User login
A 7-year-old female presents with persistent pimples on the nose and cheeks for approximately 1 year
Diagnosis
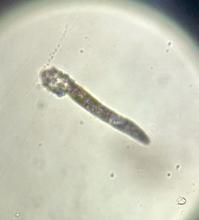
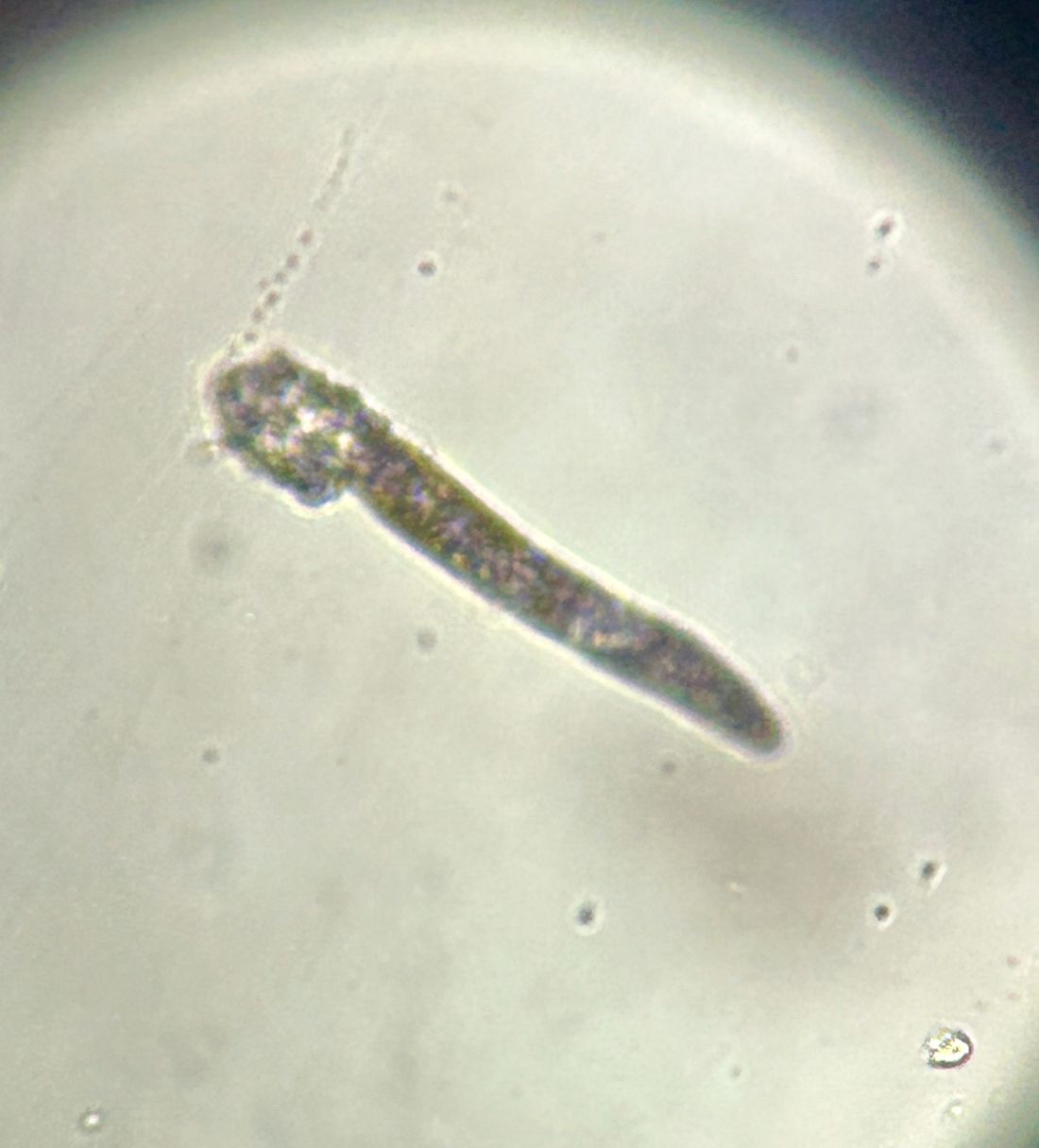
During the visit, skin scrapings were performed, revealing several Demodex mites, confirming the diagnosis of demodicosis.
Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis are the two common species implicated. The life cycle of Demodex spp. occurs in the sebaceous glands, leading to mechanical and chemical irritation of the skin.
Various immune responses are also triggered, such as a keratinocyte response via Toll-like receptor 2. Patients usually present with non-specific symptoms such as skin erythema, irritation, peeling, and dryness on the cheeks, eyelids, and paranasal areas. Patients may develop a maculopapular or rosacea-like rash.
Diagnosis is often made through microscopic examination of a skin sample in KOH solution. In rare occasions, a skin surface standardization biopsy method may be used, which determines the density of mites per 1 cm2. Dermoscopy may identify spiky white structures. Molecular methods such as PCR can be used but are not standard.
The differential diagnosis may include acne, rosacea, folliculitis, and Candida infection. Demodicosis can be differentiated by history and further studies including dermoscopy.
Acne vulgaris is an inflammatory disease of the skin’s pilosebaceous unit, primarily involving the face and trunk. It can present with comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules. Secondary signs suggestive of acne vulgaris include scars, erythema, and hyperpigmentation. All forms of acne share a common pathogenesis resulting in the formation of microcomedones, precursors for all clinical acne lesions. In this patient, the absence of microcomedones and the presence of primary inflammatory papules localized to the nose and cheeks suggested an alternative diagnosis.
Rosacea was also considered in the differential diagnosis. Rosacea is an inflammatory dermatosis characterized by erythema, telangiectasia, recurrent flushing, and inflammatory lesions including papulopustules and swelling, primarily affecting the face. The pathogenesis of rosacea is not fully understood but is suggested to involve immune-mediated responses. Vascular dysregulation and reactive oxygen species damage keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. A higher incidence of rosacea in those with a family history and UV exposure is a known trigger. Demodex folliculorum and Helicobacter pylori are also implicated. Occasionally, Demodex infestation and rosacea may co-occur, and treatment with topical metronidazole can be helpful.
Folliculitis is an infection and inflammation of the hair follicles, forming pustules or erythematous papules over hair-covered skin. It is commonly caused by bacterial infection but can also be due to fungi, viruses, and noninfectious causes such as eosinophilic folliculitis. Diagnosis is clinical, based on physical exam and history, such as recent increased sweating or scratching. KOH prep can be used for Malassezia folliculitis and skin biopsy for eosinophilic folliculitis. Treatment targets the underlying cause. Most bacterial folliculitis cases resolve without treatment, but topical antibiotics may be used. Fungal folliculitis requires oral antifungals, and herpes simplex folliculitis can be treated with antiviral medications.
Cutaneous candidiasis is an infection of the skin by various Candida species, commonly C. albicans. Superficial infections of the skin and mucous membranes, such as intertrigo, are common types. Risk factors include immunosuppression, endocrine disorders, or compromised blood flow. Increased humidity, occlusion, broken skin barriers, and altered skin microbial flora contribute to Candida infection. Diagnosis is clinical but can be confirmed by KOH prep, microscopy, and culture. Treatment involves anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal medications. Topical clotrimazole, nystatin, and miconazole are commonly used. Recurrence is prevented by keeping the affected area dry with barrier creams.
Therapeutic goals include arresting mite reproduction, elimination, and preventing recurrent infestations. Treatment may last several months, and the choice of drug depends on patient factors. There have been no standardized treatment studies or long-term effectiveness analyses. Antibiotics such as tetracycline, metronidazole, doxycycline, and ivermectin may be used to prevent proliferation. Permethrin, benzyl benzoate, crotamiton, lindane, and sulfur have also been used. Metronidazole is a common treatment for demodicosis, as was used in our patient for several weeks until the lesions cleared. Systemic metronidazole therapy may be indicated for reducing Demodex spp. density. Severe cases, particularly in immunocompromised individuals, may require oral ivermectin. Appropriate hygiene is important for prevention, such as washing the face with non-oily cleansers and laundering linens regularly.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Mr. Lee is a medical student at the University of California San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Chudzicka-Strugała I et al. Demodicosis in different age groups and alternative treatment options—A review. J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 19;12(4):1649. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041649.
Eichenfield DZ et al. Management of acne vulgaris: A review. JAMA. 2021 Nov 23;326(20):2055-2067. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.17633.
Sharma A et al. Rosacea management: A comprehensive review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 May;21(5):1895-1904. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14816.
Taudorf EH et al. Cutaneous candidiasis — an evidence-based review of topical and systemic treatments to inform clinical practice. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Oct;33(10):1863-1873. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15782.
Winters RD, Mitchell M. Folliculitis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547754/
Diagnosis
During the visit, skin scrapings were performed, revealing several Demodex mites, confirming the diagnosis of demodicosis.
Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis are the two common species implicated. The life cycle of Demodex spp. occurs in the sebaceous glands, leading to mechanical and chemical irritation of the skin.
Various immune responses are also triggered, such as a keratinocyte response via Toll-like receptor 2. Patients usually present with non-specific symptoms such as skin erythema, irritation, peeling, and dryness on the cheeks, eyelids, and paranasal areas. Patients may develop a maculopapular or rosacea-like rash.
Diagnosis is often made through microscopic examination of a skin sample in KOH solution. In rare occasions, a skin surface standardization biopsy method may be used, which determines the density of mites per 1 cm2. Dermoscopy may identify spiky white structures. Molecular methods such as PCR can be used but are not standard.
The differential diagnosis may include acne, rosacea, folliculitis, and Candida infection. Demodicosis can be differentiated by history and further studies including dermoscopy.
Acne vulgaris is an inflammatory disease of the skin’s pilosebaceous unit, primarily involving the face and trunk. It can present with comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules. Secondary signs suggestive of acne vulgaris include scars, erythema, and hyperpigmentation. All forms of acne share a common pathogenesis resulting in the formation of microcomedones, precursors for all clinical acne lesions. In this patient, the absence of microcomedones and the presence of primary inflammatory papules localized to the nose and cheeks suggested an alternative diagnosis.
Rosacea was also considered in the differential diagnosis. Rosacea is an inflammatory dermatosis characterized by erythema, telangiectasia, recurrent flushing, and inflammatory lesions including papulopustules and swelling, primarily affecting the face. The pathogenesis of rosacea is not fully understood but is suggested to involve immune-mediated responses. Vascular dysregulation and reactive oxygen species damage keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. A higher incidence of rosacea in those with a family history and UV exposure is a known trigger. Demodex folliculorum and Helicobacter pylori are also implicated. Occasionally, Demodex infestation and rosacea may co-occur, and treatment with topical metronidazole can be helpful.
Folliculitis is an infection and inflammation of the hair follicles, forming pustules or erythematous papules over hair-covered skin. It is commonly caused by bacterial infection but can also be due to fungi, viruses, and noninfectious causes such as eosinophilic folliculitis. Diagnosis is clinical, based on physical exam and history, such as recent increased sweating or scratching. KOH prep can be used for Malassezia folliculitis and skin biopsy for eosinophilic folliculitis. Treatment targets the underlying cause. Most bacterial folliculitis cases resolve without treatment, but topical antibiotics may be used. Fungal folliculitis requires oral antifungals, and herpes simplex folliculitis can be treated with antiviral medications.
Cutaneous candidiasis is an infection of the skin by various Candida species, commonly C. albicans. Superficial infections of the skin and mucous membranes, such as intertrigo, are common types. Risk factors include immunosuppression, endocrine disorders, or compromised blood flow. Increased humidity, occlusion, broken skin barriers, and altered skin microbial flora contribute to Candida infection. Diagnosis is clinical but can be confirmed by KOH prep, microscopy, and culture. Treatment involves anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal medications. Topical clotrimazole, nystatin, and miconazole are commonly used. Recurrence is prevented by keeping the affected area dry with barrier creams.
Therapeutic goals include arresting mite reproduction, elimination, and preventing recurrent infestations. Treatment may last several months, and the choice of drug depends on patient factors. There have been no standardized treatment studies or long-term effectiveness analyses. Antibiotics such as tetracycline, metronidazole, doxycycline, and ivermectin may be used to prevent proliferation. Permethrin, benzyl benzoate, crotamiton, lindane, and sulfur have also been used. Metronidazole is a common treatment for demodicosis, as was used in our patient for several weeks until the lesions cleared. Systemic metronidazole therapy may be indicated for reducing Demodex spp. density. Severe cases, particularly in immunocompromised individuals, may require oral ivermectin. Appropriate hygiene is important for prevention, such as washing the face with non-oily cleansers and laundering linens regularly.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Mr. Lee is a medical student at the University of California San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Chudzicka-Strugała I et al. Demodicosis in different age groups and alternative treatment options—A review. J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 19;12(4):1649. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041649.
Eichenfield DZ et al. Management of acne vulgaris: A review. JAMA. 2021 Nov 23;326(20):2055-2067. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.17633.
Sharma A et al. Rosacea management: A comprehensive review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 May;21(5):1895-1904. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14816.
Taudorf EH et al. Cutaneous candidiasis — an evidence-based review of topical and systemic treatments to inform clinical practice. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Oct;33(10):1863-1873. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15782.
Winters RD, Mitchell M. Folliculitis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547754/
Diagnosis
During the visit, skin scrapings were performed, revealing several Demodex mites, confirming the diagnosis of demodicosis.
Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis are the two common species implicated. The life cycle of Demodex spp. occurs in the sebaceous glands, leading to mechanical and chemical irritation of the skin.
Various immune responses are also triggered, such as a keratinocyte response via Toll-like receptor 2. Patients usually present with non-specific symptoms such as skin erythema, irritation, peeling, and dryness on the cheeks, eyelids, and paranasal areas. Patients may develop a maculopapular or rosacea-like rash.
Diagnosis is often made through microscopic examination of a skin sample in KOH solution. In rare occasions, a skin surface standardization biopsy method may be used, which determines the density of mites per 1 cm2. Dermoscopy may identify spiky white structures. Molecular methods such as PCR can be used but are not standard.
The differential diagnosis may include acne, rosacea, folliculitis, and Candida infection. Demodicosis can be differentiated by history and further studies including dermoscopy.
Acne vulgaris is an inflammatory disease of the skin’s pilosebaceous unit, primarily involving the face and trunk. It can present with comedones, papules, pustules, and nodules. Secondary signs suggestive of acne vulgaris include scars, erythema, and hyperpigmentation. All forms of acne share a common pathogenesis resulting in the formation of microcomedones, precursors for all clinical acne lesions. In this patient, the absence of microcomedones and the presence of primary inflammatory papules localized to the nose and cheeks suggested an alternative diagnosis.
Rosacea was also considered in the differential diagnosis. Rosacea is an inflammatory dermatosis characterized by erythema, telangiectasia, recurrent flushing, and inflammatory lesions including papulopustules and swelling, primarily affecting the face. The pathogenesis of rosacea is not fully understood but is suggested to involve immune-mediated responses. Vascular dysregulation and reactive oxygen species damage keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. A higher incidence of rosacea in those with a family history and UV exposure is a known trigger. Demodex folliculorum and Helicobacter pylori are also implicated. Occasionally, Demodex infestation and rosacea may co-occur, and treatment with topical metronidazole can be helpful.
Folliculitis is an infection and inflammation of the hair follicles, forming pustules or erythematous papules over hair-covered skin. It is commonly caused by bacterial infection but can also be due to fungi, viruses, and noninfectious causes such as eosinophilic folliculitis. Diagnosis is clinical, based on physical exam and history, such as recent increased sweating or scratching. KOH prep can be used for Malassezia folliculitis and skin biopsy for eosinophilic folliculitis. Treatment targets the underlying cause. Most bacterial folliculitis cases resolve without treatment, but topical antibiotics may be used. Fungal folliculitis requires oral antifungals, and herpes simplex folliculitis can be treated with antiviral medications.
Cutaneous candidiasis is an infection of the skin by various Candida species, commonly C. albicans. Superficial infections of the skin and mucous membranes, such as intertrigo, are common types. Risk factors include immunosuppression, endocrine disorders, or compromised blood flow. Increased humidity, occlusion, broken skin barriers, and altered skin microbial flora contribute to Candida infection. Diagnosis is clinical but can be confirmed by KOH prep, microscopy, and culture. Treatment involves anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antifungal medications. Topical clotrimazole, nystatin, and miconazole are commonly used. Recurrence is prevented by keeping the affected area dry with barrier creams.
Therapeutic goals include arresting mite reproduction, elimination, and preventing recurrent infestations. Treatment may last several months, and the choice of drug depends on patient factors. There have been no standardized treatment studies or long-term effectiveness analyses. Antibiotics such as tetracycline, metronidazole, doxycycline, and ivermectin may be used to prevent proliferation. Permethrin, benzyl benzoate, crotamiton, lindane, and sulfur have also been used. Metronidazole is a common treatment for demodicosis, as was used in our patient for several weeks until the lesions cleared. Systemic metronidazole therapy may be indicated for reducing Demodex spp. density. Severe cases, particularly in immunocompromised individuals, may require oral ivermectin. Appropriate hygiene is important for prevention, such as washing the face with non-oily cleansers and laundering linens regularly.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Mr. Lee is a medical student at the University of California San Diego.
Suggested Reading
Chudzicka-Strugała I et al. Demodicosis in different age groups and alternative treatment options—A review. J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 19;12(4):1649. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041649.
Eichenfield DZ et al. Management of acne vulgaris: A review. JAMA. 2021 Nov 23;326(20):2055-2067. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.17633.
Sharma A et al. Rosacea management: A comprehensive review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 May;21(5):1895-1904. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14816.
Taudorf EH et al. Cutaneous candidiasis — an evidence-based review of topical and systemic treatments to inform clinical practice. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Oct;33(10):1863-1873. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15782.
Winters RD, Mitchell M. Folliculitis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547754/
A 7-year-old female presents with persistent pimples on the nose and cheeks for approximately 1 year. She had been treated with several topical antibiotics and acne washes without resolution of the lesions. There were no signs of early puberty, and the child had no history of medical conditions. Her mother has a history of rosacea. Physical examination revealed erythematous papules on the nose and cheeks bilaterally.