User login
Diffuse Painful Plaques in the Setting of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare Complex Infection
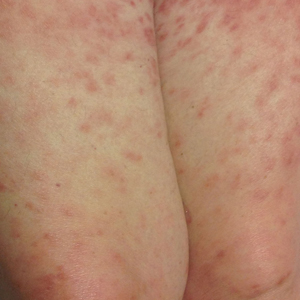
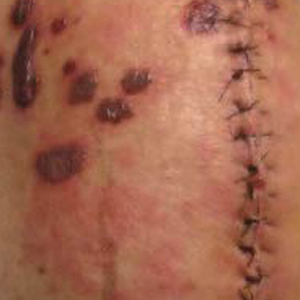
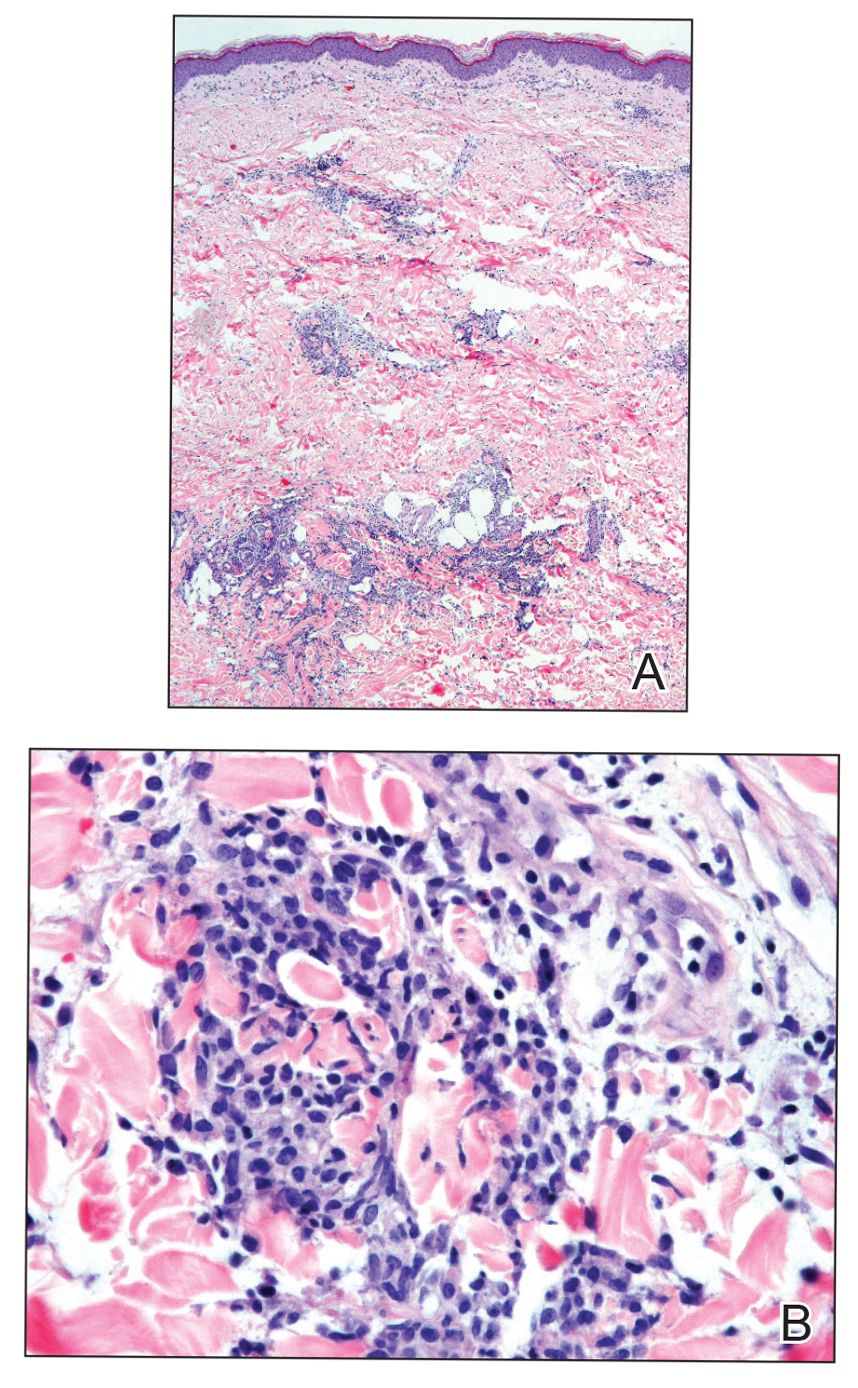
Histopathologic evaluation revealed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal inflammation. The epidermis exhibited some vacuolar interface change and effacement with relatively sparse dyskeratotic cells. A lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate surrounded the blood vessels, nerves, and adnexal structures and extended into the subcutaneous fat (Figure). Acid-fast, Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver, Gram, Fite, Treponema pallidum, and Alcian blue stains were performed at our institution and were all negative. Biopsies sent to the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Program demonstrated scattered extracellular acid-fast organisms on Fite staining in the specimen of the forearm. Polymerase chain reaction testing for Mycobacterium leprae DNA was negative. DNA sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene matched Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC). In the workup of the hepatic mass, the patient incidentally was found to have large-cell transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and therefore was treated with bendamustine and rituximab as an outpatient. The patient received 1 chemotherapy infusion every 4 weeks for a total of 10 rounds. At 10-week follow-up after 2 rounds of chemotherapy, all of the skin lesions had resolved despite no antibiotic therapy for atypical infections.
Disseminated infection with MAC is relatively rare in healthy as well as immunocompromised individuals. Clinical disease most commonly is seen as an opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS who have CD4 counts less than 50/mm3 (reference range, 500-1400/mm3) or in those with preexisting lung disease.1 Cutaneous involvement has been observed in only 14% of non-AIDS patients with disseminated MAC infection.2 In another study of 76 patients with MAC infection, only 2 involved the skin or soft tissue.3 Infection of the skin without concurrent pulmonary MAC infection is rare, though trauma may cause isolated skin infection. The cutaneous presentation of MAC infection is highly variable and may include erythematous papules, pustules, panniculitis, infiltrated plaques, verrucous lesions, and draining sinuses.3 The lesions have been reported to be painful.1
Cutaneous findings occur in up to 25% of patients with CLL, either due to the seeding of leukemic cells or other secondary lesions.4 Leukemia cutis, or skin involvement by B-cell CLL, most commonly presents in the head and neck region as chronic and relapsing erythematous papules and plaques.5 It histologically presents as monomorphic lymphocytic infiltrates accentuated around periadnexal and perivascular structures, with some extending into adipose tissue.2 In our case, histopathology demonstrated a lack of monomorphous infiltrate and thus was inconsistent with leukemia cutis. Similarly, lack of pale pink deposits and lack of neutrophilic infiltrates or degenerated collagen makes amyloidosis and palisaded neutrophilic granulomatous dermatitis incorrect diagnoses, respectively.
We hypothesize that the initially undetected worsening of CLL resulted in an immunocompromised state, which facilitated this unique presentation of cutaneous MAC infection in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient with no clinical symptoms of active pulmonary disease. The rash was the presenting sign of both the cutaneous MAC infection and worsening CLL. Additionally, our patient's cutaneous MAC facial involvement clinically resembled the leonine facies that is classic in lepromatous leprosy. Rare reports have been published addressing this similarity.6
Treatment of MAC pulmonary disease usually includes a combination of clarithromycin or azithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol (for nodular/bronchiectatic disease), with or without amikacin or streptomycin.7 For limited pulmonary disease in patients with adequate pulmonary reserve, surgical resection may be considered in combination with the multidrug MAC pulmonary treatment regimen for 3 months to 1 year. Patients with localized MAC disease involving only the skin, soft tissue, tendons, and joints usually are treated with surgical excision in combination with clarithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol for 6 to 12 months.7 In our patient, we believe that chemotherapy and the subsequent reconstituted immune system likely cleared the MAC infection without targeted antibiotic treatment.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank David Scollard, MD, PhD, and Barbara Stryjewska, MD, from the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Association (Baton Rouge, Louisiana).
- Robak E, Robak T. Skin lesions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:855-865.
- Plaza JA, Comfere NI, Gibson LE, et al. Unusual cutaneous manifestations of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:772-780.
- Sivanesan SP, Khera P, Buckthal-McCuin J, et al. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex associated with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:E25-E26.
- Horsburgh CR, Mason UG, Farhi DC, et al. Disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1985;64:36-48.
- Bodle EE, Cunningham JA, Della-Latta P, et al. Epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients without HIV infection, New York City. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:290-296.
- Boyd AS, Robbins J. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection in an HIV+ patient mimicking histoid leprosy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:39-41.
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare Complex Infection
Histopathologic evaluation revealed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal inflammation. The epidermis exhibited some vacuolar interface change and effacement with relatively sparse dyskeratotic cells. A lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate surrounded the blood vessels, nerves, and adnexal structures and extended into the subcutaneous fat (Figure). Acid-fast, Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver, Gram, Fite, Treponema pallidum, and Alcian blue stains were performed at our institution and were all negative. Biopsies sent to the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Program demonstrated scattered extracellular acid-fast organisms on Fite staining in the specimen of the forearm. Polymerase chain reaction testing for Mycobacterium leprae DNA was negative. DNA sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene matched Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC). In the workup of the hepatic mass, the patient incidentally was found to have large-cell transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and therefore was treated with bendamustine and rituximab as an outpatient. The patient received 1 chemotherapy infusion every 4 weeks for a total of 10 rounds. At 10-week follow-up after 2 rounds of chemotherapy, all of the skin lesions had resolved despite no antibiotic therapy for atypical infections.

Disseminated infection with MAC is relatively rare in healthy as well as immunocompromised individuals. Clinical disease most commonly is seen as an opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS who have CD4 counts less than 50/mm3 (reference range, 500-1400/mm3) or in those with preexisting lung disease.1 Cutaneous involvement has been observed in only 14% of non-AIDS patients with disseminated MAC infection.2 In another study of 76 patients with MAC infection, only 2 involved the skin or soft tissue.3 Infection of the skin without concurrent pulmonary MAC infection is rare, though trauma may cause isolated skin infection. The cutaneous presentation of MAC infection is highly variable and may include erythematous papules, pustules, panniculitis, infiltrated plaques, verrucous lesions, and draining sinuses.3 The lesions have been reported to be painful.1
Cutaneous findings occur in up to 25% of patients with CLL, either due to the seeding of leukemic cells or other secondary lesions.4 Leukemia cutis, or skin involvement by B-cell CLL, most commonly presents in the head and neck region as chronic and relapsing erythematous papules and plaques.5 It histologically presents as monomorphic lymphocytic infiltrates accentuated around periadnexal and perivascular structures, with some extending into adipose tissue.2 In our case, histopathology demonstrated a lack of monomorphous infiltrate and thus was inconsistent with leukemia cutis. Similarly, lack of pale pink deposits and lack of neutrophilic infiltrates or degenerated collagen makes amyloidosis and palisaded neutrophilic granulomatous dermatitis incorrect diagnoses, respectively.
We hypothesize that the initially undetected worsening of CLL resulted in an immunocompromised state, which facilitated this unique presentation of cutaneous MAC infection in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient with no clinical symptoms of active pulmonary disease. The rash was the presenting sign of both the cutaneous MAC infection and worsening CLL. Additionally, our patient's cutaneous MAC facial involvement clinically resembled the leonine facies that is classic in lepromatous leprosy. Rare reports have been published addressing this similarity.6
Treatment of MAC pulmonary disease usually includes a combination of clarithromycin or azithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol (for nodular/bronchiectatic disease), with or without amikacin or streptomycin.7 For limited pulmonary disease in patients with adequate pulmonary reserve, surgical resection may be considered in combination with the multidrug MAC pulmonary treatment regimen for 3 months to 1 year. Patients with localized MAC disease involving only the skin, soft tissue, tendons, and joints usually are treated with surgical excision in combination with clarithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol for 6 to 12 months.7 In our patient, we believe that chemotherapy and the subsequent reconstituted immune system likely cleared the MAC infection without targeted antibiotic treatment.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank David Scollard, MD, PhD, and Barbara Stryjewska, MD, from the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Association (Baton Rouge, Louisiana).
The Diagnosis: Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare Complex Infection
Histopathologic evaluation revealed superficial and deep perivascular and periadnexal inflammation. The epidermis exhibited some vacuolar interface change and effacement with relatively sparse dyskeratotic cells. A lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate surrounded the blood vessels, nerves, and adnexal structures and extended into the subcutaneous fat (Figure). Acid-fast, Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver, Gram, Fite, Treponema pallidum, and Alcian blue stains were performed at our institution and were all negative. Biopsies sent to the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Program demonstrated scattered extracellular acid-fast organisms on Fite staining in the specimen of the forearm. Polymerase chain reaction testing for Mycobacterium leprae DNA was negative. DNA sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene matched Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC). In the workup of the hepatic mass, the patient incidentally was found to have large-cell transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and therefore was treated with bendamustine and rituximab as an outpatient. The patient received 1 chemotherapy infusion every 4 weeks for a total of 10 rounds. At 10-week follow-up after 2 rounds of chemotherapy, all of the skin lesions had resolved despite no antibiotic therapy for atypical infections.

Disseminated infection with MAC is relatively rare in healthy as well as immunocompromised individuals. Clinical disease most commonly is seen as an opportunistic infection in patients with AIDS who have CD4 counts less than 50/mm3 (reference range, 500-1400/mm3) or in those with preexisting lung disease.1 Cutaneous involvement has been observed in only 14% of non-AIDS patients with disseminated MAC infection.2 In another study of 76 patients with MAC infection, only 2 involved the skin or soft tissue.3 Infection of the skin without concurrent pulmonary MAC infection is rare, though trauma may cause isolated skin infection. The cutaneous presentation of MAC infection is highly variable and may include erythematous papules, pustules, panniculitis, infiltrated plaques, verrucous lesions, and draining sinuses.3 The lesions have been reported to be painful.1
Cutaneous findings occur in up to 25% of patients with CLL, either due to the seeding of leukemic cells or other secondary lesions.4 Leukemia cutis, or skin involvement by B-cell CLL, most commonly presents in the head and neck region as chronic and relapsing erythematous papules and plaques.5 It histologically presents as monomorphic lymphocytic infiltrates accentuated around periadnexal and perivascular structures, with some extending into adipose tissue.2 In our case, histopathology demonstrated a lack of monomorphous infiltrate and thus was inconsistent with leukemia cutis. Similarly, lack of pale pink deposits and lack of neutrophilic infiltrates or degenerated collagen makes amyloidosis and palisaded neutrophilic granulomatous dermatitis incorrect diagnoses, respectively.
We hypothesize that the initially undetected worsening of CLL resulted in an immunocompromised state, which facilitated this unique presentation of cutaneous MAC infection in a human immunodeficiency virus-negative patient with no clinical symptoms of active pulmonary disease. The rash was the presenting sign of both the cutaneous MAC infection and worsening CLL. Additionally, our patient's cutaneous MAC facial involvement clinically resembled the leonine facies that is classic in lepromatous leprosy. Rare reports have been published addressing this similarity.6
Treatment of MAC pulmonary disease usually includes a combination of clarithromycin or azithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol (for nodular/bronchiectatic disease), with or without amikacin or streptomycin.7 For limited pulmonary disease in patients with adequate pulmonary reserve, surgical resection may be considered in combination with the multidrug MAC pulmonary treatment regimen for 3 months to 1 year. Patients with localized MAC disease involving only the skin, soft tissue, tendons, and joints usually are treated with surgical excision in combination with clarithromycin, rifampin, and ethambutol for 6 to 12 months.7 In our patient, we believe that chemotherapy and the subsequent reconstituted immune system likely cleared the MAC infection without targeted antibiotic treatment.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank David Scollard, MD, PhD, and Barbara Stryjewska, MD, from the National Hansen's Disease (Leprosy) Association (Baton Rouge, Louisiana).
- Robak E, Robak T. Skin lesions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:855-865.
- Plaza JA, Comfere NI, Gibson LE, et al. Unusual cutaneous manifestations of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:772-780.
- Sivanesan SP, Khera P, Buckthal-McCuin J, et al. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex associated with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:E25-E26.
- Horsburgh CR, Mason UG, Farhi DC, et al. Disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1985;64:36-48.
- Bodle EE, Cunningham JA, Della-Latta P, et al. Epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients without HIV infection, New York City. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:290-296.
- Boyd AS, Robbins J. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection in an HIV+ patient mimicking histoid leprosy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:39-41.
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.
- Robak E, Robak T. Skin lesions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48:855-865.
- Plaza JA, Comfere NI, Gibson LE, et al. Unusual cutaneous manifestations of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:772-780.
- Sivanesan SP, Khera P, Buckthal-McCuin J, et al. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex associated with immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:E25-E26.
- Horsburgh CR, Mason UG, Farhi DC, et al. Disseminated infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1985;64:36-48.
- Bodle EE, Cunningham JA, Della-Latta P, et al. Epidemiology of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients without HIV infection, New York City. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:290-296.
- Boyd AS, Robbins J. Cutaneous Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infection in an HIV+ patient mimicking histoid leprosy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:39-41.
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367-416.

Drug-induced Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis in a Patient With a Vancomycin-impregnated Cement Spacer
Case Report
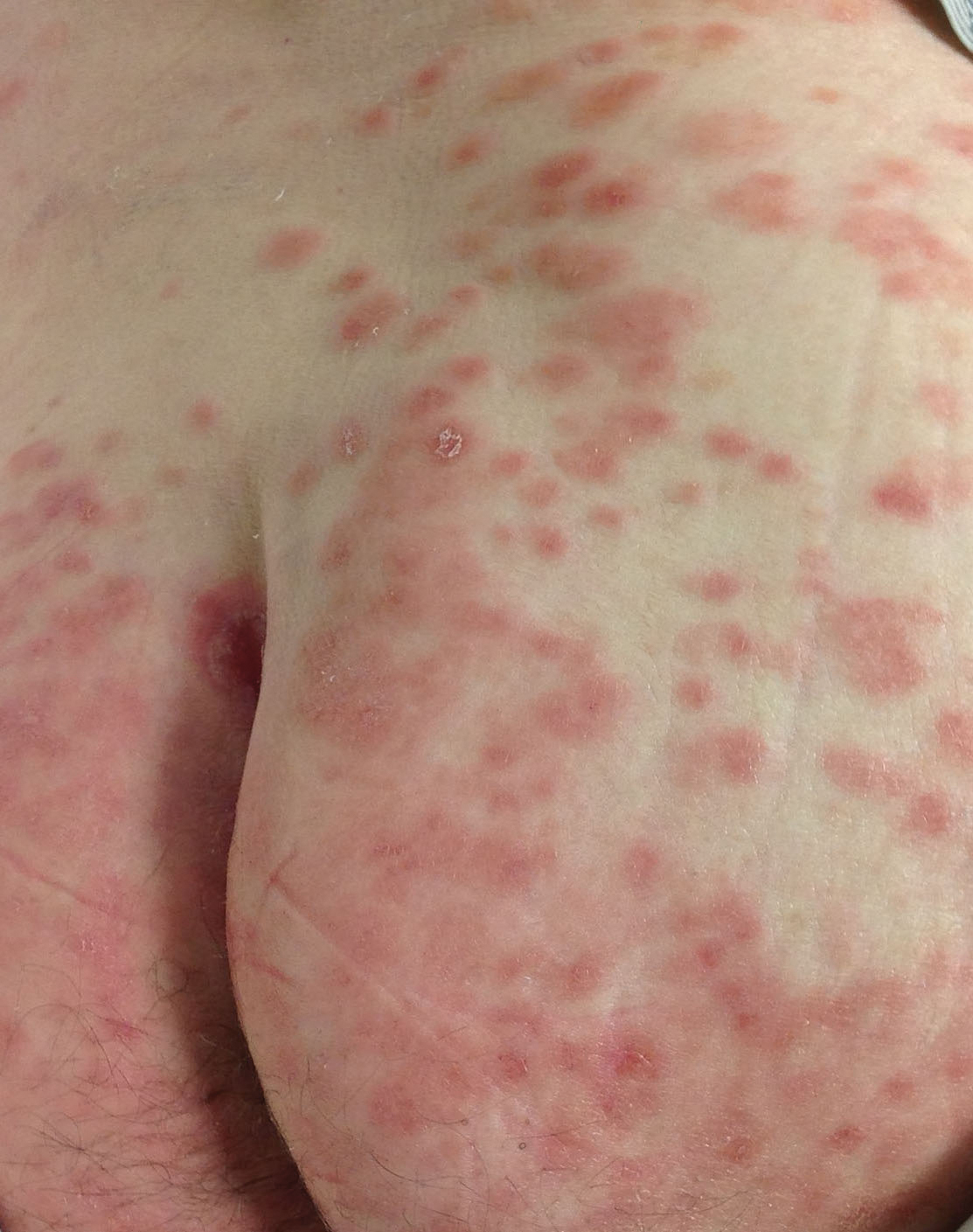
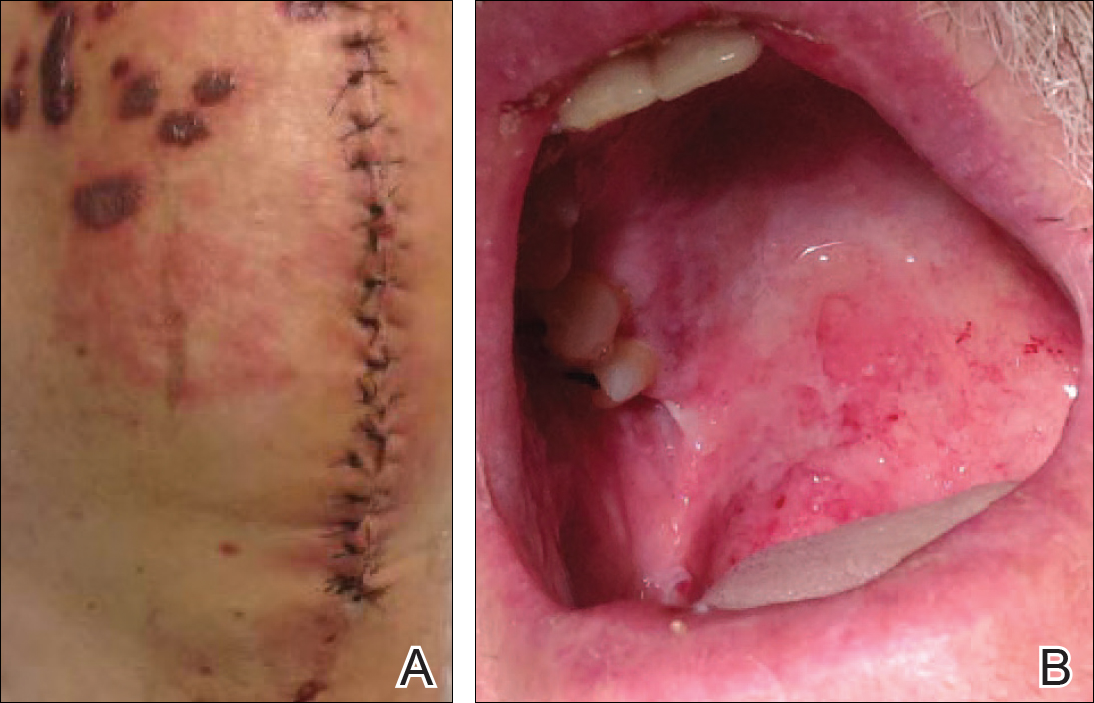
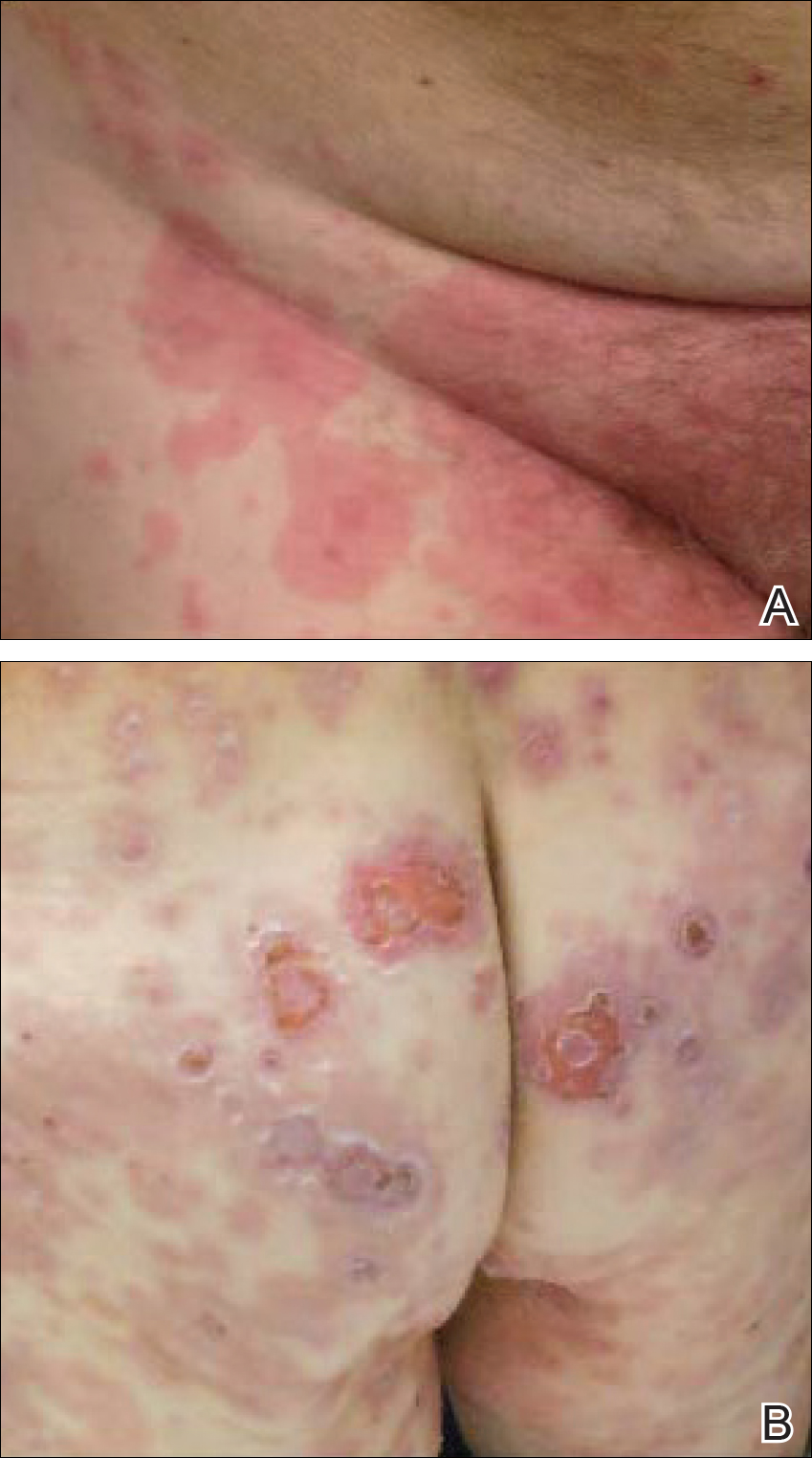
A 77-year-old man was admitted to the general medicine service at our institution for treatment of a diffuse macular eruption and hemorrhagic bullae 12 days after undergoing left-knee revision arthroplasty during which a cement spacer impregnated with vancomycin and tobramycin was placed. At the time of the surgery, the patient also received intravenous (IV) vancomycin and oral ciprofloxacin, which were continued postoperatively until his hospital presentation. The patient was recovering well until postoperative day 7, when he developed painful swelling and erythema surrounding the surgical wound on the left knee. Concerned that his symptoms indicated a flare of gout, he restarted a former allopurinol prescription from an outside physician after 2 years of nonuse. The skin changes progressed distally on the left leg over the next 48 hours. By postoperative day 10, he had developed serosanguinous blisters on the left knee (Figure 1A) and oral mucosa (Figure 1B), as well as erythematous nodules on the bilateral palms. He presented to our institution for emergent care on postoperative day 12 following progression of the eruption to the inguinal region (Figure 2A), buttocks (Figure 2B), and abdominal region.
Due to concerns about a potential drug reaction, the IV vancomycin, oral ciprofloxacin, and oral allopurinol were discontinued on hospital admission.
Oral prednisone 60 mg once daily and oral dapsone 25 mg once daily were initiated on hospital days 4 and 6 (postoperative days 15 and 17), respectively. A 6-week course of oral ciprofloxacin 750 mg twice daily and daptomycin 8 mg/kg once daily was initiated for bacterial coverage on hospital day 5 (postoperative day 16). Topical triamcinolone and an anesthetic mouthwash also were used to treat the mucosal involvement. The lesions stabilized on the third day of steroid therapy, and the patient was discharged 7 days after hospital admission (postoperative day 18). Dapsone was rapidly increased to 100 mg once daily over the next week for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis. An increase in prednisone to 80 mg once daily was required 3 days after the patient was discharged due to worsening oral lesions. Five days after discharge, the patient was readmitted to the hospital for 3 days due to acute kidney injury (AKI) in which his baseline creatinine level tripled. The cause of renal impairment was unknown, resulting in empiric discontinuation of dapsone on postoperative day 27. Prophylaxis for P jirovecii pneumonia was replaced with once-monthly inhaled pentamidine. Prednisone was tapered 20 days after the original presentation (postoperative day 32) following gradual improvement of both the skin and oral lesions. At dermatology follow-up 2 weeks later, doxycycline 100 mg twice daily was added for residual inflammation of the left leg. A deep vein thrombosis was discovered in the left leg 10 days later, and 3 months of anticoagulation therapy was initiated with discontinuation of the doxycycline. The patient continued to have renal insufficiency several weeks after dapsone discontinuation and developed prominent peripheral motor neuropathy with bilateral thenar atrophy. He did not experience any skin eruptions or relapses in the weeks following prednisone cessation and underwent successful removal of the cement spacer with full left-knee reconstruction 4 months after his initial presentation to our institution. At 9-month dermatology follow-up, the LABD remained in remission.
Comment
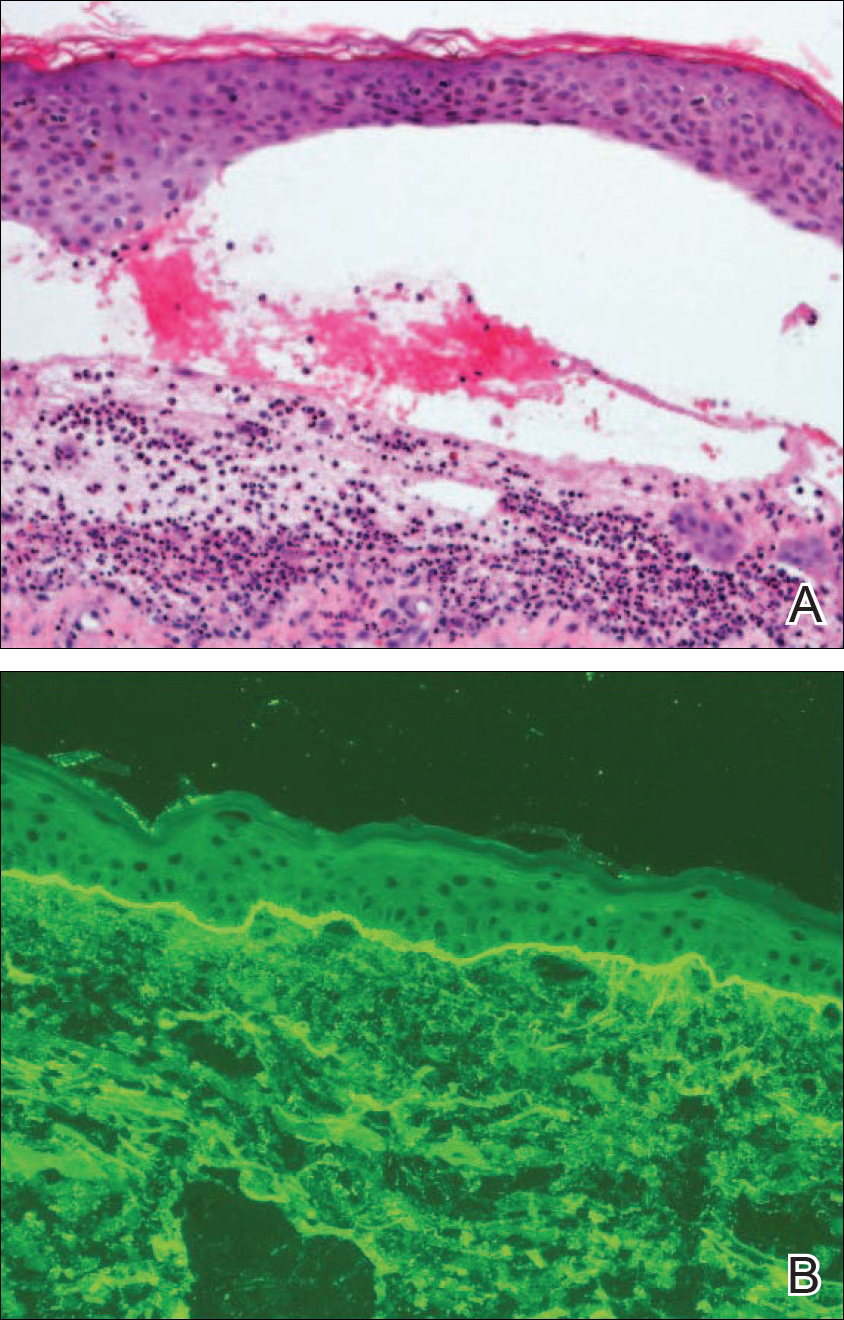
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis is a well-documented autoimmune mucocutaneous disorder characterized by linear IgA deposits at the dermoepidermal junction. The development of autoantibodies to antigens within the basement membrane zone leads to both cellular and humoral immune responses that facilitate the subepidermal blistering rash in LABD.2,3 Linear IgA bullous dermatosis affects all ages and races with a bimodal epidemiology. The adult form typically appears after 60 years of age, whereas the childhood form (chronic bullous disease of childhood) appears between 6 months and 6 years of age.3 Medications—particularly vancomycin—are responsible for a substantial portion of cases.1-4 In one review, vancomycin was implicated in almost half (22/52 [42.3%]) of drug-related cases of LABD.4 Other associated medications include captopril, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, phenytoin, and diclo-fenac.3,4 Vancomycin-associated LABD has a substantially shorter time to onset of symptoms, with a mean of 8.6 days compared to 63.8 days for other causative agents.4
The initial treatment of drug-induced LABD is immediate discontinuation of the suspected agent(s) and supportive care.9 Although future avoidance of vancomycin is recommended in patients with a history of LABD, there are reported cases of successful rechallenges.4,10 The early removal of our patient’s cement spacer was discouraged by both the orthopedics and infectious disease consultation services due to potential complications as well as the patient’s gradual improvement during his hospital course.
Dapsone is considered the standard systemic treatment for LABD. Sulfapyridine is an alternative to dapsone, or a combination of these 2 drugs may be used. Corticosteroids can be added to each of these regimens to achieve remission, as in our case.2 Although dapsone was discontinued in the setting of the patient’s AKI, the vancomycin in the dual-eluting spacer was more likely the culprit. A review of 544 postoperative outcomes following the use of an antibiotic-impregnated cement spacer (AICS) during 2-stage arthroplasty displayed an 8- to 10-fold increase in the development of AKIs compared to the rate of AKIs following primary joint arthroplasty.10 While our patient’s AKI was not attributed to dapsone, his prominent peripheral motor neuropathy with resultant bilateral thenar atrophy was a rare complication of dapsone use. While dapsone-associated neuropathy has been reported in daily dosages of as low as 75 mg, it typically is seen in doses of at least 300 mg per day and in larger cumulative dosages.11
Despite having a well-characterized vancomycin-induced LABD in the setting of known vancomycin exposure, our patient’s case was particularly challenging given the continued presence of the vancomycin-impregnated cement spacer (VICS) in the left knee, resulting in vancomycin levels at admission and during subsequent measurements over 2 weeks that were all several-fold higher than the renal clearance predicted.
Vancomycin-associated LABD does not appear to be dose dependent and has been reported at both subtherapeutic1-3 and supratherapeutic levels,5-9 whereas toxicity reactions are more common at supratherapeutic levels.9 The literature on AICS use suggests that drug elution occurs at relatively unpredictable rates based on a variety of factors, including the type of cement used and the initial antibiotic concentration.12,13 Furthermore, the addition of tobramycin to VICSs has been found to increase the rate of vancomycin delivery through a phenomenon known as passive opportunism.14
As AICS devices allow for the delivery of higher concentrations of antibiotics to a localized area, systemic complications are considered rare but have been reported.13 Our report describes a rare case of LABD in the setting of a VICS. One clinical aspect of our case that supports the implication of VICS as the cause of the patient’s LABD is the concentration of bullae overlying the incision site on the left knee. A case of a desquamating rash in a patient with an implanted VICS has been documented in which the early lesions were localized to the surgical leg, as in our case.15 Unlike our case, there was a history of Stevens-Johnson syndrome following previous vancomycin exposure. A case of a gentamicin-impregnated cement spacer causing allergic dermatitis that was most prominent in the surgical leg also has been reported.16 An isomorphic phenomenon (Köbner phenomenon) has been suggested in the setting of
- Plunkett RW, Chiarello SE, Beutner EH. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis in one of two piroxicam-induced eruptions: a distinct direct immunofluorescence trend revealed by the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:691-696.
- Guide SV, Marinkovich MP. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis. Clin Dermatol. 2001;19:719-727.
- Fortuna G, Marinkovich MP. Linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:38-50.
- Fortuna G, Salas-Alanis JC, Guidetti E, et al. A critical reappraisal of the current data on drug-induced linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis: a real and separate nosological entity? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:988-994.
- Kuechle MK, Stegemeir E, Maynard B, et al. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis: report of six cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30(2, pt 1):187-192.
- Neughebauer BI, Negron G, Pelton S, et al. Bullous skin disease: an unusual allergic reaction to vancomycin. Am J Med Sci. 2002;323:273-278.
- Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981;30:239-245.
- Wiadrowski TP, Reid CM. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous disease following antibiotics. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:196-199.
- Dang LV, Byrom L, Muir J, et al. Vancomycin-induced linear IgA with mucosal and ocular involvement: a case report. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2014;22:e119-e121.
- Luu A, Syed F, Raman G, et al. Two-stage arthroplasty for prosthetic joint infection: a systematic review of acute kidney injury, systemic toxicity and infection control [published online April 8, 2013]. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:1490.e1-1498.e1.
- Daneshmend TK. The neurotoxicity of dapsone. Adverse Drug React Acute Poisoning Rev. 1984;3:43-58.
- Jacobs C, Christensen CP, Berend ME. Static and mobile antibiotic-impregnated cement spacers for the management of prosthetic joint infection. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17:356-368.
- Springer BD, Lee GC, Osmon D, et al. Systemic safety of high-dose antibiotic-loaded cement spacers after resection of an infected total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;427:47-51.
- Penner MJ, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Elution characteristics of vancomycin and tobramycin combined in acrylic bone-cement. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11:939-944.
- Williams B, Hanson A, Sha B. Diffuse desquamating rash following exposure to vancomycin-impregnated bone cement. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48:1061-1065.
- Haeberle M, Wittner B. Is gentamicin-loaded bone cement a risk for developing systemic allergic dermatitis? Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:176-177.
- McDonald HC, York NR, Pandya AG. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis demonstrating the isomorphic phenomenon. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:897-898.
Case Report
A 77-year-old man was admitted to the general medicine service at our institution for treatment of a diffuse macular eruption and hemorrhagic bullae 12 days after undergoing left-knee revision arthroplasty during which a cement spacer impregnated with vancomycin and tobramycin was placed. At the time of the surgery, the patient also received intravenous (IV) vancomycin and oral ciprofloxacin, which were continued postoperatively until his hospital presentation. The patient was recovering well until postoperative day 7, when he developed painful swelling and erythema surrounding the surgical wound on the left knee. Concerned that his symptoms indicated a flare of gout, he restarted a former allopurinol prescription from an outside physician after 2 years of nonuse. The skin changes progressed distally on the left leg over the next 48 hours. By postoperative day 10, he had developed serosanguinous blisters on the left knee (Figure 1A) and oral mucosa (Figure 1B), as well as erythematous nodules on the bilateral palms. He presented to our institution for emergent care on postoperative day 12 following progression of the eruption to the inguinal region (Figure 2A), buttocks (Figure 2B), and abdominal region.


Due to concerns about a potential drug reaction, the IV vancomycin, oral ciprofloxacin, and oral allopurinol were discontinued on hospital admission.

Oral prednisone 60 mg once daily and oral dapsone 25 mg once daily were initiated on hospital days 4 and 6 (postoperative days 15 and 17), respectively. A 6-week course of oral ciprofloxacin 750 mg twice daily and daptomycin 8 mg/kg once daily was initiated for bacterial coverage on hospital day 5 (postoperative day 16). Topical triamcinolone and an anesthetic mouthwash also were used to treat the mucosal involvement. The lesions stabilized on the third day of steroid therapy, and the patient was discharged 7 days after hospital admission (postoperative day 18). Dapsone was rapidly increased to 100 mg once daily over the next week for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis. An increase in prednisone to 80 mg once daily was required 3 days after the patient was discharged due to worsening oral lesions. Five days after discharge, the patient was readmitted to the hospital for 3 days due to acute kidney injury (AKI) in which his baseline creatinine level tripled. The cause of renal impairment was unknown, resulting in empiric discontinuation of dapsone on postoperative day 27. Prophylaxis for P jirovecii pneumonia was replaced with once-monthly inhaled pentamidine. Prednisone was tapered 20 days after the original presentation (postoperative day 32) following gradual improvement of both the skin and oral lesions. At dermatology follow-up 2 weeks later, doxycycline 100 mg twice daily was added for residual inflammation of the left leg. A deep vein thrombosis was discovered in the left leg 10 days later, and 3 months of anticoagulation therapy was initiated with discontinuation of the doxycycline. The patient continued to have renal insufficiency several weeks after dapsone discontinuation and developed prominent peripheral motor neuropathy with bilateral thenar atrophy. He did not experience any skin eruptions or relapses in the weeks following prednisone cessation and underwent successful removal of the cement spacer with full left-knee reconstruction 4 months after his initial presentation to our institution. At 9-month dermatology follow-up, the LABD remained in remission.
Comment
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis is a well-documented autoimmune mucocutaneous disorder characterized by linear IgA deposits at the dermoepidermal junction. The development of autoantibodies to antigens within the basement membrane zone leads to both cellular and humoral immune responses that facilitate the subepidermal blistering rash in LABD.2,3 Linear IgA bullous dermatosis affects all ages and races with a bimodal epidemiology. The adult form typically appears after 60 years of age, whereas the childhood form (chronic bullous disease of childhood) appears between 6 months and 6 years of age.3 Medications—particularly vancomycin—are responsible for a substantial portion of cases.1-4 In one review, vancomycin was implicated in almost half (22/52 [42.3%]) of drug-related cases of LABD.4 Other associated medications include captopril, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, phenytoin, and diclo-fenac.3,4 Vancomycin-associated LABD has a substantially shorter time to onset of symptoms, with a mean of 8.6 days compared to 63.8 days for other causative agents.4
The initial treatment of drug-induced LABD is immediate discontinuation of the suspected agent(s) and supportive care.9 Although future avoidance of vancomycin is recommended in patients with a history of LABD, there are reported cases of successful rechallenges.4,10 The early removal of our patient’s cement spacer was discouraged by both the orthopedics and infectious disease consultation services due to potential complications as well as the patient’s gradual improvement during his hospital course.
Dapsone is considered the standard systemic treatment for LABD. Sulfapyridine is an alternative to dapsone, or a combination of these 2 drugs may be used. Corticosteroids can be added to each of these regimens to achieve remission, as in our case.2 Although dapsone was discontinued in the setting of the patient’s AKI, the vancomycin in the dual-eluting spacer was more likely the culprit. A review of 544 postoperative outcomes following the use of an antibiotic-impregnated cement spacer (AICS) during 2-stage arthroplasty displayed an 8- to 10-fold increase in the development of AKIs compared to the rate of AKIs following primary joint arthroplasty.10 While our patient’s AKI was not attributed to dapsone, his prominent peripheral motor neuropathy with resultant bilateral thenar atrophy was a rare complication of dapsone use. While dapsone-associated neuropathy has been reported in daily dosages of as low as 75 mg, it typically is seen in doses of at least 300 mg per day and in larger cumulative dosages.11
Despite having a well-characterized vancomycin-induced LABD in the setting of known vancomycin exposure, our patient’s case was particularly challenging given the continued presence of the vancomycin-impregnated cement spacer (VICS) in the left knee, resulting in vancomycin levels at admission and during subsequent measurements over 2 weeks that were all several-fold higher than the renal clearance predicted.
Vancomycin-associated LABD does not appear to be dose dependent and has been reported at both subtherapeutic1-3 and supratherapeutic levels,5-9 whereas toxicity reactions are more common at supratherapeutic levels.9 The literature on AICS use suggests that drug elution occurs at relatively unpredictable rates based on a variety of factors, including the type of cement used and the initial antibiotic concentration.12,13 Furthermore, the addition of tobramycin to VICSs has been found to increase the rate of vancomycin delivery through a phenomenon known as passive opportunism.14
As AICS devices allow for the delivery of higher concentrations of antibiotics to a localized area, systemic complications are considered rare but have been reported.13 Our report describes a rare case of LABD in the setting of a VICS. One clinical aspect of our case that supports the implication of VICS as the cause of the patient’s LABD is the concentration of bullae overlying the incision site on the left knee. A case of a desquamating rash in a patient with an implanted VICS has been documented in which the early lesions were localized to the surgical leg, as in our case.15 Unlike our case, there was a history of Stevens-Johnson syndrome following previous vancomycin exposure. A case of a gentamicin-impregnated cement spacer causing allergic dermatitis that was most prominent in the surgical leg also has been reported.16 An isomorphic phenomenon (Köbner phenomenon) has been suggested in the setting of
Case Report
A 77-year-old man was admitted to the general medicine service at our institution for treatment of a diffuse macular eruption and hemorrhagic bullae 12 days after undergoing left-knee revision arthroplasty during which a cement spacer impregnated with vancomycin and tobramycin was placed. At the time of the surgery, the patient also received intravenous (IV) vancomycin and oral ciprofloxacin, which were continued postoperatively until his hospital presentation. The patient was recovering well until postoperative day 7, when he developed painful swelling and erythema surrounding the surgical wound on the left knee. Concerned that his symptoms indicated a flare of gout, he restarted a former allopurinol prescription from an outside physician after 2 years of nonuse. The skin changes progressed distally on the left leg over the next 48 hours. By postoperative day 10, he had developed serosanguinous blisters on the left knee (Figure 1A) and oral mucosa (Figure 1B), as well as erythematous nodules on the bilateral palms. He presented to our institution for emergent care on postoperative day 12 following progression of the eruption to the inguinal region (Figure 2A), buttocks (Figure 2B), and abdominal region.


Due to concerns about a potential drug reaction, the IV vancomycin, oral ciprofloxacin, and oral allopurinol were discontinued on hospital admission.

Oral prednisone 60 mg once daily and oral dapsone 25 mg once daily were initiated on hospital days 4 and 6 (postoperative days 15 and 17), respectively. A 6-week course of oral ciprofloxacin 750 mg twice daily and daptomycin 8 mg/kg once daily was initiated for bacterial coverage on hospital day 5 (postoperative day 16). Topical triamcinolone and an anesthetic mouthwash also were used to treat the mucosal involvement. The lesions stabilized on the third day of steroid therapy, and the patient was discharged 7 days after hospital admission (postoperative day 18). Dapsone was rapidly increased to 100 mg once daily over the next week for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis. An increase in prednisone to 80 mg once daily was required 3 days after the patient was discharged due to worsening oral lesions. Five days after discharge, the patient was readmitted to the hospital for 3 days due to acute kidney injury (AKI) in which his baseline creatinine level tripled. The cause of renal impairment was unknown, resulting in empiric discontinuation of dapsone on postoperative day 27. Prophylaxis for P jirovecii pneumonia was replaced with once-monthly inhaled pentamidine. Prednisone was tapered 20 days after the original presentation (postoperative day 32) following gradual improvement of both the skin and oral lesions. At dermatology follow-up 2 weeks later, doxycycline 100 mg twice daily was added for residual inflammation of the left leg. A deep vein thrombosis was discovered in the left leg 10 days later, and 3 months of anticoagulation therapy was initiated with discontinuation of the doxycycline. The patient continued to have renal insufficiency several weeks after dapsone discontinuation and developed prominent peripheral motor neuropathy with bilateral thenar atrophy. He did not experience any skin eruptions or relapses in the weeks following prednisone cessation and underwent successful removal of the cement spacer with full left-knee reconstruction 4 months after his initial presentation to our institution. At 9-month dermatology follow-up, the LABD remained in remission.
Comment
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis is a well-documented autoimmune mucocutaneous disorder characterized by linear IgA deposits at the dermoepidermal junction. The development of autoantibodies to antigens within the basement membrane zone leads to both cellular and humoral immune responses that facilitate the subepidermal blistering rash in LABD.2,3 Linear IgA bullous dermatosis affects all ages and races with a bimodal epidemiology. The adult form typically appears after 60 years of age, whereas the childhood form (chronic bullous disease of childhood) appears between 6 months and 6 years of age.3 Medications—particularly vancomycin—are responsible for a substantial portion of cases.1-4 In one review, vancomycin was implicated in almost half (22/52 [42.3%]) of drug-related cases of LABD.4 Other associated medications include captopril, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, phenytoin, and diclo-fenac.3,4 Vancomycin-associated LABD has a substantially shorter time to onset of symptoms, with a mean of 8.6 days compared to 63.8 days for other causative agents.4
The initial treatment of drug-induced LABD is immediate discontinuation of the suspected agent(s) and supportive care.9 Although future avoidance of vancomycin is recommended in patients with a history of LABD, there are reported cases of successful rechallenges.4,10 The early removal of our patient’s cement spacer was discouraged by both the orthopedics and infectious disease consultation services due to potential complications as well as the patient’s gradual improvement during his hospital course.
Dapsone is considered the standard systemic treatment for LABD. Sulfapyridine is an alternative to dapsone, or a combination of these 2 drugs may be used. Corticosteroids can be added to each of these regimens to achieve remission, as in our case.2 Although dapsone was discontinued in the setting of the patient’s AKI, the vancomycin in the dual-eluting spacer was more likely the culprit. A review of 544 postoperative outcomes following the use of an antibiotic-impregnated cement spacer (AICS) during 2-stage arthroplasty displayed an 8- to 10-fold increase in the development of AKIs compared to the rate of AKIs following primary joint arthroplasty.10 While our patient’s AKI was not attributed to dapsone, his prominent peripheral motor neuropathy with resultant bilateral thenar atrophy was a rare complication of dapsone use. While dapsone-associated neuropathy has been reported in daily dosages of as low as 75 mg, it typically is seen in doses of at least 300 mg per day and in larger cumulative dosages.11
Despite having a well-characterized vancomycin-induced LABD in the setting of known vancomycin exposure, our patient’s case was particularly challenging given the continued presence of the vancomycin-impregnated cement spacer (VICS) in the left knee, resulting in vancomycin levels at admission and during subsequent measurements over 2 weeks that were all several-fold higher than the renal clearance predicted.
Vancomycin-associated LABD does not appear to be dose dependent and has been reported at both subtherapeutic1-3 and supratherapeutic levels,5-9 whereas toxicity reactions are more common at supratherapeutic levels.9 The literature on AICS use suggests that drug elution occurs at relatively unpredictable rates based on a variety of factors, including the type of cement used and the initial antibiotic concentration.12,13 Furthermore, the addition of tobramycin to VICSs has been found to increase the rate of vancomycin delivery through a phenomenon known as passive opportunism.14
As AICS devices allow for the delivery of higher concentrations of antibiotics to a localized area, systemic complications are considered rare but have been reported.13 Our report describes a rare case of LABD in the setting of a VICS. One clinical aspect of our case that supports the implication of VICS as the cause of the patient’s LABD is the concentration of bullae overlying the incision site on the left knee. A case of a desquamating rash in a patient with an implanted VICS has been documented in which the early lesions were localized to the surgical leg, as in our case.15 Unlike our case, there was a history of Stevens-Johnson syndrome following previous vancomycin exposure. A case of a gentamicin-impregnated cement spacer causing allergic dermatitis that was most prominent in the surgical leg also has been reported.16 An isomorphic phenomenon (Köbner phenomenon) has been suggested in the setting of
- Plunkett RW, Chiarello SE, Beutner EH. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis in one of two piroxicam-induced eruptions: a distinct direct immunofluorescence trend revealed by the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:691-696.
- Guide SV, Marinkovich MP. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis. Clin Dermatol. 2001;19:719-727.
- Fortuna G, Marinkovich MP. Linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:38-50.
- Fortuna G, Salas-Alanis JC, Guidetti E, et al. A critical reappraisal of the current data on drug-induced linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis: a real and separate nosological entity? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:988-994.
- Kuechle MK, Stegemeir E, Maynard B, et al. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis: report of six cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30(2, pt 1):187-192.
- Neughebauer BI, Negron G, Pelton S, et al. Bullous skin disease: an unusual allergic reaction to vancomycin. Am J Med Sci. 2002;323:273-278.
- Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981;30:239-245.
- Wiadrowski TP, Reid CM. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous disease following antibiotics. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:196-199.
- Dang LV, Byrom L, Muir J, et al. Vancomycin-induced linear IgA with mucosal and ocular involvement: a case report. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2014;22:e119-e121.
- Luu A, Syed F, Raman G, et al. Two-stage arthroplasty for prosthetic joint infection: a systematic review of acute kidney injury, systemic toxicity and infection control [published online April 8, 2013]. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:1490.e1-1498.e1.
- Daneshmend TK. The neurotoxicity of dapsone. Adverse Drug React Acute Poisoning Rev. 1984;3:43-58.
- Jacobs C, Christensen CP, Berend ME. Static and mobile antibiotic-impregnated cement spacers for the management of prosthetic joint infection. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17:356-368.
- Springer BD, Lee GC, Osmon D, et al. Systemic safety of high-dose antibiotic-loaded cement spacers after resection of an infected total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;427:47-51.
- Penner MJ, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Elution characteristics of vancomycin and tobramycin combined in acrylic bone-cement. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11:939-944.
- Williams B, Hanson A, Sha B. Diffuse desquamating rash following exposure to vancomycin-impregnated bone cement. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48:1061-1065.
- Haeberle M, Wittner B. Is gentamicin-loaded bone cement a risk for developing systemic allergic dermatitis? Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:176-177.
- McDonald HC, York NR, Pandya AG. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis demonstrating the isomorphic phenomenon. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:897-898.
- Plunkett RW, Chiarello SE, Beutner EH. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis in one of two piroxicam-induced eruptions: a distinct direct immunofluorescence trend revealed by the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:691-696.
- Guide SV, Marinkovich MP. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis. Clin Dermatol. 2001;19:719-727.
- Fortuna G, Marinkovich MP. Linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:38-50.
- Fortuna G, Salas-Alanis JC, Guidetti E, et al. A critical reappraisal of the current data on drug-induced linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis: a real and separate nosological entity? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:988-994.
- Kuechle MK, Stegemeir E, Maynard B, et al. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis: report of six cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30(2, pt 1):187-192.
- Neughebauer BI, Negron G, Pelton S, et al. Bullous skin disease: an unusual allergic reaction to vancomycin. Am J Med Sci. 2002;323:273-278.
- Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981;30:239-245.
- Wiadrowski TP, Reid CM. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous disease following antibiotics. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:196-199.
- Dang LV, Byrom L, Muir J, et al. Vancomycin-induced linear IgA with mucosal and ocular involvement: a case report. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2014;22:e119-e121.
- Luu A, Syed F, Raman G, et al. Two-stage arthroplasty for prosthetic joint infection: a systematic review of acute kidney injury, systemic toxicity and infection control [published online April 8, 2013]. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:1490.e1-1498.e1.
- Daneshmend TK. The neurotoxicity of dapsone. Adverse Drug React Acute Poisoning Rev. 1984;3:43-58.
- Jacobs C, Christensen CP, Berend ME. Static and mobile antibiotic-impregnated cement spacers for the management of prosthetic joint infection. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17:356-368.
- Springer BD, Lee GC, Osmon D, et al. Systemic safety of high-dose antibiotic-loaded cement spacers after resection of an infected total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;427:47-51.
- Penner MJ, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Elution characteristics of vancomycin and tobramycin combined in acrylic bone-cement. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11:939-944.
- Williams B, Hanson A, Sha B. Diffuse desquamating rash following exposure to vancomycin-impregnated bone cement. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48:1061-1065.
- Haeberle M, Wittner B. Is gentamicin-loaded bone cement a risk for developing systemic allergic dermatitis? Contact Dermatitis. 2009;60:176-177.
- McDonald HC, York NR, Pandya AG. Drug-induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis demonstrating the isomorphic phenomenon. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62:897-898.
Practice Points
- Linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD) is an autoimmune mucocutaneous disorder characterized by linear IgA deposits at the dermoepidermal junction.
- A substantial number of cases of LABD are drug related, with vancomycin most commonly implicated.
- While antibiotic-impregnated cement spacers deliver high concentrations of local medications, systemic reactions are still possible.
- Dapsone is the first-line treatment for LABD.