User login
Top DEI Topics to Incorporate Into Dermatology Residency Training: An Electronic Delphi Consensus Study
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs seek to improve dermatologic education and clinical care for an increasingly diverse patient population as well as to recruit and sustain a physician workforce that reflects the diversity of the patients they serve.1,2 In dermatology, only 4.2% and 3.0% of practicing dermatologists self-identify as being of Hispanic and African American ethnicity, respectively, compared with 18.5% and 13.4% of the general population, respectively.3 Creating an educational system that works to meet the goals of DEI is essential to improve health outcomes and address disparities. The lack of robust DEI-related curricula during residency training may limit the ability of practicing dermatologists to provide comprehensive and culturally sensitive care. It has been shown that racial concordance between patients and physicians has a positive impact on patient satisfaction by fostering a trusting patient-physician relationship.4
It is the responsibility of all dermatologists to create an environment where patients from any background can feel comfortable, which can be cultivated by establishing patient-centered communication and cultural humility.5 These skills can be strengthened via the implementation of DEI-related curricula during residency training. Augmenting exposure of these topics during training can optimize the delivery of dermatologic care by providing residents with the tools and confidence needed to care for patients of culturally diverse backgrounds. Enhancing DEI education is crucial to not only improve the recognition and treatment of dermatologic conditions in all skin and hair types but also to minimize misconceptions, stigma, health disparities, and discrimination faced by historically marginalized communities. Creating a culture of inclusion is of paramount importance to build successful relationships with patients and colleagues of culturally diverse backgrounds.6
There are multiple efforts underway to increase DEI education across the field of dermatology, including the development of DEI task forces in professional organizations and societies that serve to expand DEI-related research, mentorship, and education. The American Academy of Dermatology has been leading efforts to create a curriculum focused on skin of color, particularly addressing inadequate educational training on how dermatologic conditions manifest in this population.7 The Skin of Color Society has similar efforts underway and is developing a speakers bureau to give leading experts a platform to lecture dermatology trainees as well as patient and community audiences on various topics in skin of color.8 These are just 2 of many professional dermatology organizations that are advocating for expanded education on DEI; however, consistently integrating DEI-related topics into dermatology residency training curricula remains a gap in pedagogy. To identify the DEI-related topics of greatest relevance to the dermatology resident curricula, we implemented a modified electronic Delphi (e-Delphi) consensus process to provide standardized recommendations.
Methods
A 2-round modified e-Delphi method was utilized (Figure). An initial list of potential curricular topics was formulated by an expert panel consisting of 5 dermatologists from the Association of Professors of Dermatology DEI subcommittee and the American Academy of Dermatology Diversity Task Force (A.M.A., S.B., R.V., S.D.W., J.I.S.). Initial topics were selected via several meetings among the panel members to discuss existing DEI concerns and issues that were deemed relevant due to education gaps in residency training. The list of topics was further expanded with recommendations obtained via an email sent to dermatology program directors on the Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve, which solicited voluntary participation of academic dermatologists, including program directors and dermatology residents.
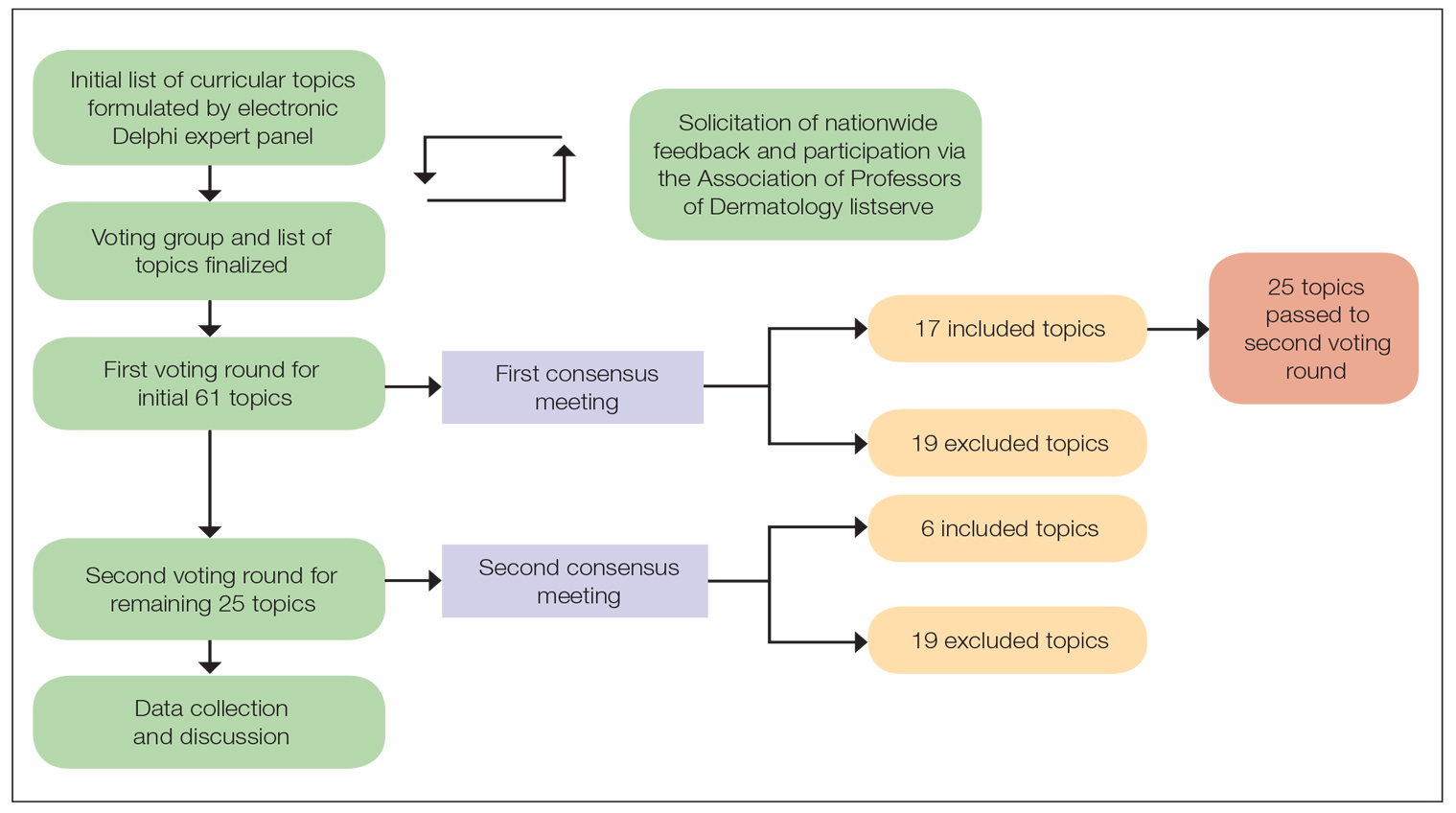
There were 2 voting rounds, with each round consisting of questions scored on a Likert scale ranging from 1 to 5 (1=not essential, 2=probably not essential, 3=neutral, 4=probably essential, 5=definitely essential). The inclusion criteria to classify a topic as necessary for integration into the dermatology residency curriculum included 95% (18/19) or more of respondents rating the topic as probably essential or definitely essential; if more than 90% (17/19) of respondents rated the topic as probably essential or definitely essential and less than 10% (2/19) rated it as not essential or probably not essential, the topic was still included as part of the suggested curriculum. Topics that received ratings of probably essential or definitely essential by less than 80% (15/19) of respondents were removed from consideration. The topics that did not meet inclusion or exclusion criteria during the first round of voting were refined by the e-Delphi steering committee (V.S.E-C. and F-A.R.) based on open-ended feedback from the voting group provided at the end of the survey and subsequently passed to the second round of voting.
Results
Participants—A total of 19 respondents participated in both voting rounds, the majority (80% [15/19]) of whom were program directors or dermatologists affiliated with academia or development of DEI education; the remaining 20% [4/19]) were dermatology residents.
Open-Ended Feedback—Voting group members were able to provide open-ended feedback for each of the sets of topics after the survey, which the steering committee utilized to modify the topics as needed for the final voting round. For example, “structural racism/discrimination” was originally mentioned as a topic, but several participants suggested including specific types of racism; therefore, the wording was changed to “racism: types, definitions” to encompass broader definitions and types of racism.
Survey Results—Two genres of topics were surveyed in each voting round: clinical and nonclinical. Participants voted on a total of 61 topics, with 23 ultimately selected in the final list of consensus curricular topics. Of those, 9 were clinical and 14 nonclinical. All topics deemed necessary for inclusion in residency curricula are presented in eTables 1 and 2.
During the first round of voting, the e-Delphi panel reached a consensus to include the following 17 topics as essential to dermatology residency training (along with the percentage of voters who classified them as probably essential or definitely essential): how to mitigate bias in clinical and workplace settings (100% [40/40]); social determinants of health-related disparities in dermatology (100% [40/40]); hairstyling practices across different hair textures (100% [40/40]); definitions and examples of microaggressions (97.50% [39/40]); definition, background, and types of bias (97.50% [39/40]); manifestations of bias in the clinical setting (97.44% [38/39]); racial and ethnic disparities in dermatology (97.44% [38/39]); keloids (97.37% [37/38]); differences in dermoscopic presentations in skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); skin cancer in patients with skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); disparities due to bias (95.00% [38/40]); how to apply cultural humility and safety to patients of different cultural backgrounds (94.87% [37/40]); best practices in providing care to patients with limited English proficiency (94.87% [37/40]); hair loss in patients with textured hair (94.74% [36/38]); pseudofolliculitis barbae and acne keloidalis nuchae (94.60% [35/37]); disparities regarding people experiencing homelessness (92.31% [36/39]); and definitions and types of racism and other forms of discrimination (92.31% [36/39]). eTable 1 provides a list of suggested resources to incorporate these topics into the educational components of residency curricula. The resources provided were not part of the voting process, and they were not considered in the consensus analysis; they are included here as suggested educational catalysts.
During the second round of voting, 25 topics were evaluated. Of those, the following 6 topics were proposed to be included as essential in residency training: differences in prevalence and presentation of common inflammatory disorders (100% [29/29]); manifestations of bias in the learning environment (96.55%); antiracist action and how to decrease the effects of structural racism in clinical and educational settings (96.55% [28/29]); diversity of images in dermatology education (96.55% [28/29]); pigmentary disorders and their psychological effects (96.55% [28/29]); and LGBTQ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer) dermatologic health care (96.55% [28/29]). eTable 2 includes these topics as well as suggested resources to help incorporate them into training.
Comment
This study utilized a modified e-Delphi technique to identify relevant clinical and nonclinical DEI topics that should be incorporated into dermatology residency curricula. The panel members reached a consensus for 9 clinical DEI-related topics. The respondents agreed that the topics related to skin and hair conditions in patients with skin of color as well as textured hair were crucial to residency education. Skin cancer, hair loss, pseudofolliculitis barbae, acne keloidalis nuchae, keloids, pigmentary disorders, and their varying presentations in patients with skin of color were among the recommended topics. The panel also recommended educating residents on the variable visual presentations of inflammatory conditions in skin of color. Addressing the needs of diverse patients—for example, those belonging to the LGBTQ community—also was deemed important for inclusion.
The remaining 14 chosen topics were nonclinical items addressing concepts such as bias and health care disparities as well as cultural humility and safety.9 Cultural humility and safety focus on developing cultural awareness by creating a safe setting for patients rather than encouraging power relationships between them and their physicians. Various topics related to racism also were recommended to be included in residency curricula, including education on implementation of antiracist action in the workplace.
Many of the nonclinical topics are intertwined; for instance, learning about health care disparities in patients with limited English proficiency allows for improved best practices in delivering care to patients from this population. The first step in overcoming bias and subsequent disparities is acknowledging how the perpetuation of bias leads to disparities after being taught tools to recognize it.
Our group’s guidance on DEI topics should help dermatology residency program leaders as they design and refine program curricula. There are multiple avenues for incorporating education on these topics, including lectures, interactive workshops, role-playing sessions, book or journal clubs, and discussion circles. Many of these topics/programs may already be included in programs’ didactic curricula, which would minimize the burden of finding space to educate on these topics. Institutional cultural change is key to ensuring truly diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplaces. Educating tomorrow’s dermatologists on these topics is a first step toward achieving that cultural change.
Limitations—A limitation of this e-Delphi survey is that only a selection of experts in this field was included. Additionally, we were concerned that the Likert scale format and the bar we set for inclusion and exclusion may have failed to adequately capture participants’ nuanced opinions. As such, participants were able to provide open-ended feedback, and suggestions for alternate wording or other changes were considered by the steering committee. Finally, inclusion recommendations identified in this survey were developed specifically for US dermatology residents.
Conclusion
In this e-Delphi consensus assessment of DEI-related topics, we recommend the inclusion of 23 topics into dermatology residency program curricula to improve medical training and the patient-physician relationship as well as to create better health outcomes. We also provide specific sample resource recommendations in eTables 1 and 2 to facilitate inclusion of these topics into residency curricula across the country.
- US Census Bureau projections show a slower growing, older, more diverse nation a half century from now. News release. US Census Bureau. December 12, 2012. Accessed August 14, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/population/cb12243.html#:~:text=12%2C%202012,U.S.%20Census%20Bureau%20Projections%20Show%20a%20Slower%20Growing%2C%20Older%2C%20More,by%20the%20U.S.%20Census%20Bureau
- Lopez S, Lourido JO, Lim HW, et al. The call to action to increase racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a retrospective, cross-sectional study to monitor progress. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;86:E121-E123. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.10.011
- El-Kashlan N, Alexis A. Disparities in dermatology: a reflection. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:27-29.
- Laveist TA, Nuru-Jeter A. Is doctor-patient race concordance associated with greater satisfaction with care? J Health Soc Behav. 2002;43:296-306.
- Street RL Jr, O’Malley KJ, Cooper LA, et al. Understanding concordance in patient-physician relationships: personal and ethnic dimensions of shared identity. Ann Fam Med. 2008;6:198-205. doi:10.1370/afm.821
- Dadrass F, Bowers S, Shinkai K, et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion in dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:257-263. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.10.006
- Diversity and the Academy. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.aad.org/member/career/diversity
- SOCS speaks. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/news-media/socs-speaks
- Solchanyk D, Ekeh O, Saffran L, et al. Integrating cultural humility into the medical education curriculum: strategies for educators. Teach Learn Med. 2021;33:554-560. doi:10.1080/10401334.2021.1877711
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs seek to improve dermatologic education and clinical care for an increasingly diverse patient population as well as to recruit and sustain a physician workforce that reflects the diversity of the patients they serve.1,2 In dermatology, only 4.2% and 3.0% of practicing dermatologists self-identify as being of Hispanic and African American ethnicity, respectively, compared with 18.5% and 13.4% of the general population, respectively.3 Creating an educational system that works to meet the goals of DEI is essential to improve health outcomes and address disparities. The lack of robust DEI-related curricula during residency training may limit the ability of practicing dermatologists to provide comprehensive and culturally sensitive care. It has been shown that racial concordance between patients and physicians has a positive impact on patient satisfaction by fostering a trusting patient-physician relationship.4
It is the responsibility of all dermatologists to create an environment where patients from any background can feel comfortable, which can be cultivated by establishing patient-centered communication and cultural humility.5 These skills can be strengthened via the implementation of DEI-related curricula during residency training. Augmenting exposure of these topics during training can optimize the delivery of dermatologic care by providing residents with the tools and confidence needed to care for patients of culturally diverse backgrounds. Enhancing DEI education is crucial to not only improve the recognition and treatment of dermatologic conditions in all skin and hair types but also to minimize misconceptions, stigma, health disparities, and discrimination faced by historically marginalized communities. Creating a culture of inclusion is of paramount importance to build successful relationships with patients and colleagues of culturally diverse backgrounds.6
There are multiple efforts underway to increase DEI education across the field of dermatology, including the development of DEI task forces in professional organizations and societies that serve to expand DEI-related research, mentorship, and education. The American Academy of Dermatology has been leading efforts to create a curriculum focused on skin of color, particularly addressing inadequate educational training on how dermatologic conditions manifest in this population.7 The Skin of Color Society has similar efforts underway and is developing a speakers bureau to give leading experts a platform to lecture dermatology trainees as well as patient and community audiences on various topics in skin of color.8 These are just 2 of many professional dermatology organizations that are advocating for expanded education on DEI; however, consistently integrating DEI-related topics into dermatology residency training curricula remains a gap in pedagogy. To identify the DEI-related topics of greatest relevance to the dermatology resident curricula, we implemented a modified electronic Delphi (e-Delphi) consensus process to provide standardized recommendations.
Methods
A 2-round modified e-Delphi method was utilized (Figure). An initial list of potential curricular topics was formulated by an expert panel consisting of 5 dermatologists from the Association of Professors of Dermatology DEI subcommittee and the American Academy of Dermatology Diversity Task Force (A.M.A., S.B., R.V., S.D.W., J.I.S.). Initial topics were selected via several meetings among the panel members to discuss existing DEI concerns and issues that were deemed relevant due to education gaps in residency training. The list of topics was further expanded with recommendations obtained via an email sent to dermatology program directors on the Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve, which solicited voluntary participation of academic dermatologists, including program directors and dermatology residents.

There were 2 voting rounds, with each round consisting of questions scored on a Likert scale ranging from 1 to 5 (1=not essential, 2=probably not essential, 3=neutral, 4=probably essential, 5=definitely essential). The inclusion criteria to classify a topic as necessary for integration into the dermatology residency curriculum included 95% (18/19) or more of respondents rating the topic as probably essential or definitely essential; if more than 90% (17/19) of respondents rated the topic as probably essential or definitely essential and less than 10% (2/19) rated it as not essential or probably not essential, the topic was still included as part of the suggested curriculum. Topics that received ratings of probably essential or definitely essential by less than 80% (15/19) of respondents were removed from consideration. The topics that did not meet inclusion or exclusion criteria during the first round of voting were refined by the e-Delphi steering committee (V.S.E-C. and F-A.R.) based on open-ended feedback from the voting group provided at the end of the survey and subsequently passed to the second round of voting.
Results
Participants—A total of 19 respondents participated in both voting rounds, the majority (80% [15/19]) of whom were program directors or dermatologists affiliated with academia or development of DEI education; the remaining 20% [4/19]) were dermatology residents.
Open-Ended Feedback—Voting group members were able to provide open-ended feedback for each of the sets of topics after the survey, which the steering committee utilized to modify the topics as needed for the final voting round. For example, “structural racism/discrimination” was originally mentioned as a topic, but several participants suggested including specific types of racism; therefore, the wording was changed to “racism: types, definitions” to encompass broader definitions and types of racism.
Survey Results—Two genres of topics were surveyed in each voting round: clinical and nonclinical. Participants voted on a total of 61 topics, with 23 ultimately selected in the final list of consensus curricular topics. Of those, 9 were clinical and 14 nonclinical. All topics deemed necessary for inclusion in residency curricula are presented in eTables 1 and 2.
During the first round of voting, the e-Delphi panel reached a consensus to include the following 17 topics as essential to dermatology residency training (along with the percentage of voters who classified them as probably essential or definitely essential): how to mitigate bias in clinical and workplace settings (100% [40/40]); social determinants of health-related disparities in dermatology (100% [40/40]); hairstyling practices across different hair textures (100% [40/40]); definitions and examples of microaggressions (97.50% [39/40]); definition, background, and types of bias (97.50% [39/40]); manifestations of bias in the clinical setting (97.44% [38/39]); racial and ethnic disparities in dermatology (97.44% [38/39]); keloids (97.37% [37/38]); differences in dermoscopic presentations in skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); skin cancer in patients with skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); disparities due to bias (95.00% [38/40]); how to apply cultural humility and safety to patients of different cultural backgrounds (94.87% [37/40]); best practices in providing care to patients with limited English proficiency (94.87% [37/40]); hair loss in patients with textured hair (94.74% [36/38]); pseudofolliculitis barbae and acne keloidalis nuchae (94.60% [35/37]); disparities regarding people experiencing homelessness (92.31% [36/39]); and definitions and types of racism and other forms of discrimination (92.31% [36/39]). eTable 1 provides a list of suggested resources to incorporate these topics into the educational components of residency curricula. The resources provided were not part of the voting process, and they were not considered in the consensus analysis; they are included here as suggested educational catalysts.
During the second round of voting, 25 topics were evaluated. Of those, the following 6 topics were proposed to be included as essential in residency training: differences in prevalence and presentation of common inflammatory disorders (100% [29/29]); manifestations of bias in the learning environment (96.55%); antiracist action and how to decrease the effects of structural racism in clinical and educational settings (96.55% [28/29]); diversity of images in dermatology education (96.55% [28/29]); pigmentary disorders and their psychological effects (96.55% [28/29]); and LGBTQ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer) dermatologic health care (96.55% [28/29]). eTable 2 includes these topics as well as suggested resources to help incorporate them into training.
Comment
This study utilized a modified e-Delphi technique to identify relevant clinical and nonclinical DEI topics that should be incorporated into dermatology residency curricula. The panel members reached a consensus for 9 clinical DEI-related topics. The respondents agreed that the topics related to skin and hair conditions in patients with skin of color as well as textured hair were crucial to residency education. Skin cancer, hair loss, pseudofolliculitis barbae, acne keloidalis nuchae, keloids, pigmentary disorders, and their varying presentations in patients with skin of color were among the recommended topics. The panel also recommended educating residents on the variable visual presentations of inflammatory conditions in skin of color. Addressing the needs of diverse patients—for example, those belonging to the LGBTQ community—also was deemed important for inclusion.
The remaining 14 chosen topics were nonclinical items addressing concepts such as bias and health care disparities as well as cultural humility and safety.9 Cultural humility and safety focus on developing cultural awareness by creating a safe setting for patients rather than encouraging power relationships between them and their physicians. Various topics related to racism also were recommended to be included in residency curricula, including education on implementation of antiracist action in the workplace.
Many of the nonclinical topics are intertwined; for instance, learning about health care disparities in patients with limited English proficiency allows for improved best practices in delivering care to patients from this population. The first step in overcoming bias and subsequent disparities is acknowledging how the perpetuation of bias leads to disparities after being taught tools to recognize it.
Our group’s guidance on DEI topics should help dermatology residency program leaders as they design and refine program curricula. There are multiple avenues for incorporating education on these topics, including lectures, interactive workshops, role-playing sessions, book or journal clubs, and discussion circles. Many of these topics/programs may already be included in programs’ didactic curricula, which would minimize the burden of finding space to educate on these topics. Institutional cultural change is key to ensuring truly diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplaces. Educating tomorrow’s dermatologists on these topics is a first step toward achieving that cultural change.
Limitations—A limitation of this e-Delphi survey is that only a selection of experts in this field was included. Additionally, we were concerned that the Likert scale format and the bar we set for inclusion and exclusion may have failed to adequately capture participants’ nuanced opinions. As such, participants were able to provide open-ended feedback, and suggestions for alternate wording or other changes were considered by the steering committee. Finally, inclusion recommendations identified in this survey were developed specifically for US dermatology residents.
Conclusion
In this e-Delphi consensus assessment of DEI-related topics, we recommend the inclusion of 23 topics into dermatology residency program curricula to improve medical training and the patient-physician relationship as well as to create better health outcomes. We also provide specific sample resource recommendations in eTables 1 and 2 to facilitate inclusion of these topics into residency curricula across the country.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs seek to improve dermatologic education and clinical care for an increasingly diverse patient population as well as to recruit and sustain a physician workforce that reflects the diversity of the patients they serve.1,2 In dermatology, only 4.2% and 3.0% of practicing dermatologists self-identify as being of Hispanic and African American ethnicity, respectively, compared with 18.5% and 13.4% of the general population, respectively.3 Creating an educational system that works to meet the goals of DEI is essential to improve health outcomes and address disparities. The lack of robust DEI-related curricula during residency training may limit the ability of practicing dermatologists to provide comprehensive and culturally sensitive care. It has been shown that racial concordance between patients and physicians has a positive impact on patient satisfaction by fostering a trusting patient-physician relationship.4
It is the responsibility of all dermatologists to create an environment where patients from any background can feel comfortable, which can be cultivated by establishing patient-centered communication and cultural humility.5 These skills can be strengthened via the implementation of DEI-related curricula during residency training. Augmenting exposure of these topics during training can optimize the delivery of dermatologic care by providing residents with the tools and confidence needed to care for patients of culturally diverse backgrounds. Enhancing DEI education is crucial to not only improve the recognition and treatment of dermatologic conditions in all skin and hair types but also to minimize misconceptions, stigma, health disparities, and discrimination faced by historically marginalized communities. Creating a culture of inclusion is of paramount importance to build successful relationships with patients and colleagues of culturally diverse backgrounds.6
There are multiple efforts underway to increase DEI education across the field of dermatology, including the development of DEI task forces in professional organizations and societies that serve to expand DEI-related research, mentorship, and education. The American Academy of Dermatology has been leading efforts to create a curriculum focused on skin of color, particularly addressing inadequate educational training on how dermatologic conditions manifest in this population.7 The Skin of Color Society has similar efforts underway and is developing a speakers bureau to give leading experts a platform to lecture dermatology trainees as well as patient and community audiences on various topics in skin of color.8 These are just 2 of many professional dermatology organizations that are advocating for expanded education on DEI; however, consistently integrating DEI-related topics into dermatology residency training curricula remains a gap in pedagogy. To identify the DEI-related topics of greatest relevance to the dermatology resident curricula, we implemented a modified electronic Delphi (e-Delphi) consensus process to provide standardized recommendations.
Methods
A 2-round modified e-Delphi method was utilized (Figure). An initial list of potential curricular topics was formulated by an expert panel consisting of 5 dermatologists from the Association of Professors of Dermatology DEI subcommittee and the American Academy of Dermatology Diversity Task Force (A.M.A., S.B., R.V., S.D.W., J.I.S.). Initial topics were selected via several meetings among the panel members to discuss existing DEI concerns and issues that were deemed relevant due to education gaps in residency training. The list of topics was further expanded with recommendations obtained via an email sent to dermatology program directors on the Association of Professors of Dermatology listserve, which solicited voluntary participation of academic dermatologists, including program directors and dermatology residents.

There were 2 voting rounds, with each round consisting of questions scored on a Likert scale ranging from 1 to 5 (1=not essential, 2=probably not essential, 3=neutral, 4=probably essential, 5=definitely essential). The inclusion criteria to classify a topic as necessary for integration into the dermatology residency curriculum included 95% (18/19) or more of respondents rating the topic as probably essential or definitely essential; if more than 90% (17/19) of respondents rated the topic as probably essential or definitely essential and less than 10% (2/19) rated it as not essential or probably not essential, the topic was still included as part of the suggested curriculum. Topics that received ratings of probably essential or definitely essential by less than 80% (15/19) of respondents were removed from consideration. The topics that did not meet inclusion or exclusion criteria during the first round of voting were refined by the e-Delphi steering committee (V.S.E-C. and F-A.R.) based on open-ended feedback from the voting group provided at the end of the survey and subsequently passed to the second round of voting.
Results
Participants—A total of 19 respondents participated in both voting rounds, the majority (80% [15/19]) of whom were program directors or dermatologists affiliated with academia or development of DEI education; the remaining 20% [4/19]) were dermatology residents.
Open-Ended Feedback—Voting group members were able to provide open-ended feedback for each of the sets of topics after the survey, which the steering committee utilized to modify the topics as needed for the final voting round. For example, “structural racism/discrimination” was originally mentioned as a topic, but several participants suggested including specific types of racism; therefore, the wording was changed to “racism: types, definitions” to encompass broader definitions and types of racism.
Survey Results—Two genres of topics were surveyed in each voting round: clinical and nonclinical. Participants voted on a total of 61 topics, with 23 ultimately selected in the final list of consensus curricular topics. Of those, 9 were clinical and 14 nonclinical. All topics deemed necessary for inclusion in residency curricula are presented in eTables 1 and 2.
During the first round of voting, the e-Delphi panel reached a consensus to include the following 17 topics as essential to dermatology residency training (along with the percentage of voters who classified them as probably essential or definitely essential): how to mitigate bias in clinical and workplace settings (100% [40/40]); social determinants of health-related disparities in dermatology (100% [40/40]); hairstyling practices across different hair textures (100% [40/40]); definitions and examples of microaggressions (97.50% [39/40]); definition, background, and types of bias (97.50% [39/40]); manifestations of bias in the clinical setting (97.44% [38/39]); racial and ethnic disparities in dermatology (97.44% [38/39]); keloids (97.37% [37/38]); differences in dermoscopic presentations in skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); skin cancer in patients with skin of color (97.30% [36/37]); disparities due to bias (95.00% [38/40]); how to apply cultural humility and safety to patients of different cultural backgrounds (94.87% [37/40]); best practices in providing care to patients with limited English proficiency (94.87% [37/40]); hair loss in patients with textured hair (94.74% [36/38]); pseudofolliculitis barbae and acne keloidalis nuchae (94.60% [35/37]); disparities regarding people experiencing homelessness (92.31% [36/39]); and definitions and types of racism and other forms of discrimination (92.31% [36/39]). eTable 1 provides a list of suggested resources to incorporate these topics into the educational components of residency curricula. The resources provided were not part of the voting process, and they were not considered in the consensus analysis; they are included here as suggested educational catalysts.
During the second round of voting, 25 topics were evaluated. Of those, the following 6 topics were proposed to be included as essential in residency training: differences in prevalence and presentation of common inflammatory disorders (100% [29/29]); manifestations of bias in the learning environment (96.55%); antiracist action and how to decrease the effects of structural racism in clinical and educational settings (96.55% [28/29]); diversity of images in dermatology education (96.55% [28/29]); pigmentary disorders and their psychological effects (96.55% [28/29]); and LGBTQ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer) dermatologic health care (96.55% [28/29]). eTable 2 includes these topics as well as suggested resources to help incorporate them into training.
Comment
This study utilized a modified e-Delphi technique to identify relevant clinical and nonclinical DEI topics that should be incorporated into dermatology residency curricula. The panel members reached a consensus for 9 clinical DEI-related topics. The respondents agreed that the topics related to skin and hair conditions in patients with skin of color as well as textured hair were crucial to residency education. Skin cancer, hair loss, pseudofolliculitis barbae, acne keloidalis nuchae, keloids, pigmentary disorders, and their varying presentations in patients with skin of color were among the recommended topics. The panel also recommended educating residents on the variable visual presentations of inflammatory conditions in skin of color. Addressing the needs of diverse patients—for example, those belonging to the LGBTQ community—also was deemed important for inclusion.
The remaining 14 chosen topics were nonclinical items addressing concepts such as bias and health care disparities as well as cultural humility and safety.9 Cultural humility and safety focus on developing cultural awareness by creating a safe setting for patients rather than encouraging power relationships between them and their physicians. Various topics related to racism also were recommended to be included in residency curricula, including education on implementation of antiracist action in the workplace.
Many of the nonclinical topics are intertwined; for instance, learning about health care disparities in patients with limited English proficiency allows for improved best practices in delivering care to patients from this population. The first step in overcoming bias and subsequent disparities is acknowledging how the perpetuation of bias leads to disparities after being taught tools to recognize it.
Our group’s guidance on DEI topics should help dermatology residency program leaders as they design and refine program curricula. There are multiple avenues for incorporating education on these topics, including lectures, interactive workshops, role-playing sessions, book or journal clubs, and discussion circles. Many of these topics/programs may already be included in programs’ didactic curricula, which would minimize the burden of finding space to educate on these topics. Institutional cultural change is key to ensuring truly diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplaces. Educating tomorrow’s dermatologists on these topics is a first step toward achieving that cultural change.
Limitations—A limitation of this e-Delphi survey is that only a selection of experts in this field was included. Additionally, we were concerned that the Likert scale format and the bar we set for inclusion and exclusion may have failed to adequately capture participants’ nuanced opinions. As such, participants were able to provide open-ended feedback, and suggestions for alternate wording or other changes were considered by the steering committee. Finally, inclusion recommendations identified in this survey were developed specifically for US dermatology residents.
Conclusion
In this e-Delphi consensus assessment of DEI-related topics, we recommend the inclusion of 23 topics into dermatology residency program curricula to improve medical training and the patient-physician relationship as well as to create better health outcomes. We also provide specific sample resource recommendations in eTables 1 and 2 to facilitate inclusion of these topics into residency curricula across the country.
- US Census Bureau projections show a slower growing, older, more diverse nation a half century from now. News release. US Census Bureau. December 12, 2012. Accessed August 14, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/population/cb12243.html#:~:text=12%2C%202012,U.S.%20Census%20Bureau%20Projections%20Show%20a%20Slower%20Growing%2C%20Older%2C%20More,by%20the%20U.S.%20Census%20Bureau
- Lopez S, Lourido JO, Lim HW, et al. The call to action to increase racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a retrospective, cross-sectional study to monitor progress. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;86:E121-E123. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.10.011
- El-Kashlan N, Alexis A. Disparities in dermatology: a reflection. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:27-29.
- Laveist TA, Nuru-Jeter A. Is doctor-patient race concordance associated with greater satisfaction with care? J Health Soc Behav. 2002;43:296-306.
- Street RL Jr, O’Malley KJ, Cooper LA, et al. Understanding concordance in patient-physician relationships: personal and ethnic dimensions of shared identity. Ann Fam Med. 2008;6:198-205. doi:10.1370/afm.821
- Dadrass F, Bowers S, Shinkai K, et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion in dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:257-263. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.10.006
- Diversity and the Academy. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.aad.org/member/career/diversity
- SOCS speaks. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/news-media/socs-speaks
- Solchanyk D, Ekeh O, Saffran L, et al. Integrating cultural humility into the medical education curriculum: strategies for educators. Teach Learn Med. 2021;33:554-560. doi:10.1080/10401334.2021.1877711
- US Census Bureau projections show a slower growing, older, more diverse nation a half century from now. News release. US Census Bureau. December 12, 2012. Accessed August 14, 2024. https://www.census.gov/newsroom/releases/archives/population/cb12243.html#:~:text=12%2C%202012,U.S.%20Census%20Bureau%20Projections%20Show%20a%20Slower%20Growing%2C%20Older%2C%20More,by%20the%20U.S.%20Census%20Bureau
- Lopez S, Lourido JO, Lim HW, et al. The call to action to increase racial and ethnic diversity in dermatology: a retrospective, cross-sectional study to monitor progress. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;86:E121-E123. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.10.011
- El-Kashlan N, Alexis A. Disparities in dermatology: a reflection. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022;15:27-29.
- Laveist TA, Nuru-Jeter A. Is doctor-patient race concordance associated with greater satisfaction with care? J Health Soc Behav. 2002;43:296-306.
- Street RL Jr, O’Malley KJ, Cooper LA, et al. Understanding concordance in patient-physician relationships: personal and ethnic dimensions of shared identity. Ann Fam Med. 2008;6:198-205. doi:10.1370/afm.821
- Dadrass F, Bowers S, Shinkai K, et al. Diversity, equity, and inclusion in dermatology residency. Dermatol Clin. 2023;41:257-263. doi:10.1016/j.det.2022.10.006
- Diversity and the Academy. American Academy of Dermatology website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://www.aad.org/member/career/diversity
- SOCS speaks. Skin of Color Society website. Accessed August 22, 2024. https://skinofcolorsociety.org/news-media/socs-speaks
- Solchanyk D, Ekeh O, Saffran L, et al. Integrating cultural humility into the medical education curriculum: strategies for educators. Teach Learn Med. 2021;33:554-560. doi:10.1080/10401334.2021.1877711
PRACTICE POINTS
- Advancing curricula related to diversity, equity, and inclusion in dermatology training can improve health outcomes, address health care workforce disparities, and enhance clinical care for diverse patient populations.
- Education on patient-centered communication, cultural humility, and the impact of social determinants of health results in dermatology residents who are better equipped with the necessary tools to effectively care for patients from diverse backgrounds.
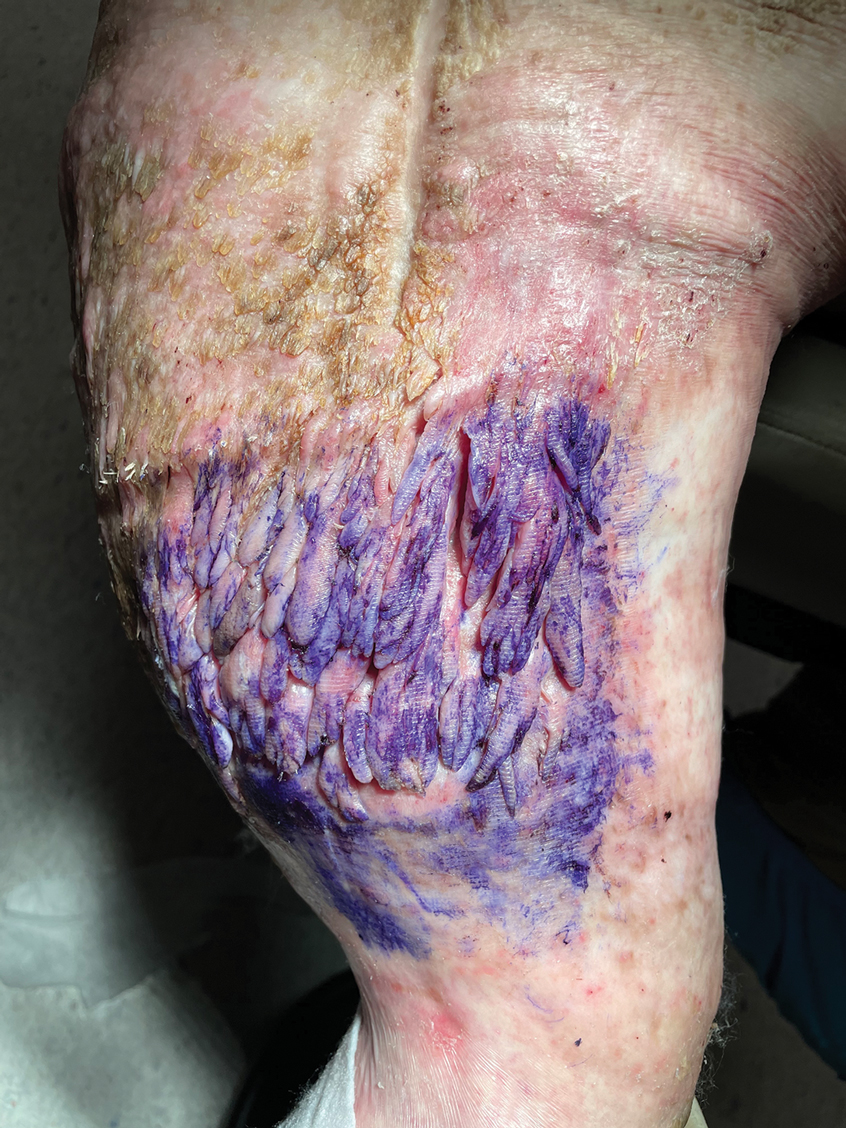
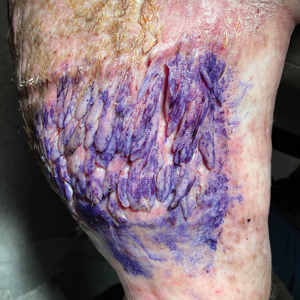
Multiple Fingerlike Projections on the Leg
The Diagnosis: Elephantiasis Nostras Verrucosa
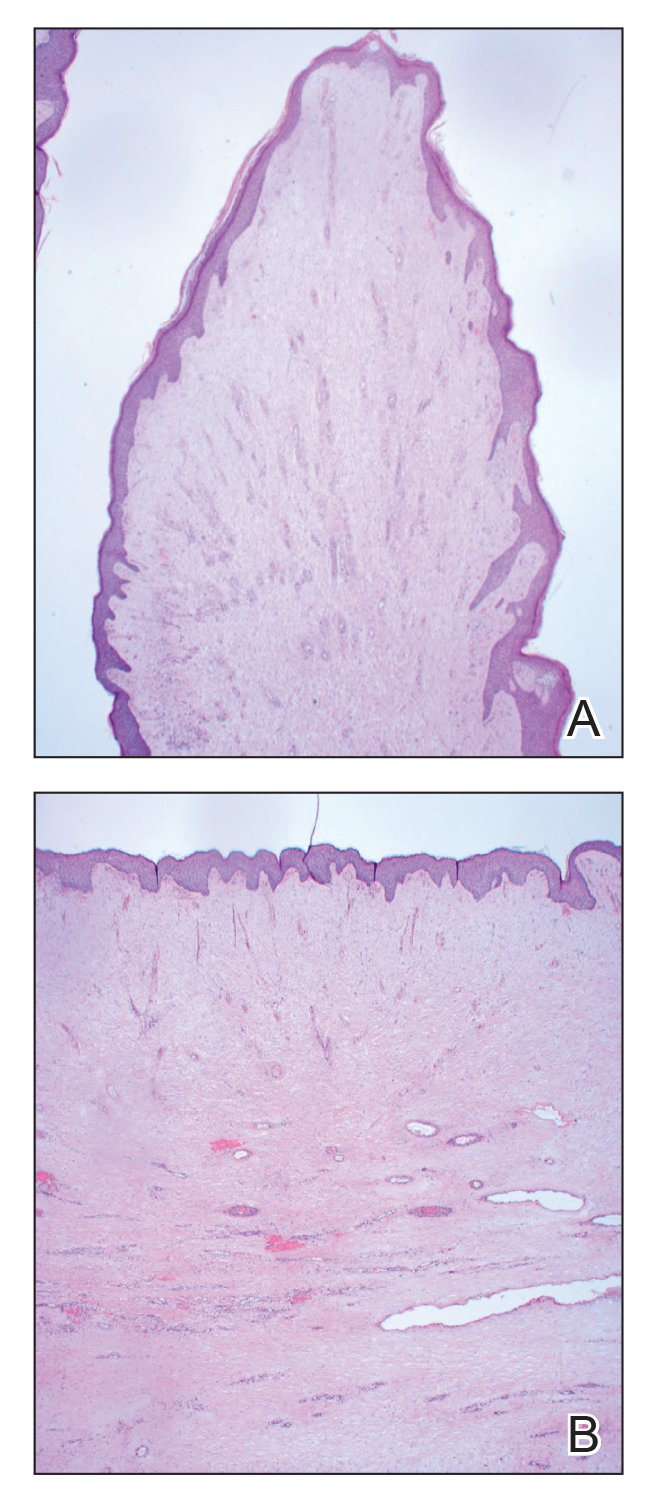
Histopathology revealed a benign fibroepithelial polyp demonstrating areas of hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and focal papillomatosis (Figure, A). Increased superficial vessels with dilated lymphatics, stellate fibroblasts, edematous stroma, and plasmolymphocytosis also were noted (Figure, B). Clinical and histopathological findings led to a diagnosis of lymphedema papules in the setting of elephantiasis nostra verrucosa (ENV).
Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa is a complication of long-standing nonfilarial obstruction of lymphatic drainage leading to grotesque enlargement of the affected areas. Common cutaneous manifestations of ENV include nonpitting edema, dermal fibrosis, and extensive hyperkeratosis with verrucous and papillomatous lesions.1 In the beginning stages of ENV, the skin has a cobblestonelike appearance. As the disease progresses, the verrucous lesions continue to enlarge, giving the affected area a mossy appearance. Although less common, groupings of large papillomas similar to our patient’s presentation also can form.2 Ulcer formation is more likely to occur in advanced disease states, increasing the risk for bacterial and fungal colonization. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa classically affects the legs; however, this condition can develop in any area with chronic lymphedema. Cases of ENV involving the arms, abdomen, scrotum, and ear have been documented.3-5
The pathogenesis of ENV involves the proliferation of fibroblasts and fibrosis secondary to lymphostasis and inflammation.6 When interstitial fluid builds up in the affected region, the protein-rich fluid is believed to trigger fibrogenesis and increase macrophage, keratinocyte, and adipocyte activity.7 Because of this inflammatory process, dilation and fibrosis of the lymphatic channels develop. Lymphatic obstruction can have several etiologies, most notably infection and malignancy. Staphylococcal lymphangitis and erysipelas create fibrosis of the lymphatic system and are the main infectious causes of ENV.6 Large tumors or lymphomas are insidious causes of lymphatic obstruction and should be ruled out when investigating for ENV. Other risk factors include obesity, chronic venous insufficiency, surgery, trauma, radiation, and uncontrolled congestive heart failure.1,6,8
An ENV diagnosis is clinicopathologic, involving a comprehensive metabolic panel and complete blood cell count with differential. A biopsy is needed for pathologic confirmation and to rule out malignancy. Histologically, ENV is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, dermal fibrosis, hyperkeratosis of the epidermis, and dilated lymphatic vessels.6,8 Additional studies for diagnosis include wound and lymph node culture, Wood lamp examination, and lymphoscintigraphy.
Given the chronic and progressive nature of the disease, ENV is difficult to treat. There currently is no standard of treatment, but the mainstay of management involves reducing peripheral edema. Lifestyle changes including weight loss, extremity elevation, and increased ambulation are helpful first-line therapies.3 Compression of the affected extremity using stockings or intermittent pneumatic compression devices has proven to be beneficial with long-term use.7 Patients should be followed for wound care to prevent the infection of ulcers.2 Pharmacologic treatments include systemic retinoids, which have been shown to reduce the appearance of hyperkeratosis, verrucous lesions, and papillomatous nodules.6 Prophylactic antibiotics are reserved for advanced stages of disease or in patients with recurrent infections.2,7 In severe cases of ENV that are unresponsive to medical management, surgical intervention such as lymphatic anastomosis and debulking may be considered.9,10
Other diagnoses to consider for ENV include pretibial myxedema, lymphatic filariasis, Stewart-Treves syndrome, and papillomatosis cutis carcinoides. Pretibial myxedema is an uncommon dermatologic manifestation of Graves disease. It is a local autoimmune reaction in the cutaneous tissue characterized by hyperpigmentation, nonpitting edema, and nodules on the anterior leg. Histopathology shows increased hyaluronic acid and chondroitin as well as compression of dermal lymphatics.11
Filariasis is a parasitic infection caused by Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi or Brugia timori, and Onchocerca volvulus.6 This condition presents with elephantiasis of the affected extremities but should be considered in areas endemic for filarial parasites such as tropical and subtropical countries.12 Eosinophilia and identification of microfilaria in a peripheral blood smear would indicate parasitic infection. Stewart-Treves syndrome is a rare angiosarcoma that arises in areas of chronic lymphedema. This condition classically is seen on the upper extremities following a mastectomy with lymphadenectomy, lymph node irradiation, or both.
Stewart-Treves syndrome presents with coalescing purpuric macules and nodules that eventually coalesce into cutaneous masses. Histopathology reveals proliferating vascular channels that split apart dermal collagen with hyperchromatism and pleomorphism in the tumor endothelial cells that line these channels.13
Papillomatosis cutis carcinoides is a low-grade squamous cell carcinoma that occurs secondary to human papillomavirus commonly affecting the mouth, anogenital area, and the plantar surfaces of the feet. It presents with exophytic growths and ulcerated tumors that are unilateral and asymmetrical. The presence of blunt-shaped tumor projections extending deep into the dermis to form sinuses and keratin-filled cysts is characteristic of papillomatosis cutis carcinoides.14
- Dean SM, Zirwas MJ, Horst AV. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: an institutional analysis of 21 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64: 1104-1110. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.047
- Fife CE, Farrow W, Hebert AA, et al. Skin and wound care in lymphedema patients: a taxonomy, primer, and literature review. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2017;30:305-318. doi:10.1097/01.ASW.0000520501.23702.82
- Boyd J, Sloan S, Meffert J. Elephantiasis nostrum verrucosa of the abdomen: clinical results with tazarotene. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004; 3:446-448.
- Nakai K, Taoka R, Sugimoto M, et al. Genital elephantiasis possibly caused by chronic inguinal eczema with streptococcal infection. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E196-E198. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14746
- Carlson JA, Mazza J, Kircher K, et al. Otophyma: a case report and review of the literature of lymphedema (elephantiasis) of the ear. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:67-72. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31815cd937
- Sisto K, Khachemoune A. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9:141-146. doi:10.2165/00128071-200809030-00001
- Yoho RM, Budny AM, Pea AS. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2006;96:442-444. doi:10.7547/0960442
- Yosipovitch G, DeVore A, Dawn A. Obesity and the skin: skin physiology and skin manifestations of obesity. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:901-920. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.12.004
- Iwao F, Sato-Matsumura KC, Sawamura D, et al. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa successfully treated by surgical debridement. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:939-941. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2004.30267.x
- Tiwari A, Cheng KS, Button M, et al. Differential diagnosis, investigation, and current treatment of lower limb lymphedema. Arch Surg. 2003;138:152-161. doi:10.1001/archsurg.138.2.152
- Fatourechi V. Pretibial myxedema: pathophysiology and treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2005;6:295-309. doi:10.2165 /00128071-200506050-00003
- Addiss DG, Brady MA. Morbidity management in the Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis: a review of the scientific literature. Filaria J. 2007;6:2. doi:10.1186/1475-2883-6-2
- Bernia E, Rios-Viñuela E, Requena C. Stewart-Treves syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:721. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0341
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-24. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(95)90177-9
The Diagnosis: Elephantiasis Nostras Verrucosa
Histopathology revealed a benign fibroepithelial polyp demonstrating areas of hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and focal papillomatosis (Figure, A). Increased superficial vessels with dilated lymphatics, stellate fibroblasts, edematous stroma, and plasmolymphocytosis also were noted (Figure, B). Clinical and histopathological findings led to a diagnosis of lymphedema papules in the setting of elephantiasis nostra verrucosa (ENV).

Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa is a complication of long-standing nonfilarial obstruction of lymphatic drainage leading to grotesque enlargement of the affected areas. Common cutaneous manifestations of ENV include nonpitting edema, dermal fibrosis, and extensive hyperkeratosis with verrucous and papillomatous lesions.1 In the beginning stages of ENV, the skin has a cobblestonelike appearance. As the disease progresses, the verrucous lesions continue to enlarge, giving the affected area a mossy appearance. Although less common, groupings of large papillomas similar to our patient’s presentation also can form.2 Ulcer formation is more likely to occur in advanced disease states, increasing the risk for bacterial and fungal colonization. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa classically affects the legs; however, this condition can develop in any area with chronic lymphedema. Cases of ENV involving the arms, abdomen, scrotum, and ear have been documented.3-5
The pathogenesis of ENV involves the proliferation of fibroblasts and fibrosis secondary to lymphostasis and inflammation.6 When interstitial fluid builds up in the affected region, the protein-rich fluid is believed to trigger fibrogenesis and increase macrophage, keratinocyte, and adipocyte activity.7 Because of this inflammatory process, dilation and fibrosis of the lymphatic channels develop. Lymphatic obstruction can have several etiologies, most notably infection and malignancy. Staphylococcal lymphangitis and erysipelas create fibrosis of the lymphatic system and are the main infectious causes of ENV.6 Large tumors or lymphomas are insidious causes of lymphatic obstruction and should be ruled out when investigating for ENV. Other risk factors include obesity, chronic venous insufficiency, surgery, trauma, radiation, and uncontrolled congestive heart failure.1,6,8
An ENV diagnosis is clinicopathologic, involving a comprehensive metabolic panel and complete blood cell count with differential. A biopsy is needed for pathologic confirmation and to rule out malignancy. Histologically, ENV is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, dermal fibrosis, hyperkeratosis of the epidermis, and dilated lymphatic vessels.6,8 Additional studies for diagnosis include wound and lymph node culture, Wood lamp examination, and lymphoscintigraphy.
Given the chronic and progressive nature of the disease, ENV is difficult to treat. There currently is no standard of treatment, but the mainstay of management involves reducing peripheral edema. Lifestyle changes including weight loss, extremity elevation, and increased ambulation are helpful first-line therapies.3 Compression of the affected extremity using stockings or intermittent pneumatic compression devices has proven to be beneficial with long-term use.7 Patients should be followed for wound care to prevent the infection of ulcers.2 Pharmacologic treatments include systemic retinoids, which have been shown to reduce the appearance of hyperkeratosis, verrucous lesions, and papillomatous nodules.6 Prophylactic antibiotics are reserved for advanced stages of disease or in patients with recurrent infections.2,7 In severe cases of ENV that are unresponsive to medical management, surgical intervention such as lymphatic anastomosis and debulking may be considered.9,10
Other diagnoses to consider for ENV include pretibial myxedema, lymphatic filariasis, Stewart-Treves syndrome, and papillomatosis cutis carcinoides. Pretibial myxedema is an uncommon dermatologic manifestation of Graves disease. It is a local autoimmune reaction in the cutaneous tissue characterized by hyperpigmentation, nonpitting edema, and nodules on the anterior leg. Histopathology shows increased hyaluronic acid and chondroitin as well as compression of dermal lymphatics.11
Filariasis is a parasitic infection caused by Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi or Brugia timori, and Onchocerca volvulus.6 This condition presents with elephantiasis of the affected extremities but should be considered in areas endemic for filarial parasites such as tropical and subtropical countries.12 Eosinophilia and identification of microfilaria in a peripheral blood smear would indicate parasitic infection. Stewart-Treves syndrome is a rare angiosarcoma that arises in areas of chronic lymphedema. This condition classically is seen on the upper extremities following a mastectomy with lymphadenectomy, lymph node irradiation, or both.
Stewart-Treves syndrome presents with coalescing purpuric macules and nodules that eventually coalesce into cutaneous masses. Histopathology reveals proliferating vascular channels that split apart dermal collagen with hyperchromatism and pleomorphism in the tumor endothelial cells that line these channels.13
Papillomatosis cutis carcinoides is a low-grade squamous cell carcinoma that occurs secondary to human papillomavirus commonly affecting the mouth, anogenital area, and the plantar surfaces of the feet. It presents with exophytic growths and ulcerated tumors that are unilateral and asymmetrical. The presence of blunt-shaped tumor projections extending deep into the dermis to form sinuses and keratin-filled cysts is characteristic of papillomatosis cutis carcinoides.14
The Diagnosis: Elephantiasis Nostras Verrucosa
Histopathology revealed a benign fibroepithelial polyp demonstrating areas of hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and focal papillomatosis (Figure, A). Increased superficial vessels with dilated lymphatics, stellate fibroblasts, edematous stroma, and plasmolymphocytosis also were noted (Figure, B). Clinical and histopathological findings led to a diagnosis of lymphedema papules in the setting of elephantiasis nostra verrucosa (ENV).

Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa is a complication of long-standing nonfilarial obstruction of lymphatic drainage leading to grotesque enlargement of the affected areas. Common cutaneous manifestations of ENV include nonpitting edema, dermal fibrosis, and extensive hyperkeratosis with verrucous and papillomatous lesions.1 In the beginning stages of ENV, the skin has a cobblestonelike appearance. As the disease progresses, the verrucous lesions continue to enlarge, giving the affected area a mossy appearance. Although less common, groupings of large papillomas similar to our patient’s presentation also can form.2 Ulcer formation is more likely to occur in advanced disease states, increasing the risk for bacterial and fungal colonization. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa classically affects the legs; however, this condition can develop in any area with chronic lymphedema. Cases of ENV involving the arms, abdomen, scrotum, and ear have been documented.3-5
The pathogenesis of ENV involves the proliferation of fibroblasts and fibrosis secondary to lymphostasis and inflammation.6 When interstitial fluid builds up in the affected region, the protein-rich fluid is believed to trigger fibrogenesis and increase macrophage, keratinocyte, and adipocyte activity.7 Because of this inflammatory process, dilation and fibrosis of the lymphatic channels develop. Lymphatic obstruction can have several etiologies, most notably infection and malignancy. Staphylococcal lymphangitis and erysipelas create fibrosis of the lymphatic system and are the main infectious causes of ENV.6 Large tumors or lymphomas are insidious causes of lymphatic obstruction and should be ruled out when investigating for ENV. Other risk factors include obesity, chronic venous insufficiency, surgery, trauma, radiation, and uncontrolled congestive heart failure.1,6,8
An ENV diagnosis is clinicopathologic, involving a comprehensive metabolic panel and complete blood cell count with differential. A biopsy is needed for pathologic confirmation and to rule out malignancy. Histologically, ENV is characterized by pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia, dermal fibrosis, hyperkeratosis of the epidermis, and dilated lymphatic vessels.6,8 Additional studies for diagnosis include wound and lymph node culture, Wood lamp examination, and lymphoscintigraphy.
Given the chronic and progressive nature of the disease, ENV is difficult to treat. There currently is no standard of treatment, but the mainstay of management involves reducing peripheral edema. Lifestyle changes including weight loss, extremity elevation, and increased ambulation are helpful first-line therapies.3 Compression of the affected extremity using stockings or intermittent pneumatic compression devices has proven to be beneficial with long-term use.7 Patients should be followed for wound care to prevent the infection of ulcers.2 Pharmacologic treatments include systemic retinoids, which have been shown to reduce the appearance of hyperkeratosis, verrucous lesions, and papillomatous nodules.6 Prophylactic antibiotics are reserved for advanced stages of disease or in patients with recurrent infections.2,7 In severe cases of ENV that are unresponsive to medical management, surgical intervention such as lymphatic anastomosis and debulking may be considered.9,10
Other diagnoses to consider for ENV include pretibial myxedema, lymphatic filariasis, Stewart-Treves syndrome, and papillomatosis cutis carcinoides. Pretibial myxedema is an uncommon dermatologic manifestation of Graves disease. It is a local autoimmune reaction in the cutaneous tissue characterized by hyperpigmentation, nonpitting edema, and nodules on the anterior leg. Histopathology shows increased hyaluronic acid and chondroitin as well as compression of dermal lymphatics.11
Filariasis is a parasitic infection caused by Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi or Brugia timori, and Onchocerca volvulus.6 This condition presents with elephantiasis of the affected extremities but should be considered in areas endemic for filarial parasites such as tropical and subtropical countries.12 Eosinophilia and identification of microfilaria in a peripheral blood smear would indicate parasitic infection. Stewart-Treves syndrome is a rare angiosarcoma that arises in areas of chronic lymphedema. This condition classically is seen on the upper extremities following a mastectomy with lymphadenectomy, lymph node irradiation, or both.
Stewart-Treves syndrome presents with coalescing purpuric macules and nodules that eventually coalesce into cutaneous masses. Histopathology reveals proliferating vascular channels that split apart dermal collagen with hyperchromatism and pleomorphism in the tumor endothelial cells that line these channels.13
Papillomatosis cutis carcinoides is a low-grade squamous cell carcinoma that occurs secondary to human papillomavirus commonly affecting the mouth, anogenital area, and the plantar surfaces of the feet. It presents with exophytic growths and ulcerated tumors that are unilateral and asymmetrical. The presence of blunt-shaped tumor projections extending deep into the dermis to form sinuses and keratin-filled cysts is characteristic of papillomatosis cutis carcinoides.14
- Dean SM, Zirwas MJ, Horst AV. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: an institutional analysis of 21 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64: 1104-1110. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.047
- Fife CE, Farrow W, Hebert AA, et al. Skin and wound care in lymphedema patients: a taxonomy, primer, and literature review. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2017;30:305-318. doi:10.1097/01.ASW.0000520501.23702.82
- Boyd J, Sloan S, Meffert J. Elephantiasis nostrum verrucosa of the abdomen: clinical results with tazarotene. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004; 3:446-448.
- Nakai K, Taoka R, Sugimoto M, et al. Genital elephantiasis possibly caused by chronic inguinal eczema with streptococcal infection. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E196-E198. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14746
- Carlson JA, Mazza J, Kircher K, et al. Otophyma: a case report and review of the literature of lymphedema (elephantiasis) of the ear. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:67-72. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31815cd937
- Sisto K, Khachemoune A. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9:141-146. doi:10.2165/00128071-200809030-00001
- Yoho RM, Budny AM, Pea AS. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2006;96:442-444. doi:10.7547/0960442
- Yosipovitch G, DeVore A, Dawn A. Obesity and the skin: skin physiology and skin manifestations of obesity. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:901-920. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.12.004
- Iwao F, Sato-Matsumura KC, Sawamura D, et al. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa successfully treated by surgical debridement. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:939-941. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2004.30267.x
- Tiwari A, Cheng KS, Button M, et al. Differential diagnosis, investigation, and current treatment of lower limb lymphedema. Arch Surg. 2003;138:152-161. doi:10.1001/archsurg.138.2.152
- Fatourechi V. Pretibial myxedema: pathophysiology and treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2005;6:295-309. doi:10.2165 /00128071-200506050-00003
- Addiss DG, Brady MA. Morbidity management in the Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis: a review of the scientific literature. Filaria J. 2007;6:2. doi:10.1186/1475-2883-6-2
- Bernia E, Rios-Viñuela E, Requena C. Stewart-Treves syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:721. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0341
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-24. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(95)90177-9
- Dean SM, Zirwas MJ, Horst AV. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: an institutional analysis of 21 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64: 1104-1110. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.047
- Fife CE, Farrow W, Hebert AA, et al. Skin and wound care in lymphedema patients: a taxonomy, primer, and literature review. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2017;30:305-318. doi:10.1097/01.ASW.0000520501.23702.82
- Boyd J, Sloan S, Meffert J. Elephantiasis nostrum verrucosa of the abdomen: clinical results with tazarotene. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004; 3:446-448.
- Nakai K, Taoka R, Sugimoto M, et al. Genital elephantiasis possibly caused by chronic inguinal eczema with streptococcal infection. J Dermatol. 2019;46:E196-E198. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14746
- Carlson JA, Mazza J, Kircher K, et al. Otophyma: a case report and review of the literature of lymphedema (elephantiasis) of the ear. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;30:67-72. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e31815cd937
- Sisto K, Khachemoune A. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9:141-146. doi:10.2165/00128071-200809030-00001
- Yoho RM, Budny AM, Pea AS. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2006;96:442-444. doi:10.7547/0960442
- Yosipovitch G, DeVore A, Dawn A. Obesity and the skin: skin physiology and skin manifestations of obesity. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:901-920. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.12.004
- Iwao F, Sato-Matsumura KC, Sawamura D, et al. Elephantiasis nostras verrucosa successfully treated by surgical debridement. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:939-941. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2004.30267.x
- Tiwari A, Cheng KS, Button M, et al. Differential diagnosis, investigation, and current treatment of lower limb lymphedema. Arch Surg. 2003;138:152-161. doi:10.1001/archsurg.138.2.152
- Fatourechi V. Pretibial myxedema: pathophysiology and treatment options. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2005;6:295-309. doi:10.2165 /00128071-200506050-00003
- Addiss DG, Brady MA. Morbidity management in the Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis: a review of the scientific literature. Filaria J. 2007;6:2. doi:10.1186/1475-2883-6-2
- Bernia E, Rios-Viñuela E, Requena C. Stewart-Treves syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:721. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0341
- Schwartz RA. Verrucous carcinoma of the skin and mucosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:1-24. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(95)90177-9
A 61-year-old man presented with painful skin growths on the right pretibial region of several months’ duration. The patient reported pain due to friction between the lesions and underlying skin, leading to erosions. His medical history was remarkable for morbid obesity (body mass index of 62), chronic venous stasis, and chronic lymphedema. The patient was followed for wound care of venous stasis ulcers. Dermatologic examination revealed multiple 5- to 30-mm, flesh-colored, fingerlike projections on the right tibial region. A biopsy was obtained and submitted for histopathologic analysis.