User login
Diagnosis: Venous Malformation
Although present at birth, they are not always clinically evident early in life. They also tend to grow with the child without spontaneous regression, causing potential cosmetic concerns or complications from impingement on surrounding tissue.
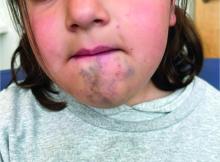
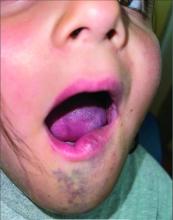
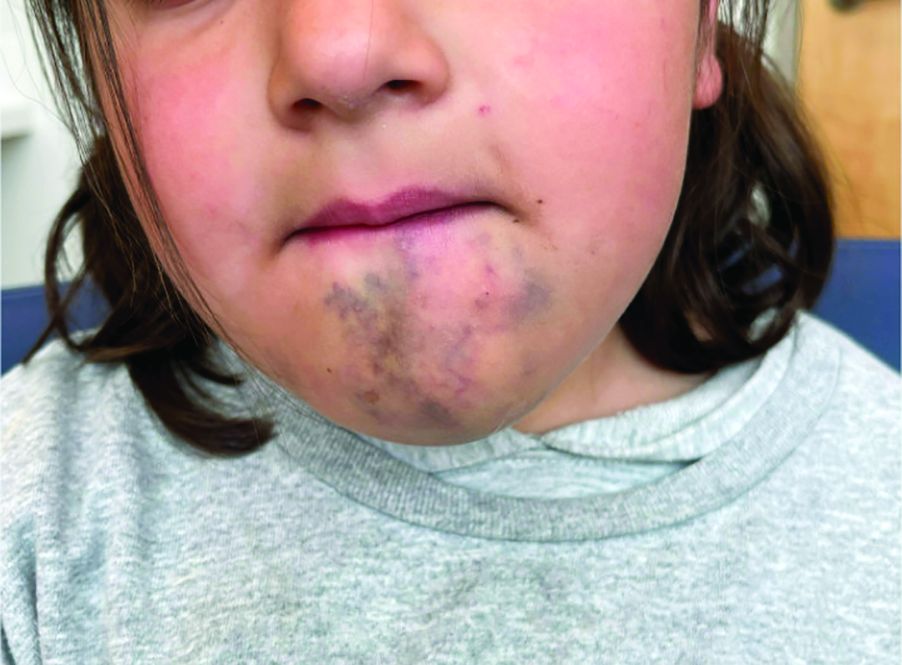
Venous malformations appear with a bluish color appearing beneath the skin and can vary significantly in size and severity. Venous malformations are compressible and characterized by low to stagnant blood flow, which can spontaneously thrombose. Clinically, this may cause pain, swelling, skin changes, tissue and limb overgrowth, or functional impairment depending on location and size.
Venous malformations result from disorganized angiogenesis secondary to sporadic mutations in somatic cells. The most common implicated gene is TEK, a receptor tyrosine kinase. PIK3CA has also been involved. Both genes are involved in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which regulates cell growth, proliferation, and angiogenesis. In venous endothelial cells, abnormal angiogenesis and vessel maturation may lead to venous malformation formation. Dysplastic vessels frequently separate from normal veins but may be contiguous with the deep venous system.
Diagnosis involves clinical history and physical examination. Imaging with ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilized. While ultrasound may be preferred for superficial venous malformations, MRI or MRI with MR angiography (MRA) is the preferred method for venous malformation assessment. Genetic testing may be appropriate for complex malformations, as classification of lesions by underlying mutation may allow targeted therapy.
This patient’s past MRI and MRA findings were consistent with a venous malformation.
Treatment
Venous malformations rarely regress spontaneously. Treatment is required if venous malformations are symptomatic, which may include pain, swelling, deformity, thrombosis, or interference with daily activities of living. Treatment plans require consideration of patient goals of care. The main categories of therapy are embolization/sclerotherapy, surgical resection, and molecular targeted therapy.
Sclerotherapy is a well-tolerated and efficacious first-line therapy. It can be used as either nonsurgical curative therapy or preoperative adjunct therapy to minimize blood loss before surgical resection. While surgical resection may cause scarring, multimodal approaches with sclerotherapy or laser therapy can decrease complications. Molecular therapies aim to reduce vascular proliferation and symptoms. Referral to hematology/oncology for evaluation and consideration of chemotherapeutic agents may be required. Sirolimus has been shown in mice models to inhibit an endothelial cell tyrosine kinase receptor that plays a role in venous malformation growth. Multiple studies have proved its efficacy in managing complicated vascular anomalies, including venous malformations. Alpelisib is an inhibitor of PI3KCA, which is part of the pathway that contributes to venous malformation formation. Dactolisib, a dual inhibitor of the PI3KA and mTOR pathways, and rebastinib, a TEK inhibitor, are being investigated.
Differential Diagnoses
The differential diagnosis includes dermal melanocytosis, nevus of Ota, hemangioma of infancy, and ashy dermatosis. In addition, venous malformations can be part of more complex vascular malformations.
Dermal melanocytosis, also known as Mongolian spots, are blue-gray patches of discoloration on the skin that appear at birth or shortly after. They result from the arrest of dermal melanocytes in the dermis during fetal life and tissue modeling. They are commonly observed in those of Asian or African descent with darker skin types. Most often, they are located in the lumbar or sacral-gluteal region. Unlike venous malformations, they are benign and do not involve vascular abnormalities. They typically fade over time.
Nevus of Ota is a benign congenital condition that presents with blue-gray or brown patches of pigmentation on the skin around the eyes, cheeks, and forehead. They are dermal melanocytes with a speckled instead of uniform appearance. Nevus of Ota primarily affects individuals of Asian descent and typically presents in the trigeminal nerve distribution region. Treatment can be done to minimize deformity, generally with pigmented laser surgery.
Hemangiomas of infancy are common benign tumors of infancy caused by endothelial cell proliferation. They are characterized by rapid growth followed by spontaneous involution within the first year of life and for several years. Hemangiomas can be superficial, deep, or mixed with features of both superficial and deep. Superficial hemangiomas present as raised, lobulated, and bright red while deep hemangiomas present as a bluish-hued nodule, plaque, or tumor. They are diagnosed clinically but skin biopsies and imaging can confirm the suspected diagnosis. While hemangiomas may self-resolve, complicated hemangiomas can be treated with topical timolol, oral propranolol, topical and intralesional corticosteroids, pulsed-dye laser, and surgical resection.
Ashy dermatosis is a term for asymptomatic, gray-blue or ashy patches distributed symmetrically on the trunk, head, neck, and upper extremities. It primarily affects individuals with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick III-V), and is more common in patients with Hispanic, Asian, or African backgrounds. The direct cause of ashy dermatosis is unknown but it is thought to be linked to drug ingestion, genetics, infection, and immune-mediated mechanisms. The general treatment includes topical corticosteroids, clofazimine, topical calcineurin inhibitors, oral dapsone, phototherapy, topical retinoids, or isotretinoin to reduce inflammation and pigmentation.
Danny Lee and Samuel Le serve as research fellows and Jolina Bui as research associate in the Pediatric Dermatology Division of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is Distinguished Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics and Vice-Chair of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. The authors have no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Agarwal P, Patel BC. Nevus of Ota and Ito. [Updated 2023 Jul 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
Dompmartin A et al. The VASCERN-VASCA Working Group Diagnostic and Management Pathways for Venous Malformations. J Vasc Anom (Phila). 2023 Mar 23;4(2):e064.
Dompmartin A et al. Venous malformation: Update on aetiopathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Phlebology. 2010 Oct;25(5):224-235.
Gupta D, Thappa DM. Mongolian spots. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013 Jul-Aug;79(4):469-478.
Krowchuk DP et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Infantile Hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019 Jan;143(1):e20183475.
Nguyen K, Khachemoune A. Ashy dermatosis: A review. Dermatol Online J. 2019 May 15;25(5):13030/qt44f462s8.
Patel ND, Chong AT et al. Venous Malformations. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2022 Dec 20;39(5):498-507.
Diagnosis: Venous Malformation
Although present at birth, they are not always clinically evident early in life. They also tend to grow with the child without spontaneous regression, causing potential cosmetic concerns or complications from impingement on surrounding tissue.
Venous malformations appear with a bluish color appearing beneath the skin and can vary significantly in size and severity. Venous malformations are compressible and characterized by low to stagnant blood flow, which can spontaneously thrombose. Clinically, this may cause pain, swelling, skin changes, tissue and limb overgrowth, or functional impairment depending on location and size.
Venous malformations result from disorganized angiogenesis secondary to sporadic mutations in somatic cells. The most common implicated gene is TEK, a receptor tyrosine kinase. PIK3CA has also been involved. Both genes are involved in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which regulates cell growth, proliferation, and angiogenesis. In venous endothelial cells, abnormal angiogenesis and vessel maturation may lead to venous malformation formation. Dysplastic vessels frequently separate from normal veins but may be contiguous with the deep venous system.
Diagnosis involves clinical history and physical examination. Imaging with ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilized. While ultrasound may be preferred for superficial venous malformations, MRI or MRI with MR angiography (MRA) is the preferred method for venous malformation assessment. Genetic testing may be appropriate for complex malformations, as classification of lesions by underlying mutation may allow targeted therapy.
This patient’s past MRI and MRA findings were consistent with a venous malformation.
Treatment
Venous malformations rarely regress spontaneously. Treatment is required if venous malformations are symptomatic, which may include pain, swelling, deformity, thrombosis, or interference with daily activities of living. Treatment plans require consideration of patient goals of care. The main categories of therapy are embolization/sclerotherapy, surgical resection, and molecular targeted therapy.
Sclerotherapy is a well-tolerated and efficacious first-line therapy. It can be used as either nonsurgical curative therapy or preoperative adjunct therapy to minimize blood loss before surgical resection. While surgical resection may cause scarring, multimodal approaches with sclerotherapy or laser therapy can decrease complications. Molecular therapies aim to reduce vascular proliferation and symptoms. Referral to hematology/oncology for evaluation and consideration of chemotherapeutic agents may be required. Sirolimus has been shown in mice models to inhibit an endothelial cell tyrosine kinase receptor that plays a role in venous malformation growth. Multiple studies have proved its efficacy in managing complicated vascular anomalies, including venous malformations. Alpelisib is an inhibitor of PI3KCA, which is part of the pathway that contributes to venous malformation formation. Dactolisib, a dual inhibitor of the PI3KA and mTOR pathways, and rebastinib, a TEK inhibitor, are being investigated.
Differential Diagnoses
The differential diagnosis includes dermal melanocytosis, nevus of Ota, hemangioma of infancy, and ashy dermatosis. In addition, venous malformations can be part of more complex vascular malformations.
Dermal melanocytosis, also known as Mongolian spots, are blue-gray patches of discoloration on the skin that appear at birth or shortly after. They result from the arrest of dermal melanocytes in the dermis during fetal life and tissue modeling. They are commonly observed in those of Asian or African descent with darker skin types. Most often, they are located in the lumbar or sacral-gluteal region. Unlike venous malformations, they are benign and do not involve vascular abnormalities. They typically fade over time.
Nevus of Ota is a benign congenital condition that presents with blue-gray or brown patches of pigmentation on the skin around the eyes, cheeks, and forehead. They are dermal melanocytes with a speckled instead of uniform appearance. Nevus of Ota primarily affects individuals of Asian descent and typically presents in the trigeminal nerve distribution region. Treatment can be done to minimize deformity, generally with pigmented laser surgery.
Hemangiomas of infancy are common benign tumors of infancy caused by endothelial cell proliferation. They are characterized by rapid growth followed by spontaneous involution within the first year of life and for several years. Hemangiomas can be superficial, deep, or mixed with features of both superficial and deep. Superficial hemangiomas present as raised, lobulated, and bright red while deep hemangiomas present as a bluish-hued nodule, plaque, or tumor. They are diagnosed clinically but skin biopsies and imaging can confirm the suspected diagnosis. While hemangiomas may self-resolve, complicated hemangiomas can be treated with topical timolol, oral propranolol, topical and intralesional corticosteroids, pulsed-dye laser, and surgical resection.
Ashy dermatosis is a term for asymptomatic, gray-blue or ashy patches distributed symmetrically on the trunk, head, neck, and upper extremities. It primarily affects individuals with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick III-V), and is more common in patients with Hispanic, Asian, or African backgrounds. The direct cause of ashy dermatosis is unknown but it is thought to be linked to drug ingestion, genetics, infection, and immune-mediated mechanisms. The general treatment includes topical corticosteroids, clofazimine, topical calcineurin inhibitors, oral dapsone, phototherapy, topical retinoids, or isotretinoin to reduce inflammation and pigmentation.
Danny Lee and Samuel Le serve as research fellows and Jolina Bui as research associate in the Pediatric Dermatology Division of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is Distinguished Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics and Vice-Chair of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. The authors have no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Agarwal P, Patel BC. Nevus of Ota and Ito. [Updated 2023 Jul 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
Dompmartin A et al. The VASCERN-VASCA Working Group Diagnostic and Management Pathways for Venous Malformations. J Vasc Anom (Phila). 2023 Mar 23;4(2):e064.
Dompmartin A et al. Venous malformation: Update on aetiopathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Phlebology. 2010 Oct;25(5):224-235.
Gupta D, Thappa DM. Mongolian spots. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013 Jul-Aug;79(4):469-478.
Krowchuk DP et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Infantile Hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019 Jan;143(1):e20183475.
Nguyen K, Khachemoune A. Ashy dermatosis: A review. Dermatol Online J. 2019 May 15;25(5):13030/qt44f462s8.
Patel ND, Chong AT et al. Venous Malformations. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2022 Dec 20;39(5):498-507.
Diagnosis: Venous Malformation
Although present at birth, they are not always clinically evident early in life. They also tend to grow with the child without spontaneous regression, causing potential cosmetic concerns or complications from impingement on surrounding tissue.
Venous malformations appear with a bluish color appearing beneath the skin and can vary significantly in size and severity. Venous malformations are compressible and characterized by low to stagnant blood flow, which can spontaneously thrombose. Clinically, this may cause pain, swelling, skin changes, tissue and limb overgrowth, or functional impairment depending on location and size.
Venous malformations result from disorganized angiogenesis secondary to sporadic mutations in somatic cells. The most common implicated gene is TEK, a receptor tyrosine kinase. PIK3CA has also been involved. Both genes are involved in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which regulates cell growth, proliferation, and angiogenesis. In venous endothelial cells, abnormal angiogenesis and vessel maturation may lead to venous malformation formation. Dysplastic vessels frequently separate from normal veins but may be contiguous with the deep venous system.
Diagnosis involves clinical history and physical examination. Imaging with ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilized. While ultrasound may be preferred for superficial venous malformations, MRI or MRI with MR angiography (MRA) is the preferred method for venous malformation assessment. Genetic testing may be appropriate for complex malformations, as classification of lesions by underlying mutation may allow targeted therapy.
This patient’s past MRI and MRA findings were consistent with a venous malformation.
Treatment
Venous malformations rarely regress spontaneously. Treatment is required if venous malformations are symptomatic, which may include pain, swelling, deformity, thrombosis, or interference with daily activities of living. Treatment plans require consideration of patient goals of care. The main categories of therapy are embolization/sclerotherapy, surgical resection, and molecular targeted therapy.
Sclerotherapy is a well-tolerated and efficacious first-line therapy. It can be used as either nonsurgical curative therapy or preoperative adjunct therapy to minimize blood loss before surgical resection. While surgical resection may cause scarring, multimodal approaches with sclerotherapy or laser therapy can decrease complications. Molecular therapies aim to reduce vascular proliferation and symptoms. Referral to hematology/oncology for evaluation and consideration of chemotherapeutic agents may be required. Sirolimus has been shown in mice models to inhibit an endothelial cell tyrosine kinase receptor that plays a role in venous malformation growth. Multiple studies have proved its efficacy in managing complicated vascular anomalies, including venous malformations. Alpelisib is an inhibitor of PI3KCA, which is part of the pathway that contributes to venous malformation formation. Dactolisib, a dual inhibitor of the PI3KA and mTOR pathways, and rebastinib, a TEK inhibitor, are being investigated.
Differential Diagnoses
The differential diagnosis includes dermal melanocytosis, nevus of Ota, hemangioma of infancy, and ashy dermatosis. In addition, venous malformations can be part of more complex vascular malformations.
Dermal melanocytosis, also known as Mongolian spots, are blue-gray patches of discoloration on the skin that appear at birth or shortly after. They result from the arrest of dermal melanocytes in the dermis during fetal life and tissue modeling. They are commonly observed in those of Asian or African descent with darker skin types. Most often, they are located in the lumbar or sacral-gluteal region. Unlike venous malformations, they are benign and do not involve vascular abnormalities. They typically fade over time.
Nevus of Ota is a benign congenital condition that presents with blue-gray or brown patches of pigmentation on the skin around the eyes, cheeks, and forehead. They are dermal melanocytes with a speckled instead of uniform appearance. Nevus of Ota primarily affects individuals of Asian descent and typically presents in the trigeminal nerve distribution region. Treatment can be done to minimize deformity, generally with pigmented laser surgery.
Hemangiomas of infancy are common benign tumors of infancy caused by endothelial cell proliferation. They are characterized by rapid growth followed by spontaneous involution within the first year of life and for several years. Hemangiomas can be superficial, deep, or mixed with features of both superficial and deep. Superficial hemangiomas present as raised, lobulated, and bright red while deep hemangiomas present as a bluish-hued nodule, plaque, or tumor. They are diagnosed clinically but skin biopsies and imaging can confirm the suspected diagnosis. While hemangiomas may self-resolve, complicated hemangiomas can be treated with topical timolol, oral propranolol, topical and intralesional corticosteroids, pulsed-dye laser, and surgical resection.
Ashy dermatosis is a term for asymptomatic, gray-blue or ashy patches distributed symmetrically on the trunk, head, neck, and upper extremities. It primarily affects individuals with darker skin types (Fitzpatrick III-V), and is more common in patients with Hispanic, Asian, or African backgrounds. The direct cause of ashy dermatosis is unknown but it is thought to be linked to drug ingestion, genetics, infection, and immune-mediated mechanisms. The general treatment includes topical corticosteroids, clofazimine, topical calcineurin inhibitors, oral dapsone, phototherapy, topical retinoids, or isotretinoin to reduce inflammation and pigmentation.
Danny Lee and Samuel Le serve as research fellows and Jolina Bui as research associate in the Pediatric Dermatology Division of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is Distinguished Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics and Vice-Chair of the Department of Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. The authors have no relevant financial disclosures.
Suggested Reading
Agarwal P, Patel BC. Nevus of Ota and Ito. [Updated 2023 Jul 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
Dompmartin A et al. The VASCERN-VASCA Working Group Diagnostic and Management Pathways for Venous Malformations. J Vasc Anom (Phila). 2023 Mar 23;4(2):e064.
Dompmartin A et al. Venous malformation: Update on aetiopathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Phlebology. 2010 Oct;25(5):224-235.
Gupta D, Thappa DM. Mongolian spots. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013 Jul-Aug;79(4):469-478.
Krowchuk DP et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Infantile Hemangiomas. Pediatrics. 2019 Jan;143(1):e20183475.
Nguyen K, Khachemoune A. Ashy dermatosis: A review. Dermatol Online J. 2019 May 15;25(5):13030/qt44f462s8.
Patel ND, Chong AT et al. Venous Malformations. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2022 Dec 20;39(5):498-507.
A 6-year-old girl presents with a bruise-like lesion on the lip, tongue, and chin area present since birth. The family states that her tongue has been increasing in size and is painful. On physical exam, she presents with left lower mucosal lip fullness and an overlying violaceous hue extending into the oral mucosa and onto the left tongue. The left portion of the dorsal tongue displays an increased thickness and bluish discoloration and there is a pink, smooth papule on the left anterolateral tongue.