2 Acquired EV has been identified in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus, as well as in immunosuppressed patients with organ transplantation, Hodgkin lymphoma, systemic lupus erythematosus, and IgM deficiency, and in patients taking immunosuppressive medications such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.1,3 The diagnosis is clinicopathological with potential polymerase chain reaction studies to identify underlying HPV types.
Acquired EV presents as hypopigmented to red, tinea versicolor-like macules or as verrucous, flat-topped papules on the trunk, arms, and/or legs.4 Histopathology reveals viral epidermal cytopathic changes, blue cytoplasm, and coarse hypogranulosis.4
There is no standardized treatment regimen for acquired EV, and no single approach has proven to yield an efficacious clinical outcome. Topical treatment options include steroids, retinoids, immunomodulators, cryotherapy, and electrosurgery, whereas retinoids or interferon alfa have been used as oral systemic therapy. Photodynamic therapy also has been shown to improve symptoms.3 Combination therapy such as interferon alfa with zidovudine or imiquimod with oral isotretinoin has shown better results than any single treatment.4 Due to the underlying HPV infection and its role in promotion of skin cancer development, lesions can characteristically undergo malignant transformations into Bowen disease but most commonly invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), with initial lesions preferentially affecting sun-exposed areas due to the synergistic effect of UV light with EV-HPV lesions. The EV-HPV strains 5, 8, and 41 carry the highest oncogenic potential.5 Little is known of the true incidence of oncogenicity for acquired EV. Regardless, consistent sun protection and lifelong clinical examinations are critical for prognosis.5
The differential diagnosis of EV presenting in a tattoo includes allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous sarcoidosis, pityriasis versicolor, and SCC. The pathology is critical to differentiate between these entities. The most frequently reported skin reactions to tattoo ink include inflammatory diseases (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, granulomatous reaction) or infectious diseases (eg, bacterial, viral, fungal).6 Allergic contact dermatitis, typically red pigment, is a common tattoo reaction. The most common histologic feature, however, is spongiosis, which results from intercellular edema. It often is limited to the lower epidermis but may affect the upper layers if the reaction is severe.7 Cutaneous sarcoidosis is a great masquerader that can present in various ways; however, its salient features on pathology are noncaseating granuloma involving the basal cell layer and epithelioid granuloma consisting of Langerhans giant cells.8 Although pityriasis versicolor can present in young immunocompromised adults, histologically salient features are the presence of both spores and hyphae in the stratum corneum.9 Although immunosuppression is a known risk factor for SCC, it is characterized histologically by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis with thickened and elongated rete ridges. Scattered atypical cells and frequent mitoses are present.10
The Diagnosis: Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis
Histopathologic examination demonstrated acanthosis and coarse hypergranulosis with enlarged keratinocytes exhibiting blue cytoplasmic discoloration (Figure), which was suggestive of acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV).

Acquired EV is a rare dermatologic condition associated with specific human papillomavirus (HPV) types that presents with recalcitrant lesions most commonly in the setting of immunosuppression.1 The most common HPV types associated with EV are HPV-5 and -8, but associations with HPV-3, -9, -10, -12, -14, -15, -17, -19 to -25, -36 to -38, -47, and -50 also have been reported.1,2 Acquired EV has been identified in individuals with human immunodeficiency virus, as well as in immunosuppressed patients with organ transplantation, Hodgkin lymphoma, systemic lupus erythematosus, and IgM deficiency, and in patients taking immunosuppressive medications such as tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.1,3 The diagnosis is clinicopathological with potential polymerase chain reaction studies to identify underlying HPV types.
Acquired EV presents as hypopigmented to red, tinea versicolor-like macules or as verrucous, flat-topped papules on the trunk, arms, and/or legs.4 Histopathology reveals viral epidermal cytopathic changes, blue cytoplasm, and coarse hypogranulosis.4
There is no standardized treatment regimen for acquired EV, and no single approach has proven to yield an efficacious clinical outcome. Topical treatment options include steroids, retinoids, immunomodulators, cryotherapy, and electrosurgery, whereas retinoids or interferon alfa have been used as oral systemic therapy. Photodynamic therapy also has been shown to improve symptoms.3 Combination therapy such as interferon alfa with zidovudine or imiquimod with oral isotretinoin has shown better results than any single treatment.4 Due to the underlying HPV infection and its role in promotion of skin cancer development, lesions can characteristically undergo malignant transformations into Bowen disease but most commonly invasive squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), with initial lesions preferentially affecting sun-exposed areas due to the synergistic effect of UV light with EV-HPV lesions. The EV-HPV strains 5, 8, and 41 carry the highest oncogenic potential.5 Little is known of the true incidence of oncogenicity for acquired EV. Regardless, consistent sun protection and lifelong clinical examinations are critical for prognosis.5
The differential diagnosis of EV presenting in a tattoo includes allergic contact dermatitis, cutaneous sarcoidosis, pityriasis versicolor, and SCC. The pathology is critical to differentiate between these entities. The most frequently reported skin reactions to tattoo ink include inflammatory diseases (eg, allergic contact dermatitis, granulomatous reaction) or infectious diseases (eg, bacterial, viral, fungal).6 Allergic contact dermatitis, typically red pigment, is a common tattoo reaction. The most common histologic feature, however, is spongiosis, which results from intercellular edema. It often is limited to the lower epidermis but may affect the upper layers if the reaction is severe.7 Cutaneous sarcoidosis is a great masquerader that can present in various ways; however, its salient features on pathology are noncaseating granuloma involving the basal cell layer and epithelioid granuloma consisting of Langerhans giant cells.8 Although pityriasis versicolor can present in young immunocompromised adults, histologically salient features are the presence of both spores and hyphae in the stratum corneum.9 Although immunosuppression is a known risk factor for SCC, it is characterized histologically by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and acanthosis with thickened and elongated rete ridges. Scattered atypical cells and frequent mitoses are present.10
- Schultz B, Nguyen CV, Jacobson-Dunlop E. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in setting of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol Case Rep. 2018;4:805-807.
- DeVilliers EM, Fauquet C, Brocker TR, et al. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology. 2004;324:17-27.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Berk DR, Bruckner AL, Lu D. Epidermodysplasia verruciform-like lesions in an HIV patient. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:1.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Cappello M, et al. Skin diseases and tattoos: a five-year experience. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:644-648.
- Nixon RL, Mowad CM, Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:242-259.
- Ferringer T. Granulomatous and histiocytic diseases. In: Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko C, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. China: Elsevier; 2019:175-176.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1329-1346.
- Soyer HP, Rigel DS, McMeniman E. Actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1887-1884.
- Schultz B, Nguyen CV, Jacobson-Dunlop E. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis in setting of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol Case Rep. 2018;4:805-807.
- DeVilliers EM, Fauquet C, Brocker TR, et al. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology. 2004;324:17-27.
- Zampetti A, Giurdanella F, Manco S, et al. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis: a comprehensive review and a proposal for treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:974-980.
- Henley JK, Hossler EW. Acquired epidermodysplasia verruciformis occurring in a renal transplant recipient. Cutis. 2017;99:E9-E12.
- Berk DR, Bruckner AL, Lu D. Epidermodysplasia verruciform-like lesions in an HIV patient. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:1.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Cappello M, et al. Skin diseases and tattoos: a five-year experience. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:644-648.
- Nixon RL, Mowad CM, Marks JG Jr. Allergic contact dermatitis. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:242-259.
- Ferringer T. Granulomatous and histiocytic diseases. In: Elston DM, Ferringer T, Ko C, et al, eds. Dermatopathology. 3rd ed. China: Elsevier; 2019:175-176.
- Elewski BE, Hughey LC, Hunt KM, et al. Fungal diseases. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1329-1346.
- Soyer HP, Rigel DS, McMeniman E. Actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. In: Bolognia J, Jorizzo JL, Schaffer JV, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2018:1887-1884.
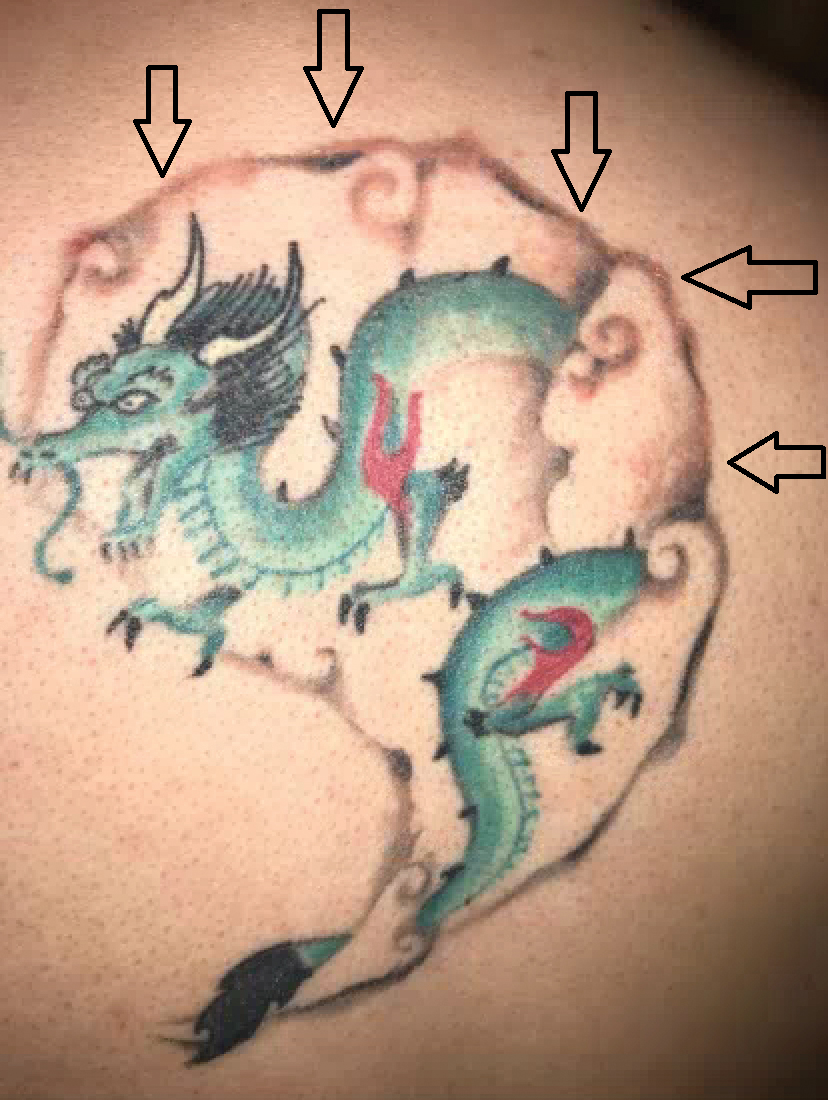
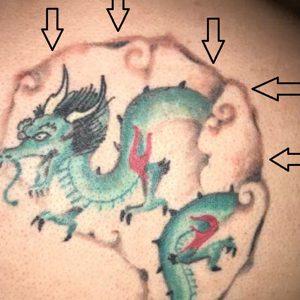
A 29-year-old man presented with increased redness, dryness, and pruritus at the periphery of a tattoo (arrows) on the upper back of 4 months' duration. He was diagnosed with human immunodeficiency virus 8 months prior to presentation and had a history of cystic fibrosis, eczema, and genital molluscum contagiosum. Laboratory analysis 1 month prior revealed a CD4 count of 42 cells/mm3 (reference range, 500-1200 cells/mm3), and the viral load was 2388 copies/mL (reference range, 20-10,000,000 copies/mL). Physical examination revealed multiple erythematous, eczematous, linear plaques along the dark gray lines of the tattoo. A 1.1.2 ×0.7.2 ×0.1-cm shave biopsy specimen was obtained. After the biopsy, tretinoin cream 0.1% and betamethasone dipropionate ointment 0.05% were prescribed to be alternately applied on the tattoo lesions until resolution.
Tense Bullae on the Hands
The Diagnosis: Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder characterized by tense bullae, skin fragility, atrophic scarring, and milia formation.1 Blisters occur on a noninflammatory base in the classic variant and are trauma induced, hence the predilection for the extensor surfaces.2 Mucosal involvement also has been described.1 The characteristic findings in EBA are IgG autoantibodies directed at the N-terminal collagenous domain of type VII collagen, which composes the anchoring fibrils in the basement membrane zone.1 Differentiating EBA from other subepidermal bullous diseases, especially bullous pemphigoid (BP), can be difficult, necessitating specialized tests.
Biopsy of the perilesional skin can help identify the location of the blister formation. Our patient's biopsy showed a subepidermal blister with granulocytes. The differential diagnosis of a subepidermal blister includes BP, herpes gestationis, cicatricial pemphigoid, EBA, bullous systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatitis herpetiformis, linear IgA disease, and porphyria cutanea tarda.
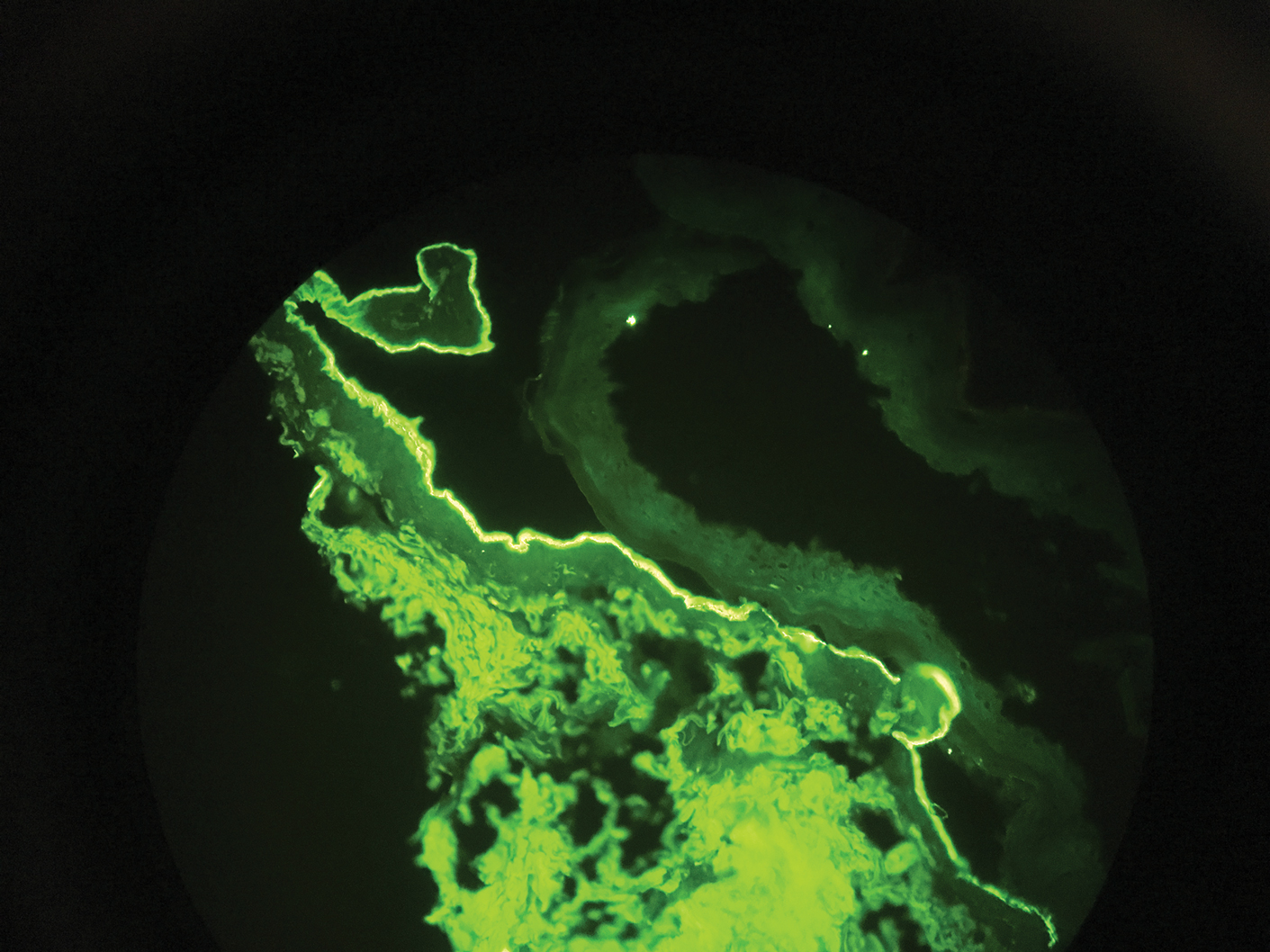
Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) was performed on the biopsy from our patient, which showed linear/particulate IgG, C3, and IgA deposits in the basement membrane zone, narrowing the differential diagnosis to BP or EBA. To differentiate EBA from BP, DIF of perilesional skin using a salt-split preparation was performed. This test distinguishes the location of the immunoreactants at the basement membrane zone. The antibody complexes in BP are found on the epidermal side of the split, while the antibody complexes in EBA are found on the dermal side of the split. Indirect immunofluorescence on salt-split skin also has been used to distinguish EBA from BP but is only conclusive if there are circulating autoantibodies to the basement membrane zone in the serum, which occurs in approximately 50% of patients with EBA and 15% of patients with BP.3 The immune complexes in our patient were found to be on the dermal side of the split after DIF on salt-split skin, confirming the diagnosis of EBA (Figure).
Differentiating EBA from BP has great value, as the diagnosis affects treatment options. Bullous pemphigoid is fairly easy to treat, with most patients responding to prednisone.3 Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita usually is resistant to therapy. The disease course is chronic with exacerbations and remissions. Dapsone often is used to control the disease, though this therapy for EBA is not currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The recommended initial dose of dapsone is 50 mg daily and should be increased by 50 mg each week until remission, usually 100 to 250 mg.4 We prescribed dapsone for our patient upon clinical suspicion of EBA before the DIF on salt-split skin was completed. A trial of prednisone may be warranted for EBA if there is no response to dapsone or colchicine, but the response is unpredictable. Cyclosporine usually results in a quick response and may be considered if there is clinically severe disease and other treatment alternatives have failed.4
- Ishii N, Hamada T, Dainichi T, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: what's new. J Dermatol. 2010;37:220-230.
- Lehman JS, Camilleri MJ, Gibsom LE. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: concise review and practical considerations. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:227-236.
- Woodley D. Immunofluorescence on the salt-split skin for the diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:229-231.
- Mutasim DF. Bullous diseases. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:978-982.
The Diagnosis: Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder characterized by tense bullae, skin fragility, atrophic scarring, and milia formation.1 Blisters occur on a noninflammatory base in the classic variant and are trauma induced, hence the predilection for the extensor surfaces.2 Mucosal involvement also has been described.1 The characteristic findings in EBA are IgG autoantibodies directed at the N-terminal collagenous domain of type VII collagen, which composes the anchoring fibrils in the basement membrane zone.1 Differentiating EBA from other subepidermal bullous diseases, especially bullous pemphigoid (BP), can be difficult, necessitating specialized tests.
Biopsy of the perilesional skin can help identify the location of the blister formation. Our patient's biopsy showed a subepidermal blister with granulocytes. The differential diagnosis of a subepidermal blister includes BP, herpes gestationis, cicatricial pemphigoid, EBA, bullous systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatitis herpetiformis, linear IgA disease, and porphyria cutanea tarda.
Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) was performed on the biopsy from our patient, which showed linear/particulate IgG, C3, and IgA deposits in the basement membrane zone, narrowing the differential diagnosis to BP or EBA. To differentiate EBA from BP, DIF of perilesional skin using a salt-split preparation was performed. This test distinguishes the location of the immunoreactants at the basement membrane zone. The antibody complexes in BP are found on the epidermal side of the split, while the antibody complexes in EBA are found on the dermal side of the split. Indirect immunofluorescence on salt-split skin also has been used to distinguish EBA from BP but is only conclusive if there are circulating autoantibodies to the basement membrane zone in the serum, which occurs in approximately 50% of patients with EBA and 15% of patients with BP.3 The immune complexes in our patient were found to be on the dermal side of the split after DIF on salt-split skin, confirming the diagnosis of EBA (Figure).
Differentiating EBA from BP has great value, as the diagnosis affects treatment options. Bullous pemphigoid is fairly easy to treat, with most patients responding to prednisone.3 Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita usually is resistant to therapy. The disease course is chronic with exacerbations and remissions. Dapsone often is used to control the disease, though this therapy for EBA is not currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The recommended initial dose of dapsone is 50 mg daily and should be increased by 50 mg each week until remission, usually 100 to 250 mg.4 We prescribed dapsone for our patient upon clinical suspicion of EBA before the DIF on salt-split skin was completed. A trial of prednisone may be warranted for EBA if there is no response to dapsone or colchicine, but the response is unpredictable. Cyclosporine usually results in a quick response and may be considered if there is clinically severe disease and other treatment alternatives have failed.4
The Diagnosis: Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA) is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder characterized by tense bullae, skin fragility, atrophic scarring, and milia formation.1 Blisters occur on a noninflammatory base in the classic variant and are trauma induced, hence the predilection for the extensor surfaces.2 Mucosal involvement also has been described.1 The characteristic findings in EBA are IgG autoantibodies directed at the N-terminal collagenous domain of type VII collagen, which composes the anchoring fibrils in the basement membrane zone.1 Differentiating EBA from other subepidermal bullous diseases, especially bullous pemphigoid (BP), can be difficult, necessitating specialized tests.
Biopsy of the perilesional skin can help identify the location of the blister formation. Our patient's biopsy showed a subepidermal blister with granulocytes. The differential diagnosis of a subepidermal blister includes BP, herpes gestationis, cicatricial pemphigoid, EBA, bullous systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatitis herpetiformis, linear IgA disease, and porphyria cutanea tarda.
Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) was performed on the biopsy from our patient, which showed linear/particulate IgG, C3, and IgA deposits in the basement membrane zone, narrowing the differential diagnosis to BP or EBA. To differentiate EBA from BP, DIF of perilesional skin using a salt-split preparation was performed. This test distinguishes the location of the immunoreactants at the basement membrane zone. The antibody complexes in BP are found on the epidermal side of the split, while the antibody complexes in EBA are found on the dermal side of the split. Indirect immunofluorescence on salt-split skin also has been used to distinguish EBA from BP but is only conclusive if there are circulating autoantibodies to the basement membrane zone in the serum, which occurs in approximately 50% of patients with EBA and 15% of patients with BP.3 The immune complexes in our patient were found to be on the dermal side of the split after DIF on salt-split skin, confirming the diagnosis of EBA (Figure).
Differentiating EBA from BP has great value, as the diagnosis affects treatment options. Bullous pemphigoid is fairly easy to treat, with most patients responding to prednisone.3 Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita usually is resistant to therapy. The disease course is chronic with exacerbations and remissions. Dapsone often is used to control the disease, though this therapy for EBA is not currently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. The recommended initial dose of dapsone is 50 mg daily and should be increased by 50 mg each week until remission, usually 100 to 250 mg.4 We prescribed dapsone for our patient upon clinical suspicion of EBA before the DIF on salt-split skin was completed. A trial of prednisone may be warranted for EBA if there is no response to dapsone or colchicine, but the response is unpredictable. Cyclosporine usually results in a quick response and may be considered if there is clinically severe disease and other treatment alternatives have failed.4
- Ishii N, Hamada T, Dainichi T, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: what's new. J Dermatol. 2010;37:220-230.
- Lehman JS, Camilleri MJ, Gibsom LE. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: concise review and practical considerations. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:227-236.
- Woodley D. Immunofluorescence on the salt-split skin for the diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:229-231.
- Mutasim DF. Bullous diseases. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:978-982.
- Ishii N, Hamada T, Dainichi T, et al. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: what's new. J Dermatol. 2010;37:220-230.
- Lehman JS, Camilleri MJ, Gibsom LE. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: concise review and practical considerations. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:227-236.
- Woodley D. Immunofluorescence on the salt-split skin for the diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:229-231.
- Mutasim DF. Bullous diseases. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:978-982.
A 75-year-old man presented to our clinic with nonpainful, nonpruritic, tense bullae and erosions on the dorsal aspects of the hands and extensor surfaces of the elbows of 1 month's duration. The patient also had erythematous erosions and crusted papules on the left cheek and surrounding the left eye. He denied any new medications, history of liver or kidney disease, or history of hepatitis or human immunodeficiency virus. There were no obvious exacerbating factors, including exposure to sunlight. Direct immunofluorescence using a salt-split preparation was performed on a biopsy of the perilesional skin.
Bowel-Associated Dermatosis-Arthritis Syndrome in a Patient With Crohn Disease
To the Editor:
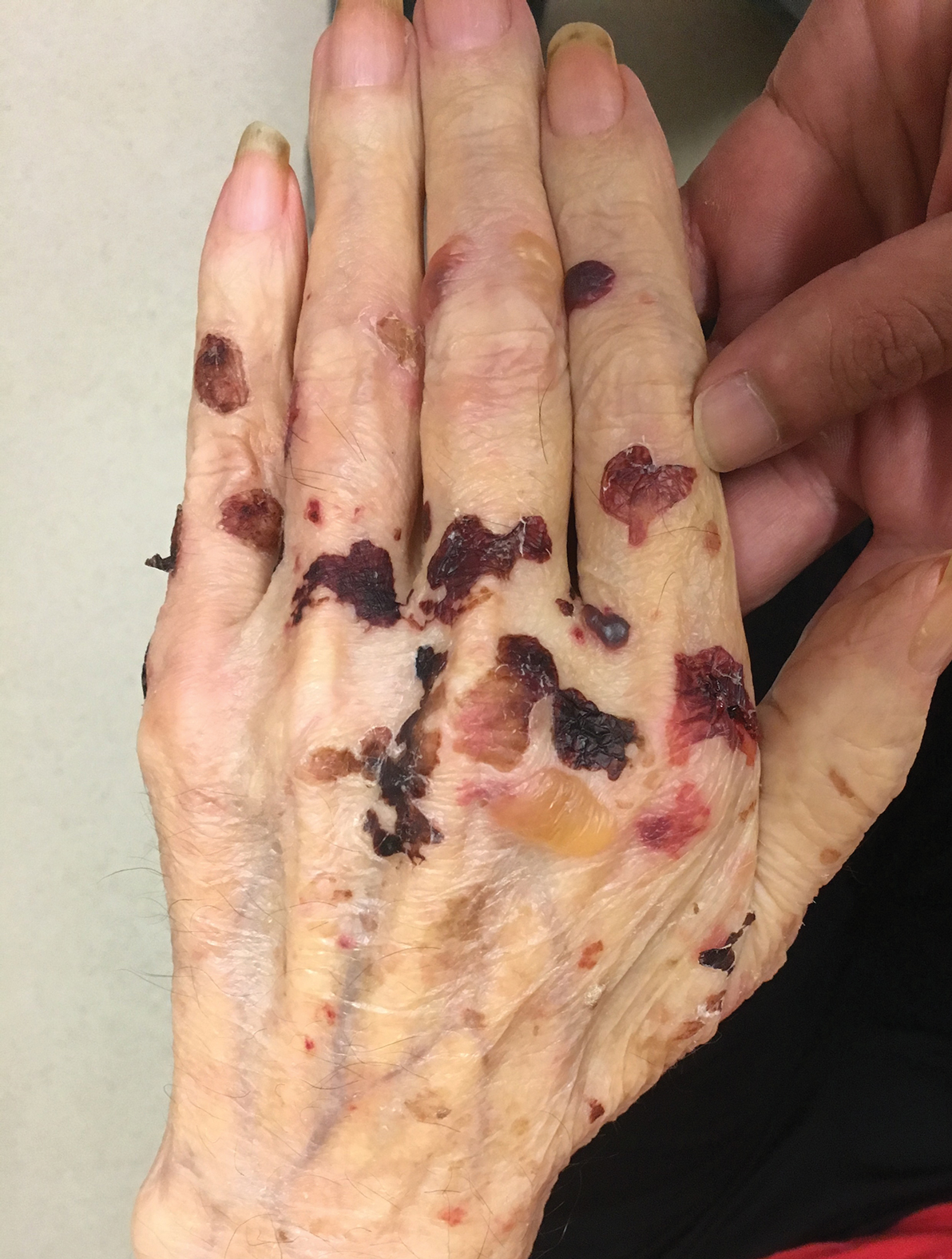
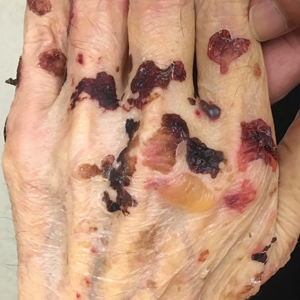
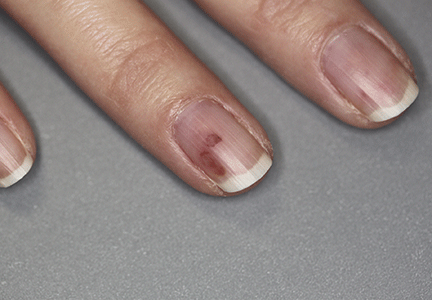
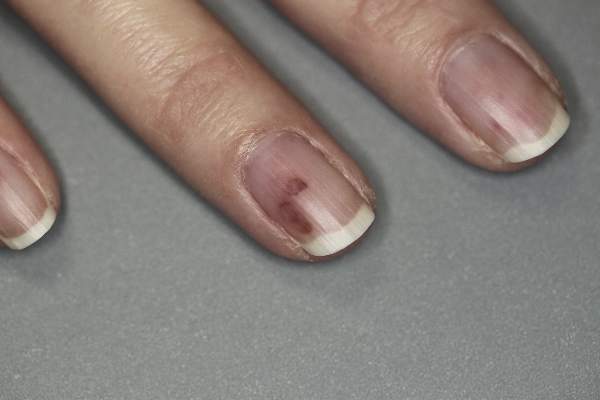
A 42-year-old woman with Crohn disease of 10 years’ duration presented to the clinic with a chief concern of nonpruritic pustular lesions on the bilateral arms. Physical examination revealed several pustules on the arms with secondary excoriation. She also had a warm tender nodule on the left upper shin and subungual hemorrhages under the fingernails (Figure 1). The patient had previously undergone infliximab therapy, which was discontinued 10 months prior to presentation in anticipation of a partial colectomy and temporary ileostomy that was performed 8 months prior to presentation. She recently had developed bilateral, radiating, sharp lower extremity pain extending from the feet to the hips over the last 2 weeks and swelling of the bilateral legs that impaired her ability to ambulate. Additionally, she had recently traveled to Colorado and a Lyme disease workup was initiated at an outside hospital in Colorado; however, the results were pending. The outside hospital also performed a spinal tap that was negative. At our clinic, biopsies were performed on the shin nodule and a right palmar pustule (Figure 2). There was clinical suspicion of erythema nodosum and subcorneal pustular dermatosis or a vesiculopustular skin manifestation of the patient’s Crohn disease. The patient was switched from generic doxycycline to a brand name variant 150 mg every night at bedtime for 2 weeks. She subsequently was admitted to the inpatient rheumatology service for a complete systemic workup.

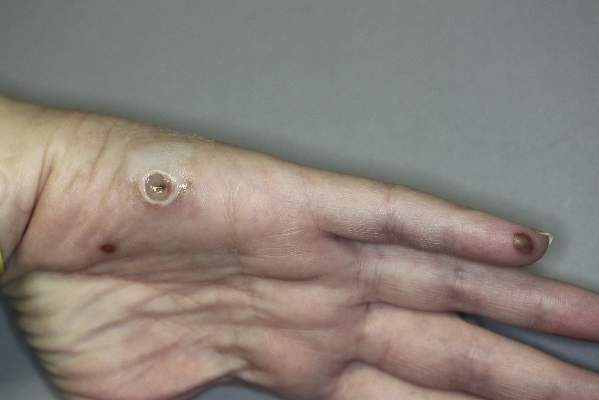
The punch biopsy of the left upper shin demonstrated operative hemorrhage and periadnexal lymphocytic inflammation without evidence of fungal or bacterial elements by Gram or Gomori methenamine-silver stain. Clinically, the diagnosis was most likely erythema nodosum, though insufficient hypodermis was present to make the diagnosis with pathology. The shave biopsy of the right medial palm was nondiagnostic but showed a transected pustule with no bacterial or fungal elements by Gram or Gomori methenamine-silver stain (Figure 3). Given the clinical context, the likely pathologic diagnosis was vesiculopustular Crohn disease.
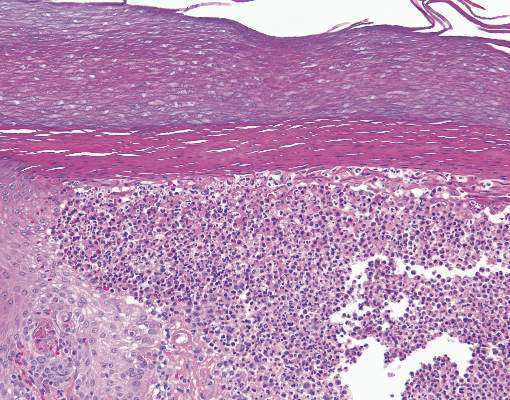
Our patient was started on an empiric steroid trial with rapid improvement of the arthralgia and rash. The presumed diagnosis was a Crohn disease flare and the patient was discharged on an 8-week steroid taper. Three weeks later at a follow-up appointment, the patient’s skin lesions had nearly resolved. The swelling of the legs and feet had substantially decreased, but the joint pain, primarily in the ankles, persisted.
Routine laboratory studies showed a hemoglobin level of 11.6 g/dL (reference range, 12–15 g/dL), white blood cell count of 9.1 K/μL (reference range, 4.5–11.0 K/μL), C-reactive protein level of 20.15 mg/dL (reference range, <1.0 mg/dL), and an antinuclear antibody titer of 160 (<80). Serology for Lyme disease was negative. Serum chemistries were all within reference range and an echocardiogram was normal.
Up to one-third of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) experience extraintestinal manifestations of their condition. Of these patients, nearly one-third will develop cutaneous manifestations.1 The most common skin diseases associated with IBD are pyoderma gangrenosum and erythema nodosum.2 The differential diagnoses considered in this unique case included early pyoderma gangrenosum, subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease), and vesiculopustular Crohn disease. Vesiculopustular Crohn disease is a rare component of IBD and also can be present in bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome (BADAS). In BADAS, symptoms often include arthritis and systemic symptoms such as fever and malaise. The skin manifestations typically involve the arms and trunk. It often is seen after intestinal bypass surgery but also can be present in patients with gastrointestinal diseases such as IBD.3 Due to its early association with bypass surgery, BADAS previously was referred to as bowel bypass syndrome but has since been seen in relation to other intestinal surgeries and IBD.4 Patients with BADAS often present with episodes of fever, fatigue, and malaise, in addition to arthralgia and cutaneous eruptions. Cases of BADAS related to IBD instead of bypass surgery often can be less severe in nature. Unlike many of these previously reported cases, our patient’s joint pain primarily was in the knees and ankles, whereas typical cases of BADAS cause upper extremity (ie, shoulder, elbow) arthralgia. Our patient occasionally experienced upper extremity pain, but it was less frequent and less severe than the knee and ankle pain. The vesiculopustular lesions in BADAS usually begin as 3- to 10-mm painful macules that then develop into aseptic pustular lesions. These manifestations arise on the upper arms and chest or trunk and can be accompanied by erythema nodosum on the legs.4
It has been hypothesized that BADAS occurs as an immune reaction to bacterial overgrowth in the bowel from IBD, infection, or surgery. The reaction is in response to a bacterial antigen and manifests cutaneously.5 This same pathogenesis is thought to cause various other manifestations of Crohn disease such as erythema nodosum. Bacteria that incite this immune response include Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, and Streptococcus.
Resolution of both vesiculopustular Crohn disease and of BADAS often occurs with treatment of the underlying IBD but also can be improved with steroids and antibiotics. However, response to antibiotics often is variable.5,6 The mainstay for treatment remains steroids and management of underlying bowel disease.
Bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome often is overlooked when compiling differential diagnoses for neutrophilic dermatoses but should be considered in patients with bowel disease or recent surgery. Because the syndrome can be recurrent, early diagnosis can help to prevent and treat relapsing courses of BADAS.
- Trost LB, McDonnell JK. Important cutaneous manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Postgrad Med J. 2005;81:580-585.
- Havemann BD. A pustular skin rash in a woman with 2 weeks of diarrhea. MedGenMed. 2005;7:11.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo J, Rapini RP. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2008.
- Huang B, Chandra S, Shih DQ. Skin manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Front Physiol. 2012;3:13.
- Truchuelo MT, Alcántara J, Vano-Galván S, et al. Bowel associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome: another cutaneous manifestation of inflammatory intestinal disease. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:1596-1598.
- Ashok D, Kiely P. Bowel associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2007;1:81.
To the Editor:
A 42-year-old woman with Crohn disease of 10 years’ duration presented to the clinic with a chief concern of nonpruritic pustular lesions on the bilateral arms. Physical examination revealed several pustules on the arms with secondary excoriation. She also had a warm tender nodule on the left upper shin and subungual hemorrhages under the fingernails (Figure 1). The patient had previously undergone infliximab therapy, which was discontinued 10 months prior to presentation in anticipation of a partial colectomy and temporary ileostomy that was performed 8 months prior to presentation. She recently had developed bilateral, radiating, sharp lower extremity pain extending from the feet to the hips over the last 2 weeks and swelling of the bilateral legs that impaired her ability to ambulate. Additionally, she had recently traveled to Colorado and a Lyme disease workup was initiated at an outside hospital in Colorado; however, the results were pending. The outside hospital also performed a spinal tap that was negative. At our clinic, biopsies were performed on the shin nodule and a right palmar pustule (Figure 2). There was clinical suspicion of erythema nodosum and subcorneal pustular dermatosis or a vesiculopustular skin manifestation of the patient’s Crohn disease. The patient was switched from generic doxycycline to a brand name variant 150 mg every night at bedtime for 2 weeks. She subsequently was admitted to the inpatient rheumatology service for a complete systemic workup.


The punch biopsy of the left upper shin demonstrated operative hemorrhage and periadnexal lymphocytic inflammation without evidence of fungal or bacterial elements by Gram or Gomori methenamine-silver stain. Clinically, the diagnosis was most likely erythema nodosum, though insufficient hypodermis was present to make the diagnosis with pathology. The shave biopsy of the right medial palm was nondiagnostic but showed a transected pustule with no bacterial or fungal elements by Gram or Gomori methenamine-silver stain (Figure 3). Given the clinical context, the likely pathologic diagnosis was vesiculopustular Crohn disease.

Our patient was started on an empiric steroid trial with rapid improvement of the arthralgia and rash. The presumed diagnosis was a Crohn disease flare and the patient was discharged on an 8-week steroid taper. Three weeks later at a follow-up appointment, the patient’s skin lesions had nearly resolved. The swelling of the legs and feet had substantially decreased, but the joint pain, primarily in the ankles, persisted.
Routine laboratory studies showed a hemoglobin level of 11.6 g/dL (reference range, 12–15 g/dL), white blood cell count of 9.1 K/μL (reference range, 4.5–11.0 K/μL), C-reactive protein level of 20.15 mg/dL (reference range, <1.0 mg/dL), and an antinuclear antibody titer of 160 (<80). Serology for Lyme disease was negative. Serum chemistries were all within reference range and an echocardiogram was normal.
Up to one-third of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) experience extraintestinal manifestations of their condition. Of these patients, nearly one-third will develop cutaneous manifestations.1 The most common skin diseases associated with IBD are pyoderma gangrenosum and erythema nodosum.2 The differential diagnoses considered in this unique case included early pyoderma gangrenosum, subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease), and vesiculopustular Crohn disease. Vesiculopustular Crohn disease is a rare component of IBD and also can be present in bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome (BADAS). In BADAS, symptoms often include arthritis and systemic symptoms such as fever and malaise. The skin manifestations typically involve the arms and trunk. It often is seen after intestinal bypass surgery but also can be present in patients with gastrointestinal diseases such as IBD.3 Due to its early association with bypass surgery, BADAS previously was referred to as bowel bypass syndrome but has since been seen in relation to other intestinal surgeries and IBD.4 Patients with BADAS often present with episodes of fever, fatigue, and malaise, in addition to arthralgia and cutaneous eruptions. Cases of BADAS related to IBD instead of bypass surgery often can be less severe in nature. Unlike many of these previously reported cases, our patient’s joint pain primarily was in the knees and ankles, whereas typical cases of BADAS cause upper extremity (ie, shoulder, elbow) arthralgia. Our patient occasionally experienced upper extremity pain, but it was less frequent and less severe than the knee and ankle pain. The vesiculopustular lesions in BADAS usually begin as 3- to 10-mm painful macules that then develop into aseptic pustular lesions. These manifestations arise on the upper arms and chest or trunk and can be accompanied by erythema nodosum on the legs.4
It has been hypothesized that BADAS occurs as an immune reaction to bacterial overgrowth in the bowel from IBD, infection, or surgery. The reaction is in response to a bacterial antigen and manifests cutaneously.5 This same pathogenesis is thought to cause various other manifestations of Crohn disease such as erythema nodosum. Bacteria that incite this immune response include Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, and Streptococcus.
Resolution of both vesiculopustular Crohn disease and of BADAS often occurs with treatment of the underlying IBD but also can be improved with steroids and antibiotics. However, response to antibiotics often is variable.5,6 The mainstay for treatment remains steroids and management of underlying bowel disease.
Bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome often is overlooked when compiling differential diagnoses for neutrophilic dermatoses but should be considered in patients with bowel disease or recent surgery. Because the syndrome can be recurrent, early diagnosis can help to prevent and treat relapsing courses of BADAS.
To the Editor:
A 42-year-old woman with Crohn disease of 10 years’ duration presented to the clinic with a chief concern of nonpruritic pustular lesions on the bilateral arms. Physical examination revealed several pustules on the arms with secondary excoriation. She also had a warm tender nodule on the left upper shin and subungual hemorrhages under the fingernails (Figure 1). The patient had previously undergone infliximab therapy, which was discontinued 10 months prior to presentation in anticipation of a partial colectomy and temporary ileostomy that was performed 8 months prior to presentation. She recently had developed bilateral, radiating, sharp lower extremity pain extending from the feet to the hips over the last 2 weeks and swelling of the bilateral legs that impaired her ability to ambulate. Additionally, she had recently traveled to Colorado and a Lyme disease workup was initiated at an outside hospital in Colorado; however, the results were pending. The outside hospital also performed a spinal tap that was negative. At our clinic, biopsies were performed on the shin nodule and a right palmar pustule (Figure 2). There was clinical suspicion of erythema nodosum and subcorneal pustular dermatosis or a vesiculopustular skin manifestation of the patient’s Crohn disease. The patient was switched from generic doxycycline to a brand name variant 150 mg every night at bedtime for 2 weeks. She subsequently was admitted to the inpatient rheumatology service for a complete systemic workup.


The punch biopsy of the left upper shin demonstrated operative hemorrhage and periadnexal lymphocytic inflammation without evidence of fungal or bacterial elements by Gram or Gomori methenamine-silver stain. Clinically, the diagnosis was most likely erythema nodosum, though insufficient hypodermis was present to make the diagnosis with pathology. The shave biopsy of the right medial palm was nondiagnostic but showed a transected pustule with no bacterial or fungal elements by Gram or Gomori methenamine-silver stain (Figure 3). Given the clinical context, the likely pathologic diagnosis was vesiculopustular Crohn disease.

Our patient was started on an empiric steroid trial with rapid improvement of the arthralgia and rash. The presumed diagnosis was a Crohn disease flare and the patient was discharged on an 8-week steroid taper. Three weeks later at a follow-up appointment, the patient’s skin lesions had nearly resolved. The swelling of the legs and feet had substantially decreased, but the joint pain, primarily in the ankles, persisted.
Routine laboratory studies showed a hemoglobin level of 11.6 g/dL (reference range, 12–15 g/dL), white blood cell count of 9.1 K/μL (reference range, 4.5–11.0 K/μL), C-reactive protein level of 20.15 mg/dL (reference range, <1.0 mg/dL), and an antinuclear antibody titer of 160 (<80). Serology for Lyme disease was negative. Serum chemistries were all within reference range and an echocardiogram was normal.
Up to one-third of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) experience extraintestinal manifestations of their condition. Of these patients, nearly one-third will develop cutaneous manifestations.1 The most common skin diseases associated with IBD are pyoderma gangrenosum and erythema nodosum.2 The differential diagnoses considered in this unique case included early pyoderma gangrenosum, subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease), and vesiculopustular Crohn disease. Vesiculopustular Crohn disease is a rare component of IBD and also can be present in bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome (BADAS). In BADAS, symptoms often include arthritis and systemic symptoms such as fever and malaise. The skin manifestations typically involve the arms and trunk. It often is seen after intestinal bypass surgery but also can be present in patients with gastrointestinal diseases such as IBD.3 Due to its early association with bypass surgery, BADAS previously was referred to as bowel bypass syndrome but has since been seen in relation to other intestinal surgeries and IBD.4 Patients with BADAS often present with episodes of fever, fatigue, and malaise, in addition to arthralgia and cutaneous eruptions. Cases of BADAS related to IBD instead of bypass surgery often can be less severe in nature. Unlike many of these previously reported cases, our patient’s joint pain primarily was in the knees and ankles, whereas typical cases of BADAS cause upper extremity (ie, shoulder, elbow) arthralgia. Our patient occasionally experienced upper extremity pain, but it was less frequent and less severe than the knee and ankle pain. The vesiculopustular lesions in BADAS usually begin as 3- to 10-mm painful macules that then develop into aseptic pustular lesions. These manifestations arise on the upper arms and chest or trunk and can be accompanied by erythema nodosum on the legs.4
It has been hypothesized that BADAS occurs as an immune reaction to bacterial overgrowth in the bowel from IBD, infection, or surgery. The reaction is in response to a bacterial antigen and manifests cutaneously.5 This same pathogenesis is thought to cause various other manifestations of Crohn disease such as erythema nodosum. Bacteria that incite this immune response include Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, and Streptococcus.
Resolution of both vesiculopustular Crohn disease and of BADAS often occurs with treatment of the underlying IBD but also can be improved with steroids and antibiotics. However, response to antibiotics often is variable.5,6 The mainstay for treatment remains steroids and management of underlying bowel disease.
Bowel-associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome often is overlooked when compiling differential diagnoses for neutrophilic dermatoses but should be considered in patients with bowel disease or recent surgery. Because the syndrome can be recurrent, early diagnosis can help to prevent and treat relapsing courses of BADAS.
- Trost LB, McDonnell JK. Important cutaneous manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Postgrad Med J. 2005;81:580-585.
- Havemann BD. A pustular skin rash in a woman with 2 weeks of diarrhea. MedGenMed. 2005;7:11.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo J, Rapini RP. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2008.
- Huang B, Chandra S, Shih DQ. Skin manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Front Physiol. 2012;3:13.
- Truchuelo MT, Alcántara J, Vano-Galván S, et al. Bowel associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome: another cutaneous manifestation of inflammatory intestinal disease. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:1596-1598.
- Ashok D, Kiely P. Bowel associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2007;1:81.
- Trost LB, McDonnell JK. Important cutaneous manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Postgrad Med J. 2005;81:580-585.
- Havemann BD. A pustular skin rash in a woman with 2 weeks of diarrhea. MedGenMed. 2005;7:11.
- Bolognia JL, Jorizzo J, Rapini RP. Dermatology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2008.
- Huang B, Chandra S, Shih DQ. Skin manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Front Physiol. 2012;3:13.
- Truchuelo MT, Alcántara J, Vano-Galván S, et al. Bowel associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome: another cutaneous manifestation of inflammatory intestinal disease. Int J Dermatol. 2013;52:1596-1598.
- Ashok D, Kiely P. Bowel associated dermatosis-arthritis syndrome: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2007;1:81.