ANSWER
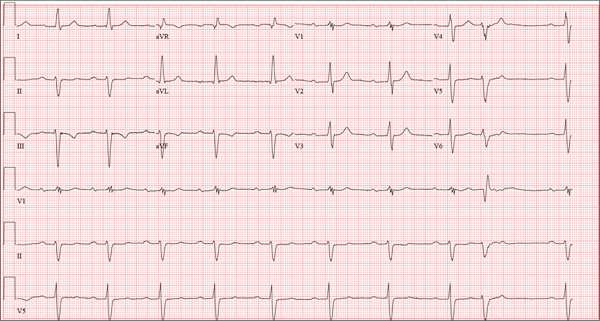
The correct interpretation includes sinus bradycardia with first-degree block, a single premature atrial beat with aberrancy, right bundle branch block, left anterior fascicular block (bifascicular block), left ventricular hypertrophy, and T-wave inversions in the inferior leads.
In sinus bradycardia, there is a P wave for every QRS complex with a rate less than 60 beats/min. First-degree block is evidenced by a PR interval ≥ 200 ms.
A single premature atrial contraction is seen as the ninth beat on the ECG. Aberrancy refers to the appearance of the QRS complex; the impulse arises above the AV node but propagates down the AV node and His-Purkinje system to the ventricles before the conduction system is fully repolarized. This results in a QRS complex with intrinsic conduction similar to a normally conducted beat, which then becomes wide and uncharacteristic. Additionally, it resets the sinus node, resulting in a pause before the next normally conducted P wave.
A right bundle branch block is evidenced by the presence of normal conduction with a QRS duration > 120 ms, a terminal R wave in lead V1 (R, rR’, rsR’, or qR), and slurred S waves in leads I and V6.
The presence of left anterior fascicular block is confirmed by the left-axis deviation (–59° in this ECG), a qR complex in leads I and aVL, and an rS pattern in leads II, III, and aVF. The presence of both a right bundle and left anterior fascicular block constitutes bifascicular block. (This is a conduction problem and does not refer to blockage in the arteries, as the patient believed!)
Criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy are met when the sum of the S wave in V1 and the R wave in either V5 or V6 is ≥ 35 mm and the R wave in aVL is ≥ 11 mm.
Two other things to note in this ECG are the presence of T-wave inversions in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF) which are of unclear reason; and the presence of biphasic P waves that do not meet criteria for either right or left atrial hypertrophy.