User login
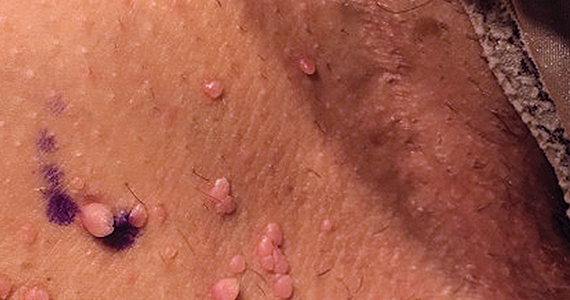
Can you identify these numerous papules in the groin area?
Condylomata acuminata
Condylomata acuminata (CA), or anogenital warts, are the cutaneous manifestation of infection by human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted primarily via sexual contact with infected skin or mucosa, although it also may result from nonsexual contact or vertical transmission during vaginal delivery.1 More than 200 types of HPV have been identified; however, genotypes 6 and 11 are most commonly implicated in the development of CA and are associated with a low risk for oncogenesis. Nevertheless, CA pose a tremendous economic and psychological burden on the health care system and those affected, respectively, representing the most common sexually transmitted viral disease in the United States.2
Clinical presentation
CA present as discrete or clustered smooth, papillomatous, sessile, exophytic papules or plaques, often lacking the thick, horny scale seen in common warts, and they may be broad based or pedunculated.2 The anogenital region is affected, including the external genitalia, perineum, perianal area, and adjacent skin such as the mons pubis and inguinal folds. Extension into the urethra or vaginal, cervical, and anal canals is possible, although rarely beyond the dentate line.2,3 Lesions typically are asymptomatic but may be extensive or disfiguring, often noticed by patients upon self-inspection and leading to significant distress. Symptoms such as pruritus, pain, bleeding, or discharge may develop in traumatized or secondarily infected lesions.1,3
Diagnosis
Although CA can be diagnosed clinically, biopsy facilitates definitive diagnosis in less clear-cut cases.1,3 Histologically, CA are characterized by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis, with the presence of koilocytes in the epidermis.2
Treatment
Treatment of CA is challenging, as there are currently no antiviral therapies available to cure the condition. Treatment options include destructive, immunomodulatory, and antiproliferative therapies, either alone or in combination. There is no first-line therapy indicated for CA, and treatment selection is dependent on multiple patient-specific factors, including the size, number, and anatomic location of the lesions, as well as ease of treatment and adverse effects.2
Topical therapies. For external CA, there are several treatments that may be applied by patients themselves, including topical podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, and sinecatechins (TABLE).1 Podophyllotoxin (brand name Condylox) is an antiproliferative agent available as a 0.15% cream or 0.5% solution.1,2 It should be applied twice daily for 3 consecutive days per week for up to 4 weeks. Podophyllotoxin is contraindicated in pregnancy and may cause local irritation.2
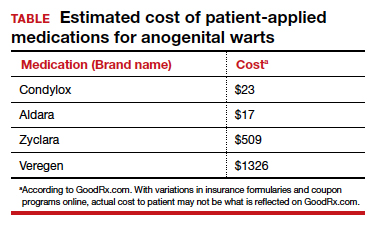
Imiquimod (brand names Aldara and Zyclara) is an immunomodulatory, available as a 5% and 3.75% cream. For external genital warts, the cream should be applied 3 times per week for up to 16 weeks; for perianal warts it should be applied daily for up to 8 weeks. Adverse effects of imiquimod include local irritation and systemic flu-like symptoms and are prominent with the 3.75% formulation, reducing adherence.1,2,4
In-office treatment options include cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid (TCA), intralesional immunotherapy, laser therapy, phototherapy, and surgical options.2 Liquid nitrogen is cost-effective, efficacious, and safe for use in pregnancy; it is used in 2 to 3 freeze/thaw cycles per cryotherapy session to induce cellular damage.1,2 Its disadvantages include adverse effects, such as blistering, ulceration, dyspigmentation, and scarring. In addition, subclinical lesions in adjacent skin are not addressed during treatment.2
TCA is a caustic agent applied in the office once weekly or every 2 to 3 weeks for a maximum of 3 to 4 months, with similar benefits to cryotherapy in terms of ease of application and safety in pregnancy. There is the risk of blistering and ulceration in treated lesions as well as in inadvertently treated adjacent skin.1
Intralesional immunotherapy with Candida antigen (brand name Candin) is used in 3 sessions 4 to 6 weeks apart and is safe, with minimal adverse effects.2
Laser therapy treatment options include carbon dioxide laser therapy and ND:YAG laser. Their use is limited, however, by availability and cost.1,2
CA may be removed surgically via shave excision, scissor excision, curettage, and electrosurgery. These procedures can be painful, however, requiring local anesthesia and having a prolonged healing course.1,2
CA recurrence
CA unfortunately has a high rate of recurrence despite treatment, and patients require extensive counseling. Patients should be screened for other sexually transmitted infections and advised to notify their sexual partners. If followed properly, safe sexual practices, including condom use and limiting sexual partners, may prevent further transmission.1 The quadrivalent HPV vaccine (effective for the prevention of infection with HPV genotypes 6, 11, 16, and 18 in unexposed individuals) is ineffective in treating patients with pre-existing CA but can protect against the acquisition of other HPV genotypes included in the vaccine.1,5
Arriving at the diagnosis
Acrochordons are a common skin finding in the groin, but the onset is more gradual and the individual lesions tend to be more pedunculated. Molluscum is also on the differential and can affect the genitalia. Molluscum lesions have a characteristic central dimple or dell, which is absent in CA.
CASE Treatment course
The patient was treated with successive sessions of cryotherapy in combination with a course of topical imiquimod followed by several injections with Candida antigen, with persistence of some lesions as well as recurrence.
- Steben M, Garland SM. Genital warts. Best Prac Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;28:1063-1073.
- Fathi R, Tsoukas MM. Genital warts and other HPV infections: established and novel therapies. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:299-306.
- Lynde C, Vender R, Bourcier M, et al. Clinical features of external genital warts. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17 (suppl 2):S55-60.
- Scheinfeld N. Update on the treatment of genital warts. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:18559.
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007;56:1-24.
Condylomata acuminata
Condylomata acuminata (CA), or anogenital warts, are the cutaneous manifestation of infection by human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted primarily via sexual contact with infected skin or mucosa, although it also may result from nonsexual contact or vertical transmission during vaginal delivery.1 More than 200 types of HPV have been identified; however, genotypes 6 and 11 are most commonly implicated in the development of CA and are associated with a low risk for oncogenesis. Nevertheless, CA pose a tremendous economic and psychological burden on the health care system and those affected, respectively, representing the most common sexually transmitted viral disease in the United States.2
Clinical presentation
CA present as discrete or clustered smooth, papillomatous, sessile, exophytic papules or plaques, often lacking the thick, horny scale seen in common warts, and they may be broad based or pedunculated.2 The anogenital region is affected, including the external genitalia, perineum, perianal area, and adjacent skin such as the mons pubis and inguinal folds. Extension into the urethra or vaginal, cervical, and anal canals is possible, although rarely beyond the dentate line.2,3 Lesions typically are asymptomatic but may be extensive or disfiguring, often noticed by patients upon self-inspection and leading to significant distress. Symptoms such as pruritus, pain, bleeding, or discharge may develop in traumatized or secondarily infected lesions.1,3
Diagnosis
Although CA can be diagnosed clinically, biopsy facilitates definitive diagnosis in less clear-cut cases.1,3 Histologically, CA are characterized by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis, with the presence of koilocytes in the epidermis.2
Treatment
Treatment of CA is challenging, as there are currently no antiviral therapies available to cure the condition. Treatment options include destructive, immunomodulatory, and antiproliferative therapies, either alone or in combination. There is no first-line therapy indicated for CA, and treatment selection is dependent on multiple patient-specific factors, including the size, number, and anatomic location of the lesions, as well as ease of treatment and adverse effects.2
Topical therapies. For external CA, there are several treatments that may be applied by patients themselves, including topical podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, and sinecatechins (TABLE).1 Podophyllotoxin (brand name Condylox) is an antiproliferative agent available as a 0.15% cream or 0.5% solution.1,2 It should be applied twice daily for 3 consecutive days per week for up to 4 weeks. Podophyllotoxin is contraindicated in pregnancy and may cause local irritation.2

Imiquimod (brand names Aldara and Zyclara) is an immunomodulatory, available as a 5% and 3.75% cream. For external genital warts, the cream should be applied 3 times per week for up to 16 weeks; for perianal warts it should be applied daily for up to 8 weeks. Adverse effects of imiquimod include local irritation and systemic flu-like symptoms and are prominent with the 3.75% formulation, reducing adherence.1,2,4
In-office treatment options include cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid (TCA), intralesional immunotherapy, laser therapy, phototherapy, and surgical options.2 Liquid nitrogen is cost-effective, efficacious, and safe for use in pregnancy; it is used in 2 to 3 freeze/thaw cycles per cryotherapy session to induce cellular damage.1,2 Its disadvantages include adverse effects, such as blistering, ulceration, dyspigmentation, and scarring. In addition, subclinical lesions in adjacent skin are not addressed during treatment.2
TCA is a caustic agent applied in the office once weekly or every 2 to 3 weeks for a maximum of 3 to 4 months, with similar benefits to cryotherapy in terms of ease of application and safety in pregnancy. There is the risk of blistering and ulceration in treated lesions as well as in inadvertently treated adjacent skin.1
Intralesional immunotherapy with Candida antigen (brand name Candin) is used in 3 sessions 4 to 6 weeks apart and is safe, with minimal adverse effects.2
Laser therapy treatment options include carbon dioxide laser therapy and ND:YAG laser. Their use is limited, however, by availability and cost.1,2
CA may be removed surgically via shave excision, scissor excision, curettage, and electrosurgery. These procedures can be painful, however, requiring local anesthesia and having a prolonged healing course.1,2
CA recurrence
CA unfortunately has a high rate of recurrence despite treatment, and patients require extensive counseling. Patients should be screened for other sexually transmitted infections and advised to notify their sexual partners. If followed properly, safe sexual practices, including condom use and limiting sexual partners, may prevent further transmission.1 The quadrivalent HPV vaccine (effective for the prevention of infection with HPV genotypes 6, 11, 16, and 18 in unexposed individuals) is ineffective in treating patients with pre-existing CA but can protect against the acquisition of other HPV genotypes included in the vaccine.1,5
Arriving at the diagnosis
Acrochordons are a common skin finding in the groin, but the onset is more gradual and the individual lesions tend to be more pedunculated. Molluscum is also on the differential and can affect the genitalia. Molluscum lesions have a characteristic central dimple or dell, which is absent in CA.
CASE Treatment course
The patient was treated with successive sessions of cryotherapy in combination with a course of topical imiquimod followed by several injections with Candida antigen, with persistence of some lesions as well as recurrence.
Condylomata acuminata
Condylomata acuminata (CA), or anogenital warts, are the cutaneous manifestation of infection by human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted primarily via sexual contact with infected skin or mucosa, although it also may result from nonsexual contact or vertical transmission during vaginal delivery.1 More than 200 types of HPV have been identified; however, genotypes 6 and 11 are most commonly implicated in the development of CA and are associated with a low risk for oncogenesis. Nevertheless, CA pose a tremendous economic and psychological burden on the health care system and those affected, respectively, representing the most common sexually transmitted viral disease in the United States.2
Clinical presentation
CA present as discrete or clustered smooth, papillomatous, sessile, exophytic papules or plaques, often lacking the thick, horny scale seen in common warts, and they may be broad based or pedunculated.2 The anogenital region is affected, including the external genitalia, perineum, perianal area, and adjacent skin such as the mons pubis and inguinal folds. Extension into the urethra or vaginal, cervical, and anal canals is possible, although rarely beyond the dentate line.2,3 Lesions typically are asymptomatic but may be extensive or disfiguring, often noticed by patients upon self-inspection and leading to significant distress. Symptoms such as pruritus, pain, bleeding, or discharge may develop in traumatized or secondarily infected lesions.1,3
Diagnosis
Although CA can be diagnosed clinically, biopsy facilitates definitive diagnosis in less clear-cut cases.1,3 Histologically, CA are characterized by hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis, with the presence of koilocytes in the epidermis.2
Treatment
Treatment of CA is challenging, as there are currently no antiviral therapies available to cure the condition. Treatment options include destructive, immunomodulatory, and antiproliferative therapies, either alone or in combination. There is no first-line therapy indicated for CA, and treatment selection is dependent on multiple patient-specific factors, including the size, number, and anatomic location of the lesions, as well as ease of treatment and adverse effects.2
Topical therapies. For external CA, there are several treatments that may be applied by patients themselves, including topical podophyllotoxin, imiquimod, and sinecatechins (TABLE).1 Podophyllotoxin (brand name Condylox) is an antiproliferative agent available as a 0.15% cream or 0.5% solution.1,2 It should be applied twice daily for 3 consecutive days per week for up to 4 weeks. Podophyllotoxin is contraindicated in pregnancy and may cause local irritation.2

Imiquimod (brand names Aldara and Zyclara) is an immunomodulatory, available as a 5% and 3.75% cream. For external genital warts, the cream should be applied 3 times per week for up to 16 weeks; for perianal warts it should be applied daily for up to 8 weeks. Adverse effects of imiquimod include local irritation and systemic flu-like symptoms and are prominent with the 3.75% formulation, reducing adherence.1,2,4
In-office treatment options include cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid (TCA), intralesional immunotherapy, laser therapy, phototherapy, and surgical options.2 Liquid nitrogen is cost-effective, efficacious, and safe for use in pregnancy; it is used in 2 to 3 freeze/thaw cycles per cryotherapy session to induce cellular damage.1,2 Its disadvantages include adverse effects, such as blistering, ulceration, dyspigmentation, and scarring. In addition, subclinical lesions in adjacent skin are not addressed during treatment.2
TCA is a caustic agent applied in the office once weekly or every 2 to 3 weeks for a maximum of 3 to 4 months, with similar benefits to cryotherapy in terms of ease of application and safety in pregnancy. There is the risk of blistering and ulceration in treated lesions as well as in inadvertently treated adjacent skin.1
Intralesional immunotherapy with Candida antigen (brand name Candin) is used in 3 sessions 4 to 6 weeks apart and is safe, with minimal adverse effects.2
Laser therapy treatment options include carbon dioxide laser therapy and ND:YAG laser. Their use is limited, however, by availability and cost.1,2
CA may be removed surgically via shave excision, scissor excision, curettage, and electrosurgery. These procedures can be painful, however, requiring local anesthesia and having a prolonged healing course.1,2
CA recurrence
CA unfortunately has a high rate of recurrence despite treatment, and patients require extensive counseling. Patients should be screened for other sexually transmitted infections and advised to notify their sexual partners. If followed properly, safe sexual practices, including condom use and limiting sexual partners, may prevent further transmission.1 The quadrivalent HPV vaccine (effective for the prevention of infection with HPV genotypes 6, 11, 16, and 18 in unexposed individuals) is ineffective in treating patients with pre-existing CA but can protect against the acquisition of other HPV genotypes included in the vaccine.1,5
Arriving at the diagnosis
Acrochordons are a common skin finding in the groin, but the onset is more gradual and the individual lesions tend to be more pedunculated. Molluscum is also on the differential and can affect the genitalia. Molluscum lesions have a characteristic central dimple or dell, which is absent in CA.
CASE Treatment course
The patient was treated with successive sessions of cryotherapy in combination with a course of topical imiquimod followed by several injections with Candida antigen, with persistence of some lesions as well as recurrence.
- Steben M, Garland SM. Genital warts. Best Prac Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;28:1063-1073.
- Fathi R, Tsoukas MM. Genital warts and other HPV infections: established and novel therapies. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:299-306.
- Lynde C, Vender R, Bourcier M, et al. Clinical features of external genital warts. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17 (suppl 2):S55-60.
- Scheinfeld N. Update on the treatment of genital warts. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:18559.
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007;56:1-24.
- Steben M, Garland SM. Genital warts. Best Prac Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2014;28:1063-1073.
- Fathi R, Tsoukas MM. Genital warts and other HPV infections: established and novel therapies. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:299-306.
- Lynde C, Vender R, Bourcier M, et al. Clinical features of external genital warts. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17 (suppl 2):S55-60.
- Scheinfeld N. Update on the treatment of genital warts. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:18559.
- Markowitz LE, Dunne EF, Saraiya M, et al; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus Vaccine: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2007;56:1-24.
CASE Skin tags on the groin
A 47-year-old woman with no personal history of skin cancer presents to a dermatologist for annual skin surveillance examination. She notes multiple “pink skin tags” on the groin, present for 4 months. She says they are asymptomatic and have not been treated previously. She states that she is in a long-term monogamous relationship. Physical examination reveals multiple smooth, flat-topped, pedunculated pink papules on the bilateral upper inner thighs. Shave biopsy of a lesion on the right upper medial thigh is performed to aid in diagnosis (FIGURE 1).
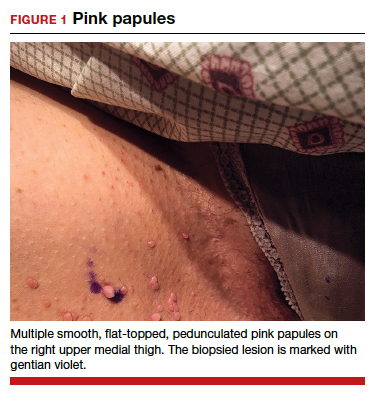
Persistent vulvar itch: What is the diagnosis?
Genital lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is an inflammatory skin condition that develops secondary to persistent rubbing or scratching of skin. Although LSC can occur anywhere on the body, genital LSC develops in association with genital itch, with the itch often described as intense and unrelenting. The itching sensation leads to scratching and rubbing of the area, which can provide temporary symptomatic relief.1,2 However, this action of rubbing and scratching stimulates local cutaneous nerves, inducing an even more intense itch sensation. This process, identified as the ‘itch-scratch cycle,’ plays a prominent role in all cases of LSC.1
On physical examination LSC appears as poorly defined, pink to red plaques with accentuated skin markings on bilateral labia majora. Less commonly, it can present as asymmetrical or unilateral plaques.3 LSC can extend onto labia minora, mons pubis, and medial thighs. However, the vagina is spared.1 Excoriations, marked by their geometric, angular appearance, often can be appreciated overlying plaques of LSC. Additionally, crusting, scale, broken hairs, hyperpigmentation, and scarring may be seen in LSC.2
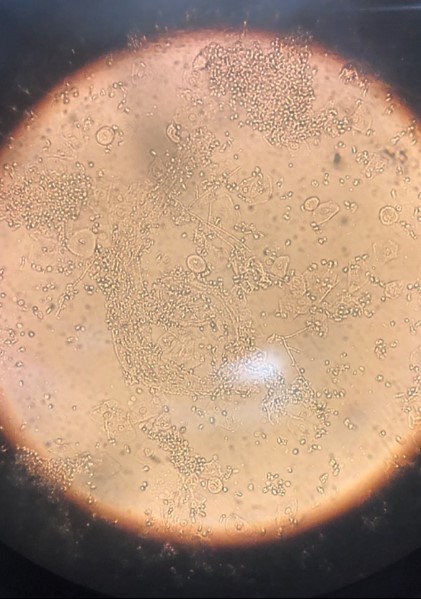
In this case, white discharge was noted on vaginal examination, which was suspicious for vaginal candidiasis. Wet mount examination revealed multiple candida hyphae and spores (FIGURE 2), confirming vaginal candidiasis. This vulvovaginal fungal infection caused persistent vulvar pruritus, with subsequent development of LSC due to prolonged scratching. The patient was treated with both oral fluconazole and topical mometasone ointment, for vaginal candidiasis and vulvar LSC, respectively. Mometasone ointment is categorized as a class II (high potency) topical steroid. However, it is worth noting that mometasone cream is categorized as a class IV (medium potency) topical steroid.
FIGURE 2 Wet mount of vaginal discharge, revealing candida hyphae and spores
Treatment
Successful treatment of LSC requires addressing 4 elements, including recognizing and treating the underlying etiology, restoring barrier function, reducing inflammation, and interrupting the itch-scratch cycle.3
Identifying the underlying etiology. Knowing the etiology of vulvar pruritus is a key step in resolution of the condition because LSC is driven by repetitive rubbing and scratching behaviors in response to the itch. The differential diagnosis for vulvar pruritus is broad. Evaluation and workup should be tailored to suit each unique patient presentation. A review of past medical history and full-body skin examination can identify a contributing inflammatory skin disease, such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus, or autoimmune vesiculobullous disease (pemphigus).1,2 Careful review of products applied in the genital area can reveal an underlying irritant or allergic contact dermatitis. Scented soap or detergent commonly cause vulvar dermatitis.1 A speculum examination may suggest inflammatory vaginitis or atrophic vaginitis (genitourinary syndrome of menopause); run off of vaginal discharge onto the vulvar skin can result in vulvar pruritus. Vaginal wet mount can diagnose vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomonas infection, and bacterial vaginitis.1 A skin scraping with mineral oil or potassium hydroxide can suggest scabies infestation or cutaneous dermatophyte infection, respectively.2 Treatment of vulvar pruritus should be initiated based on diagnosis.
Restoring barrier function. The repetitive scratching and rubbing behaviors disrupt the cutaneous barrier layer and lead to stimulation of the local nerves. This creates more itch and further traumatization to the barrier. Barrier function can be restored through soaking the area, with sitz baths or damp towels. Following 20- to 30-minute soaks, a lubricant, such as petroleum jelly, should be applied to the area.3
Reducing inflammation. To reduce inflammation, topical steroids should be applied to areas of LSC.3 In severe cases, high potency topical steroids should be prescribed. Examples of high potency topical steroids include:
- clobetasol propionate 0.05%
- betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%
- halobetasol propionate 0.05%.
Ointment is the choice vehicle because it is both more potent and associated with decreased stinging sensation. High potency steroid ointment should be applied twice daily for at least 2 to 4 weeks. The transition to lower potency topical steroids, such as triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% ointment, can be made as the LSC improves.2
Interrupting the itch-scratch cycle. As noted above, persistent rubbing and scratching generates increased itch sensation. Thus, breaking the itch-scratch cycle is essential. Nighttime scratching can be improved with hydroxyzine. The effective dosage ranges between 25 and 75 mg and should be titrated up slowly every 5 to 7 days. Sedation is a major adverse effect of hydroxyzine, limiting the treatment of daytime itching. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as citalopram, also have been found to be effective. Over the counter, nonsedation antihistamines have not been found to be useful in breaking the itch-scratch cycle. The clinical course of LSC is chronic (as the name implies), waxing and waning, and sometimes can be challenging to treat—some patients require years-long continued follow-up and treatment.3
- Savas JA, Pichardo RO. Female genital itch. Dermatologic Clin. 2018;36:225-243.
- Chibnall R. Vulvar pruritus and lichen simplex chronicus. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:379-388.
- Lynch PJ. Lichen simplex chronicus (atopic/neurodermatitis) of the anogenital region. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:8-19.
Genital lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is an inflammatory skin condition that develops secondary to persistent rubbing or scratching of skin. Although LSC can occur anywhere on the body, genital LSC develops in association with genital itch, with the itch often described as intense and unrelenting. The itching sensation leads to scratching and rubbing of the area, which can provide temporary symptomatic relief.1,2 However, this action of rubbing and scratching stimulates local cutaneous nerves, inducing an even more intense itch sensation. This process, identified as the ‘itch-scratch cycle,’ plays a prominent role in all cases of LSC.1
On physical examination LSC appears as poorly defined, pink to red plaques with accentuated skin markings on bilateral labia majora. Less commonly, it can present as asymmetrical or unilateral plaques.3 LSC can extend onto labia minora, mons pubis, and medial thighs. However, the vagina is spared.1 Excoriations, marked by their geometric, angular appearance, often can be appreciated overlying plaques of LSC. Additionally, crusting, scale, broken hairs, hyperpigmentation, and scarring may be seen in LSC.2
In this case, white discharge was noted on vaginal examination, which was suspicious for vaginal candidiasis. Wet mount examination revealed multiple candida hyphae and spores (FIGURE 2), confirming vaginal candidiasis. This vulvovaginal fungal infection caused persistent vulvar pruritus, with subsequent development of LSC due to prolonged scratching. The patient was treated with both oral fluconazole and topical mometasone ointment, for vaginal candidiasis and vulvar LSC, respectively. Mometasone ointment is categorized as a class II (high potency) topical steroid. However, it is worth noting that mometasone cream is categorized as a class IV (medium potency) topical steroid.
FIGURE 2 Wet mount of vaginal discharge, revealing candida hyphae and spores

Treatment
Successful treatment of LSC requires addressing 4 elements, including recognizing and treating the underlying etiology, restoring barrier function, reducing inflammation, and interrupting the itch-scratch cycle.3
Identifying the underlying etiology. Knowing the etiology of vulvar pruritus is a key step in resolution of the condition because LSC is driven by repetitive rubbing and scratching behaviors in response to the itch. The differential diagnosis for vulvar pruritus is broad. Evaluation and workup should be tailored to suit each unique patient presentation. A review of past medical history and full-body skin examination can identify a contributing inflammatory skin disease, such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus, or autoimmune vesiculobullous disease (pemphigus).1,2 Careful review of products applied in the genital area can reveal an underlying irritant or allergic contact dermatitis. Scented soap or detergent commonly cause vulvar dermatitis.1 A speculum examination may suggest inflammatory vaginitis or atrophic vaginitis (genitourinary syndrome of menopause); run off of vaginal discharge onto the vulvar skin can result in vulvar pruritus. Vaginal wet mount can diagnose vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomonas infection, and bacterial vaginitis.1 A skin scraping with mineral oil or potassium hydroxide can suggest scabies infestation or cutaneous dermatophyte infection, respectively.2 Treatment of vulvar pruritus should be initiated based on diagnosis.
Restoring barrier function. The repetitive scratching and rubbing behaviors disrupt the cutaneous barrier layer and lead to stimulation of the local nerves. This creates more itch and further traumatization to the barrier. Barrier function can be restored through soaking the area, with sitz baths or damp towels. Following 20- to 30-minute soaks, a lubricant, such as petroleum jelly, should be applied to the area.3
Reducing inflammation. To reduce inflammation, topical steroids should be applied to areas of LSC.3 In severe cases, high potency topical steroids should be prescribed. Examples of high potency topical steroids include:
- clobetasol propionate 0.05%
- betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%
- halobetasol propionate 0.05%.
Ointment is the choice vehicle because it is both more potent and associated with decreased stinging sensation. High potency steroid ointment should be applied twice daily for at least 2 to 4 weeks. The transition to lower potency topical steroids, such as triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% ointment, can be made as the LSC improves.2
Interrupting the itch-scratch cycle. As noted above, persistent rubbing and scratching generates increased itch sensation. Thus, breaking the itch-scratch cycle is essential. Nighttime scratching can be improved with hydroxyzine. The effective dosage ranges between 25 and 75 mg and should be titrated up slowly every 5 to 7 days. Sedation is a major adverse effect of hydroxyzine, limiting the treatment of daytime itching. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as citalopram, also have been found to be effective. Over the counter, nonsedation antihistamines have not been found to be useful in breaking the itch-scratch cycle. The clinical course of LSC is chronic (as the name implies), waxing and waning, and sometimes can be challenging to treat—some patients require years-long continued follow-up and treatment.3
Genital lichen simplex chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is an inflammatory skin condition that develops secondary to persistent rubbing or scratching of skin. Although LSC can occur anywhere on the body, genital LSC develops in association with genital itch, with the itch often described as intense and unrelenting. The itching sensation leads to scratching and rubbing of the area, which can provide temporary symptomatic relief.1,2 However, this action of rubbing and scratching stimulates local cutaneous nerves, inducing an even more intense itch sensation. This process, identified as the ‘itch-scratch cycle,’ plays a prominent role in all cases of LSC.1
On physical examination LSC appears as poorly defined, pink to red plaques with accentuated skin markings on bilateral labia majora. Less commonly, it can present as asymmetrical or unilateral plaques.3 LSC can extend onto labia minora, mons pubis, and medial thighs. However, the vagina is spared.1 Excoriations, marked by their geometric, angular appearance, often can be appreciated overlying plaques of LSC. Additionally, crusting, scale, broken hairs, hyperpigmentation, and scarring may be seen in LSC.2
In this case, white discharge was noted on vaginal examination, which was suspicious for vaginal candidiasis. Wet mount examination revealed multiple candida hyphae and spores (FIGURE 2), confirming vaginal candidiasis. This vulvovaginal fungal infection caused persistent vulvar pruritus, with subsequent development of LSC due to prolonged scratching. The patient was treated with both oral fluconazole and topical mometasone ointment, for vaginal candidiasis and vulvar LSC, respectively. Mometasone ointment is categorized as a class II (high potency) topical steroid. However, it is worth noting that mometasone cream is categorized as a class IV (medium potency) topical steroid.
FIGURE 2 Wet mount of vaginal discharge, revealing candida hyphae and spores

Treatment
Successful treatment of LSC requires addressing 4 elements, including recognizing and treating the underlying etiology, restoring barrier function, reducing inflammation, and interrupting the itch-scratch cycle.3
Identifying the underlying etiology. Knowing the etiology of vulvar pruritus is a key step in resolution of the condition because LSC is driven by repetitive rubbing and scratching behaviors in response to the itch. The differential diagnosis for vulvar pruritus is broad. Evaluation and workup should be tailored to suit each unique patient presentation. A review of past medical history and full-body skin examination can identify a contributing inflammatory skin disease, such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus, or autoimmune vesiculobullous disease (pemphigus).1,2 Careful review of products applied in the genital area can reveal an underlying irritant or allergic contact dermatitis. Scented soap or detergent commonly cause vulvar dermatitis.1 A speculum examination may suggest inflammatory vaginitis or atrophic vaginitis (genitourinary syndrome of menopause); run off of vaginal discharge onto the vulvar skin can result in vulvar pruritus. Vaginal wet mount can diagnose vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomonas infection, and bacterial vaginitis.1 A skin scraping with mineral oil or potassium hydroxide can suggest scabies infestation or cutaneous dermatophyte infection, respectively.2 Treatment of vulvar pruritus should be initiated based on diagnosis.
Restoring barrier function. The repetitive scratching and rubbing behaviors disrupt the cutaneous barrier layer and lead to stimulation of the local nerves. This creates more itch and further traumatization to the barrier. Barrier function can be restored through soaking the area, with sitz baths or damp towels. Following 20- to 30-minute soaks, a lubricant, such as petroleum jelly, should be applied to the area.3
Reducing inflammation. To reduce inflammation, topical steroids should be applied to areas of LSC.3 In severe cases, high potency topical steroids should be prescribed. Examples of high potency topical steroids include:
- clobetasol propionate 0.05%
- betamethasone dipropionate 0.05%
- halobetasol propionate 0.05%.
Ointment is the choice vehicle because it is both more potent and associated with decreased stinging sensation. High potency steroid ointment should be applied twice daily for at least 2 to 4 weeks. The transition to lower potency topical steroids, such as triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% ointment, can be made as the LSC improves.2
Interrupting the itch-scratch cycle. As noted above, persistent rubbing and scratching generates increased itch sensation. Thus, breaking the itch-scratch cycle is essential. Nighttime scratching can be improved with hydroxyzine. The effective dosage ranges between 25 and 75 mg and should be titrated up slowly every 5 to 7 days. Sedation is a major adverse effect of hydroxyzine, limiting the treatment of daytime itching. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as citalopram, also have been found to be effective. Over the counter, nonsedation antihistamines have not been found to be useful in breaking the itch-scratch cycle. The clinical course of LSC is chronic (as the name implies), waxing and waning, and sometimes can be challenging to treat—some patients require years-long continued follow-up and treatment.3
- Savas JA, Pichardo RO. Female genital itch. Dermatologic Clin. 2018;36:225-243.
- Chibnall R. Vulvar pruritus and lichen simplex chronicus. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:379-388.
- Lynch PJ. Lichen simplex chronicus (atopic/neurodermatitis) of the anogenital region. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:8-19.
- Savas JA, Pichardo RO. Female genital itch. Dermatologic Clin. 2018;36:225-243.
- Chibnall R. Vulvar pruritus and lichen simplex chronicus. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2017;44:379-388.
- Lynch PJ. Lichen simplex chronicus (atopic/neurodermatitis) of the anogenital region. Dermatol Ther. 2004;17:8-19.
CASE Lingering vulvar pruritus developed during traveling
A 48-year-old premenopausal Hispanic woman with past medical history of breast cancer presents to a dermatologist with the chief complaint of persistent vulvar pruritus. The vulvar itching began while traveling and has continued for 6 months. Previous treatments have been trialed, including over-the-counter feminine hygiene products, wipes, and hydrocortisone ointment.
Physical examination reveals pink, symmetric, bilateral lichenified plaques on the labia majora, without evidence of atrophy or scarring ( FIGURE 1 ). Scant white vaginal discharge is also noted.
FIGURE 1 Bilateral labia majora show lichenification
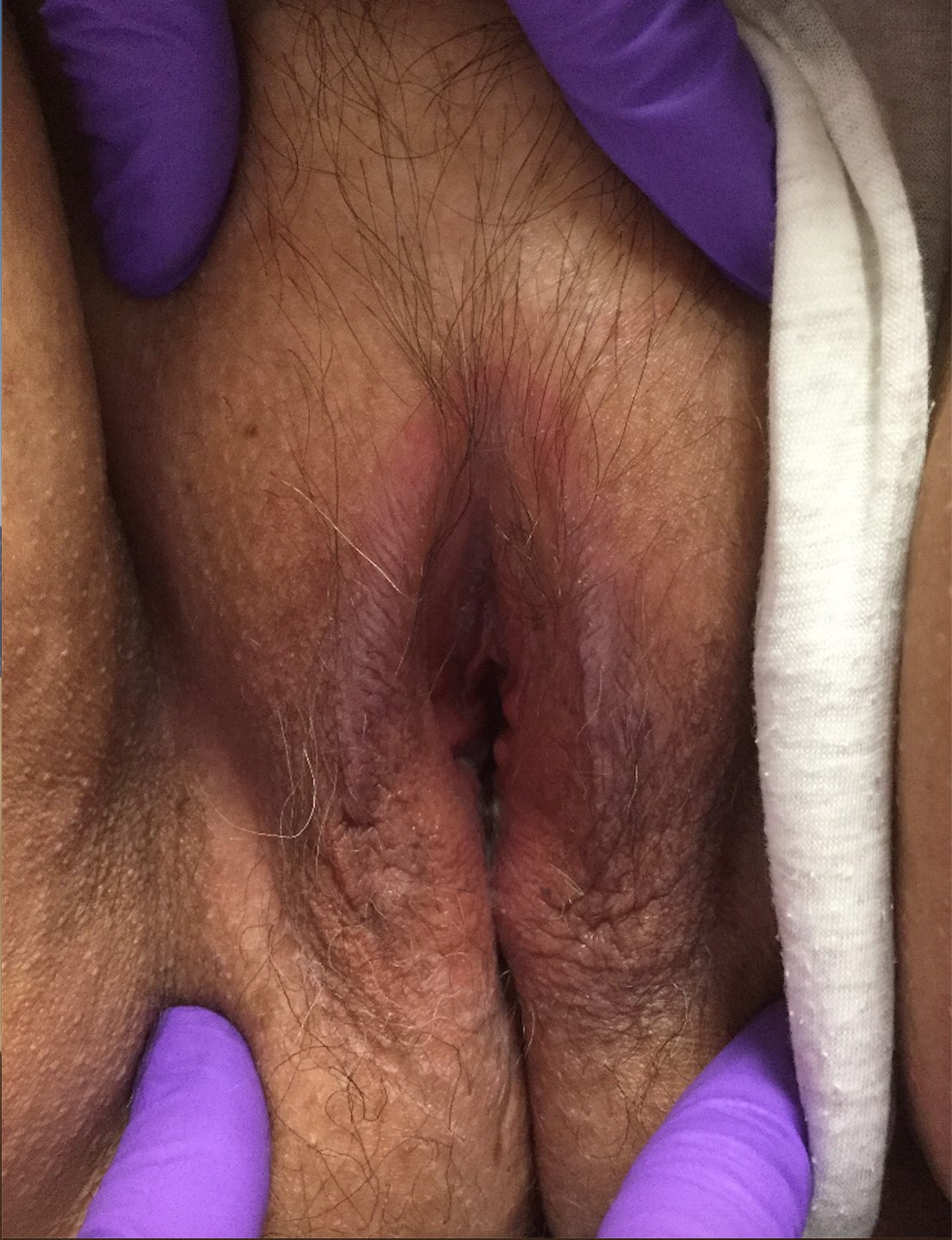
Figure caption: On bilateral labia majora, symmetric, pink plaques with accentuated skin markings (lichenification) noted on physical examination. Scant white vaginal discharge was noted on exam but is inconspicuous in photo.
Two cases of genital pruritus: What is the one diagnosis?
Lichen sclerosus
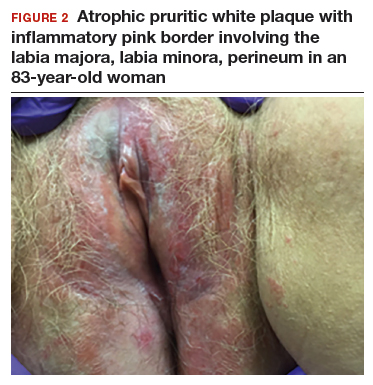
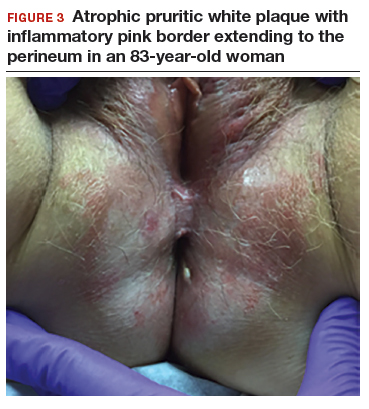
Lichen sclerosus is an inflammatory skin disease that primarily affects the genital and perianal skin of postmenopausal women. The mean age of onset is the mid- to late 50s; fewer than 15% of lichen sclerosus cases present in children.1,2 Case 1 represents presentation of vulvar lichen sclerosus in a premenopausal woman, which is uncommon.
The classic presentation of lichen sclerosus is a well-defined white, atrophic plaque with a wrinkled surface appearance located on the vulva, perineum, and perianal skin. Less commonly, examination may reveal white papules and macules, pallor with overlying edema, or hyperpigmentation. Loss of labia minora tissue and phimosis of the clitoral hood also are often present in patients with untreated lichen sclerosus.
Additionally, secondary changes, such as erosions, fissuring, and blisters, can be seen on examination. The most frequent symptom associated with lichen sclerosus is intense itching of the affected area. Other symptoms include dyspareunia, dysuria, sexual dysfunction, and bleeding. Occasionally, lichen sclerosus is asymptomatic.1 Like other autoimmune conditions, lichen sclerosus may persist indefinitely, highlighting the importance of effective treatment.
How should we evaluate and treat patients with these symptoms?
Perform a skin biopsy and start treatment with very high–potency topical corticosteroid ointment daily for at least 6 weeks.
Skin biopsy. Definitive diagnosis of lichen sclerosus is made based on a skin biopsy. Because treatment can impact the interpretation of a skin biopsy, a biopsy is optimally performed prior to treatment initiation.
The patient in Case 1 underwent biopsy of the left labia majora. Results were consistent with early lichen sclerosus. The patient in Case 2 was reluctant to proceed with vulvar biopsy.
A biopsy specimen should be taken from the affected area that is most white in appearance.1
Topical treatment. To induce remission, twice-daily application of very high–potency topical corticosteroid ointment to the affected area for at least 6 weeks is recommended. Once the skin color and texture have normalized, the topical corticosteroid strength (and frequency of application) can slowly be reduced to the lowest potency/frequency at which the patient remains in remission. Examples of very high–, high-, moderate-, and low-potency corticosteroid ointments are listed in the TABLE.
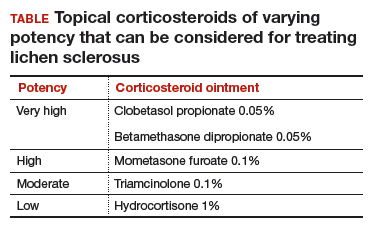
Follow-up. Evaluate the patient every 3 months until the topical steroid potency remains stable and the skin appearance is normal.
Treat early, and aggressively, to prevent complications
Early diagnosis and aggressive intervention are important in managing this disease process. If diagnosis and treatment are delayed, significant scarring and deformation of the vulva can occur.1
Neoplastic transformation of lichen sclerosus into vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma can occur (mean incidence, 2.8%). However, the literature reports significant variability in the incidence, ranging between 0% and 31%.3 Published reports support decreased scarring and future development of malignancies in patients who adhere to treatment recommendations.4
Symptoms resolved
In both cases described here, the patients were treated with clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily for 6 weeks. Both women reported complete resolution of pruritus after treatment. As can be seen in the posttreatment photo of the patient described in Case 1, her vulvar inflammation resolved (FIGURE 4).
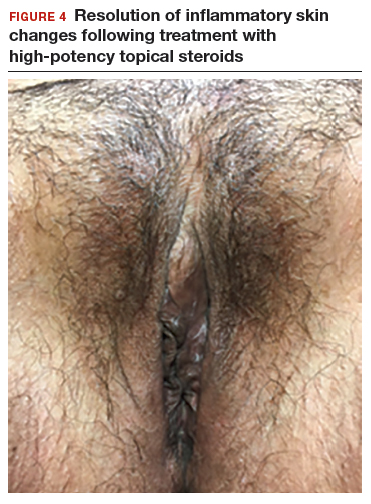
These cases represent the varied exam findings in patients experiencing vulvar pruritus with early (Case 1) versus more advanced (Case 2) lichen sclerosus. In addition, they underscore that appropriate evaluation and management of lichen sclerosus can produce excellent treatment results.
- Lee A, Fischer G. Diagnosis and treatment of vulvar lichen sclerosus: an update for dermatologists. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:695.
- Tong LX, Sun GS, Teng JM. Pediatric lichen sclerosus: a review of the epidemiology and treatment options. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:593-599.
- Micheletti L, Preti M, Radici G, et al. Vulvar lichen sclerosus and neoplastic transformation: a retrospective study of 976 cases. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:180-183.
- Lee A, Bradford J, Fischer G. Long-term management of adult vulvar lichen sclerosus: a prospective cohort study of 507 women. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1061-1067.
Lichen sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus is an inflammatory skin disease that primarily affects the genital and perianal skin of postmenopausal women. The mean age of onset is the mid- to late 50s; fewer than 15% of lichen sclerosus cases present in children.1,2 Case 1 represents presentation of vulvar lichen sclerosus in a premenopausal woman, which is uncommon.
The classic presentation of lichen sclerosus is a well-defined white, atrophic plaque with a wrinkled surface appearance located on the vulva, perineum, and perianal skin. Less commonly, examination may reveal white papules and macules, pallor with overlying edema, or hyperpigmentation. Loss of labia minora tissue and phimosis of the clitoral hood also are often present in patients with untreated lichen sclerosus.
Additionally, secondary changes, such as erosions, fissuring, and blisters, can be seen on examination. The most frequent symptom associated with lichen sclerosus is intense itching of the affected area. Other symptoms include dyspareunia, dysuria, sexual dysfunction, and bleeding. Occasionally, lichen sclerosus is asymptomatic.1 Like other autoimmune conditions, lichen sclerosus may persist indefinitely, highlighting the importance of effective treatment.
How should we evaluate and treat patients with these symptoms?
Perform a skin biopsy and start treatment with very high–potency topical corticosteroid ointment daily for at least 6 weeks.
Skin biopsy. Definitive diagnosis of lichen sclerosus is made based on a skin biopsy. Because treatment can impact the interpretation of a skin biopsy, a biopsy is optimally performed prior to treatment initiation.
The patient in Case 1 underwent biopsy of the left labia majora. Results were consistent with early lichen sclerosus. The patient in Case 2 was reluctant to proceed with vulvar biopsy.
A biopsy specimen should be taken from the affected area that is most white in appearance.1
Topical treatment. To induce remission, twice-daily application of very high–potency topical corticosteroid ointment to the affected area for at least 6 weeks is recommended. Once the skin color and texture have normalized, the topical corticosteroid strength (and frequency of application) can slowly be reduced to the lowest potency/frequency at which the patient remains in remission. Examples of very high–, high-, moderate-, and low-potency corticosteroid ointments are listed in the TABLE.

Follow-up. Evaluate the patient every 3 months until the topical steroid potency remains stable and the skin appearance is normal.
Treat early, and aggressively, to prevent complications
Early diagnosis and aggressive intervention are important in managing this disease process. If diagnosis and treatment are delayed, significant scarring and deformation of the vulva can occur.1
Neoplastic transformation of lichen sclerosus into vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma can occur (mean incidence, 2.8%). However, the literature reports significant variability in the incidence, ranging between 0% and 31%.3 Published reports support decreased scarring and future development of malignancies in patients who adhere to treatment recommendations.4
Symptoms resolved
In both cases described here, the patients were treated with clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily for 6 weeks. Both women reported complete resolution of pruritus after treatment. As can be seen in the posttreatment photo of the patient described in Case 1, her vulvar inflammation resolved (FIGURE 4).

These cases represent the varied exam findings in patients experiencing vulvar pruritus with early (Case 1) versus more advanced (Case 2) lichen sclerosus. In addition, they underscore that appropriate evaluation and management of lichen sclerosus can produce excellent treatment results.
Lichen sclerosus
Lichen sclerosus is an inflammatory skin disease that primarily affects the genital and perianal skin of postmenopausal women. The mean age of onset is the mid- to late 50s; fewer than 15% of lichen sclerosus cases present in children.1,2 Case 1 represents presentation of vulvar lichen sclerosus in a premenopausal woman, which is uncommon.
The classic presentation of lichen sclerosus is a well-defined white, atrophic plaque with a wrinkled surface appearance located on the vulva, perineum, and perianal skin. Less commonly, examination may reveal white papules and macules, pallor with overlying edema, or hyperpigmentation. Loss of labia minora tissue and phimosis of the clitoral hood also are often present in patients with untreated lichen sclerosus.
Additionally, secondary changes, such as erosions, fissuring, and blisters, can be seen on examination. The most frequent symptom associated with lichen sclerosus is intense itching of the affected area. Other symptoms include dyspareunia, dysuria, sexual dysfunction, and bleeding. Occasionally, lichen sclerosus is asymptomatic.1 Like other autoimmune conditions, lichen sclerosus may persist indefinitely, highlighting the importance of effective treatment.
How should we evaluate and treat patients with these symptoms?
Perform a skin biopsy and start treatment with very high–potency topical corticosteroid ointment daily for at least 6 weeks.
Skin biopsy. Definitive diagnosis of lichen sclerosus is made based on a skin biopsy. Because treatment can impact the interpretation of a skin biopsy, a biopsy is optimally performed prior to treatment initiation.
The patient in Case 1 underwent biopsy of the left labia majora. Results were consistent with early lichen sclerosus. The patient in Case 2 was reluctant to proceed with vulvar biopsy.
A biopsy specimen should be taken from the affected area that is most white in appearance.1
Topical treatment. To induce remission, twice-daily application of very high–potency topical corticosteroid ointment to the affected area for at least 6 weeks is recommended. Once the skin color and texture have normalized, the topical corticosteroid strength (and frequency of application) can slowly be reduced to the lowest potency/frequency at which the patient remains in remission. Examples of very high–, high-, moderate-, and low-potency corticosteroid ointments are listed in the TABLE.

Follow-up. Evaluate the patient every 3 months until the topical steroid potency remains stable and the skin appearance is normal.
Treat early, and aggressively, to prevent complications
Early diagnosis and aggressive intervention are important in managing this disease process. If diagnosis and treatment are delayed, significant scarring and deformation of the vulva can occur.1
Neoplastic transformation of lichen sclerosus into vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma can occur (mean incidence, 2.8%). However, the literature reports significant variability in the incidence, ranging between 0% and 31%.3 Published reports support decreased scarring and future development of malignancies in patients who adhere to treatment recommendations.4
Symptoms resolved
In both cases described here, the patients were treated with clobetasol 0.05% ointment twice daily for 6 weeks. Both women reported complete resolution of pruritus after treatment. As can be seen in the posttreatment photo of the patient described in Case 1, her vulvar inflammation resolved (FIGURE 4).

These cases represent the varied exam findings in patients experiencing vulvar pruritus with early (Case 1) versus more advanced (Case 2) lichen sclerosus. In addition, they underscore that appropriate evaluation and management of lichen sclerosus can produce excellent treatment results.
- Lee A, Fischer G. Diagnosis and treatment of vulvar lichen sclerosus: an update for dermatologists. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:695.
- Tong LX, Sun GS, Teng JM. Pediatric lichen sclerosus: a review of the epidemiology and treatment options. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:593-599.
- Micheletti L, Preti M, Radici G, et al. Vulvar lichen sclerosus and neoplastic transformation: a retrospective study of 976 cases. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:180-183.
- Lee A, Bradford J, Fischer G. Long-term management of adult vulvar lichen sclerosus: a prospective cohort study of 507 women. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1061-1067.
- Lee A, Fischer G. Diagnosis and treatment of vulvar lichen sclerosus: an update for dermatologists. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:695.
- Tong LX, Sun GS, Teng JM. Pediatric lichen sclerosus: a review of the epidemiology and treatment options. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:593-599.
- Micheletti L, Preti M, Radici G, et al. Vulvar lichen sclerosus and neoplastic transformation: a retrospective study of 976 cases. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:180-183.
- Lee A, Bradford J, Fischer G. Long-term management of adult vulvar lichen sclerosus: a prospective cohort study of 507 women. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:1061-1067.
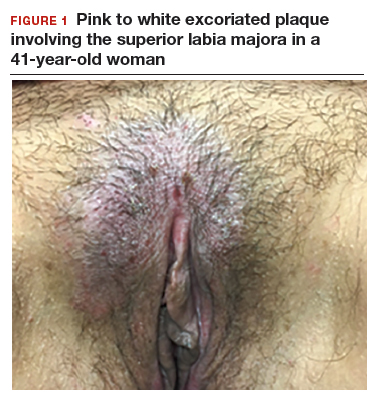
CASE 1: Vulvar pruritus affecting a woman’s quality of life
A 41-year-old premenopausal white woman presented to her gynecologist with intense vulvar pruritus for a 6-month duration, with a recent increase in severity (FIGURE 1). She tried treating it with topical antifungal cream, hydrocortisone ointment, and coconut oil, with no improvement. She noted that the intense itching was interfering with her sleep and marriage. The patient denied having an increase in urinary frequency or urgency, dysuria, hematochezia, or bowel changes.
CASE 2: Older woman with long-term persistent genital pruritus
An 83-year-old postmenopausal white woman presented to the dermatology clinic for a regular skin examination. The patient endorsed symptoms of vulvar and perianal pruritus that had persisted for more than 6 months (FIGURES 2 and 3). The genital itching occurred throughout most of the day. The patient previously treated her symptoms with an over-the-counter antifungal cream, which minimally improved the itching.