User login
Achieving Excellence in Hepatitis B Virus Care for Veterans in the VHA (FULL)
Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which is transmitted through percutaneous (ie, puncture through the skin) or mucosal (ie, direct contact with mucous membranes) exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Hepatitis B virus can cause chronic infection, resulting in cirrhosis of the liver, liver cancer, liver failure, and death. Persons with chronic infection also serve as the main reservoir for continued HBV transmission.1
Individuals at highest risk for infection include those born in geographic regions with a high prevalence of HBV, those with sexual partners or household contacts with chronic HBV infection, men who have sex with men (MSM), those with HIV, and individuals who inject drugs. Pregnant women also are a population of concern given the potential for perinatal transmission.2
About 850,000 to 2.2 million people in the US (about 0.3% of the civilian US population) are chronically infected with HBV.3 The prevalence of chronic HBV is much higher (10%-19%) among Asian Americans, those of Pacific Island descent, and other immigrant populations from highly endemic countries.4 In the US, HBV is responsible for 2,000 to 4,000 preventable deaths annually, primarily from cirrhosis, liver cancer, and hepatic failure.4 In the civilian US population, reported cases of acute HBV decreased 0.3% from 2011 to 2012, increased 5.4% in 2013 with an 8.5% decrease in 2014, and a 20.7% increase in 2015.4 Injection drug use is likely driving the most recent increase.5
Not all individuals exposed to HBV will develop chronic infection, and the risk of chronic HBV infection depends on an individual’s age at the time of exposure. For example, about 95% of infants exposed to HBV perinatally will develop a chronic infection compared with 5% of exposed adults.6 Of those with chronic HBV, a small proportion will develop cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with increasing risk as viral DNA concentrations increase. Additional risk factors for cirrhosis include being older, male, having a persistently elevated alanine transaminase, viral superinfections, HBV reversion/reactivation, genotype, and various markers of disease severity (HCC).6 Of note, chronic HBV infection may cause HCC even in the absence of cirrhosis.7 In addition, immunosuppression (eg, from cancer chemotherapy) may allow HBV reactivation, which may result in fulminant hepatic failure. In the Veterans Health Affairs (VHA) health care system, about 17% of those with known chronic HBV also carry a diagnosis of cirrhosis.
Vaccination is the mainstay of efforts to prevent HBV infection. The first commercially available HBV vaccine was approved by the FDA in 1981, with subsequent FDA approval in 1986 of a vaccine manufactured using recombinant DNA technology.8 In 1991, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended universal childhood vaccination for HBV, with subsequent recommendations for vaccination of adolescents and adults in high-risk groups in 1995, and in 1999 all remaining unvaccinated children aged ≤ 19 years.9 Military policy has been to provide hepatitis B immunization to personnel assigned to the Korean peninsula since 1986 and to all recruits since 2001.10
Following publication of an Institute of Medicine/National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) report, in 2011 the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) released the first National Viral Hepatitis Action Plan.11 The current HHS Action Plan, along with the NASEM National Strategy for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and C: Phase Two Report, commissioned by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), outlines a national strategy to prevent new viral hepatitis infections; reduce deaths and improve the health of people living with viral hepatitis; reduce viral hepatitis health disparities; and coordinate, monitor, and report on implementation of viral hepatitis activities.12 The VA is a critical partner in this federal collaborative effort to achieve excellence in viral hepatitis care.
In August 2016, the HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions Programs in the VA Office of Specialty Care Services convened a National Hepatitis B Working Group consisting of VA subject matter experts (SMEs) and representatives from the VA Central Office stakeholder program offices, with a charge of developing a strategic plan to ensure excellence in HBV prevention, care, and management across the VHA. The task included addressing supportive processes and barriers at each level of the organization through a public health framework and using a population health management approach.
The VA National Strategic Plan for Excellence in HBV Care was focused on the following overarching aims:
- Characterizing the current state of care for veterans with HBV in VA care;
- Developing and disseminating clinical guidance on high-quality care for patients with HBV;
- Developing population data and informatics tools to streamline the identification and monitoring of patients with chronic HBV; and
- Evaluating VHA care for patients with HBV over time.
Care for Veterans With HBV at the VA
The VA health care system is America’s largest integrated health care system, providing care at 1,243 health care facilities, including 170 medical centers and 1,063 outpatient sites of care serving 9 million enrolled veterans each year.13 As of January 2018, there were 10,743 individuals with serologic evidence for chronic HBV infection in VA care, based on a definition of 2 or more detectable surface antigen (sAg) or hepatitis B DNA tests recorded at least 6 months apart.1 About 2,000 additional VA patients have a history of a single positive sAg test. These patients have unclear HBV status and require a second sAg test to determine whether they have a chronic infection.
The prevalence of HBV infection among veterans in VA care is slightly higher than that in the US civilian population at 0.4%.14 Studies of selected subpopulations of veterans have found high seropositivity of prior or chronic HBV infection among homeless veterans and veterans admitted to a psychiatric hospital.15,16 The data from 2015 suggest that homeless veterans have a chronic HBV infection rate of 1.0%.14 Of those with known chronic HBV infection, the plurality are white (40.4%) or African American (40.2%), male (92.4%), with a mean age of 59.9 (SD 12.0) years. According to National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group personal correspondence, the geographic territories with the largest chronic HBV caseload include the Southeast, Gulf Coast, and West Coast. As of January 2018, 1,210 veterans in care have HBV-related cirrhosis.
HBV Screening in VA
The current VA HBV screening guidelines follow those of the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF).17 HBV screening is recommended for unvaccinated individuals in high-risk groups, such as patients with HIV or hepatitis C virus (HCV), those on hemodialysis, those with elevated alanine transaminase/aspartate transaminase of unknown etiology, those on immunosuppressive therapy, injection drug users, the MSM population, people with household contact with an HBV-infected person, people born to an HBV-infected mother, those with risk factors for HBV exposure prior to vaccination, pregnant women, and people born in highly endemic areas regardless of vaccination status.2 The VHA recommends against standardized risk assessment and laboratory screening for HBV infection in the asymptomatic general patient population. However, if risk factors become known during the course of providing usual clinical care, then laboratory screening should be considered.2
Of the 6.1 million VHA users
HBV Care and VA Antiviral Treatment
In a study of an HBV care cascade, Serper and colleagues reviewed a cohort of veterans in the VA with HBV. About 50% of the patients with known chronic HBV in the VA system from 1999 to 2013 had received infectious diseases or gastroenterology/hepatology specialty care in the previous 2 years.19 Follow-up data from the National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group indicated that this remains the case: 52.3% of patients with documented chronic HBV had received specialty care from VA sources in the prior 2 years. Serper and colleagues also reported that among veterans in VHA care with chronic HBV infection and cirrhosis from 1999 to 2013, annual imaging was < 50%, and initiation of antiviral treatment was only 39%. Antiviral therapy and liver imaging were both independently associated with lower mortality for patients with HBV and cirrhosis.19
A review of studies that evaluated the delivery of care for patients with HBV in U.S. civilian populations, including retrospective reviews of private payer claims databases and chart reviews, the Kaiser Permanente claims database, and community gastrointestinal (GI) practice chart reviews, revealed similar practice patterns with those in the VA.20 Across the US, rates of antiviral therapy and HCC surveillance for those with HBV cirrhosis were low, ranging from 14% to 50% and 19% to 60%, respectively. Several of these studies also found that being seen by an HBV specialist was associated with improved care.20
Antiviral treatment of individuals with cirrhosis and chronic HBV infection can reduce the risk of progression to decompensated cirrhosis and liver cancer. Among current VA patients with HBV cirrhosis, 62.4% received at least 1 month of HBV antiviral medication in the prior year. Additionally, biannual liver imaging is recommended in this population to screen for the development of HCC. According to National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group personal correspondence, nationally, 51.2% of individuals with HBV cirrhosis had received at least one instance of liver imaging within the past 6 months, and 71.2% received imaging within the past 12 months.
Prevention of HBV Infection and Sequelae
Vaccination rates in the US vary by age group, with higher immunization rates among those born after 1991 than the rates of those born earlier. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 1988 to 2012 reported 33% immunity among veterans aged < 50 years and 6% among those aged ≥ 50 years.21 In addition to individuals who received childhood vaccination in the 1990s, all new military recruits assigned to the Korean Peninsula were vaccinated for HBV as of 1986, and those joining the military after 2002 received mandatory vaccination.
The VA follows the ACIP/CDC hepatitis B immunization guidelines.22-24 The VA currently recommends HBV immunization among previously unvaccinated adults at increased risk of contracting HBV infection and for any other adult who is seeking protection from HBV infection. The VA also offers general recommendations for prevention of transmission between veterans with known chronic HBV to their household, sexual, or drug-using partners. Transmission prevention guidelines also provide recommendations for vaccination of pregnant women with HBV risk factors and women at risk for HBV infection during pregnancy.22
HBV Care Guidance
One of the core tasks of the VA National Hepatitis B Working Group, given its broad, multidisciplinary expertise in HBV, was developing general clinical guidelines for the provision of high-quality care for patients with HBV. The group reviewed current literature and scientific evidence on care for patients with HBV. The working group relied heavily on the VA’s national guidelines for HBV screening and immunization, which are based on recommendations from the USPSTF, ACIP, CDC, and professional societies. The professional society guidelines included the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease’s Guidelines for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B, the America College of Gastroenterology’s Practice Guidelines: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries, the American Gastroenterological Association Institute’s Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hepatitis B Reactivation during Immunosuppressive Drug Therapy, and CDC’s Guidelines for Screening Pregnant Women for HBV.19,22-27
The working group identified areas for HBV quality improvement that were consistent with the VA and professional guidelines, specific and measurable using VA data, clinically relevant, feasible, and achievable in a defined time period. Areas for targeted improvement will include testing for HBV among high-risk patients, increasing antiviral treatment and HCC surveillance of veterans with HBV-related cirrhosis, decreasing progression of chronic HBV to cirrhosis, and expanding prevention measures, such as immunization among those at high risk for HBV and prevention of HBV reactivation.
At a national level, development of specific and measurable quality of care indicators for HBV will aid in assessing gaps in care and developing strategies to address these gaps. A broader discussion of care for patients with HBV quality with front-line health care providers (HCPs) will be paired with increased education and providing clinical support tools for those HCPs and facilities without access to specialty GI services.
Clinical pharmacists will be critical targets for the dissemination of guidance for HBV care paired with clinical informatics support tools and clinical educational opportunities. As of 2015, there were about 7,700 clinical pharmacists in the VHA and 3,200 had a scope of practice that included prescribing authority. As a result, 20% of HCV prescriptions in the VA in fiscal year 2015
Identification and Monitoring
The HBV working group and the VA Viral Hepatitis Technical Advisory Group are working with field HCPs to develop several informatics tools to promote HBV case identification and quality monitoring. These groups identified several barriers to HBV case identification and monitoring. The following informatics tools are either available or in development to reduce these barriers:
- A local clinical case registry of patients with HBV infection based on ICD codes, which allows users to create custom reports to identify, monitor, and track care;
- Because of the risk of HBV reactivation in patients with chronic HBV infection who receive anti-CD20 agents, such as rituximab, a medication order check to improve HBV screening among veterans receiving anti-CD20 medication;
- Validated patient reports based on laboratory diagnosis of HBV, drawn from all results across the VHA since 1999, made available to all facilities;
- Interactive reports summarizing quality of care for patients with HBV infection, based on facility-level indicators in development by the national HBV working group, will be distributed and enable geographic comparison;
- An HBV immunization clinical reminder that will prompt frontline HCPs to test and vaccinate; and
- An HBV clinical dashboard that will enable HCPs and facilities to identify all their HBV-positive veterans and track their care and outcomes over time.
Evaluating VA Care for Patients with HBV
As indicators of quality of HBV care are refined for VA patients and the health care delivery system, guidance will be made broadly available to frontline HCPs and administrators. The HBV quality of care recommendations will be paired with a suite of clinical informatics tools and virtual educational trainings to ensure that VA HCPs and facilities can streamline care for patients with HBV infection as much as possible. Quality improvement will be measured nationally each year, and strategies to address persistent variability and gaps in care will be developed in collaboration with the VA SME’s, facilities, and HCPs.
Conclusion
Hepatitis B virus is at least as prevalent among veterans who are cared for at VA facilities as it is in the US civilian population. Although care for patients with HBV infection in the VA is similar to care for patients with HBV infection in the community, the VA recognizes areas for improved HBV prevention, testing, care, and treatment. The VA has begun a continuous quality improvement strategic plan to enhance the level of care for patients with HBV infection in VA care. Centralized coordination and communication of VA data combined with veteran- and field-centered policies and operational planning and execution will allow clinically relevant improvements in HBV diagnosis, treatment, and prevention among veterans served by VA.
Click here to read the digital edition.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis B FAQs for health professionals: overview and statistics. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/hbvfaq .htm#overview. Updated January 11, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
2.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Surveillance for viral hepatitis—United States, 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2015surveillance/index.htm. Updated June 19, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
4. Kim WR. Epidemiology of hepatitis B in the United States. Hepatology. 2009;49(suppl 5):S28-S34.
5. Harris AM, Iqbal K, Schillie S, et al. Increases in acute hepatitis B virus infections— Kentucky, Tennessee, and West Virginia, 2006-2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(3):47-50.
6. Liaw YF, Chu CM. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2009;373(9663):582-592.
7. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118-1127.
8. Weinbaum CM, Williams I, Mast EE, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Recommendations for identification and public health management of persons with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008;57(RR-8):1-20.
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Achievements in public health: hepatitis B vaccination—United States, 1982-2002. MMWR. 2002;51(25):549-552, 563.
10. Grabenstein JD, Pittman PR, Greenwood JT, Engler RJ. Immunization to protect the US Armed Forces: heritage, current practice, and prospects. Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28:3-26.
11. Colvin HM, Mitchell AE, eds; Institute of Medicine. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2010.
12. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. A National Strategy for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and C: Phase Two Report. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2017.
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Providing health care for veterans. https://www.va.gov/health. Updated February 20, 2018. Accessed February 22, 2018.
14. Noska AJ, Belperio PS, Loomis TP, O’Toole TP, Backus LI. Prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis C virus, and hepatitis B virus among homeless and nonhomeless United States veterans. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(2):252-258.
15. Gelberg L, Robertson MJ, Leake B, et al. Hepatitis B among homeless and other impoverished US military veterans in residential care in Los Angeles. Public Health. 2001;115(4):286-291.
16. Tabibian JH, Wirshing DA, Pierre JM, et al. Hepatitis B and C among veterans in a psychiatric ward. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(6):1693-1698
17. US Preventive Services Task Force. Final recommendation statement: screening for hepatitis B virus infection in nonpregnant adolescents and adults. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/RecommendationStatementFinal/hepatitis-b-virus-infection-screening-2014. Published May 2014. Updated February 2018. Accessed February 22, 2018.
18. Backus LI, Belperio PS, Loomis TP, Han SH, Mole LA. Screening for and prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection among high-risk veterans under the care of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs: a case report. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(12):926-928.
19. Serper M, Choi G, Forde KA, Kaplan DE. Care delivery and outcomes among US veterans with hepatitis B: a national cohort study. Hepatology. 2016;63(6):1774-1782.
20. Mellinger J, Fontana RJ. Quality of care metrics in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016;63(6):1755-1758.
21. Roberts H, Kruszon-Moran D, Ly KN, et al. Prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in U.S. households: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1988-2012. Hepatology. 2016;63(2):388-397.
22. US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Clinical Preventive Service Guidance Statements: Hepatitis B Immunization. http://vaww.prevention.va.gov/CPS/Hepatitis_B_Immunization.asp. Nonpublic document. Source not verified.
23. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Recommended immunization schedule for adults aged 19 years or older, United States, 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/adult.html. Accessed February 12, 2018.
24. Schillie S, Vellozzi C, Reingold A, et al. Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus infection in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR. 2018;67(1):1-31.
25. Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Murad MH; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016;63(1):261-283.
26. Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(1):18-35.
27. Reddy KR, Beavers KL, Hammond SP, Lim JK, Falck-Ytter YT; American Gastroenterological Association Institute. American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(1):215-219, quiz e16-e17.
28. Ourth H, Groppi J, Morreale AP, Quicci-Roberts K. Clinical pharmacist prescribing activities in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1406-1415.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which is transmitted through percutaneous (ie, puncture through the skin) or mucosal (ie, direct contact with mucous membranes) exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Hepatitis B virus can cause chronic infection, resulting in cirrhosis of the liver, liver cancer, liver failure, and death. Persons with chronic infection also serve as the main reservoir for continued HBV transmission.1
Individuals at highest risk for infection include those born in geographic regions with a high prevalence of HBV, those with sexual partners or household contacts with chronic HBV infection, men who have sex with men (MSM), those with HIV, and individuals who inject drugs. Pregnant women also are a population of concern given the potential for perinatal transmission.2
About 850,000 to 2.2 million people in the US (about 0.3% of the civilian US population) are chronically infected with HBV.3 The prevalence of chronic HBV is much higher (10%-19%) among Asian Americans, those of Pacific Island descent, and other immigrant populations from highly endemic countries.4 In the US, HBV is responsible for 2,000 to 4,000 preventable deaths annually, primarily from cirrhosis, liver cancer, and hepatic failure.4 In the civilian US population, reported cases of acute HBV decreased 0.3% from 2011 to 2012, increased 5.4% in 2013 with an 8.5% decrease in 2014, and a 20.7% increase in 2015.4 Injection drug use is likely driving the most recent increase.5
Not all individuals exposed to HBV will develop chronic infection, and the risk of chronic HBV infection depends on an individual’s age at the time of exposure. For example, about 95% of infants exposed to HBV perinatally will develop a chronic infection compared with 5% of exposed adults.6 Of those with chronic HBV, a small proportion will develop cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with increasing risk as viral DNA concentrations increase. Additional risk factors for cirrhosis include being older, male, having a persistently elevated alanine transaminase, viral superinfections, HBV reversion/reactivation, genotype, and various markers of disease severity (HCC).6 Of note, chronic HBV infection may cause HCC even in the absence of cirrhosis.7 In addition, immunosuppression (eg, from cancer chemotherapy) may allow HBV reactivation, which may result in fulminant hepatic failure. In the Veterans Health Affairs (VHA) health care system, about 17% of those with known chronic HBV also carry a diagnosis of cirrhosis.
Vaccination is the mainstay of efforts to prevent HBV infection. The first commercially available HBV vaccine was approved by the FDA in 1981, with subsequent FDA approval in 1986 of a vaccine manufactured using recombinant DNA technology.8 In 1991, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended universal childhood vaccination for HBV, with subsequent recommendations for vaccination of adolescents and adults in high-risk groups in 1995, and in 1999 all remaining unvaccinated children aged ≤ 19 years.9 Military policy has been to provide hepatitis B immunization to personnel assigned to the Korean peninsula since 1986 and to all recruits since 2001.10
Following publication of an Institute of Medicine/National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) report, in 2011 the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) released the first National Viral Hepatitis Action Plan.11 The current HHS Action Plan, along with the NASEM National Strategy for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and C: Phase Two Report, commissioned by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), outlines a national strategy to prevent new viral hepatitis infections; reduce deaths and improve the health of people living with viral hepatitis; reduce viral hepatitis health disparities; and coordinate, monitor, and report on implementation of viral hepatitis activities.12 The VA is a critical partner in this federal collaborative effort to achieve excellence in viral hepatitis care.
In August 2016, the HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions Programs in the VA Office of Specialty Care Services convened a National Hepatitis B Working Group consisting of VA subject matter experts (SMEs) and representatives from the VA Central Office stakeholder program offices, with a charge of developing a strategic plan to ensure excellence in HBV prevention, care, and management across the VHA. The task included addressing supportive processes and barriers at each level of the organization through a public health framework and using a population health management approach.
The VA National Strategic Plan for Excellence in HBV Care was focused on the following overarching aims:
- Characterizing the current state of care for veterans with HBV in VA care;
- Developing and disseminating clinical guidance on high-quality care for patients with HBV;
- Developing population data and informatics tools to streamline the identification and monitoring of patients with chronic HBV; and
- Evaluating VHA care for patients with HBV over time.
Care for Veterans With HBV at the VA
The VA health care system is America’s largest integrated health care system, providing care at 1,243 health care facilities, including 170 medical centers and 1,063 outpatient sites of care serving 9 million enrolled veterans each year.13 As of January 2018, there were 10,743 individuals with serologic evidence for chronic HBV infection in VA care, based on a definition of 2 or more detectable surface antigen (sAg) or hepatitis B DNA tests recorded at least 6 months apart.1 About 2,000 additional VA patients have a history of a single positive sAg test. These patients have unclear HBV status and require a second sAg test to determine whether they have a chronic infection.
The prevalence of HBV infection among veterans in VA care is slightly higher than that in the US civilian population at 0.4%.14 Studies of selected subpopulations of veterans have found high seropositivity of prior or chronic HBV infection among homeless veterans and veterans admitted to a psychiatric hospital.15,16 The data from 2015 suggest that homeless veterans have a chronic HBV infection rate of 1.0%.14 Of those with known chronic HBV infection, the plurality are white (40.4%) or African American (40.2%), male (92.4%), with a mean age of 59.9 (SD 12.0) years. According to National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group personal correspondence, the geographic territories with the largest chronic HBV caseload include the Southeast, Gulf Coast, and West Coast. As of January 2018, 1,210 veterans in care have HBV-related cirrhosis.
HBV Screening in VA
The current VA HBV screening guidelines follow those of the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF).17 HBV screening is recommended for unvaccinated individuals in high-risk groups, such as patients with HIV or hepatitis C virus (HCV), those on hemodialysis, those with elevated alanine transaminase/aspartate transaminase of unknown etiology, those on immunosuppressive therapy, injection drug users, the MSM population, people with household contact with an HBV-infected person, people born to an HBV-infected mother, those with risk factors for HBV exposure prior to vaccination, pregnant women, and people born in highly endemic areas regardless of vaccination status.2 The VHA recommends against standardized risk assessment and laboratory screening for HBV infection in the asymptomatic general patient population. However, if risk factors become known during the course of providing usual clinical care, then laboratory screening should be considered.2
Of the 6.1 million VHA users
HBV Care and VA Antiviral Treatment
In a study of an HBV care cascade, Serper and colleagues reviewed a cohort of veterans in the VA with HBV. About 50% of the patients with known chronic HBV in the VA system from 1999 to 2013 had received infectious diseases or gastroenterology/hepatology specialty care in the previous 2 years.19 Follow-up data from the National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group indicated that this remains the case: 52.3% of patients with documented chronic HBV had received specialty care from VA sources in the prior 2 years. Serper and colleagues also reported that among veterans in VHA care with chronic HBV infection and cirrhosis from 1999 to 2013, annual imaging was < 50%, and initiation of antiviral treatment was only 39%. Antiviral therapy and liver imaging were both independently associated with lower mortality for patients with HBV and cirrhosis.19
A review of studies that evaluated the delivery of care for patients with HBV in U.S. civilian populations, including retrospective reviews of private payer claims databases and chart reviews, the Kaiser Permanente claims database, and community gastrointestinal (GI) practice chart reviews, revealed similar practice patterns with those in the VA.20 Across the US, rates of antiviral therapy and HCC surveillance for those with HBV cirrhosis were low, ranging from 14% to 50% and 19% to 60%, respectively. Several of these studies also found that being seen by an HBV specialist was associated with improved care.20
Antiviral treatment of individuals with cirrhosis and chronic HBV infection can reduce the risk of progression to decompensated cirrhosis and liver cancer. Among current VA patients with HBV cirrhosis, 62.4% received at least 1 month of HBV antiviral medication in the prior year. Additionally, biannual liver imaging is recommended in this population to screen for the development of HCC. According to National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group personal correspondence, nationally, 51.2% of individuals with HBV cirrhosis had received at least one instance of liver imaging within the past 6 months, and 71.2% received imaging within the past 12 months.
Prevention of HBV Infection and Sequelae
Vaccination rates in the US vary by age group, with higher immunization rates among those born after 1991 than the rates of those born earlier. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 1988 to 2012 reported 33% immunity among veterans aged < 50 years and 6% among those aged ≥ 50 years.21 In addition to individuals who received childhood vaccination in the 1990s, all new military recruits assigned to the Korean Peninsula were vaccinated for HBV as of 1986, and those joining the military after 2002 received mandatory vaccination.
The VA follows the ACIP/CDC hepatitis B immunization guidelines.22-24 The VA currently recommends HBV immunization among previously unvaccinated adults at increased risk of contracting HBV infection and for any other adult who is seeking protection from HBV infection. The VA also offers general recommendations for prevention of transmission between veterans with known chronic HBV to their household, sexual, or drug-using partners. Transmission prevention guidelines also provide recommendations for vaccination of pregnant women with HBV risk factors and women at risk for HBV infection during pregnancy.22
HBV Care Guidance
One of the core tasks of the VA National Hepatitis B Working Group, given its broad, multidisciplinary expertise in HBV, was developing general clinical guidelines for the provision of high-quality care for patients with HBV. The group reviewed current literature and scientific evidence on care for patients with HBV. The working group relied heavily on the VA’s national guidelines for HBV screening and immunization, which are based on recommendations from the USPSTF, ACIP, CDC, and professional societies. The professional society guidelines included the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease’s Guidelines for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B, the America College of Gastroenterology’s Practice Guidelines: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries, the American Gastroenterological Association Institute’s Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hepatitis B Reactivation during Immunosuppressive Drug Therapy, and CDC’s Guidelines for Screening Pregnant Women for HBV.19,22-27
The working group identified areas for HBV quality improvement that were consistent with the VA and professional guidelines, specific and measurable using VA data, clinically relevant, feasible, and achievable in a defined time period. Areas for targeted improvement will include testing for HBV among high-risk patients, increasing antiviral treatment and HCC surveillance of veterans with HBV-related cirrhosis, decreasing progression of chronic HBV to cirrhosis, and expanding prevention measures, such as immunization among those at high risk for HBV and prevention of HBV reactivation.
At a national level, development of specific and measurable quality of care indicators for HBV will aid in assessing gaps in care and developing strategies to address these gaps. A broader discussion of care for patients with HBV quality with front-line health care providers (HCPs) will be paired with increased education and providing clinical support tools for those HCPs and facilities without access to specialty GI services.
Clinical pharmacists will be critical targets for the dissemination of guidance for HBV care paired with clinical informatics support tools and clinical educational opportunities. As of 2015, there were about 7,700 clinical pharmacists in the VHA and 3,200 had a scope of practice that included prescribing authority. As a result, 20% of HCV prescriptions in the VA in fiscal year 2015
Identification and Monitoring
The HBV working group and the VA Viral Hepatitis Technical Advisory Group are working with field HCPs to develop several informatics tools to promote HBV case identification and quality monitoring. These groups identified several barriers to HBV case identification and monitoring. The following informatics tools are either available or in development to reduce these barriers:
- A local clinical case registry of patients with HBV infection based on ICD codes, which allows users to create custom reports to identify, monitor, and track care;
- Because of the risk of HBV reactivation in patients with chronic HBV infection who receive anti-CD20 agents, such as rituximab, a medication order check to improve HBV screening among veterans receiving anti-CD20 medication;
- Validated patient reports based on laboratory diagnosis of HBV, drawn from all results across the VHA since 1999, made available to all facilities;
- Interactive reports summarizing quality of care for patients with HBV infection, based on facility-level indicators in development by the national HBV working group, will be distributed and enable geographic comparison;
- An HBV immunization clinical reminder that will prompt frontline HCPs to test and vaccinate; and
- An HBV clinical dashboard that will enable HCPs and facilities to identify all their HBV-positive veterans and track their care and outcomes over time.
Evaluating VA Care for Patients with HBV
As indicators of quality of HBV care are refined for VA patients and the health care delivery system, guidance will be made broadly available to frontline HCPs and administrators. The HBV quality of care recommendations will be paired with a suite of clinical informatics tools and virtual educational trainings to ensure that VA HCPs and facilities can streamline care for patients with HBV infection as much as possible. Quality improvement will be measured nationally each year, and strategies to address persistent variability and gaps in care will be developed in collaboration with the VA SME’s, facilities, and HCPs.
Conclusion
Hepatitis B virus is at least as prevalent among veterans who are cared for at VA facilities as it is in the US civilian population. Although care for patients with HBV infection in the VA is similar to care for patients with HBV infection in the community, the VA recognizes areas for improved HBV prevention, testing, care, and treatment. The VA has begun a continuous quality improvement strategic plan to enhance the level of care for patients with HBV infection in VA care. Centralized coordination and communication of VA data combined with veteran- and field-centered policies and operational planning and execution will allow clinically relevant improvements in HBV diagnosis, treatment, and prevention among veterans served by VA.
Click here to read the digital edition.
Hepatitis B is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which is transmitted through percutaneous (ie, puncture through the skin) or mucosal (ie, direct contact with mucous membranes) exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Hepatitis B virus can cause chronic infection, resulting in cirrhosis of the liver, liver cancer, liver failure, and death. Persons with chronic infection also serve as the main reservoir for continued HBV transmission.1
Individuals at highest risk for infection include those born in geographic regions with a high prevalence of HBV, those with sexual partners or household contacts with chronic HBV infection, men who have sex with men (MSM), those with HIV, and individuals who inject drugs. Pregnant women also are a population of concern given the potential for perinatal transmission.2
About 850,000 to 2.2 million people in the US (about 0.3% of the civilian US population) are chronically infected with HBV.3 The prevalence of chronic HBV is much higher (10%-19%) among Asian Americans, those of Pacific Island descent, and other immigrant populations from highly endemic countries.4 In the US, HBV is responsible for 2,000 to 4,000 preventable deaths annually, primarily from cirrhosis, liver cancer, and hepatic failure.4 In the civilian US population, reported cases of acute HBV decreased 0.3% from 2011 to 2012, increased 5.4% in 2013 with an 8.5% decrease in 2014, and a 20.7% increase in 2015.4 Injection drug use is likely driving the most recent increase.5
Not all individuals exposed to HBV will develop chronic infection, and the risk of chronic HBV infection depends on an individual’s age at the time of exposure. For example, about 95% of infants exposed to HBV perinatally will develop a chronic infection compared with 5% of exposed adults.6 Of those with chronic HBV, a small proportion will develop cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with increasing risk as viral DNA concentrations increase. Additional risk factors for cirrhosis include being older, male, having a persistently elevated alanine transaminase, viral superinfections, HBV reversion/reactivation, genotype, and various markers of disease severity (HCC).6 Of note, chronic HBV infection may cause HCC even in the absence of cirrhosis.7 In addition, immunosuppression (eg, from cancer chemotherapy) may allow HBV reactivation, which may result in fulminant hepatic failure. In the Veterans Health Affairs (VHA) health care system, about 17% of those with known chronic HBV also carry a diagnosis of cirrhosis.
Vaccination is the mainstay of efforts to prevent HBV infection. The first commercially available HBV vaccine was approved by the FDA in 1981, with subsequent FDA approval in 1986 of a vaccine manufactured using recombinant DNA technology.8 In 1991, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended universal childhood vaccination for HBV, with subsequent recommendations for vaccination of adolescents and adults in high-risk groups in 1995, and in 1999 all remaining unvaccinated children aged ≤ 19 years.9 Military policy has been to provide hepatitis B immunization to personnel assigned to the Korean peninsula since 1986 and to all recruits since 2001.10
Following publication of an Institute of Medicine/National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) report, in 2011 the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) released the first National Viral Hepatitis Action Plan.11 The current HHS Action Plan, along with the NASEM National Strategy for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and C: Phase Two Report, commissioned by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), outlines a national strategy to prevent new viral hepatitis infections; reduce deaths and improve the health of people living with viral hepatitis; reduce viral hepatitis health disparities; and coordinate, monitor, and report on implementation of viral hepatitis activities.12 The VA is a critical partner in this federal collaborative effort to achieve excellence in viral hepatitis care.
In August 2016, the HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions Programs in the VA Office of Specialty Care Services convened a National Hepatitis B Working Group consisting of VA subject matter experts (SMEs) and representatives from the VA Central Office stakeholder program offices, with a charge of developing a strategic plan to ensure excellence in HBV prevention, care, and management across the VHA. The task included addressing supportive processes and barriers at each level of the organization through a public health framework and using a population health management approach.
The VA National Strategic Plan for Excellence in HBV Care was focused on the following overarching aims:
- Characterizing the current state of care for veterans with HBV in VA care;
- Developing and disseminating clinical guidance on high-quality care for patients with HBV;
- Developing population data and informatics tools to streamline the identification and monitoring of patients with chronic HBV; and
- Evaluating VHA care for patients with HBV over time.
Care for Veterans With HBV at the VA
The VA health care system is America’s largest integrated health care system, providing care at 1,243 health care facilities, including 170 medical centers and 1,063 outpatient sites of care serving 9 million enrolled veterans each year.13 As of January 2018, there were 10,743 individuals with serologic evidence for chronic HBV infection in VA care, based on a definition of 2 or more detectable surface antigen (sAg) or hepatitis B DNA tests recorded at least 6 months apart.1 About 2,000 additional VA patients have a history of a single positive sAg test. These patients have unclear HBV status and require a second sAg test to determine whether they have a chronic infection.
The prevalence of HBV infection among veterans in VA care is slightly higher than that in the US civilian population at 0.4%.14 Studies of selected subpopulations of veterans have found high seropositivity of prior or chronic HBV infection among homeless veterans and veterans admitted to a psychiatric hospital.15,16 The data from 2015 suggest that homeless veterans have a chronic HBV infection rate of 1.0%.14 Of those with known chronic HBV infection, the plurality are white (40.4%) or African American (40.2%), male (92.4%), with a mean age of 59.9 (SD 12.0) years. According to National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group personal correspondence, the geographic territories with the largest chronic HBV caseload include the Southeast, Gulf Coast, and West Coast. As of January 2018, 1,210 veterans in care have HBV-related cirrhosis.
HBV Screening in VA
The current VA HBV screening guidelines follow those of the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF).17 HBV screening is recommended for unvaccinated individuals in high-risk groups, such as patients with HIV or hepatitis C virus (HCV), those on hemodialysis, those with elevated alanine transaminase/aspartate transaminase of unknown etiology, those on immunosuppressive therapy, injection drug users, the MSM population, people with household contact with an HBV-infected person, people born to an HBV-infected mother, those with risk factors for HBV exposure prior to vaccination, pregnant women, and people born in highly endemic areas regardless of vaccination status.2 The VHA recommends against standardized risk assessment and laboratory screening for HBV infection in the asymptomatic general patient population. However, if risk factors become known during the course of providing usual clinical care, then laboratory screening should be considered.2
Of the 6.1 million VHA users
HBV Care and VA Antiviral Treatment
In a study of an HBV care cascade, Serper and colleagues reviewed a cohort of veterans in the VA with HBV. About 50% of the patients with known chronic HBV in the VA system from 1999 to 2013 had received infectious diseases or gastroenterology/hepatology specialty care in the previous 2 years.19 Follow-up data from the National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group indicated that this remains the case: 52.3% of patients with documented chronic HBV had received specialty care from VA sources in the prior 2 years. Serper and colleagues also reported that among veterans in VHA care with chronic HBV infection and cirrhosis from 1999 to 2013, annual imaging was < 50%, and initiation of antiviral treatment was only 39%. Antiviral therapy and liver imaging were both independently associated with lower mortality for patients with HBV and cirrhosis.19
A review of studies that evaluated the delivery of care for patients with HBV in U.S. civilian populations, including retrospective reviews of private payer claims databases and chart reviews, the Kaiser Permanente claims database, and community gastrointestinal (GI) practice chart reviews, revealed similar practice patterns with those in the VA.20 Across the US, rates of antiviral therapy and HCC surveillance for those with HBV cirrhosis were low, ranging from 14% to 50% and 19% to 60%, respectively. Several of these studies also found that being seen by an HBV specialist was associated with improved care.20
Antiviral treatment of individuals with cirrhosis and chronic HBV infection can reduce the risk of progression to decompensated cirrhosis and liver cancer. Among current VA patients with HBV cirrhosis, 62.4% received at least 1 month of HBV antiviral medication in the prior year. Additionally, biannual liver imaging is recommended in this population to screen for the development of HCC. According to National HIV, Hepatitis and Related Conditions Data and Analysis Group personal correspondence, nationally, 51.2% of individuals with HBV cirrhosis had received at least one instance of liver imaging within the past 6 months, and 71.2% received imaging within the past 12 months.
Prevention of HBV Infection and Sequelae
Vaccination rates in the US vary by age group, with higher immunization rates among those born after 1991 than the rates of those born earlier. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 1988 to 2012 reported 33% immunity among veterans aged < 50 years and 6% among those aged ≥ 50 years.21 In addition to individuals who received childhood vaccination in the 1990s, all new military recruits assigned to the Korean Peninsula were vaccinated for HBV as of 1986, and those joining the military after 2002 received mandatory vaccination.
The VA follows the ACIP/CDC hepatitis B immunization guidelines.22-24 The VA currently recommends HBV immunization among previously unvaccinated adults at increased risk of contracting HBV infection and for any other adult who is seeking protection from HBV infection. The VA also offers general recommendations for prevention of transmission between veterans with known chronic HBV to their household, sexual, or drug-using partners. Transmission prevention guidelines also provide recommendations for vaccination of pregnant women with HBV risk factors and women at risk for HBV infection during pregnancy.22
HBV Care Guidance
One of the core tasks of the VA National Hepatitis B Working Group, given its broad, multidisciplinary expertise in HBV, was developing general clinical guidelines for the provision of high-quality care for patients with HBV. The group reviewed current literature and scientific evidence on care for patients with HBV. The working group relied heavily on the VA’s national guidelines for HBV screening and immunization, which are based on recommendations from the USPSTF, ACIP, CDC, and professional societies. The professional society guidelines included the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease’s Guidelines for Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B, the America College of Gastroenterology’s Practice Guidelines: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries, the American Gastroenterological Association Institute’s Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hepatitis B Reactivation during Immunosuppressive Drug Therapy, and CDC’s Guidelines for Screening Pregnant Women for HBV.19,22-27
The working group identified areas for HBV quality improvement that were consistent with the VA and professional guidelines, specific and measurable using VA data, clinically relevant, feasible, and achievable in a defined time period. Areas for targeted improvement will include testing for HBV among high-risk patients, increasing antiviral treatment and HCC surveillance of veterans with HBV-related cirrhosis, decreasing progression of chronic HBV to cirrhosis, and expanding prevention measures, such as immunization among those at high risk for HBV and prevention of HBV reactivation.
At a national level, development of specific and measurable quality of care indicators for HBV will aid in assessing gaps in care and developing strategies to address these gaps. A broader discussion of care for patients with HBV quality with front-line health care providers (HCPs) will be paired with increased education and providing clinical support tools for those HCPs and facilities without access to specialty GI services.
Clinical pharmacists will be critical targets for the dissemination of guidance for HBV care paired with clinical informatics support tools and clinical educational opportunities. As of 2015, there were about 7,700 clinical pharmacists in the VHA and 3,200 had a scope of practice that included prescribing authority. As a result, 20% of HCV prescriptions in the VA in fiscal year 2015
Identification and Monitoring
The HBV working group and the VA Viral Hepatitis Technical Advisory Group are working with field HCPs to develop several informatics tools to promote HBV case identification and quality monitoring. These groups identified several barriers to HBV case identification and monitoring. The following informatics tools are either available or in development to reduce these barriers:
- A local clinical case registry of patients with HBV infection based on ICD codes, which allows users to create custom reports to identify, monitor, and track care;
- Because of the risk of HBV reactivation in patients with chronic HBV infection who receive anti-CD20 agents, such as rituximab, a medication order check to improve HBV screening among veterans receiving anti-CD20 medication;
- Validated patient reports based on laboratory diagnosis of HBV, drawn from all results across the VHA since 1999, made available to all facilities;
- Interactive reports summarizing quality of care for patients with HBV infection, based on facility-level indicators in development by the national HBV working group, will be distributed and enable geographic comparison;
- An HBV immunization clinical reminder that will prompt frontline HCPs to test and vaccinate; and
- An HBV clinical dashboard that will enable HCPs and facilities to identify all their HBV-positive veterans and track their care and outcomes over time.
Evaluating VA Care for Patients with HBV
As indicators of quality of HBV care are refined for VA patients and the health care delivery system, guidance will be made broadly available to frontline HCPs and administrators. The HBV quality of care recommendations will be paired with a suite of clinical informatics tools and virtual educational trainings to ensure that VA HCPs and facilities can streamline care for patients with HBV infection as much as possible. Quality improvement will be measured nationally each year, and strategies to address persistent variability and gaps in care will be developed in collaboration with the VA SME’s, facilities, and HCPs.
Conclusion
Hepatitis B virus is at least as prevalent among veterans who are cared for at VA facilities as it is in the US civilian population. Although care for patients with HBV infection in the VA is similar to care for patients with HBV infection in the community, the VA recognizes areas for improved HBV prevention, testing, care, and treatment. The VA has begun a continuous quality improvement strategic plan to enhance the level of care for patients with HBV infection in VA care. Centralized coordination and communication of VA data combined with veteran- and field-centered policies and operational planning and execution will allow clinically relevant improvements in HBV diagnosis, treatment, and prevention among veterans served by VA.
Click here to read the digital edition.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis B FAQs for health professionals: overview and statistics. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/hbvfaq .htm#overview. Updated January 11, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
2.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Surveillance for viral hepatitis—United States, 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2015surveillance/index.htm. Updated June 19, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
4. Kim WR. Epidemiology of hepatitis B in the United States. Hepatology. 2009;49(suppl 5):S28-S34.
5. Harris AM, Iqbal K, Schillie S, et al. Increases in acute hepatitis B virus infections— Kentucky, Tennessee, and West Virginia, 2006-2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(3):47-50.
6. Liaw YF, Chu CM. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2009;373(9663):582-592.
7. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118-1127.
8. Weinbaum CM, Williams I, Mast EE, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Recommendations for identification and public health management of persons with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008;57(RR-8):1-20.
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Achievements in public health: hepatitis B vaccination—United States, 1982-2002. MMWR. 2002;51(25):549-552, 563.
10. Grabenstein JD, Pittman PR, Greenwood JT, Engler RJ. Immunization to protect the US Armed Forces: heritage, current practice, and prospects. Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28:3-26.
11. Colvin HM, Mitchell AE, eds; Institute of Medicine. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2010.
12. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. A National Strategy for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and C: Phase Two Report. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2017.
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Providing health care for veterans. https://www.va.gov/health. Updated February 20, 2018. Accessed February 22, 2018.
14. Noska AJ, Belperio PS, Loomis TP, O’Toole TP, Backus LI. Prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis C virus, and hepatitis B virus among homeless and nonhomeless United States veterans. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(2):252-258.
15. Gelberg L, Robertson MJ, Leake B, et al. Hepatitis B among homeless and other impoverished US military veterans in residential care in Los Angeles. Public Health. 2001;115(4):286-291.
16. Tabibian JH, Wirshing DA, Pierre JM, et al. Hepatitis B and C among veterans in a psychiatric ward. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(6):1693-1698
17. US Preventive Services Task Force. Final recommendation statement: screening for hepatitis B virus infection in nonpregnant adolescents and adults. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/RecommendationStatementFinal/hepatitis-b-virus-infection-screening-2014. Published May 2014. Updated February 2018. Accessed February 22, 2018.
18. Backus LI, Belperio PS, Loomis TP, Han SH, Mole LA. Screening for and prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection among high-risk veterans under the care of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs: a case report. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(12):926-928.
19. Serper M, Choi G, Forde KA, Kaplan DE. Care delivery and outcomes among US veterans with hepatitis B: a national cohort study. Hepatology. 2016;63(6):1774-1782.
20. Mellinger J, Fontana RJ. Quality of care metrics in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016;63(6):1755-1758.
21. Roberts H, Kruszon-Moran D, Ly KN, et al. Prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in U.S. households: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1988-2012. Hepatology. 2016;63(2):388-397.
22. US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Clinical Preventive Service Guidance Statements: Hepatitis B Immunization. http://vaww.prevention.va.gov/CPS/Hepatitis_B_Immunization.asp. Nonpublic document. Source not verified.
23. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Recommended immunization schedule for adults aged 19 years or older, United States, 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/adult.html. Accessed February 12, 2018.
24. Schillie S, Vellozzi C, Reingold A, et al. Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus infection in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR. 2018;67(1):1-31.
25. Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Murad MH; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016;63(1):261-283.
26. Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(1):18-35.
27. Reddy KR, Beavers KL, Hammond SP, Lim JK, Falck-Ytter YT; American Gastroenterological Association Institute. American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(1):215-219, quiz e16-e17.
28. Ourth H, Groppi J, Morreale AP, Quicci-Roberts K. Clinical pharmacist prescribing activities in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1406-1415.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis B FAQs for health professionals: overview and statistics. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/hbvfaq .htm#overview. Updated January 11, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
2.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Surveillance for viral hepatitis—United States, 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2015surveillance/index.htm. Updated June 19, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
4. Kim WR. Epidemiology of hepatitis B in the United States. Hepatology. 2009;49(suppl 5):S28-S34.
5. Harris AM, Iqbal K, Schillie S, et al. Increases in acute hepatitis B virus infections— Kentucky, Tennessee, and West Virginia, 2006-2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65(3):47-50.
6. Liaw YF, Chu CM. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2009;373(9663):582-592.
7. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118-1127.
8. Weinbaum CM, Williams I, Mast EE, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Recommendations for identification and public health management of persons with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008;57(RR-8):1-20.
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Achievements in public health: hepatitis B vaccination—United States, 1982-2002. MMWR. 2002;51(25):549-552, 563.
10. Grabenstein JD, Pittman PR, Greenwood JT, Engler RJ. Immunization to protect the US Armed Forces: heritage, current practice, and prospects. Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28:3-26.
11. Colvin HM, Mitchell AE, eds; Institute of Medicine. Hepatitis and Liver Cancer: A National Strategy for Prevention and Control of Hepatitis B and C. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2010.
12. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. A National Strategy for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and C: Phase Two Report. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2017.
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Providing health care for veterans. https://www.va.gov/health. Updated February 20, 2018. Accessed February 22, 2018.
14. Noska AJ, Belperio PS, Loomis TP, O’Toole TP, Backus LI. Prevalence of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis C virus, and hepatitis B virus among homeless and nonhomeless United States veterans. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;65(2):252-258.
15. Gelberg L, Robertson MJ, Leake B, et al. Hepatitis B among homeless and other impoverished US military veterans in residential care in Los Angeles. Public Health. 2001;115(4):286-291.
16. Tabibian JH, Wirshing DA, Pierre JM, et al. Hepatitis B and C among veterans in a psychiatric ward. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(6):1693-1698
17. US Preventive Services Task Force. Final recommendation statement: screening for hepatitis B virus infection in nonpregnant adolescents and adults. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/Page/Document/RecommendationStatementFinal/hepatitis-b-virus-infection-screening-2014. Published May 2014. Updated February 2018. Accessed February 22, 2018.
18. Backus LI, Belperio PS, Loomis TP, Han SH, Mole LA. Screening for and prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection among high-risk veterans under the care of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs: a case report. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(12):926-928.
19. Serper M, Choi G, Forde KA, Kaplan DE. Care delivery and outcomes among US veterans with hepatitis B: a national cohort study. Hepatology. 2016;63(6):1774-1782.
20. Mellinger J, Fontana RJ. Quality of care metrics in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016;63(6):1755-1758.
21. Roberts H, Kruszon-Moran D, Ly KN, et al. Prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in U.S. households: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1988-2012. Hepatology. 2016;63(2):388-397.
22. US Department of Veterans Affairs. National Clinical Preventive Service Guidance Statements: Hepatitis B Immunization. http://vaww.prevention.va.gov/CPS/Hepatitis_B_Immunization.asp. Nonpublic document. Source not verified.
23. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Recommended immunization schedule for adults aged 19 years or older, United States, 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/adult.html. Accessed February 12, 2018.
24. Schillie S, Vellozzi C, Reingold A, et al. Prevention of Hepatitis B Virus infection in the United States: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR. 2018;67(1):1-31.
25. Terrault NA, Bzowej NH, Chang KM, Hwang JP, Jonas MM, Murad MH; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. AASLD guidelines for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2016;63(1):261-283.
26. Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. ACG clinical guideline: evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(1):18-35.
27. Reddy KR, Beavers KL, Hammond SP, Lim JK, Falck-Ytter YT; American Gastroenterological Association Institute. American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(1):215-219, quiz e16-e17.
28. Ourth H, Groppi J, Morreale AP, Quicci-Roberts K. Clinical pharmacist prescribing activities in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1406-1415.
Hepatitis A Virus Prevention and Vaccination Within and Outside the VHA in Light of Recent Outbreaks (FULL)
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) can result in acute infection characterized by fatigue, nausea, jaundice (yellowing of the skin) and, rarely, acute liver failure and death.1,2 In the US, HAV yearly incidence (per 100,000) has decreased from 11.7 cases in 1996 to 0.4 cases in 2015, largely due to the 2006 recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that all infants receive HAV vaccination.3,4
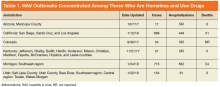
In 2017, multiple HAV outbreaks occurred in Arizona, California, Colorado, Kentucky, Michigan, and Utah with infections concentrated among those who were homeless, used illicit drugs (both injection and noninjection), or had close contact with these groups (Table 1).5-7
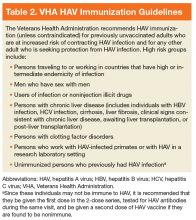
In response, the CDC has recommended the administration of HAV vaccine or immune globulin (IG) as postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) to people in high-risk groups including unvaccinated individuals exposed to HAV within the prior 2 weeks.5 While the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) in the Department of Veteran’s Affairs (VA) has not noted a significant increase in the number of reported HAV infections, there have been cases of hospitalization within the VA health care system due to HAV in at least 2 of the outbreak areas. The VA facilities in outbreak areas are responding by supporting county disease-control measures that include ensuring handwashing stations and vaccinations for high-risk, in-care populations and employees in direct contact with patients at high risk for HAV.
This review provides information on HAV transmission and clinical manifestations, guidelines on the prevention of HAV infection, and baseline data on current HAV susceptibility and immunization rates in the VHA.
Transmission and Clinical Manifestations
Hepatitis A virus is primarily transmitted by ingestion of small amounts of infected stool (ie, fecal-oral route) via direct person-to-person contact or through exposure to contaminated food or water.9,10 Groups at high risk of HAV infection include those in direct contact with HAV-infected individuals, users of injection or non-injection drugs, men who have sex with men (MSM), travelers to high-risk countries, individuals with clotting disorders, and those who work with nonhuman primates.11 Individuals who are homeless are susceptible to HAV due to poor sanitary conditions, and MSM are at increased risk of HAV acquisition via exposure to infected stool during sexual activity.
Complications of acute HAV infection, including fulminant liver failure and death, are more common among patients infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV).12,13 While infection with HIV does not independently increase the risk of HAV acquisition, about 75% of new HIV infections in the US are among MSM or IV drug users who are at increased risk of HAV infection.14 In addition, duration of HAV viremia and resulting HAV transmissibility may be increased in HIV-infected individuals.15-17
After infection, HAV remains asymptomatic (the incubation period) for an average of 28 days with a range of 15 to 50 days.18,19 Most children younger than 6 years remain asymptomatic while older children and adults typically experience symptoms including fever, fatigue, poor appetite, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-colored stools, and jaundice.2,20,21 Symptoms typically last less than 2 months but can persist or relapse for up to 6 months in 10% to 15% of symptomatic individuals.22,23 Those with HAV infection are capable of viral transmission from the beginning of the incubation period until about a week after jaundice appears.24 Unlike HBV and HCV, HAV does not cause chronic infection.
Fulminant liver failure, characterized by encephalopathy, jaundice, and elevated international normalized ratio (INR), occurs in < 1% of HAV infections and is more common in those with underlying liver disease and older individuals.13,25-27 In one retrospective review of fulminant liver failure from HAV infection, about half of the patients required liver transplantation or died within 3 weeks of presentation.12
Other than supportive care, there are no specific treatments for acute HAV infection. However, the CDC recommends that healthy individuals aged between 1 and 40 years with known or suspected exposure to HAV within the prior 2 weeks receive 1 dose of a single-antigen HAV vaccination. The CDC also recommends that recently exposed individuals aged < 1 year or > 40 years, or patients who are immunocompromised, have chronic liver disease (CLD), or are allergic to HAV vaccine or a vaccine component should receive a single IG injection. In addition, the CDC recommends that health care providers report all cases of acute HAV to state and local health departments.28
In patients with typical symptoms of acute viral hepatitis (eg, headache, fever, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea) and either jaundice or elevated serum aminotransferase levels, confirmation of HAV infection is required with either a positive serologic test for immunoglobulin M (IgM) anti-HAV antibody or an epidemiologic link (eg, recent household or close contact) to a person with laboratory-confirmed HAV.5 Serum IgM anti-HAV antibodies are first detectable when symptoms begin and remain detectable for about 3 to 6 months.29,30 Serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) anti-HAV antibodies, which provide lifelong protection against reinfection, appear as symptoms improve and persist indefinitely.31,32 Therefore, the presence of anti-HAV IgG and the absence of anti-HAV IgM is indicative of immunity to HAV via past infection or vaccination.
HAV Prevention in The VHA
The mainstay of HAV prevention is vaccination with 2 doses of inactivated, single-antigen hepatitis A vaccine or 3 doses of combination (HAV and HBV) vaccine.11 Both single antigen and combination HAV vaccines are safe in immunocompromised and pregnant patients.33-39 The HAV vaccination results in 100% anti-HAV IgG seropositivity among healthy individuals, although immunogenicity might be lower for those who are immunocompromised or with CLD.31,40-47 The VHA recommends HAV immunization, unless contraindicated, for previously unvaccinated
In addition to vaccination, addressing risk factors for HAV infection and its complications could reduce the burden of disease. For instance, recent outbreaks highlight that homeless individuals and users of injection and noninjection drugs are particularly vulnerable to infections transmitted via fecal-oral contamination. Broad strategies to address homelessness and related sanitation concerns are needed to help reduce the likelihood of future HAV outbreaks.49 Specific measures to combat HAV include providing access to clean water, adequate hygiene, and clean needles for people who inject drugs.11 Hepatitis A virus can be destroyed by heating food to ≥ 185 °F for at least 1 minute, chlorinating contaminated water, or cleaning contaminated surfaces with a solution of household bleach and water.50 Moreover, it is important to identify and treat risk factors for complications of HAV infection. This includes identifying individuals with HCV and ensuring that they are immune to HAV, given data that HCV-infected individuals are at increased risk of fulminant hepatic failure from HAV.12,13
Active-duty service members have long been considered at higher risk of HAV infections due to deployments in endemic areas and exposure to contaminated food and water.51,52 Shortly after the FDA approved HAV vaccination in 1995, the Department of Defense (DoD) mandated screening and HAV immunization for all incoming active-duty service members and those deployed to areas of high endemicity.53 However, US veterans who were discharged before the adoption of universal HAV vaccination remain at increased risk for HAV infection, particularly given the high prevalence of CLD, homelessness, and substance use disord
Methods
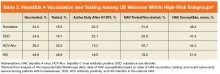
A cross-sectional analysis of veterans in VA care from June 1, 2016 to June 1, 2017 was performed to determine national rates of HAV susceptibility among patients with HCV exposure, homelessness, SUD, or HIV infection. The definitions of homelessness, SUD (alcohol, cannabis, opioid, sedatives, hallucinogens, inhalants, stimulants, or tobacco), and HIV infection were based on the presence of appropriate ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes. History of HCV exposure was based on a positive HCV antibody test. Presence of HAV vaccination was determined based on CPT codes for administration of the single-antigen HAV vaccination or combination HAV/HBV vaccination.
While HIV infection is not independently considered an indication for HAV vaccination, the authors included this group given its high proportion of patients with other risk factors, including MSM and IV drug use. All data were obtained from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW), a comprehensive national repository of all laboratory, diagnosis, and prescription results (including vaccines) within the VHA since 1999.
Hepatitis A virus nonsusceptibility was defined as (1) documented receipt of HAV vaccination within the VHA; (2) anti-HAV IgG antibody testing within the VHA; or (3) active-duty service after October 1997. It was considered likely that patients who received HAV testing either showed evidence of HAV immunity (eg, positive anti-HAV IgG) or were anti-HAV IgG negative and subsequently immunized. Therefore, patients with anti-HAV IgG antibody testing were counted presumptively as nonsusceptible. The DoD implemented a universal HAV vaccination policy in 1995, therefore, 1997 was chosen as a time at which the military’s universal HAV vaccination campaign was likely to have achieved near 100% vaccination coverage of active-duty military.
Results
The cohort included 5,896,451 patients in VA care, including 381,628 (6.5%) who were homeless, 455,344 (7.7%) with SUD, 225,889 (3.8%) with a lifetime history of positive HCV antibody (indicating past HCV exposure), and 29,166 (0.5%) with HIV infection.
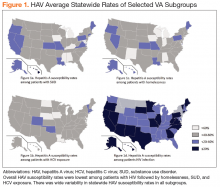
There was wide geographic variability in rates of HAV susceptibility (Figure 1).
Discussion
Widespread HAV vaccination has decreased the incidence of HAV infection in the US dramatically. Nevertheless, recent outbreaks demonstrate that substantial population susceptibility and associated risk for HAV-related morbidity and mortality remains, particularly in high-risk populations. Although the VHA has not experienced a significant increase in acute HAV infections to date, this cross-sectional analysis highlights that a large proportion of VA patients in traditionally high-risk groups remain susceptible to HAV infection.
Strengths
Strengths of this analysis include a current reflection of HAV susceptibility within the national VHA, thus informing HAV testing and vaccination strategies. This study also involves a very large cohort, which is possible because the VHA is the largest integrated healthcare system in the US. Lastly, because the VHA uses electronic medical records, there was nearly complete capture of HAV vaccinations and testing obtained through the VHA.
Limitations
This cross-sectional analysis has several potential limitations. First, findings may not be generalizable outside the VHA. In addition, determination of homelessness, substance abuse, and HIV infection were based on ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes, which have been used in previous studies but may be subject to misclassification. The authors deliberately included all patients with positive HCV antibody testing to include those with current or prior risk factors for HAV acquisition. This population does not reflect patients with HCV viremia who received HAV testing or vaccination. Lastly, misattribution of HAV susceptibility could have occurred if patients with negative HAV IgG results were not vaccinated or if patients previously received HAV vaccination outside the VHA.
Conclusion
To mitigate the risk of future HAV outbreaks, continued efforts should be made to increase vaccination among high-risk groups, improve awareness of additional prevention measures, and address risk factors for HAV acquisition, particularly in areas with active outbreaks. Further study is suggested to identify geographic areas with large caseloads of at-risk patients and to highlight best practices utilized by VHA facilities that achieved high vaccine coverage rates. Recommended approaches likely will need to include efforts to improve hygiene and reduce risks for HAV exposure associated with SUD and homelessness.
Click here to read the digital edition.
1. Kemmer NM, Miskovsky EP. Hepatitis A. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2000;14(3):605-615.
2. Tong MJ, el-Farra NS, Grew MI. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: recent experience in a community teaching hospital. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S15-S18.
3. Murphy TV, Denniston MM, Hill HA, et al. Progress toward eliminating hepatitis a disease in the United States. MMWR Suppl. 2016;65(1):29-41.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Viral hepatitis surveillance, United States, 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2015surveillance/pdfs/2015HepSurveillanceRpt.pdf. Published 2015. Accessed February 12, 2018.
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2017 – Outbreaks of hepatitis A in multiple states among people who are homeless and people who use drugs. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/outbreaks/2017March-HepatitisA.htm. Updated February 7, 2018. Accessed February 12, 2018.
6. Hepatitis A cases more than double in 2017; if you’re at risk, get vaccinated [press release]. https://www.colorado.gov/pacific/cdphe/news/hep-a-cases-doubled. Published August 30,2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
7. Alltucker K. Hepatitis A outbreak spread to Maricopa County homeless from San Diego, officials say. Azcentral website. October 7, 2017. https://www.azcentral.com/story/news/local /arizona-health/2017/10/07/hepatitis-outbreak-spread-maricopa-county-homeless-san-diego-officials-say/740185001/. Accessed February 12, 2018.
8. Savage RD, Rosella LC, Brown KA, Khan K, Crowcroft NS. Underreporting of hepatitis A in non-endemic countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:281.
9. Purcell RH, Wong DC, Shapiro M. Relative infectivity of hepatitis A virus by the oral and intravenous routes in 2 species of nonhuman primates. J Infect Dis. 2002;185(11):1668-1671.
10. Tassopoulos NC, Papaevangelou GJ, Ticehurst JR, Purcell RH. Fecal excretion of Greek strains of hepatitis A virus in patients with hepatitis A and in experimentally infected chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1986;154(2):231-237.
11. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis A questions and answers for health professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hav/havfaq.htm. Updated November 8, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
12. Taylor RM, Davern T, Munoz S, et al; US Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Fulminant hepatitis A virus infection in the United States: Incidence, prognosis, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2006;44(6):1589-1597.
13. Vento S, Garofano T, Renzini C, et al. Fulminant hepatitis associated with hepatitis A virus superinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(5):286-290.
14. Singh S, Johnson AS, McCray E, Hall HI. CDC - HIV incidence, prevalence and undiagnosed infections in men who have sex with men - HIV incidence decreased among all transmission categories except MSM. Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI); February 13-16,2017; Seattle, WA. http://www .natap.org/2017/CROI/croi_116.htm. Accessed February 12, 2018.
15. Fonquernie L, Meynard JL, Charrois A, Delamare C, Meyohas MC, Frottier J. Occurrence of acute hepatitis A in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32(2):297-299.
16. Ida S, Tachikawa N, Nakajima A, et al. Influence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection on acute hepatitis A virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34(3):379-385.
17. Costa-Mattioli M, Allavena C, Poirier AS, Billaudel S, Raffi F, Ferré V. Prolonged hepatitis A infection in an HIV-1 seropositive patient. J Med Virol. 2002;68(1):7-11.
18. Neefe JR, Gellis SS, Stokes J Jr. Homologous serum hepatitis and infectious (epidemic) hepatitis; studies in volunteers bearing on immunological and other characteristics of the etiological agents. Am J Med. 1946;1:3-22.
19. Krugman S, Giles JP, Hammond J. Infectious hepatitis. Evidence for two distinctive clinical, epidemiological, and immunological types of infection. JAMA. 1967;200(5):365-373.
20. Hadler SC, Webster HM, Erben JJ, Swanson JE, Maynard JE. Hepatitis A in day-care centers. A community-wide assessment. N Engl J Med. 1980;302(22):1222-1227.
21. Lednar WM, Lemon SM, Kirkpatrick JW, Redfield RR, Fields ML, Kelley PW. Frequency of illness associated with epidemic hepatitis A virus infections in adults. Am J Epidemiol. 1985;122(2):226-233.
22. Gordon SC, Reddy KR, Schiff L, Schiff ER. Prolonged intrahepatic cholestasis secondary to acute hepatitis A. Ann Intern Med. 1984;101(5):635-637.
23. Schiff ER. Atypical clinical manifestations of hepatitis A. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S18-S20.
24. Richardson M, Elliman D, Maguire H, Simpson J, Nicoll A. Evidence base of incubation periods, periods of infectiousness and exclusion policies for the control of communicable diseases in schools and preschools. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20(4):380-391.
25. Willner IR, Uhl MD, Howard SC, Williams EQ, Riely CA, Waters B. Serious hepatitis A: an analysis of patients hospitalized during an urban epidemic in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128(2):111-114.
26. Rezende G, Roque-Afonso AM, Samuel D, et al. Viral and clinical factors associated with the fulminant course of hepatitis A infection. Hepatology. 2003;38(3):613-618.
27. Lemon SM. Type A viral hepatitis. New developments in an old disease. N Engl J Med. 1985;313(17):1059-1067.
28. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for viral hepatitis surveillance and case management. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/surveillance guidelines.htm. Updated May 31, 2015. Accessed February 8, 2018.
29. Kao HW, Ashcavai M, Redeker AG. The persistence of hepatitis A IgM antibody after acute clinical hepatitis A. Hepatology. 1984;4(5):933-936.
30. Liaw YF, Yang CY, Chu CM, Huang MJ. Appearance and persistence of hepatitis A IgM antibody in acute clinical hepatitis A observed in an outbreak. Infection. 1986;14(4):156-158.
31. Plumb ID, Bulkow LR, Bruce MG, et al. Persistence of antibody to Hepatitis A virus 20 years after receipt of Hepatitis A vaccine in Alaska. J Viral Hepat. 2017;24(7):608-612.
32. Koff RS. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of hepatitis A virus infection. Vaccine. 1992;10 (suppl 1):S15-S17.
33. Clemens R, Safary A, Hepburn A, Roche C, Stanbury WJ, André FE. Clinical experience with an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S44-S49.
34. Ambrosch F, André FE, Delem A, et al. Simultaneous vaccination against hepatitis A and B: results of a controlled study. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S142-S145.
35. Gil A, González A, Dal-Ré R, Calero JR. Interference assessment of yellow fever vaccine with the immune response to a single-dose inactivated hepatitis A vaccine (1440 EL.U.). A controlled study in adults. Vaccine. 1996;14(11):1028-1030.
36. Jong EC, Kaplan KM, Eves KA, Taddeo CA, Lakkis HD, Kuter BJ. An open randomized study of inactivated hepatitis A vaccine administered concomitantly with typhoid fever and yellow fever vaccines. J Travel Med. 2002;9(2):66-70.
37. Nolan T, Bernstein H, Blatter MM, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine administered concomitantly with diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis and haemophilus influenzae type B vaccines to children less than 2 years of age. Pediatrics. 2006;118(3):e602-e609.
38. Usonis V, Meriste S, Bakasenas V, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a combined hepatitis A and B vaccine administered concomitantly with either a measles-mumps-rubella or a diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis-inactivated poliomyelitis vaccine mixed with a Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine in infants aged 12-18 months. Vaccine. 2005;23(20):2602-2606.
39. Moro PL, Museru OI, Niu M, Lewis P, Broder K. Reports to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after hepatitis A and hepatitis AB vaccines in pregnant women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;210(6):561.e1-561.e-6.
40. André FE, D’Hondt E, Delem A, Safary A. Clinical assessment of the safety and efficacy of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: rationale and summary of findings. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S160-S168.
41. Just M, Berger R. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of inactivated hepatitis A vaccines. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S110-S113.
42. McMahon BJ, Williams J, Bulkow L, et al. Immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in Alaska Native children and Native and non-Native adults. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(3):676-679.
43. Balcarek KB, Bagley MR, Pass RF, Schiff ER, Krause DS. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in preschool children. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S70-S72.
44. Bell BP, Negus S, Fiore AE, et al. Immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in infants and young children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007;26(2):116-122.
45. Arguedas MR, Johnson A, Eloubeidi MA, Fallon MB. Immunogenicity of hepatitis A vaccination in decompensated cirrhotic patients. Hepatology. 2001;34(1):28-31.
46. Overton ET, Nurutdinova D, Sungkanuparph S, Seyfried W, Groger RK, Powderly WG. Predictors of immunity after hepatitis A vaccination in HIV-infected persons. J Viral Hepat. 2007;14(3):189-193.
47. Askling HH, Rombo L, van Vollenhoven R, et al. Hepatitis A vaccine for immunosuppressed patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective, open-label, multi-centre study. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2014;12(2):134-142.
48. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VHA national hepatitis A immunization guidelines. http://vaww.prevention.va.gov/CPS/Hepatitis_A_Immunization.asp. Nonpublic document. Source not verified.
49. Kushel M. Hepatitis A outbreak in California - addressing the root cause. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(3):211-213.
50. Millard J, Appleton H, Parry JV. Studies on heat inactivation of hepatitis A virus with special reference to shellfish. Part 1. Procedures for infection and recovery of virus from laboratory-maintained cockles. Epidemiol Infect. 1987;98(3):397-414.
51. Hoke CH, Jr., Binn LN, Egan JE, et al. Hepatitis A in the US Army: epidemiology and vaccine development. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S75-S79.
52. Dooley DP. History of U.S. military contributions to the study of viral hepatitis. Mil Med. 2005;170(suppl 4):71-76.
53. Grabenstein JD, Pittman PR, Greenwood JT, Engler RJ. Immunization to protect the US Armed Forces: heritage, current practice, and prospects. Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28:3-26.
54. Beste LA, Leipertz SL, Green PK, Dominitz JA, Ross D, Ioannou GN. Trends in burden of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma by underlying liver disease in US veterans, 2001-2013. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(6):1471-1482.e1475; quiz e17-e18.
55. Fargo J, Metraux S, Byrne T, et al. Prevalence and risk of homelessness among US veterans. Prev Chronic Dis. 2012;9:E45.
56. Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77.
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) can result in acute infection characterized by fatigue, nausea, jaundice (yellowing of the skin) and, rarely, acute liver failure and death.1,2 In the US, HAV yearly incidence (per 100,000) has decreased from 11.7 cases in 1996 to 0.4 cases in 2015, largely due to the 2006 recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that all infants receive HAV vaccination.3,4
In 2017, multiple HAV outbreaks occurred in Arizona, California, Colorado, Kentucky, Michigan, and Utah with infections concentrated among those who were homeless, used illicit drugs (both injection and noninjection), or had close contact with these groups (Table 1).5-7
In response, the CDC has recommended the administration of HAV vaccine or immune globulin (IG) as postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) to people in high-risk groups including unvaccinated individuals exposed to HAV within the prior 2 weeks.5 While the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) in the Department of Veteran’s Affairs (VA) has not noted a significant increase in the number of reported HAV infections, there have been cases of hospitalization within the VA health care system due to HAV in at least 2 of the outbreak areas. The VA facilities in outbreak areas are responding by supporting county disease-control measures that include ensuring handwashing stations and vaccinations for high-risk, in-care populations and employees in direct contact with patients at high risk for HAV.
This review provides information on HAV transmission and clinical manifestations, guidelines on the prevention of HAV infection, and baseline data on current HAV susceptibility and immunization rates in the VHA.
Transmission and Clinical Manifestations
Hepatitis A virus is primarily transmitted by ingestion of small amounts of infected stool (ie, fecal-oral route) via direct person-to-person contact or through exposure to contaminated food or water.9,10 Groups at high risk of HAV infection include those in direct contact with HAV-infected individuals, users of injection or non-injection drugs, men who have sex with men (MSM), travelers to high-risk countries, individuals with clotting disorders, and those who work with nonhuman primates.11 Individuals who are homeless are susceptible to HAV due to poor sanitary conditions, and MSM are at increased risk of HAV acquisition via exposure to infected stool during sexual activity.
Complications of acute HAV infection, including fulminant liver failure and death, are more common among patients infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV).12,13 While infection with HIV does not independently increase the risk of HAV acquisition, about 75% of new HIV infections in the US are among MSM or IV drug users who are at increased risk of HAV infection.14 In addition, duration of HAV viremia and resulting HAV transmissibility may be increased in HIV-infected individuals.15-17
After infection, HAV remains asymptomatic (the incubation period) for an average of 28 days with a range of 15 to 50 days.18,19 Most children younger than 6 years remain asymptomatic while older children and adults typically experience symptoms including fever, fatigue, poor appetite, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-colored stools, and jaundice.2,20,21 Symptoms typically last less than 2 months but can persist or relapse for up to 6 months in 10% to 15% of symptomatic individuals.22,23 Those with HAV infection are capable of viral transmission from the beginning of the incubation period until about a week after jaundice appears.24 Unlike HBV and HCV, HAV does not cause chronic infection.
Fulminant liver failure, characterized by encephalopathy, jaundice, and elevated international normalized ratio (INR), occurs in < 1% of HAV infections and is more common in those with underlying liver disease and older individuals.13,25-27 In one retrospective review of fulminant liver failure from HAV infection, about half of the patients required liver transplantation or died within 3 weeks of presentation.12
Other than supportive care, there are no specific treatments for acute HAV infection. However, the CDC recommends that healthy individuals aged between 1 and 40 years with known or suspected exposure to HAV within the prior 2 weeks receive 1 dose of a single-antigen HAV vaccination. The CDC also recommends that recently exposed individuals aged < 1 year or > 40 years, or patients who are immunocompromised, have chronic liver disease (CLD), or are allergic to HAV vaccine or a vaccine component should receive a single IG injection. In addition, the CDC recommends that health care providers report all cases of acute HAV to state and local health departments.28
In patients with typical symptoms of acute viral hepatitis (eg, headache, fever, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea) and either jaundice or elevated serum aminotransferase levels, confirmation of HAV infection is required with either a positive serologic test for immunoglobulin M (IgM) anti-HAV antibody or an epidemiologic link (eg, recent household or close contact) to a person with laboratory-confirmed HAV.5 Serum IgM anti-HAV antibodies are first detectable when symptoms begin and remain detectable for about 3 to 6 months.29,30 Serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) anti-HAV antibodies, which provide lifelong protection against reinfection, appear as symptoms improve and persist indefinitely.31,32 Therefore, the presence of anti-HAV IgG and the absence of anti-HAV IgM is indicative of immunity to HAV via past infection or vaccination.
HAV Prevention in The VHA
The mainstay of HAV prevention is vaccination with 2 doses of inactivated, single-antigen hepatitis A vaccine or 3 doses of combination (HAV and HBV) vaccine.11 Both single antigen and combination HAV vaccines are safe in immunocompromised and pregnant patients.33-39 The HAV vaccination results in 100% anti-HAV IgG seropositivity among healthy individuals, although immunogenicity might be lower for those who are immunocompromised or with CLD.31,40-47 The VHA recommends HAV immunization, unless contraindicated, for previously unvaccinated
In addition to vaccination, addressing risk factors for HAV infection and its complications could reduce the burden of disease. For instance, recent outbreaks highlight that homeless individuals and users of injection and noninjection drugs are particularly vulnerable to infections transmitted via fecal-oral contamination. Broad strategies to address homelessness and related sanitation concerns are needed to help reduce the likelihood of future HAV outbreaks.49 Specific measures to combat HAV include providing access to clean water, adequate hygiene, and clean needles for people who inject drugs.11 Hepatitis A virus can be destroyed by heating food to ≥ 185 °F for at least 1 minute, chlorinating contaminated water, or cleaning contaminated surfaces with a solution of household bleach and water.50 Moreover, it is important to identify and treat risk factors for complications of HAV infection. This includes identifying individuals with HCV and ensuring that they are immune to HAV, given data that HCV-infected individuals are at increased risk of fulminant hepatic failure from HAV.12,13
Active-duty service members have long been considered at higher risk of HAV infections due to deployments in endemic areas and exposure to contaminated food and water.51,52 Shortly after the FDA approved HAV vaccination in 1995, the Department of Defense (DoD) mandated screening and HAV immunization for all incoming active-duty service members and those deployed to areas of high endemicity.53 However, US veterans who were discharged before the adoption of universal HAV vaccination remain at increased risk for HAV infection, particularly given the high prevalence of CLD, homelessness, and substance use disord
Methods
A cross-sectional analysis of veterans in VA care from June 1, 2016 to June 1, 2017 was performed to determine national rates of HAV susceptibility among patients with HCV exposure, homelessness, SUD, or HIV infection. The definitions of homelessness, SUD (alcohol, cannabis, opioid, sedatives, hallucinogens, inhalants, stimulants, or tobacco), and HIV infection were based on the presence of appropriate ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes. History of HCV exposure was based on a positive HCV antibody test. Presence of HAV vaccination was determined based on CPT codes for administration of the single-antigen HAV vaccination or combination HAV/HBV vaccination.
While HIV infection is not independently considered an indication for HAV vaccination, the authors included this group given its high proportion of patients with other risk factors, including MSM and IV drug use. All data were obtained from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW), a comprehensive national repository of all laboratory, diagnosis, and prescription results (including vaccines) within the VHA since 1999.
Hepatitis A virus nonsusceptibility was defined as (1) documented receipt of HAV vaccination within the VHA; (2) anti-HAV IgG antibody testing within the VHA; or (3) active-duty service after October 1997. It was considered likely that patients who received HAV testing either showed evidence of HAV immunity (eg, positive anti-HAV IgG) or were anti-HAV IgG negative and subsequently immunized. Therefore, patients with anti-HAV IgG antibody testing were counted presumptively as nonsusceptible. The DoD implemented a universal HAV vaccination policy in 1995, therefore, 1997 was chosen as a time at which the military’s universal HAV vaccination campaign was likely to have achieved near 100% vaccination coverage of active-duty military.
Results
The cohort included 5,896,451 patients in VA care, including 381,628 (6.5%) who were homeless, 455,344 (7.7%) with SUD, 225,889 (3.8%) with a lifetime history of positive HCV antibody (indicating past HCV exposure), and 29,166 (0.5%) with HIV infection.
There was wide geographic variability in rates of HAV susceptibility (Figure 1).
Discussion
Widespread HAV vaccination has decreased the incidence of HAV infection in the US dramatically. Nevertheless, recent outbreaks demonstrate that substantial population susceptibility and associated risk for HAV-related morbidity and mortality remains, particularly in high-risk populations. Although the VHA has not experienced a significant increase in acute HAV infections to date, this cross-sectional analysis highlights that a large proportion of VA patients in traditionally high-risk groups remain susceptible to HAV infection.
Strengths
Strengths of this analysis include a current reflection of HAV susceptibility within the national VHA, thus informing HAV testing and vaccination strategies. This study also involves a very large cohort, which is possible because the VHA is the largest integrated healthcare system in the US. Lastly, because the VHA uses electronic medical records, there was nearly complete capture of HAV vaccinations and testing obtained through the VHA.
Limitations
This cross-sectional analysis has several potential limitations. First, findings may not be generalizable outside the VHA. In addition, determination of homelessness, substance abuse, and HIV infection were based on ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes, which have been used in previous studies but may be subject to misclassification. The authors deliberately included all patients with positive HCV antibody testing to include those with current or prior risk factors for HAV acquisition. This population does not reflect patients with HCV viremia who received HAV testing or vaccination. Lastly, misattribution of HAV susceptibility could have occurred if patients with negative HAV IgG results were not vaccinated or if patients previously received HAV vaccination outside the VHA.
Conclusion
To mitigate the risk of future HAV outbreaks, continued efforts should be made to increase vaccination among high-risk groups, improve awareness of additional prevention measures, and address risk factors for HAV acquisition, particularly in areas with active outbreaks. Further study is suggested to identify geographic areas with large caseloads of at-risk patients and to highlight best practices utilized by VHA facilities that achieved high vaccine coverage rates. Recommended approaches likely will need to include efforts to improve hygiene and reduce risks for HAV exposure associated with SUD and homelessness.
Click here to read the digital edition.
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) can result in acute infection characterized by fatigue, nausea, jaundice (yellowing of the skin) and, rarely, acute liver failure and death.1,2 In the US, HAV yearly incidence (per 100,000) has decreased from 11.7 cases in 1996 to 0.4 cases in 2015, largely due to the 2006 recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that all infants receive HAV vaccination.3,4
In 2017, multiple HAV outbreaks occurred in Arizona, California, Colorado, Kentucky, Michigan, and Utah with infections concentrated among those who were homeless, used illicit drugs (both injection and noninjection), or had close contact with these groups (Table 1).5-7
In response, the CDC has recommended the administration of HAV vaccine or immune globulin (IG) as postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) to people in high-risk groups including unvaccinated individuals exposed to HAV within the prior 2 weeks.5 While the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) in the Department of Veteran’s Affairs (VA) has not noted a significant increase in the number of reported HAV infections, there have been cases of hospitalization within the VA health care system due to HAV in at least 2 of the outbreak areas. The VA facilities in outbreak areas are responding by supporting county disease-control measures that include ensuring handwashing stations and vaccinations for high-risk, in-care populations and employees in direct contact with patients at high risk for HAV.
This review provides information on HAV transmission and clinical manifestations, guidelines on the prevention of HAV infection, and baseline data on current HAV susceptibility and immunization rates in the VHA.
Transmission and Clinical Manifestations
Hepatitis A virus is primarily transmitted by ingestion of small amounts of infected stool (ie, fecal-oral route) via direct person-to-person contact or through exposure to contaminated food or water.9,10 Groups at high risk of HAV infection include those in direct contact with HAV-infected individuals, users of injection or non-injection drugs, men who have sex with men (MSM), travelers to high-risk countries, individuals with clotting disorders, and those who work with nonhuman primates.11 Individuals who are homeless are susceptible to HAV due to poor sanitary conditions, and MSM are at increased risk of HAV acquisition via exposure to infected stool during sexual activity.
Complications of acute HAV infection, including fulminant liver failure and death, are more common among patients infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV).12,13 While infection with HIV does not independently increase the risk of HAV acquisition, about 75% of new HIV infections in the US are among MSM or IV drug users who are at increased risk of HAV infection.14 In addition, duration of HAV viremia and resulting HAV transmissibility may be increased in HIV-infected individuals.15-17
After infection, HAV remains asymptomatic (the incubation period) for an average of 28 days with a range of 15 to 50 days.18,19 Most children younger than 6 years remain asymptomatic while older children and adults typically experience symptoms including fever, fatigue, poor appetite, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-colored stools, and jaundice.2,20,21 Symptoms typically last less than 2 months but can persist or relapse for up to 6 months in 10% to 15% of symptomatic individuals.22,23 Those with HAV infection are capable of viral transmission from the beginning of the incubation period until about a week after jaundice appears.24 Unlike HBV and HCV, HAV does not cause chronic infection.
Fulminant liver failure, characterized by encephalopathy, jaundice, and elevated international normalized ratio (INR), occurs in < 1% of HAV infections and is more common in those with underlying liver disease and older individuals.13,25-27 In one retrospective review of fulminant liver failure from HAV infection, about half of the patients required liver transplantation or died within 3 weeks of presentation.12
Other than supportive care, there are no specific treatments for acute HAV infection. However, the CDC recommends that healthy individuals aged between 1 and 40 years with known or suspected exposure to HAV within the prior 2 weeks receive 1 dose of a single-antigen HAV vaccination. The CDC also recommends that recently exposed individuals aged < 1 year or > 40 years, or patients who are immunocompromised, have chronic liver disease (CLD), or are allergic to HAV vaccine or a vaccine component should receive a single IG injection. In addition, the CDC recommends that health care providers report all cases of acute HAV to state and local health departments.28
In patients with typical symptoms of acute viral hepatitis (eg, headache, fever, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea) and either jaundice or elevated serum aminotransferase levels, confirmation of HAV infection is required with either a positive serologic test for immunoglobulin M (IgM) anti-HAV antibody or an epidemiologic link (eg, recent household or close contact) to a person with laboratory-confirmed HAV.5 Serum IgM anti-HAV antibodies are first detectable when symptoms begin and remain detectable for about 3 to 6 months.29,30 Serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) anti-HAV antibodies, which provide lifelong protection against reinfection, appear as symptoms improve and persist indefinitely.31,32 Therefore, the presence of anti-HAV IgG and the absence of anti-HAV IgM is indicative of immunity to HAV via past infection or vaccination.
HAV Prevention in The VHA
The mainstay of HAV prevention is vaccination with 2 doses of inactivated, single-antigen hepatitis A vaccine or 3 doses of combination (HAV and HBV) vaccine.11 Both single antigen and combination HAV vaccines are safe in immunocompromised and pregnant patients.33-39 The HAV vaccination results in 100% anti-HAV IgG seropositivity among healthy individuals, although immunogenicity might be lower for those who are immunocompromised or with CLD.31,40-47 The VHA recommends HAV immunization, unless contraindicated, for previously unvaccinated
In addition to vaccination, addressing risk factors for HAV infection and its complications could reduce the burden of disease. For instance, recent outbreaks highlight that homeless individuals and users of injection and noninjection drugs are particularly vulnerable to infections transmitted via fecal-oral contamination. Broad strategies to address homelessness and related sanitation concerns are needed to help reduce the likelihood of future HAV outbreaks.49 Specific measures to combat HAV include providing access to clean water, adequate hygiene, and clean needles for people who inject drugs.11 Hepatitis A virus can be destroyed by heating food to ≥ 185 °F for at least 1 minute, chlorinating contaminated water, or cleaning contaminated surfaces with a solution of household bleach and water.50 Moreover, it is important to identify and treat risk factors for complications of HAV infection. This includes identifying individuals with HCV and ensuring that they are immune to HAV, given data that HCV-infected individuals are at increased risk of fulminant hepatic failure from HAV.12,13
Active-duty service members have long been considered at higher risk of HAV infections due to deployments in endemic areas and exposure to contaminated food and water.51,52 Shortly after the FDA approved HAV vaccination in 1995, the Department of Defense (DoD) mandated screening and HAV immunization for all incoming active-duty service members and those deployed to areas of high endemicity.53 However, US veterans who were discharged before the adoption of universal HAV vaccination remain at increased risk for HAV infection, particularly given the high prevalence of CLD, homelessness, and substance use disord
Methods
A cross-sectional analysis of veterans in VA care from June 1, 2016 to June 1, 2017 was performed to determine national rates of HAV susceptibility among patients with HCV exposure, homelessness, SUD, or HIV infection. The definitions of homelessness, SUD (alcohol, cannabis, opioid, sedatives, hallucinogens, inhalants, stimulants, or tobacco), and HIV infection were based on the presence of appropriate ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes. History of HCV exposure was based on a positive HCV antibody test. Presence of HAV vaccination was determined based on CPT codes for administration of the single-antigen HAV vaccination or combination HAV/HBV vaccination.
While HIV infection is not independently considered an indication for HAV vaccination, the authors included this group given its high proportion of patients with other risk factors, including MSM and IV drug use. All data were obtained from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW), a comprehensive national repository of all laboratory, diagnosis, and prescription results (including vaccines) within the VHA since 1999.
Hepatitis A virus nonsusceptibility was defined as (1) documented receipt of HAV vaccination within the VHA; (2) anti-HAV IgG antibody testing within the VHA; or (3) active-duty service after October 1997. It was considered likely that patients who received HAV testing either showed evidence of HAV immunity (eg, positive anti-HAV IgG) or were anti-HAV IgG negative and subsequently immunized. Therefore, patients with anti-HAV IgG antibody testing were counted presumptively as nonsusceptible. The DoD implemented a universal HAV vaccination policy in 1995, therefore, 1997 was chosen as a time at which the military’s universal HAV vaccination campaign was likely to have achieved near 100% vaccination coverage of active-duty military.
Results
The cohort included 5,896,451 patients in VA care, including 381,628 (6.5%) who were homeless, 455,344 (7.7%) with SUD, 225,889 (3.8%) with a lifetime history of positive HCV antibody (indicating past HCV exposure), and 29,166 (0.5%) with HIV infection.
There was wide geographic variability in rates of HAV susceptibility (Figure 1).
Discussion
Widespread HAV vaccination has decreased the incidence of HAV infection in the US dramatically. Nevertheless, recent outbreaks demonstrate that substantial population susceptibility and associated risk for HAV-related morbidity and mortality remains, particularly in high-risk populations. Although the VHA has not experienced a significant increase in acute HAV infections to date, this cross-sectional analysis highlights that a large proportion of VA patients in traditionally high-risk groups remain susceptible to HAV infection.
Strengths
Strengths of this analysis include a current reflection of HAV susceptibility within the national VHA, thus informing HAV testing and vaccination strategies. This study also involves a very large cohort, which is possible because the VHA is the largest integrated healthcare system in the US. Lastly, because the VHA uses electronic medical records, there was nearly complete capture of HAV vaccinations and testing obtained through the VHA.
Limitations
This cross-sectional analysis has several potential limitations. First, findings may not be generalizable outside the VHA. In addition, determination of homelessness, substance abuse, and HIV infection were based on ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes, which have been used in previous studies but may be subject to misclassification. The authors deliberately included all patients with positive HCV antibody testing to include those with current or prior risk factors for HAV acquisition. This population does not reflect patients with HCV viremia who received HAV testing or vaccination. Lastly, misattribution of HAV susceptibility could have occurred if patients with negative HAV IgG results were not vaccinated or if patients previously received HAV vaccination outside the VHA.
Conclusion
To mitigate the risk of future HAV outbreaks, continued efforts should be made to increase vaccination among high-risk groups, improve awareness of additional prevention measures, and address risk factors for HAV acquisition, particularly in areas with active outbreaks. Further study is suggested to identify geographic areas with large caseloads of at-risk patients and to highlight best practices utilized by VHA facilities that achieved high vaccine coverage rates. Recommended approaches likely will need to include efforts to improve hygiene and reduce risks for HAV exposure associated with SUD and homelessness.
Click here to read the digital edition.
1. Kemmer NM, Miskovsky EP. Hepatitis A. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2000;14(3):605-615.
2. Tong MJ, el-Farra NS, Grew MI. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: recent experience in a community teaching hospital. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S15-S18.
3. Murphy TV, Denniston MM, Hill HA, et al. Progress toward eliminating hepatitis a disease in the United States. MMWR Suppl. 2016;65(1):29-41.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Viral hepatitis surveillance, United States, 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2015surveillance/pdfs/2015HepSurveillanceRpt.pdf. Published 2015. Accessed February 12, 2018.
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2017 – Outbreaks of hepatitis A in multiple states among people who are homeless and people who use drugs. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/outbreaks/2017March-HepatitisA.htm. Updated February 7, 2018. Accessed February 12, 2018.
6. Hepatitis A cases more than double in 2017; if you’re at risk, get vaccinated [press release]. https://www.colorado.gov/pacific/cdphe/news/hep-a-cases-doubled. Published August 30,2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
7. Alltucker K. Hepatitis A outbreak spread to Maricopa County homeless from San Diego, officials say. Azcentral website. October 7, 2017. https://www.azcentral.com/story/news/local /arizona-health/2017/10/07/hepatitis-outbreak-spread-maricopa-county-homeless-san-diego-officials-say/740185001/. Accessed February 12, 2018.
8. Savage RD, Rosella LC, Brown KA, Khan K, Crowcroft NS. Underreporting of hepatitis A in non-endemic countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:281.
9. Purcell RH, Wong DC, Shapiro M. Relative infectivity of hepatitis A virus by the oral and intravenous routes in 2 species of nonhuman primates. J Infect Dis. 2002;185(11):1668-1671.
10. Tassopoulos NC, Papaevangelou GJ, Ticehurst JR, Purcell RH. Fecal excretion of Greek strains of hepatitis A virus in patients with hepatitis A and in experimentally infected chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1986;154(2):231-237.
11. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis A questions and answers for health professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hav/havfaq.htm. Updated November 8, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
12. Taylor RM, Davern T, Munoz S, et al; US Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Fulminant hepatitis A virus infection in the United States: Incidence, prognosis, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2006;44(6):1589-1597.
13. Vento S, Garofano T, Renzini C, et al. Fulminant hepatitis associated with hepatitis A virus superinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(5):286-290.
14. Singh S, Johnson AS, McCray E, Hall HI. CDC - HIV incidence, prevalence and undiagnosed infections in men who have sex with men - HIV incidence decreased among all transmission categories except MSM. Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI); February 13-16,2017; Seattle, WA. http://www .natap.org/2017/CROI/croi_116.htm. Accessed February 12, 2018.
15. Fonquernie L, Meynard JL, Charrois A, Delamare C, Meyohas MC, Frottier J. Occurrence of acute hepatitis A in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32(2):297-299.
16. Ida S, Tachikawa N, Nakajima A, et al. Influence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection on acute hepatitis A virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34(3):379-385.
17. Costa-Mattioli M, Allavena C, Poirier AS, Billaudel S, Raffi F, Ferré V. Prolonged hepatitis A infection in an HIV-1 seropositive patient. J Med Virol. 2002;68(1):7-11.
18. Neefe JR, Gellis SS, Stokes J Jr. Homologous serum hepatitis and infectious (epidemic) hepatitis; studies in volunteers bearing on immunological and other characteristics of the etiological agents. Am J Med. 1946;1:3-22.
19. Krugman S, Giles JP, Hammond J. Infectious hepatitis. Evidence for two distinctive clinical, epidemiological, and immunological types of infection. JAMA. 1967;200(5):365-373.
20. Hadler SC, Webster HM, Erben JJ, Swanson JE, Maynard JE. Hepatitis A in day-care centers. A community-wide assessment. N Engl J Med. 1980;302(22):1222-1227.
21. Lednar WM, Lemon SM, Kirkpatrick JW, Redfield RR, Fields ML, Kelley PW. Frequency of illness associated with epidemic hepatitis A virus infections in adults. Am J Epidemiol. 1985;122(2):226-233.
22. Gordon SC, Reddy KR, Schiff L, Schiff ER. Prolonged intrahepatic cholestasis secondary to acute hepatitis A. Ann Intern Med. 1984;101(5):635-637.
23. Schiff ER. Atypical clinical manifestations of hepatitis A. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S18-S20.
24. Richardson M, Elliman D, Maguire H, Simpson J, Nicoll A. Evidence base of incubation periods, periods of infectiousness and exclusion policies for the control of communicable diseases in schools and preschools. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20(4):380-391.
25. Willner IR, Uhl MD, Howard SC, Williams EQ, Riely CA, Waters B. Serious hepatitis A: an analysis of patients hospitalized during an urban epidemic in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128(2):111-114.
26. Rezende G, Roque-Afonso AM, Samuel D, et al. Viral and clinical factors associated with the fulminant course of hepatitis A infection. Hepatology. 2003;38(3):613-618.
27. Lemon SM. Type A viral hepatitis. New developments in an old disease. N Engl J Med. 1985;313(17):1059-1067.
28. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for viral hepatitis surveillance and case management. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/surveillance guidelines.htm. Updated May 31, 2015. Accessed February 8, 2018.
29. Kao HW, Ashcavai M, Redeker AG. The persistence of hepatitis A IgM antibody after acute clinical hepatitis A. Hepatology. 1984;4(5):933-936.
30. Liaw YF, Yang CY, Chu CM, Huang MJ. Appearance and persistence of hepatitis A IgM antibody in acute clinical hepatitis A observed in an outbreak. Infection. 1986;14(4):156-158.
31. Plumb ID, Bulkow LR, Bruce MG, et al. Persistence of antibody to Hepatitis A virus 20 years after receipt of Hepatitis A vaccine in Alaska. J Viral Hepat. 2017;24(7):608-612.
32. Koff RS. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of hepatitis A virus infection. Vaccine. 1992;10 (suppl 1):S15-S17.
33. Clemens R, Safary A, Hepburn A, Roche C, Stanbury WJ, André FE. Clinical experience with an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S44-S49.
34. Ambrosch F, André FE, Delem A, et al. Simultaneous vaccination against hepatitis A and B: results of a controlled study. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S142-S145.
35. Gil A, González A, Dal-Ré R, Calero JR. Interference assessment of yellow fever vaccine with the immune response to a single-dose inactivated hepatitis A vaccine (1440 EL.U.). A controlled study in adults. Vaccine. 1996;14(11):1028-1030.
36. Jong EC, Kaplan KM, Eves KA, Taddeo CA, Lakkis HD, Kuter BJ. An open randomized study of inactivated hepatitis A vaccine administered concomitantly with typhoid fever and yellow fever vaccines. J Travel Med. 2002;9(2):66-70.
37. Nolan T, Bernstein H, Blatter MM, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine administered concomitantly with diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis and haemophilus influenzae type B vaccines to children less than 2 years of age. Pediatrics. 2006;118(3):e602-e609.
38. Usonis V, Meriste S, Bakasenas V, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a combined hepatitis A and B vaccine administered concomitantly with either a measles-mumps-rubella or a diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis-inactivated poliomyelitis vaccine mixed with a Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine in infants aged 12-18 months. Vaccine. 2005;23(20):2602-2606.
39. Moro PL, Museru OI, Niu M, Lewis P, Broder K. Reports to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after hepatitis A and hepatitis AB vaccines in pregnant women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;210(6):561.e1-561.e-6.
40. André FE, D’Hondt E, Delem A, Safary A. Clinical assessment of the safety and efficacy of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: rationale and summary of findings. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S160-S168.
41. Just M, Berger R. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of inactivated hepatitis A vaccines. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S110-S113.
42. McMahon BJ, Williams J, Bulkow L, et al. Immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in Alaska Native children and Native and non-Native adults. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(3):676-679.
43. Balcarek KB, Bagley MR, Pass RF, Schiff ER, Krause DS. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in preschool children. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S70-S72.
44. Bell BP, Negus S, Fiore AE, et al. Immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in infants and young children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007;26(2):116-122.
45. Arguedas MR, Johnson A, Eloubeidi MA, Fallon MB. Immunogenicity of hepatitis A vaccination in decompensated cirrhotic patients. Hepatology. 2001;34(1):28-31.
46. Overton ET, Nurutdinova D, Sungkanuparph S, Seyfried W, Groger RK, Powderly WG. Predictors of immunity after hepatitis A vaccination in HIV-infected persons. J Viral Hepat. 2007;14(3):189-193.
47. Askling HH, Rombo L, van Vollenhoven R, et al. Hepatitis A vaccine for immunosuppressed patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective, open-label, multi-centre study. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2014;12(2):134-142.
48. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VHA national hepatitis A immunization guidelines. http://vaww.prevention.va.gov/CPS/Hepatitis_A_Immunization.asp. Nonpublic document. Source not verified.
49. Kushel M. Hepatitis A outbreak in California - addressing the root cause. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(3):211-213.
50. Millard J, Appleton H, Parry JV. Studies on heat inactivation of hepatitis A virus with special reference to shellfish. Part 1. Procedures for infection and recovery of virus from laboratory-maintained cockles. Epidemiol Infect. 1987;98(3):397-414.
51. Hoke CH, Jr., Binn LN, Egan JE, et al. Hepatitis A in the US Army: epidemiology and vaccine development. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S75-S79.
52. Dooley DP. History of U.S. military contributions to the study of viral hepatitis. Mil Med. 2005;170(suppl 4):71-76.
53. Grabenstein JD, Pittman PR, Greenwood JT, Engler RJ. Immunization to protect the US Armed Forces: heritage, current practice, and prospects. Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28:3-26.
54. Beste LA, Leipertz SL, Green PK, Dominitz JA, Ross D, Ioannou GN. Trends in burden of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma by underlying liver disease in US veterans, 2001-2013. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(6):1471-1482.e1475; quiz e17-e18.
55. Fargo J, Metraux S, Byrne T, et al. Prevalence and risk of homelessness among US veterans. Prev Chronic Dis. 2012;9:E45.
56. Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77.
1. Kemmer NM, Miskovsky EP. Hepatitis A. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2000;14(3):605-615.
2. Tong MJ, el-Farra NS, Grew MI. Clinical manifestations of hepatitis A: recent experience in a community teaching hospital. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S15-S18.
3. Murphy TV, Denniston MM, Hill HA, et al. Progress toward eliminating hepatitis a disease in the United States. MMWR Suppl. 2016;65(1):29-41.
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Viral hepatitis surveillance, United States, 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/2015surveillance/pdfs/2015HepSurveillanceRpt.pdf. Published 2015. Accessed February 12, 2018.
5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2017 – Outbreaks of hepatitis A in multiple states among people who are homeless and people who use drugs. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/outbreaks/2017March-HepatitisA.htm. Updated February 7, 2018. Accessed February 12, 2018.
6. Hepatitis A cases more than double in 2017; if you’re at risk, get vaccinated [press release]. https://www.colorado.gov/pacific/cdphe/news/hep-a-cases-doubled. Published August 30,2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
7. Alltucker K. Hepatitis A outbreak spread to Maricopa County homeless from San Diego, officials say. Azcentral website. October 7, 2017. https://www.azcentral.com/story/news/local /arizona-health/2017/10/07/hepatitis-outbreak-spread-maricopa-county-homeless-san-diego-officials-say/740185001/. Accessed February 12, 2018.
8. Savage RD, Rosella LC, Brown KA, Khan K, Crowcroft NS. Underreporting of hepatitis A in non-endemic countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:281.
9. Purcell RH, Wong DC, Shapiro M. Relative infectivity of hepatitis A virus by the oral and intravenous routes in 2 species of nonhuman primates. J Infect Dis. 2002;185(11):1668-1671.
10. Tassopoulos NC, Papaevangelou GJ, Ticehurst JR, Purcell RH. Fecal excretion of Greek strains of hepatitis A virus in patients with hepatitis A and in experimentally infected chimpanzees. J Infect Dis. 1986;154(2):231-237.
11. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis A questions and answers for health professionals. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hav/havfaq.htm. Updated November 8, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
12. Taylor RM, Davern T, Munoz S, et al; US Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Fulminant hepatitis A virus infection in the United States: Incidence, prognosis, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2006;44(6):1589-1597.
13. Vento S, Garofano T, Renzini C, et al. Fulminant hepatitis associated with hepatitis A virus superinfection in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(5):286-290.
14. Singh S, Johnson AS, McCray E, Hall HI. CDC - HIV incidence, prevalence and undiagnosed infections in men who have sex with men - HIV incidence decreased among all transmission categories except MSM. Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI); February 13-16,2017; Seattle, WA. http://www .natap.org/2017/CROI/croi_116.htm. Accessed February 12, 2018.
15. Fonquernie L, Meynard JL, Charrois A, Delamare C, Meyohas MC, Frottier J. Occurrence of acute hepatitis A in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32(2):297-299.
16. Ida S, Tachikawa N, Nakajima A, et al. Influence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection on acute hepatitis A virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34(3):379-385.
17. Costa-Mattioli M, Allavena C, Poirier AS, Billaudel S, Raffi F, Ferré V. Prolonged hepatitis A infection in an HIV-1 seropositive patient. J Med Virol. 2002;68(1):7-11.
18. Neefe JR, Gellis SS, Stokes J Jr. Homologous serum hepatitis and infectious (epidemic) hepatitis; studies in volunteers bearing on immunological and other characteristics of the etiological agents. Am J Med. 1946;1:3-22.
19. Krugman S, Giles JP, Hammond J. Infectious hepatitis. Evidence for two distinctive clinical, epidemiological, and immunological types of infection. JAMA. 1967;200(5):365-373.
20. Hadler SC, Webster HM, Erben JJ, Swanson JE, Maynard JE. Hepatitis A in day-care centers. A community-wide assessment. N Engl J Med. 1980;302(22):1222-1227.
21. Lednar WM, Lemon SM, Kirkpatrick JW, Redfield RR, Fields ML, Kelley PW. Frequency of illness associated with epidemic hepatitis A virus infections in adults. Am J Epidemiol. 1985;122(2):226-233.
22. Gordon SC, Reddy KR, Schiff L, Schiff ER. Prolonged intrahepatic cholestasis secondary to acute hepatitis A. Ann Intern Med. 1984;101(5):635-637.
23. Schiff ER. Atypical clinical manifestations of hepatitis A. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S18-S20.
24. Richardson M, Elliman D, Maguire H, Simpson J, Nicoll A. Evidence base of incubation periods, periods of infectiousness and exclusion policies for the control of communicable diseases in schools and preschools. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20(4):380-391.
25. Willner IR, Uhl MD, Howard SC, Williams EQ, Riely CA, Waters B. Serious hepatitis A: an analysis of patients hospitalized during an urban epidemic in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128(2):111-114.
26. Rezende G, Roque-Afonso AM, Samuel D, et al. Viral and clinical factors associated with the fulminant course of hepatitis A infection. Hepatology. 2003;38(3):613-618.
27. Lemon SM. Type A viral hepatitis. New developments in an old disease. N Engl J Med. 1985;313(17):1059-1067.
28. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for viral hepatitis surveillance and case management. https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/statistics/surveillance guidelines.htm. Updated May 31, 2015. Accessed February 8, 2018.
29. Kao HW, Ashcavai M, Redeker AG. The persistence of hepatitis A IgM antibody after acute clinical hepatitis A. Hepatology. 1984;4(5):933-936.
30. Liaw YF, Yang CY, Chu CM, Huang MJ. Appearance and persistence of hepatitis A IgM antibody in acute clinical hepatitis A observed in an outbreak. Infection. 1986;14(4):156-158.
31. Plumb ID, Bulkow LR, Bruce MG, et al. Persistence of antibody to Hepatitis A virus 20 years after receipt of Hepatitis A vaccine in Alaska. J Viral Hepat. 2017;24(7):608-612.
32. Koff RS. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of hepatitis A virus infection. Vaccine. 1992;10 (suppl 1):S15-S17.
33. Clemens R, Safary A, Hepburn A, Roche C, Stanbury WJ, André FE. Clinical experience with an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S44-S49.
34. Ambrosch F, André FE, Delem A, et al. Simultaneous vaccination against hepatitis A and B: results of a controlled study. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S142-S145.
35. Gil A, González A, Dal-Ré R, Calero JR. Interference assessment of yellow fever vaccine with the immune response to a single-dose inactivated hepatitis A vaccine (1440 EL.U.). A controlled study in adults. Vaccine. 1996;14(11):1028-1030.
36. Jong EC, Kaplan KM, Eves KA, Taddeo CA, Lakkis HD, Kuter BJ. An open randomized study of inactivated hepatitis A vaccine administered concomitantly with typhoid fever and yellow fever vaccines. J Travel Med. 2002;9(2):66-70.
37. Nolan T, Bernstein H, Blatter MM, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine administered concomitantly with diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis and haemophilus influenzae type B vaccines to children less than 2 years of age. Pediatrics. 2006;118(3):e602-e609.
38. Usonis V, Meriste S, Bakasenas V, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a combined hepatitis A and B vaccine administered concomitantly with either a measles-mumps-rubella or a diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis-inactivated poliomyelitis vaccine mixed with a Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine in infants aged 12-18 months. Vaccine. 2005;23(20):2602-2606.
39. Moro PL, Museru OI, Niu M, Lewis P, Broder K. Reports to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System after hepatitis A and hepatitis AB vaccines in pregnant women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;210(6):561.e1-561.e-6.
40. André FE, D’Hondt E, Delem A, Safary A. Clinical assessment of the safety and efficacy of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine: rationale and summary of findings. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S160-S168.
41. Just M, Berger R. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of inactivated hepatitis A vaccines. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S110-S113.
42. McMahon BJ, Williams J, Bulkow L, et al. Immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in Alaska Native children and Native and non-Native adults. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(3):676-679.
43. Balcarek KB, Bagley MR, Pass RF, Schiff ER, Krause DS. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in preschool children. J Infect Dis. 1995;171(suppl 1):S70-S72.
44. Bell BP, Negus S, Fiore AE, et al. Immunogenicity of an inactivated hepatitis A vaccine in infants and young children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007;26(2):116-122.
45. Arguedas MR, Johnson A, Eloubeidi MA, Fallon MB. Immunogenicity of hepatitis A vaccination in decompensated cirrhotic patients. Hepatology. 2001;34(1):28-31.
46. Overton ET, Nurutdinova D, Sungkanuparph S, Seyfried W, Groger RK, Powderly WG. Predictors of immunity after hepatitis A vaccination in HIV-infected persons. J Viral Hepat. 2007;14(3):189-193.
47. Askling HH, Rombo L, van Vollenhoven R, et al. Hepatitis A vaccine for immunosuppressed patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective, open-label, multi-centre study. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2014;12(2):134-142.
48. US Department of Veterans Affairs. VHA national hepatitis A immunization guidelines. http://vaww.prevention.va.gov/CPS/Hepatitis_A_Immunization.asp. Nonpublic document. Source not verified.
49. Kushel M. Hepatitis A outbreak in California - addressing the root cause. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(3):211-213.
50. Millard J, Appleton H, Parry JV. Studies on heat inactivation of hepatitis A virus with special reference to shellfish. Part 1. Procedures for infection and recovery of virus from laboratory-maintained cockles. Epidemiol Infect. 1987;98(3):397-414.
51. Hoke CH, Jr., Binn LN, Egan JE, et al. Hepatitis A in the US Army: epidemiology and vaccine development. Vaccine. 1992;10(suppl 1):S75-S79.
52. Dooley DP. History of U.S. military contributions to the study of viral hepatitis. Mil Med. 2005;170(suppl 4):71-76.
53. Grabenstein JD, Pittman PR, Greenwood JT, Engler RJ. Immunization to protect the US Armed Forces: heritage, current practice, and prospects. Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28:3-26.
54. Beste LA, Leipertz SL, Green PK, Dominitz JA, Ross D, Ioannou GN. Trends in burden of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma by underlying liver disease in US veterans, 2001-2013. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(6):1471-1482.e1475; quiz e17-e18.
55. Fargo J, Metraux S, Byrne T, et al. Prevalence and risk of homelessness among US veterans. Prev Chronic Dis. 2012;9:E45.
56. Teeters JB, Lancaster CL, Brown DG, Back SE. Substance use disorders in military veterans: prevalence and treatment challenges. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2017;8:69-77.
Accessibility and Uptake of Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis for HIV Prevention in the VHA (FULL)
Despite important advances in treatment and prevention over the past 30 years, HIV remains a significant public health concern in the US, with nearly 40,000 new HIV infections. annually.1 Among the estimated 1.1 million Americans currently living with HIV, 1 in 8 remains undiagnosed, and only half (49%) are virally suppressed.2 Although data demonstrate that viral suppression virtually eliminates the risk of transmission among people living with HIV, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV remains an integral part of a coordinated effort to reduce transmission. Uptake of PrEP is particularly vital considering the large percentage of people in the US living with HIV who are not virally suppressed because they have not started, are unable to stay on HIV antiretroviral treatment, or have not been diagnosed.
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is the largest single provider of care to HIV-infected individuals in the US, with more than 28,000 veterans in care with HIV in 2016 (data from the VA National HIV Clinical Registry Reports, written communication from Population Health Service, Office of Patient Care Services, January 2018).
The only FDA-approved medication for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis is tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC), a fixed-dose combination of 2 antiretroviral medications that are also used to treat HIV. Its efficacy has been proven among numerous populations at risk for HIV, including those with sexual and injection drug use risk factors.4,5 Use of TDF/FTC for PrEP has been available at the VA since its July 2012 FDA approval. In May 2014, the US Public Health Service (PHS) and the US Department of Health and Human Services released the first comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for PrEP. Soon after, in September 2014, the VA released more formal guidance on the use of TDF/FTC for HIV PrEP as outlined by the PHS.6 Similar to patterns outside the VA, PrEP uptake across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has been modest and variable.
A recent VHA analysis of the variability in PrEP uptake identified about 1,600 patients who had been prescribed PrEP in the VA as of June 2017 among about 6 million veterans in care. Across VA medical facilities, the absolute number of PrEP initiations ranged from 0 to 109 with the maximum PrEP initiation rate at 146.4/100,000 veterans in care. Eight facilities did not initiate a single PrEP prescription over the 5-year period. This study presents strategicefforts undertaken by the VA to increase access to and uptake of PrEP across the health care system and to decrease disparities in HIV prevention care.
VA National Pr EP Working Group
In the beginning of 2017, the HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions (HHRC) programs within the VHA Office of Specialty Care Services convened a national working group to better measure and address the gaps in PrEP usage across the health care system. This multidisciplinary PrEP Working Group was composed of more than 40 members with expertise in HIV clinical care and PrEP, including physicians, clinical pharmacists, advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs), physician assistants (PAs), social workers, psychologists, implementation scientists, and representatives from other VA programs with a relevant programmatic or policy interest in PrEP.
Implementation Targets
The National PrEP Working Group identified increased PrEP uptake across the VHA system as the primary implementation target with a specific focus on increasing PrEP use in primary care clinics and among those at highest risk. As noted earlier, overall uptake of PrEP across VHA medical facilities has been modest; however, new PrEP initiations have increased in each 12-month period since FDA approval (Figure 1).
To rapidly understand barriers to accessing PrEP, the National PrEP Working Group developed and deployed an informal survey to HIV clinicians at all VA facilities, with nearly half responding (n = 68). These frontline providers identified several important and common barriers inhibiting PrEP uptake, including knowledge gaps among providers without infectious diseases training
Patient adherence was not identified by providers as a significant barrier to PrEP uptake in this informal survey. A recent analysis of adherence among a national cohort of veterans on HIV PrEP in VA care between July 2012 and June 2016 found that adherence in the first year of PrEP was high with some differences detected by age, race, and gender.8
As an initial step in addressing these identified barriers to prescribing PrEP in the VHA, the National PrEP Working Group developed several provider education materials, trainings, and support tools to impact the overarching goal, and identified implementation targets of increasing access outside of primary care and among noninfectious disease and nonphysician clinicians, ensuring high-quality PrEP care in all settings, and targeting PrEP uptake to at-risk populations (Table).
Increasing PrEP Use in Primary Care and Women’s Health Clinics
As of June 2017, physicians (staff, interns, residents, and fellows) accounted for more than three-quarters of VA PrEP index prescriptions. Among staff physicians, infectious diseases specialists initiated 67% of all prescriptions. Clinical pharmacists prescribed only 6%; APRNs and PAs prescribed 16% of initiations. This is unsurprising, as the field survey identified lack of awareness and specific training on PrEP care among providers without infectious diseases training as a common barrier.
The VA is the largest US employer of nurses, including more than 5,500 APRNs. In December 2016, the VA granted full practice authority to APRNs across the health care system, regardless of state restrictions in most cases.9
In 2015, the VA employed about 7,700 clinical pharmacists, 3,200 of whom had an active SOP that allowed for prescribing authority. In fiscal year 2015, clinical pharmacists were responsible for at least 20% of all hepatitis C virus (HCV) prescriptions and 69% of prescriptions for anticoagulants across the system.10 Clinical pharmacists are increasingly recognized for their extensive contributions to increasing access to treatment in the VA across a broad spectrum of clinical issues. With this infrastructure and expertise, clinical pharmacists also are well positioned to expand their scope to include PrEP.
To that end, the National PrEP Working Group worked closely with clinical pharmacists in the field and from the VA Academic Detailing Service (ADS) within the VA Pharmacy Benefits Management Services office. The ADS supports the development of scholarly, balanced, evidence-based educational tools and information for frontline VA providers using one-on-one social marketing techniques to impact specific clinical targets. These interventions are delivered by clinical pharmacists to empower VA clinicians and promote evidence-based clinical care to help reduce variability in practice across the system.11 An ADS module for PrEP has been developed and will be available in 2018 across the VHA to facilities participating in the ADS.
A virtual accredited training program on prescribing PrEP and monitoring patients on PrEP designed for clinical pharmacists will be delivered early in 2018 to complement these materials and will be open to all prescribers interested in learning more about PrEP. By offering a complement of training and clinical support tools, most of which are detailed in other sections of this article, the National PrEP Working Group is creating educational opportunities that are accessible in a variety of different formats to decrease knowledge barriers over PrEP prescribing and build over time a broader pool of VA clinicians trained in PrEP care.
Ensuring High-Quality PrEP Care
One system-level concern about expanding PrEP to providers without infectious diseases training is the quality of follow-up care. In order to aid noninfectious diseases clinicians, and nonphysician providers who are not as familiar with PrEP, several clinical support tools have been created, including (1) VA’s Clinical Considerations for PrEP to Prevent HIV Infection, which is aligned with CDC clinical guidance12; (2) a PrEP clinical criterion check list; (3) clinical support tools, such as prepopulated electronic health record (EHR) templates and order menus to facilitate PrEP prescribing and monitoring in busy primary care clinical settings; and (4) PrEP-specific texts in the Annie App, an automated text-messaging application developed by the VA Office of Connected Care, which supports medication adherence, appointment attendance, vitals tracking, and education.13
Available evidence indicates that there is potential for disparities in PrEP effectiveness in the VA related to varying medication adherence. Analysis of pharmacy refill records found that adherence with TDF/FTC was high in the first year after PrEP initiation (median proportion of days covered in the first year was 74%), but adherence was lower among veterans in VA care who were African American, women, and/or under age 45 years.8 This highlights the importance of enhanced services, such as Annie, to support PrEP adherence in at-risk groups as well as monitoring of HIV risk factors to ensure PrEP is still indicated.
Targeting PrEP Uptake for High-Risk Veterans
Although the VA’s overarching goal is to increase access to and uptake of PrEP across the VHA, it also is important to direct resources to those at greatest risk of acquiring HIV infection. The National PrEP Working Group has focused on the following critical implementation issues in the VA’s strategic approach to HIV prevention, with a specific focus on the geographic disparities between PrEP uptake and HIV risk across the VHA as well as disparities based on rurality, race/ethnicity, and gender.
The majority of the VHA patient population is male (91% in 2016).14 A VHA analysis of PrEP initiations in the VA indicates that in June 2017, 97% of veterans in VA care receiving PrEP were male, 69% were white, 88% resided in urban areas, and the average age was 41.6 years. An analysis of PrEP initiation in the VA indicates that current PrEP uptake is clustered in a few geographic areas and that some areas with high HIV incidence had low uptake.15 States with the highest risk of HIV infection are in the Southeast, followed by parts of the West, Midwest, and Northeast (Figure 2).16,17
Rural areas are increasingly impacted by the HIV epidemic in the US, but access to PrEP is often limited in rural communities.19 Several rural counties in the Southeastern US now have rates of new HIV infection comparable with those historically seen in only the largest cities.1 In addition, recent outbreaks of HIV and hepatitis C virus infection related to needle sharing highlight the need for HIV prevention programs in rural areas impacted by the opioid epidemic.20
About 1 in 4 veterans overall—and 16% of veterans in care who are HIV-positive—reside in rural areas, but only 4.3% of veterans who had initiated PrEP through 2017 resided in rural areas.21,22 In order to address the need to improve access to PrEP in many rural-serving VHA facilities, the PrEP Working Group has emphasized the increased utilization of virtual care (telehealth, Annie App, the Virtual Medical Room) and broadening the pool of available PrEP prescribers to include noninfectious diseases physicians, pharmacists, and APRNs.
Important racial and ethnic disparities also exist in PrEP access nationally. For example, in the US as a whole, African American MSM, followed by Latino MSM continue to be at highest risk for HIV infection.1 In 2015, 45% of all new HIV infections in the US were among African Americans, 26% of whom were women and 58% identified as gay or bisexual.23 A recent analysis of US retail pharmacies that dispensed FTC/TDF analyzed the racial demographics of PrEP uptake and found that the majority of PrEP initiations were among whites (74%), followed by Hispanics (12%) and African Americans (10%); and females of all races made up 20.7%.24 The VA is performing better than these national averages. Of the 688 PrEP prescriptions in the VA in 2016, 64% of recipients identified themselves as white and 23% as African American. Hispanic ethnicity was reported by 13%.
There are several limitations to identifying a specific implementation target for PrEP across the VA system, including the challenge of accurately identifying the population at risk via the EHR or clinical informatics tools. For example, strong risk factors for HIV acquisition include IV drug use, receptive anal intercourse without a condom, and needlesticks.
Behaviors that pose lower risk, such as vaginal intercourse or insertive anal intercourse could contribute to a higher overall lifetime risk if these behaviors occur frequently.25 Behavioral risk factors are not well captured in the VA EHR, making it difficult to identify potential PrEP candidates through population health tools. Additionally, stigma and discrimination may make it difficult for a patient to disclose to their clinician and for a clinician to inquire into behavioral risk factors. The criminalization of HIV-related risk behaviors in some states also may complicate the identification of potential PrEP candidates.26,27 These issues contribute to the challenges that providers face in screening for HIV risk and that patients face in disclosing their personal risk.
To address these regional, rural, and ethnic disparities and enhance the identification of potential PrEP recipients, the National PrEP Working Group is developing a suite of tools to support frontline providers in identifying potential PrEP recipients and expanding care to those at highest risk and who may be more difficult to reach due to rurality, concerns about stigma, or other issues.
- Clinical support tools to identify potential PrEP recipients, such as a clinical reminder that identifies patients at high risk for HIV based on diagnosis codes, and a PrEP clinical dashboard;
- A telehealth protocol for PrEP care and promotion of the VA Virtual Medical Room, which allows providers to video conference with patients in their home; and
- Social media outreach and awareness campaigns targeted at veterans to increase PrEP awareness are being shared through VA Facebook and Twitter accounts, blog posts, and www.hiv.va.gov posts (Figure 4).
Implementation Strategy & Evaluation
During the calendar year 2017, the PrEP Working Group met monthly and in smaller subcommittees to develop the strategic plan, products, and tools described earlier. On World AIDS Day, a virtual live meeting on PrEP was made available to all providers across the system and will be made available for continuing education training through the VA online employee education system. During 2018, the primary focus of the PrEP Working Group will be the continued development and refinement of provider education materials, clinical tools, and data tracking as well as increasing veteran outreach through social media and other awareness campaigns planned throughout the year.
Annual assessment of PrEP uptake will evaluate progress on the primary implementation target and areas of clinical practice: (1) increase number of PrEP prescriptions overall; (2) ensure PrEP is prescribed at all VA facilities; (3) increase preciptions by noninfectious diseases provider; (4) increase prescriptions by clinical pharmacists and APRNs; (5) monitor quality of care, including by discipline/practice setting; (6) increase PrEP prescriptions in facilities in endemic areas; and (7) increase the proportion of PrEP prescriptions for veterans of color.
In 2019 and 2020, additional targeted intervention and outreach plans will be developed for sites with difficulty meeting implementation targets. Sites in highly HIV-endemic areas will be a priority, and outreach will be designed to assist in the identification of facility-level barriers to PrEP use.
Conclusion
HIV remains an important public health issue in the US and among veterans in VA care, and prevention is a critical component to combat the epidemic. The VHA is the largest single provider of HIV care in the US with facilities and community-based outpatient clinics in all states and US territories.
The VA seems to be performing better in terms of the proportion of PrEP uptake among racial groups at highest risk for HIV compared with a US sample from retail pharmacies, which may be, in part, driven by the cost of PrEP and follow-up sexually transmitted infection testing.24 However, a considerable gap remain in VHA PrEP uptake among populations at highest risk for HIV in the US.
With the investment of a National PrEP Working Group, the VA is charting a course to augment its HIV prevention services to exceed the US nationally. The National PrEP Working Group will continue to develop specific, measurable, and impactful targets guided by state-of-the-art scientific evidence and surveillance data and a suite of educational and clinical resources designed to assist frontline providers, facilities, and patients in meeting clearly defined implementation targets.
Click here to read the digital edition.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV surveillance report, 2016; Vol 28. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveillance -report-2016-vol-28.pdf. Published November 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV continuum of care, US, 2014, overall and by age, race/ethnicity, transmission route and sex. https://www.cdc .gov/nchhstp/newsroom/2017/HIV-Continuum-of-Care.html. Updated September 12, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
3. Branson BM, Handsfield HH, Lampe MA, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Revised recommendations for HIV testing of adults, adolescents, and pregnant women in health-care settings. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006;55(RR-14):1-17.
4. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves first medication to reduce HIV risk [press release]. https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/news/1254/fda-approves-first-drug -for-reducing-the-risk-of-sexually-acquired-hiv-infection. Published July 12, 2012. Accessed February 14, 2018.
5. Fonner VA, Dalglish SL, Kennedy CE, et al. Effectiveness and safety of oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis for all populations. AIDS. 2016;30(12):1973-1983.
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2014: a clinical practice guideline. http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Published 2014. Accessed February 12, 2018.
7. Smith DK, Mendoza MC, Stryker JE, Rose CE. PrEP awareness and attitudes in a national survey of primary care clinicians in the United States, 2009-2015. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0156592.
8. Van Epps P, Maier M, Lund B, et al. Medication adherence in a nationwide cohort of veterans initiating pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018;77(3):272-278.
9. US Department of Veterans Affairs. 38 CFR Part 17, RIN 2900-AP44. Advance Practice Registered Nurses. Federal Register, Rules and Regulations. 81(240) December 14, 2016
10. Ourth H, Groppi J, Morreale AP, Quicci-Roberts K. Clinical pharmacist prescribing activities in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1406-1415.
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Pharmacy Benefits Management Academic Detailing Service. VA academic detailing implementation guide. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/VA_Academic_Detailing_Implementation_Guide.pdf. Published September 2016. Accessed February 12, 2018.
12. Veterans Health Administration US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Specialty Services, HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions Programs. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV infection: clinical considerations from the Department of Veterans Affairs National HIV Program. https://www.hiv.va.gov/pdf/PrEP-considerations.pdf. Published September 2016. Accessed January 4, 2018.
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Mobile Health. Annie app for clinicians. https://mobile.va.gov/app/annie-app-clinicians. Published September 2016. Accessed January 4, 2018.
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. VA utilization profile FY 2016. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/Quickfacts/VA_Utilization_Profile.pdf. Published . November 2017. Accessed March 5, 2018.
15. Van Epps P. Pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: the use and effectiveness of PrEP in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA). Abstract presented at: Infectious Diseases Week 2016; October 26-30, 2016; New Orleans, LA. https://idsa.confex.com/idsa/2016/webprogram/Paper60122.html. Accessed February 12, 2018.
16. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2016 conference on retroviruses and opportunistic infections, lifetime risk of HIV diagnosis by state: https://www.cdc .gov/nchhstp/newsroom/images/2016/CROI_lifetime_risk_state.jpg. Published February 24, 2016. Accessed February 12, 2018.
17. Elopre L, Kudroff K, Westfall AO, Overton ET, Mugavero MJ. Brief report: the right people, right places, and right practices: disparities in PrEP access among African American men, women, and MSM in the Deep South. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;74(1):56-59.
18. Wu H, Mendoza MC, Huang YA, Hayes T, Smith DK, Hoover KW. Uptake of HIV preexposure prophylaxis among commercially insured persons-United States, 2010-2014. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(2):144-149.
19. Schafer KR, Albrecht H, Dillingham R, et al. The continuum of HIV care in rural communities in the United States and Canada: what is known and future research directions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;75(1):355-344.
20. Conrad C, Bradley HM, Broz D, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). community outbreak of hiv infection linked to injection drug use of oxymorphone—Indiana, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(16):443-444.
21. Ohl ME, Richardson K, Kaboli P, Perencevich E, Vaughan-Sarrazin M. Geographic access and use of infectious diseases specialty and general primary care services by veterans with HIV infection: implications for telehealth and shared care programs. J Rural Health. 2014;30(4):412-421.
22. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans’ health care challenges. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp. Updated February 9, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
23. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV among African Americans. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/group/racialethnic/africanamericans/index.html. Updated February 9, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
24. Bush S, Magnuson D, Rawlings K, et al. Racial characteristics of FTC/TDF for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) users in the US. Paper presented at: ASM Microbe Conference 2016; June 16-20, 2016; Boston, MA.
25. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV risk behaviors. https://www.cdc .gov/hiv/pdf/risk/estimates/cdc-hiv-risk-behaviors.pdf. Published December 2015. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
26. Lehman JS, Carr MH, Nichol AJ, et al. Prevalence and public health implications of state laws that criminalize potential HIV exposure in the United States. AIDS Behav. 2014;18(6):997-1006.
27. US Department of Justice, Civil Rights Division. Best practices guide to reform HIV-specific criminal laws to align with scientifically-supported factors. https://www.hivlawandpolicy.org/sites/default/files/DOj-HIV-Criminal-Law-Best-Practices-Guide.pdf. March 2014. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
28. Backus L, Czarnogorski M, Yip G, et al. HIV care continuum applied to the US Department of Veterans Affairs: HIV virologic outcomes in an integrated health care system. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;69(4):474-480.
Despite important advances in treatment and prevention over the past 30 years, HIV remains a significant public health concern in the US, with nearly 40,000 new HIV infections. annually.1 Among the estimated 1.1 million Americans currently living with HIV, 1 in 8 remains undiagnosed, and only half (49%) are virally suppressed.2 Although data demonstrate that viral suppression virtually eliminates the risk of transmission among people living with HIV, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV remains an integral part of a coordinated effort to reduce transmission. Uptake of PrEP is particularly vital considering the large percentage of people in the US living with HIV who are not virally suppressed because they have not started, are unable to stay on HIV antiretroviral treatment, or have not been diagnosed.
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is the largest single provider of care to HIV-infected individuals in the US, with more than 28,000 veterans in care with HIV in 2016 (data from the VA National HIV Clinical Registry Reports, written communication from Population Health Service, Office of Patient Care Services, January 2018).
The only FDA-approved medication for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis is tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC), a fixed-dose combination of 2 antiretroviral medications that are also used to treat HIV. Its efficacy has been proven among numerous populations at risk for HIV, including those with sexual and injection drug use risk factors.4,5 Use of TDF/FTC for PrEP has been available at the VA since its July 2012 FDA approval. In May 2014, the US Public Health Service (PHS) and the US Department of Health and Human Services released the first comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for PrEP. Soon after, in September 2014, the VA released more formal guidance on the use of TDF/FTC for HIV PrEP as outlined by the PHS.6 Similar to patterns outside the VA, PrEP uptake across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has been modest and variable.
A recent VHA analysis of the variability in PrEP uptake identified about 1,600 patients who had been prescribed PrEP in the VA as of June 2017 among about 6 million veterans in care. Across VA medical facilities, the absolute number of PrEP initiations ranged from 0 to 109 with the maximum PrEP initiation rate at 146.4/100,000 veterans in care. Eight facilities did not initiate a single PrEP prescription over the 5-year period. This study presents strategicefforts undertaken by the VA to increase access to and uptake of PrEP across the health care system and to decrease disparities in HIV prevention care.
VA National Pr EP Working Group
In the beginning of 2017, the HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions (HHRC) programs within the VHA Office of Specialty Care Services convened a national working group to better measure and address the gaps in PrEP usage across the health care system. This multidisciplinary PrEP Working Group was composed of more than 40 members with expertise in HIV clinical care and PrEP, including physicians, clinical pharmacists, advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs), physician assistants (PAs), social workers, psychologists, implementation scientists, and representatives from other VA programs with a relevant programmatic or policy interest in PrEP.
Implementation Targets
The National PrEP Working Group identified increased PrEP uptake across the VHA system as the primary implementation target with a specific focus on increasing PrEP use in primary care clinics and among those at highest risk. As noted earlier, overall uptake of PrEP across VHA medical facilities has been modest; however, new PrEP initiations have increased in each 12-month period since FDA approval (Figure 1).
To rapidly understand barriers to accessing PrEP, the National PrEP Working Group developed and deployed an informal survey to HIV clinicians at all VA facilities, with nearly half responding (n = 68). These frontline providers identified several important and common barriers inhibiting PrEP uptake, including knowledge gaps among providers without infectious diseases training
Patient adherence was not identified by providers as a significant barrier to PrEP uptake in this informal survey. A recent analysis of adherence among a national cohort of veterans on HIV PrEP in VA care between July 2012 and June 2016 found that adherence in the first year of PrEP was high with some differences detected by age, race, and gender.8
As an initial step in addressing these identified barriers to prescribing PrEP in the VHA, the National PrEP Working Group developed several provider education materials, trainings, and support tools to impact the overarching goal, and identified implementation targets of increasing access outside of primary care and among noninfectious disease and nonphysician clinicians, ensuring high-quality PrEP care in all settings, and targeting PrEP uptake to at-risk populations (Table).
Increasing PrEP Use in Primary Care and Women’s Health Clinics
As of June 2017, physicians (staff, interns, residents, and fellows) accounted for more than three-quarters of VA PrEP index prescriptions. Among staff physicians, infectious diseases specialists initiated 67% of all prescriptions. Clinical pharmacists prescribed only 6%; APRNs and PAs prescribed 16% of initiations. This is unsurprising, as the field survey identified lack of awareness and specific training on PrEP care among providers without infectious diseases training as a common barrier.
The VA is the largest US employer of nurses, including more than 5,500 APRNs. In December 2016, the VA granted full practice authority to APRNs across the health care system, regardless of state restrictions in most cases.9
In 2015, the VA employed about 7,700 clinical pharmacists, 3,200 of whom had an active SOP that allowed for prescribing authority. In fiscal year 2015, clinical pharmacists were responsible for at least 20% of all hepatitis C virus (HCV) prescriptions and 69% of prescriptions for anticoagulants across the system.10 Clinical pharmacists are increasingly recognized for their extensive contributions to increasing access to treatment in the VA across a broad spectrum of clinical issues. With this infrastructure and expertise, clinical pharmacists also are well positioned to expand their scope to include PrEP.
To that end, the National PrEP Working Group worked closely with clinical pharmacists in the field and from the VA Academic Detailing Service (ADS) within the VA Pharmacy Benefits Management Services office. The ADS supports the development of scholarly, balanced, evidence-based educational tools and information for frontline VA providers using one-on-one social marketing techniques to impact specific clinical targets. These interventions are delivered by clinical pharmacists to empower VA clinicians and promote evidence-based clinical care to help reduce variability in practice across the system.11 An ADS module for PrEP has been developed and will be available in 2018 across the VHA to facilities participating in the ADS.
A virtual accredited training program on prescribing PrEP and monitoring patients on PrEP designed for clinical pharmacists will be delivered early in 2018 to complement these materials and will be open to all prescribers interested in learning more about PrEP. By offering a complement of training and clinical support tools, most of which are detailed in other sections of this article, the National PrEP Working Group is creating educational opportunities that are accessible in a variety of different formats to decrease knowledge barriers over PrEP prescribing and build over time a broader pool of VA clinicians trained in PrEP care.
Ensuring High-Quality PrEP Care
One system-level concern about expanding PrEP to providers without infectious diseases training is the quality of follow-up care. In order to aid noninfectious diseases clinicians, and nonphysician providers who are not as familiar with PrEP, several clinical support tools have been created, including (1) VA’s Clinical Considerations for PrEP to Prevent HIV Infection, which is aligned with CDC clinical guidance12; (2) a PrEP clinical criterion check list; (3) clinical support tools, such as prepopulated electronic health record (EHR) templates and order menus to facilitate PrEP prescribing and monitoring in busy primary care clinical settings; and (4) PrEP-specific texts in the Annie App, an automated text-messaging application developed by the VA Office of Connected Care, which supports medication adherence, appointment attendance, vitals tracking, and education.13
Available evidence indicates that there is potential for disparities in PrEP effectiveness in the VA related to varying medication adherence. Analysis of pharmacy refill records found that adherence with TDF/FTC was high in the first year after PrEP initiation (median proportion of days covered in the first year was 74%), but adherence was lower among veterans in VA care who were African American, women, and/or under age 45 years.8 This highlights the importance of enhanced services, such as Annie, to support PrEP adherence in at-risk groups as well as monitoring of HIV risk factors to ensure PrEP is still indicated.
Targeting PrEP Uptake for High-Risk Veterans
Although the VA’s overarching goal is to increase access to and uptake of PrEP across the VHA, it also is important to direct resources to those at greatest risk of acquiring HIV infection. The National PrEP Working Group has focused on the following critical implementation issues in the VA’s strategic approach to HIV prevention, with a specific focus on the geographic disparities between PrEP uptake and HIV risk across the VHA as well as disparities based on rurality, race/ethnicity, and gender.
The majority of the VHA patient population is male (91% in 2016).14 A VHA analysis of PrEP initiations in the VA indicates that in June 2017, 97% of veterans in VA care receiving PrEP were male, 69% were white, 88% resided in urban areas, and the average age was 41.6 years. An analysis of PrEP initiation in the VA indicates that current PrEP uptake is clustered in a few geographic areas and that some areas with high HIV incidence had low uptake.15 States with the highest risk of HIV infection are in the Southeast, followed by parts of the West, Midwest, and Northeast (Figure 2).16,17
Rural areas are increasingly impacted by the HIV epidemic in the US, but access to PrEP is often limited in rural communities.19 Several rural counties in the Southeastern US now have rates of new HIV infection comparable with those historically seen in only the largest cities.1 In addition, recent outbreaks of HIV and hepatitis C virus infection related to needle sharing highlight the need for HIV prevention programs in rural areas impacted by the opioid epidemic.20
About 1 in 4 veterans overall—and 16% of veterans in care who are HIV-positive—reside in rural areas, but only 4.3% of veterans who had initiated PrEP through 2017 resided in rural areas.21,22 In order to address the need to improve access to PrEP in many rural-serving VHA facilities, the PrEP Working Group has emphasized the increased utilization of virtual care (telehealth, Annie App, the Virtual Medical Room) and broadening the pool of available PrEP prescribers to include noninfectious diseases physicians, pharmacists, and APRNs.
Important racial and ethnic disparities also exist in PrEP access nationally. For example, in the US as a whole, African American MSM, followed by Latino MSM continue to be at highest risk for HIV infection.1 In 2015, 45% of all new HIV infections in the US were among African Americans, 26% of whom were women and 58% identified as gay or bisexual.23 A recent analysis of US retail pharmacies that dispensed FTC/TDF analyzed the racial demographics of PrEP uptake and found that the majority of PrEP initiations were among whites (74%), followed by Hispanics (12%) and African Americans (10%); and females of all races made up 20.7%.24 The VA is performing better than these national averages. Of the 688 PrEP prescriptions in the VA in 2016, 64% of recipients identified themselves as white and 23% as African American. Hispanic ethnicity was reported by 13%.
There are several limitations to identifying a specific implementation target for PrEP across the VA system, including the challenge of accurately identifying the population at risk via the EHR or clinical informatics tools. For example, strong risk factors for HIV acquisition include IV drug use, receptive anal intercourse without a condom, and needlesticks.
Behaviors that pose lower risk, such as vaginal intercourse or insertive anal intercourse could contribute to a higher overall lifetime risk if these behaviors occur frequently.25 Behavioral risk factors are not well captured in the VA EHR, making it difficult to identify potential PrEP candidates through population health tools. Additionally, stigma and discrimination may make it difficult for a patient to disclose to their clinician and for a clinician to inquire into behavioral risk factors. The criminalization of HIV-related risk behaviors in some states also may complicate the identification of potential PrEP candidates.26,27 These issues contribute to the challenges that providers face in screening for HIV risk and that patients face in disclosing their personal risk.
To address these regional, rural, and ethnic disparities and enhance the identification of potential PrEP recipients, the National PrEP Working Group is developing a suite of tools to support frontline providers in identifying potential PrEP recipients and expanding care to those at highest risk and who may be more difficult to reach due to rurality, concerns about stigma, or other issues.
- Clinical support tools to identify potential PrEP recipients, such as a clinical reminder that identifies patients at high risk for HIV based on diagnosis codes, and a PrEP clinical dashboard;
- A telehealth protocol for PrEP care and promotion of the VA Virtual Medical Room, which allows providers to video conference with patients in their home; and
- Social media outreach and awareness campaigns targeted at veterans to increase PrEP awareness are being shared through VA Facebook and Twitter accounts, blog posts, and www.hiv.va.gov posts (Figure 4).
Implementation Strategy & Evaluation
During the calendar year 2017, the PrEP Working Group met monthly and in smaller subcommittees to develop the strategic plan, products, and tools described earlier. On World AIDS Day, a virtual live meeting on PrEP was made available to all providers across the system and will be made available for continuing education training through the VA online employee education system. During 2018, the primary focus of the PrEP Working Group will be the continued development and refinement of provider education materials, clinical tools, and data tracking as well as increasing veteran outreach through social media and other awareness campaigns planned throughout the year.
Annual assessment of PrEP uptake will evaluate progress on the primary implementation target and areas of clinical practice: (1) increase number of PrEP prescriptions overall; (2) ensure PrEP is prescribed at all VA facilities; (3) increase preciptions by noninfectious diseases provider; (4) increase prescriptions by clinical pharmacists and APRNs; (5) monitor quality of care, including by discipline/practice setting; (6) increase PrEP prescriptions in facilities in endemic areas; and (7) increase the proportion of PrEP prescriptions for veterans of color.
In 2019 and 2020, additional targeted intervention and outreach plans will be developed for sites with difficulty meeting implementation targets. Sites in highly HIV-endemic areas will be a priority, and outreach will be designed to assist in the identification of facility-level barriers to PrEP use.
Conclusion
HIV remains an important public health issue in the US and among veterans in VA care, and prevention is a critical component to combat the epidemic. The VHA is the largest single provider of HIV care in the US with facilities and community-based outpatient clinics in all states and US territories.
The VA seems to be performing better in terms of the proportion of PrEP uptake among racial groups at highest risk for HIV compared with a US sample from retail pharmacies, which may be, in part, driven by the cost of PrEP and follow-up sexually transmitted infection testing.24 However, a considerable gap remain in VHA PrEP uptake among populations at highest risk for HIV in the US.
With the investment of a National PrEP Working Group, the VA is charting a course to augment its HIV prevention services to exceed the US nationally. The National PrEP Working Group will continue to develop specific, measurable, and impactful targets guided by state-of-the-art scientific evidence and surveillance data and a suite of educational and clinical resources designed to assist frontline providers, facilities, and patients in meeting clearly defined implementation targets.
Click here to read the digital edition.
Despite important advances in treatment and prevention over the past 30 years, HIV remains a significant public health concern in the US, with nearly 40,000 new HIV infections. annually.1 Among the estimated 1.1 million Americans currently living with HIV, 1 in 8 remains undiagnosed, and only half (49%) are virally suppressed.2 Although data demonstrate that viral suppression virtually eliminates the risk of transmission among people living with HIV, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV remains an integral part of a coordinated effort to reduce transmission. Uptake of PrEP is particularly vital considering the large percentage of people in the US living with HIV who are not virally suppressed because they have not started, are unable to stay on HIV antiretroviral treatment, or have not been diagnosed.
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is the largest single provider of care to HIV-infected individuals in the US, with more than 28,000 veterans in care with HIV in 2016 (data from the VA National HIV Clinical Registry Reports, written communication from Population Health Service, Office of Patient Care Services, January 2018).
The only FDA-approved medication for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis is tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC), a fixed-dose combination of 2 antiretroviral medications that are also used to treat HIV. Its efficacy has been proven among numerous populations at risk for HIV, including those with sexual and injection drug use risk factors.4,5 Use of TDF/FTC for PrEP has been available at the VA since its July 2012 FDA approval. In May 2014, the US Public Health Service (PHS) and the US Department of Health and Human Services released the first comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for PrEP. Soon after, in September 2014, the VA released more formal guidance on the use of TDF/FTC for HIV PrEP as outlined by the PHS.6 Similar to patterns outside the VA, PrEP uptake across the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has been modest and variable.
A recent VHA analysis of the variability in PrEP uptake identified about 1,600 patients who had been prescribed PrEP in the VA as of June 2017 among about 6 million veterans in care. Across VA medical facilities, the absolute number of PrEP initiations ranged from 0 to 109 with the maximum PrEP initiation rate at 146.4/100,000 veterans in care. Eight facilities did not initiate a single PrEP prescription over the 5-year period. This study presents strategicefforts undertaken by the VA to increase access to and uptake of PrEP across the health care system and to decrease disparities in HIV prevention care.
VA National Pr EP Working Group
In the beginning of 2017, the HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions (HHRC) programs within the VHA Office of Specialty Care Services convened a national working group to better measure and address the gaps in PrEP usage across the health care system. This multidisciplinary PrEP Working Group was composed of more than 40 members with expertise in HIV clinical care and PrEP, including physicians, clinical pharmacists, advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs), physician assistants (PAs), social workers, psychologists, implementation scientists, and representatives from other VA programs with a relevant programmatic or policy interest in PrEP.
Implementation Targets
The National PrEP Working Group identified increased PrEP uptake across the VHA system as the primary implementation target with a specific focus on increasing PrEP use in primary care clinics and among those at highest risk. As noted earlier, overall uptake of PrEP across VHA medical facilities has been modest; however, new PrEP initiations have increased in each 12-month period since FDA approval (Figure 1).
To rapidly understand barriers to accessing PrEP, the National PrEP Working Group developed and deployed an informal survey to HIV clinicians at all VA facilities, with nearly half responding (n = 68). These frontline providers identified several important and common barriers inhibiting PrEP uptake, including knowledge gaps among providers without infectious diseases training
Patient adherence was not identified by providers as a significant barrier to PrEP uptake in this informal survey. A recent analysis of adherence among a national cohort of veterans on HIV PrEP in VA care between July 2012 and June 2016 found that adherence in the first year of PrEP was high with some differences detected by age, race, and gender.8
As an initial step in addressing these identified barriers to prescribing PrEP in the VHA, the National PrEP Working Group developed several provider education materials, trainings, and support tools to impact the overarching goal, and identified implementation targets of increasing access outside of primary care and among noninfectious disease and nonphysician clinicians, ensuring high-quality PrEP care in all settings, and targeting PrEP uptake to at-risk populations (Table).
Increasing PrEP Use in Primary Care and Women’s Health Clinics
As of June 2017, physicians (staff, interns, residents, and fellows) accounted for more than three-quarters of VA PrEP index prescriptions. Among staff physicians, infectious diseases specialists initiated 67% of all prescriptions. Clinical pharmacists prescribed only 6%; APRNs and PAs prescribed 16% of initiations. This is unsurprising, as the field survey identified lack of awareness and specific training on PrEP care among providers without infectious diseases training as a common barrier.
The VA is the largest US employer of nurses, including more than 5,500 APRNs. In December 2016, the VA granted full practice authority to APRNs across the health care system, regardless of state restrictions in most cases.9
In 2015, the VA employed about 7,700 clinical pharmacists, 3,200 of whom had an active SOP that allowed for prescribing authority. In fiscal year 2015, clinical pharmacists were responsible for at least 20% of all hepatitis C virus (HCV) prescriptions and 69% of prescriptions for anticoagulants across the system.10 Clinical pharmacists are increasingly recognized for their extensive contributions to increasing access to treatment in the VA across a broad spectrum of clinical issues. With this infrastructure and expertise, clinical pharmacists also are well positioned to expand their scope to include PrEP.
To that end, the National PrEP Working Group worked closely with clinical pharmacists in the field and from the VA Academic Detailing Service (ADS) within the VA Pharmacy Benefits Management Services office. The ADS supports the development of scholarly, balanced, evidence-based educational tools and information for frontline VA providers using one-on-one social marketing techniques to impact specific clinical targets. These interventions are delivered by clinical pharmacists to empower VA clinicians and promote evidence-based clinical care to help reduce variability in practice across the system.11 An ADS module for PrEP has been developed and will be available in 2018 across the VHA to facilities participating in the ADS.
A virtual accredited training program on prescribing PrEP and monitoring patients on PrEP designed for clinical pharmacists will be delivered early in 2018 to complement these materials and will be open to all prescribers interested in learning more about PrEP. By offering a complement of training and clinical support tools, most of which are detailed in other sections of this article, the National PrEP Working Group is creating educational opportunities that are accessible in a variety of different formats to decrease knowledge barriers over PrEP prescribing and build over time a broader pool of VA clinicians trained in PrEP care.
Ensuring High-Quality PrEP Care
One system-level concern about expanding PrEP to providers without infectious diseases training is the quality of follow-up care. In order to aid noninfectious diseases clinicians, and nonphysician providers who are not as familiar with PrEP, several clinical support tools have been created, including (1) VA’s Clinical Considerations for PrEP to Prevent HIV Infection, which is aligned with CDC clinical guidance12; (2) a PrEP clinical criterion check list; (3) clinical support tools, such as prepopulated electronic health record (EHR) templates and order menus to facilitate PrEP prescribing and monitoring in busy primary care clinical settings; and (4) PrEP-specific texts in the Annie App, an automated text-messaging application developed by the VA Office of Connected Care, which supports medication adherence, appointment attendance, vitals tracking, and education.13
Available evidence indicates that there is potential for disparities in PrEP effectiveness in the VA related to varying medication adherence. Analysis of pharmacy refill records found that adherence with TDF/FTC was high in the first year after PrEP initiation (median proportion of days covered in the first year was 74%), but adherence was lower among veterans in VA care who were African American, women, and/or under age 45 years.8 This highlights the importance of enhanced services, such as Annie, to support PrEP adherence in at-risk groups as well as monitoring of HIV risk factors to ensure PrEP is still indicated.
Targeting PrEP Uptake for High-Risk Veterans
Although the VA’s overarching goal is to increase access to and uptake of PrEP across the VHA, it also is important to direct resources to those at greatest risk of acquiring HIV infection. The National PrEP Working Group has focused on the following critical implementation issues in the VA’s strategic approach to HIV prevention, with a specific focus on the geographic disparities between PrEP uptake and HIV risk across the VHA as well as disparities based on rurality, race/ethnicity, and gender.
The majority of the VHA patient population is male (91% in 2016).14 A VHA analysis of PrEP initiations in the VA indicates that in June 2017, 97% of veterans in VA care receiving PrEP were male, 69% were white, 88% resided in urban areas, and the average age was 41.6 years. An analysis of PrEP initiation in the VA indicates that current PrEP uptake is clustered in a few geographic areas and that some areas with high HIV incidence had low uptake.15 States with the highest risk of HIV infection are in the Southeast, followed by parts of the West, Midwest, and Northeast (Figure 2).16,17
Rural areas are increasingly impacted by the HIV epidemic in the US, but access to PrEP is often limited in rural communities.19 Several rural counties in the Southeastern US now have rates of new HIV infection comparable with those historically seen in only the largest cities.1 In addition, recent outbreaks of HIV and hepatitis C virus infection related to needle sharing highlight the need for HIV prevention programs in rural areas impacted by the opioid epidemic.20
About 1 in 4 veterans overall—and 16% of veterans in care who are HIV-positive—reside in rural areas, but only 4.3% of veterans who had initiated PrEP through 2017 resided in rural areas.21,22 In order to address the need to improve access to PrEP in many rural-serving VHA facilities, the PrEP Working Group has emphasized the increased utilization of virtual care (telehealth, Annie App, the Virtual Medical Room) and broadening the pool of available PrEP prescribers to include noninfectious diseases physicians, pharmacists, and APRNs.
Important racial and ethnic disparities also exist in PrEP access nationally. For example, in the US as a whole, African American MSM, followed by Latino MSM continue to be at highest risk for HIV infection.1 In 2015, 45% of all new HIV infections in the US were among African Americans, 26% of whom were women and 58% identified as gay or bisexual.23 A recent analysis of US retail pharmacies that dispensed FTC/TDF analyzed the racial demographics of PrEP uptake and found that the majority of PrEP initiations were among whites (74%), followed by Hispanics (12%) and African Americans (10%); and females of all races made up 20.7%.24 The VA is performing better than these national averages. Of the 688 PrEP prescriptions in the VA in 2016, 64% of recipients identified themselves as white and 23% as African American. Hispanic ethnicity was reported by 13%.
There are several limitations to identifying a specific implementation target for PrEP across the VA system, including the challenge of accurately identifying the population at risk via the EHR or clinical informatics tools. For example, strong risk factors for HIV acquisition include IV drug use, receptive anal intercourse without a condom, and needlesticks.
Behaviors that pose lower risk, such as vaginal intercourse or insertive anal intercourse could contribute to a higher overall lifetime risk if these behaviors occur frequently.25 Behavioral risk factors are not well captured in the VA EHR, making it difficult to identify potential PrEP candidates through population health tools. Additionally, stigma and discrimination may make it difficult for a patient to disclose to their clinician and for a clinician to inquire into behavioral risk factors. The criminalization of HIV-related risk behaviors in some states also may complicate the identification of potential PrEP candidates.26,27 These issues contribute to the challenges that providers face in screening for HIV risk and that patients face in disclosing their personal risk.
To address these regional, rural, and ethnic disparities and enhance the identification of potential PrEP recipients, the National PrEP Working Group is developing a suite of tools to support frontline providers in identifying potential PrEP recipients and expanding care to those at highest risk and who may be more difficult to reach due to rurality, concerns about stigma, or other issues.
- Clinical support tools to identify potential PrEP recipients, such as a clinical reminder that identifies patients at high risk for HIV based on diagnosis codes, and a PrEP clinical dashboard;
- A telehealth protocol for PrEP care and promotion of the VA Virtual Medical Room, which allows providers to video conference with patients in their home; and
- Social media outreach and awareness campaigns targeted at veterans to increase PrEP awareness are being shared through VA Facebook and Twitter accounts, blog posts, and www.hiv.va.gov posts (Figure 4).
Implementation Strategy & Evaluation
During the calendar year 2017, the PrEP Working Group met monthly and in smaller subcommittees to develop the strategic plan, products, and tools described earlier. On World AIDS Day, a virtual live meeting on PrEP was made available to all providers across the system and will be made available for continuing education training through the VA online employee education system. During 2018, the primary focus of the PrEP Working Group will be the continued development and refinement of provider education materials, clinical tools, and data tracking as well as increasing veteran outreach through social media and other awareness campaigns planned throughout the year.
Annual assessment of PrEP uptake will evaluate progress on the primary implementation target and areas of clinical practice: (1) increase number of PrEP prescriptions overall; (2) ensure PrEP is prescribed at all VA facilities; (3) increase preciptions by noninfectious diseases provider; (4) increase prescriptions by clinical pharmacists and APRNs; (5) monitor quality of care, including by discipline/practice setting; (6) increase PrEP prescriptions in facilities in endemic areas; and (7) increase the proportion of PrEP prescriptions for veterans of color.
In 2019 and 2020, additional targeted intervention and outreach plans will be developed for sites with difficulty meeting implementation targets. Sites in highly HIV-endemic areas will be a priority, and outreach will be designed to assist in the identification of facility-level barriers to PrEP use.
Conclusion
HIV remains an important public health issue in the US and among veterans in VA care, and prevention is a critical component to combat the epidemic. The VHA is the largest single provider of HIV care in the US with facilities and community-based outpatient clinics in all states and US territories.
The VA seems to be performing better in terms of the proportion of PrEP uptake among racial groups at highest risk for HIV compared with a US sample from retail pharmacies, which may be, in part, driven by the cost of PrEP and follow-up sexually transmitted infection testing.24 However, a considerable gap remain in VHA PrEP uptake among populations at highest risk for HIV in the US.
With the investment of a National PrEP Working Group, the VA is charting a course to augment its HIV prevention services to exceed the US nationally. The National PrEP Working Group will continue to develop specific, measurable, and impactful targets guided by state-of-the-art scientific evidence and surveillance data and a suite of educational and clinical resources designed to assist frontline providers, facilities, and patients in meeting clearly defined implementation targets.
Click here to read the digital edition.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV surveillance report, 2016; Vol 28. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveillance -report-2016-vol-28.pdf. Published November 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV continuum of care, US, 2014, overall and by age, race/ethnicity, transmission route and sex. https://www.cdc .gov/nchhstp/newsroom/2017/HIV-Continuum-of-Care.html. Updated September 12, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
3. Branson BM, Handsfield HH, Lampe MA, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Revised recommendations for HIV testing of adults, adolescents, and pregnant women in health-care settings. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006;55(RR-14):1-17.
4. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves first medication to reduce HIV risk [press release]. https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/news/1254/fda-approves-first-drug -for-reducing-the-risk-of-sexually-acquired-hiv-infection. Published July 12, 2012. Accessed February 14, 2018.
5. Fonner VA, Dalglish SL, Kennedy CE, et al. Effectiveness and safety of oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis for all populations. AIDS. 2016;30(12):1973-1983.
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2014: a clinical practice guideline. http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Published 2014. Accessed February 12, 2018.
7. Smith DK, Mendoza MC, Stryker JE, Rose CE. PrEP awareness and attitudes in a national survey of primary care clinicians in the United States, 2009-2015. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0156592.
8. Van Epps P, Maier M, Lund B, et al. Medication adherence in a nationwide cohort of veterans initiating pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018;77(3):272-278.
9. US Department of Veterans Affairs. 38 CFR Part 17, RIN 2900-AP44. Advance Practice Registered Nurses. Federal Register, Rules and Regulations. 81(240) December 14, 2016
10. Ourth H, Groppi J, Morreale AP, Quicci-Roberts K. Clinical pharmacist prescribing activities in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1406-1415.
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Pharmacy Benefits Management Academic Detailing Service. VA academic detailing implementation guide. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/VA_Academic_Detailing_Implementation_Guide.pdf. Published September 2016. Accessed February 12, 2018.
12. Veterans Health Administration US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Specialty Services, HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions Programs. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV infection: clinical considerations from the Department of Veterans Affairs National HIV Program. https://www.hiv.va.gov/pdf/PrEP-considerations.pdf. Published September 2016. Accessed January 4, 2018.
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Mobile Health. Annie app for clinicians. https://mobile.va.gov/app/annie-app-clinicians. Published September 2016. Accessed January 4, 2018.
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. VA utilization profile FY 2016. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/Quickfacts/VA_Utilization_Profile.pdf. Published . November 2017. Accessed March 5, 2018.
15. Van Epps P. Pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: the use and effectiveness of PrEP in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA). Abstract presented at: Infectious Diseases Week 2016; October 26-30, 2016; New Orleans, LA. https://idsa.confex.com/idsa/2016/webprogram/Paper60122.html. Accessed February 12, 2018.
16. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2016 conference on retroviruses and opportunistic infections, lifetime risk of HIV diagnosis by state: https://www.cdc .gov/nchhstp/newsroom/images/2016/CROI_lifetime_risk_state.jpg. Published February 24, 2016. Accessed February 12, 2018.
17. Elopre L, Kudroff K, Westfall AO, Overton ET, Mugavero MJ. Brief report: the right people, right places, and right practices: disparities in PrEP access among African American men, women, and MSM in the Deep South. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;74(1):56-59.
18. Wu H, Mendoza MC, Huang YA, Hayes T, Smith DK, Hoover KW. Uptake of HIV preexposure prophylaxis among commercially insured persons-United States, 2010-2014. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(2):144-149.
19. Schafer KR, Albrecht H, Dillingham R, et al. The continuum of HIV care in rural communities in the United States and Canada: what is known and future research directions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;75(1):355-344.
20. Conrad C, Bradley HM, Broz D, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). community outbreak of hiv infection linked to injection drug use of oxymorphone—Indiana, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(16):443-444.
21. Ohl ME, Richardson K, Kaboli P, Perencevich E, Vaughan-Sarrazin M. Geographic access and use of infectious diseases specialty and general primary care services by veterans with HIV infection: implications for telehealth and shared care programs. J Rural Health. 2014;30(4):412-421.
22. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans’ health care challenges. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp. Updated February 9, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
23. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV among African Americans. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/group/racialethnic/africanamericans/index.html. Updated February 9, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
24. Bush S, Magnuson D, Rawlings K, et al. Racial characteristics of FTC/TDF for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) users in the US. Paper presented at: ASM Microbe Conference 2016; June 16-20, 2016; Boston, MA.
25. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV risk behaviors. https://www.cdc .gov/hiv/pdf/risk/estimates/cdc-hiv-risk-behaviors.pdf. Published December 2015. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
26. Lehman JS, Carr MH, Nichol AJ, et al. Prevalence and public health implications of state laws that criminalize potential HIV exposure in the United States. AIDS Behav. 2014;18(6):997-1006.
27. US Department of Justice, Civil Rights Division. Best practices guide to reform HIV-specific criminal laws to align with scientifically-supported factors. https://www.hivlawandpolicy.org/sites/default/files/DOj-HIV-Criminal-Law-Best-Practices-Guide.pdf. March 2014. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
28. Backus L, Czarnogorski M, Yip G, et al. HIV care continuum applied to the US Department of Veterans Affairs: HIV virologic outcomes in an integrated health care system. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;69(4):474-480.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV surveillance report, 2016; Vol 28. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveillance -report-2016-vol-28.pdf. Published November 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV continuum of care, US, 2014, overall and by age, race/ethnicity, transmission route and sex. https://www.cdc .gov/nchhstp/newsroom/2017/HIV-Continuum-of-Care.html. Updated September 12, 2017. Accessed February 12, 2018.
3. Branson BM, Handsfield HH, Lampe MA, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Revised recommendations for HIV testing of adults, adolescents, and pregnant women in health-care settings. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006;55(RR-14):1-17.
4. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves first medication to reduce HIV risk [press release]. https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/news/1254/fda-approves-first-drug -for-reducing-the-risk-of-sexually-acquired-hiv-infection. Published July 12, 2012. Accessed February 14, 2018.
5. Fonner VA, Dalglish SL, Kennedy CE, et al. Effectiveness and safety of oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis for all populations. AIDS. 2016;30(12):1973-1983.
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2014: a clinical practice guideline. http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Published 2014. Accessed February 12, 2018.
7. Smith DK, Mendoza MC, Stryker JE, Rose CE. PrEP awareness and attitudes in a national survey of primary care clinicians in the United States, 2009-2015. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0156592.
8. Van Epps P, Maier M, Lund B, et al. Medication adherence in a nationwide cohort of veterans initiating pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018;77(3):272-278.
9. US Department of Veterans Affairs. 38 CFR Part 17, RIN 2900-AP44. Advance Practice Registered Nurses. Federal Register, Rules and Regulations. 81(240) December 14, 2016
10. Ourth H, Groppi J, Morreale AP, Quicci-Roberts K. Clinical pharmacist prescribing activities in the Veterans Health Administration. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2016;73(18):1406-1415.
11. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Pharmacy Benefits Management Academic Detailing Service. VA academic detailing implementation guide. https://www.pbm.va.gov/PBM/AcademicDetailingService/Documents/VA_Academic_Detailing_Implementation_Guide.pdf. Published September 2016. Accessed February 12, 2018.
12. Veterans Health Administration US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Specialty Services, HIV, Hepatitis, and Related Conditions Programs. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) to prevent HIV infection: clinical considerations from the Department of Veterans Affairs National HIV Program. https://www.hiv.va.gov/pdf/PrEP-considerations.pdf. Published September 2016. Accessed January 4, 2018.
13. US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Mobile Health. Annie app for clinicians. https://mobile.va.gov/app/annie-app-clinicians. Published September 2016. Accessed January 4, 2018.
14. US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Veterans Analysis and Statistics. VA utilization profile FY 2016. https://www.va.gov/vetdata/docs/Quickfacts/VA_Utilization_Profile.pdf. Published . November 2017. Accessed March 5, 2018.
15. Van Epps P. Pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention: the use and effectiveness of PrEP in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA). Abstract presented at: Infectious Diseases Week 2016; October 26-30, 2016; New Orleans, LA. https://idsa.confex.com/idsa/2016/webprogram/Paper60122.html. Accessed February 12, 2018.
16. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2016 conference on retroviruses and opportunistic infections, lifetime risk of HIV diagnosis by state: https://www.cdc .gov/nchhstp/newsroom/images/2016/CROI_lifetime_risk_state.jpg. Published February 24, 2016. Accessed February 12, 2018.
17. Elopre L, Kudroff K, Westfall AO, Overton ET, Mugavero MJ. Brief report: the right people, right places, and right practices: disparities in PrEP access among African American men, women, and MSM in the Deep South. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;74(1):56-59.
18. Wu H, Mendoza MC, Huang YA, Hayes T, Smith DK, Hoover KW. Uptake of HIV preexposure prophylaxis among commercially insured persons-United States, 2010-2014. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(2):144-149.
19. Schafer KR, Albrecht H, Dillingham R, et al. The continuum of HIV care in rural communities in the United States and Canada: what is known and future research directions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2017;75(1):355-344.
20. Conrad C, Bradley HM, Broz D, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). community outbreak of hiv infection linked to injection drug use of oxymorphone—Indiana, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(16):443-444.
21. Ohl ME, Richardson K, Kaboli P, Perencevich E, Vaughan-Sarrazin M. Geographic access and use of infectious diseases specialty and general primary care services by veterans with HIV infection: implications for telehealth and shared care programs. J Rural Health. 2014;30(4):412-421.
22. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. Rural veterans’ health care challenges. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/aboutus/ruralvets.asp. Updated February 9, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
23. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV among African Americans. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/group/racialethnic/africanamericans/index.html. Updated February 9, 2018. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
24. Bush S, Magnuson D, Rawlings K, et al. Racial characteristics of FTC/TDF for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) users in the US. Paper presented at: ASM Microbe Conference 2016; June 16-20, 2016; Boston, MA.
25. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV risk behaviors. https://www.cdc .gov/hiv/pdf/risk/estimates/cdc-hiv-risk-behaviors.pdf. Published December 2015. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
26. Lehman JS, Carr MH, Nichol AJ, et al. Prevalence and public health implications of state laws that criminalize potential HIV exposure in the United States. AIDS Behav. 2014;18(6):997-1006.
27. US Department of Justice, Civil Rights Division. Best practices guide to reform HIV-specific criminal laws to align with scientifically-supported factors. https://www.hivlawandpolicy.org/sites/default/files/DOj-HIV-Criminal-Law-Best-Practices-Guide.pdf. March 2014. Accessed on February 12, 2018.
28. Backus L, Czarnogorski M, Yip G, et al. HIV care continuum applied to the US Department of Veterans Affairs: HIV virologic outcomes in an integrated health care system. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015;69(4):474-480.
Hepatitis C Clinical Dashboards: Improving Liver Specialty Care Access and Quality
The VHA cares for 170,000 patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, making it the largest single provider of medical care to chronic HCV patients in the U.S.1 Although HCV treatment rates within the VHA outpace those of the private sector, only half of patients with HCV infection within the VHA have accessed a liver specialist and less than a quarter have received antiviral medication.2-4
Newer HCV treatment regimens promise treatment sustained virologic response (SVR) rates—a marker of viral clearance posttreatment—of ≥ 90% in most cases but require careful patient selection and management.5 In particular, the estimated 24% of patients with HCV infection with advanced liver disease require more rapid consideration for therapy to reduce complications of cirrhosis such as liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma, and death.6 With the advent of promising HCV therapies and rising rates of cirrhosis, there is an urgent need for population health management approach to deliver HCV care more widely and effectively.5,7
Rationale for Clinical Dashboards
Although the VHA hosts the largest integrated electronic medical record (EMR) system in the U.S., an EMR on its own does not guarantee improved patient care or access.8 EMRs can be used to document health care delivery, but they do not routinely provide information about the burden of disease in a population, nor do they identify patients most in need of care.
Clinical dashboards are tools that are geared to provide clinicians with relevant data to improve patient care. Early clinical dashboard development across the VHA was primary care focused, targeting patients with diabetes, ischemic heart disease, and hypertension. This national primary care dashboard provides clinically relevant, actionable data and enables the clinical provider to track patient progress. In addition, regional data can be aggregated for use by VISN managers.
While the impact of dashboards on quality of care is not well investigated, it remains a vital tool with the potential to transform care.9
HCV dashboards have been developed by individual VISNs and facilities across the VHA. HCV dashboards serve to identify patients most in need of antiviral therapy, expand outreach to those previously unseen by specialty care, sort patients by severity of liver disease, track treatment status, and calculate SVR.
Current HCV dashboards incorporate elements derived from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW), a national VA data repository consisting of data from all facilities’ electronic medical record systems. Updated information from the previous day is made available in VISN data warehouses and is refreshed nightly. The final result is user-friendly clinical data available in near-real time to dashboard users.
VISN 21 HCV Dashboard
Purpose and Elements
The VISN 21 HCV dashboard will be discussed as a prototype. Graphics of the VISN 21 dashboard interface are presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard was developed by pharmacists with specialty training in medical informatics, health care analytics, and data management. The dashboard addresses 3 previously unmet needs in HCV care: population management, patient treatment outcome tracking, and administrative planning.
Population management. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard allows for a centralized approach to care across a large geographic area containing multiple facilities. One important function is to identify patients with advanced liver disease as well as those who have not been seen in specialty care within the previous 2 years. It also allows for pretreatment screening through identification of HCV viral characteristics (eg, genotype, viral load) and selected comorbidities (eg, renal function, mental health conditions) that may influence candidacy for specific antiviral therapies. Individual patient reports can be stratified by facility (eg, clinic or VAMC) to identify the burden of disease within a specific location.
Patient treatment outcome tracking. The HCV dashboard allows tracking of the numbers and characteristics of patients who have previously received antiviral therapy. The number of patients achieving virologic cure may be tracked at the VISN and station levels, or displayed based on user-selected parameters, such as treatment history.
Administrative planning. The high costs of HCV antiviral medication requires careful budgetary planning and close communication with local and regional leadership. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard provides information crucial to assessing future treatment needs. Specifically, it allows administrators to view the number of patients actively being treated. The dashboard also allows for comparison of treatment rates among different facilities and help allocate resources where needed.
Design Architecture
To construct the source data for the dashboards, relevant data elements are pulled into a base table using Structured Query Language (SQL) code. Subsequently, SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) (Microsoft, Redmond, WA) compiles the dashboard output into an interactive and user-friendly interface that can be tailored to individual end users’ needs.
Dashboard development process. Through collaboration and survey of clinical providers, clinical factors necessary to decide patient and treatment readiness were identified. Relevant data elements include HCV genotype, selected medical and psychiatric comorbidities, prior receipt of treatment, and presence of advanced liver disease. While liver disease severity may be determined by invasive means, such as liver biopsy, the dashboard offers a noninvasive assessment using laboratory values (eg, calculated Fibrosis 4 score, Model for End Stage Liver Disease score).10,11
Once dashboard elements were selected, the variables were operationalized using data available in the CDW within the prescription, diagnostic, and laboratory data tables. As code was written, output was validated through chart review to ensure accuracy. Further validation was performed through comparison of the dashboard data with the clinical case registry, a registry of HCV viremic confirmed patients. Throughout dashboard development, the product was presented to end users to solicit requests for modifications. The code was refined over time to incorporate end user input.
Dashboard user interface. SSRS allows users to customize reports based on any variables defined within the data set including facility, severity of disease, HCV genotype, and prior antiviral treatment history among others. Results are displayed with summary information, including the total number of patients in the selected cohort, the number of patients who have been referred to a specialty liver clinic, and the number of patients who have been determined to achieve SVR. The end user has the option to export the results to excel for further use (eg, patient lists for telephone follow-up).
User recruitment. After piloting, the VISN 21 HCV dashboard was introduced during monthly pharmacy meetings and clinical telehealth encounters with providers. Feedback was solicited during the presentations and through postdevelopment surveys. In particular, providers requested spreadsheet-friendly formatting, additional informational fields consisting of mental health and substance abuse diagnoses, and identification of all patients with HCV regardless
of disease severity. A key element of dashboard refinement includes enhancing usability by solicitation of user feedback with subsequent tailoring of the user interface.12
Challenges
Many challenges exist in clinical dashboard development, expansion, and implementation including data integrity, workflow, and work culture. Data elements are often variable within a single facility, and this variation increases when identifying the same elements across facilities. For example, a laboratory test name (eg, “serum creatinine”) may exist with 2 to 3 different labels (eg, “creat,” “SCr,” “serum Cr”) within a single facility. As the variation increases, potential for inappropriate laboratory tests may be increased. Specialty clinic names also vary within and between facilities.
Local nomenclature for HCV clinic names may include “liver,” “infectious disease,” “hepatitis c,” or some variation, making it crucial for the dashboard developer to work closely with clinical staff to accurately matchspecialty clinic names being pulled from the data warehouse. Given the complexities of naming nomenclature within VA data, dashboard development requires a substantial investment of code customization and validation.
Ongoing dashboard maintenance is another important challenge due to the need for staff trained in SQL coding and familiarity with VA data warehouse architecture. Consequently, until the VHA dedicates resources to maintain such dashboards, only VISNs with existing technical knowledge and staffing will benefit from dashboards.
Usability, typically defined as “…effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction with which the intended users can achieve their tasks in the intended context of product use,” is an additional consideration as the HCV clinical dashboard disseminates nationally.13 Standard clinic workflow is not always conducive to the use of dashboards. VHA providers use the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) to review and document patient notes. However, accessing the HCV dashboard involves a site hosted outside of CPRS, thereby requiring the user to take several extra steps. These and other usability factors will need to be considered as the dashboard disseminates more widely.
Finally, data describing the effectiveness of clinical dashboards is very limited. VISN 21 is tracking the number of users accessing the dashboard. However, further study is needed to determine if clinical dashboards improve patient access and quality of care as well as factors to enhance usability
Conclusion
Clinical dashboards have the ability to transform each clinical provider into a population health manager who can readily identify patients most in need of care within their facility catchment area and beyond. As HCV dashboard development and implementation grows across the VHA, there is a need to pair clinical and technological advancements with greater patient outreach and shared best practices. Understanding the factors that tie improved quality of care with usability as well as investment in dashboard development and related efforts will likely keep the VHA in the forefront of chronic care delivery.
Author disclosures
The authors report no actual or potential conflicts of interest with regard to this article.
Disclaimer
The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of Federal Practitioner, Frontline Medical Communications Inc., the U.S. Government, or any of its agencies. This article may discuss unlabeled or investigational use of certain drugs. Please review complete prescribing information for specific drugs or drug combinations—including indications, contraindications, warnings, and adverse effects—before administering pharmacologic therapy to patients.
1. Dominitz JA, Boyko EJ, Koepsell TD, et al. Elevated prevalence of hepatitis C infection in users of United States veterans medical centers. Hepatology. 2005;41(1):88-96.
2. United States Department of Veterans Affairs. HCV Viremic Veterans in VHA Care in 2013 with First Fill in the Year or Ever Filled a VHA Outpatient Prescription for a HCV Antiviral Medication for the Nation, by VISN and by Station Description. http://vaww.hepatitis.va.gov/data-reports/ccr2013/RegMed-AnyFirstEverInCare-Jan14-HCVVir-HCV-2013-All.asp. Accessed October 10, 2014.
3. Rongey C, Shen H, Hamilton N, Backus LI, Asch SM, Knight S. Impact of rural residence and health system structure on quality of liver care. PloS One. 2013;8(12):e84826.
4. Beste LA, Ioannou GN. Prevalence and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs [published online ahead of print January 19, 2015]. Epidemiologic Reviews. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxu002.
5. Lawitz E, Poordad FF, Pang PS, et al. Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir fixed-dose combination with and without ribavirin in treatment-naive and previously treated patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus infection (LONESTAR): an openlabel, randomised, phase 2 trial [published correction appears in Lancet. 2014;383(9920):870]. Lancet. 2014;383(9916):515-523.
6. United States Department of Veterans Affairs. HCV Viremic Veterans in VHA Care in 2013 who had a VHA Diagnosis of Fibrosis/Cirrhosis by FIB-4 in the year for the Nation, by VISN and by Station. http://vaww.hepatitis.va.gov/data-reports/ccr2013/Cond-FIB4CurInCare-Jan14HCVVir-2013-All.asp. Accessed October 10, 2014.
7. Kanwal F, Hoang T, Kramer JR, et al. Increasing prevalence of HCC and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(4):1182-1188.e1.
8. Furukawa MF, King J, Patel V, Hsiao CJ, Adler-Milstein J, Jha AK. Despite substantial progress in EHR adoption, health information exchange and patient engagement remain low in office settings. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33(9):1672-1679.
9. Vrieze SI, Docherty A, Thuras P, et al. Best practices: The electronic medical record is an invaluable clinical tool: Let’s start using it. Psychiatric Serv. 2013;64(10):946-949.
10. Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B, et al. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. Comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology. 2007;46(1):32-36.
11. Kamath PS, Kim WR; Advanced Liver Disease Study Group. The model for endstage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology. 2007;45(3):797-805.
12. Goldberg L, Lide B, Lowry S, et al. Usability and accessibility in consumer health informatics current trends and future challenges. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40(5 suppl 2):S187-S197.
13. Schumacher RM, Lowry SZ; National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST Guide to the Processes Approach for Improving the Usability of Electronic Health Records. http://www.nist.gov/itl/hit/upload/Guide_Final_Publication_Version.pdf. Published November 29, 2010. Accessed November 24, 2014.
The VHA cares for 170,000 patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, making it the largest single provider of medical care to chronic HCV patients in the U.S.1 Although HCV treatment rates within the VHA outpace those of the private sector, only half of patients with HCV infection within the VHA have accessed a liver specialist and less than a quarter have received antiviral medication.2-4
Newer HCV treatment regimens promise treatment sustained virologic response (SVR) rates—a marker of viral clearance posttreatment—of ≥ 90% in most cases but require careful patient selection and management.5 In particular, the estimated 24% of patients with HCV infection with advanced liver disease require more rapid consideration for therapy to reduce complications of cirrhosis such as liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma, and death.6 With the advent of promising HCV therapies and rising rates of cirrhosis, there is an urgent need for population health management approach to deliver HCV care more widely and effectively.5,7
Rationale for Clinical Dashboards
Although the VHA hosts the largest integrated electronic medical record (EMR) system in the U.S., an EMR on its own does not guarantee improved patient care or access.8 EMRs can be used to document health care delivery, but they do not routinely provide information about the burden of disease in a population, nor do they identify patients most in need of care.
Clinical dashboards are tools that are geared to provide clinicians with relevant data to improve patient care. Early clinical dashboard development across the VHA was primary care focused, targeting patients with diabetes, ischemic heart disease, and hypertension. This national primary care dashboard provides clinically relevant, actionable data and enables the clinical provider to track patient progress. In addition, regional data can be aggregated for use by VISN managers.
While the impact of dashboards on quality of care is not well investigated, it remains a vital tool with the potential to transform care.9
HCV dashboards have been developed by individual VISNs and facilities across the VHA. HCV dashboards serve to identify patients most in need of antiviral therapy, expand outreach to those previously unseen by specialty care, sort patients by severity of liver disease, track treatment status, and calculate SVR.
Current HCV dashboards incorporate elements derived from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW), a national VA data repository consisting of data from all facilities’ electronic medical record systems. Updated information from the previous day is made available in VISN data warehouses and is refreshed nightly. The final result is user-friendly clinical data available in near-real time to dashboard users.
VISN 21 HCV Dashboard
Purpose and Elements
The VISN 21 HCV dashboard will be discussed as a prototype. Graphics of the VISN 21 dashboard interface are presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard was developed by pharmacists with specialty training in medical informatics, health care analytics, and data management. The dashboard addresses 3 previously unmet needs in HCV care: population management, patient treatment outcome tracking, and administrative planning.
Population management. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard allows for a centralized approach to care across a large geographic area containing multiple facilities. One important function is to identify patients with advanced liver disease as well as those who have not been seen in specialty care within the previous 2 years. It also allows for pretreatment screening through identification of HCV viral characteristics (eg, genotype, viral load) and selected comorbidities (eg, renal function, mental health conditions) that may influence candidacy for specific antiviral therapies. Individual patient reports can be stratified by facility (eg, clinic or VAMC) to identify the burden of disease within a specific location.
Patient treatment outcome tracking. The HCV dashboard allows tracking of the numbers and characteristics of patients who have previously received antiviral therapy. The number of patients achieving virologic cure may be tracked at the VISN and station levels, or displayed based on user-selected parameters, such as treatment history.
Administrative planning. The high costs of HCV antiviral medication requires careful budgetary planning and close communication with local and regional leadership. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard provides information crucial to assessing future treatment needs. Specifically, it allows administrators to view the number of patients actively being treated. The dashboard also allows for comparison of treatment rates among different facilities and help allocate resources where needed.
Design Architecture
To construct the source data for the dashboards, relevant data elements are pulled into a base table using Structured Query Language (SQL) code. Subsequently, SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) (Microsoft, Redmond, WA) compiles the dashboard output into an interactive and user-friendly interface that can be tailored to individual end users’ needs.
Dashboard development process. Through collaboration and survey of clinical providers, clinical factors necessary to decide patient and treatment readiness were identified. Relevant data elements include HCV genotype, selected medical and psychiatric comorbidities, prior receipt of treatment, and presence of advanced liver disease. While liver disease severity may be determined by invasive means, such as liver biopsy, the dashboard offers a noninvasive assessment using laboratory values (eg, calculated Fibrosis 4 score, Model for End Stage Liver Disease score).10,11
Once dashboard elements were selected, the variables were operationalized using data available in the CDW within the prescription, diagnostic, and laboratory data tables. As code was written, output was validated through chart review to ensure accuracy. Further validation was performed through comparison of the dashboard data with the clinical case registry, a registry of HCV viremic confirmed patients. Throughout dashboard development, the product was presented to end users to solicit requests for modifications. The code was refined over time to incorporate end user input.
Dashboard user interface. SSRS allows users to customize reports based on any variables defined within the data set including facility, severity of disease, HCV genotype, and prior antiviral treatment history among others. Results are displayed with summary information, including the total number of patients in the selected cohort, the number of patients who have been referred to a specialty liver clinic, and the number of patients who have been determined to achieve SVR. The end user has the option to export the results to excel for further use (eg, patient lists for telephone follow-up).
User recruitment. After piloting, the VISN 21 HCV dashboard was introduced during monthly pharmacy meetings and clinical telehealth encounters with providers. Feedback was solicited during the presentations and through postdevelopment surveys. In particular, providers requested spreadsheet-friendly formatting, additional informational fields consisting of mental health and substance abuse diagnoses, and identification of all patients with HCV regardless
of disease severity. A key element of dashboard refinement includes enhancing usability by solicitation of user feedback with subsequent tailoring of the user interface.12
Challenges
Many challenges exist in clinical dashboard development, expansion, and implementation including data integrity, workflow, and work culture. Data elements are often variable within a single facility, and this variation increases when identifying the same elements across facilities. For example, a laboratory test name (eg, “serum creatinine”) may exist with 2 to 3 different labels (eg, “creat,” “SCr,” “serum Cr”) within a single facility. As the variation increases, potential for inappropriate laboratory tests may be increased. Specialty clinic names also vary within and between facilities.
Local nomenclature for HCV clinic names may include “liver,” “infectious disease,” “hepatitis c,” or some variation, making it crucial for the dashboard developer to work closely with clinical staff to accurately matchspecialty clinic names being pulled from the data warehouse. Given the complexities of naming nomenclature within VA data, dashboard development requires a substantial investment of code customization and validation.
Ongoing dashboard maintenance is another important challenge due to the need for staff trained in SQL coding and familiarity with VA data warehouse architecture. Consequently, until the VHA dedicates resources to maintain such dashboards, only VISNs with existing technical knowledge and staffing will benefit from dashboards.
Usability, typically defined as “…effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction with which the intended users can achieve their tasks in the intended context of product use,” is an additional consideration as the HCV clinical dashboard disseminates nationally.13 Standard clinic workflow is not always conducive to the use of dashboards. VHA providers use the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) to review and document patient notes. However, accessing the HCV dashboard involves a site hosted outside of CPRS, thereby requiring the user to take several extra steps. These and other usability factors will need to be considered as the dashboard disseminates more widely.
Finally, data describing the effectiveness of clinical dashboards is very limited. VISN 21 is tracking the number of users accessing the dashboard. However, further study is needed to determine if clinical dashboards improve patient access and quality of care as well as factors to enhance usability
Conclusion
Clinical dashboards have the ability to transform each clinical provider into a population health manager who can readily identify patients most in need of care within their facility catchment area and beyond. As HCV dashboard development and implementation grows across the VHA, there is a need to pair clinical and technological advancements with greater patient outreach and shared best practices. Understanding the factors that tie improved quality of care with usability as well as investment in dashboard development and related efforts will likely keep the VHA in the forefront of chronic care delivery.
Author disclosures
The authors report no actual or potential conflicts of interest with regard to this article.
Disclaimer
The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of Federal Practitioner, Frontline Medical Communications Inc., the U.S. Government, or any of its agencies. This article may discuss unlabeled or investigational use of certain drugs. Please review complete prescribing information for specific drugs or drug combinations—including indications, contraindications, warnings, and adverse effects—before administering pharmacologic therapy to patients.
The VHA cares for 170,000 patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, making it the largest single provider of medical care to chronic HCV patients in the U.S.1 Although HCV treatment rates within the VHA outpace those of the private sector, only half of patients with HCV infection within the VHA have accessed a liver specialist and less than a quarter have received antiviral medication.2-4
Newer HCV treatment regimens promise treatment sustained virologic response (SVR) rates—a marker of viral clearance posttreatment—of ≥ 90% in most cases but require careful patient selection and management.5 In particular, the estimated 24% of patients with HCV infection with advanced liver disease require more rapid consideration for therapy to reduce complications of cirrhosis such as liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma, and death.6 With the advent of promising HCV therapies and rising rates of cirrhosis, there is an urgent need for population health management approach to deliver HCV care more widely and effectively.5,7
Rationale for Clinical Dashboards
Although the VHA hosts the largest integrated electronic medical record (EMR) system in the U.S., an EMR on its own does not guarantee improved patient care or access.8 EMRs can be used to document health care delivery, but they do not routinely provide information about the burden of disease in a population, nor do they identify patients most in need of care.
Clinical dashboards are tools that are geared to provide clinicians with relevant data to improve patient care. Early clinical dashboard development across the VHA was primary care focused, targeting patients with diabetes, ischemic heart disease, and hypertension. This national primary care dashboard provides clinically relevant, actionable data and enables the clinical provider to track patient progress. In addition, regional data can be aggregated for use by VISN managers.
While the impact of dashboards on quality of care is not well investigated, it remains a vital tool with the potential to transform care.9
HCV dashboards have been developed by individual VISNs and facilities across the VHA. HCV dashboards serve to identify patients most in need of antiviral therapy, expand outreach to those previously unseen by specialty care, sort patients by severity of liver disease, track treatment status, and calculate SVR.
Current HCV dashboards incorporate elements derived from the VA Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW), a national VA data repository consisting of data from all facilities’ electronic medical record systems. Updated information from the previous day is made available in VISN data warehouses and is refreshed nightly. The final result is user-friendly clinical data available in near-real time to dashboard users.
VISN 21 HCV Dashboard
Purpose and Elements
The VISN 21 HCV dashboard will be discussed as a prototype. Graphics of the VISN 21 dashboard interface are presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard was developed by pharmacists with specialty training in medical informatics, health care analytics, and data management. The dashboard addresses 3 previously unmet needs in HCV care: population management, patient treatment outcome tracking, and administrative planning.
Population management. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard allows for a centralized approach to care across a large geographic area containing multiple facilities. One important function is to identify patients with advanced liver disease as well as those who have not been seen in specialty care within the previous 2 years. It also allows for pretreatment screening through identification of HCV viral characteristics (eg, genotype, viral load) and selected comorbidities (eg, renal function, mental health conditions) that may influence candidacy for specific antiviral therapies. Individual patient reports can be stratified by facility (eg, clinic or VAMC) to identify the burden of disease within a specific location.
Patient treatment outcome tracking. The HCV dashboard allows tracking of the numbers and characteristics of patients who have previously received antiviral therapy. The number of patients achieving virologic cure may be tracked at the VISN and station levels, or displayed based on user-selected parameters, such as treatment history.
Administrative planning. The high costs of HCV antiviral medication requires careful budgetary planning and close communication with local and regional leadership. The VISN 21 HCV dashboard provides information crucial to assessing future treatment needs. Specifically, it allows administrators to view the number of patients actively being treated. The dashboard also allows for comparison of treatment rates among different facilities and help allocate resources where needed.
Design Architecture
To construct the source data for the dashboards, relevant data elements are pulled into a base table using Structured Query Language (SQL) code. Subsequently, SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) (Microsoft, Redmond, WA) compiles the dashboard output into an interactive and user-friendly interface that can be tailored to individual end users’ needs.
Dashboard development process. Through collaboration and survey of clinical providers, clinical factors necessary to decide patient and treatment readiness were identified. Relevant data elements include HCV genotype, selected medical and psychiatric comorbidities, prior receipt of treatment, and presence of advanced liver disease. While liver disease severity may be determined by invasive means, such as liver biopsy, the dashboard offers a noninvasive assessment using laboratory values (eg, calculated Fibrosis 4 score, Model for End Stage Liver Disease score).10,11
Once dashboard elements were selected, the variables were operationalized using data available in the CDW within the prescription, diagnostic, and laboratory data tables. As code was written, output was validated through chart review to ensure accuracy. Further validation was performed through comparison of the dashboard data with the clinical case registry, a registry of HCV viremic confirmed patients. Throughout dashboard development, the product was presented to end users to solicit requests for modifications. The code was refined over time to incorporate end user input.
Dashboard user interface. SSRS allows users to customize reports based on any variables defined within the data set including facility, severity of disease, HCV genotype, and prior antiviral treatment history among others. Results are displayed with summary information, including the total number of patients in the selected cohort, the number of patients who have been referred to a specialty liver clinic, and the number of patients who have been determined to achieve SVR. The end user has the option to export the results to excel for further use (eg, patient lists for telephone follow-up).
User recruitment. After piloting, the VISN 21 HCV dashboard was introduced during monthly pharmacy meetings and clinical telehealth encounters with providers. Feedback was solicited during the presentations and through postdevelopment surveys. In particular, providers requested spreadsheet-friendly formatting, additional informational fields consisting of mental health and substance abuse diagnoses, and identification of all patients with HCV regardless
of disease severity. A key element of dashboard refinement includes enhancing usability by solicitation of user feedback with subsequent tailoring of the user interface.12
Challenges
Many challenges exist in clinical dashboard development, expansion, and implementation including data integrity, workflow, and work culture. Data elements are often variable within a single facility, and this variation increases when identifying the same elements across facilities. For example, a laboratory test name (eg, “serum creatinine”) may exist with 2 to 3 different labels (eg, “creat,” “SCr,” “serum Cr”) within a single facility. As the variation increases, potential for inappropriate laboratory tests may be increased. Specialty clinic names also vary within and between facilities.
Local nomenclature for HCV clinic names may include “liver,” “infectious disease,” “hepatitis c,” or some variation, making it crucial for the dashboard developer to work closely with clinical staff to accurately matchspecialty clinic names being pulled from the data warehouse. Given the complexities of naming nomenclature within VA data, dashboard development requires a substantial investment of code customization and validation.
Ongoing dashboard maintenance is another important challenge due to the need for staff trained in SQL coding and familiarity with VA data warehouse architecture. Consequently, until the VHA dedicates resources to maintain such dashboards, only VISNs with existing technical knowledge and staffing will benefit from dashboards.
Usability, typically defined as “…effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction with which the intended users can achieve their tasks in the intended context of product use,” is an additional consideration as the HCV clinical dashboard disseminates nationally.13 Standard clinic workflow is not always conducive to the use of dashboards. VHA providers use the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) to review and document patient notes. However, accessing the HCV dashboard involves a site hosted outside of CPRS, thereby requiring the user to take several extra steps. These and other usability factors will need to be considered as the dashboard disseminates more widely.
Finally, data describing the effectiveness of clinical dashboards is very limited. VISN 21 is tracking the number of users accessing the dashboard. However, further study is needed to determine if clinical dashboards improve patient access and quality of care as well as factors to enhance usability
Conclusion
Clinical dashboards have the ability to transform each clinical provider into a population health manager who can readily identify patients most in need of care within their facility catchment area and beyond. As HCV dashboard development and implementation grows across the VHA, there is a need to pair clinical and technological advancements with greater patient outreach and shared best practices. Understanding the factors that tie improved quality of care with usability as well as investment in dashboard development and related efforts will likely keep the VHA in the forefront of chronic care delivery.
Author disclosures
The authors report no actual or potential conflicts of interest with regard to this article.
Disclaimer
The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of Federal Practitioner, Frontline Medical Communications Inc., the U.S. Government, or any of its agencies. This article may discuss unlabeled or investigational use of certain drugs. Please review complete prescribing information for specific drugs or drug combinations—including indications, contraindications, warnings, and adverse effects—before administering pharmacologic therapy to patients.
1. Dominitz JA, Boyko EJ, Koepsell TD, et al. Elevated prevalence of hepatitis C infection in users of United States veterans medical centers. Hepatology. 2005;41(1):88-96.
2. United States Department of Veterans Affairs. HCV Viremic Veterans in VHA Care in 2013 with First Fill in the Year or Ever Filled a VHA Outpatient Prescription for a HCV Antiviral Medication for the Nation, by VISN and by Station Description. http://vaww.hepatitis.va.gov/data-reports/ccr2013/RegMed-AnyFirstEverInCare-Jan14-HCVVir-HCV-2013-All.asp. Accessed October 10, 2014.
3. Rongey C, Shen H, Hamilton N, Backus LI, Asch SM, Knight S. Impact of rural residence and health system structure on quality of liver care. PloS One. 2013;8(12):e84826.
4. Beste LA, Ioannou GN. Prevalence and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs [published online ahead of print January 19, 2015]. Epidemiologic Reviews. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxu002.
5. Lawitz E, Poordad FF, Pang PS, et al. Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir fixed-dose combination with and without ribavirin in treatment-naive and previously treated patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus infection (LONESTAR): an openlabel, randomised, phase 2 trial [published correction appears in Lancet. 2014;383(9920):870]. Lancet. 2014;383(9916):515-523.
6. United States Department of Veterans Affairs. HCV Viremic Veterans in VHA Care in 2013 who had a VHA Diagnosis of Fibrosis/Cirrhosis by FIB-4 in the year for the Nation, by VISN and by Station. http://vaww.hepatitis.va.gov/data-reports/ccr2013/Cond-FIB4CurInCare-Jan14HCVVir-2013-All.asp. Accessed October 10, 2014.
7. Kanwal F, Hoang T, Kramer JR, et al. Increasing prevalence of HCC and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(4):1182-1188.e1.
8. Furukawa MF, King J, Patel V, Hsiao CJ, Adler-Milstein J, Jha AK. Despite substantial progress in EHR adoption, health information exchange and patient engagement remain low in office settings. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33(9):1672-1679.
9. Vrieze SI, Docherty A, Thuras P, et al. Best practices: The electronic medical record is an invaluable clinical tool: Let’s start using it. Psychiatric Serv. 2013;64(10):946-949.
10. Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B, et al. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. Comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology. 2007;46(1):32-36.
11. Kamath PS, Kim WR; Advanced Liver Disease Study Group. The model for endstage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology. 2007;45(3):797-805.
12. Goldberg L, Lide B, Lowry S, et al. Usability and accessibility in consumer health informatics current trends and future challenges. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40(5 suppl 2):S187-S197.
13. Schumacher RM, Lowry SZ; National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST Guide to the Processes Approach for Improving the Usability of Electronic Health Records. http://www.nist.gov/itl/hit/upload/Guide_Final_Publication_Version.pdf. Published November 29, 2010. Accessed November 24, 2014.
1. Dominitz JA, Boyko EJ, Koepsell TD, et al. Elevated prevalence of hepatitis C infection in users of United States veterans medical centers. Hepatology. 2005;41(1):88-96.
2. United States Department of Veterans Affairs. HCV Viremic Veterans in VHA Care in 2013 with First Fill in the Year or Ever Filled a VHA Outpatient Prescription for a HCV Antiviral Medication for the Nation, by VISN and by Station Description. http://vaww.hepatitis.va.gov/data-reports/ccr2013/RegMed-AnyFirstEverInCare-Jan14-HCVVir-HCV-2013-All.asp. Accessed October 10, 2014.
3. Rongey C, Shen H, Hamilton N, Backus LI, Asch SM, Knight S. Impact of rural residence and health system structure on quality of liver care. PloS One. 2013;8(12):e84826.
4. Beste LA, Ioannou GN. Prevalence and Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection in the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs [published online ahead of print January 19, 2015]. Epidemiologic Reviews. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxu002.
5. Lawitz E, Poordad FF, Pang PS, et al. Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir fixed-dose combination with and without ribavirin in treatment-naive and previously treated patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus infection (LONESTAR): an openlabel, randomised, phase 2 trial [published correction appears in Lancet. 2014;383(9920):870]. Lancet. 2014;383(9916):515-523.
6. United States Department of Veterans Affairs. HCV Viremic Veterans in VHA Care in 2013 who had a VHA Diagnosis of Fibrosis/Cirrhosis by FIB-4 in the year for the Nation, by VISN and by Station. http://vaww.hepatitis.va.gov/data-reports/ccr2013/Cond-FIB4CurInCare-Jan14HCVVir-2013-All.asp. Accessed October 10, 2014.
7. Kanwal F, Hoang T, Kramer JR, et al. Increasing prevalence of HCC and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(4):1182-1188.e1.
8. Furukawa MF, King J, Patel V, Hsiao CJ, Adler-Milstein J, Jha AK. Despite substantial progress in EHR adoption, health information exchange and patient engagement remain low in office settings. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33(9):1672-1679.
9. Vrieze SI, Docherty A, Thuras P, et al. Best practices: The electronic medical record is an invaluable clinical tool: Let’s start using it. Psychiatric Serv. 2013;64(10):946-949.
10. Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B, et al. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. Comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology. 2007;46(1):32-36.
11. Kamath PS, Kim WR; Advanced Liver Disease Study Group. The model for endstage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology. 2007;45(3):797-805.
12. Goldberg L, Lide B, Lowry S, et al. Usability and accessibility in consumer health informatics current trends and future challenges. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40(5 suppl 2):S187-S197.
13. Schumacher RM, Lowry SZ; National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST Guide to the Processes Approach for Improving the Usability of Electronic Health Records. http://www.nist.gov/itl/hit/upload/Guide_Final_Publication_Version.pdf. Published November 29, 2010. Accessed November 24, 2014.