User login
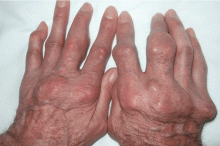
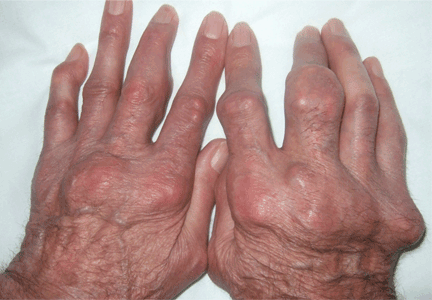
Giant nodules on the hands
Q: Which is the most likely diagnosis?
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Nodular osteoarthritis
- Tophaceous gout
- Pseudogout
- Xanthoma tuberosum
A: Tophaceous gout is the diagnosis. This patient’s serum urate level was 9 mg/dL (normal range 4.0–8.0) despite allopurinol therapy, with normal levels of lipids, urea, and creatinine. Polarized light microscopy of aspirated synovial fluid showed monosodium urate crystals, thus confirming the diagnosis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is typically polyarticular and symmetrical and spares the distal interphalangeal joints. Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules may mimic gouty tophi.
Pseudogout shares some of the features of gout. It results from deposits of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in and around the joints. The diagnosis is made by identifying the crystals on microscopy when calcinosis is seen on x-ray. Tophaceous nodules almost never occur.
Xanthoma tuberosum is associated with hypercholesterolemia, particularly with elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Lesions occur on pressure areas such as the knees or elbows and vary in size and shape from small papules to firm, lobulated tumors. They are yellow or orange, often with an erythematous halo. They are not associated with chronic proliferative arthritis.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF GOUT
Gout is a common metabolic disease characterized by an intermittent course of acute inflammatory arthritis initially affecting one or a few joints. Almost all patients have hyperuricemia, but serum urate levels can be normal or low during an acute attack. On the other hand, many hyperuricemic patients never have a clinical event.
If the hyperuricemia is untreated, some patients develop chronic polyarthritis and nephrolithiasis.1 Inadequate treatment of hyperuricemia may result in chronic tophaceous gout. Although tophaceous gout usually is a sign of long-standing hyperuricemia, tophi can in rare cases be a first symptom of the disorder.2
Even though our patient had been on allopurinol therapy, the dose was not high enough to achieve a serum urate level significantly below the saturation point of urate (about 6.7 mg/dL).
- Logan JA, Morrison E, McGill PE. Serum uric acid in acute gout. Ann Rheum Dis 1997; 56:696–697.
- Thissen CA, Frank J, Lucker GP. Tophi as first clinical sign of gout. Int J Dermatol 2008; 47( suppl 1):49–51.
Q: Which is the most likely diagnosis?
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Nodular osteoarthritis
- Tophaceous gout
- Pseudogout
- Xanthoma tuberosum
A: Tophaceous gout is the diagnosis. This patient’s serum urate level was 9 mg/dL (normal range 4.0–8.0) despite allopurinol therapy, with normal levels of lipids, urea, and creatinine. Polarized light microscopy of aspirated synovial fluid showed monosodium urate crystals, thus confirming the diagnosis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is typically polyarticular and symmetrical and spares the distal interphalangeal joints. Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules may mimic gouty tophi.
Pseudogout shares some of the features of gout. It results from deposits of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in and around the joints. The diagnosis is made by identifying the crystals on microscopy when calcinosis is seen on x-ray. Tophaceous nodules almost never occur.
Xanthoma tuberosum is associated with hypercholesterolemia, particularly with elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Lesions occur on pressure areas such as the knees or elbows and vary in size and shape from small papules to firm, lobulated tumors. They are yellow or orange, often with an erythematous halo. They are not associated with chronic proliferative arthritis.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF GOUT
Gout is a common metabolic disease characterized by an intermittent course of acute inflammatory arthritis initially affecting one or a few joints. Almost all patients have hyperuricemia, but serum urate levels can be normal or low during an acute attack. On the other hand, many hyperuricemic patients never have a clinical event.
If the hyperuricemia is untreated, some patients develop chronic polyarthritis and nephrolithiasis.1 Inadequate treatment of hyperuricemia may result in chronic tophaceous gout. Although tophaceous gout usually is a sign of long-standing hyperuricemia, tophi can in rare cases be a first symptom of the disorder.2
Even though our patient had been on allopurinol therapy, the dose was not high enough to achieve a serum urate level significantly below the saturation point of urate (about 6.7 mg/dL).
Q: Which is the most likely diagnosis?
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Nodular osteoarthritis
- Tophaceous gout
- Pseudogout
- Xanthoma tuberosum
A: Tophaceous gout is the diagnosis. This patient’s serum urate level was 9 mg/dL (normal range 4.0–8.0) despite allopurinol therapy, with normal levels of lipids, urea, and creatinine. Polarized light microscopy of aspirated synovial fluid showed monosodium urate crystals, thus confirming the diagnosis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is typically polyarticular and symmetrical and spares the distal interphalangeal joints. Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules may mimic gouty tophi.
Pseudogout shares some of the features of gout. It results from deposits of calcium pyrophosphate crystals in and around the joints. The diagnosis is made by identifying the crystals on microscopy when calcinosis is seen on x-ray. Tophaceous nodules almost never occur.
Xanthoma tuberosum is associated with hypercholesterolemia, particularly with elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Lesions occur on pressure areas such as the knees or elbows and vary in size and shape from small papules to firm, lobulated tumors. They are yellow or orange, often with an erythematous halo. They are not associated with chronic proliferative arthritis.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF GOUT
Gout is a common metabolic disease characterized by an intermittent course of acute inflammatory arthritis initially affecting one or a few joints. Almost all patients have hyperuricemia, but serum urate levels can be normal or low during an acute attack. On the other hand, many hyperuricemic patients never have a clinical event.
If the hyperuricemia is untreated, some patients develop chronic polyarthritis and nephrolithiasis.1 Inadequate treatment of hyperuricemia may result in chronic tophaceous gout. Although tophaceous gout usually is a sign of long-standing hyperuricemia, tophi can in rare cases be a first symptom of the disorder.2
Even though our patient had been on allopurinol therapy, the dose was not high enough to achieve a serum urate level significantly below the saturation point of urate (about 6.7 mg/dL).
- Logan JA, Morrison E, McGill PE. Serum uric acid in acute gout. Ann Rheum Dis 1997; 56:696–697.
- Thissen CA, Frank J, Lucker GP. Tophi as first clinical sign of gout. Int J Dermatol 2008; 47( suppl 1):49–51.
- Logan JA, Morrison E, McGill PE. Serum uric acid in acute gout. Ann Rheum Dis 1997; 56:696–697.
- Thissen CA, Frank J, Lucker GP. Tophi as first clinical sign of gout. Int J Dermatol 2008; 47( suppl 1):49–51.
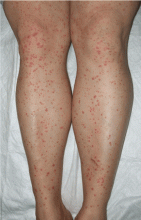
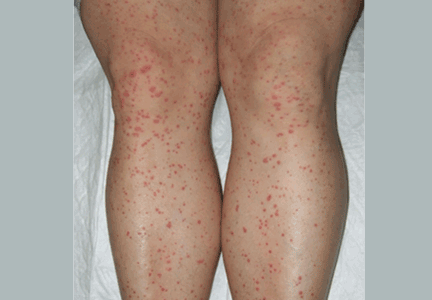
Palpable purpura
Q: Which is the most likely diagnosis?
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy)
- Kaposi sarcoma not related to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura
- Polyarteritis nodosa
A: The correct answer is Henoch-Schönlein purpura.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is an autoimmune disease caused by specific antibodies against platelet-membrane glycoproteins. It is characterized by thrombocytopenia not explainable by contact with toxic substances or by other causes. Along with nonpalpable purpura, other common signs are epistaxis, gingival bleeding, menorrhagia, and retinal hemorrhage.
Scurvy is an uncommon deficiency of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). The elderly and alcoholics are at higher risk, as they do not take in enough vitamin C in the diet. Patients usually show perifollicular hemorrhages of the skin and mucous membranes, typically petechial hemorrhage or ecchymosis of the gums around the upper incisors. Other cutaneous signs are follicular hyperkeratosis on the forearms, small corkscrew hairs, and sicca syndrome, which is more common in adults.
Non-HIV Kaposi sarcoma usually affects elderly patients, with pink, red, or brown papules or nodules on the legs and, less commonly, on the head and neck. Histopathologic examination shows newly formed irregular blood vessels with an inflammatory infiltrate of plasma cells and lymphocytes; immunohistochemical human herpes virus staining is usually positive.
Polyarteritis nodosa is a systemic vasculitis that affects medium or small arteries with necrotizing inflammation; renal glomeruli and arterioles, capillaries, and venules are unaffected. Skin manifestations include palpable purpura, livedo reticularis, ulcers, and distal gangrene. The condition also usually affects the kidneys, the heart, and the musculoskeletal and nervous systems.
A SYSTEMIC VASCULITIS
Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a systemic vasculitis affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and joints. Palpable purpura and joint pain are the most common and consistent presenting symptoms. The kidneys are affected in about one-third of children and in 60% of adults, and this is the major factor determining the long-term outcome.1
In our patient, laboratory testing that included a complete blood cell count, biochemical testing (including IgA levels), urinary sediment, and coagulation studies showed no abnormalities except elevations of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the concentration of C-reactive protein (an acute-phase reactant). These can be normal in some patients. Renal involvement was also not present.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis relies on clinical manifestations. Because Henoch-Schönlein purpura is less common in adults, biopsy plays a more important role in establishing the diagnosis in this age group, and it does this by demonstrating leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a predominance of IgA deposition under immunofluorescence. Recent studies in children showed that an elevated IgA concentration along with reduced IgM levels was associated with a higher rate of severe complications.2 However, depending on the age of the biopsied lesion, IgA may not be detected.
TREATMENT DIRECTED AT SYMPTOMS
Our patient received oral corticosteroids 0.5 mg/kg per day for 20 days, and the lesions resolved by 4 weeks.
Management of Henoch-Schönlein purpura is mainly directed at the symptoms, with oral hydration and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For severe cases, a short course of corticosteroids (0.5–1 mg/kg) may be used.
Although no controlled clinical trial has proven that Henoch-Schönlein purpura responds to corticosteroids, colchicine, or other drugs, corticosteroids are used most often, especially in patients with renal disease. Patients with severe renal insufficiency, abdominal pain, joint involvement, or bleeding should be hospitalized. Plasmapheresis3 has been used in severe cases.
HENOCH-SCHÖNLEIN PURPURA AND MALIGNANCY
During a follow-up evaluation 1 month later, our patient was diagnosed with adenocarcinoma of the breast. This highlights the value of a workup for cancer in adults with cutaneous vasculitis.
Cutaneous vasculitis can represent a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with a malignant tumor. The pathophysiology of this association is unclear, but one proposed mechanism is the exaggerated production of antibodies that react against tumor neoantigens, leading to the formation of immune complexes, or that occasionally recognize endothelial cells because of similarities with tumor antigens. Another theory is that abnormally high levels of inflammatory cytokines are produced by neoplastic cells or in response to decreased immune complex clearance.
Yet another theory is that hyperviscosity of the blood, seen in some cancers, increases the contact time for deposition of immune complexes and causes endothelial damage. Drugs used to treat cancer have also been reported to produce Henoch-Schönlein purpura.4
Although hematologic malignancy is three to five times more common than solid tumors in patients with small-vessel vasculitis, the disease has been associated with solid tumors of the liver, skin, colon, and breast in adults over age 40.5 An evaluation for neoplasm is therefore reasonable in adults with Henoch-Schönlein purpura, as is an evaluation for tumor recurrence or metastasis if the patient has been previously treated for a malignant tumor.
- Rieu P, Noël LH. Henoch-Schönlein nephritis in children and adults. Morphological features and clinicopathological correlations. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1999; 150:151–159.
- Fretzayas A, Sionti I, Moustaki M, Nicolaidou P. Clinical impact of altered immunoglobulin levels in Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Pediatr Int 2009; 51:381–384.
- Donghi D, Schanz U, Sahrbacher U, et al. Life-threatening or organimpairing Henoch-Schönlein purpura: plasmapheresis may save lives and limit organ damage. Dermatology 2009; 219:167–170.
- Mitsui H, Shibagaki N, Kawamura T, Matsue H, Shimada S. A clinical study of Henoch-Schönlein purpura associated with malignancy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009; 23:394–401.
- Maestri A, Malacarne P, Santini A. Henoch-Schönlein syndrome associated with breast cancer. A case report. Angiology 1995; 46:625–627.
Q: Which is the most likely diagnosis?
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy)
- Kaposi sarcoma not related to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura
- Polyarteritis nodosa
A: The correct answer is Henoch-Schönlein purpura.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is an autoimmune disease caused by specific antibodies against platelet-membrane glycoproteins. It is characterized by thrombocytopenia not explainable by contact with toxic substances or by other causes. Along with nonpalpable purpura, other common signs are epistaxis, gingival bleeding, menorrhagia, and retinal hemorrhage.
Scurvy is an uncommon deficiency of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). The elderly and alcoholics are at higher risk, as they do not take in enough vitamin C in the diet. Patients usually show perifollicular hemorrhages of the skin and mucous membranes, typically petechial hemorrhage or ecchymosis of the gums around the upper incisors. Other cutaneous signs are follicular hyperkeratosis on the forearms, small corkscrew hairs, and sicca syndrome, which is more common in adults.
Non-HIV Kaposi sarcoma usually affects elderly patients, with pink, red, or brown papules or nodules on the legs and, less commonly, on the head and neck. Histopathologic examination shows newly formed irregular blood vessels with an inflammatory infiltrate of plasma cells and lymphocytes; immunohistochemical human herpes virus staining is usually positive.
Polyarteritis nodosa is a systemic vasculitis that affects medium or small arteries with necrotizing inflammation; renal glomeruli and arterioles, capillaries, and venules are unaffected. Skin manifestations include palpable purpura, livedo reticularis, ulcers, and distal gangrene. The condition also usually affects the kidneys, the heart, and the musculoskeletal and nervous systems.
A SYSTEMIC VASCULITIS
Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a systemic vasculitis affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and joints. Palpable purpura and joint pain are the most common and consistent presenting symptoms. The kidneys are affected in about one-third of children and in 60% of adults, and this is the major factor determining the long-term outcome.1
In our patient, laboratory testing that included a complete blood cell count, biochemical testing (including IgA levels), urinary sediment, and coagulation studies showed no abnormalities except elevations of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the concentration of C-reactive protein (an acute-phase reactant). These can be normal in some patients. Renal involvement was also not present.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis relies on clinical manifestations. Because Henoch-Schönlein purpura is less common in adults, biopsy plays a more important role in establishing the diagnosis in this age group, and it does this by demonstrating leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a predominance of IgA deposition under immunofluorescence. Recent studies in children showed that an elevated IgA concentration along with reduced IgM levels was associated with a higher rate of severe complications.2 However, depending on the age of the biopsied lesion, IgA may not be detected.
TREATMENT DIRECTED AT SYMPTOMS
Our patient received oral corticosteroids 0.5 mg/kg per day for 20 days, and the lesions resolved by 4 weeks.
Management of Henoch-Schönlein purpura is mainly directed at the symptoms, with oral hydration and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For severe cases, a short course of corticosteroids (0.5–1 mg/kg) may be used.
Although no controlled clinical trial has proven that Henoch-Schönlein purpura responds to corticosteroids, colchicine, or other drugs, corticosteroids are used most often, especially in patients with renal disease. Patients with severe renal insufficiency, abdominal pain, joint involvement, or bleeding should be hospitalized. Plasmapheresis3 has been used in severe cases.
HENOCH-SCHÖNLEIN PURPURA AND MALIGNANCY
During a follow-up evaluation 1 month later, our patient was diagnosed with adenocarcinoma of the breast. This highlights the value of a workup for cancer in adults with cutaneous vasculitis.
Cutaneous vasculitis can represent a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with a malignant tumor. The pathophysiology of this association is unclear, but one proposed mechanism is the exaggerated production of antibodies that react against tumor neoantigens, leading to the formation of immune complexes, or that occasionally recognize endothelial cells because of similarities with tumor antigens. Another theory is that abnormally high levels of inflammatory cytokines are produced by neoplastic cells or in response to decreased immune complex clearance.
Yet another theory is that hyperviscosity of the blood, seen in some cancers, increases the contact time for deposition of immune complexes and causes endothelial damage. Drugs used to treat cancer have also been reported to produce Henoch-Schönlein purpura.4
Although hematologic malignancy is three to five times more common than solid tumors in patients with small-vessel vasculitis, the disease has been associated with solid tumors of the liver, skin, colon, and breast in adults over age 40.5 An evaluation for neoplasm is therefore reasonable in adults with Henoch-Schönlein purpura, as is an evaluation for tumor recurrence or metastasis if the patient has been previously treated for a malignant tumor.
Q: Which is the most likely diagnosis?
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy)
- Kaposi sarcoma not related to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura
- Polyarteritis nodosa
A: The correct answer is Henoch-Schönlein purpura.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is an autoimmune disease caused by specific antibodies against platelet-membrane glycoproteins. It is characterized by thrombocytopenia not explainable by contact with toxic substances or by other causes. Along with nonpalpable purpura, other common signs are epistaxis, gingival bleeding, menorrhagia, and retinal hemorrhage.
Scurvy is an uncommon deficiency of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). The elderly and alcoholics are at higher risk, as they do not take in enough vitamin C in the diet. Patients usually show perifollicular hemorrhages of the skin and mucous membranes, typically petechial hemorrhage or ecchymosis of the gums around the upper incisors. Other cutaneous signs are follicular hyperkeratosis on the forearms, small corkscrew hairs, and sicca syndrome, which is more common in adults.
Non-HIV Kaposi sarcoma usually affects elderly patients, with pink, red, or brown papules or nodules on the legs and, less commonly, on the head and neck. Histopathologic examination shows newly formed irregular blood vessels with an inflammatory infiltrate of plasma cells and lymphocytes; immunohistochemical human herpes virus staining is usually positive.
Polyarteritis nodosa is a systemic vasculitis that affects medium or small arteries with necrotizing inflammation; renal glomeruli and arterioles, capillaries, and venules are unaffected. Skin manifestations include palpable purpura, livedo reticularis, ulcers, and distal gangrene. The condition also usually affects the kidneys, the heart, and the musculoskeletal and nervous systems.
A SYSTEMIC VASCULITIS
Henoch-Schönlein purpura is a systemic vasculitis affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and joints. Palpable purpura and joint pain are the most common and consistent presenting symptoms. The kidneys are affected in about one-third of children and in 60% of adults, and this is the major factor determining the long-term outcome.1
In our patient, laboratory testing that included a complete blood cell count, biochemical testing (including IgA levels), urinary sediment, and coagulation studies showed no abnormalities except elevations of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the concentration of C-reactive protein (an acute-phase reactant). These can be normal in some patients. Renal involvement was also not present.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis relies on clinical manifestations. Because Henoch-Schönlein purpura is less common in adults, biopsy plays a more important role in establishing the diagnosis in this age group, and it does this by demonstrating leukocytoclastic vasculitis with a predominance of IgA deposition under immunofluorescence. Recent studies in children showed that an elevated IgA concentration along with reduced IgM levels was associated with a higher rate of severe complications.2 However, depending on the age of the biopsied lesion, IgA may not be detected.
TREATMENT DIRECTED AT SYMPTOMS
Our patient received oral corticosteroids 0.5 mg/kg per day for 20 days, and the lesions resolved by 4 weeks.
Management of Henoch-Schönlein purpura is mainly directed at the symptoms, with oral hydration and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For severe cases, a short course of corticosteroids (0.5–1 mg/kg) may be used.
Although no controlled clinical trial has proven that Henoch-Schönlein purpura responds to corticosteroids, colchicine, or other drugs, corticosteroids are used most often, especially in patients with renal disease. Patients with severe renal insufficiency, abdominal pain, joint involvement, or bleeding should be hospitalized. Plasmapheresis3 has been used in severe cases.
HENOCH-SCHÖNLEIN PURPURA AND MALIGNANCY
During a follow-up evaluation 1 month later, our patient was diagnosed with adenocarcinoma of the breast. This highlights the value of a workup for cancer in adults with cutaneous vasculitis.
Cutaneous vasculitis can represent a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with a malignant tumor. The pathophysiology of this association is unclear, but one proposed mechanism is the exaggerated production of antibodies that react against tumor neoantigens, leading to the formation of immune complexes, or that occasionally recognize endothelial cells because of similarities with tumor antigens. Another theory is that abnormally high levels of inflammatory cytokines are produced by neoplastic cells or in response to decreased immune complex clearance.
Yet another theory is that hyperviscosity of the blood, seen in some cancers, increases the contact time for deposition of immune complexes and causes endothelial damage. Drugs used to treat cancer have also been reported to produce Henoch-Schönlein purpura.4
Although hematologic malignancy is three to five times more common than solid tumors in patients with small-vessel vasculitis, the disease has been associated with solid tumors of the liver, skin, colon, and breast in adults over age 40.5 An evaluation for neoplasm is therefore reasonable in adults with Henoch-Schönlein purpura, as is an evaluation for tumor recurrence or metastasis if the patient has been previously treated for a malignant tumor.
- Rieu P, Noël LH. Henoch-Schönlein nephritis in children and adults. Morphological features and clinicopathological correlations. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1999; 150:151–159.
- Fretzayas A, Sionti I, Moustaki M, Nicolaidou P. Clinical impact of altered immunoglobulin levels in Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Pediatr Int 2009; 51:381–384.
- Donghi D, Schanz U, Sahrbacher U, et al. Life-threatening or organimpairing Henoch-Schönlein purpura: plasmapheresis may save lives and limit organ damage. Dermatology 2009; 219:167–170.
- Mitsui H, Shibagaki N, Kawamura T, Matsue H, Shimada S. A clinical study of Henoch-Schönlein purpura associated with malignancy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009; 23:394–401.
- Maestri A, Malacarne P, Santini A. Henoch-Schönlein syndrome associated with breast cancer. A case report. Angiology 1995; 46:625–627.
- Rieu P, Noël LH. Henoch-Schönlein nephritis in children and adults. Morphological features and clinicopathological correlations. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1999; 150:151–159.
- Fretzayas A, Sionti I, Moustaki M, Nicolaidou P. Clinical impact of altered immunoglobulin levels in Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Pediatr Int 2009; 51:381–384.
- Donghi D, Schanz U, Sahrbacher U, et al. Life-threatening or organimpairing Henoch-Schönlein purpura: plasmapheresis may save lives and limit organ damage. Dermatology 2009; 219:167–170.
- Mitsui H, Shibagaki N, Kawamura T, Matsue H, Shimada S. A clinical study of Henoch-Schönlein purpura associated with malignancy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2009; 23:394–401.
- Maestri A, Malacarne P, Santini A. Henoch-Schönlein syndrome associated with breast cancer. A case report. Angiology 1995; 46:625–627.