User login
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.
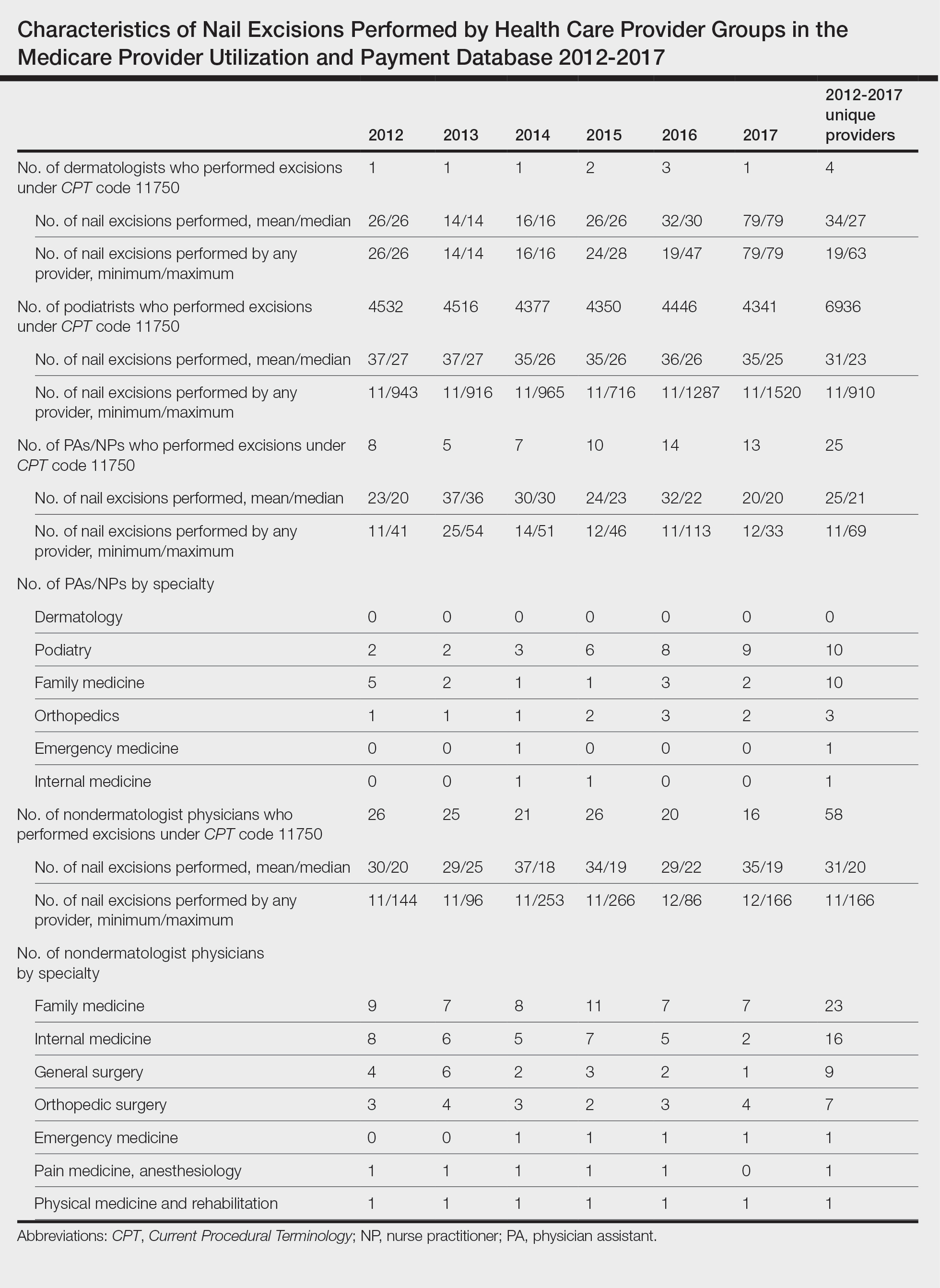
A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).
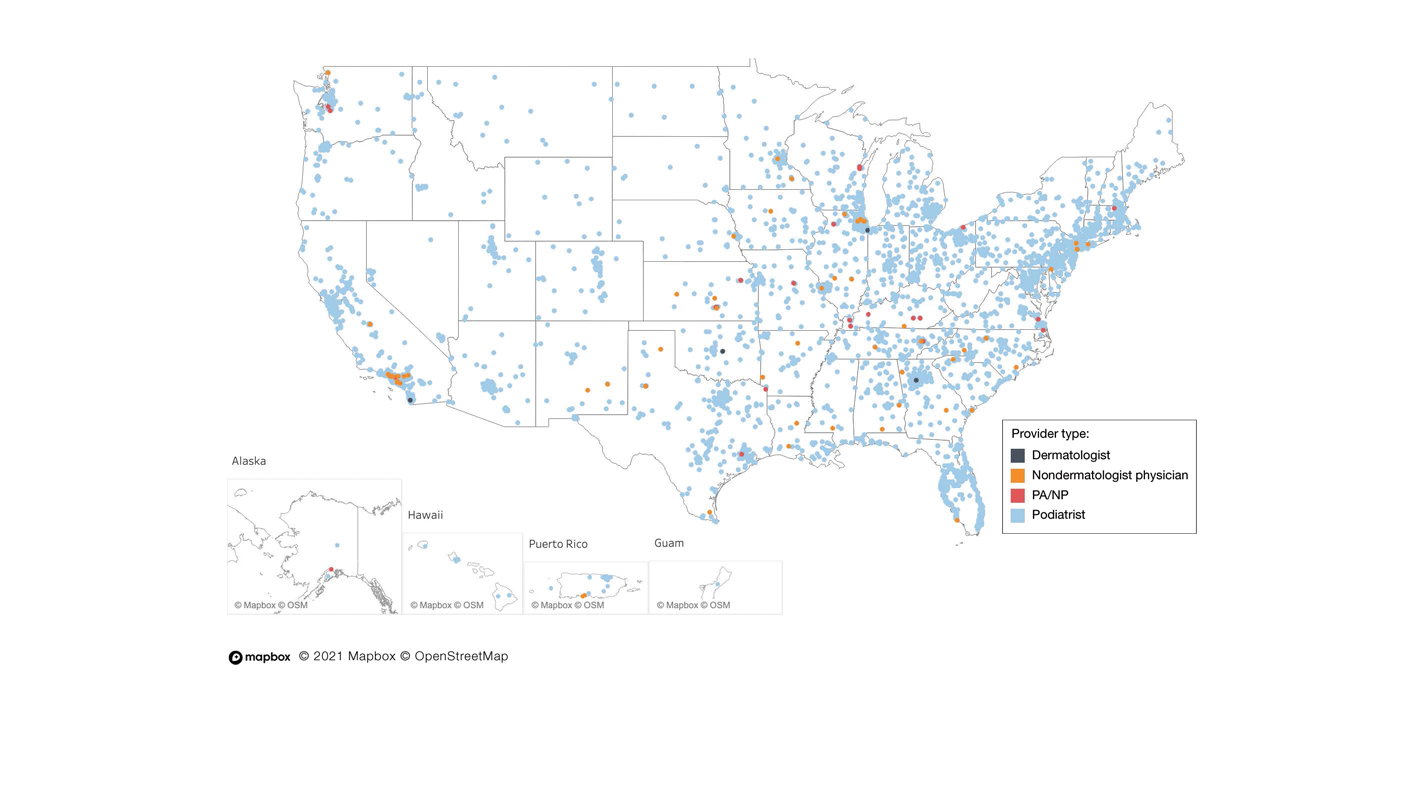
Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.

A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).

Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.

A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).

Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists are considered nail experts but perform nail excisions less frequently than their podiatric counterparts and physicians in other specialties.
- Aspects of podiatric surgical training should be incorporated into dermatology residency to increase competency and comfort of dermatologists in nail excision procedures.
- Dermatologists may not be perceived as nail experts by the public, indicating a need for increased community education on the role of dermatologists in treating nail disease.