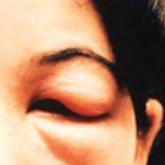
Having experienced the devastating effects of the “kissing bug” in September 2016, “Chagas Disease: Creeping into Family Practice” (2016;26[11]:38-45) was a timely article for me. I am writing to thank the authors for giving my case more credence and to issue a note of caution: People may have a strong reaction to the bite of this bug and therefore assume it to be from a spider. In some cases, including my own, bite-related anaphylaxis can send a person to the emergency department. After being bitten, I lost consciousness, fell down a flight of stairs, and sustained a bimalleolar fracture of my right ankle that required surgery. I later found the bug and submitted it to the CDC for testing; it was infected with Trypanosoma cruzi, the parasite that causes Chagas disease.
I want others to be aware that severe allergic reactions can result from the bite of a beetle-like bug, such as the kissing bug. I am taking it upon myself to educate my patients and colleagues and have also employed an exterminator for my home. If a person is bitten by this cone-nosed, prehistoric-looking bug, it should not be touched, but it should be collected and kept in the freezer until it can be sent to the CDC. If the bug is found to be positive for the parasite, an antibody test should then be performed on the affected person. I am lucky that my antibody test came back negative for the disease.
Constance Wylie, RN, MSN, FNP-C
Sacramento, CA