CHICAGO – Reoperative bariatric surgery has impressively low major morbidity and mortality, substantial 1-year weight loss, and a high rate of resolution of the common obesity-linked comorbid conditions, according to an analysis of a large national database.
These data demonstrate that outcomes after contemporary reoperative bariatric surgery are better than believed by insurance carriers, who often deny coverage for these procedures because of a misperception that complication rates are high and benefits uncertain, Dr. Ranjan Sudan said at the annual Digestive Disease Week.
"I think that these data need to get out there to the stakeholders," added Dr. Sudan, a bariatric surgeon and a digestive disorders specialist who is vice chair of education in the department of surgery at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
He presented an analysis of outcomes after reoperative surgery that was carried out by a task force of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. He and his coinvestigators reviewed all 451,485 bariatric surgery operations entered into the society’s prospective database during a 5-year period ending in spring 2012. The procedures were performed by 1,029 participating surgeons at 709 U.S. hospitals.
The focus of this analysis was on the 6.3% of operations that were reoperations. A total of 70% of the reoperations were corrective operations, essentially redos of the same type of procedure performed initially. The other 30% were conversion procedures, as when a patient who had a gastric band procedure on the first go-round subsequently was converted to a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve procedure.
The mean length of stay for primary bariatric operations was 1.78 days, compared with 2.04 days for reoperative corrective procedures and 2.86 days for conversion operations.
The 30-day incidence of serious adverse events, such as leaks, bleeding, or pulmonary embolism, was 1.61% for primary procedures, nearly identical at 1.66% for corrective reoperations, and 3.26% for conversion procedures. The 1-year rate of serious adverse events was 1.87% for primary bariatric operations, 1.9% for corrective procedures, and 3.61% for conversions.
The mortality rate in patients undergoing a primary operation was 0.10% at 30 days and 0.17% at 1 year. Among patients who underwent reoperative bariatric surgery, the 30-day and 1-year mortality rates were 0.14% and 0.26%, respectively.
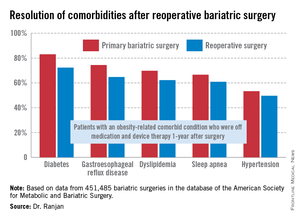
"Most bariatric surgery patients do not need reoperations. It’s gratifying to see that among those who do, the severe complication rates were low and acceptable and comorbidities often resolved [see chart]," Dr. Sudan declared.
The 1-year rate of excess weight loss following reoperative surgery averaged 36%.
Discussant Dr. Alfons Pomp liked what he saw from the registry.
"Your data show just how good we as bariatric surgeons are to operate on these surgically difficult, very obese, and seriously ill patients, mostly laparoscopically, and get pretty amazing results," commented Dr. Pomp, professor of surgery and chief of GI metabolic and bariatric surgery at Cornell University in New York.
The registry study was funded by Covidien. Dr. Sudan reported having no financial conflicts of interest.