User login
Postherpetic Pink, Smooth, Annular Convalescing Plaques
The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
A biopsy of a lesion on the right flank demonstrated granulomatous inflammation and interstitial mucin (Figure), characteristic of granuloma annulare (GA).1,2 Granuloma annulare is a relatively common skin disorder with an unknown etiology. It typically presents as smooth, annular, erythematous plaques.1 The most common variants of GA are localized, generalized, and subcutaneous. Our case demonstrated Wolf isotopic response, an unrelated skin disease that forms at the same location as a previously healed skin lesion.2 It is important to be aware of this phenomenon so that it is not confused with a recurrence of herpes zoster virus (HZV).
Although relatively infrequent, GA is the most common isotopic response following HZV infections.3-5 Other postherpetic isotopic eruptions include cutaneous malignancies, lichen planus, sarcoidosis, morphea, reactive perforating collagenosis, psoriasis, and infections, among others.3,5,6 The time between HZV infection and GA can be variable, ranging from a few weeks to many years apart.3
Oftentimes GA will spontaneously resolve within 2 years; however, recurrence is common.7-9 There currently are no standard treatment guidelines. The most promising treatment options include intralesional or topical glucocorticoids for localized GA as well as phototherapy or hydroxychloroquine for widespread disease.8,10

Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (also called actinic granuloma) is a rare idiopathic inflammatory skin disease. It is characterized by erythematous annular papules or plaques mainly found on sun-exposed skin, such as the backs of the hands, forearms, or face.11,12 Therefore, based on the distribution of our patient’s lesions, annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma was an unlikely diagnosis. Furthermore, it is not a known postherpetic isotopic reaction. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma can appear histologically similar to GA. Differentiating histologic features include a nonpalisading granuloma as well as the absence of mucin and necrobiosis.12
Annular lichen planus is a long-recognized but uncommon clinical variant of lichen planus that typically presents as pruritic, purple, annular plaques on the penis, scrotum, or intertriginous areas.13 The violaceous coloring is more characteristic of lichen planus. Histology is helpful in differentiating from GA.
Nummular eczema presents as scattered, welldefined, pruritic, erythematous, coin-shaped, coin-sized plaques in patients with diffusely dry skin.14 The scaling and serous crusting as well as more prominent pruritus help distinguish it from GA. The appearance of nummular eczema is quite characteristic; therefore, a biopsy typically is unnecessary for diagnosis. However, a potassium hydroxide wet mount examination of a skin scraping should be performed if tinea corporis also is suspected.
Superficial erythema annulare centrifugum classically presents as an annular or arciform pruritic lesion with an advancing outer erythematous edge with an inner rim of scale that most commonly occurs on the lower extremities. 15 The presence of pruritus and trailing scale helps distinguish this lesion from GA. Histologically, there are epidermal changes of hyperplasia, spongiosis, and parakeratosis, as well as lymphohistiocytic infiltrate surrounding the superficial dermal vessels.16
We report this case to highlight GA as the most common postherpetic isotopic response. It should be on the differential diagnosis when a patient presents with erythematous, smooth, annular plaques occurring in the distribution of a resolved case of HZV.
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: clinical and histologic variants, epidemiology, and genetics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:457-465.
- . Wolf R, Brenner S, Ruocco V, et al. Isotopic response. Int J Dermatol. 1995;34:341-348.
- Kapoor R, Piris A, Saavedra AP, et al. Wolf isotopic response manifesting as postherpetic granuloma annulare: a case series. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:255-258.
- Ezra N, Ahdout J, Haley JC, et al. Granuloma annulare in a zoster scar of a patient with multiple myeloma. Cutis. 2011;87:240-244.
- Noh TW, Park SH, Kang YS, et al. Morphea developing at the site of healed herpes zoster. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:242-245.
- Ruocco V, Ruocco E, Ghersetich I, et al. Isotopic response after herpesvirus infection: an update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:90-94.
- Sparrow G, Abell E. Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica treated by jet injector. Br J Dermatol. 1975;93:85-89.
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: pathogenesis, disease associations and triggers, and therapeutic options. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:467-479.
- Thornsberry LA, English JC. Etiology, diagnosis, and therapeutic management of granuloma annulare: an update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:279-290.
- Rubin CB, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: a retrospective series of 133 patients. Cutis. 2019;103:102-106.
- Stein JA, Fangman B, Strober B. Actinic granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:19.
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456.
- Reich HL, Nguyen JT, James WD. Annular lichen planus: a case series of 20 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:595-599.
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Nummular eczema: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:146-155.
- Weyers W, Diaz-Cascajo C, Weyers I. Erythema annulare centrifugum: results of a clinicopathologic study of 73 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:451-462.
- Coronel-Pérez IM, Morillo-Andújar M. Erythema annulare centrifugum responding to natural ultraviolet light [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:177-178.
The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
A biopsy of a lesion on the right flank demonstrated granulomatous inflammation and interstitial mucin (Figure), characteristic of granuloma annulare (GA).1,2 Granuloma annulare is a relatively common skin disorder with an unknown etiology. It typically presents as smooth, annular, erythematous plaques.1 The most common variants of GA are localized, generalized, and subcutaneous. Our case demonstrated Wolf isotopic response, an unrelated skin disease that forms at the same location as a previously healed skin lesion.2 It is important to be aware of this phenomenon so that it is not confused with a recurrence of herpes zoster virus (HZV).
Although relatively infrequent, GA is the most common isotopic response following HZV infections.3-5 Other postherpetic isotopic eruptions include cutaneous malignancies, lichen planus, sarcoidosis, morphea, reactive perforating collagenosis, psoriasis, and infections, among others.3,5,6 The time between HZV infection and GA can be variable, ranging from a few weeks to many years apart.3
Oftentimes GA will spontaneously resolve within 2 years; however, recurrence is common.7-9 There currently are no standard treatment guidelines. The most promising treatment options include intralesional or topical glucocorticoids for localized GA as well as phototherapy or hydroxychloroquine for widespread disease.8,10

Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (also called actinic granuloma) is a rare idiopathic inflammatory skin disease. It is characterized by erythematous annular papules or plaques mainly found on sun-exposed skin, such as the backs of the hands, forearms, or face.11,12 Therefore, based on the distribution of our patient’s lesions, annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma was an unlikely diagnosis. Furthermore, it is not a known postherpetic isotopic reaction. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma can appear histologically similar to GA. Differentiating histologic features include a nonpalisading granuloma as well as the absence of mucin and necrobiosis.12
Annular lichen planus is a long-recognized but uncommon clinical variant of lichen planus that typically presents as pruritic, purple, annular plaques on the penis, scrotum, or intertriginous areas.13 The violaceous coloring is more characteristic of lichen planus. Histology is helpful in differentiating from GA.
Nummular eczema presents as scattered, welldefined, pruritic, erythematous, coin-shaped, coin-sized plaques in patients with diffusely dry skin.14 The scaling and serous crusting as well as more prominent pruritus help distinguish it from GA. The appearance of nummular eczema is quite characteristic; therefore, a biopsy typically is unnecessary for diagnosis. However, a potassium hydroxide wet mount examination of a skin scraping should be performed if tinea corporis also is suspected.
Superficial erythema annulare centrifugum classically presents as an annular or arciform pruritic lesion with an advancing outer erythematous edge with an inner rim of scale that most commonly occurs on the lower extremities. 15 The presence of pruritus and trailing scale helps distinguish this lesion from GA. Histologically, there are epidermal changes of hyperplasia, spongiosis, and parakeratosis, as well as lymphohistiocytic infiltrate surrounding the superficial dermal vessels.16
We report this case to highlight GA as the most common postherpetic isotopic response. It should be on the differential diagnosis when a patient presents with erythematous, smooth, annular plaques occurring in the distribution of a resolved case of HZV.
The Diagnosis: Granuloma Annulare
A biopsy of a lesion on the right flank demonstrated granulomatous inflammation and interstitial mucin (Figure), characteristic of granuloma annulare (GA).1,2 Granuloma annulare is a relatively common skin disorder with an unknown etiology. It typically presents as smooth, annular, erythematous plaques.1 The most common variants of GA are localized, generalized, and subcutaneous. Our case demonstrated Wolf isotopic response, an unrelated skin disease that forms at the same location as a previously healed skin lesion.2 It is important to be aware of this phenomenon so that it is not confused with a recurrence of herpes zoster virus (HZV).
Although relatively infrequent, GA is the most common isotopic response following HZV infections.3-5 Other postherpetic isotopic eruptions include cutaneous malignancies, lichen planus, sarcoidosis, morphea, reactive perforating collagenosis, psoriasis, and infections, among others.3,5,6 The time between HZV infection and GA can be variable, ranging from a few weeks to many years apart.3
Oftentimes GA will spontaneously resolve within 2 years; however, recurrence is common.7-9 There currently are no standard treatment guidelines. The most promising treatment options include intralesional or topical glucocorticoids for localized GA as well as phototherapy or hydroxychloroquine for widespread disease.8,10

Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (also called actinic granuloma) is a rare idiopathic inflammatory skin disease. It is characterized by erythematous annular papules or plaques mainly found on sun-exposed skin, such as the backs of the hands, forearms, or face.11,12 Therefore, based on the distribution of our patient’s lesions, annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma was an unlikely diagnosis. Furthermore, it is not a known postherpetic isotopic reaction. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma can appear histologically similar to GA. Differentiating histologic features include a nonpalisading granuloma as well as the absence of mucin and necrobiosis.12
Annular lichen planus is a long-recognized but uncommon clinical variant of lichen planus that typically presents as pruritic, purple, annular plaques on the penis, scrotum, or intertriginous areas.13 The violaceous coloring is more characteristic of lichen planus. Histology is helpful in differentiating from GA.
Nummular eczema presents as scattered, welldefined, pruritic, erythematous, coin-shaped, coin-sized plaques in patients with diffusely dry skin.14 The scaling and serous crusting as well as more prominent pruritus help distinguish it from GA. The appearance of nummular eczema is quite characteristic; therefore, a biopsy typically is unnecessary for diagnosis. However, a potassium hydroxide wet mount examination of a skin scraping should be performed if tinea corporis also is suspected.
Superficial erythema annulare centrifugum classically presents as an annular or arciform pruritic lesion with an advancing outer erythematous edge with an inner rim of scale that most commonly occurs on the lower extremities. 15 The presence of pruritus and trailing scale helps distinguish this lesion from GA. Histologically, there are epidermal changes of hyperplasia, spongiosis, and parakeratosis, as well as lymphohistiocytic infiltrate surrounding the superficial dermal vessels.16
We report this case to highlight GA as the most common postherpetic isotopic response. It should be on the differential diagnosis when a patient presents with erythematous, smooth, annular plaques occurring in the distribution of a resolved case of HZV.
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: clinical and histologic variants, epidemiology, and genetics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:457-465.
- . Wolf R, Brenner S, Ruocco V, et al. Isotopic response. Int J Dermatol. 1995;34:341-348.
- Kapoor R, Piris A, Saavedra AP, et al. Wolf isotopic response manifesting as postherpetic granuloma annulare: a case series. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:255-258.
- Ezra N, Ahdout J, Haley JC, et al. Granuloma annulare in a zoster scar of a patient with multiple myeloma. Cutis. 2011;87:240-244.
- Noh TW, Park SH, Kang YS, et al. Morphea developing at the site of healed herpes zoster. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:242-245.
- Ruocco V, Ruocco E, Ghersetich I, et al. Isotopic response after herpesvirus infection: an update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:90-94.
- Sparrow G, Abell E. Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica treated by jet injector. Br J Dermatol. 1975;93:85-89.
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: pathogenesis, disease associations and triggers, and therapeutic options. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:467-479.
- Thornsberry LA, English JC. Etiology, diagnosis, and therapeutic management of granuloma annulare: an update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:279-290.
- Rubin CB, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: a retrospective series of 133 patients. Cutis. 2019;103:102-106.
- Stein JA, Fangman B, Strober B. Actinic granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:19.
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456.
- Reich HL, Nguyen JT, James WD. Annular lichen planus: a case series of 20 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:595-599.
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Nummular eczema: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:146-155.
- Weyers W, Diaz-Cascajo C, Weyers I. Erythema annulare centrifugum: results of a clinicopathologic study of 73 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:451-462.
- Coronel-Pérez IM, Morillo-Andújar M. Erythema annulare centrifugum responding to natural ultraviolet light [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:177-178.
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: clinical and histologic variants, epidemiology, and genetics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:457-465.
- . Wolf R, Brenner S, Ruocco V, et al. Isotopic response. Int J Dermatol. 1995;34:341-348.
- Kapoor R, Piris A, Saavedra AP, et al. Wolf isotopic response manifesting as postherpetic granuloma annulare: a case series. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:255-258.
- Ezra N, Ahdout J, Haley JC, et al. Granuloma annulare in a zoster scar of a patient with multiple myeloma. Cutis. 2011;87:240-244.
- Noh TW, Park SH, Kang YS, et al. Morphea developing at the site of healed herpes zoster. Ann Dermatol. 2011;23:242-245.
- Ruocco V, Ruocco E, Ghersetich I, et al. Isotopic response after herpesvirus infection: an update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:90-94.
- Sparrow G, Abell E. Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica treated by jet injector. Br J Dermatol. 1975;93:85-89.
- Piette EW, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: pathogenesis, disease associations and triggers, and therapeutic options. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:467-479.
- Thornsberry LA, English JC. Etiology, diagnosis, and therapeutic management of granuloma annulare: an update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013;14:279-290.
- Rubin CB, Rosenbach M. Granuloma annulare: a retrospective series of 133 patients. Cutis. 2019;103:102-106.
- Stein JA, Fangman B, Strober B. Actinic granuloma. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:19.
- Mistry AM, Patel R, Mistry M, et al. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma. Cureus. 2020;12:E11456.
- Reich HL, Nguyen JT, James WD. Annular lichen planus: a case series of 20 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:595-599.
- Leung AKC, Lam JM, Leong KF, et al. Nummular eczema: an updated review. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2020;14:146-155.
- Weyers W, Diaz-Cascajo C, Weyers I. Erythema annulare centrifugum: results of a clinicopathologic study of 73 patients. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:451-462.
- Coronel-Pérez IM, Morillo-Andújar M. Erythema annulare centrifugum responding to natural ultraviolet light [in Spanish]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:177-178.
An 82-year-old man presented with painful, pink, smooth, annular convalescing plaques on the right back, flank, and abdomen in a zosteriform distribution involving the T10/11 dermatome. He had a history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus, and 12 months prior to presentation he had an outbreak of herpes zoster virus in the same distribution that was treated with valacyclovir 1000 mg 3 times daily for 7 days. Over the following month he noticed a resolution of blisters and crusting as they morphed into the current lesions.

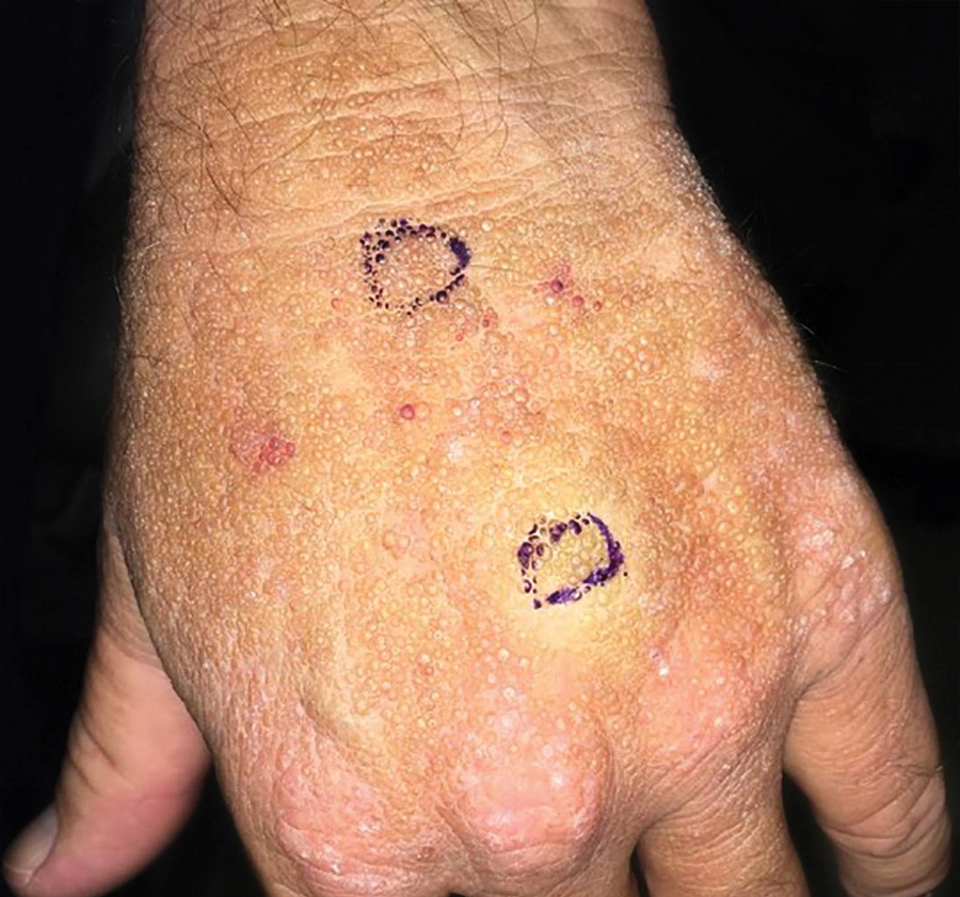
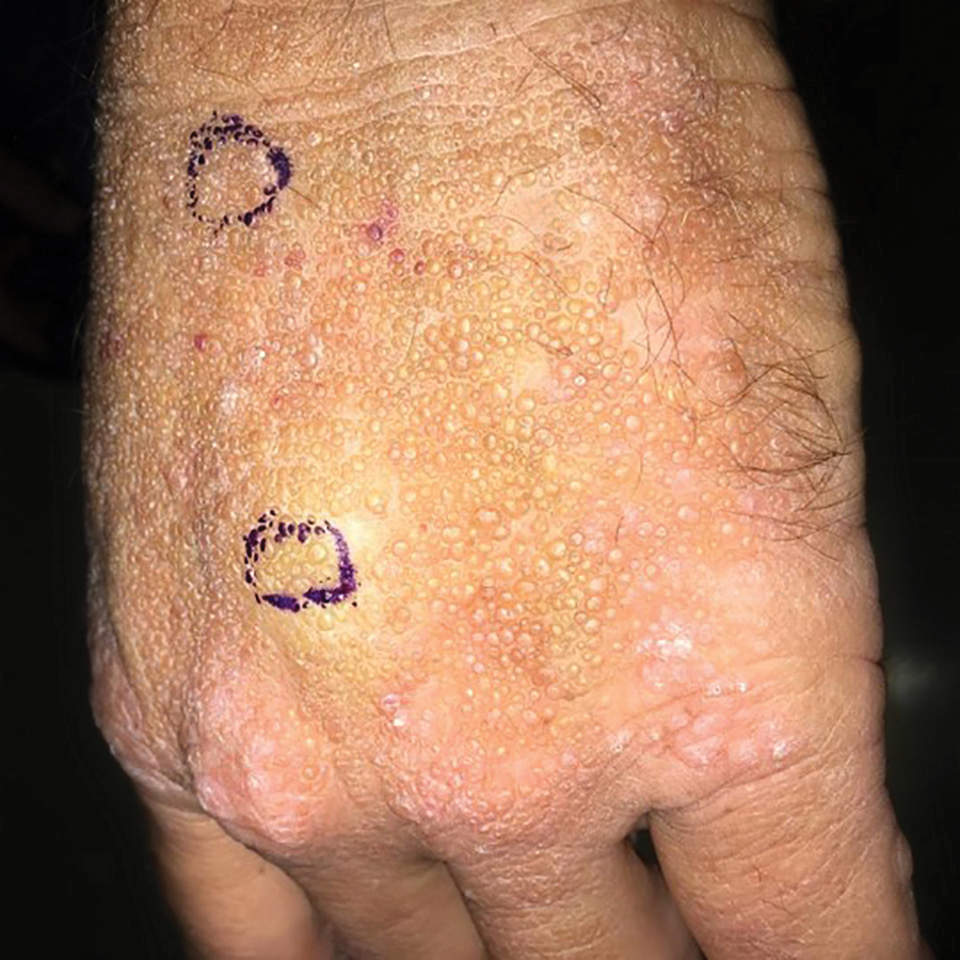
Smooth Papules on the Left Hand
The Diagnosis: Adult Colloid Milium
A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and histopathologic evaluation revealed collections of amorphic eosinophilic material and fissures in the papillary dermis with sparing of the dermoepidermal junction, indicating adult colloid milium (Figure 1).
Adult colloid milium is an uncommon condition with grouped translucent to whitish papules that present on sun-exposed skin on the hands, face, neck, or ears in middle-aged adults.1 It has been associated with petrochemical exposure, tanning bed use, and excessive sun exposure. Our patient had a history of sun exposure, specifically to the left hand while driving. This condition is widely thought to be a result of photoinduced damage to elastic fibers and may potentially be a popular variant of severe solar elastosis.2 Due to vascular fragility, trauma to these locations often will result in hemorrhage into individual lesions, as observed in our patient (Figure 2).
Adult colloid milium is diagnosed clinically and may mimic lichen or systemic amyloidosis, syringomas, lipoid proteinosis, molluscum contagiosum, steatocystoma multiplex, and sarcoidosis.2
Biopsy often is helpful in determining the diagnosis. Histopathology reveals amorphous eosinophilic deposits with fissures in the papillary dermis. These deposits are thought to be remnants of degenerated elastic fibers. Stains often are helpful, as the deposits are weakly apple-green birefringent on Congo red stain and are periodic acid-Schiff and thioflavin T positive. Laminin and type IV collagen stains are negative with adult colloid milium but are positive with amyloidosis and lipoid proteinosis.3 Electron microscopy also may help distinguish between amyloidosis and adult colloid milium, as these conditions may have a similar histologic appearance.
Treatment has not proven to be consistently helpful, as cryotherapy and dermabrasion have been the mainstay of treatment, often with disappointing results.4 Laser treatment has been shown to be of some benefit in treating these lesions.2
- Touart DM, Sau P. Cutaneous deposition diseases. part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2, pt 1):149-171.
- Pourrabbani S, Marra DE, Iwasaki J, et al. Colloid milium: a review and update. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:293-296.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2012.
- Netscher DT, Sharma S, Kinner BM, et al. Adult-type colloid milium of hands and face successfully treated with dermabrasion. South Med J. 1996;89:1004-1007.
The Diagnosis: Adult Colloid Milium
A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and histopathologic evaluation revealed collections of amorphic eosinophilic material and fissures in the papillary dermis with sparing of the dermoepidermal junction, indicating adult colloid milium (Figure 1).
Adult colloid milium is an uncommon condition with grouped translucent to whitish papules that present on sun-exposed skin on the hands, face, neck, or ears in middle-aged adults.1 It has been associated with petrochemical exposure, tanning bed use, and excessive sun exposure. Our patient had a history of sun exposure, specifically to the left hand while driving. This condition is widely thought to be a result of photoinduced damage to elastic fibers and may potentially be a popular variant of severe solar elastosis.2 Due to vascular fragility, trauma to these locations often will result in hemorrhage into individual lesions, as observed in our patient (Figure 2).
Adult colloid milium is diagnosed clinically and may mimic lichen or systemic amyloidosis, syringomas, lipoid proteinosis, molluscum contagiosum, steatocystoma multiplex, and sarcoidosis.2
Biopsy often is helpful in determining the diagnosis. Histopathology reveals amorphous eosinophilic deposits with fissures in the papillary dermis. These deposits are thought to be remnants of degenerated elastic fibers. Stains often are helpful, as the deposits are weakly apple-green birefringent on Congo red stain and are periodic acid-Schiff and thioflavin T positive. Laminin and type IV collagen stains are negative with adult colloid milium but are positive with amyloidosis and lipoid proteinosis.3 Electron microscopy also may help distinguish between amyloidosis and adult colloid milium, as these conditions may have a similar histologic appearance.
Treatment has not proven to be consistently helpful, as cryotherapy and dermabrasion have been the mainstay of treatment, often with disappointing results.4 Laser treatment has been shown to be of some benefit in treating these lesions.2
The Diagnosis: Adult Colloid Milium
A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and histopathologic evaluation revealed collections of amorphic eosinophilic material and fissures in the papillary dermis with sparing of the dermoepidermal junction, indicating adult colloid milium (Figure 1).
Adult colloid milium is an uncommon condition with grouped translucent to whitish papules that present on sun-exposed skin on the hands, face, neck, or ears in middle-aged adults.1 It has been associated with petrochemical exposure, tanning bed use, and excessive sun exposure. Our patient had a history of sun exposure, specifically to the left hand while driving. This condition is widely thought to be a result of photoinduced damage to elastic fibers and may potentially be a popular variant of severe solar elastosis.2 Due to vascular fragility, trauma to these locations often will result in hemorrhage into individual lesions, as observed in our patient (Figure 2).
Adult colloid milium is diagnosed clinically and may mimic lichen or systemic amyloidosis, syringomas, lipoid proteinosis, molluscum contagiosum, steatocystoma multiplex, and sarcoidosis.2
Biopsy often is helpful in determining the diagnosis. Histopathology reveals amorphous eosinophilic deposits with fissures in the papillary dermis. These deposits are thought to be remnants of degenerated elastic fibers. Stains often are helpful, as the deposits are weakly apple-green birefringent on Congo red stain and are periodic acid-Schiff and thioflavin T positive. Laminin and type IV collagen stains are negative with adult colloid milium but are positive with amyloidosis and lipoid proteinosis.3 Electron microscopy also may help distinguish between amyloidosis and adult colloid milium, as these conditions may have a similar histologic appearance.
Treatment has not proven to be consistently helpful, as cryotherapy and dermabrasion have been the mainstay of treatment, often with disappointing results.4 Laser treatment has been shown to be of some benefit in treating these lesions.2
- Touart DM, Sau P. Cutaneous deposition diseases. part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2, pt 1):149-171.
- Pourrabbani S, Marra DE, Iwasaki J, et al. Colloid milium: a review and update. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:293-296.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2012.
- Netscher DT, Sharma S, Kinner BM, et al. Adult-type colloid milium of hands and face successfully treated with dermabrasion. South Med J. 1996;89:1004-1007.
- Touart DM, Sau P. Cutaneous deposition diseases. part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(2, pt 1):149-171.
- Pourrabbani S, Marra DE, Iwasaki J, et al. Colloid milium: a review and update. J Drugs Dermatol. 2007;6:293-296.
- Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar A, et al. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2012.
- Netscher DT, Sharma S, Kinner BM, et al. Adult-type colloid milium of hands and face successfully treated with dermabrasion. South Med J. 1996;89:1004-1007.
A 41-year-old man presented to the outpatient dermatology clinic with multiple smooth papules on the left hand of 7 years' duration. The papules had been steadily increasing in number, and the patient reported that they were frequently symptomatic with a burning itching sensation. Physical examination revealed multiple 1- to 3-mm, dome-shaped, translucent to flesh-colored papules on the left hand with a few scattered bright red papules. No similar lesions were present on the right hand or elsewhere on the body. He had a history of hypertension but was otherwise healthy with no other chronic medical conditions.