User login
Pigmented Basal Cell Carcinoma With Annular Leukoderma
To the Editor:
Annular leukoderma, or the halo phenomenon, is a circular reaction of hypopigmentation that most commonly is observed alongside congenital nevi, acquired melanocytic nevi, blue nevi, Spitz nevi, vitiligo, and rarely melanoma.1 There is limited literature on the mechanism of the halo phenomenon. Most of the literature proposes a T cell–mediated immune response to antigens, which causes not only surrounding pigment loss but also heralds the regression of central lesions.2 Others have suggested a vascular mechanism, with blood shunted away from the lesions.3 Because guidelines discourage biopsy of typical halo nevi, it becomes important to evaluate lesions for worrisome features such as ulceration or asymmetry, especially in older patients. We present a case of a pigmented basal cell carcinoma (BCC) that exhibited the halo phenomenon. Four other cases have been described in the literature.3-6
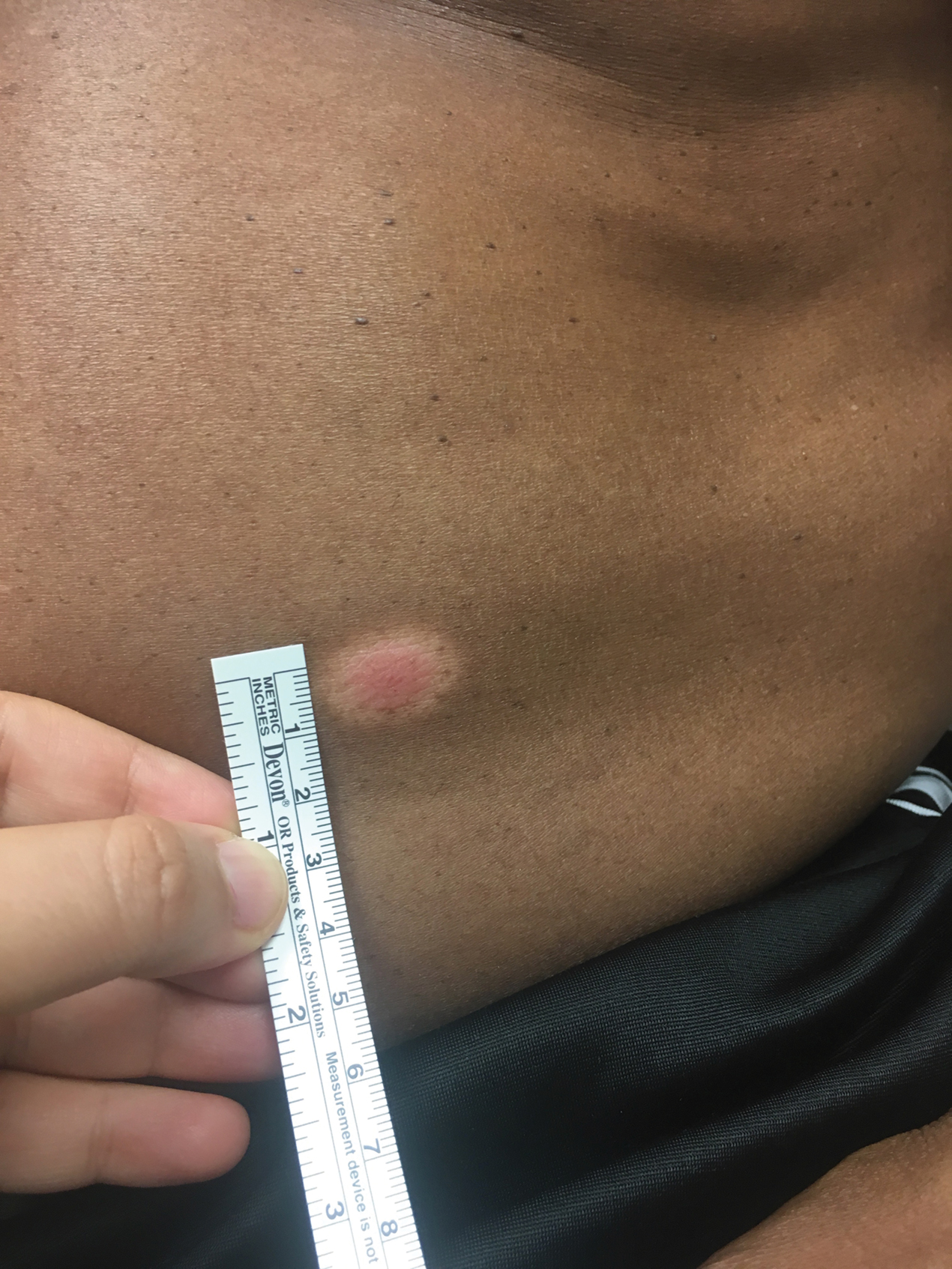
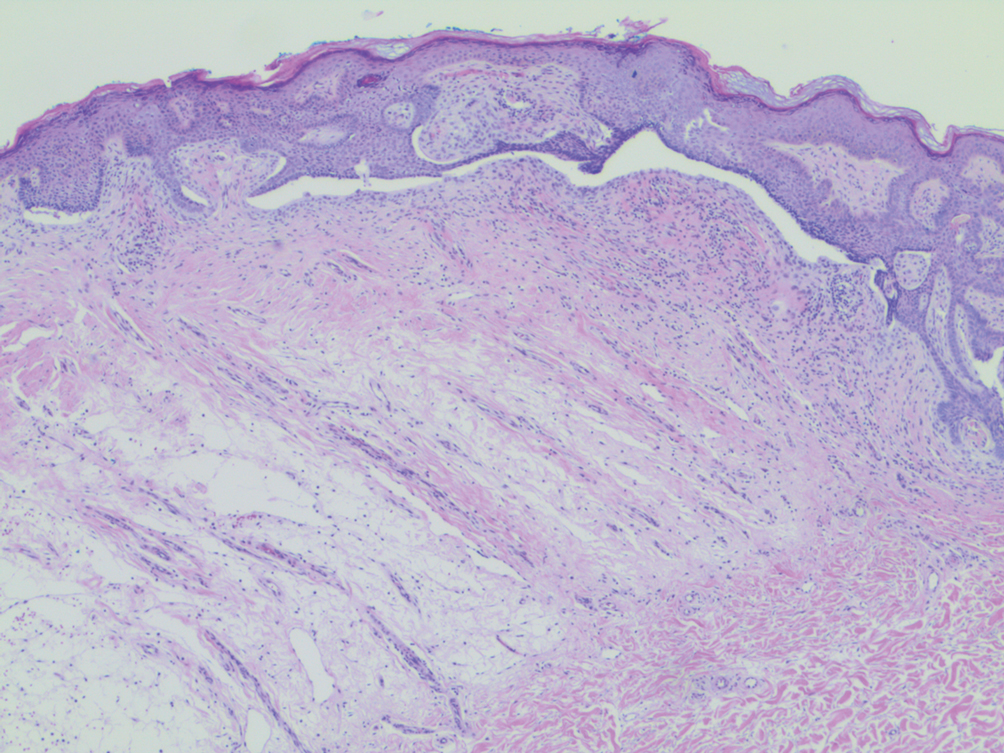
A 53-year-old man presented for evaluation of an asymptomatic lesion on the left side of the abdomen of approximately 8 months’ duration. He had no personal or family history of skin cancer. Physical examination revealed a central 1-cm, pink, verrucous papule surrounded by a 2×1.2-cm, depigmented, circular patch on the left side of the inferior abdomen (Figure 1). Upon questioning, the patient produced cell phone photographs of the trunk from 3 years prior, which did not show any lesions present. Full-body skin examination did not reveal any other concerning pigmented lesions. Excisional biopsy was performed due to concern for amelanotic melanoma, and histopathology revealed a superficial and pigmented BCC (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry with Melan-A was negative for atypical melanocytes, with no uptake in the leukoderma areas.
The clinical presentation initially was concerning for amelanotic melanoma. All melanoma subtypes may appear as hypomelanotic lesions, though these most commonly are observed in the desmoplastic or nodular subtypes. Amelanotic melanomas may present as well-defined red or pink macules, plaques, or nodules, with some tumors presenting with light brown pigmentation.7
The differential diagnosis for lesions with the halo phenomenon is large. In adults, the halo phenomenon may be concerning for malignant or regressing melanoma. As an immunogenic tumor, melanoma’s immunogenic melanocytes may incite a cell-mediated immune response to antigens common to neoplastic and normal melanocytes, which can clinically manifest not only as local annular leukoderma but also as distant vitiligo or halo nevi.7 The halo phenomenon more commonly is associated with benign processes such as vitiligo and halo nevi in children. In most children, halo nevi occur as an isolated phenomenon but still warrant a complete skin examination for melanoma and vitiligo. The presence of halo nevi has been associated with distant vitiligo—possibly through shared immunologic mechanisms—especially if patients present with the Koebner phenomenon, multiple halo nevi, or a family history of vitiligo.8 A prospective study also found that the presence of halo nevi was an independent risk factor for the progression of segmental vitiligo to mixed vitiligo.9 Hormones also may play a role in the leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum, or halo, nevi. Halo nevi most commonly affect adolescents and pregnant women. It has been postulated that congenital nevi may be unique in their response to altered estrogen levels, increasing the rate not only of halo nevi but also of melanoma in pregnant women.10
Our patient’s final histologic diagnosis was pigmented BCC, which comprises only 6% of all BCCs.3 The proposed mechanism is that melanocytes colonize the tumor in the surrounding stroma and produce excess melanin. Basal cell carcinoma with halo phenomenon is a rare presentation. As in our case, 2 prior BCC reports also involved patients older than 50 years,3,5 with the 2 other cases describing women in their late twenties and early thirties.4,6 Additionally, 2 of 4 reports described patients with a history of multiple BCCs.3,5
In summary, the seemingly benign halo phenomenon may accompany malignant processes such as nonmelanoma skin cancer. Careful consideration of lesion time course and atypia is imperative for proper clinical suspicion in such cases.
- Mooney MA, Barr RJ, Buxton MG. Halo nevus or halo phenomenon? a study of 142 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:342-348.
- Zeff RA, Freitag A, Grin CM, et al. The immune response in halo nevi. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:620-624.
- Johnson DB, Ceilley RI. Basal cell carcinoma with annular leukoderma mimicking leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:352-353.
- Basak PY, Meric G, Ciris M. Basal cell carcinoma with halo phenomenon in a young female: significance of dermatoscopy in early diagnosis. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:214.
- Pembroke AC, Liddell K. Basal cell epithelioma with a hypopigmented halo. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:317.
- Rustemeyer J, Günther L, Deichert L. A rare association: basal cell carcinoma in a vitiliginous macula. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;15:175-177.
- Naveh HP, Rao UN, Butterfield LH. Melanoma‐associated leukoderma—immunology in black and white? Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013;26:796-804.
- Zhou H, Wu L-C, Chen M-K, et al. Factors associated with development of vitiligo in patients with halo nevus. Chinese Med J. 2017;130:2703.
- Ezzedine K, Diallo A, Léauté‐Labrèze C, et al. Halo naevi and leukotrichia are strong predictors of the passage to mixed vitiligo in a subgroup of segmental vitiligo. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:539-544.
- Nading MA, Nanney LB, Ellis DL. Pregnancy and estrogen receptor β expression in a large congenital nevus. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:691-694.
To the Editor:
Annular leukoderma, or the halo phenomenon, is a circular reaction of hypopigmentation that most commonly is observed alongside congenital nevi, acquired melanocytic nevi, blue nevi, Spitz nevi, vitiligo, and rarely melanoma.1 There is limited literature on the mechanism of the halo phenomenon. Most of the literature proposes a T cell–mediated immune response to antigens, which causes not only surrounding pigment loss but also heralds the regression of central lesions.2 Others have suggested a vascular mechanism, with blood shunted away from the lesions.3 Because guidelines discourage biopsy of typical halo nevi, it becomes important to evaluate lesions for worrisome features such as ulceration or asymmetry, especially in older patients. We present a case of a pigmented basal cell carcinoma (BCC) that exhibited the halo phenomenon. Four other cases have been described in the literature.3-6
A 53-year-old man presented for evaluation of an asymptomatic lesion on the left side of the abdomen of approximately 8 months’ duration. He had no personal or family history of skin cancer. Physical examination revealed a central 1-cm, pink, verrucous papule surrounded by a 2×1.2-cm, depigmented, circular patch on the left side of the inferior abdomen (Figure 1). Upon questioning, the patient produced cell phone photographs of the trunk from 3 years prior, which did not show any lesions present. Full-body skin examination did not reveal any other concerning pigmented lesions. Excisional biopsy was performed due to concern for amelanotic melanoma, and histopathology revealed a superficial and pigmented BCC (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry with Melan-A was negative for atypical melanocytes, with no uptake in the leukoderma areas.
The clinical presentation initially was concerning for amelanotic melanoma. All melanoma subtypes may appear as hypomelanotic lesions, though these most commonly are observed in the desmoplastic or nodular subtypes. Amelanotic melanomas may present as well-defined red or pink macules, plaques, or nodules, with some tumors presenting with light brown pigmentation.7
The differential diagnosis for lesions with the halo phenomenon is large. In adults, the halo phenomenon may be concerning for malignant or regressing melanoma. As an immunogenic tumor, melanoma’s immunogenic melanocytes may incite a cell-mediated immune response to antigens common to neoplastic and normal melanocytes, which can clinically manifest not only as local annular leukoderma but also as distant vitiligo or halo nevi.7 The halo phenomenon more commonly is associated with benign processes such as vitiligo and halo nevi in children. In most children, halo nevi occur as an isolated phenomenon but still warrant a complete skin examination for melanoma and vitiligo. The presence of halo nevi has been associated with distant vitiligo—possibly through shared immunologic mechanisms—especially if patients present with the Koebner phenomenon, multiple halo nevi, or a family history of vitiligo.8 A prospective study also found that the presence of halo nevi was an independent risk factor for the progression of segmental vitiligo to mixed vitiligo.9 Hormones also may play a role in the leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum, or halo, nevi. Halo nevi most commonly affect adolescents and pregnant women. It has been postulated that congenital nevi may be unique in their response to altered estrogen levels, increasing the rate not only of halo nevi but also of melanoma in pregnant women.10
Our patient’s final histologic diagnosis was pigmented BCC, which comprises only 6% of all BCCs.3 The proposed mechanism is that melanocytes colonize the tumor in the surrounding stroma and produce excess melanin. Basal cell carcinoma with halo phenomenon is a rare presentation. As in our case, 2 prior BCC reports also involved patients older than 50 years,3,5 with the 2 other cases describing women in their late twenties and early thirties.4,6 Additionally, 2 of 4 reports described patients with a history of multiple BCCs.3,5
In summary, the seemingly benign halo phenomenon may accompany malignant processes such as nonmelanoma skin cancer. Careful consideration of lesion time course and atypia is imperative for proper clinical suspicion in such cases.
To the Editor:
Annular leukoderma, or the halo phenomenon, is a circular reaction of hypopigmentation that most commonly is observed alongside congenital nevi, acquired melanocytic nevi, blue nevi, Spitz nevi, vitiligo, and rarely melanoma.1 There is limited literature on the mechanism of the halo phenomenon. Most of the literature proposes a T cell–mediated immune response to antigens, which causes not only surrounding pigment loss but also heralds the regression of central lesions.2 Others have suggested a vascular mechanism, with blood shunted away from the lesions.3 Because guidelines discourage biopsy of typical halo nevi, it becomes important to evaluate lesions for worrisome features such as ulceration or asymmetry, especially in older patients. We present a case of a pigmented basal cell carcinoma (BCC) that exhibited the halo phenomenon. Four other cases have been described in the literature.3-6
A 53-year-old man presented for evaluation of an asymptomatic lesion on the left side of the abdomen of approximately 8 months’ duration. He had no personal or family history of skin cancer. Physical examination revealed a central 1-cm, pink, verrucous papule surrounded by a 2×1.2-cm, depigmented, circular patch on the left side of the inferior abdomen (Figure 1). Upon questioning, the patient produced cell phone photographs of the trunk from 3 years prior, which did not show any lesions present. Full-body skin examination did not reveal any other concerning pigmented lesions. Excisional biopsy was performed due to concern for amelanotic melanoma, and histopathology revealed a superficial and pigmented BCC (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry with Melan-A was negative for atypical melanocytes, with no uptake in the leukoderma areas.
The clinical presentation initially was concerning for amelanotic melanoma. All melanoma subtypes may appear as hypomelanotic lesions, though these most commonly are observed in the desmoplastic or nodular subtypes. Amelanotic melanomas may present as well-defined red or pink macules, plaques, or nodules, with some tumors presenting with light brown pigmentation.7
The differential diagnosis for lesions with the halo phenomenon is large. In adults, the halo phenomenon may be concerning for malignant or regressing melanoma. As an immunogenic tumor, melanoma’s immunogenic melanocytes may incite a cell-mediated immune response to antigens common to neoplastic and normal melanocytes, which can clinically manifest not only as local annular leukoderma but also as distant vitiligo or halo nevi.7 The halo phenomenon more commonly is associated with benign processes such as vitiligo and halo nevi in children. In most children, halo nevi occur as an isolated phenomenon but still warrant a complete skin examination for melanoma and vitiligo. The presence of halo nevi has been associated with distant vitiligo—possibly through shared immunologic mechanisms—especially if patients present with the Koebner phenomenon, multiple halo nevi, or a family history of vitiligo.8 A prospective study also found that the presence of halo nevi was an independent risk factor for the progression of segmental vitiligo to mixed vitiligo.9 Hormones also may play a role in the leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum, or halo, nevi. Halo nevi most commonly affect adolescents and pregnant women. It has been postulated that congenital nevi may be unique in their response to altered estrogen levels, increasing the rate not only of halo nevi but also of melanoma in pregnant women.10
Our patient’s final histologic diagnosis was pigmented BCC, which comprises only 6% of all BCCs.3 The proposed mechanism is that melanocytes colonize the tumor in the surrounding stroma and produce excess melanin. Basal cell carcinoma with halo phenomenon is a rare presentation. As in our case, 2 prior BCC reports also involved patients older than 50 years,3,5 with the 2 other cases describing women in their late twenties and early thirties.4,6 Additionally, 2 of 4 reports described patients with a history of multiple BCCs.3,5
In summary, the seemingly benign halo phenomenon may accompany malignant processes such as nonmelanoma skin cancer. Careful consideration of lesion time course and atypia is imperative for proper clinical suspicion in such cases.
- Mooney MA, Barr RJ, Buxton MG. Halo nevus or halo phenomenon? a study of 142 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:342-348.
- Zeff RA, Freitag A, Grin CM, et al. The immune response in halo nevi. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:620-624.
- Johnson DB, Ceilley RI. Basal cell carcinoma with annular leukoderma mimicking leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:352-353.
- Basak PY, Meric G, Ciris M. Basal cell carcinoma with halo phenomenon in a young female: significance of dermatoscopy in early diagnosis. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:214.
- Pembroke AC, Liddell K. Basal cell epithelioma with a hypopigmented halo. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:317.
- Rustemeyer J, Günther L, Deichert L. A rare association: basal cell carcinoma in a vitiliginous macula. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;15:175-177.
- Naveh HP, Rao UN, Butterfield LH. Melanoma‐associated leukoderma—immunology in black and white? Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013;26:796-804.
- Zhou H, Wu L-C, Chen M-K, et al. Factors associated with development of vitiligo in patients with halo nevus. Chinese Med J. 2017;130:2703.
- Ezzedine K, Diallo A, Léauté‐Labrèze C, et al. Halo naevi and leukotrichia are strong predictors of the passage to mixed vitiligo in a subgroup of segmental vitiligo. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:539-544.
- Nading MA, Nanney LB, Ellis DL. Pregnancy and estrogen receptor β expression in a large congenital nevus. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:691-694.
- Mooney MA, Barr RJ, Buxton MG. Halo nevus or halo phenomenon? a study of 142 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:342-348.
- Zeff RA, Freitag A, Grin CM, et al. The immune response in halo nevi. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:620-624.
- Johnson DB, Ceilley RI. Basal cell carcinoma with annular leukoderma mimicking leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum. Arch Dermatol. 1980;116:352-353.
- Basak PY, Meric G, Ciris M. Basal cell carcinoma with halo phenomenon in a young female: significance of dermatoscopy in early diagnosis. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:214.
- Pembroke AC, Liddell K. Basal cell epithelioma with a hypopigmented halo. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:317.
- Rustemeyer J, Günther L, Deichert L. A rare association: basal cell carcinoma in a vitiliginous macula. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;15:175-177.
- Naveh HP, Rao UN, Butterfield LH. Melanoma‐associated leukoderma—immunology in black and white? Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013;26:796-804.
- Zhou H, Wu L-C, Chen M-K, et al. Factors associated with development of vitiligo in patients with halo nevus. Chinese Med J. 2017;130:2703.
- Ezzedine K, Diallo A, Léauté‐Labrèze C, et al. Halo naevi and leukotrichia are strong predictors of the passage to mixed vitiligo in a subgroup of segmental vitiligo. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:539-544.
- Nading MA, Nanney LB, Ellis DL. Pregnancy and estrogen receptor β expression in a large congenital nevus. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145:691-694.
Practice Points
- Annular leukoderma, or the halo phenomenon, is a circular reaction of hypopigmentation that more commonly is associated with benign processes such as halo nevi.
- The halo phenomenon may accompany malignant processes, such as nonmelanoma skin cancer. Careful consideration of lesion time course and atypia is imperative for proper clinical suspicion in such cases.