User login
Nailing the Nail Biopsy: Surgical Instruments and Their Function in Nail Biopsy Procedures
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
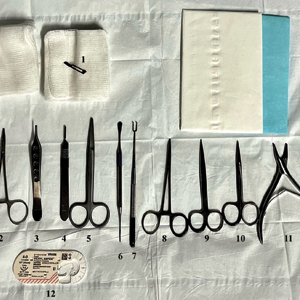
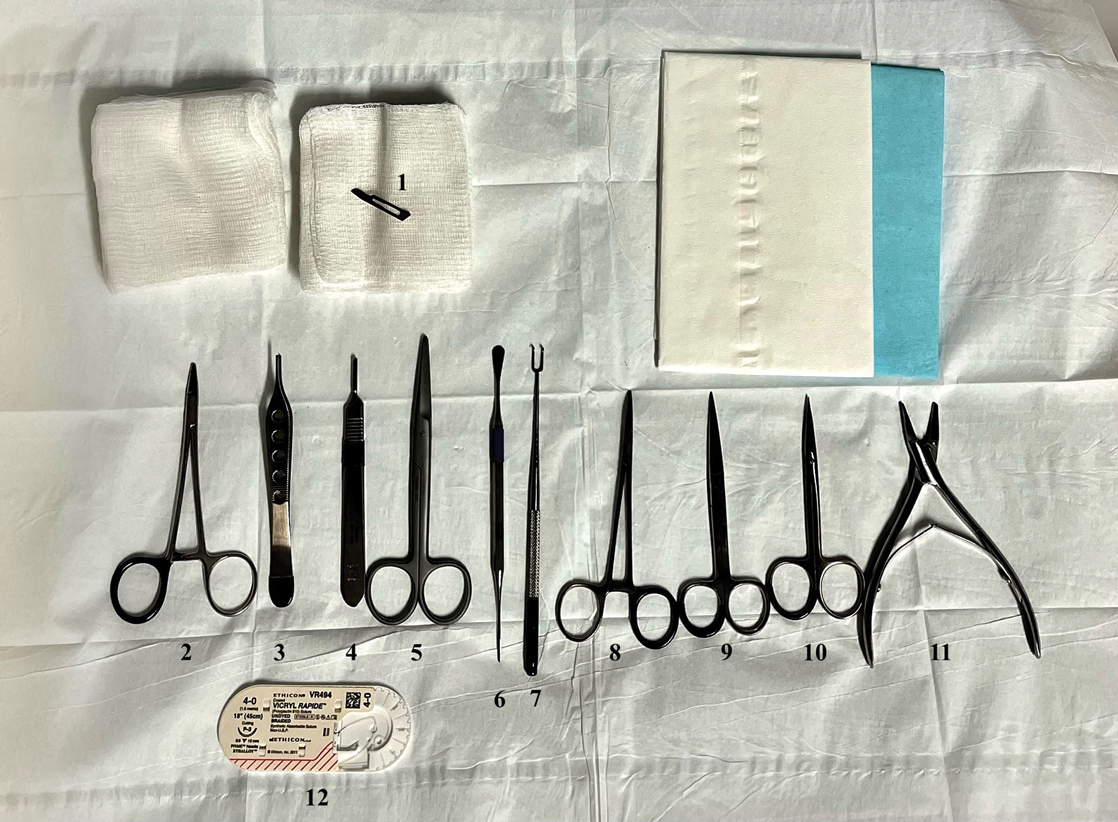
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.
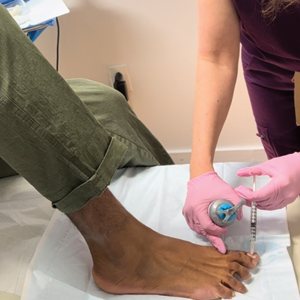
After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.

After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
Practice Gap
The term nail biopsy (NB) may refer to a punch, excisional, shave, or longitudinal biopsy of the nail matrix and/or nail bed.1 Nail surgeries, including NBs, are performed relatively infrequently. In a study using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017, only 1.01% of Mohs surgeons and 0.28% of general dermatologists in the United States performed NBs. Thirty-one states had no dermatologist-performed NBs, while 3 states had no nail biopsies performed by any physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant, indicating that there is a shortage of dermatology clinicians performing nail surgeries.2
Dermatologists may not be performing NBs due to unfamiliarity with nail unit anatomy and lack of formal NB training during residency.3 In a survey of 240 dermatology residents in the United States, 58% reported performing fewer than 10 nail procedures during residency, with 25% observing only.4 Of those surveyed, 1% had no exposure to nail procedures during 3 years of residency. Furthermore, when asked to assess their competency in nail surgery on a scale of not competent, competent, and very competent, approximately 30% responded that they were not competent.4 Without sufficient education on procedures involving the nail unit, residents may be reluctant to incorporate nail surgery into their clinical practice.
Due to their complexity, NBs require the use of several specialized surgical instruments that are not used for other dermatologic procedures, and residents and attending physicians who have limited nail training may be unfamiliar with these tools. To address this educational gap, we sought to create a guide that details the surgical instruments used for the nail matrix tangential excision (shave) biopsy technique—the most common technique used in our nail specialty clinic. This guide is intended for educational use by dermatologists who wish to incorporate NB as part of their practice.
Tools and Technique
As a major referral center, our New York City–based nail specialty clinic performs a large volume of NBs, many of them performed for clinically concerning longitudinal melanonychias for which a nail matrix shave biopsy most often is performed. We utilize a standardized tray consisting of 12 surgical instruments that are needed to successfully perform a NB from start to finish (Figure). In addition to standard surgical tray items, such as sutures and tissue scissors, additional specialized instruments are necessary for NB procedures, including a nail elevator, an English nail splitter, and skin hook.

After the initial incisions are made at 45° angles to the proximal nail fold surrounding the longitudinal band, the nail elevator is used to separate the proximal nail plate from the underlying nail bed. The English nail splitter is used to create a transverse split separating the proximal from the distal nail plate, and the proximal nail plate then is retracted using a clamp. The skin hook is used to retract the proximal nail fold to expose the pigment in the nail matrix, which is biopsied using the #15 blade and sent for histopathology. The proximal nail fold and retracted nail plate then are put back in place, and absorbable sutures are used to repair the defect. In certain cases, a 3-mm punch biopsy may be used to sample the nail plate and/or the surrounding soft tissue.
Practice Implications
A guide to surgical tools used during NB procedures, including less commonly encountered tools such as a nail elevator and English nail splitter, helps to close the educational gap of NB procedures among dermatology trainees and attending physicians. In conjunction with practical training with cadavers and models, a guide to surgical tools can be reviewed by trainees before hands-on exposure to nail surgery in a clinical setting. By increasing awareness of the tools needed to complete the procedure from start to finish, dermatologists may feel more prepared and confident in their ability to perform NBs, ultimately allowing for more rapid diagnosis of nail malignancies.
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
- Grover C, Bansal S. Nail biopsy: a user’s manual. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2018;9:3-15. doi:10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_268_17
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Hare AQ, Rich P. Clinical and educational gaps in diagnosis of nail disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2016;34:269-273. doi:10.1016/j.det.2016.02.002
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.e4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
Melasma Risk Factors: A Matched Cohort Study Using Data From the All of Us Research Program
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
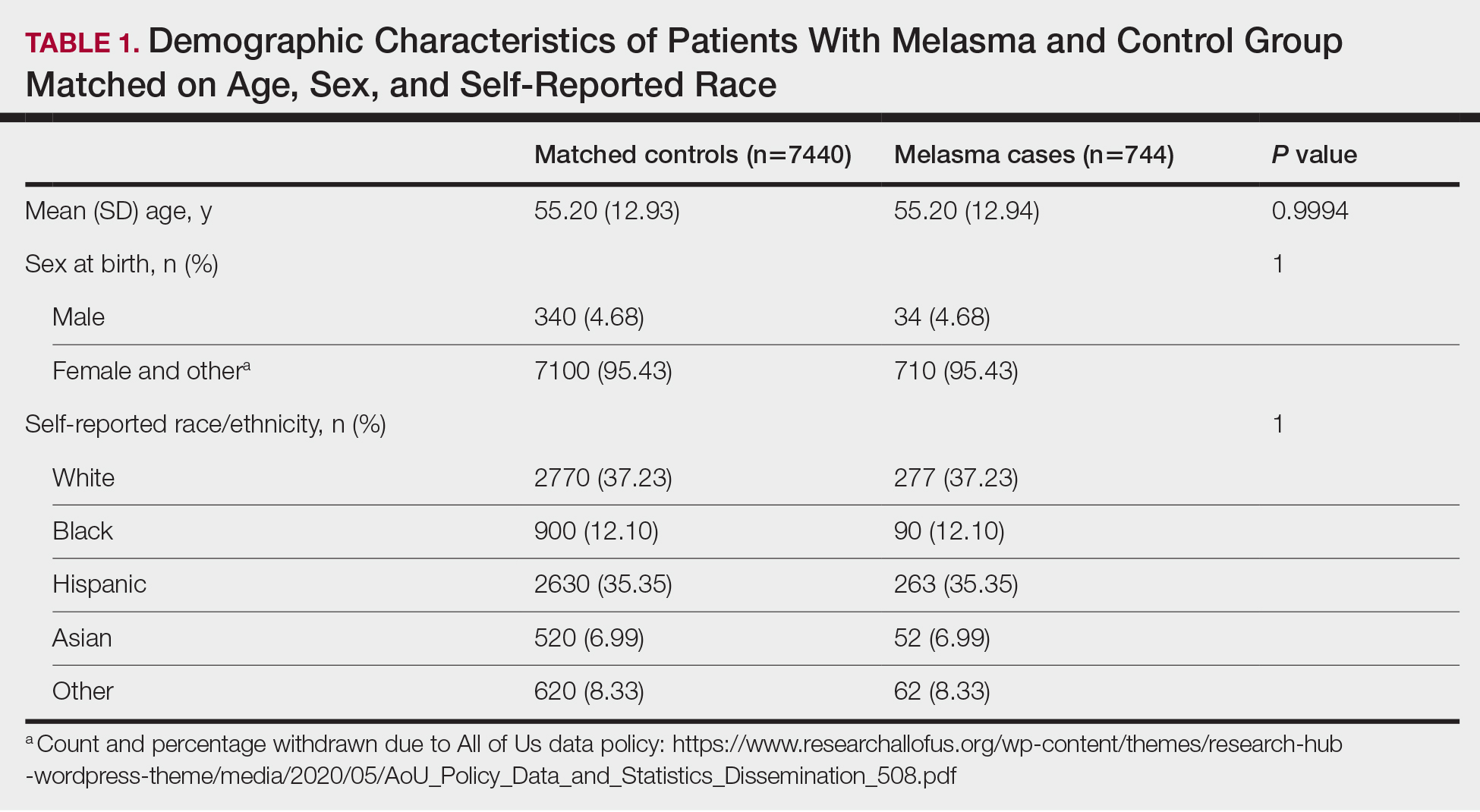
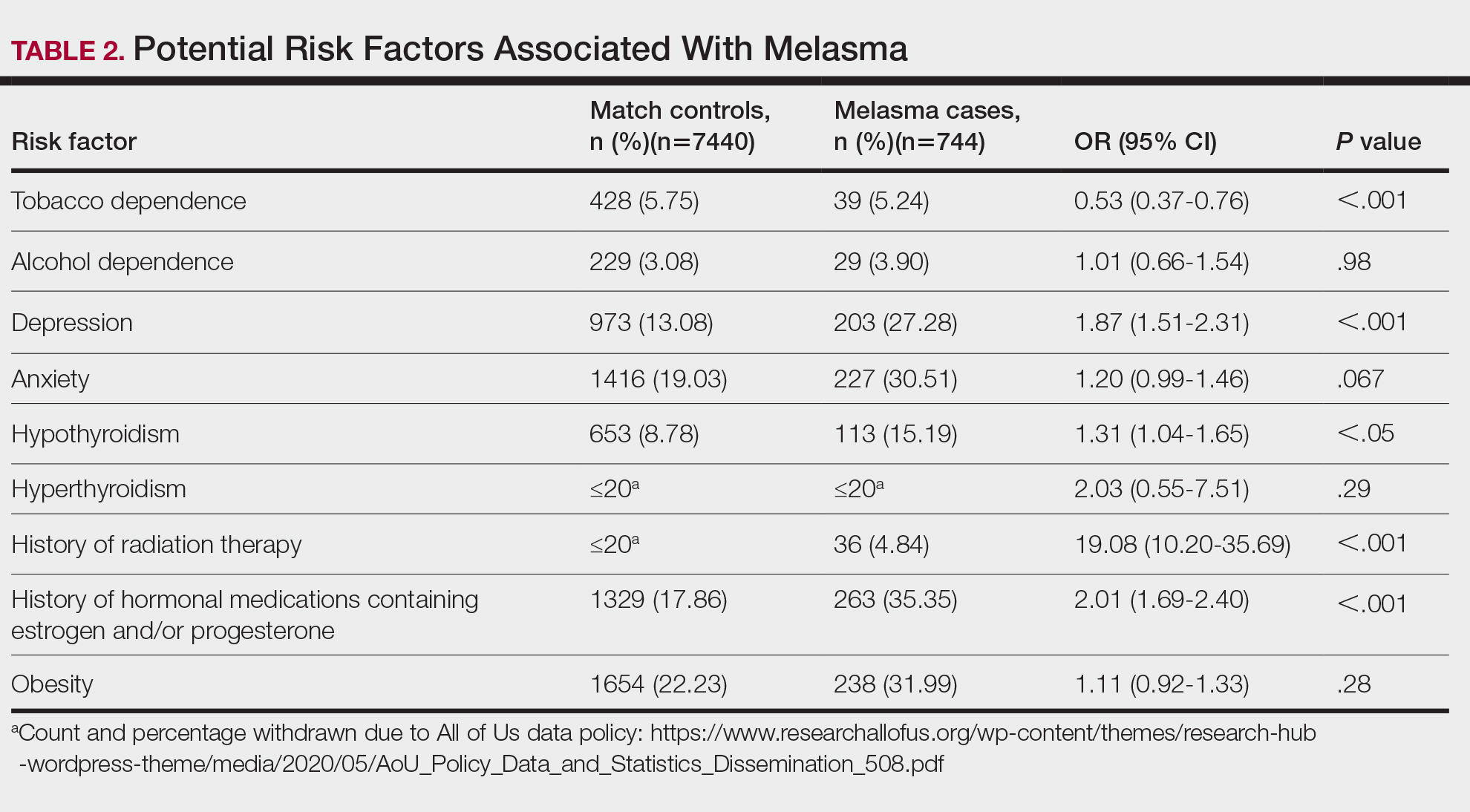
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.
Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.


Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
To the Editor:
Melasma (also known as chloasma) is characterized by symmetric hyperpigmented patches affecting sun-exposed areas. Women commonly develop this condition during pregnancy, suggesting a connection between melasma and increased female sex hormone levels.1 Other hypothesized risk factors include sun exposure, genetic susceptibility, estrogen and/or progesterone therapy, and thyroid abnormalities but have not been corroborated.2 Treatment options are limited because the pathogenesis is poorly understood; thus, we aimed to analyze melasma risk factors using a national database with a nested case-control approach.
We conducted a matched case-control study using the Registered Tier dataset (version 7) from the National Institute of Health’s All of Us Research Program (https://allofus.nih.gov/), which is available to authorized users through the program’s Researcher Workbench and includes more than 413,000 total participants enrolled from May 1, 2018, through July 1, 2022. Cases included patients 18 years and older with a diagnosis of melasma (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification code L81.1 [Chloasma]; concept ID 4264234 [Chloasma]; and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine [SNOMED] code 36209000 [Chloasma]), and controls without a diagnosis of melasma were matched in a 1:10 ratio based on age, sex, and self-reported race. Concept IDs and SNOMED codes were used to identify individuals in each cohort with a diagnosis of alcohol dependence (concept IDs 433753, 435243, 4218106; SNOMED codes 15167005, 66590003, 7200002), depression (concept ID 440383; SNOMED code 35489007), hypothyroidism (concept ID 140673; SNOMED code 40930008), hyperthyroidism (concept ID 4142479; SNOMED code 34486009), anxiety (concept IDs 441542, 442077, 434613; SNOMED codes 48694002, 197480006, 21897009), tobacco dependence (concept IDs 37109023, 437264, 4099811; SNOMED codes 16077091000119107, 89765005, 191887008), or obesity (concept IDs 433736 and 434005; SNOMED codes 414916001 and 238136002), or with a history of radiation therapy (concept IDs 4085340, 4311117, 4061844, 4029715; SNOMED codes 24803000, 85983004, 200861004, 108290001) or hormonal medications containing estrogen and/or progesterone, including oral medications and implants (concept IDs 21602445, 40254009, 21602514, 21603814, 19049228, 21602529, 1549080, 1551673, 1549254, 21602472, 21602446, 21602450, 21602515, 21602566, 21602473, 21602567, 21602488, 21602585, 1596779, 1586808, 21602524). In our case cohort, diagnoses and exposures to treatments were only considered for analysis if they occurred prior to melasma diagnosis.
Multivariate logistic regression was performed to calculate odds ratios and P values between melasma and each comorbidity or exposure to the treatments specified. Statistical significance was set at P<.05.
We identified 744 melasma cases (mean age, 55.20 years; 95.43% female; 12.10% Black) and 7440 controls with similar demographics (ie, age, sex, race/ethnicity) between groups (all P>.05 [Table 1]). Patients with a melasma diagnosis were more likely to have a pre-existing diagnosis of depression (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.51-2.31 [P<.001]) or hypothyroidism (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.04-1.65 [P<.05]), or a history of radiation therapy (OR, 19.08; 95% CI, 10.20-35.69 [P<.001]) and/or estrogen and/or progesterone therapy (OR, 2.01; 95% CI, 1.69-2.40 [P<.001]) prior to melasma diagnosis. A diagnosis of anxiety prior to melasma diagnosis trended toward an association with melasma (P=.067). Pre-existing alcohol dependence, obesity, and hyperthyroidism were not associated with melasma (P=.98, P=.28, and P=.29, respectively). A diagnosis of tobacco dependence was associated with a decreased melasma risk (OR, 0.53, 95% CI, 0.37-0.76)[P<.001])(Table 2).
Our study results suggest that pre-existing depression was a risk factor for subsequent melasma diagnosis. Depression may exacerbate stress, leading to increased activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis as well as increased levels of cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which subsequently act on melanocytes to increase melanogenesis.3 A retrospective study of 254 participants, including 127 with melasma, showed that increased melasma severity was associated with higher rates of depression (P=.002)2; however, the risk for melasma following a depression diagnosis has not been reported.
Our results also showed that hypothyroidism was associated with an increased risk for melasma. On a cellular level, hypothyroidism can cause systemic inflammation, potentailly leading to increased stress and melanogenesis via activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.4 These findings are similar to a systematic review and meta-analysis reporting increased thyroid-stimulating hormone, anti–thyroid peroxidase, and antithyroglobulin antibody levels associated with increased melasma risk (mean difference between cases and controls, 0.33 [95% CI, 0.18-0.47]; pooled association, P=.020; mean difference between cases and controls, 0.28 [95% CI, 0.01-0.55], respectively).5
Patients in our cohort who had a history of radiation therapy were 19 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to findings of a survey-based study of 421 breast cancer survivors in which 336 (79.81%) reported hyperpigmentation in irradiated areas.6 Patients in our cohort who had a history of estrogen and/or progesterone therapy were 2 times more likely to develop melasma, similar to a case-control study of 207 patients with melasma and 207 controls that showed combined oral contraceptives increased risk for melasma (OR, 1.23 [95% CI, 1.08-1.41; P<.01).3
Tobacco use is not a well-known protective factor against melasma. Prior studies have indicated that tobacco smoking activates melanocytes via the Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, leading to hyperpigmentation.7 Although exposure to cigarette smoke decreases angiogenesis and would more likely lead to hyperpigmentation, nicotine exposure has been shown to increase angiogenesis, which could lead to increased blood flow and partially explain the protection against melasma demonstrated in our cohort.8 Future studies are needed to explore this relationship.


Limitations of our study include lack of information about melasma severity and information about prior melasma treatment in our cohort as well as possible misdiagnosis reported in the dataset.
Our results demonstrated that pre-existing depression and hypothyroidism as well as a history of radiation or estrogen and/or progesterone therapies are potential risk factors for melasma. Therefore, we recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction, and patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/or progesterone therapy should be counseled on their increased risk for melasma. Future studies are needed to determine whether treatment of comorbidities such as hypothyroidism and depression improve melasma severity. The decreased risk for melasma associated with tobacco use also requires further investigation.
Acknowledgments—The All of Us Research Program is supported by the National Institutes of Health, Office of the Director: Regional Medical Centers: 1 OT2 OD026549; 1 OT2 OD026554; 1 OT2 OD026557; 1 OT2 OD026556; 1 OT2 OD026550; 1 OT2 OD 026552; 1 OT2 OD026553; 1 OT2 OD026548; 1 OT2 OD026551; 1 OT2 OD026555; IAA #: AOD 16037; Federally Qualified Health Centers: HHSN 263201600085U; Data and Research Center: 5 U2C OD023196; Biobank: 1 U24 OD023121; The Participant Center: U24 OD023176; Participant Technology Systems Center: 1 U24 OD023163; Communications and Engagement: 3 OT2 OD023205; 3 OT2 OD023206; and Community Partners: 1 OT2 OD025277; 3 OT2 OD025315; 1 OT2 OD025337; 1 OT2 OD025276.
In addition, the All of Us Research Program would not be possible without the partnership of its participants, who we gratefully acknowledge for their contributions and without whom this research would not have been possible. We also thank the All of Us Research Program for making the participant data examined in this study available to us.
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
- Filoni A, Mariano M, Cameli N. Melasma: how hormones can modulate skin pigmentation. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18:458-463. doi:10.1111/jocd.12877
- Platsidaki E, Efstathiou V, Markantoni V, et al. Self-esteem, depression, anxiety and quality of life in patients with melasma living in a sunny mediterranean area: results from a prospective cross-sectional study. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13:1127-1136. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00915-1
- Handel AC, Lima PB, Tonolli VM, et al. Risk factors for facial melasma in women: a case-control study. Br J Dermatol. 2014;171:588-594. doi:10.1111/bjd.13059
- Erge E, Kiziltunc C, Balci SB, et al. A novel inflammatory marker for the diagnosis of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: platelet-count-to-lymphocyte-count ratio (published January 22, 2023). Diseases. 2023;11:15. doi:10.3390/diseases11010015
- Kheradmand M, Afshari M, Damiani G, et al. Melasma and thyroid disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2019;58:1231-1238. doi:10.1111/ijd.14497
- Chu CN, Hu KC, Wu RS, et al. Radiation-irritated skin and hyperpigmentation may impact the quality of life of breast cancer patients after whole breast radiotherapy (published March 31, 2021). BMC Cancer. 2021;21:330. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08047-5
- Nakamura M, Ueda Y, Hayashi M, et al. Tobacco smoke-induced skin pigmentation is mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Exp Dermatol. 2013;22:556-558. doi:10.1111/exd.12170
- Ejaz S, Lim CW. Toxicological overview of cigarette smoking on angiogenesis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2005;20:335-344. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2005.03.011
Practice Points
- Treatment options for melasma are limited due to its poorly understood pathogenesis.
- Depression and hypothyroidism and/or history of exposure to radiation and hormonal therapies may increase melasma risk.
- We recommend that patients with melasma be screened for depression and thyroid dysfunction. Patients undergoing radiation therapy or starting estrogen and/ or progesterone therapy should be counseled on the increased risk for melasma.
Optimizing Patient Care With Teledermatology: Improving Access, Efficiency, and Satisfaction
Telemedicine interest, which was relatively quiescent prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has surged in popularity in the past few years.1 It can now be utilized seamlessly in dermatology practices to deliver exceptional patient care while reducing costs and travel time and offering dermatologists flexibility and improved work-life balance. Teledermatology applications include synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid platforms.2 For synchronous teledermatology, patient visits are carried out in real time with audio and video technology.3 For asynchronous teledermatology—also known as the store-and-forward model—the dermatologist receives the patient’s history and photographs and then renders an assessment and treatment plan.2 Hybrid teledermatology uses real-time audio and video conferencing for history taking, assessment and treatment plan, and patient education, with photographs sent asynchronously.3 Telemedicine may not be initially intuitive or easy to integrate into clinical practice, but with time and effort, it will complement your dermatology practice, making it run more efficiently.
Patient Satisfaction With Teledermatology
Studies generally have shown very high patient satisfaction rates and shorter wait times with teledermatology vs in-person visits; for example, in a systematic review of 15 teledermatology studies including 7781 patients, more than 80% of participants reported high satisfaction with their telemedicine visit, with up to 92% reporting that they would choose to do a televisit again.4 In a retrospective analysis of 615 Zocdoc physicians, 65% of whom were dermatologists, mean wait times were 2.4 days for virtual appointments compared with 11.7 days for in-person appointments.5 Similarly, in a retrospective single-institution study, mean wait times for televisits were 14.3 days compared with 34.7 days for in-person referrals.6
Follow-Up Visits for Nail Disorders Via Teledermatology
Teledermatology may be particularly well suited for treating patients with nail disorders. In a prospective observational study, Onyeka et al7 accessed 813 images from 63 dermatology patients via teledermatology over a 6-month period to assess distance, focus, brightness, background, and image quality; of them, 83% were rated as high quality. Notably, images of nail disorders, skin growths, or pigmentation disorders were rated as having better image quality than images of inflammatory skin conditions (odds ratio [OR], 4.2-12.9 [P<.005]).7 In a retrospective study of 107 telemedicine visits for nail disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic, patients with longitudinal melanonychia were recommended for in-person visits for physical examination and dermoscopy, as were patients with suspected onychomycosis, who required nail plate sampling for diagnostic confirmation; however, approximately half of visits did not require in-person follow-up, including those patients with confirmed onychomycosis.8 Onychomycosis patients could be examined for clinical improvement and counseled on medication compliance via telemedicine. Other patients who did not require in-person follow-ups were those with traumatic nail disorders such as subungual hematoma and retronychia as well as those with body‐focused repetitive behaviors, including habit-tic nail deformity, onychophagia, and onychotillomania.8
Patients undergoing nail biopsies to rule out malignancies or to diagnose inflammatory nail disorders also may be managed via telemedicine. Patients for whom nail biopsies are recommended often are anxious about the procedure, which may be due to portrayal of nail trauma in the media9 or lack of accurate information on nail biopsies online.10 Therefore, counseling via telemedicine about the details of the procedure in a patient-friendly way (eg, showing an animated video and narrating it11) can allay anxiety without the inconvenience, cost, and time missed from work associated with traveling to an in-person visit. In addition, postoperative counseling ideally is performed via telemedicine because complications following nail procedures are uncommon. In a retrospective study of 502 patients who underwent a nail biopsy at a single academic center, only 14 developed surgical site infections within 8 days on average (range, 5–13 days), with a higher infection risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (P<.0003).12
Advantages and Limitations
There are many benefits to incorporating telemedicine into dermatology practices, including reduced overhead costs, convenience and time saved for patients, and flexibility and improved work-life balance for dermatologists. In addition, because the number of in-person visits seen generally is fixed due to space constraints and work-hour restrictions, delegating follow-up visits to telemedicine can free up in-person slots for new patients and those needing procedures. However, there also are some inherent limitations to telemedicine: technology access, vision or hearing difficulties or low digital health literacy, or language barriers. In the prospective observational study by Onyeka et al7 analyzing 813 teledermatology images, patients aged 65 to 74 years sent in more clinically useful images (OR, 7.9) and images that were more often in focus (OR, 2.6) compared with patients older than 85 years.
Final Thoughts
Incorporation of telemedicine into dermatologic practice is a valuable tool for triaging patients with acute issues, improving patient care and health care access, making practices more efficient, and improving dermatologist flexibility and work-life balance. Further development of teledermatology to provide access to underserved populations prioritizing dermatologist reimbursement and progress on technologic innovations will make teledermatology even more useful in the coming years.
- He A, Ti Kim T, Nguyen KD. Utilization of teledermatology services for dermatological diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1059-1062.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Wang RH, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL, et al. Synchronous and asynchronous teledermatology: a narrative review of strengths and limitations. J Telemed Telecare. 2022;28:533-538.
- Miller J, Jones E. Shaping the future of teledermatology: a literature review of patient and provider satisfaction with synchronous teledermatology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:1903-1909.
- Gu L, Xiang L, Lipner SR. Analysis of availability of online dermatology appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:517-520.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an eConsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;83:1633-1638.
- Onyeka S, Kim J, Eid E, et al. Quality of images submitted by older patients to a teledermatology platform. Abstract presented at the Society of Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting; May 15-18, 2024; Dallas, TX.
- Chang MJ, Stewart CR, Lipner SR. Retrospective study of nail telemedicine visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14630.
- Albucker SJ, Falotico JM, Lipner SR. A real nail biter: a cross-sectional study of 75 nail trauma scenes in international films and television series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2023;27:288-291.
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Hill RC, Ho B, Lipner SR. Assuaging patient anxiety about nail biopsies with an animated educational video. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online March 29, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.03.031.
- Axler E, Lu A, Darrell M, et al. Surgical site infections are uncommon following nail biopsies in a single-center case-control study of 502 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online May 15, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.05.017
Telemedicine interest, which was relatively quiescent prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has surged in popularity in the past few years.1 It can now be utilized seamlessly in dermatology practices to deliver exceptional patient care while reducing costs and travel time and offering dermatologists flexibility and improved work-life balance. Teledermatology applications include synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid platforms.2 For synchronous teledermatology, patient visits are carried out in real time with audio and video technology.3 For asynchronous teledermatology—also known as the store-and-forward model—the dermatologist receives the patient’s history and photographs and then renders an assessment and treatment plan.2 Hybrid teledermatology uses real-time audio and video conferencing for history taking, assessment and treatment plan, and patient education, with photographs sent asynchronously.3 Telemedicine may not be initially intuitive or easy to integrate into clinical practice, but with time and effort, it will complement your dermatology practice, making it run more efficiently.
Patient Satisfaction With Teledermatology
Studies generally have shown very high patient satisfaction rates and shorter wait times with teledermatology vs in-person visits; for example, in a systematic review of 15 teledermatology studies including 7781 patients, more than 80% of participants reported high satisfaction with their telemedicine visit, with up to 92% reporting that they would choose to do a televisit again.4 In a retrospective analysis of 615 Zocdoc physicians, 65% of whom were dermatologists, mean wait times were 2.4 days for virtual appointments compared with 11.7 days for in-person appointments.5 Similarly, in a retrospective single-institution study, mean wait times for televisits were 14.3 days compared with 34.7 days for in-person referrals.6
Follow-Up Visits for Nail Disorders Via Teledermatology
Teledermatology may be particularly well suited for treating patients with nail disorders. In a prospective observational study, Onyeka et al7 accessed 813 images from 63 dermatology patients via teledermatology over a 6-month period to assess distance, focus, brightness, background, and image quality; of them, 83% were rated as high quality. Notably, images of nail disorders, skin growths, or pigmentation disorders were rated as having better image quality than images of inflammatory skin conditions (odds ratio [OR], 4.2-12.9 [P<.005]).7 In a retrospective study of 107 telemedicine visits for nail disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic, patients with longitudinal melanonychia were recommended for in-person visits for physical examination and dermoscopy, as were patients with suspected onychomycosis, who required nail plate sampling for diagnostic confirmation; however, approximately half of visits did not require in-person follow-up, including those patients with confirmed onychomycosis.8 Onychomycosis patients could be examined for clinical improvement and counseled on medication compliance via telemedicine. Other patients who did not require in-person follow-ups were those with traumatic nail disorders such as subungual hematoma and retronychia as well as those with body‐focused repetitive behaviors, including habit-tic nail deformity, onychophagia, and onychotillomania.8
Patients undergoing nail biopsies to rule out malignancies or to diagnose inflammatory nail disorders also may be managed via telemedicine. Patients for whom nail biopsies are recommended often are anxious about the procedure, which may be due to portrayal of nail trauma in the media9 or lack of accurate information on nail biopsies online.10 Therefore, counseling via telemedicine about the details of the procedure in a patient-friendly way (eg, showing an animated video and narrating it11) can allay anxiety without the inconvenience, cost, and time missed from work associated with traveling to an in-person visit. In addition, postoperative counseling ideally is performed via telemedicine because complications following nail procedures are uncommon. In a retrospective study of 502 patients who underwent a nail biopsy at a single academic center, only 14 developed surgical site infections within 8 days on average (range, 5–13 days), with a higher infection risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (P<.0003).12
Advantages and Limitations
There are many benefits to incorporating telemedicine into dermatology practices, including reduced overhead costs, convenience and time saved for patients, and flexibility and improved work-life balance for dermatologists. In addition, because the number of in-person visits seen generally is fixed due to space constraints and work-hour restrictions, delegating follow-up visits to telemedicine can free up in-person slots for new patients and those needing procedures. However, there also are some inherent limitations to telemedicine: technology access, vision or hearing difficulties or low digital health literacy, or language barriers. In the prospective observational study by Onyeka et al7 analyzing 813 teledermatology images, patients aged 65 to 74 years sent in more clinically useful images (OR, 7.9) and images that were more often in focus (OR, 2.6) compared with patients older than 85 years.
Final Thoughts
Incorporation of telemedicine into dermatologic practice is a valuable tool for triaging patients with acute issues, improving patient care and health care access, making practices more efficient, and improving dermatologist flexibility and work-life balance. Further development of teledermatology to provide access to underserved populations prioritizing dermatologist reimbursement and progress on technologic innovations will make teledermatology even more useful in the coming years.
Telemedicine interest, which was relatively quiescent prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, has surged in popularity in the past few years.1 It can now be utilized seamlessly in dermatology practices to deliver exceptional patient care while reducing costs and travel time and offering dermatologists flexibility and improved work-life balance. Teledermatology applications include synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid platforms.2 For synchronous teledermatology, patient visits are carried out in real time with audio and video technology.3 For asynchronous teledermatology—also known as the store-and-forward model—the dermatologist receives the patient’s history and photographs and then renders an assessment and treatment plan.2 Hybrid teledermatology uses real-time audio and video conferencing for history taking, assessment and treatment plan, and patient education, with photographs sent asynchronously.3 Telemedicine may not be initially intuitive or easy to integrate into clinical practice, but with time and effort, it will complement your dermatology practice, making it run more efficiently.
Patient Satisfaction With Teledermatology
Studies generally have shown very high patient satisfaction rates and shorter wait times with teledermatology vs in-person visits; for example, in a systematic review of 15 teledermatology studies including 7781 patients, more than 80% of participants reported high satisfaction with their telemedicine visit, with up to 92% reporting that they would choose to do a televisit again.4 In a retrospective analysis of 615 Zocdoc physicians, 65% of whom were dermatologists, mean wait times were 2.4 days for virtual appointments compared with 11.7 days for in-person appointments.5 Similarly, in a retrospective single-institution study, mean wait times for televisits were 14.3 days compared with 34.7 days for in-person referrals.6
Follow-Up Visits for Nail Disorders Via Teledermatology
Teledermatology may be particularly well suited for treating patients with nail disorders. In a prospective observational study, Onyeka et al7 accessed 813 images from 63 dermatology patients via teledermatology over a 6-month period to assess distance, focus, brightness, background, and image quality; of them, 83% were rated as high quality. Notably, images of nail disorders, skin growths, or pigmentation disorders were rated as having better image quality than images of inflammatory skin conditions (odds ratio [OR], 4.2-12.9 [P<.005]).7 In a retrospective study of 107 telemedicine visits for nail disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic, patients with longitudinal melanonychia were recommended for in-person visits for physical examination and dermoscopy, as were patients with suspected onychomycosis, who required nail plate sampling for diagnostic confirmation; however, approximately half of visits did not require in-person follow-up, including those patients with confirmed onychomycosis.8 Onychomycosis patients could be examined for clinical improvement and counseled on medication compliance via telemedicine. Other patients who did not require in-person follow-ups were those with traumatic nail disorders such as subungual hematoma and retronychia as well as those with body‐focused repetitive behaviors, including habit-tic nail deformity, onychophagia, and onychotillomania.8
Patients undergoing nail biopsies to rule out malignancies or to diagnose inflammatory nail disorders also may be managed via telemedicine. Patients for whom nail biopsies are recommended often are anxious about the procedure, which may be due to portrayal of nail trauma in the media9 or lack of accurate information on nail biopsies online.10 Therefore, counseling via telemedicine about the details of the procedure in a patient-friendly way (eg, showing an animated video and narrating it11) can allay anxiety without the inconvenience, cost, and time missed from work associated with traveling to an in-person visit. In addition, postoperative counseling ideally is performed via telemedicine because complications following nail procedures are uncommon. In a retrospective study of 502 patients who underwent a nail biopsy at a single academic center, only 14 developed surgical site infections within 8 days on average (range, 5–13 days), with a higher infection risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (P<.0003).12
Advantages and Limitations
There are many benefits to incorporating telemedicine into dermatology practices, including reduced overhead costs, convenience and time saved for patients, and flexibility and improved work-life balance for dermatologists. In addition, because the number of in-person visits seen generally is fixed due to space constraints and work-hour restrictions, delegating follow-up visits to telemedicine can free up in-person slots for new patients and those needing procedures. However, there also are some inherent limitations to telemedicine: technology access, vision or hearing difficulties or low digital health literacy, or language barriers. In the prospective observational study by Onyeka et al7 analyzing 813 teledermatology images, patients aged 65 to 74 years sent in more clinically useful images (OR, 7.9) and images that were more often in focus (OR, 2.6) compared with patients older than 85 years.
Final Thoughts
Incorporation of telemedicine into dermatologic practice is a valuable tool for triaging patients with acute issues, improving patient care and health care access, making practices more efficient, and improving dermatologist flexibility and work-life balance. Further development of teledermatology to provide access to underserved populations prioritizing dermatologist reimbursement and progress on technologic innovations will make teledermatology even more useful in the coming years.
- He A, Ti Kim T, Nguyen KD. Utilization of teledermatology services for dermatological diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1059-1062.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Wang RH, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL, et al. Synchronous and asynchronous teledermatology: a narrative review of strengths and limitations. J Telemed Telecare. 2022;28:533-538.
- Miller J, Jones E. Shaping the future of teledermatology: a literature review of patient and provider satisfaction with synchronous teledermatology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:1903-1909.
- Gu L, Xiang L, Lipner SR. Analysis of availability of online dermatology appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:517-520.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an eConsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;83:1633-1638.
- Onyeka S, Kim J, Eid E, et al. Quality of images submitted by older patients to a teledermatology platform. Abstract presented at the Society of Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting; May 15-18, 2024; Dallas, TX.
- Chang MJ, Stewart CR, Lipner SR. Retrospective study of nail telemedicine visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14630.
- Albucker SJ, Falotico JM, Lipner SR. A real nail biter: a cross-sectional study of 75 nail trauma scenes in international films and television series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2023;27:288-291.
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Hill RC, Ho B, Lipner SR. Assuaging patient anxiety about nail biopsies with an animated educational video. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online March 29, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.03.031.
- Axler E, Lu A, Darrell M, et al. Surgical site infections are uncommon following nail biopsies in a single-center case-control study of 502 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online May 15, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.05.017
- He A, Ti Kim T, Nguyen KD. Utilization of teledermatology services for dermatological diagnoses during the COVID-19 pandemic. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1059-1062.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Wang RH, Barbieri JS, Kovarik CL, et al. Synchronous and asynchronous teledermatology: a narrative review of strengths and limitations. J Telemed Telecare. 2022;28:533-538.
- Miller J, Jones E. Shaping the future of teledermatology: a literature review of patient and provider satisfaction with synchronous teledermatology during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;47:1903-1909.
- Gu L, Xiang L, Lipner SR. Analysis of availability of online dermatology appointments during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:517-520.
- Wang RF, Trinidad J, Lawrence J, et al. Improved patient access and outcomes with the integration of an eConsult program (teledermatology) within a large academic medical center. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;83:1633-1638.
- Onyeka S, Kim J, Eid E, et al. Quality of images submitted by older patients to a teledermatology platform. Abstract presented at the Society of Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting; May 15-18, 2024; Dallas, TX.
- Chang MJ, Stewart CR, Lipner SR. Retrospective study of nail telemedicine visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14630.
- Albucker SJ, Falotico JM, Lipner SR. A real nail biter: a cross-sectional study of 75 nail trauma scenes in international films and television series. J Cutan Med Surg. 2023;27:288-291.
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Hill RC, Ho B, Lipner SR. Assuaging patient anxiety about nail biopsies with an animated educational video. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online March 29, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.03.031.
- Axler E, Lu A, Darrell M, et al. Surgical site infections are uncommon following nail biopsies in a single-center case-control study of 502 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online May 15, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2024.05.017
Practice Points
- Incorporation of telemedicine into dermatologic practice can improve patient access, reduce costs, and offer dermatologists flexibility and improved work-life balance.
- Patient satisfaction with telemedicine is exceedingly high, and teledermatology may be particularly well suited for caring for patients with nail disorders.
Tackling Inflammatory and Infectious Nail Disorders in Children
Nail disorders are common among pediatric patients but often are underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed because of their unique disease manifestations. These conditions may severely impact quality of life. There are few nail disease clinical trials that include children. Consequently, most treatment recommendations are based on case series and expert consensus recommendations. We review inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in pediatric patients. By describing characteristics, clinical manifestations, and management approaches for these conditions, we aim to provide guidance to dermatologists in their diagnosis and treatment.
INFLAMMATORY NAIL DISORDERS
Nail Psoriasis
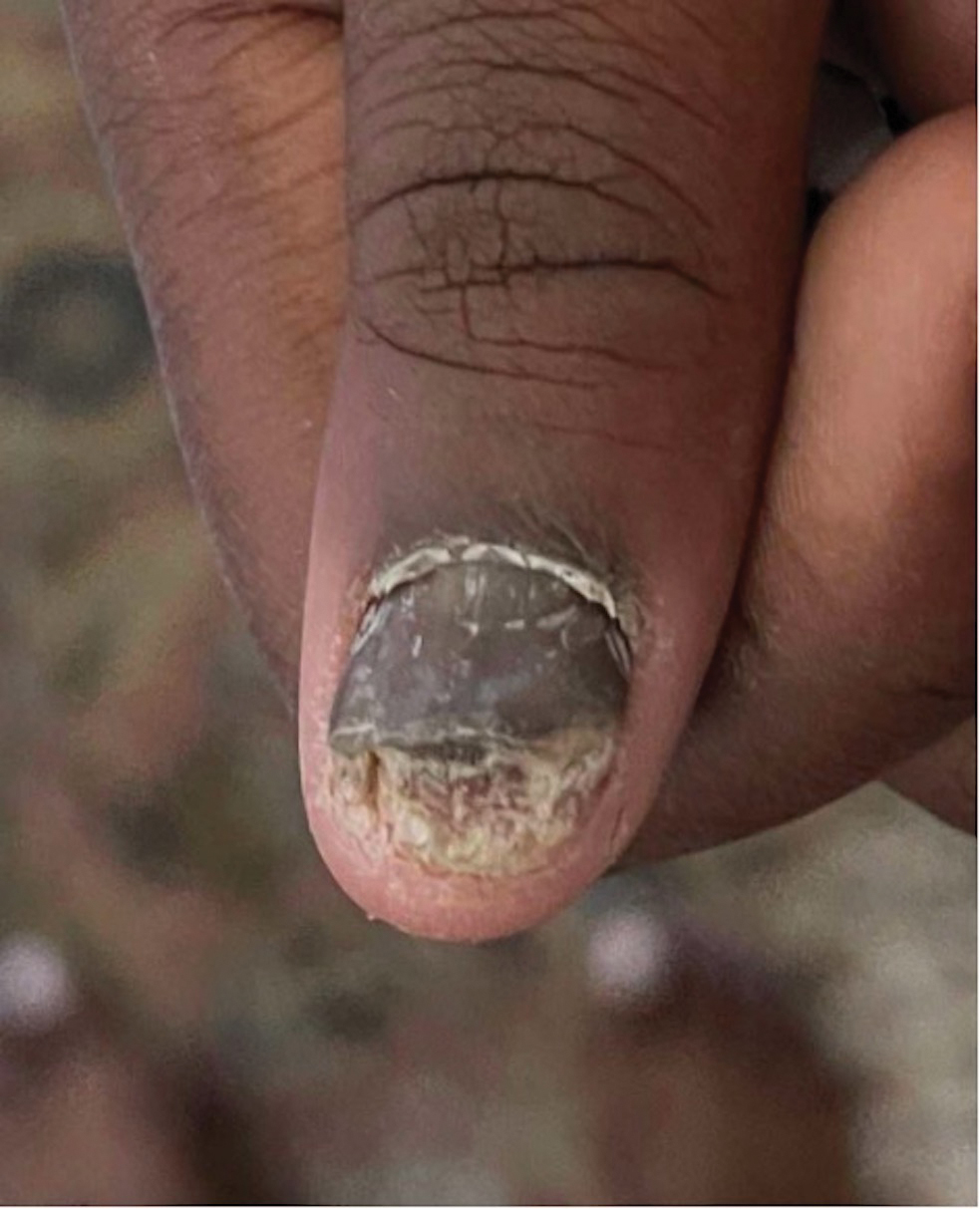
Nail involvement in children with psoriasis is common, with prevalence estimates ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail matrix psoriasis may manifest with pitting (large irregular pits) and leukonychia as well as chromonychia and nail plate crumbling. Onycholysis, oil drop spots (salmon patches), and subungual hyperkeratosis can be seen in nail bed psoriasis. Nail pitting is the most frequently observed clinical finding (Figure 1).2,3 In a cross-sectional multicenter study of 313 children with cutaneous psoriasis in France, nail findings were present in 101 patients (32.3%). There were associations between nail findings and presence of psoriatic arthritis (P=.03), palmoplantar psoriasis (P<.001), and severity of psoriatic disease, defined as use of systemic treatment with phototherapy (psoralen plus UVA, UVB), traditional systemic treatment (acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporine), or a biologic (P=.003).4
Topical steroids and vitamin D analogues may be used with or without occlusion and may be efficacious.5 Several case reports describe systemic treatments for psoriasis in children, including methotrexate, acitretin, and apremilast (approved for children 6 years and older for plaque psoriasis by the US Food and Drug Administration [FDA]).2 There are 5 biologic drugs currently approved for the treatment of pediatric psoriasis—adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab—and 6 drugs currently undergoing phase 3 studies—brodalumab, guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, certolizumab pegol, and deucravacitinib (Table 1).6-15 Adalimumab is specifically approved for moderate to severe nail psoriasis in adults 18 years and older.
Intralesional steroid injections are sometimes useful in the management of nail matrix psoriasis; however, appropriate patient selection is critical due to the pain associated with the procedure. In a prospective study of 16 children (age range, 9–17 years) with nail psoriasis treated with intralesional triamcinolone (ILTAC) 2.5 to 5 mg/mL every 4 to 8 weeks for a minimum of 3 to 6 months, 9 patients achieved resolution and 6 had improvement of clinical findings.16 Local adverse events were mild, including injection-site pain (66%), subungual hematoma (n=1), Beau lines (n=1), proximal nail fold hypopigmentation (n=2), and proximal nail fold atrophy (n=2). Because the proximal nail fold in children is thinner than in adults, there may be an increased risk for nail fold hypopigmentation and atrophy in children. Therefore, a maximum ILTAC concentration of 2.5 mg/mL with 0.2 mL maximum volume per nail per session is recommended for children younger than 15 years.16
Nail Lichen Planus
Nail lichen planus (NLP) is uncommon in children, with few biopsy-proven cases documented in the literature.17 Common clinical findings are onychorrhexis, nail plate thinning, fissuring, splitting, and atrophy with koilonychia.5 Although pterygium development (irreversible nail matrix scarring) is uncommon in pediatric patients, NLP can be progressive and may cause irreversible destruction of the nail matrix and subsequent nail loss, warranting therapeutic intervention.18
Treatment of NLP may be difficult, as there are no options that work in all patients. Current literature supports the use of systemic corticosteroids or ILTAC for the treatment of NLP; however, recurrence rates can be high. According to an expert consensus paper on NLP treatment, ILTAC may be injected in a concentration of 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/mL according to disease severity.19 In severe or resistant cases, intramuscular (IM) triamcinolone may be considered, especially if more than 3 nails are affected. A dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/mo for at least 3 to 6 months is recommended for both children and adults, with 1 mg/kg/mo recommended in the active treatment phase (first 2–3 months).19 In a retrospective review of 5 pediatric patients with NLP treated with IM triamcinolone 0.5 mg/kg/mo, 3 patients had resolution and 2 improved with treatment.20 In a prospective study of 10 children with NLP, IM triamcinolone at a dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg every 30 days for 3 to 6 months resulted in resolution of nail findings in 9 patients.17 In a prospective study of 14 pediatric patients with NLP treated with 2.5 to 5 mg/mL of ILTAC, 10 achieved resolution and 3 improved.16
Intralesional triamcinolone injections may be better suited for teenagers compared to younger children who may be more apprehensive of needles. To minimize pain, it is recommended to inject ILTAC slowly at room temperature, with use of “talkesthesia” and vibration devices, 1% lidocaine, or ethyl chloride spray.18
Trachyonychia
Trachyonychia is characterized by the presence of sandpaperlike nails. It manifests with brittle thin nails with longitudinal ridging, onychoschizia, and thickened hyperkeratotic cuticles. Trachyonychia typically involves multiple nails, with a peak age of onset between 3 and 12 years.21,22 There are 2 variants: the opaque type with rough longitudinal ridging, and the shiny variant with opalescent nails and pits that reflect light. The opaque variant is more common and is associated with psoriasis, whereas the shiny variant is less common and is associated with alopecia areata.23 Although most cases are idiopathic, some are associated with psoriasis and alopecia areata, as previously noted, as well as atopic dermatitis (AD) and lichen planus.22,24
Fortunately, trachyonychia does not lead to permanent nail damage or pterygium, making treatment primarily focused on addressing functional and cosmetic concerns.24 Spontaneous resolution occurs in approximately 50% of patients. In a prospective study of 11 patients with idiopathic trachyonychia, there was partial improvement in 5 of 9 patients treated with topical steroids, 1 with only petrolatum, and 1 with vitamin supplements. Complete resolution was reported in 1 patient treated with topical steroids.25 Because trachyonychia often is self-resolving, no treatment is required and a conservative approach is strongly recommended.26 Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and 5-fluorouracil. Intralesional triamcinolone, systemic cyclosporine, retinoids, systemic corticosteroids, and tofacitinib have been described in case reports, though none of these have been shown to be 100% efficacious.24
Nail Lichen Striatus
Lichen striatus involving the nail is uncommon and is characterized by onycholysis, longitudinal ridging, splitting, and fraying, as well as what appears to be a subungual tumor. It can encompass the entire nail or may be isolated to a portion of the nail (Figure 2). Usually, a Blaschko-linear array of flesh-colored papules on the more proximal digit directly adjacent to the nail dystrophy will be seen, though nail findings can occur in isolation.27-29 The underlying pathophysiology is not clear; however, one hypothesis is that a triggering event, such as trauma, induces the expression of antigens that elicit a self-limiting immune-mediated response by CD8 T lymphocytes.30
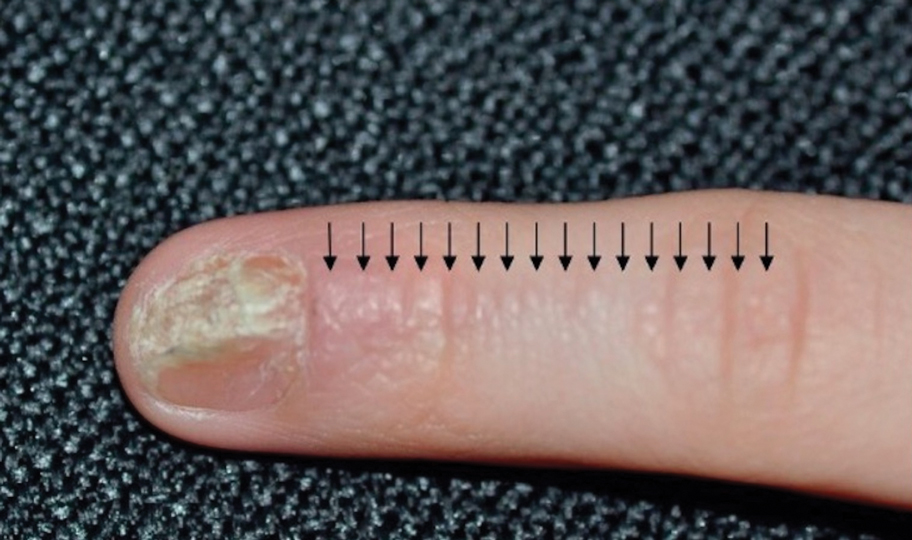
Generally, nail lichen striatus spontaneously resolves in 1 to 2 years without treatment. In a prospective study of 5 patients with nail lichen striatus, the median time to resolution was 22.6 months (range, 10–30 months).31 Topical steroids may be used for pruritus. In one case report, a 3-year-old boy with nail lichen striatus of 4 months’ duration was treated with tacrolimus ointment 0.03% daily for 3 months.28
Nail AD
Nail changes with AD may be more common in adults than children or are underreported. In a study of 777 adults with AD, nail dystrophy was present in 124 patients (16%), whereas in a study of 250 pediatric patients with AD (aged 0-2 years), nail dystrophy was present in only 4 patients.32,33
Periungual inflammation from AD causes the nail changes.34 In a cross-sectional study of 24 pediatric patients with nail dystrophy due to AD, transverse grooves (Beau lines) were present in 25% (6/24), nail pitting in 16.7% (4/24), koilonychia in 16.7% (4/24), trachyonychia in 12.5% (3/24), leukonychia in 12.5% (3/24), brachyonychia in 8.3% (2/24), melanonychia in 8.3% (2/24), onychomadesis in 8.3% (2/24), onychoschizia in 8.3% (2/24), and onycholysis in 8.3% (2/24). There was an association between disease severity and presence of toenail dystrophy (P=.03).35
Topical steroids with or without occlusion can be used to treat nail changes. Although there is limited literature describing the treatment of nail AD in children, a 61-year-old man with nail changes associated with AD achieved resolution with 3 months of treatment with dupilumab.36 Anecdotally, most patients will improve with usual cutaneous AD management.
INFECTIOUS NAIL DISORDERS
Viral Infections
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease—Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood viral infection caused by various enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16, with the A6 variant causing more severe disease. Fever and painful vesicles involving the oral mucosa as well as palms and soles give the disease its name. Nail changes are common. In a prospective study involving 130 patients with laboratory-confirmed coxsackievirus CA6 serotype infection, 37% developed onychomadesis vs only 5% of 145 cases with non-CA6 enterovirus infection who developed nail findings. There was an association between CA6 infection and presence of nail changes (P<.001).37
Findings ranging from transverse grooves (Beau lines) to complete nail shedding (onychomadesis)(Figure 3) may be seen.38,39 Nail findings in HFMD are due to transient inhibition of nail growth and present approximately 3 to 6 weeks after infection.40 Onychomadesis is seen in 30% to 68% of patients with HFMD.37,41,42 Nail findings in HFMD spontaneously resolve with nail growth (2–3 mm per month for fingernails and 1 mm per month for toenails) and do not require specific treatment. Although the appearance of nail changes associated with HFMD can be disturbing, dermatologists can reassure children and their parents that the nails will resolve with the next cycle of growth.
Kawasaki Disease—Kawasaki disease (KD) is a vasculitis primarily affecting children and infants. Although the specific pathogen and pathophysiology is not entirely clear, clinical observations have suggested an infectious cause, most likely a virus.43 In Japan, more than 15,000 cases of KD are documented annually, while approximately 4200 cases are seen in the United States.44 In a prospective study from 1984 to 1990, 4 of 26 (15.4%) patients with KD presented with nail manifestations during the late acute phase or early convalescent phase of disease. There were no significant associations between nail dystrophy and severity of KD, such as coronary artery aneurysm.45
Nail changes reported in children with KD include onychomadesis, onycholysis, orange-brown chromonychia, splinter hemorrhages, Beau lines, and pincer nails. In a review of nail changes associated with KD from 1980 to 2021, orange-brown transverse chromonychia, which may evolve into transverse leukonychia, was the most common nail finding reported, occurring in 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients.44 It has been hypothesized that nail changes may result from blood flow disturbance due to the underlying vasculitis.46 Nail changes appear several weeks after the onset of fever and are self-limited. Resolution occurs with nail growth, with no treatment required.
FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails that occurs in 0.2% to 5.5% of pediatric patients, and its prevalence may be increasing, which may be due to environmental factors or increased rates of diabetes mellitus and obesity in the pediatric population.47 Onychomycosis represents 15.5% of nail dystrophies in pediatric patients.48 Some dermatologists treat presumptive onychomycosis without confirmation; however, we do not recommend that approach. Because the differential is broad and the duration of treatment is long, mycologic examination (potassium hydroxide preparation, fungal culture, polymerase chain reaction, and/or histopathology) should be obtained to confirm onychomycosis prior to initiation of antifungal management. Family members of affected individuals should be evaluated and treated, if indicated, for onychomycosis and tinea pedis, as household transmission is common.
Currently, there are 2 topical FDA-approved treatments for pediatric onychomycosis in children 6 years and older (Table 2).49,50 There is a discussion of the need for confirmatory testing for onychomycosis in children, particularly when systemic treatment is prescribed. In a retrospective review of 269 pediatric patients with onychomycosis prescribed terbinafine, 53.5% (n=144) underwent laboratory monitoring of liver function and complete blood cell counts, and 12.5% had grade 1 laboratory abnormalities either prior to (12/144 [8.3%]) or during (6/144 [4.2%]) therapy.51 Baseline transaminase monitoring is recommended, though subsequent routine laboratory monitoring in healthy children may have limited utility with associated increased costs, incidental findings, and patient discomfort and likely is not needed.51
Pediatric onychomycosis responds better to topical therapy than adult disease, and pediatric patients do not always require systemic treatment.52 Ciclopirox is not FDA approved for the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis, but in a 32-week clinical trial of ciclopirox lacquer 8% use in 40 patients, 77% (27/35) of treated patients achieved mycologic cure. Overall, 71% of treated patients (25/35) vs 22% (2/9) of controls achieved efficacy (defined as investigator global assessment score of 2 or lower).52 In an open-label, single-arm clinical trial assessing tavaborole solution 5% applied once daily for 48 weeks for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients (aged 6–17 years), 36.2% (20/55) of patients achieved mycologic cure, and 8.5% (5/55) achieved complete cure at week 52 with mild or minimal adverse effects.53 In an open-label, phase 4 study of the safety and efficacy of efinaconazole solution 10% applied once daily for 48 weeks in pediatric patients (aged 6 to 16 years) (n=60), 65% (35/60) achieved mycologic cure, 42% (25/60) achieved clinical cure, and 40% (24/60) achieved complete cure at 52 weeks. The most common adverse effects of efinaconazole were local and included ingrown toenail (1/60), application-site dermatitis (1/60), application-site vesicles (1/60), and application-site pain (1/60).54
In a systematic review of systemic antifungals for onychomycosis in 151 pediatric patients, itraconazole, fluconazole, griseofulvin, and terbinafine resulted in complete cure rates similar to those of the adult population, with excellent safety profiles.55 Depending on the situation, initiation of treatment with topical medications followed by addition of systemic antifungal agents only if needed may be an appropriate course of action.
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
Acute Paronychia
Acute paronychia is a nail-fold infection that develops after the protective nail barrier has been compromised.56 In children, thumb-sucking, nail-biting, frequent oral manipulation of the digits, and poor skin hygiene are risk factors. Acute paronychia also may develop in association with congenital malalignment of the great toenails.57
Clinical manifestations include localized pain, erythema, and nail fold edema (Figure 4). Purulent material and abscess formation may ensue. Staphylococcus aureus as well as methicillin-resistant S aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are classically the most common causes of acute paronychia. Treatment of paronychia is based on severity. In mild cases, warm soaks with topical antibiotics are indicated. Oral antibiotics should be prescribed for more severe presentations. If there is no improvement after 48 hours, surgical drainage is required to facilitate healing.56
FINAL THOUGHTS
Inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in children are relatively common and may impact the physical and emotional well-being of young patients. By understanding the distinctive features of these nail disorders in pediatric patients, dermatologists can provide anticipatory guidance and informed treatment options to children and their parents. Further research is needed to expand our understanding of pediatric nail disorders and create targeted therapeutic interventions, particularly for NLP and psoriasis.
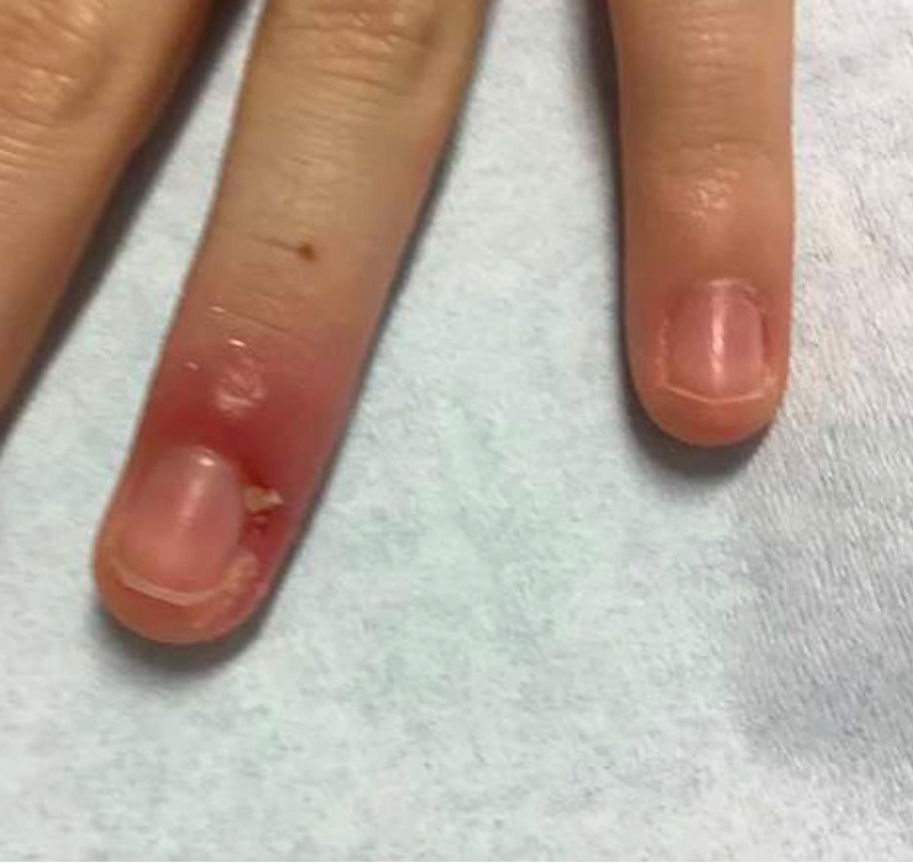
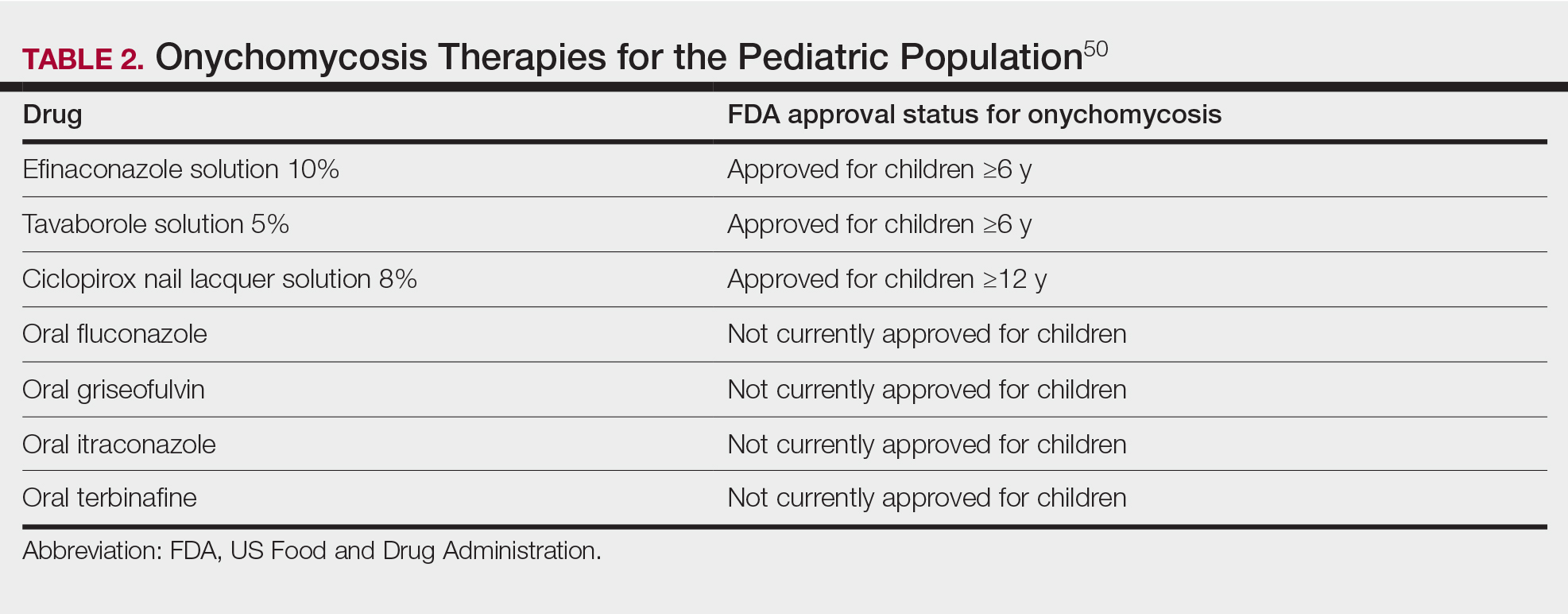
- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207. doi:10.1111/pde.13402
- Plachouri KM, Mulita F, Georgiou S. Management of pediatric nail psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:292-294. doi:10.12788/cutis.0386
- Smith RJ, Rubin AI. Pediatric nail disorders: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:506-515. doi:10.1097/mop.0000000000000921
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63. doi:10.1111/pde.13028
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112. doi:10.2165/11537110-000000000-00000
- Lee JYY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Nogueira M, Paller AS, Torres T. Targeted therapy for pediatric psoriasis. Paediatr Drugs. May 2021;23:203-212. doi:10.1007/s40272-021-00443-5
- Hanoodi M, Mittal M. Methotrexate. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556114/
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-179
- Paller AS, Seyger MMB, Magariños GA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of up to 108 weeks of ixekizumab in pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: the IXORA-PEDS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:533-541. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0655
- Diotallevi F, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Biological treatments for pediatric psoriasis: state of the art and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11128. doi:10.3390/ijms231911128
- Nash P, Mease PJ, Kirkham B, et al. Secukinumab provides sustained improvement in nail psoriasis, signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis and low rate of radiographic progression in patients with concomitant nail involvement: 2-year results from the Phase III FUTURE 5 study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40:952-959. doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3nuz51
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385. doi:10.1111/pde.13767
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriaticonycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2616
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352. doi:10.1159/000096202
- Iorizzo M, Gioia Di Chiacchio N, Di Chiacchio N, et al. Intralesional steroid injections for inflammatory nail dystrophies in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023;40:759-761. doi:10.1111/pde.15295
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Cambiaghi S, et al. Nail lichen planus in children: clinical features, response to treatment, and long-term follow-up. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1027-1032.
- Lipner SR. Nail lichen planus: a true nail emergency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:e177-e178. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.065
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Piraccini BM, Saccani E, Starace M, et al. Nail lichen planus: response to treatment and long term follow-up. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:489-496. doi:10.1684/ejd.2010.0952
- Mahajan R, Kaushik A, De D, et al. Pediatric trachyonychia- a retrospective study of 17 cases. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:689-690. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_42_21
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Trachyonychia. J Pediatr. 2020;216:239-239.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.08.034
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
- Jacobsen AA, Tosti A. Trachyonychia and twenty-nail dystrophy: a comprehensive review and discussion of diagnostic accuracy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2016;2:7-13. doi:10.1159/000445544
- Kumar MG, Ciliberto H, Bayliss SJ. Long-term follow-up of pediatric trachyonychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:198-200. doi:10.1111/pde.12427
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Iorizzo M. Trachyonychia and related disorders: evaluation and treatment plans. Dermatolog Ther. 2002;15:121-125. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8019.2002.01511.x
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Lichen striatus with nail involvement in a 6-year-old boy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2020;2020:1494760. doi:10.1155/2020/1494760
- Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00720.x
- Iorizzo M, Rubin AI, Starace M. Nail lichen striatus: is dermoscopy useful for the diagnosis? Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:859-863. doi:10.1111/pde.13916
- Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1993.tb00399.x
- Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(6, pt 1):908-913. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80270-8
- Simpson EL, Thompson MM, Hanifin JM. Prevalence and morphology of hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2006;17:123-127. doi:10.2310/6620.2006.06005
- Sarifakioglu E, Yilmaz AE, Gorpelioglu C. Nail alterations in 250 infant patients: a clinical study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:741-744. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02592.x
- Milanesi N, D’Erme AM, Gola M. Nail improvement during alitretinoin treatment: three case reports and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:533-536. doi:10.1111/ced.12584
- Chung BY, Choi YW, Kim HO, et al. Nail dystrophy in patients with atopic dermatitis and its association with disease severity. Ann Dermatol. 2019;31:121-126. doi:10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.121
- Navarro-Triviño FJ, Vega-Castillo JJ, Ruiz-Villaverde R. Nail changes successfully treated with dupilumab in a patient with severe atopic dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2021;62:e468-e469. doi:10.1111/ajd.13633
- Wei SH, Huang YP, Liu MC, et al. An outbreak of coxsackievirus A6 hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with onychomadesis in Taiwan, 2010. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:346. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-11-346
- Shin JY, Cho BK, Park HJ. A clinical study of nail changes occurring secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: onychomadesis and Beau’s lines. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:280-283. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.280
- Verma S, Singal A. Nail changes in hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD). Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021;12:656-657. doi:10.4103 /idoj.IDOJ_271_20
- Giordano LMC, de la Fuente LA, Lorca JMB, et al. Onychomadesis secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: a frequent manifestation and cause of concern for parents. Article in Spanish. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018;89:380-383. doi:10.4067/s0370-41062018005000203
- Justino MCA, da SMD, Souza MF, et al. Atypical hand-foot-mouth disease in Belém, Amazon region, northern Brazil, with detection of coxsackievirus A6. J Clin Virol. 2020;126:104307. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104307
- Cheng FF, Zhang BB, Cao ML, et al. Clinical characteristics of 68 children with atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6: a single-center retrospective analysis. Transl Pediatr. 2022;11:1502-1509. doi:10.21037/tp-22-352
- Nagata S. Causes of Kawasaki disease-from past to present. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:18. doi:10.3389/fped.2019.00018
- Mitsuishi T, Miyata K, Ando A, et al. Characteristic nail lesions in Kawasaki disease: case series and literature review. J Dermatol. 2022;49:232-238. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16276
- Lindsley CB. Nail-bed lines in Kawasaki disease. Am J Dis Child. 1992;146:659-660. doi:10.1001/archpedi.1992.02160180017005
- Matsumura O, Nakagishi Y. Pincer nails upon convalescence from Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2022;246:279. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2022.03.002
- Solís-Arias MP, García-Romero MT. Onychomycosis in children. a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:123-130. doi:10.1111/ijd.13392
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Onychomycosis in children: safety and efficacy of antifungal agents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:552-559. doi:10.1111/pde.13561
- 49. Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Shear NH, et al. Labeled use of efinaconazole topical solution 10% in treating onychomycosis in children and a review of the management of pediatric onychomycosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13613. doi:10.1111/dth.13613
- Falotico JM, Lipner SR. Updated perspectives on the diagnosis and management of onychomycosis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:1933-1957. doi:10.2147/ccid.S362635
- Patel D, Castelo-Soccio LA, Rubin AI, et al. Laboratory monitoring during systemic terbinafine therapy for pediatric onychomycosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1326-1327. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4483
- Friedlander SF, Chan YC, Chan YH, et al. Onychomycosis does not always require systemic treatment for cure: a trial using topical therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:316-322. doi:10.1111/pde.12064
- Rich P, Spellman M, Purohit V, et al. Tavaborole 5% topical solution for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients: results from a phase 4 open-label study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:190-195.
- Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Abramovits W, et al. JUBLIA (efinaconazole 10% solution) in the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis. Skinmed. 2021;19:206-210.
- Gupta AK, Paquet M. Systemic antifungals to treat onychomycosis in children: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:294-302. doi:10.1111/pde.12048
- Leggit JC. Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96:44-51.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Congenital malalignment of the great toenails with acute paronychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e288-e289.doi:10.1111/pde.12924
Nail disorders are common among pediatric patients but often are underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed because of their unique disease manifestations. These conditions may severely impact quality of life. There are few nail disease clinical trials that include children. Consequently, most treatment recommendations are based on case series and expert consensus recommendations. We review inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in pediatric patients. By describing characteristics, clinical manifestations, and management approaches for these conditions, we aim to provide guidance to dermatologists in their diagnosis and treatment.
INFLAMMATORY NAIL DISORDERS
Nail Psoriasis
Nail involvement in children with psoriasis is common, with prevalence estimates ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail matrix psoriasis may manifest with pitting (large irregular pits) and leukonychia as well as chromonychia and nail plate crumbling. Onycholysis, oil drop spots (salmon patches), and subungual hyperkeratosis can be seen in nail bed psoriasis. Nail pitting is the most frequently observed clinical finding (Figure 1).2,3 In a cross-sectional multicenter study of 313 children with cutaneous psoriasis in France, nail findings were present in 101 patients (32.3%). There were associations between nail findings and presence of psoriatic arthritis (P=.03), palmoplantar psoriasis (P<.001), and severity of psoriatic disease, defined as use of systemic treatment with phototherapy (psoralen plus UVA, UVB), traditional systemic treatment (acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporine), or a biologic (P=.003).4
Topical steroids and vitamin D analogues may be used with or without occlusion and may be efficacious.5 Several case reports describe systemic treatments for psoriasis in children, including methotrexate, acitretin, and apremilast (approved for children 6 years and older for plaque psoriasis by the US Food and Drug Administration [FDA]).2 There are 5 biologic drugs currently approved for the treatment of pediatric psoriasis—adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab—and 6 drugs currently undergoing phase 3 studies—brodalumab, guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, certolizumab pegol, and deucravacitinib (Table 1).6-15 Adalimumab is specifically approved for moderate to severe nail psoriasis in adults 18 years and older.


Intralesional steroid injections are sometimes useful in the management of nail matrix psoriasis; however, appropriate patient selection is critical due to the pain associated with the procedure. In a prospective study of 16 children (age range, 9–17 years) with nail psoriasis treated with intralesional triamcinolone (ILTAC) 2.5 to 5 mg/mL every 4 to 8 weeks for a minimum of 3 to 6 months, 9 patients achieved resolution and 6 had improvement of clinical findings.16 Local adverse events were mild, including injection-site pain (66%), subungual hematoma (n=1), Beau lines (n=1), proximal nail fold hypopigmentation (n=2), and proximal nail fold atrophy (n=2). Because the proximal nail fold in children is thinner than in adults, there may be an increased risk for nail fold hypopigmentation and atrophy in children. Therefore, a maximum ILTAC concentration of 2.5 mg/mL with 0.2 mL maximum volume per nail per session is recommended for children younger than 15 years.16
Nail Lichen Planus
Nail lichen planus (NLP) is uncommon in children, with few biopsy-proven cases documented in the literature.17 Common clinical findings are onychorrhexis, nail plate thinning, fissuring, splitting, and atrophy with koilonychia.5 Although pterygium development (irreversible nail matrix scarring) is uncommon in pediatric patients, NLP can be progressive and may cause irreversible destruction of the nail matrix and subsequent nail loss, warranting therapeutic intervention.18
Treatment of NLP may be difficult, as there are no options that work in all patients. Current literature supports the use of systemic corticosteroids or ILTAC for the treatment of NLP; however, recurrence rates can be high. According to an expert consensus paper on NLP treatment, ILTAC may be injected in a concentration of 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/mL according to disease severity.19 In severe or resistant cases, intramuscular (IM) triamcinolone may be considered, especially if more than 3 nails are affected. A dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/mo for at least 3 to 6 months is recommended for both children and adults, with 1 mg/kg/mo recommended in the active treatment phase (first 2–3 months).19 In a retrospective review of 5 pediatric patients with NLP treated with IM triamcinolone 0.5 mg/kg/mo, 3 patients had resolution and 2 improved with treatment.20 In a prospective study of 10 children with NLP, IM triamcinolone at a dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg every 30 days for 3 to 6 months resulted in resolution of nail findings in 9 patients.17 In a prospective study of 14 pediatric patients with NLP treated with 2.5 to 5 mg/mL of ILTAC, 10 achieved resolution and 3 improved.16
Intralesional triamcinolone injections may be better suited for teenagers compared to younger children who may be more apprehensive of needles. To minimize pain, it is recommended to inject ILTAC slowly at room temperature, with use of “talkesthesia” and vibration devices, 1% lidocaine, or ethyl chloride spray.18
Trachyonychia
Trachyonychia is characterized by the presence of sandpaperlike nails. It manifests with brittle thin nails with longitudinal ridging, onychoschizia, and thickened hyperkeratotic cuticles. Trachyonychia typically involves multiple nails, with a peak age of onset between 3 and 12 years.21,22 There are 2 variants: the opaque type with rough longitudinal ridging, and the shiny variant with opalescent nails and pits that reflect light. The opaque variant is more common and is associated with psoriasis, whereas the shiny variant is less common and is associated with alopecia areata.23 Although most cases are idiopathic, some are associated with psoriasis and alopecia areata, as previously noted, as well as atopic dermatitis (AD) and lichen planus.22,24
Fortunately, trachyonychia does not lead to permanent nail damage or pterygium, making treatment primarily focused on addressing functional and cosmetic concerns.24 Spontaneous resolution occurs in approximately 50% of patients. In a prospective study of 11 patients with idiopathic trachyonychia, there was partial improvement in 5 of 9 patients treated with topical steroids, 1 with only petrolatum, and 1 with vitamin supplements. Complete resolution was reported in 1 patient treated with topical steroids.25 Because trachyonychia often is self-resolving, no treatment is required and a conservative approach is strongly recommended.26 Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and 5-fluorouracil. Intralesional triamcinolone, systemic cyclosporine, retinoids, systemic corticosteroids, and tofacitinib have been described in case reports, though none of these have been shown to be 100% efficacious.24
Nail Lichen Striatus
Lichen striatus involving the nail is uncommon and is characterized by onycholysis, longitudinal ridging, splitting, and fraying, as well as what appears to be a subungual tumor. It can encompass the entire nail or may be isolated to a portion of the nail (Figure 2). Usually, a Blaschko-linear array of flesh-colored papules on the more proximal digit directly adjacent to the nail dystrophy will be seen, though nail findings can occur in isolation.27-29 The underlying pathophysiology is not clear; however, one hypothesis is that a triggering event, such as trauma, induces the expression of antigens that elicit a self-limiting immune-mediated response by CD8 T lymphocytes.30

Generally, nail lichen striatus spontaneously resolves in 1 to 2 years without treatment. In a prospective study of 5 patients with nail lichen striatus, the median time to resolution was 22.6 months (range, 10–30 months).31 Topical steroids may be used for pruritus. In one case report, a 3-year-old boy with nail lichen striatus of 4 months’ duration was treated with tacrolimus ointment 0.03% daily for 3 months.28
Nail AD
Nail changes with AD may be more common in adults than children or are underreported. In a study of 777 adults with AD, nail dystrophy was present in 124 patients (16%), whereas in a study of 250 pediatric patients with AD (aged 0-2 years), nail dystrophy was present in only 4 patients.32,33
Periungual inflammation from AD causes the nail changes.34 In a cross-sectional study of 24 pediatric patients with nail dystrophy due to AD, transverse grooves (Beau lines) were present in 25% (6/24), nail pitting in 16.7% (4/24), koilonychia in 16.7% (4/24), trachyonychia in 12.5% (3/24), leukonychia in 12.5% (3/24), brachyonychia in 8.3% (2/24), melanonychia in 8.3% (2/24), onychomadesis in 8.3% (2/24), onychoschizia in 8.3% (2/24), and onycholysis in 8.3% (2/24). There was an association between disease severity and presence of toenail dystrophy (P=.03).35
Topical steroids with or without occlusion can be used to treat nail changes. Although there is limited literature describing the treatment of nail AD in children, a 61-year-old man with nail changes associated with AD achieved resolution with 3 months of treatment with dupilumab.36 Anecdotally, most patients will improve with usual cutaneous AD management.
INFECTIOUS NAIL DISORDERS
Viral Infections
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease—Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood viral infection caused by various enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16, with the A6 variant causing more severe disease. Fever and painful vesicles involving the oral mucosa as well as palms and soles give the disease its name. Nail changes are common. In a prospective study involving 130 patients with laboratory-confirmed coxsackievirus CA6 serotype infection, 37% developed onychomadesis vs only 5% of 145 cases with non-CA6 enterovirus infection who developed nail findings. There was an association between CA6 infection and presence of nail changes (P<.001).37
Findings ranging from transverse grooves (Beau lines) to complete nail shedding (onychomadesis)(Figure 3) may be seen.38,39 Nail findings in HFMD are due to transient inhibition of nail growth and present approximately 3 to 6 weeks after infection.40 Onychomadesis is seen in 30% to 68% of patients with HFMD.37,41,42 Nail findings in HFMD spontaneously resolve with nail growth (2–3 mm per month for fingernails and 1 mm per month for toenails) and do not require specific treatment. Although the appearance of nail changes associated with HFMD can be disturbing, dermatologists can reassure children and their parents that the nails will resolve with the next cycle of growth.
Kawasaki Disease—Kawasaki disease (KD) is a vasculitis primarily affecting children and infants. Although the specific pathogen and pathophysiology is not entirely clear, clinical observations have suggested an infectious cause, most likely a virus.43 In Japan, more than 15,000 cases of KD are documented annually, while approximately 4200 cases are seen in the United States.44 In a prospective study from 1984 to 1990, 4 of 26 (15.4%) patients with KD presented with nail manifestations during the late acute phase or early convalescent phase of disease. There were no significant associations between nail dystrophy and severity of KD, such as coronary artery aneurysm.45
Nail changes reported in children with KD include onychomadesis, onycholysis, orange-brown chromonychia, splinter hemorrhages, Beau lines, and pincer nails. In a review of nail changes associated with KD from 1980 to 2021, orange-brown transverse chromonychia, which may evolve into transverse leukonychia, was the most common nail finding reported, occurring in 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients.44 It has been hypothesized that nail changes may result from blood flow disturbance due to the underlying vasculitis.46 Nail changes appear several weeks after the onset of fever and are self-limited. Resolution occurs with nail growth, with no treatment required.

FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails that occurs in 0.2% to 5.5% of pediatric patients, and its prevalence may be increasing, which may be due to environmental factors or increased rates of diabetes mellitus and obesity in the pediatric population.47 Onychomycosis represents 15.5% of nail dystrophies in pediatric patients.48 Some dermatologists treat presumptive onychomycosis without confirmation; however, we do not recommend that approach. Because the differential is broad and the duration of treatment is long, mycologic examination (potassium hydroxide preparation, fungal culture, polymerase chain reaction, and/or histopathology) should be obtained to confirm onychomycosis prior to initiation of antifungal management. Family members of affected individuals should be evaluated and treated, if indicated, for onychomycosis and tinea pedis, as household transmission is common.
Currently, there are 2 topical FDA-approved treatments for pediatric onychomycosis in children 6 years and older (Table 2).49,50 There is a discussion of the need for confirmatory testing for onychomycosis in children, particularly when systemic treatment is prescribed. In a retrospective review of 269 pediatric patients with onychomycosis prescribed terbinafine, 53.5% (n=144) underwent laboratory monitoring of liver function and complete blood cell counts, and 12.5% had grade 1 laboratory abnormalities either prior to (12/144 [8.3%]) or during (6/144 [4.2%]) therapy.51 Baseline transaminase monitoring is recommended, though subsequent routine laboratory monitoring in healthy children may have limited utility with associated increased costs, incidental findings, and patient discomfort and likely is not needed.51
Pediatric onychomycosis responds better to topical therapy than adult disease, and pediatric patients do not always require systemic treatment.52 Ciclopirox is not FDA approved for the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis, but in a 32-week clinical trial of ciclopirox lacquer 8% use in 40 patients, 77% (27/35) of treated patients achieved mycologic cure. Overall, 71% of treated patients (25/35) vs 22% (2/9) of controls achieved efficacy (defined as investigator global assessment score of 2 or lower).52 In an open-label, single-arm clinical trial assessing tavaborole solution 5% applied once daily for 48 weeks for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients (aged 6–17 years), 36.2% (20/55) of patients achieved mycologic cure, and 8.5% (5/55) achieved complete cure at week 52 with mild or minimal adverse effects.53 In an open-label, phase 4 study of the safety and efficacy of efinaconazole solution 10% applied once daily for 48 weeks in pediatric patients (aged 6 to 16 years) (n=60), 65% (35/60) achieved mycologic cure, 42% (25/60) achieved clinical cure, and 40% (24/60) achieved complete cure at 52 weeks. The most common adverse effects of efinaconazole were local and included ingrown toenail (1/60), application-site dermatitis (1/60), application-site vesicles (1/60), and application-site pain (1/60).54
In a systematic review of systemic antifungals for onychomycosis in 151 pediatric patients, itraconazole, fluconazole, griseofulvin, and terbinafine resulted in complete cure rates similar to those of the adult population, with excellent safety profiles.55 Depending on the situation, initiation of treatment with topical medications followed by addition of systemic antifungal agents only if needed may be an appropriate course of action.
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
Acute Paronychia
Acute paronychia is a nail-fold infection that develops after the protective nail barrier has been compromised.56 In children, thumb-sucking, nail-biting, frequent oral manipulation of the digits, and poor skin hygiene are risk factors. Acute paronychia also may develop in association with congenital malalignment of the great toenails.57
Clinical manifestations include localized pain, erythema, and nail fold edema (Figure 4). Purulent material and abscess formation may ensue. Staphylococcus aureus as well as methicillin-resistant S aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are classically the most common causes of acute paronychia. Treatment of paronychia is based on severity. In mild cases, warm soaks with topical antibiotics are indicated. Oral antibiotics should be prescribed for more severe presentations. If there is no improvement after 48 hours, surgical drainage is required to facilitate healing.56
FINAL THOUGHTS
Inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in children are relatively common and may impact the physical and emotional well-being of young patients. By understanding the distinctive features of these nail disorders in pediatric patients, dermatologists can provide anticipatory guidance and informed treatment options to children and their parents. Further research is needed to expand our understanding of pediatric nail disorders and create targeted therapeutic interventions, particularly for NLP and psoriasis.


Nail disorders are common among pediatric patients but often are underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed because of their unique disease manifestations. These conditions may severely impact quality of life. There are few nail disease clinical trials that include children. Consequently, most treatment recommendations are based on case series and expert consensus recommendations. We review inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in pediatric patients. By describing characteristics, clinical manifestations, and management approaches for these conditions, we aim to provide guidance to dermatologists in their diagnosis and treatment.
INFLAMMATORY NAIL DISORDERS
Nail Psoriasis
Nail involvement in children with psoriasis is common, with prevalence estimates ranging from 17% to 39.2%.1 Nail matrix psoriasis may manifest with pitting (large irregular pits) and leukonychia as well as chromonychia and nail plate crumbling. Onycholysis, oil drop spots (salmon patches), and subungual hyperkeratosis can be seen in nail bed psoriasis. Nail pitting is the most frequently observed clinical finding (Figure 1).2,3 In a cross-sectional multicenter study of 313 children with cutaneous psoriasis in France, nail findings were present in 101 patients (32.3%). There were associations between nail findings and presence of psoriatic arthritis (P=.03), palmoplantar psoriasis (P<.001), and severity of psoriatic disease, defined as use of systemic treatment with phototherapy (psoralen plus UVA, UVB), traditional systemic treatment (acitretin, methotrexate, cyclosporine), or a biologic (P=.003).4
Topical steroids and vitamin D analogues may be used with or without occlusion and may be efficacious.5 Several case reports describe systemic treatments for psoriasis in children, including methotrexate, acitretin, and apremilast (approved for children 6 years and older for plaque psoriasis by the US Food and Drug Administration [FDA]).2 There are 5 biologic drugs currently approved for the treatment of pediatric psoriasis—adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab—and 6 drugs currently undergoing phase 3 studies—brodalumab, guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab, certolizumab pegol, and deucravacitinib (Table 1).6-15 Adalimumab is specifically approved for moderate to severe nail psoriasis in adults 18 years and older.


Intralesional steroid injections are sometimes useful in the management of nail matrix psoriasis; however, appropriate patient selection is critical due to the pain associated with the procedure. In a prospective study of 16 children (age range, 9–17 years) with nail psoriasis treated with intralesional triamcinolone (ILTAC) 2.5 to 5 mg/mL every 4 to 8 weeks for a minimum of 3 to 6 months, 9 patients achieved resolution and 6 had improvement of clinical findings.16 Local adverse events were mild, including injection-site pain (66%), subungual hematoma (n=1), Beau lines (n=1), proximal nail fold hypopigmentation (n=2), and proximal nail fold atrophy (n=2). Because the proximal nail fold in children is thinner than in adults, there may be an increased risk for nail fold hypopigmentation and atrophy in children. Therefore, a maximum ILTAC concentration of 2.5 mg/mL with 0.2 mL maximum volume per nail per session is recommended for children younger than 15 years.16
Nail Lichen Planus
Nail lichen planus (NLP) is uncommon in children, with few biopsy-proven cases documented in the literature.17 Common clinical findings are onychorrhexis, nail plate thinning, fissuring, splitting, and atrophy with koilonychia.5 Although pterygium development (irreversible nail matrix scarring) is uncommon in pediatric patients, NLP can be progressive and may cause irreversible destruction of the nail matrix and subsequent nail loss, warranting therapeutic intervention.18
Treatment of NLP may be difficult, as there are no options that work in all patients. Current literature supports the use of systemic corticosteroids or ILTAC for the treatment of NLP; however, recurrence rates can be high. According to an expert consensus paper on NLP treatment, ILTAC may be injected in a concentration of 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/mL according to disease severity.19 In severe or resistant cases, intramuscular (IM) triamcinolone may be considered, especially if more than 3 nails are affected. A dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/mo for at least 3 to 6 months is recommended for both children and adults, with 1 mg/kg/mo recommended in the active treatment phase (first 2–3 months).19 In a retrospective review of 5 pediatric patients with NLP treated with IM triamcinolone 0.5 mg/kg/mo, 3 patients had resolution and 2 improved with treatment.20 In a prospective study of 10 children with NLP, IM triamcinolone at a dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg every 30 days for 3 to 6 months resulted in resolution of nail findings in 9 patients.17 In a prospective study of 14 pediatric patients with NLP treated with 2.5 to 5 mg/mL of ILTAC, 10 achieved resolution and 3 improved.16
Intralesional triamcinolone injections may be better suited for teenagers compared to younger children who may be more apprehensive of needles. To minimize pain, it is recommended to inject ILTAC slowly at room temperature, with use of “talkesthesia” and vibration devices, 1% lidocaine, or ethyl chloride spray.18
Trachyonychia
Trachyonychia is characterized by the presence of sandpaperlike nails. It manifests with brittle thin nails with longitudinal ridging, onychoschizia, and thickened hyperkeratotic cuticles. Trachyonychia typically involves multiple nails, with a peak age of onset between 3 and 12 years.21,22 There are 2 variants: the opaque type with rough longitudinal ridging, and the shiny variant with opalescent nails and pits that reflect light. The opaque variant is more common and is associated with psoriasis, whereas the shiny variant is less common and is associated with alopecia areata.23 Although most cases are idiopathic, some are associated with psoriasis and alopecia areata, as previously noted, as well as atopic dermatitis (AD) and lichen planus.22,24
Fortunately, trachyonychia does not lead to permanent nail damage or pterygium, making treatment primarily focused on addressing functional and cosmetic concerns.24 Spontaneous resolution occurs in approximately 50% of patients. In a prospective study of 11 patients with idiopathic trachyonychia, there was partial improvement in 5 of 9 patients treated with topical steroids, 1 with only petrolatum, and 1 with vitamin supplements. Complete resolution was reported in 1 patient treated with topical steroids.25 Because trachyonychia often is self-resolving, no treatment is required and a conservative approach is strongly recommended.26 Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, tazarotene, and 5-fluorouracil. Intralesional triamcinolone, systemic cyclosporine, retinoids, systemic corticosteroids, and tofacitinib have been described in case reports, though none of these have been shown to be 100% efficacious.24
Nail Lichen Striatus
Lichen striatus involving the nail is uncommon and is characterized by onycholysis, longitudinal ridging, splitting, and fraying, as well as what appears to be a subungual tumor. It can encompass the entire nail or may be isolated to a portion of the nail (Figure 2). Usually, a Blaschko-linear array of flesh-colored papules on the more proximal digit directly adjacent to the nail dystrophy will be seen, though nail findings can occur in isolation.27-29 The underlying pathophysiology is not clear; however, one hypothesis is that a triggering event, such as trauma, induces the expression of antigens that elicit a self-limiting immune-mediated response by CD8 T lymphocytes.30

Generally, nail lichen striatus spontaneously resolves in 1 to 2 years without treatment. In a prospective study of 5 patients with nail lichen striatus, the median time to resolution was 22.6 months (range, 10–30 months).31 Topical steroids may be used for pruritus. In one case report, a 3-year-old boy with nail lichen striatus of 4 months’ duration was treated with tacrolimus ointment 0.03% daily for 3 months.28
Nail AD
Nail changes with AD may be more common in adults than children or are underreported. In a study of 777 adults with AD, nail dystrophy was present in 124 patients (16%), whereas in a study of 250 pediatric patients with AD (aged 0-2 years), nail dystrophy was present in only 4 patients.32,33
Periungual inflammation from AD causes the nail changes.34 In a cross-sectional study of 24 pediatric patients with nail dystrophy due to AD, transverse grooves (Beau lines) were present in 25% (6/24), nail pitting in 16.7% (4/24), koilonychia in 16.7% (4/24), trachyonychia in 12.5% (3/24), leukonychia in 12.5% (3/24), brachyonychia in 8.3% (2/24), melanonychia in 8.3% (2/24), onychomadesis in 8.3% (2/24), onychoschizia in 8.3% (2/24), and onycholysis in 8.3% (2/24). There was an association between disease severity and presence of toenail dystrophy (P=.03).35
Topical steroids with or without occlusion can be used to treat nail changes. Although there is limited literature describing the treatment of nail AD in children, a 61-year-old man with nail changes associated with AD achieved resolution with 3 months of treatment with dupilumab.36 Anecdotally, most patients will improve with usual cutaneous AD management.
INFECTIOUS NAIL DISORDERS
Viral Infections
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease—Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood viral infection caused by various enteroviruses, most commonly coxsackievirus A16, with the A6 variant causing more severe disease. Fever and painful vesicles involving the oral mucosa as well as palms and soles give the disease its name. Nail changes are common. In a prospective study involving 130 patients with laboratory-confirmed coxsackievirus CA6 serotype infection, 37% developed onychomadesis vs only 5% of 145 cases with non-CA6 enterovirus infection who developed nail findings. There was an association between CA6 infection and presence of nail changes (P<.001).37
Findings ranging from transverse grooves (Beau lines) to complete nail shedding (onychomadesis)(Figure 3) may be seen.38,39 Nail findings in HFMD are due to transient inhibition of nail growth and present approximately 3 to 6 weeks after infection.40 Onychomadesis is seen in 30% to 68% of patients with HFMD.37,41,42 Nail findings in HFMD spontaneously resolve with nail growth (2–3 mm per month for fingernails and 1 mm per month for toenails) and do not require specific treatment. Although the appearance of nail changes associated with HFMD can be disturbing, dermatologists can reassure children and their parents that the nails will resolve with the next cycle of growth.
Kawasaki Disease—Kawasaki disease (KD) is a vasculitis primarily affecting children and infants. Although the specific pathogen and pathophysiology is not entirely clear, clinical observations have suggested an infectious cause, most likely a virus.43 In Japan, more than 15,000 cases of KD are documented annually, while approximately 4200 cases are seen in the United States.44 In a prospective study from 1984 to 1990, 4 of 26 (15.4%) patients with KD presented with nail manifestations during the late acute phase or early convalescent phase of disease. There were no significant associations between nail dystrophy and severity of KD, such as coronary artery aneurysm.45
Nail changes reported in children with KD include onychomadesis, onycholysis, orange-brown chromonychia, splinter hemorrhages, Beau lines, and pincer nails. In a review of nail changes associated with KD from 1980 to 2021, orange-brown transverse chromonychia, which may evolve into transverse leukonychia, was the most common nail finding reported, occurring in 17 of 31 (54.8%) patients.44 It has been hypothesized that nail changes may result from blood flow disturbance due to the underlying vasculitis.46 Nail changes appear several weeks after the onset of fever and are self-limited. Resolution occurs with nail growth, with no treatment required.

FUNGAL INFECTIONS
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails that occurs in 0.2% to 5.5% of pediatric patients, and its prevalence may be increasing, which may be due to environmental factors or increased rates of diabetes mellitus and obesity in the pediatric population.47 Onychomycosis represents 15.5% of nail dystrophies in pediatric patients.48 Some dermatologists treat presumptive onychomycosis without confirmation; however, we do not recommend that approach. Because the differential is broad and the duration of treatment is long, mycologic examination (potassium hydroxide preparation, fungal culture, polymerase chain reaction, and/or histopathology) should be obtained to confirm onychomycosis prior to initiation of antifungal management. Family members of affected individuals should be evaluated and treated, if indicated, for onychomycosis and tinea pedis, as household transmission is common.
Currently, there are 2 topical FDA-approved treatments for pediatric onychomycosis in children 6 years and older (Table 2).49,50 There is a discussion of the need for confirmatory testing for onychomycosis in children, particularly when systemic treatment is prescribed. In a retrospective review of 269 pediatric patients with onychomycosis prescribed terbinafine, 53.5% (n=144) underwent laboratory monitoring of liver function and complete blood cell counts, and 12.5% had grade 1 laboratory abnormalities either prior to (12/144 [8.3%]) or during (6/144 [4.2%]) therapy.51 Baseline transaminase monitoring is recommended, though subsequent routine laboratory monitoring in healthy children may have limited utility with associated increased costs, incidental findings, and patient discomfort and likely is not needed.51
Pediatric onychomycosis responds better to topical therapy than adult disease, and pediatric patients do not always require systemic treatment.52 Ciclopirox is not FDA approved for the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis, but in a 32-week clinical trial of ciclopirox lacquer 8% use in 40 patients, 77% (27/35) of treated patients achieved mycologic cure. Overall, 71% of treated patients (25/35) vs 22% (2/9) of controls achieved efficacy (defined as investigator global assessment score of 2 or lower).52 In an open-label, single-arm clinical trial assessing tavaborole solution 5% applied once daily for 48 weeks for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients (aged 6–17 years), 36.2% (20/55) of patients achieved mycologic cure, and 8.5% (5/55) achieved complete cure at week 52 with mild or minimal adverse effects.53 In an open-label, phase 4 study of the safety and efficacy of efinaconazole solution 10% applied once daily for 48 weeks in pediatric patients (aged 6 to 16 years) (n=60), 65% (35/60) achieved mycologic cure, 42% (25/60) achieved clinical cure, and 40% (24/60) achieved complete cure at 52 weeks. The most common adverse effects of efinaconazole were local and included ingrown toenail (1/60), application-site dermatitis (1/60), application-site vesicles (1/60), and application-site pain (1/60).54
In a systematic review of systemic antifungals for onychomycosis in 151 pediatric patients, itraconazole, fluconazole, griseofulvin, and terbinafine resulted in complete cure rates similar to those of the adult population, with excellent safety profiles.55 Depending on the situation, initiation of treatment with topical medications followed by addition of systemic antifungal agents only if needed may be an appropriate course of action.
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
Acute Paronychia
Acute paronychia is a nail-fold infection that develops after the protective nail barrier has been compromised.56 In children, thumb-sucking, nail-biting, frequent oral manipulation of the digits, and poor skin hygiene are risk factors. Acute paronychia also may develop in association with congenital malalignment of the great toenails.57
Clinical manifestations include localized pain, erythema, and nail fold edema (Figure 4). Purulent material and abscess formation may ensue. Staphylococcus aureus as well as methicillin-resistant S aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are classically the most common causes of acute paronychia. Treatment of paronychia is based on severity. In mild cases, warm soaks with topical antibiotics are indicated. Oral antibiotics should be prescribed for more severe presentations. If there is no improvement after 48 hours, surgical drainage is required to facilitate healing.56
FINAL THOUGHTS
Inflammatory and infectious nail disorders in children are relatively common and may impact the physical and emotional well-being of young patients. By understanding the distinctive features of these nail disorders in pediatric patients, dermatologists can provide anticipatory guidance and informed treatment options to children and their parents. Further research is needed to expand our understanding of pediatric nail disorders and create targeted therapeutic interventions, particularly for NLP and psoriasis.


- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207. doi:10.1111/pde.13402
- Plachouri KM, Mulita F, Georgiou S. Management of pediatric nail psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:292-294. doi:10.12788/cutis.0386
- Smith RJ, Rubin AI. Pediatric nail disorders: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:506-515. doi:10.1097/mop.0000000000000921
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63. doi:10.1111/pde.13028
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112. doi:10.2165/11537110-000000000-00000
- Lee JYY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Nogueira M, Paller AS, Torres T. Targeted therapy for pediatric psoriasis. Paediatr Drugs. May 2021;23:203-212. doi:10.1007/s40272-021-00443-5
- Hanoodi M, Mittal M. Methotrexate. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556114/
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-179
- Paller AS, Seyger MMB, Magariños GA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of up to 108 weeks of ixekizumab in pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: the IXORA-PEDS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:533-541. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0655
- Diotallevi F, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Biological treatments for pediatric psoriasis: state of the art and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11128. doi:10.3390/ijms231911128
- Nash P, Mease PJ, Kirkham B, et al. Secukinumab provides sustained improvement in nail psoriasis, signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis and low rate of radiographic progression in patients with concomitant nail involvement: 2-year results from the Phase III FUTURE 5 study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40:952-959. doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3nuz51
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385. doi:10.1111/pde.13767
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriaticonycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2616
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352. doi:10.1159/000096202
- Iorizzo M, Gioia Di Chiacchio N, Di Chiacchio N, et al. Intralesional steroid injections for inflammatory nail dystrophies in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023;40:759-761. doi:10.1111/pde.15295
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Cambiaghi S, et al. Nail lichen planus in children: clinical features, response to treatment, and long-term follow-up. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1027-1032.
- Lipner SR. Nail lichen planus: a true nail emergency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:e177-e178. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.065
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Piraccini BM, Saccani E, Starace M, et al. Nail lichen planus: response to treatment and long term follow-up. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:489-496. doi:10.1684/ejd.2010.0952
- Mahajan R, Kaushik A, De D, et al. Pediatric trachyonychia- a retrospective study of 17 cases. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:689-690. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_42_21
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Trachyonychia. J Pediatr. 2020;216:239-239.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.08.034
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
- Jacobsen AA, Tosti A. Trachyonychia and twenty-nail dystrophy: a comprehensive review and discussion of diagnostic accuracy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2016;2:7-13. doi:10.1159/000445544
- Kumar MG, Ciliberto H, Bayliss SJ. Long-term follow-up of pediatric trachyonychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:198-200. doi:10.1111/pde.12427
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Iorizzo M. Trachyonychia and related disorders: evaluation and treatment plans. Dermatolog Ther. 2002;15:121-125. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8019.2002.01511.x
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Lichen striatus with nail involvement in a 6-year-old boy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2020;2020:1494760. doi:10.1155/2020/1494760
- Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00720.x
- Iorizzo M, Rubin AI, Starace M. Nail lichen striatus: is dermoscopy useful for the diagnosis? Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:859-863. doi:10.1111/pde.13916
- Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1993.tb00399.x
- Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(6, pt 1):908-913. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80270-8
- Simpson EL, Thompson MM, Hanifin JM. Prevalence and morphology of hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2006;17:123-127. doi:10.2310/6620.2006.06005
- Sarifakioglu E, Yilmaz AE, Gorpelioglu C. Nail alterations in 250 infant patients: a clinical study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:741-744. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02592.x
- Milanesi N, D’Erme AM, Gola M. Nail improvement during alitretinoin treatment: three case reports and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:533-536. doi:10.1111/ced.12584
- Chung BY, Choi YW, Kim HO, et al. Nail dystrophy in patients with atopic dermatitis and its association with disease severity. Ann Dermatol. 2019;31:121-126. doi:10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.121
- Navarro-Triviño FJ, Vega-Castillo JJ, Ruiz-Villaverde R. Nail changes successfully treated with dupilumab in a patient with severe atopic dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2021;62:e468-e469. doi:10.1111/ajd.13633
- Wei SH, Huang YP, Liu MC, et al. An outbreak of coxsackievirus A6 hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with onychomadesis in Taiwan, 2010. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:346. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-11-346
- Shin JY, Cho BK, Park HJ. A clinical study of nail changes occurring secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: onychomadesis and Beau’s lines. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:280-283. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.280
- Verma S, Singal A. Nail changes in hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD). Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021;12:656-657. doi:10.4103 /idoj.IDOJ_271_20
- Giordano LMC, de la Fuente LA, Lorca JMB, et al. Onychomadesis secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: a frequent manifestation and cause of concern for parents. Article in Spanish. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018;89:380-383. doi:10.4067/s0370-41062018005000203
- Justino MCA, da SMD, Souza MF, et al. Atypical hand-foot-mouth disease in Belém, Amazon region, northern Brazil, with detection of coxsackievirus A6. J Clin Virol. 2020;126:104307. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104307
- Cheng FF, Zhang BB, Cao ML, et al. Clinical characteristics of 68 children with atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6: a single-center retrospective analysis. Transl Pediatr. 2022;11:1502-1509. doi:10.21037/tp-22-352
- Nagata S. Causes of Kawasaki disease-from past to present. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:18. doi:10.3389/fped.2019.00018
- Mitsuishi T, Miyata K, Ando A, et al. Characteristic nail lesions in Kawasaki disease: case series and literature review. J Dermatol. 2022;49:232-238. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16276
- Lindsley CB. Nail-bed lines in Kawasaki disease. Am J Dis Child. 1992;146:659-660. doi:10.1001/archpedi.1992.02160180017005
- Matsumura O, Nakagishi Y. Pincer nails upon convalescence from Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2022;246:279. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2022.03.002
- Solís-Arias MP, García-Romero MT. Onychomycosis in children. a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:123-130. doi:10.1111/ijd.13392
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Onychomycosis in children: safety and efficacy of antifungal agents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:552-559. doi:10.1111/pde.13561
- 49. Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Shear NH, et al. Labeled use of efinaconazole topical solution 10% in treating onychomycosis in children and a review of the management of pediatric onychomycosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13613. doi:10.1111/dth.13613
- Falotico JM, Lipner SR. Updated perspectives on the diagnosis and management of onychomycosis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:1933-1957. doi:10.2147/ccid.S362635
- Patel D, Castelo-Soccio LA, Rubin AI, et al. Laboratory monitoring during systemic terbinafine therapy for pediatric onychomycosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1326-1327. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4483
- Friedlander SF, Chan YC, Chan YH, et al. Onychomycosis does not always require systemic treatment for cure: a trial using topical therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:316-322. doi:10.1111/pde.12064
- Rich P, Spellman M, Purohit V, et al. Tavaborole 5% topical solution for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients: results from a phase 4 open-label study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:190-195.
- Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Abramovits W, et al. JUBLIA (efinaconazole 10% solution) in the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis. Skinmed. 2021;19:206-210.
- Gupta AK, Paquet M. Systemic antifungals to treat onychomycosis in children: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:294-302. doi:10.1111/pde.12048
- Leggit JC. Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96:44-51.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Congenital malalignment of the great toenails with acute paronychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e288-e289.doi:10.1111/pde.12924
- Uber M, Carvalho VO, Abagge KT, et al. Clinical features and nail clippings in 52 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:202-207. doi:10.1111/pde.13402
- Plachouri KM, Mulita F, Georgiou S. Management of pediatric nail psoriasis. Cutis. 2021;108:292-294. doi:10.12788/cutis.0386
- Smith RJ, Rubin AI. Pediatric nail disorders: a review. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2020;32:506-515. doi:10.1097/mop.0000000000000921
- Pourchot D, Bodemer C, Phan A, et al. Nail psoriasis: a systematic evaluation in 313 children with psoriasis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:58-63. doi:10.1111/pde.13028
- Richert B, André J. Nail disorders in children: diagnosis and management. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:101-112. doi:10.2165/11537110-000000000-00000
- Lee JYY. Severe 20-nail psoriasis successfully treated by low dose methotrexate. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15:8.
- Nogueira M, Paller AS, Torres T. Targeted therapy for pediatric psoriasis. Paediatr Drugs. May 2021;23:203-212. doi:10.1007/s40272-021-00443-5
- Hanoodi M, Mittal M. Methotrexate. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 16, 2023. Accessed July 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556114/
- Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Balderrama C. A severe case of erythrodermic psoriasis associated with advanced nail and joint manifestations: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2010;4:179. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-179
- Paller AS, Seyger MMB, Magariños GA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of up to 108 weeks of ixekizumab in pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: the IXORA-PEDS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158:533-541. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0655
- Diotallevi F, Simonetti O, Rizzetto G, et al. Biological treatments for pediatric psoriasis: state of the art and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:11128. doi:10.3390/ijms231911128
- Nash P, Mease PJ, Kirkham B, et al. Secukinumab provides sustained improvement in nail psoriasis, signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis and low rate of radiographic progression in patients with concomitant nail involvement: 2-year results from the Phase III FUTURE 5 study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40:952-959. doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/3nuz51
- Wells LE, Evans T, Hilton R, et al. Use of secukinumab in a pediatric patient leads to significant improvement in nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:384-385. doi:10.1111/pde.13767
- Watabe D, Endoh K, Maeda F, et al. Childhood-onset psoriaticonycho-pachydermo-periostitis treated successfully with infliximab. Eur J Dermatol. 2015;25:506-508. doi:10.1684/ejd.2015.2616
- Pereira TM, Vieira AP, Fernandes JC, et al. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in childhood pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 2006;213:350-352. doi:10.1159/000096202
- Iorizzo M, Gioia Di Chiacchio N, Di Chiacchio N, et al. Intralesional steroid injections for inflammatory nail dystrophies in the pediatric population. Pediatr Dermatol. 2023;40:759-761. doi:10.1111/pde.15295
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Cambiaghi S, et al. Nail lichen planus in children: clinical features, response to treatment, and long-term follow-up. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:1027-1032.
- Lipner SR. Nail lichen planus: a true nail emergency. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:e177-e178. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.11.065
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Piraccini BM, Saccani E, Starace M, et al. Nail lichen planus: response to treatment and long term follow-up. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:489-496. doi:10.1684/ejd.2010.0952
- Mahajan R, Kaushik A, De D, et al. Pediatric trachyonychia- a retrospective study of 17 cases. Indian J Dermatol. 2021;66:689-690. doi:10.4103/ijd.ijd_42_21
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Trachyonychia. J Pediatr. 2020;216:239-239.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.08.034
- Haber JS, Chairatchaneeboon M, Rubin AI. Trachyonychia: review and update on clinical aspects, histology, and therapy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;2:109-115. doi:10.1159/000449063
- Jacobsen AA, Tosti A. Trachyonychia and twenty-nail dystrophy: a comprehensive review and discussion of diagnostic accuracy. Skin Appendage Disord. 2016;2:7-13. doi:10.1159/000445544
- Kumar MG, Ciliberto H, Bayliss SJ. Long-term follow-up of pediatric trachyonychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:198-200. doi:10.1111/pde.12427
- Tosti A, Piraccini BM, Iorizzo M. Trachyonychia and related disorders: evaluation and treatment plans. Dermatolog Ther. 2002;15:121-125. doi:10.1046/j.1529-8019.2002.01511.x
- Leung AKC, Leong KF, Barankin B. Lichen striatus with nail involvement in a 6-year-old boy. Case Rep Pediatr. 2020;2020:1494760. doi:10.1155/2020/1494760
- Kim GW, Kim SH, Seo SH, et al. Lichen striatus with nail abnormality successfully treated with tacrolimus ointment. J Dermatol. 2009;36:616-617. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00720.x
- Iorizzo M, Rubin AI, Starace M. Nail lichen striatus: is dermoscopy useful for the diagnosis? Pediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:859-863. doi:10.1111/pde.13916
- Karp DL, Cohen BA. Onychodystrophy in lichen striatus. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993;10:359-361. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.1993.tb00399.x
- Tosti A, Peluso AM, Misciali C, et al. Nail lichen striatus: clinical features and long-term follow-up of five patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;36(6, pt 1):908-913. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)80270-8
- Simpson EL, Thompson MM, Hanifin JM. Prevalence and morphology of hand eczema in patients with atopic dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2006;17:123-127. doi:10.2310/6620.2006.06005
- Sarifakioglu E, Yilmaz AE, Gorpelioglu C. Nail alterations in 250 infant patients: a clinical study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008;22:741-744. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02592.x
- Milanesi N, D’Erme AM, Gola M. Nail improvement during alitretinoin treatment: three case reports and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:533-536. doi:10.1111/ced.12584
- Chung BY, Choi YW, Kim HO, et al. Nail dystrophy in patients with atopic dermatitis and its association with disease severity. Ann Dermatol. 2019;31:121-126. doi:10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.121
- Navarro-Triviño FJ, Vega-Castillo JJ, Ruiz-Villaverde R. Nail changes successfully treated with dupilumab in a patient with severe atopic dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 2021;62:e468-e469. doi:10.1111/ajd.13633
- Wei SH, Huang YP, Liu MC, et al. An outbreak of coxsackievirus A6 hand, foot, and mouth disease associated with onychomadesis in Taiwan, 2010. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:346. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-11-346
- Shin JY, Cho BK, Park HJ. A clinical study of nail changes occurring secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: onychomadesis and Beau’s lines. Ann Dermatol. 2014;26:280-283. doi:10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.280
- Verma S, Singal A. Nail changes in hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD). Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021;12:656-657. doi:10.4103 /idoj.IDOJ_271_20
- Giordano LMC, de la Fuente LA, Lorca JMB, et al. Onychomadesis secondary to hand-foot-mouth disease: a frequent manifestation and cause of concern for parents. Article in Spanish. Rev Chil Pediatr. 2018;89:380-383. doi:10.4067/s0370-41062018005000203
- Justino MCA, da SMD, Souza MF, et al. Atypical hand-foot-mouth disease in Belém, Amazon region, northern Brazil, with detection of coxsackievirus A6. J Clin Virol. 2020;126:104307. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104307
- Cheng FF, Zhang BB, Cao ML, et al. Clinical characteristics of 68 children with atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6: a single-center retrospective analysis. Transl Pediatr. 2022;11:1502-1509. doi:10.21037/tp-22-352
- Nagata S. Causes of Kawasaki disease-from past to present. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:18. doi:10.3389/fped.2019.00018
- Mitsuishi T, Miyata K, Ando A, et al. Characteristic nail lesions in Kawasaki disease: case series and literature review. J Dermatol. 2022;49:232-238. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.16276
- Lindsley CB. Nail-bed lines in Kawasaki disease. Am J Dis Child. 1992;146:659-660. doi:10.1001/archpedi.1992.02160180017005
- Matsumura O, Nakagishi Y. Pincer nails upon convalescence from Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr. 2022;246:279. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2022.03.002
- Solís-Arias MP, García-Romero MT. Onychomycosis in children. a review. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:123-130. doi:10.1111/ijd.13392
- Gupta AK, Mays RR, Versteeg SG, et al. Onychomycosis in children: safety and efficacy of antifungal agents. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:552-559. doi:10.1111/pde.13561
- 49. Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Shear NH, et al. Labeled use of efinaconazole topical solution 10% in treating onychomycosis in children and a review of the management of pediatric onychomycosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e13613. doi:10.1111/dth.13613
- Falotico JM, Lipner SR. Updated perspectives on the diagnosis and management of onychomycosis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:1933-1957. doi:10.2147/ccid.S362635
- Patel D, Castelo-Soccio LA, Rubin AI, et al. Laboratory monitoring during systemic terbinafine therapy for pediatric onychomycosis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017;153:1326-1327. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.4483
- Friedlander SF, Chan YC, Chan YH, et al. Onychomycosis does not always require systemic treatment for cure: a trial using topical therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:316-322. doi:10.1111/pde.12064
- Rich P, Spellman M, Purohit V, et al. Tavaborole 5% topical solution for the treatment of toenail onychomycosis in pediatric patients: results from a phase 4 open-label study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019;18:190-195.
- Gupta AK, Venkataraman M, Abramovits W, et al. JUBLIA (efinaconazole 10% solution) in the treatment of pediatric onychomycosis. Skinmed. 2021;19:206-210.
- Gupta AK, Paquet M. Systemic antifungals to treat onychomycosis in children: a systematic review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:294-302. doi:10.1111/pde.12048
- Leggit JC. Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96:44-51.
- Lipner SR, Scher RK. Congenital malalignment of the great toenails with acute paronychia. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:e288-e289.doi:10.1111/pde.12924
Practice Points
- Nail plate pitting is the most common clinical sign of nail psoriasis in children.
- Nail changes are common in hand, foot, and mouth disease, with the most frequent being onychomadesis.
- Because onychomycosis may resemble other nail disorders, mycologic confirmation is recommended to avoid misdiagnosis.
- Many nail conditions in children self-resolve but recognizing these manifestations is important in providing anticipatory guidance to patients and caregivers.
Enhancing Cosmetic and Functional Improvement of Recalcitrant Nail Lichen Planus With Resin Nail
Practice Gap
Lichen planus (LP)—a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the nails—is prevalent in 10% to 15% of patients and is more common in the fingernails than toenails. Clinical manifestation includes longitudinal ridges, nail plate atrophy, and splitting, which all contribute to cosmetic disfigurement and difficulty with functionality. Quality of life and daily activities may be impacted profoundly.1 First-line therapies include intralesional and systemic corticosteroids; however, efficacy is limited and recurrence is common.1,2 Lichen planus is one of the few conditions that may cause permanent and debilitating nail loss.
Tools
A resin nail can be used to improve cosmetic appearance and functionality in patients with recalcitrant nail LP. The composite resin creates a flexible nonporous nail and allows the underlying natural nail to grow. Application of resin nails has been used for toenail onychodystrophies to improve cosmesis and functionality but has not been reported for fingernails. The resin typically lasts 6 to 8 weeks on toenails.
The Technique
Application of a resin nail involves several steps (see video online). First, the affected nail should be debrided and a bonding agent applied. Next, multiple layers of resin are applied until the patient’s desired thickness is achieved (typically 2 layers), followed by a sealing agent. Finally, the nail is cured with UV light. We recommend applying sunscreen to the hand(s) prior to curing with UV light. The liquid resin allows the nail to be customized to the patient’s desired length and shape. The overall procedure takes approximately 20 minutes for a single nail.

We applied resin nail to the thumbnail of a 46-year-old woman with recalcitrant isolated nail LP of 7 years’ duration (Figure). She previously had difficulties performing everyday activities, and the resin improved her functionality. She also was pleased with the cosmetic appearance. After 2 weeks, the resin started falling off with corresponding natural nail growth. The patient denied any adverse events.
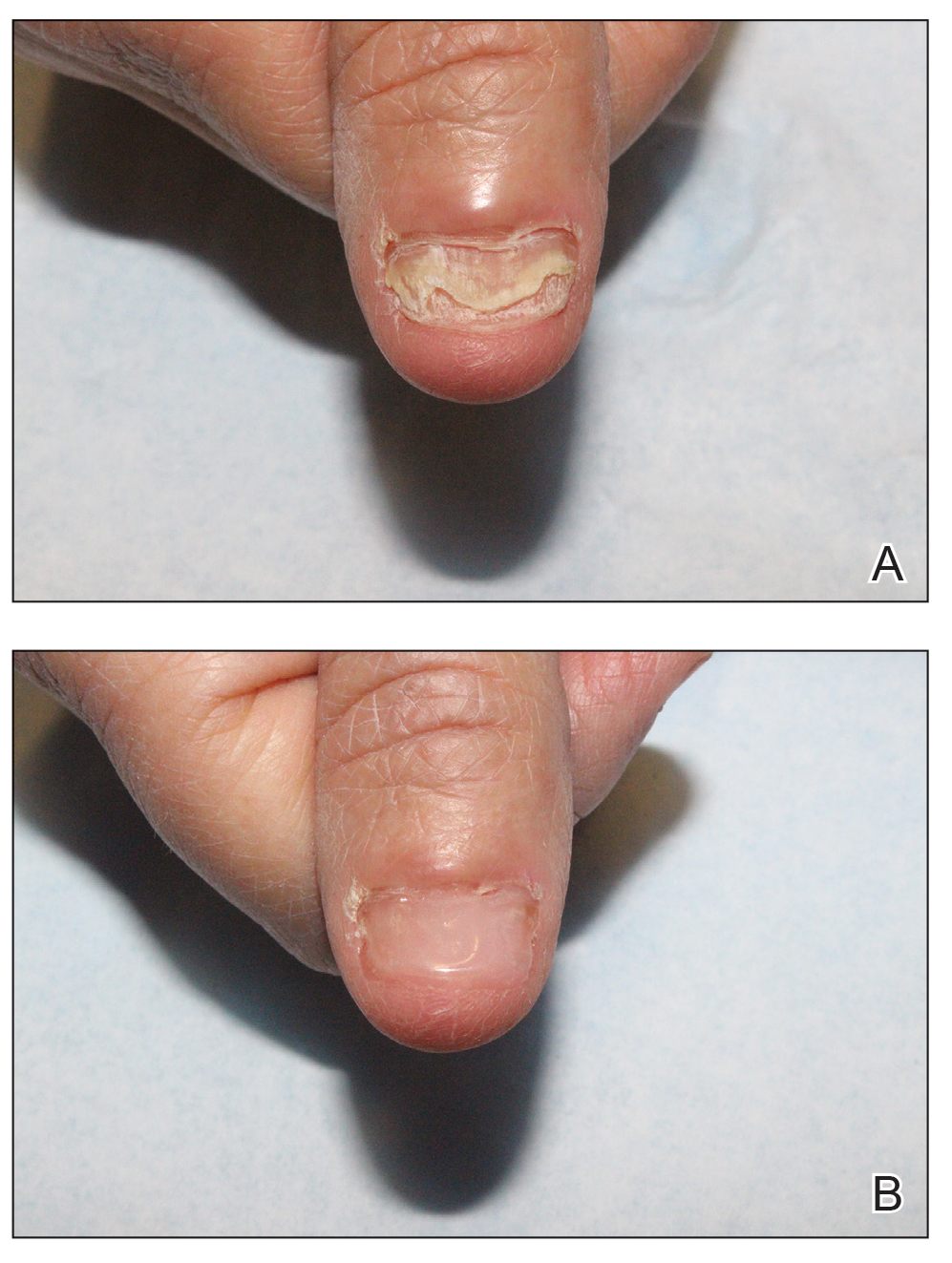
Practice Implications
Resin nail application may serve as a temporary solution to improve cosmesis and functionality in patients with recalcitrant nail LP. As shown in our patient, the resin may fall off faster on the fingernails than the toenails, likely because of the faster growth rate of fingernails and more frequent exposure from daily activities. Further studies of resin nail application for the fingernails are needed to establish duration in patients with varying levels of activity (eg, washing dishes, woodworking).
Because the resin nail may be removed easily at any time, resin nail application does not interfere with treatments such as intralesional steroid injections. For patients using a topical medication regimen, the resin nail may be applied slightly distal to the cuticle so that the medication can still be applied by the proximal nail fold of the underlying natural nail.
The resin nail should be kept short and removed after 2 to 4 weeks for the fingernails and 6 to 8 weeks for the toenails to examine the underlying natural nail. Patients may go about their daily activities with the resin nail, including applying nail polish to the resin nail, bathing, and swimming. Resin nail application may complement medical treatments and improve quality of life for patients with nail LP.
- Gupta MK, Lipner SR. Review of nail lichen planus: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:221-230. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.002
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
Practice Gap
Lichen planus (LP)—a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the nails—is prevalent in 10% to 15% of patients and is more common in the fingernails than toenails. Clinical manifestation includes longitudinal ridges, nail plate atrophy, and splitting, which all contribute to cosmetic disfigurement and difficulty with functionality. Quality of life and daily activities may be impacted profoundly.1 First-line therapies include intralesional and systemic corticosteroids; however, efficacy is limited and recurrence is common.1,2 Lichen planus is one of the few conditions that may cause permanent and debilitating nail loss.
Tools
A resin nail can be used to improve cosmetic appearance and functionality in patients with recalcitrant nail LP. The composite resin creates a flexible nonporous nail and allows the underlying natural nail to grow. Application of resin nails has been used for toenail onychodystrophies to improve cosmesis and functionality but has not been reported for fingernails. The resin typically lasts 6 to 8 weeks on toenails.
The Technique
Application of a resin nail involves several steps (see video online). First, the affected nail should be debrided and a bonding agent applied. Next, multiple layers of resin are applied until the patient’s desired thickness is achieved (typically 2 layers), followed by a sealing agent. Finally, the nail is cured with UV light. We recommend applying sunscreen to the hand(s) prior to curing with UV light. The liquid resin allows the nail to be customized to the patient’s desired length and shape. The overall procedure takes approximately 20 minutes for a single nail.

We applied resin nail to the thumbnail of a 46-year-old woman with recalcitrant isolated nail LP of 7 years’ duration (Figure). She previously had difficulties performing everyday activities, and the resin improved her functionality. She also was pleased with the cosmetic appearance. After 2 weeks, the resin started falling off with corresponding natural nail growth. The patient denied any adverse events.

Practice Implications
Resin nail application may serve as a temporary solution to improve cosmesis and functionality in patients with recalcitrant nail LP. As shown in our patient, the resin may fall off faster on the fingernails than the toenails, likely because of the faster growth rate of fingernails and more frequent exposure from daily activities. Further studies of resin nail application for the fingernails are needed to establish duration in patients with varying levels of activity (eg, washing dishes, woodworking).
Because the resin nail may be removed easily at any time, resin nail application does not interfere with treatments such as intralesional steroid injections. For patients using a topical medication regimen, the resin nail may be applied slightly distal to the cuticle so that the medication can still be applied by the proximal nail fold of the underlying natural nail.
The resin nail should be kept short and removed after 2 to 4 weeks for the fingernails and 6 to 8 weeks for the toenails to examine the underlying natural nail. Patients may go about their daily activities with the resin nail, including applying nail polish to the resin nail, bathing, and swimming. Resin nail application may complement medical treatments and improve quality of life for patients with nail LP.
Practice Gap
Lichen planus (LP)—a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the nails—is prevalent in 10% to 15% of patients and is more common in the fingernails than toenails. Clinical manifestation includes longitudinal ridges, nail plate atrophy, and splitting, which all contribute to cosmetic disfigurement and difficulty with functionality. Quality of life and daily activities may be impacted profoundly.1 First-line therapies include intralesional and systemic corticosteroids; however, efficacy is limited and recurrence is common.1,2 Lichen planus is one of the few conditions that may cause permanent and debilitating nail loss.
Tools
A resin nail can be used to improve cosmetic appearance and functionality in patients with recalcitrant nail LP. The composite resin creates a flexible nonporous nail and allows the underlying natural nail to grow. Application of resin nails has been used for toenail onychodystrophies to improve cosmesis and functionality but has not been reported for fingernails. The resin typically lasts 6 to 8 weeks on toenails.
The Technique
Application of a resin nail involves several steps (see video online). First, the affected nail should be debrided and a bonding agent applied. Next, multiple layers of resin are applied until the patient’s desired thickness is achieved (typically 2 layers), followed by a sealing agent. Finally, the nail is cured with UV light. We recommend applying sunscreen to the hand(s) prior to curing with UV light. The liquid resin allows the nail to be customized to the patient’s desired length and shape. The overall procedure takes approximately 20 minutes for a single nail.

We applied resin nail to the thumbnail of a 46-year-old woman with recalcitrant isolated nail LP of 7 years’ duration (Figure). She previously had difficulties performing everyday activities, and the resin improved her functionality. She also was pleased with the cosmetic appearance. After 2 weeks, the resin started falling off with corresponding natural nail growth. The patient denied any adverse events.

Practice Implications
Resin nail application may serve as a temporary solution to improve cosmesis and functionality in patients with recalcitrant nail LP. As shown in our patient, the resin may fall off faster on the fingernails than the toenails, likely because of the faster growth rate of fingernails and more frequent exposure from daily activities. Further studies of resin nail application for the fingernails are needed to establish duration in patients with varying levels of activity (eg, washing dishes, woodworking).
Because the resin nail may be removed easily at any time, resin nail application does not interfere with treatments such as intralesional steroid injections. For patients using a topical medication regimen, the resin nail may be applied slightly distal to the cuticle so that the medication can still be applied by the proximal nail fold of the underlying natural nail.
The resin nail should be kept short and removed after 2 to 4 weeks for the fingernails and 6 to 8 weeks for the toenails to examine the underlying natural nail. Patients may go about their daily activities with the resin nail, including applying nail polish to the resin nail, bathing, and swimming. Resin nail application may complement medical treatments and improve quality of life for patients with nail LP.
- Gupta MK, Lipner SR. Review of nail lichen planus: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:221-230. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.002
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
- Gupta MK, Lipner SR. Review of nail lichen planus: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:221-230. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.002
- Iorizzo M, Tosti A, Starace M, et al. Isolated nail lichen planus: an expert consensus on treatment of the classical form. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:1717-1723. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.056
A Cross-sectional Analysis of Regional Trends in Medicare Reimbursement for Phototherapy Services From 2010 to 2023
To the Editor:
Phototherapy regularly is utilized in the outpatient setting to address various skin pathologies, including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides.1,2 Phototherapy is broadly defined by the measured administration of nonionizing radiation within the UV range including wavelengths within the UVA (eg, psoralen sensitizer plus UVA-1) and UVB (eg, broadband UVB, narrowband UVB) spectrums.1,3 Generally, the mechanism of action is derived from effects on inflammatory components of cutaneous disorders and the induction of apoptosis, both precipitating numerous downstream events.4
From 2015 to 2018, there were more than 1.3 million outpatient phototherapy visits in the United States, with the most common procedural indications being dermatitis not otherwise specified, atopic dermatitis, and pruritus.5 From 2000 to 2015, the quantity of phototherapy services billed to Medicare trended upwards by an average of 5% per year, increasing from 334,670 in the year 2000 to 692,093 in 2015.6 Therefore, an illustration of associated costs would be beneficial. Additionally, because total cost and physician reimbursement fluctuate from year to year, studies demonstrating overall trends can inform both US policymakers and physicians. There is a paucity of research on geographical trends for procedural reimbursements in dermatology for phototherapy. Understanding geographic trends of reimbursement could duly serve to optimize dermatologist practice patterns involving access to viable and quality care for patients seeking treatment as well as draw health policymakers’ attention to striking adjustments in physician fees. Therefore, in this study we aimed to illustrate the most recent regional payment trends in phototherapy procedures for Medicare B patients.
We queried the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) database (https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/lookup-tool) for the years 2010 to 2023 for Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes common to phototherapy procedures: actinotherapy (96900); photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB (96910); photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA (96912); and photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision (96913). Nonfacility prices for these procedures were analyzed. For 2010, due to midyear alterations to Medicare reimbursement (owed to bills HR 3962 and HR 4872), the mean price data of MPFS files 2010A and 2010B were used. All dollar values were converted to January 2023 US dollars using corresponding consumer price index inflation data. The Medicare Administrative Contractors were used to group state pricing information by region in accordance with established US Census Bureau subdivisions (https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/economic-census/guidance-geographies/levels.html). Weighted percentage change in reimbursement rate was calculated using physician (MD or DO) utilization (procedure volume) data available in the 2020 Physician and Other Practitioners Public Use File (https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-physician-other-practitioners/medicare-physician-other-practitioners-by-provider-and-service). All descriptive statistics and visualization were generated using R software (v4.2.2)(R Development Core Team).
Table 1 provides physician utilization data and the corresponding number of Part B beneficiaries for phototherapy procedures in 2020. There were 65,045 services of actinotherapy provided to a total of 6855 unique Part B beneficiaries, 173,979 services of photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB provided to 13,122 unique Part B beneficiaries, 2524 services of photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA provided to a total of 357 unique Part B beneficiaries, and 37 services of photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision provided to a total of 27 unique Part B beneficiaries.
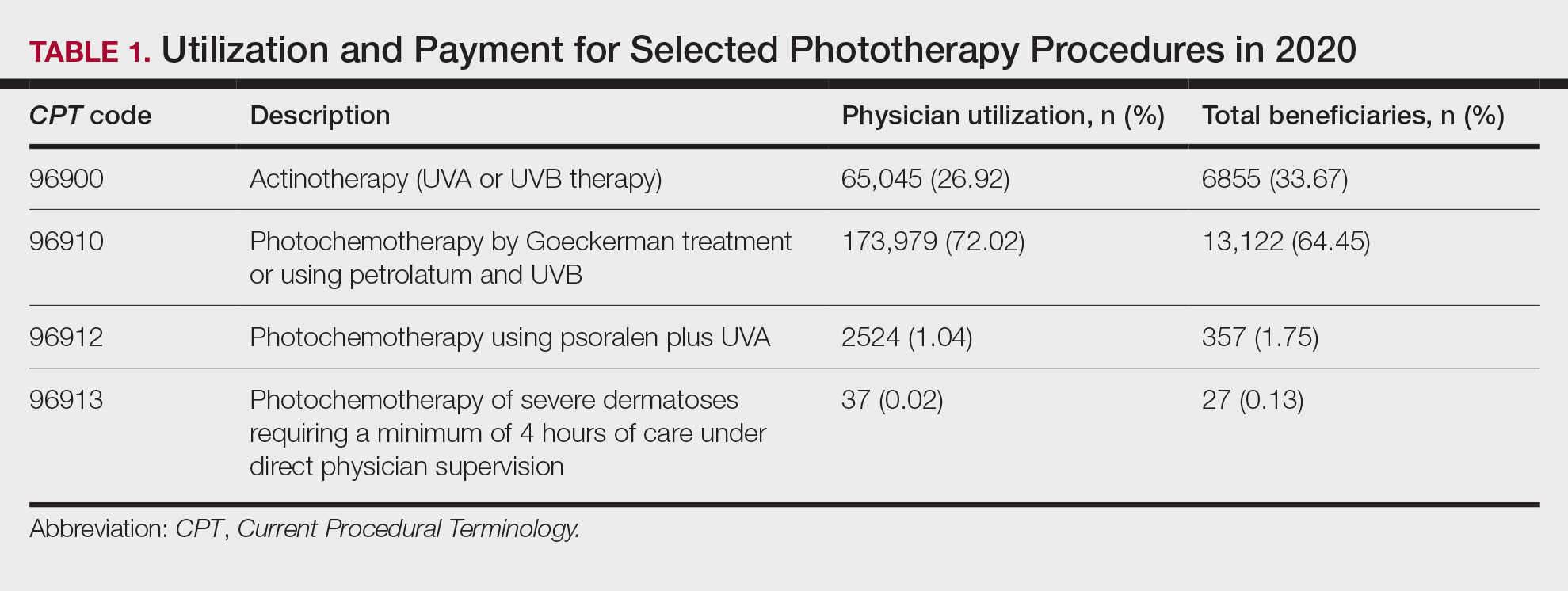
On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the North increased by 0.68% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 2). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +19.37%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+31.45%)($98.12 to $128.98; compound annual growth rate [CAGR], +0.0213), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−12.76%)($126.09 to $109.97; CAGR, −0.0105). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −11.68% ($30.21 to $26.68; CAGR, −0.0095), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.27% ($174.03 to $166.60; CAGR, −0.0034).
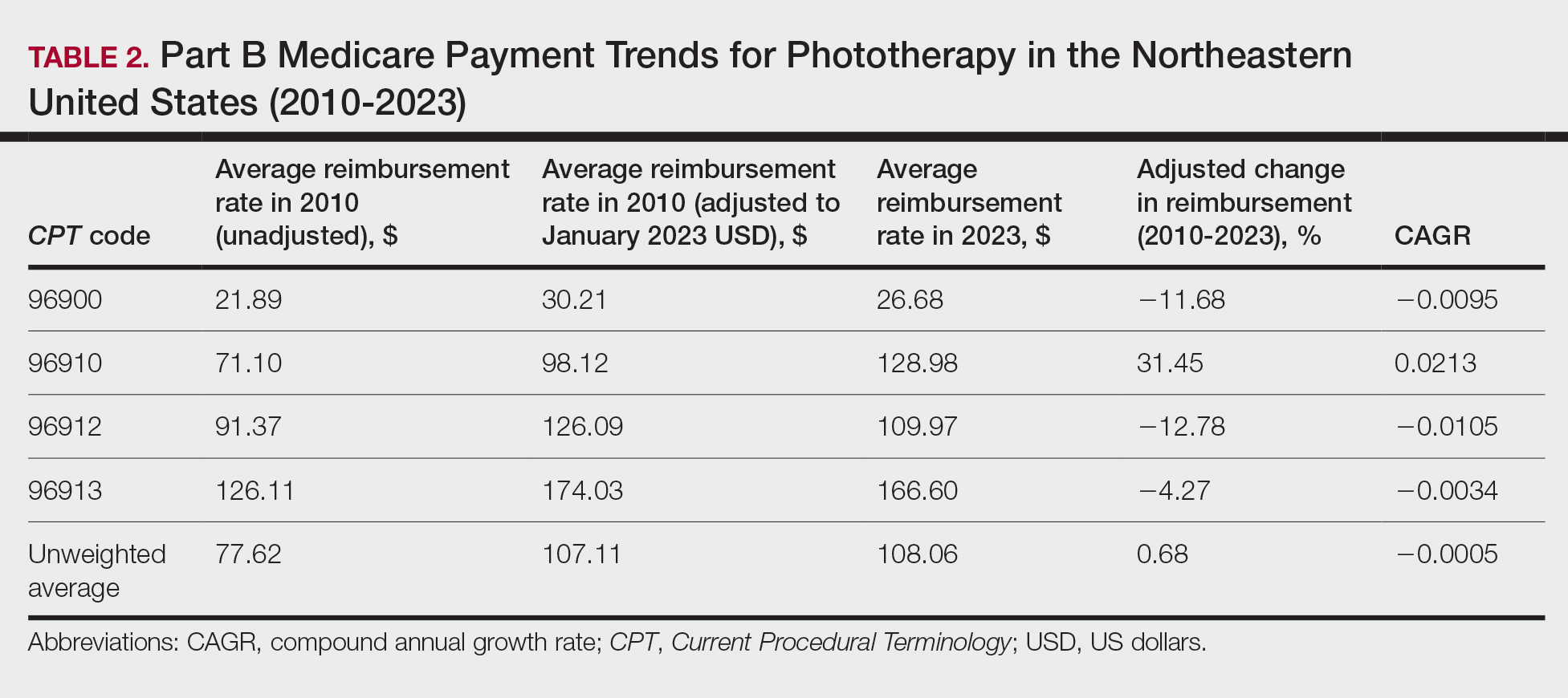
On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the Midwest increased by 8.40% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 3). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +28.53%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+41.48%)($80.42 to $113.78; CAGR, +0.0270), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−6.14%)($103.28 to $97.03; CAGR, −0.0049). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.73% ($24.69 to $23.52; CAGR, −0.0037), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was +2.99% ($142.72 to $146.99; CAGR, +0.0023).
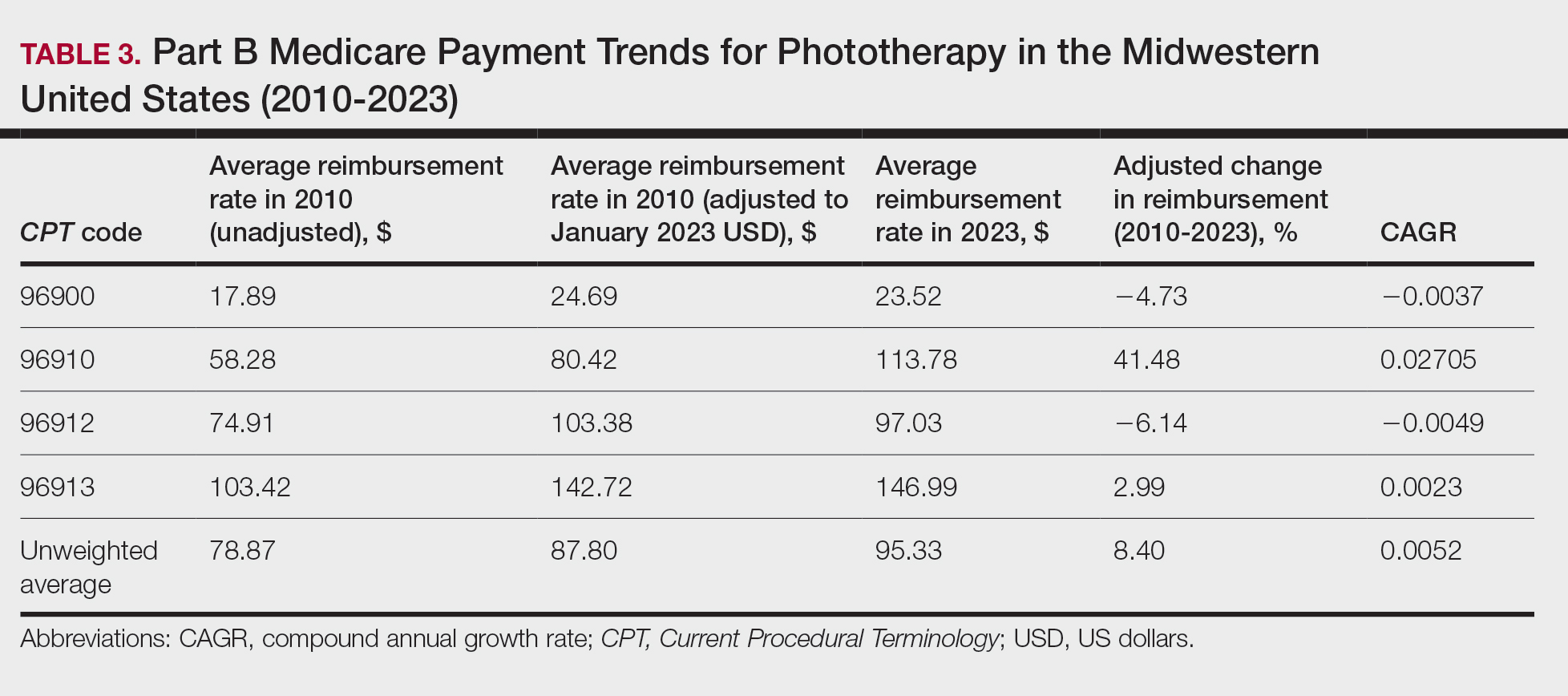
On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the South decreased by 2.62% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 4). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +15.41%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+27.26%)($90.40 to $115.04 USD; CAGR, +0.0187), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−15.50%)($116.08 to $98.09; CAGR, −0.0129). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −15.06% ($28.02 to $23.80; CAGR, −0.0125), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −7.19% ($160.11 to $148.61; CAGR, −0.0057).
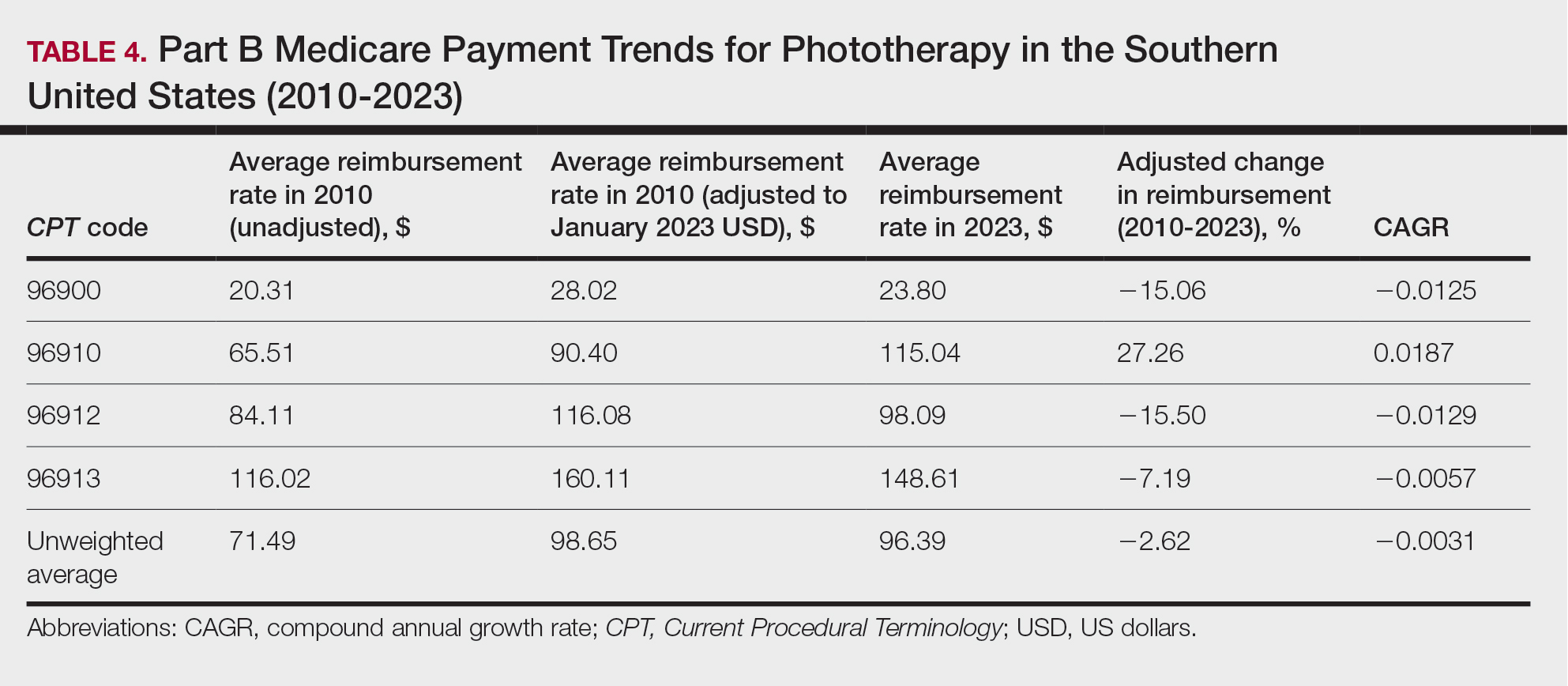
On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the West increased by 27.53% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 5). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +51.16%. Reimbursement for all analyzed procedures increased in the western United States. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+66.56%)($80.84 to $134.65; CAGR, +0.0400), and CPT code 96912 reported the lowest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+10.64%)($103.88 to $114.93; CAGR, +0.0078). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 11.54% ($24.88 to $27.75; CAGR, +0.0084), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 21.38% ($143.39 to $174.04; CAGR, +0.0150).
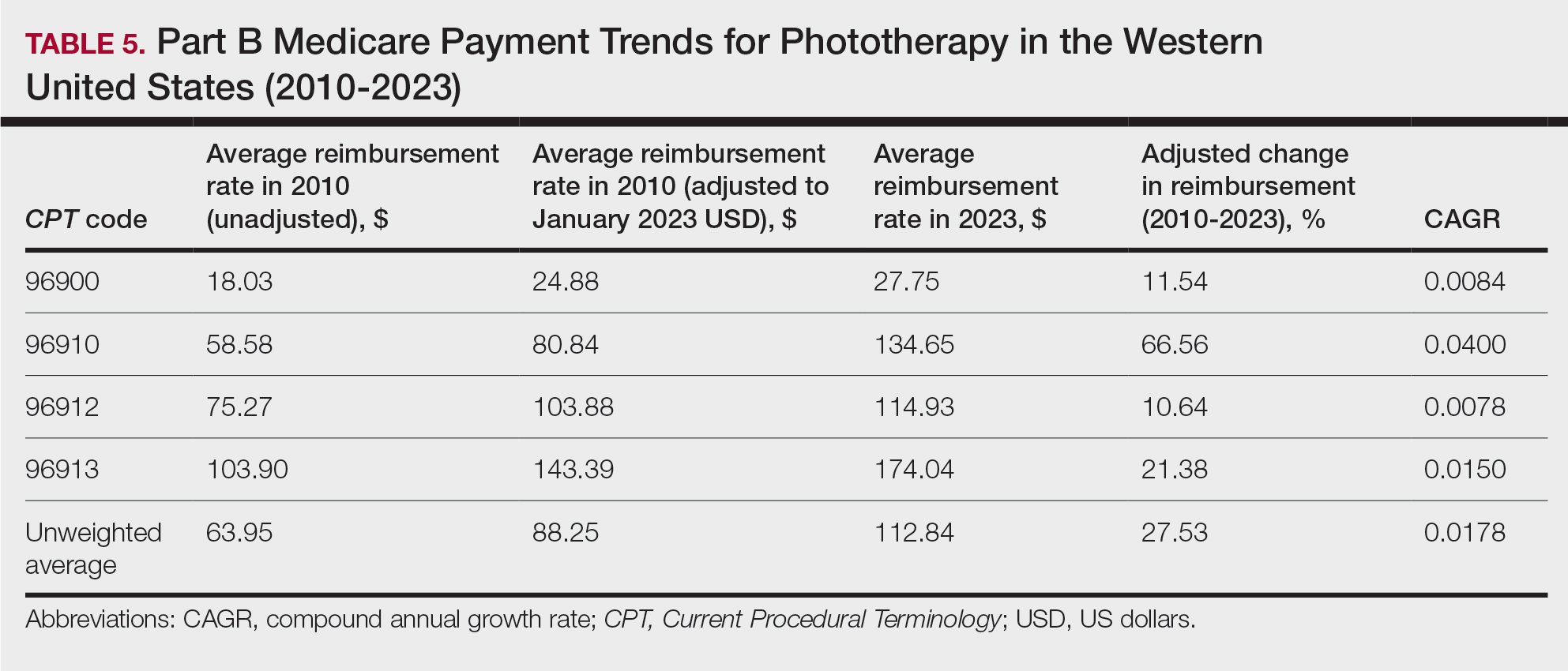
In this study evaluating geographical payment trends for phototherapy from 2010 to 2023, we demonstrated regional inconsistency in mean inflation-adjusted Medicare reimbursement rates. We found that all phototherapy procedures had increased reimbursement in the western United States, whereas all other regions reported cuts in reimbursement rates for at least half of the analyzed procedures. After adjusting for procedure utilization by physicians, weighted mean reimbursement for phototherapy increased in all US regions.
In a cross-sectional study that explored trends in the geographic distribution of dermatologists from 2012 to 2017, dermatologists in the northeastern and western United States were more likely to be located in higher-income zip codes, whereas dermatologists in the southern United States were more likely to be located in lower-income zip codes,7 suggesting that payment rate changes are not concordant with cost of living. Additionally, Lauck and colleagues8 observed that 75% of the top 20 most common procedures performed by dermatologists had decreased reimbursement (mean change, −10.8%) from 2011 to 2021. Other studies on Medicare reimbursement trends over the last 2 decades have reported major decreases within other specialties, suggesting that declining Medicare reimbursements are not unique to dermatology.9,10 It is critical to monitor these developments, as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services emphasized health care policy changes aimed at increasing reimbursements for evaluation and management services with compensatory payment cuts in billing for procedural services.11
Mazmudar et al12 previously reported a mean reimbursement decrease of −6.6% for laser/phototherapy procedures between 2007 and 2021, but these data did not include the heavily utilized Goeckerman treatment. Changes in reimbursement pose major ramifications for dermatologists—for practice size, scope, and longevity—as rates influence changes in commercial insurance reimbursements.13 Medicare plays a major role in the US health care system as the second largest expenditure14; indeed, between 2000 and 2015, Part B billing volume for phototherapy procedures increased 5% annually. However, phototherapy remains inaccessible in many locations due to unequal regional distribution of phototherapy clinics.6 Moreover, home phototherapy units are not yet widely utilized because of safety and efficacy concerns, lack of physician oversight, and difficulty obtaining insurance coverage.15 Acknowledgment and consideration of these geographical trends may persuasively allow policymakers, hospitals, and physicians to facilitate cost-effective phototherapy reimbursements that ensure continued access to quality and sustainable dermatologic care in the United States that tailor to regional needs.
In sum, this analysis reveals regional trends in Part B physician reimbursement for phototherapy procedures, with all US regions reporting a mean increase in phototherapy reimbursement after adjusting for utilization, albeit to varying degrees. Mean reimbursement for photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB increased most among phototherapy procedures. Mean reimbursement for both actinotherapy and photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA decreased in all regions except the western United States.
Limitations include the restriction to Part B MPFS and the reliance on single-year (2020) physician utilization data to compute weighted changes in average reimbursement across a multiyear range, effectively restricting sweeping conclusions. Still, this study puts forth actionable insights for dermatologists and policymakers alike to appreciate and consider.
- Rathod DG, Muneer H, Masood S. Phototherapy. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2002.
- Branisteanu DE, Dirzu DS, Toader MP, et al. Phototherapy in dermatological maladies (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:259. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11184
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.03.001
- Vieyra-Garcia PA, Wolf P. A deep dive into UV-based phototherapy: mechanisms of action and emerging molecular targets in inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;222:107784. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107784
- Oulee A, Javadi SS, Martin A, et al. Phototherapy trends in dermatology 2015-2018. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2545-2546. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.2019660
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.018
- Benlagha I, Nguyen BM. Changes in dermatology practice characteristics in the United States from 2012 to 2017. JAAD Int. 2021;3:92-101. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.005
- Lauck K, Nguyen QB, Hebert A. Trends in Medicare reimbursement within dermatology: 2011-2021. Skin. 2022;6:122-131. doi:10.25251/skin.6.2.5
- Smith JF, Moore ML, Pollock JR, et al. National and geographic trends in Medicare reimbursement rates for orthopedic shoulder and upper extremity surgery from 2000 to 2020. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31:860-867. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2021.09.001
- Haglin JM, Eltorai AEM, Richter KR, et al. Medicare reimbursement for general surgery procedures: 2000 to 2018. Ann Surg. 2020;271:17-22. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000003289
- Fleishon HB. Evaluation and management coding initiative. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17:1539-1540. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.09.057
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3453
- Clemens J, Gottlieb JD. In the shadow of a giant: Medicare’s influence on private physician payments. J Polit Econ. 2017;125:1-39. doi:10.1086/689772
- Ya J, Ezaldein HH, Scott JF. Trends in Medicare utilization by dermatologists, 2012-2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:471-474. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4212
- Rajpara AN, O’Neill JL, Nolan BV, et al. Review of home phototherapy. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:2.
To the Editor:
Phototherapy regularly is utilized in the outpatient setting to address various skin pathologies, including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides.1,2 Phototherapy is broadly defined by the measured administration of nonionizing radiation within the UV range including wavelengths within the UVA (eg, psoralen sensitizer plus UVA-1) and UVB (eg, broadband UVB, narrowband UVB) spectrums.1,3 Generally, the mechanism of action is derived from effects on inflammatory components of cutaneous disorders and the induction of apoptosis, both precipitating numerous downstream events.4
From 2015 to 2018, there were more than 1.3 million outpatient phototherapy visits in the United States, with the most common procedural indications being dermatitis not otherwise specified, atopic dermatitis, and pruritus.5 From 2000 to 2015, the quantity of phototherapy services billed to Medicare trended upwards by an average of 5% per year, increasing from 334,670 in the year 2000 to 692,093 in 2015.6 Therefore, an illustration of associated costs would be beneficial. Additionally, because total cost and physician reimbursement fluctuate from year to year, studies demonstrating overall trends can inform both US policymakers and physicians. There is a paucity of research on geographical trends for procedural reimbursements in dermatology for phototherapy. Understanding geographic trends of reimbursement could duly serve to optimize dermatologist practice patterns involving access to viable and quality care for patients seeking treatment as well as draw health policymakers’ attention to striking adjustments in physician fees. Therefore, in this study we aimed to illustrate the most recent regional payment trends in phototherapy procedures for Medicare B patients.
We queried the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) database (https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/lookup-tool) for the years 2010 to 2023 for Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes common to phototherapy procedures: actinotherapy (96900); photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB (96910); photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA (96912); and photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision (96913). Nonfacility prices for these procedures were analyzed. For 2010, due to midyear alterations to Medicare reimbursement (owed to bills HR 3962 and HR 4872), the mean price data of MPFS files 2010A and 2010B were used. All dollar values were converted to January 2023 US dollars using corresponding consumer price index inflation data. The Medicare Administrative Contractors were used to group state pricing information by region in accordance with established US Census Bureau subdivisions (https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/economic-census/guidance-geographies/levels.html). Weighted percentage change in reimbursement rate was calculated using physician (MD or DO) utilization (procedure volume) data available in the 2020 Physician and Other Practitioners Public Use File (https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-physician-other-practitioners/medicare-physician-other-practitioners-by-provider-and-service). All descriptive statistics and visualization were generated using R software (v4.2.2)(R Development Core Team).
Table 1 provides physician utilization data and the corresponding number of Part B beneficiaries for phototherapy procedures in 2020. There were 65,045 services of actinotherapy provided to a total of 6855 unique Part B beneficiaries, 173,979 services of photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB provided to 13,122 unique Part B beneficiaries, 2524 services of photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA provided to a total of 357 unique Part B beneficiaries, and 37 services of photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision provided to a total of 27 unique Part B beneficiaries.

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the North increased by 0.68% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 2). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +19.37%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+31.45%)($98.12 to $128.98; compound annual growth rate [CAGR], +0.0213), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−12.76%)($126.09 to $109.97; CAGR, −0.0105). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −11.68% ($30.21 to $26.68; CAGR, −0.0095), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.27% ($174.03 to $166.60; CAGR, −0.0034).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the Midwest increased by 8.40% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 3). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +28.53%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+41.48%)($80.42 to $113.78; CAGR, +0.0270), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−6.14%)($103.28 to $97.03; CAGR, −0.0049). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.73% ($24.69 to $23.52; CAGR, −0.0037), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was +2.99% ($142.72 to $146.99; CAGR, +0.0023).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the South decreased by 2.62% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 4). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +15.41%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+27.26%)($90.40 to $115.04 USD; CAGR, +0.0187), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−15.50%)($116.08 to $98.09; CAGR, −0.0129). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −15.06% ($28.02 to $23.80; CAGR, −0.0125), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −7.19% ($160.11 to $148.61; CAGR, −0.0057).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the West increased by 27.53% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 5). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +51.16%. Reimbursement for all analyzed procedures increased in the western United States. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+66.56%)($80.84 to $134.65; CAGR, +0.0400), and CPT code 96912 reported the lowest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+10.64%)($103.88 to $114.93; CAGR, +0.0078). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 11.54% ($24.88 to $27.75; CAGR, +0.0084), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 21.38% ($143.39 to $174.04; CAGR, +0.0150).

In this study evaluating geographical payment trends for phototherapy from 2010 to 2023, we demonstrated regional inconsistency in mean inflation-adjusted Medicare reimbursement rates. We found that all phototherapy procedures had increased reimbursement in the western United States, whereas all other regions reported cuts in reimbursement rates for at least half of the analyzed procedures. After adjusting for procedure utilization by physicians, weighted mean reimbursement for phototherapy increased in all US regions.
In a cross-sectional study that explored trends in the geographic distribution of dermatologists from 2012 to 2017, dermatologists in the northeastern and western United States were more likely to be located in higher-income zip codes, whereas dermatologists in the southern United States were more likely to be located in lower-income zip codes,7 suggesting that payment rate changes are not concordant with cost of living. Additionally, Lauck and colleagues8 observed that 75% of the top 20 most common procedures performed by dermatologists had decreased reimbursement (mean change, −10.8%) from 2011 to 2021. Other studies on Medicare reimbursement trends over the last 2 decades have reported major decreases within other specialties, suggesting that declining Medicare reimbursements are not unique to dermatology.9,10 It is critical to monitor these developments, as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services emphasized health care policy changes aimed at increasing reimbursements for evaluation and management services with compensatory payment cuts in billing for procedural services.11
Mazmudar et al12 previously reported a mean reimbursement decrease of −6.6% for laser/phototherapy procedures between 2007 and 2021, but these data did not include the heavily utilized Goeckerman treatment. Changes in reimbursement pose major ramifications for dermatologists—for practice size, scope, and longevity—as rates influence changes in commercial insurance reimbursements.13 Medicare plays a major role in the US health care system as the second largest expenditure14; indeed, between 2000 and 2015, Part B billing volume for phototherapy procedures increased 5% annually. However, phototherapy remains inaccessible in many locations due to unequal regional distribution of phototherapy clinics.6 Moreover, home phototherapy units are not yet widely utilized because of safety and efficacy concerns, lack of physician oversight, and difficulty obtaining insurance coverage.15 Acknowledgment and consideration of these geographical trends may persuasively allow policymakers, hospitals, and physicians to facilitate cost-effective phototherapy reimbursements that ensure continued access to quality and sustainable dermatologic care in the United States that tailor to regional needs.
In sum, this analysis reveals regional trends in Part B physician reimbursement for phototherapy procedures, with all US regions reporting a mean increase in phototherapy reimbursement after adjusting for utilization, albeit to varying degrees. Mean reimbursement for photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB increased most among phototherapy procedures. Mean reimbursement for both actinotherapy and photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA decreased in all regions except the western United States.
Limitations include the restriction to Part B MPFS and the reliance on single-year (2020) physician utilization data to compute weighted changes in average reimbursement across a multiyear range, effectively restricting sweeping conclusions. Still, this study puts forth actionable insights for dermatologists and policymakers alike to appreciate and consider.
To the Editor:
Phototherapy regularly is utilized in the outpatient setting to address various skin pathologies, including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides.1,2 Phototherapy is broadly defined by the measured administration of nonionizing radiation within the UV range including wavelengths within the UVA (eg, psoralen sensitizer plus UVA-1) and UVB (eg, broadband UVB, narrowband UVB) spectrums.1,3 Generally, the mechanism of action is derived from effects on inflammatory components of cutaneous disorders and the induction of apoptosis, both precipitating numerous downstream events.4
From 2015 to 2018, there were more than 1.3 million outpatient phototherapy visits in the United States, with the most common procedural indications being dermatitis not otherwise specified, atopic dermatitis, and pruritus.5 From 2000 to 2015, the quantity of phototherapy services billed to Medicare trended upwards by an average of 5% per year, increasing from 334,670 in the year 2000 to 692,093 in 2015.6 Therefore, an illustration of associated costs would be beneficial. Additionally, because total cost and physician reimbursement fluctuate from year to year, studies demonstrating overall trends can inform both US policymakers and physicians. There is a paucity of research on geographical trends for procedural reimbursements in dermatology for phototherapy. Understanding geographic trends of reimbursement could duly serve to optimize dermatologist practice patterns involving access to viable and quality care for patients seeking treatment as well as draw health policymakers’ attention to striking adjustments in physician fees. Therefore, in this study we aimed to illustrate the most recent regional payment trends in phototherapy procedures for Medicare B patients.
We queried the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS) database (https://www.cms.gov/medicare/payment/fee-schedules/physician/lookup-tool) for the years 2010 to 2023 for Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes common to phototherapy procedures: actinotherapy (96900); photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB (96910); photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA (96912); and photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision (96913). Nonfacility prices for these procedures were analyzed. For 2010, due to midyear alterations to Medicare reimbursement (owed to bills HR 3962 and HR 4872), the mean price data of MPFS files 2010A and 2010B were used. All dollar values were converted to January 2023 US dollars using corresponding consumer price index inflation data. The Medicare Administrative Contractors were used to group state pricing information by region in accordance with established US Census Bureau subdivisions (https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/economic-census/guidance-geographies/levels.html). Weighted percentage change in reimbursement rate was calculated using physician (MD or DO) utilization (procedure volume) data available in the 2020 Physician and Other Practitioners Public Use File (https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-physician-other-practitioners/medicare-physician-other-practitioners-by-provider-and-service). All descriptive statistics and visualization were generated using R software (v4.2.2)(R Development Core Team).
Table 1 provides physician utilization data and the corresponding number of Part B beneficiaries for phototherapy procedures in 2020. There were 65,045 services of actinotherapy provided to a total of 6855 unique Part B beneficiaries, 173,979 services of photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB provided to 13,122 unique Part B beneficiaries, 2524 services of photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA provided to a total of 357 unique Part B beneficiaries, and 37 services of photochemotherapy of severe dermatoses requiring a minimum of 4 hours of care under direct physician supervision provided to a total of 27 unique Part B beneficiaries.

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the North increased by 0.68% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 2). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +19.37%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+31.45%)($98.12 to $128.98; compound annual growth rate [CAGR], +0.0213), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−12.76%)($126.09 to $109.97; CAGR, −0.0105). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −11.68% ($30.21 to $26.68; CAGR, −0.0095), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.27% ($174.03 to $166.60; CAGR, −0.0034).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the Midwest increased by 8.40% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 3). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +28.53%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+41.48%)($80.42 to $113.78; CAGR, +0.0270), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−6.14%)($103.28 to $97.03; CAGR, −0.0049). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −4.73% ($24.69 to $23.52; CAGR, −0.0037), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was +2.99% ($142.72 to $146.99; CAGR, +0.0023).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the South decreased by 2.62% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 4). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +15.41%. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted change in reimbursement (+27.26%)($90.40 to $115.04 USD; CAGR, +0.0187), and CPT code 96912 reported the greatest adjusted decrease in reimbursement (−15.50%)($116.08 to $98.09; CAGR, −0.0129). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −15.06% ($28.02 to $23.80; CAGR, −0.0125), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted decrease in reimbursement was −7.19% ($160.11 to $148.61; CAGR, −0.0057).

On average (unweighted), phototherapy reimbursement rates in the West increased by 27.53% between 2010 and 2023 (Table 5). After weighting for 2020 physician utilization, the average change in reimbursement rate was +51.16%. Reimbursement for all analyzed procedures increased in the western United States. During this time period, CPT code 96910 reported the greatest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+66.56%)($80.84 to $134.65; CAGR, +0.0400), and CPT code 96912 reported the lowest adjusted increase in reimbursement (+10.64%)($103.88 to $114.93; CAGR, +0.0078). For CPT code 96900, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 11.54% ($24.88 to $27.75; CAGR, +0.0084), and for CPT code 96913, the reported adjusted increase in reimbursement was 21.38% ($143.39 to $174.04; CAGR, +0.0150).

In this study evaluating geographical payment trends for phototherapy from 2010 to 2023, we demonstrated regional inconsistency in mean inflation-adjusted Medicare reimbursement rates. We found that all phototherapy procedures had increased reimbursement in the western United States, whereas all other regions reported cuts in reimbursement rates for at least half of the analyzed procedures. After adjusting for procedure utilization by physicians, weighted mean reimbursement for phototherapy increased in all US regions.
In a cross-sectional study that explored trends in the geographic distribution of dermatologists from 2012 to 2017, dermatologists in the northeastern and western United States were more likely to be located in higher-income zip codes, whereas dermatologists in the southern United States were more likely to be located in lower-income zip codes,7 suggesting that payment rate changes are not concordant with cost of living. Additionally, Lauck and colleagues8 observed that 75% of the top 20 most common procedures performed by dermatologists had decreased reimbursement (mean change, −10.8%) from 2011 to 2021. Other studies on Medicare reimbursement trends over the last 2 decades have reported major decreases within other specialties, suggesting that declining Medicare reimbursements are not unique to dermatology.9,10 It is critical to monitor these developments, as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services emphasized health care policy changes aimed at increasing reimbursements for evaluation and management services with compensatory payment cuts in billing for procedural services.11
Mazmudar et al12 previously reported a mean reimbursement decrease of −6.6% for laser/phototherapy procedures between 2007 and 2021, but these data did not include the heavily utilized Goeckerman treatment. Changes in reimbursement pose major ramifications for dermatologists—for practice size, scope, and longevity—as rates influence changes in commercial insurance reimbursements.13 Medicare plays a major role in the US health care system as the second largest expenditure14; indeed, between 2000 and 2015, Part B billing volume for phototherapy procedures increased 5% annually. However, phototherapy remains inaccessible in many locations due to unequal regional distribution of phototherapy clinics.6 Moreover, home phototherapy units are not yet widely utilized because of safety and efficacy concerns, lack of physician oversight, and difficulty obtaining insurance coverage.15 Acknowledgment and consideration of these geographical trends may persuasively allow policymakers, hospitals, and physicians to facilitate cost-effective phototherapy reimbursements that ensure continued access to quality and sustainable dermatologic care in the United States that tailor to regional needs.
In sum, this analysis reveals regional trends in Part B physician reimbursement for phototherapy procedures, with all US regions reporting a mean increase in phototherapy reimbursement after adjusting for utilization, albeit to varying degrees. Mean reimbursement for photochemotherapy by Goeckerman treatment or using petrolatum and UVB increased most among phototherapy procedures. Mean reimbursement for both actinotherapy and photochemotherapy using psoralen plus UVA decreased in all regions except the western United States.
Limitations include the restriction to Part B MPFS and the reliance on single-year (2020) physician utilization data to compute weighted changes in average reimbursement across a multiyear range, effectively restricting sweeping conclusions. Still, this study puts forth actionable insights for dermatologists and policymakers alike to appreciate and consider.
- Rathod DG, Muneer H, Masood S. Phototherapy. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2002.
- Branisteanu DE, Dirzu DS, Toader MP, et al. Phototherapy in dermatological maladies (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:259. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11184
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.03.001
- Vieyra-Garcia PA, Wolf P. A deep dive into UV-based phototherapy: mechanisms of action and emerging molecular targets in inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;222:107784. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107784
- Oulee A, Javadi SS, Martin A, et al. Phototherapy trends in dermatology 2015-2018. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2545-2546. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.2019660
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.018
- Benlagha I, Nguyen BM. Changes in dermatology practice characteristics in the United States from 2012 to 2017. JAAD Int. 2021;3:92-101. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.005
- Lauck K, Nguyen QB, Hebert A. Trends in Medicare reimbursement within dermatology: 2011-2021. Skin. 2022;6:122-131. doi:10.25251/skin.6.2.5
- Smith JF, Moore ML, Pollock JR, et al. National and geographic trends in Medicare reimbursement rates for orthopedic shoulder and upper extremity surgery from 2000 to 2020. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31:860-867. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2021.09.001
- Haglin JM, Eltorai AEM, Richter KR, et al. Medicare reimbursement for general surgery procedures: 2000 to 2018. Ann Surg. 2020;271:17-22. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000003289
- Fleishon HB. Evaluation and management coding initiative. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17:1539-1540. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.09.057
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3453
- Clemens J, Gottlieb JD. In the shadow of a giant: Medicare’s influence on private physician payments. J Polit Econ. 2017;125:1-39. doi:10.1086/689772
- Ya J, Ezaldein HH, Scott JF. Trends in Medicare utilization by dermatologists, 2012-2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:471-474. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4212
- Rajpara AN, O’Neill JL, Nolan BV, et al. Review of home phototherapy. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:2.
- Rathod DG, Muneer H, Masood S. Phototherapy. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2002.
- Branisteanu DE, Dirzu DS, Toader MP, et al. Phototherapy in dermatological maladies (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23:259. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11184
- Barros NM, Sbroglio LL, Buffara MO, et al. Phototherapy. An Bras Dermatol. 2021;96:397-407. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2021.03.001
- Vieyra-Garcia PA, Wolf P. A deep dive into UV-based phototherapy: mechanisms of action and emerging molecular targets in inflammation and cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;222:107784. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107784
- Oulee A, Javadi SS, Martin A, et al. Phototherapy trends in dermatology 2015-2018. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2545-2546. doi:10.1080/09546634.2021.2019660
- Tan SY, Buzney E, Mostaghimi A. Trends in phototherapy utilization among Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, 2000 to 2015. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:672-679. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.03.018
- Benlagha I, Nguyen BM. Changes in dermatology practice characteristics in the United States from 2012 to 2017. JAAD Int. 2021;3:92-101. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.005
- Lauck K, Nguyen QB, Hebert A. Trends in Medicare reimbursement within dermatology: 2011-2021. Skin. 2022;6:122-131. doi:10.25251/skin.6.2.5
- Smith JF, Moore ML, Pollock JR, et al. National and geographic trends in Medicare reimbursement rates for orthopedic shoulder and upper extremity surgery from 2000 to 2020. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;31:860-867. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2021.09.001
- Haglin JM, Eltorai AEM, Richter KR, et al. Medicare reimbursement for general surgery procedures: 2000 to 2018. Ann Surg. 2020;271:17-22. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000003289
- Fleishon HB. Evaluation and management coding initiative. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17:1539-1540. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2020.09.057
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3453
- Clemens J, Gottlieb JD. In the shadow of a giant: Medicare’s influence on private physician payments. J Polit Econ. 2017;125:1-39. doi:10.1086/689772
- Ya J, Ezaldein HH, Scott JF. Trends in Medicare utilization by dermatologists, 2012-2015. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:471-474. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.4212
- Rajpara AN, O’Neill JL, Nolan BV, et al. Review of home phototherapy. Dermatol Online J. 2010;16:2.
Practice Points
- After weighting for procedure utilization, mean reimbursement for phototherapy increased across all US regions from 2010 to 2023 (mean change, +28.62%), yet with marked regional diversity.
- The southern United States reported the least growth in weighted mean reimbursement (+15.41%), and the western United States reported the greatest growth in weighted mean reimbursement (+51.16%).
- Region- and procedure-specific payment changes are especially valuable to dermatologists and policymakers alike, potentially reinvigorating payment reform discussions.
Impact of Ketogenic and Low-Glycemic Diets on Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Inflammatory skin conditions often have a relapsing and remitting course and represent a large proportion of chronic skin diseases. Common inflammatory skin disorders include acne, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), atopic dermatitis (AD), and seborrheic dermatitis (SD).1 Although each of these conditions has a unique pathogenesis, they all are driven by a background of chronic inflammation. It has been reported that diets with high levels of refined carbohydrates and saturated or trans-fatty acids may exacerbate existing inflammation.2 Consequently, dietary interventions, such as the ketogenic and low-glycemic diets, have potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects that are being assessed as stand-alone or adjunctive therapies for dermatologic diseases.
Diet may partially influence systemic inflammation through its effect on weight. Higher body mass index and obesity are linked to a low-grade inflammatory state and higher levels of circulating inflammatory markers. Therefore, weight loss leads to decreases in inflammatory cytokines, including C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor α, and IL-6.3 These cytokines and metabolic effects overlap with inflammatory skin condition pathways. It also is posited that decreased insulin release associated with weight loss results in decreased sebaceous lipogenesis and androgens, which drive keratinocyte proliferation and acne development.4,5 For instance, in a 2015 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials on psoriasis, patients in the weight loss intervention group had more substantial reductions in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) scores compared with controls receiving usual care (P=.004).6 However, in a systematic review of 35 studies on acne vulgaris, overweight and obese patients (defined by a body mass index of ≥23 kg/m2) had similar odds of having acne compared with normal-weight individuals (P=.671).7
Similar to weight loss, ketogenesis acts as a negative feedback mechanism to reduce insulin release, leading to decreased inflammation and androgens that often exacerbate inflammatory skin diseases.8 Ketogenesis ensues when daily carbohydrate intake is limited to less than 50 g, and long-term adherence to a ketogenic diet results in metabolic reliance on ketone bodies such as acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.9 These metabolites may decrease free radical damage and consequently improve signs and symptoms of acne, psoriasis, and other inflammatory skin diseases.10-12 Similarly, increased ketones also may decrease activation of the NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and Pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome and therefore reduce inflammatory markers such as IL-1β and IL-1.4,13 Several proposed mechanisms are outlined in the Table.

Collectively, low-glycemic and ketogenic diets have been proposed as potential interventions for reducing inflammatory skin conditions. These dietary approaches are hypothesized to exert their effects by facilitating weight loss, elevating ketone levels, and reducing systemic inflammation. The current review summarizes the existing evidence on ketogenic and low-glycemic diets as treatments for inflammatory skin conditions and evaluates the potential benefits of these dietary interventions in managing and improving outcomes for individuals with inflammatory skin conditions.
Methods
Using PubMed for articles indexed for MEDLINE and Google Scholar, a review of the literature was conducted with a combination of the following search terms: low-glycemic diet, inflammatory, dermatologic, ketogenic diet, inflammation, dermatology, acne, psoriasis, eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Reference citations in identified works also were reviewed. Interventional (experimental studies or clinical trials), survey-based, and observational studies that investigated the effects of low-glycemic or ketogenic diets for the treatment of inflammatory skin conditions were included. Inclusion criteria were studies assessing acne, psoriasis, SD, AD, and HS. Exclusion criteria were studies published before 1965; those written in languages other than English; and those analyzing other diets, such as the Mediterranean or low-fat diets. The search yielded a total of 11 observational studies and 4 controlled studies published between 1966 and January 2023. Because this analysis utilized publicly available data and did not qualify as human subject research, institutional review board approval was not required.
Results
Acne Vulgaris—Acne vulgaris is a disease of chronic pilosebaceous inflammation and follicular epithelial proliferation associated with Propionibacterium acnes. The association between acne and low-glycemic diets has been examined in several studies. Diet quality is measured and assessed using the glycemic index (GI), which is the effect of a single food on postprandial blood glucose, and the glycemic load, which is the GI adjusted for carbohydrates per serving.14 High levels of GI and glycemic load are associated with hyperinsulinemia and an increase in insulinlike growth factor 1 concentration that promotes
Six survey-based studies evaluated sugar intake in patients with acne compared to healthy matched controls (eTable). Among these studies, 5 reported higher glycemic loads or daily sugar intake in acne patients compared to individuals without acne.12,19,20,26,28 The remaining study was conducted in 1967 and enrolled 16 acne patients and 32 matched controls. It reported no significant difference in sugar intake between the groups (P>.05).17
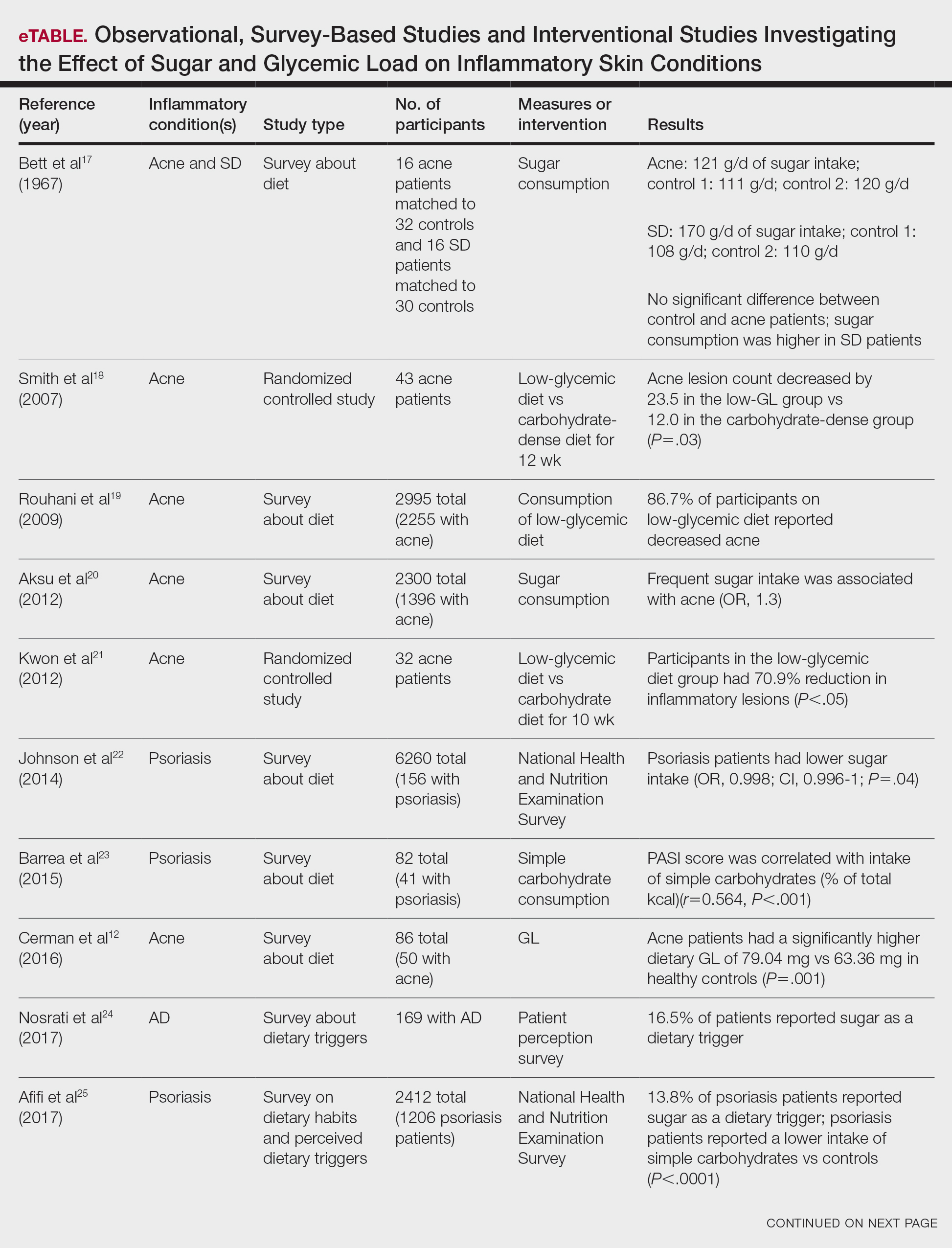

Smith et al18 randomized 43 male patients aged 15 to 25 years with facial acne into 2 cohorts for 12 weeks, each consuming either a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food [fruits, whole grains], and 30% fat) or a carbohydrate-dense diet of foods with medium to high GI based on prior documentation of the original diet. Patients were instructed to use a noncomedogenic cleanser as their only acne treatment. At 12 weeks, patients consuming the low-glycemic diet had an average of 23.5 fewer inflammatory lesions, while those in the intervention group had 12.0 fewer lesions (P=.03).18
In another controlled study by Kwon et al,21 32 male and female acne patients were randomized to a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food, and 30% fat) or a standard diet for 10 weeks. Patients on the low-glycemic diet experienced a 70.9% reduction in inflammatory lesions (P<.05). Hematoxylin and eosin staining and image analysis were performed to measure sebaceous gland surface area in the low-glycemic diet group, which decreased from 0.32 to 0.24 mm2 (P=.03). The sebaceous gland surface area in the control group was not reported. Moreover, patients on the low-glycemic diet had reduced IL-8 immunohistochemical staining (decreasing from 2.9 to 1.7 [P=.03]) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 levels (decreasing from 2.6 to 1.3 [P=.03]), suggesting suppression of ongoing inflammation. Patients on the low-glycemic diet had no significant difference in transforming growth factor β1(P=.83). In the control group, there was no difference in IL-8, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1, or transforming growth factor β1 (P>.05) on immunohistochemical staining.21
Psoriasis—Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by hyperproliferation and aberrant keratinocyte plaque formation. The innate immune response of keratinocytes in response to epidermal damage or infection begins with neutrophil recruitment and dendritic cell activation. Dendritic cell secretion of IL-23 promotes T-cell differentiation into helper T cells (TH1) that subsequently secrete IL-17 and IL-22, thereby stimulating keratinocyte proliferation and eventual plaque formation. The relationship between diet and psoriasis is poorly understood; however, hyperinsulinemia is associated with greater severity of psoriasis.31
Four observational studies examined sugar intake in psoriasis patients. Barrea et al23 conducted a survey-based study of 82 male participants (41 with psoriasis and 41 healthy controls), reporting that PASI score was correlated with intake of simple carbohydrates (percentage of total kilocalorie)(r=0.564, P<.001). Another study by Yamashita et al27 found higher sugar intake in psoriasis patients than controls (P=.003) based on surveys from 70 patients with psoriasis and 70 matched healthy controls.
These findings contrast with 2 survey-based studies by Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 of sugar intake in psoriasis patients using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Johnson et al22 reported reduced sugar intake among 156 psoriasis patients compared with 6104 unmatched controls (odds ratio, 0.998; CI, 0.996-1 [P=.04]) from 2003 to 2006. Similarly, Afifi et al25 reported decreased sugar intake in 1206 psoriasis patients compared with sex- and age-matched controls (P<.0001) in 2009 and 2010. When patients were asked about dietary triggers, 13.8% of psoriasis patients reported sugar as the most common trigger, which was more frequent than alcohol (13.6%), gluten (7.2%), and dairy (6%).25
Castaldo et al29,30 published 2 nonrandomized clinical intervention studies in 2020 and 2021 evaluating the impact of the ketogenic diet on psoriasis. In the first study, 37 psoriasis patients followed a 10-week diet consisting of 4 weeks on a ketogenic diet (500 kcal/d) followed by 6 weeks on a low-caloric Mediterranean diet.29 At the end of the intervention, there was a 17.4% reduction in PASI score, a 33.2-point reduction in itch severity score, and a 13.4-point reduction in the dermatology life quality index score; however, this study did not include a control diet group for comparison.29 The second study included 30 psoriasis patients on a ketogenic diet and 30 control patients without psoriasis on a regular diet.30 The ketogenic diet consisted of 400 to 500 g of vegetables, 20 to 30 g of fat, and a proportion of protein based on body weight with at least 12 g of whey protein and various amino acids. Patients on the ketogenic diet had significant reduction in PASI scores (value relative to clinical features, 1.4916 [P=.007]). Furthermore, concentrations of cytokines IL-2 (P=.04) and IL-1β (P=.006) decreased following the ketogenic diet but were not measured in the control group.30
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Seborrheic dermatitis is associated with overcolonization of Malassezia species near lipid-rich sebaceous glands. Malassezia hydrolyzes free fatty acids, yielding oleic acids and leading to T-cell release of IL-8 and IL-17.32 Literature is sparse regarding how dietary modifications may play a role in disease severity. In a survey study, Bett et al17 compared 16 SD patients to 1:2 matched controls (N=29) to investigate the relationship between sugar consumption and presence of disease. Two control cohorts were selected, 1 from clinic patients diagnosed with verruca and 1 matched by age and sex from a survey-based study at a facility in London, England. Sugar intake was measured both in total grams per day and in “beverage sugar” per day, defined as sugar taken in tea and coffee. There was higher total sugar and higher beverage sugar intake among the SD group compared with both control groups (P<.05).17
Atopic Dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis is a disease of epidermal barrier dysfunction and IgE-mediated allergic sensitization.33 There are several mechanisms by which skin structure may be disrupted. It is well established that filaggrin mutations inhibit stratum corneum maturation and lamellar matrix deposition.34 Upregulation of IL-4–, IL-13–, and IL-17–secreting TH2 cells also is associated with disruption of tight junctions and reduction of filaggrin.35,36 Given that a T cell–mediated inflammatory response is involved in disease pathogenesis, glycemic control is hypothesized to have therapeutic potential.
Nosrati et al24 surveyed 169 AD patients about their perceived dietary triggers through a 61-question survey based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Respondents were queried about their perceptions and dietary changes, such as removal or addition of specific food groups and trial of specific diets. Overall, 16.5% of patients reported sugar being a trigger, making it the fourth most common among those surveyed and less common than dairy (24.8%), gluten (18.3%), and alcohol (17.1%).24
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa is driven by hyperkeratosis, dilatation, and occlusion of pilosebaceous follicular ducts, whose eventual rupture evokes a local acute inflammatory response.37 The inciting event for both acne and HS involves mTOR complex–mediated follicular hyperproliferation andinsulinlike growth factor 1 stimulation of androgen receptors in pilosebaceous glands. Given the similarities between the pathogenesis of acne and HS, it is hypothesized that lifestyle changes, including diet modification, may have a beneficial effect on HS.38-40
Comment
Acne—Overall, there is strong evidence supporting the efficacy of a low-glycemic diet in the treatment of acne. Notably, among the 6 observational studies identified, there was 1 conflicting study by Bett et al17 that did not find a statistically significant difference in glucose intake between acne and control patients. However, this study included only 16 acne patients, whereas the other 5 observational studies included 32 to 2255 patients.17 The strongest evidence supporting low-glycemic dietary interventions in acne treatment is from 2 rigorous randomized clinical trials by Kwon et al21 and Smith et al.18 These trials used intention-to-treat models and maintained consistency in gender, age, and acne treatment protocols across both control and treatment groups. To ensure compliance with dietary interventions, daily telephone calls, food logs, and 24-hour urea sampling were utilized. Acne outcomes were assessed by a dermatologist who remained blinded with well-defined outcome measures. An important limitation of these studies is the difficulty in attributing the observed results solely to reduced glucose intake, as low-glycemic diets often lead to other dietary changes, including reduced fat intake and increased nutrient consumption.18,21
A 2022 systematic review of acne by Meixiong et al41 further reinforced the beneficial effects of low-glycemic diets in the management of acne patients. The group reviewed 6 interventional studies and 28 observational studies to investigate the relationship among acne, dairy, and glycemic content and found an association between decreased glucose and dairy on reduction of acne.41
It is likely that the ketogenic diet, which limits glucose, would be beneficial for acne patients. There may be added benefit through elevated ketone bodies and substantially reduced insulin secretion. However, because there are no observational or interventional studies, further research is needed to draw firm conclusions regarding diet for acne treatment. A randomized clinical trial investigating the effects of the ketogenic diet compared to the low-glycemic diet compared to a regular diet would be valuable.
Psoriasis—Among psoriasis studies, there was a lack of consensus regarding glucose intake and correlation with disease. Among the 4 observational studies, 2 reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients and 2 reported decreased glucose intake. It is plausible that the variability in studies is due to differences in sample size and diet heterogeneity among study populations. More specifically, Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 analyzed large sample sizes of 6260 and 2412 US participants, respectively, and found decreased sugar intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. In comparison, Barrea et al23 and Yamashita et al27 analyzed substantially smaller and more specific populations consisting of 82 Italian and 140 Japanese participants, respectively; both reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. These seemingly antithetical results may be explained by regional dietary differences, with varying proportions of meats, vegetables, antioxidants, and vitamins.
Moreover, the variation among studies may be further explained by the high prevalence of comorbidities among psoriasis patients. In the study by Barrea et al,23 psoriasis patients had higher fasting glucose (P=.004) and insulin (P=.022) levels than healthy patients. After adjusting for body mass index and metabolic syndrome, the correlation coefficient measuring the relationship between the PASI score and intake of simple carbohydrates changed from r=0.564 (P<.001) to r=0.352 (P=.028). The confounding impact of these comorbidities was further highlighted by Yamashita et al,27 who found statistically significant differences in glucose intake between psoriasis and healthy patients (P=.003). However, they reported diminished significance on additional subgroup analysis accounting for potential comorbidities (P=.994).27 Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 did not account for comorbidities; therefore, the 4 observational study results must be interpreted cautiously.
The 2 randomized clinical trials by Castaldo et al29,30 weakly suggest that a ketogenic diet may be beneficial for psoriasis patients. The studies have several notable limitations, including insufficient sample sizes and control groups. Thus, the decreased PASI scores reported in psoriasis patients on the ketogenic diets are challenging to interpret. Additionally, both studies placed patients on highly restrictive diets of 500 kcal/d for 4 weeks. The feasibility of recommending such a diet to patients in clinical practice is questionable. Diets of less than 500 kcal/d may be dangerous for patients with underlying comorbidities and are unlikely to serve as long-term solutions.23 To contextualize our findings, a 2022 review by Chung et al42 examined the impact of various diets—low-caloric, gluten-free, Mediterranean, Western, and ketogenic—on psoriasis and reported insufficient evidence to suggest a benefit to the ketogenic diet for psoriasis patients, though the Mediterranean diet may be well suited for psoriasis patients because of improved cardiovascular health and reduced mortality.
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Sanders et al43 found that patients with a high-fruit diet had lower odds of having SD, while those on a Western diet had higher odds of having SD. Although the study did not measure glycemic load, it is conceivable that the high glycemic load characteristic of the Western diet contributed to these findings.43 However, no studies have investigated the direct link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and SD, leaving this area open for further study.
Atopic Dermatitis—It has been hypothesized that mitigating T cell–mediated inflammation via glucose control may contribute to the improvement in AD.35,36 However, in one study, 16.5% of AD patients self-identified sugar as a dietary trigger, ranking fourth among other dietary triggers.24 Thus, the connection between glucose levels and AD warrants further exploration.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Given the role of metabolic and hormonal influence in HS as well as the overlapping pathophysiology with acne, it is possible that low-glycemic and ketogenic diets may have a role in improving HS.38-40 However, there is a gap in observation and controlled studies investigating the link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and HS.
Conclusion
Our analysis focused on interventional and observational research exploring the effects of low-glycemic and ketogenic diets on associations and treatment of inflammatory skin conditions. There is sufficient evidence to counsel acne patients on the benefits of a low-glycemic diet as an adjunctive treatment for acne. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to recommend a low-glycemic or ketogenic diet as a treatment for patients with any other inflammatory skin disease. Prospective and controlled clinical trials are needed to clarify the utility of dietary interventions for treating inflammatory skin conditions.
- Pickett K, Loveman E, Kalita N, et al. Educational interventions to improve quality of life in people with chronic inflammatory skin diseases: systematic reviews of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2015;19:1-176, v-vi.
- Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:677-685.
- Dowlatshahi EA, van der Voort EA, Arends LR, et al. Markers of systemic inflammation in psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:266-282.
- Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015;21:263-269.
- Melnik BC. Acne vulgaris: the metabolic syndrome of the pilosebaceous follicle. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:29-40.
- Upala S, Sanguankeo A. Effect of lifestyle weight loss intervention on disease severity in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39:1197-1202.
- Heng AHS, Chew FT. Systematic review of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5754.
- Paoli A, Grimaldi K, Toniolo L, et al. Nutrition and acne: therapeutic potential of ketogenic diets. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:111-117.
- Masood W, Annamaraju P, Khan Suheb MZ, et al. Ketogenic diet. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Fomin DA, McDaniel B, Crane J. The promising potential role of ketones in inflammatory dermatologic disease: a new frontier in treatment research. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:484-487.
- Zhang D, Jin W, Wu R, et al. High glucose intake exacerbates autoimmunity through reactive-oxygen-species-mediated TGF-β cytokine activation. Immunity. 2019;51:671-681.e5.
- Cerman AA, Aktas E, Altunay IK, et al. Dietary glycemic factors, insulin resistance, and adiponectin levels in acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:155-162.
- Ferrere G, Tidjani Alou M, Liu P, et al. Ketogenic diet and ketone bodies enhance the anticancer effects of PD-1 blockade. JCI Insight. 2021;6:e145207.
- Burris J, Shikany JM, Rietkerk W, et al. A Low glycemic index and glycemic load diet decreases insulin-like growth factor-1 among adults with moderate and severe acne: a short-duration, 2-week randomized controlled trial. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118:1874-1885.
- Tan JKL, Stein Gold LF, Alexis AF, et al. Current concepts in acne pathogenesis: pathways to inflammation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018;37(3S):S60-S62.
- Kim J, Ochoa MT, Krutzik SR, et al. Activation of toll-like receptor 2 in acne triggers inflammatory cytokine responses. J Immunol. 2002;169:1535-1541.
- Bett DG, Morland J, Yudkin J. Sugar consumption in acne vulgaris and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Br Med J. 1967;3:153-155.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Rouhani P, Berman B, Rouhani G. Acne improves with a popular, low glycemic diet from South Beach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(Suppl 1):AB14.
- Aksu AE, Metintas S, Saracoglu ZN, et al. Acne: prevalence and relationship with dietary habits in Eskisehir, Turkey. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1503-1509.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Johnson JA, Ma C, Kanada KN, et al. Diet and nutrition in psoriasis: analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the United States. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:327-332.
- Barrea L, Macchia PE, Tarantino G, et al. Nutrition: a key environmental dietary factor in clinical severity and cardio-metabolic risk in psoriatic male patients evaluated by 7-day food-frequency questionnaire. J Transl Med. 2015;13:303.
- Nosrati A, Afifi L, Danesh MJ, et al. Dietary modifications in atopic dermatitis: patient-reported outcomes. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:523-538.
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017;7:227-242.
- Burris J, Rietkerk W, Shikany JM, et al. Differences in dietary glycemic load and hormones in New York City adults with no and moderate/severe acne. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017;117:1375-1383.
- Yamashita H, Morita T, Ito M, et al. Dietary habits in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: low intake of meat in psoriasis and high intake of vitamin A in psoriatic arthritis. J Dermatol. 2019;46:759-769.
- Marson J, Baldwin HE. 12761 Acne, twins, and glycemic index: a sweet pilot study of diet and dietary beliefs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(Suppl):AB110.
- Castaldo G, Rastrelli L, Galdo G, et al. Aggressive weight-loss program with a ketogenic induction phase for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a proof-of-concept, single-arm, open-label clinical trial. Nutrition. 2020;74:110757.
- Castaldo G, Pagano I, Grimaldi M, et al. Effect of very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on psoriasis patients: a nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic study. J Proteome Res. 2021;20:1509-1521.
- Ip W, Kirchhof MG. Glycemic control in the treatment of psoriasis. Dermatology. 2017;233:23-29.
- Vijaya Chandra SH, Srinivas R, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Cutaneous Malassezia: commensal, pathogen, or protector? Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:614446.
- David Boothe W, Tarbox JA, Tarbox MB. Atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1027:21-37.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Hanifin JM, Boguniewicz M, et al. The role of phosphodiesterase 4 in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis and the perspective for its inhibition. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:3-10.
- Furue K, Ito T, Tsuji G, et al. The IL-13–OVOL1–FLG axis in atopic dermatitis. Immunology. 2019;158:281-286.
- Renert-Yuval Y, Guttman-Yassky E. New treatments for atopic dermatitis targeting beyond IL-4/IL-13 cytokines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:28-35.
- Sellheyer K, Krahl D. “Hidradenitis suppurativa” is acne inversa! An appeal to (finally) abandon a misnomer. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:535-540.
- Danby FW, Margesson LJ. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:779-793.
- Fernandez JM, Marr KD, Hendricks AJ, et al. Alleviating and exacerbating foods in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14246.
- Yamanaka-Takaichi M, Revankar R, Shih T, et al. Expert consensus on priority research gaps in dietary and lifestyle factors in hidradenitis suppurativa: a Delphi consensus study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2129-2136.
- Meixiong J, Ricco C, Vasavda C, et al. Diet and acne: a systematic review. JAAD Int. 2022;7:95-112.
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckland). 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Sanders MGH, Pardo LM, Ginger RS, et al. Association between diet and seborrheic dermatitis: a cross-sectional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:108-114.
Inflammatory skin conditions often have a relapsing and remitting course and represent a large proportion of chronic skin diseases. Common inflammatory skin disorders include acne, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), atopic dermatitis (AD), and seborrheic dermatitis (SD).1 Although each of these conditions has a unique pathogenesis, they all are driven by a background of chronic inflammation. It has been reported that diets with high levels of refined carbohydrates and saturated or trans-fatty acids may exacerbate existing inflammation.2 Consequently, dietary interventions, such as the ketogenic and low-glycemic diets, have potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects that are being assessed as stand-alone or adjunctive therapies for dermatologic diseases.
Diet may partially influence systemic inflammation through its effect on weight. Higher body mass index and obesity are linked to a low-grade inflammatory state and higher levels of circulating inflammatory markers. Therefore, weight loss leads to decreases in inflammatory cytokines, including C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor α, and IL-6.3 These cytokines and metabolic effects overlap with inflammatory skin condition pathways. It also is posited that decreased insulin release associated with weight loss results in decreased sebaceous lipogenesis and androgens, which drive keratinocyte proliferation and acne development.4,5 For instance, in a 2015 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials on psoriasis, patients in the weight loss intervention group had more substantial reductions in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) scores compared with controls receiving usual care (P=.004).6 However, in a systematic review of 35 studies on acne vulgaris, overweight and obese patients (defined by a body mass index of ≥23 kg/m2) had similar odds of having acne compared with normal-weight individuals (P=.671).7
Similar to weight loss, ketogenesis acts as a negative feedback mechanism to reduce insulin release, leading to decreased inflammation and androgens that often exacerbate inflammatory skin diseases.8 Ketogenesis ensues when daily carbohydrate intake is limited to less than 50 g, and long-term adherence to a ketogenic diet results in metabolic reliance on ketone bodies such as acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.9 These metabolites may decrease free radical damage and consequently improve signs and symptoms of acne, psoriasis, and other inflammatory skin diseases.10-12 Similarly, increased ketones also may decrease activation of the NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and Pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome and therefore reduce inflammatory markers such as IL-1β and IL-1.4,13 Several proposed mechanisms are outlined in the Table.

Collectively, low-glycemic and ketogenic diets have been proposed as potential interventions for reducing inflammatory skin conditions. These dietary approaches are hypothesized to exert their effects by facilitating weight loss, elevating ketone levels, and reducing systemic inflammation. The current review summarizes the existing evidence on ketogenic and low-glycemic diets as treatments for inflammatory skin conditions and evaluates the potential benefits of these dietary interventions in managing and improving outcomes for individuals with inflammatory skin conditions.
Methods
Using PubMed for articles indexed for MEDLINE and Google Scholar, a review of the literature was conducted with a combination of the following search terms: low-glycemic diet, inflammatory, dermatologic, ketogenic diet, inflammation, dermatology, acne, psoriasis, eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Reference citations in identified works also were reviewed. Interventional (experimental studies or clinical trials), survey-based, and observational studies that investigated the effects of low-glycemic or ketogenic diets for the treatment of inflammatory skin conditions were included. Inclusion criteria were studies assessing acne, psoriasis, SD, AD, and HS. Exclusion criteria were studies published before 1965; those written in languages other than English; and those analyzing other diets, such as the Mediterranean or low-fat diets. The search yielded a total of 11 observational studies and 4 controlled studies published between 1966 and January 2023. Because this analysis utilized publicly available data and did not qualify as human subject research, institutional review board approval was not required.
Results
Acne Vulgaris—Acne vulgaris is a disease of chronic pilosebaceous inflammation and follicular epithelial proliferation associated with Propionibacterium acnes. The association between acne and low-glycemic diets has been examined in several studies. Diet quality is measured and assessed using the glycemic index (GI), which is the effect of a single food on postprandial blood glucose, and the glycemic load, which is the GI adjusted for carbohydrates per serving.14 High levels of GI and glycemic load are associated with hyperinsulinemia and an increase in insulinlike growth factor 1 concentration that promotes
Six survey-based studies evaluated sugar intake in patients with acne compared to healthy matched controls (eTable). Among these studies, 5 reported higher glycemic loads or daily sugar intake in acne patients compared to individuals without acne.12,19,20,26,28 The remaining study was conducted in 1967 and enrolled 16 acne patients and 32 matched controls. It reported no significant difference in sugar intake between the groups (P>.05).17


Smith et al18 randomized 43 male patients aged 15 to 25 years with facial acne into 2 cohorts for 12 weeks, each consuming either a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food [fruits, whole grains], and 30% fat) or a carbohydrate-dense diet of foods with medium to high GI based on prior documentation of the original diet. Patients were instructed to use a noncomedogenic cleanser as their only acne treatment. At 12 weeks, patients consuming the low-glycemic diet had an average of 23.5 fewer inflammatory lesions, while those in the intervention group had 12.0 fewer lesions (P=.03).18
In another controlled study by Kwon et al,21 32 male and female acne patients were randomized to a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food, and 30% fat) or a standard diet for 10 weeks. Patients on the low-glycemic diet experienced a 70.9% reduction in inflammatory lesions (P<.05). Hematoxylin and eosin staining and image analysis were performed to measure sebaceous gland surface area in the low-glycemic diet group, which decreased from 0.32 to 0.24 mm2 (P=.03). The sebaceous gland surface area in the control group was not reported. Moreover, patients on the low-glycemic diet had reduced IL-8 immunohistochemical staining (decreasing from 2.9 to 1.7 [P=.03]) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 levels (decreasing from 2.6 to 1.3 [P=.03]), suggesting suppression of ongoing inflammation. Patients on the low-glycemic diet had no significant difference in transforming growth factor β1(P=.83). In the control group, there was no difference in IL-8, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1, or transforming growth factor β1 (P>.05) on immunohistochemical staining.21
Psoriasis—Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by hyperproliferation and aberrant keratinocyte plaque formation. The innate immune response of keratinocytes in response to epidermal damage or infection begins with neutrophil recruitment and dendritic cell activation. Dendritic cell secretion of IL-23 promotes T-cell differentiation into helper T cells (TH1) that subsequently secrete IL-17 and IL-22, thereby stimulating keratinocyte proliferation and eventual plaque formation. The relationship between diet and psoriasis is poorly understood; however, hyperinsulinemia is associated with greater severity of psoriasis.31
Four observational studies examined sugar intake in psoriasis patients. Barrea et al23 conducted a survey-based study of 82 male participants (41 with psoriasis and 41 healthy controls), reporting that PASI score was correlated with intake of simple carbohydrates (percentage of total kilocalorie)(r=0.564, P<.001). Another study by Yamashita et al27 found higher sugar intake in psoriasis patients than controls (P=.003) based on surveys from 70 patients with psoriasis and 70 matched healthy controls.
These findings contrast with 2 survey-based studies by Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 of sugar intake in psoriasis patients using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Johnson et al22 reported reduced sugar intake among 156 psoriasis patients compared with 6104 unmatched controls (odds ratio, 0.998; CI, 0.996-1 [P=.04]) from 2003 to 2006. Similarly, Afifi et al25 reported decreased sugar intake in 1206 psoriasis patients compared with sex- and age-matched controls (P<.0001) in 2009 and 2010. When patients were asked about dietary triggers, 13.8% of psoriasis patients reported sugar as the most common trigger, which was more frequent than alcohol (13.6%), gluten (7.2%), and dairy (6%).25
Castaldo et al29,30 published 2 nonrandomized clinical intervention studies in 2020 and 2021 evaluating the impact of the ketogenic diet on psoriasis. In the first study, 37 psoriasis patients followed a 10-week diet consisting of 4 weeks on a ketogenic diet (500 kcal/d) followed by 6 weeks on a low-caloric Mediterranean diet.29 At the end of the intervention, there was a 17.4% reduction in PASI score, a 33.2-point reduction in itch severity score, and a 13.4-point reduction in the dermatology life quality index score; however, this study did not include a control diet group for comparison.29 The second study included 30 psoriasis patients on a ketogenic diet and 30 control patients without psoriasis on a regular diet.30 The ketogenic diet consisted of 400 to 500 g of vegetables, 20 to 30 g of fat, and a proportion of protein based on body weight with at least 12 g of whey protein and various amino acids. Patients on the ketogenic diet had significant reduction in PASI scores (value relative to clinical features, 1.4916 [P=.007]). Furthermore, concentrations of cytokines IL-2 (P=.04) and IL-1β (P=.006) decreased following the ketogenic diet but were not measured in the control group.30
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Seborrheic dermatitis is associated with overcolonization of Malassezia species near lipid-rich sebaceous glands. Malassezia hydrolyzes free fatty acids, yielding oleic acids and leading to T-cell release of IL-8 and IL-17.32 Literature is sparse regarding how dietary modifications may play a role in disease severity. In a survey study, Bett et al17 compared 16 SD patients to 1:2 matched controls (N=29) to investigate the relationship between sugar consumption and presence of disease. Two control cohorts were selected, 1 from clinic patients diagnosed with verruca and 1 matched by age and sex from a survey-based study at a facility in London, England. Sugar intake was measured both in total grams per day and in “beverage sugar” per day, defined as sugar taken in tea and coffee. There was higher total sugar and higher beverage sugar intake among the SD group compared with both control groups (P<.05).17
Atopic Dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis is a disease of epidermal barrier dysfunction and IgE-mediated allergic sensitization.33 There are several mechanisms by which skin structure may be disrupted. It is well established that filaggrin mutations inhibit stratum corneum maturation and lamellar matrix deposition.34 Upregulation of IL-4–, IL-13–, and IL-17–secreting TH2 cells also is associated with disruption of tight junctions and reduction of filaggrin.35,36 Given that a T cell–mediated inflammatory response is involved in disease pathogenesis, glycemic control is hypothesized to have therapeutic potential.
Nosrati et al24 surveyed 169 AD patients about their perceived dietary triggers through a 61-question survey based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Respondents were queried about their perceptions and dietary changes, such as removal or addition of specific food groups and trial of specific diets. Overall, 16.5% of patients reported sugar being a trigger, making it the fourth most common among those surveyed and less common than dairy (24.8%), gluten (18.3%), and alcohol (17.1%).24
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa is driven by hyperkeratosis, dilatation, and occlusion of pilosebaceous follicular ducts, whose eventual rupture evokes a local acute inflammatory response.37 The inciting event for both acne and HS involves mTOR complex–mediated follicular hyperproliferation andinsulinlike growth factor 1 stimulation of androgen receptors in pilosebaceous glands. Given the similarities between the pathogenesis of acne and HS, it is hypothesized that lifestyle changes, including diet modification, may have a beneficial effect on HS.38-40
Comment
Acne—Overall, there is strong evidence supporting the efficacy of a low-glycemic diet in the treatment of acne. Notably, among the 6 observational studies identified, there was 1 conflicting study by Bett et al17 that did not find a statistically significant difference in glucose intake between acne and control patients. However, this study included only 16 acne patients, whereas the other 5 observational studies included 32 to 2255 patients.17 The strongest evidence supporting low-glycemic dietary interventions in acne treatment is from 2 rigorous randomized clinical trials by Kwon et al21 and Smith et al.18 These trials used intention-to-treat models and maintained consistency in gender, age, and acne treatment protocols across both control and treatment groups. To ensure compliance with dietary interventions, daily telephone calls, food logs, and 24-hour urea sampling were utilized. Acne outcomes were assessed by a dermatologist who remained blinded with well-defined outcome measures. An important limitation of these studies is the difficulty in attributing the observed results solely to reduced glucose intake, as low-glycemic diets often lead to other dietary changes, including reduced fat intake and increased nutrient consumption.18,21
A 2022 systematic review of acne by Meixiong et al41 further reinforced the beneficial effects of low-glycemic diets in the management of acne patients. The group reviewed 6 interventional studies and 28 observational studies to investigate the relationship among acne, dairy, and glycemic content and found an association between decreased glucose and dairy on reduction of acne.41
It is likely that the ketogenic diet, which limits glucose, would be beneficial for acne patients. There may be added benefit through elevated ketone bodies and substantially reduced insulin secretion. However, because there are no observational or interventional studies, further research is needed to draw firm conclusions regarding diet for acne treatment. A randomized clinical trial investigating the effects of the ketogenic diet compared to the low-glycemic diet compared to a regular diet would be valuable.
Psoriasis—Among psoriasis studies, there was a lack of consensus regarding glucose intake and correlation with disease. Among the 4 observational studies, 2 reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients and 2 reported decreased glucose intake. It is plausible that the variability in studies is due to differences in sample size and diet heterogeneity among study populations. More specifically, Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 analyzed large sample sizes of 6260 and 2412 US participants, respectively, and found decreased sugar intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. In comparison, Barrea et al23 and Yamashita et al27 analyzed substantially smaller and more specific populations consisting of 82 Italian and 140 Japanese participants, respectively; both reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. These seemingly antithetical results may be explained by regional dietary differences, with varying proportions of meats, vegetables, antioxidants, and vitamins.
Moreover, the variation among studies may be further explained by the high prevalence of comorbidities among psoriasis patients. In the study by Barrea et al,23 psoriasis patients had higher fasting glucose (P=.004) and insulin (P=.022) levels than healthy patients. After adjusting for body mass index and metabolic syndrome, the correlation coefficient measuring the relationship between the PASI score and intake of simple carbohydrates changed from r=0.564 (P<.001) to r=0.352 (P=.028). The confounding impact of these comorbidities was further highlighted by Yamashita et al,27 who found statistically significant differences in glucose intake between psoriasis and healthy patients (P=.003). However, they reported diminished significance on additional subgroup analysis accounting for potential comorbidities (P=.994).27 Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 did not account for comorbidities; therefore, the 4 observational study results must be interpreted cautiously.
The 2 randomized clinical trials by Castaldo et al29,30 weakly suggest that a ketogenic diet may be beneficial for psoriasis patients. The studies have several notable limitations, including insufficient sample sizes and control groups. Thus, the decreased PASI scores reported in psoriasis patients on the ketogenic diets are challenging to interpret. Additionally, both studies placed patients on highly restrictive diets of 500 kcal/d for 4 weeks. The feasibility of recommending such a diet to patients in clinical practice is questionable. Diets of less than 500 kcal/d may be dangerous for patients with underlying comorbidities and are unlikely to serve as long-term solutions.23 To contextualize our findings, a 2022 review by Chung et al42 examined the impact of various diets—low-caloric, gluten-free, Mediterranean, Western, and ketogenic—on psoriasis and reported insufficient evidence to suggest a benefit to the ketogenic diet for psoriasis patients, though the Mediterranean diet may be well suited for psoriasis patients because of improved cardiovascular health and reduced mortality.
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Sanders et al43 found that patients with a high-fruit diet had lower odds of having SD, while those on a Western diet had higher odds of having SD. Although the study did not measure glycemic load, it is conceivable that the high glycemic load characteristic of the Western diet contributed to these findings.43 However, no studies have investigated the direct link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and SD, leaving this area open for further study.
Atopic Dermatitis—It has been hypothesized that mitigating T cell–mediated inflammation via glucose control may contribute to the improvement in AD.35,36 However, in one study, 16.5% of AD patients self-identified sugar as a dietary trigger, ranking fourth among other dietary triggers.24 Thus, the connection between glucose levels and AD warrants further exploration.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Given the role of metabolic and hormonal influence in HS as well as the overlapping pathophysiology with acne, it is possible that low-glycemic and ketogenic diets may have a role in improving HS.38-40 However, there is a gap in observation and controlled studies investigating the link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and HS.
Conclusion
Our analysis focused on interventional and observational research exploring the effects of low-glycemic and ketogenic diets on associations and treatment of inflammatory skin conditions. There is sufficient evidence to counsel acne patients on the benefits of a low-glycemic diet as an adjunctive treatment for acne. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to recommend a low-glycemic or ketogenic diet as a treatment for patients with any other inflammatory skin disease. Prospective and controlled clinical trials are needed to clarify the utility of dietary interventions for treating inflammatory skin conditions.
Inflammatory skin conditions often have a relapsing and remitting course and represent a large proportion of chronic skin diseases. Common inflammatory skin disorders include acne, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), atopic dermatitis (AD), and seborrheic dermatitis (SD).1 Although each of these conditions has a unique pathogenesis, they all are driven by a background of chronic inflammation. It has been reported that diets with high levels of refined carbohydrates and saturated or trans-fatty acids may exacerbate existing inflammation.2 Consequently, dietary interventions, such as the ketogenic and low-glycemic diets, have potential anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects that are being assessed as stand-alone or adjunctive therapies for dermatologic diseases.
Diet may partially influence systemic inflammation through its effect on weight. Higher body mass index and obesity are linked to a low-grade inflammatory state and higher levels of circulating inflammatory markers. Therefore, weight loss leads to decreases in inflammatory cytokines, including C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor α, and IL-6.3 These cytokines and metabolic effects overlap with inflammatory skin condition pathways. It also is posited that decreased insulin release associated with weight loss results in decreased sebaceous lipogenesis and androgens, which drive keratinocyte proliferation and acne development.4,5 For instance, in a 2015 meta-analysis of 5 randomized controlled trials on psoriasis, patients in the weight loss intervention group had more substantial reductions in psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) scores compared with controls receiving usual care (P=.004).6 However, in a systematic review of 35 studies on acne vulgaris, overweight and obese patients (defined by a body mass index of ≥23 kg/m2) had similar odds of having acne compared with normal-weight individuals (P=.671).7
Similar to weight loss, ketogenesis acts as a negative feedback mechanism to reduce insulin release, leading to decreased inflammation and androgens that often exacerbate inflammatory skin diseases.8 Ketogenesis ensues when daily carbohydrate intake is limited to less than 50 g, and long-term adherence to a ketogenic diet results in metabolic reliance on ketone bodies such as acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone.9 These metabolites may decrease free radical damage and consequently improve signs and symptoms of acne, psoriasis, and other inflammatory skin diseases.10-12 Similarly, increased ketones also may decrease activation of the NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-, and Pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome and therefore reduce inflammatory markers such as IL-1β and IL-1.4,13 Several proposed mechanisms are outlined in the Table.

Collectively, low-glycemic and ketogenic diets have been proposed as potential interventions for reducing inflammatory skin conditions. These dietary approaches are hypothesized to exert their effects by facilitating weight loss, elevating ketone levels, and reducing systemic inflammation. The current review summarizes the existing evidence on ketogenic and low-glycemic diets as treatments for inflammatory skin conditions and evaluates the potential benefits of these dietary interventions in managing and improving outcomes for individuals with inflammatory skin conditions.
Methods
Using PubMed for articles indexed for MEDLINE and Google Scholar, a review of the literature was conducted with a combination of the following search terms: low-glycemic diet, inflammatory, dermatologic, ketogenic diet, inflammation, dermatology, acne, psoriasis, eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Reference citations in identified works also were reviewed. Interventional (experimental studies or clinical trials), survey-based, and observational studies that investigated the effects of low-glycemic or ketogenic diets for the treatment of inflammatory skin conditions were included. Inclusion criteria were studies assessing acne, psoriasis, SD, AD, and HS. Exclusion criteria were studies published before 1965; those written in languages other than English; and those analyzing other diets, such as the Mediterranean or low-fat diets. The search yielded a total of 11 observational studies and 4 controlled studies published between 1966 and January 2023. Because this analysis utilized publicly available data and did not qualify as human subject research, institutional review board approval was not required.
Results
Acne Vulgaris—Acne vulgaris is a disease of chronic pilosebaceous inflammation and follicular epithelial proliferation associated with Propionibacterium acnes. The association between acne and low-glycemic diets has been examined in several studies. Diet quality is measured and assessed using the glycemic index (GI), which is the effect of a single food on postprandial blood glucose, and the glycemic load, which is the GI adjusted for carbohydrates per serving.14 High levels of GI and glycemic load are associated with hyperinsulinemia and an increase in insulinlike growth factor 1 concentration that promotes
Six survey-based studies evaluated sugar intake in patients with acne compared to healthy matched controls (eTable). Among these studies, 5 reported higher glycemic loads or daily sugar intake in acne patients compared to individuals without acne.12,19,20,26,28 The remaining study was conducted in 1967 and enrolled 16 acne patients and 32 matched controls. It reported no significant difference in sugar intake between the groups (P>.05).17


Smith et al18 randomized 43 male patients aged 15 to 25 years with facial acne into 2 cohorts for 12 weeks, each consuming either a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food [fruits, whole grains], and 30% fat) or a carbohydrate-dense diet of foods with medium to high GI based on prior documentation of the original diet. Patients were instructed to use a noncomedogenic cleanser as their only acne treatment. At 12 weeks, patients consuming the low-glycemic diet had an average of 23.5 fewer inflammatory lesions, while those in the intervention group had 12.0 fewer lesions (P=.03).18
In another controlled study by Kwon et al,21 32 male and female acne patients were randomized to a low-glycemic diet (25% protein, 45% low-glycemic food, and 30% fat) or a standard diet for 10 weeks. Patients on the low-glycemic diet experienced a 70.9% reduction in inflammatory lesions (P<.05). Hematoxylin and eosin staining and image analysis were performed to measure sebaceous gland surface area in the low-glycemic diet group, which decreased from 0.32 to 0.24 mm2 (P=.03). The sebaceous gland surface area in the control group was not reported. Moreover, patients on the low-glycemic diet had reduced IL-8 immunohistochemical staining (decreasing from 2.9 to 1.7 [P=.03]) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 levels (decreasing from 2.6 to 1.3 [P=.03]), suggesting suppression of ongoing inflammation. Patients on the low-glycemic diet had no significant difference in transforming growth factor β1(P=.83). In the control group, there was no difference in IL-8, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1, or transforming growth factor β1 (P>.05) on immunohistochemical staining.21
Psoriasis—Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by hyperproliferation and aberrant keratinocyte plaque formation. The innate immune response of keratinocytes in response to epidermal damage or infection begins with neutrophil recruitment and dendritic cell activation. Dendritic cell secretion of IL-23 promotes T-cell differentiation into helper T cells (TH1) that subsequently secrete IL-17 and IL-22, thereby stimulating keratinocyte proliferation and eventual plaque formation. The relationship between diet and psoriasis is poorly understood; however, hyperinsulinemia is associated with greater severity of psoriasis.31
Four observational studies examined sugar intake in psoriasis patients. Barrea et al23 conducted a survey-based study of 82 male participants (41 with psoriasis and 41 healthy controls), reporting that PASI score was correlated with intake of simple carbohydrates (percentage of total kilocalorie)(r=0.564, P<.001). Another study by Yamashita et al27 found higher sugar intake in psoriasis patients than controls (P=.003) based on surveys from 70 patients with psoriasis and 70 matched healthy controls.
These findings contrast with 2 survey-based studies by Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 of sugar intake in psoriasis patients using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Johnson et al22 reported reduced sugar intake among 156 psoriasis patients compared with 6104 unmatched controls (odds ratio, 0.998; CI, 0.996-1 [P=.04]) from 2003 to 2006. Similarly, Afifi et al25 reported decreased sugar intake in 1206 psoriasis patients compared with sex- and age-matched controls (P<.0001) in 2009 and 2010. When patients were asked about dietary triggers, 13.8% of psoriasis patients reported sugar as the most common trigger, which was more frequent than alcohol (13.6%), gluten (7.2%), and dairy (6%).25
Castaldo et al29,30 published 2 nonrandomized clinical intervention studies in 2020 and 2021 evaluating the impact of the ketogenic diet on psoriasis. In the first study, 37 psoriasis patients followed a 10-week diet consisting of 4 weeks on a ketogenic diet (500 kcal/d) followed by 6 weeks on a low-caloric Mediterranean diet.29 At the end of the intervention, there was a 17.4% reduction in PASI score, a 33.2-point reduction in itch severity score, and a 13.4-point reduction in the dermatology life quality index score; however, this study did not include a control diet group for comparison.29 The second study included 30 psoriasis patients on a ketogenic diet and 30 control patients without psoriasis on a regular diet.30 The ketogenic diet consisted of 400 to 500 g of vegetables, 20 to 30 g of fat, and a proportion of protein based on body weight with at least 12 g of whey protein and various amino acids. Patients on the ketogenic diet had significant reduction in PASI scores (value relative to clinical features, 1.4916 [P=.007]). Furthermore, concentrations of cytokines IL-2 (P=.04) and IL-1β (P=.006) decreased following the ketogenic diet but were not measured in the control group.30
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Seborrheic dermatitis is associated with overcolonization of Malassezia species near lipid-rich sebaceous glands. Malassezia hydrolyzes free fatty acids, yielding oleic acids and leading to T-cell release of IL-8 and IL-17.32 Literature is sparse regarding how dietary modifications may play a role in disease severity. In a survey study, Bett et al17 compared 16 SD patients to 1:2 matched controls (N=29) to investigate the relationship between sugar consumption and presence of disease. Two control cohorts were selected, 1 from clinic patients diagnosed with verruca and 1 matched by age and sex from a survey-based study at a facility in London, England. Sugar intake was measured both in total grams per day and in “beverage sugar” per day, defined as sugar taken in tea and coffee. There was higher total sugar and higher beverage sugar intake among the SD group compared with both control groups (P<.05).17
Atopic Dermatitis—Atopic dermatitis is a disease of epidermal barrier dysfunction and IgE-mediated allergic sensitization.33 There are several mechanisms by which skin structure may be disrupted. It is well established that filaggrin mutations inhibit stratum corneum maturation and lamellar matrix deposition.34 Upregulation of IL-4–, IL-13–, and IL-17–secreting TH2 cells also is associated with disruption of tight junctions and reduction of filaggrin.35,36 Given that a T cell–mediated inflammatory response is involved in disease pathogenesis, glycemic control is hypothesized to have therapeutic potential.
Nosrati et al24 surveyed 169 AD patients about their perceived dietary triggers through a 61-question survey based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Respondents were queried about their perceptions and dietary changes, such as removal or addition of specific food groups and trial of specific diets. Overall, 16.5% of patients reported sugar being a trigger, making it the fourth most common among those surveyed and less common than dairy (24.8%), gluten (18.3%), and alcohol (17.1%).24
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Hidradenitis suppurativa is driven by hyperkeratosis, dilatation, and occlusion of pilosebaceous follicular ducts, whose eventual rupture evokes a local acute inflammatory response.37 The inciting event for both acne and HS involves mTOR complex–mediated follicular hyperproliferation andinsulinlike growth factor 1 stimulation of androgen receptors in pilosebaceous glands. Given the similarities between the pathogenesis of acne and HS, it is hypothesized that lifestyle changes, including diet modification, may have a beneficial effect on HS.38-40
Comment
Acne—Overall, there is strong evidence supporting the efficacy of a low-glycemic diet in the treatment of acne. Notably, among the 6 observational studies identified, there was 1 conflicting study by Bett et al17 that did not find a statistically significant difference in glucose intake between acne and control patients. However, this study included only 16 acne patients, whereas the other 5 observational studies included 32 to 2255 patients.17 The strongest evidence supporting low-glycemic dietary interventions in acne treatment is from 2 rigorous randomized clinical trials by Kwon et al21 and Smith et al.18 These trials used intention-to-treat models and maintained consistency in gender, age, and acne treatment protocols across both control and treatment groups. To ensure compliance with dietary interventions, daily telephone calls, food logs, and 24-hour urea sampling were utilized. Acne outcomes were assessed by a dermatologist who remained blinded with well-defined outcome measures. An important limitation of these studies is the difficulty in attributing the observed results solely to reduced glucose intake, as low-glycemic diets often lead to other dietary changes, including reduced fat intake and increased nutrient consumption.18,21
A 2022 systematic review of acne by Meixiong et al41 further reinforced the beneficial effects of low-glycemic diets in the management of acne patients. The group reviewed 6 interventional studies and 28 observational studies to investigate the relationship among acne, dairy, and glycemic content and found an association between decreased glucose and dairy on reduction of acne.41
It is likely that the ketogenic diet, which limits glucose, would be beneficial for acne patients. There may be added benefit through elevated ketone bodies and substantially reduced insulin secretion. However, because there are no observational or interventional studies, further research is needed to draw firm conclusions regarding diet for acne treatment. A randomized clinical trial investigating the effects of the ketogenic diet compared to the low-glycemic diet compared to a regular diet would be valuable.
Psoriasis—Among psoriasis studies, there was a lack of consensus regarding glucose intake and correlation with disease. Among the 4 observational studies, 2 reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients and 2 reported decreased glucose intake. It is plausible that the variability in studies is due to differences in sample size and diet heterogeneity among study populations. More specifically, Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 analyzed large sample sizes of 6260 and 2412 US participants, respectively, and found decreased sugar intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. In comparison, Barrea et al23 and Yamashita et al27 analyzed substantially smaller and more specific populations consisting of 82 Italian and 140 Japanese participants, respectively; both reported increased glucose intake among psoriasis patients compared to controls. These seemingly antithetical results may be explained by regional dietary differences, with varying proportions of meats, vegetables, antioxidants, and vitamins.
Moreover, the variation among studies may be further explained by the high prevalence of comorbidities among psoriasis patients. In the study by Barrea et al,23 psoriasis patients had higher fasting glucose (P=.004) and insulin (P=.022) levels than healthy patients. After adjusting for body mass index and metabolic syndrome, the correlation coefficient measuring the relationship between the PASI score and intake of simple carbohydrates changed from r=0.564 (P<.001) to r=0.352 (P=.028). The confounding impact of these comorbidities was further highlighted by Yamashita et al,27 who found statistically significant differences in glucose intake between psoriasis and healthy patients (P=.003). However, they reported diminished significance on additional subgroup analysis accounting for potential comorbidities (P=.994).27 Johnson et al22 and Afifi et al25 did not account for comorbidities; therefore, the 4 observational study results must be interpreted cautiously.
The 2 randomized clinical trials by Castaldo et al29,30 weakly suggest that a ketogenic diet may be beneficial for psoriasis patients. The studies have several notable limitations, including insufficient sample sizes and control groups. Thus, the decreased PASI scores reported in psoriasis patients on the ketogenic diets are challenging to interpret. Additionally, both studies placed patients on highly restrictive diets of 500 kcal/d for 4 weeks. The feasibility of recommending such a diet to patients in clinical practice is questionable. Diets of less than 500 kcal/d may be dangerous for patients with underlying comorbidities and are unlikely to serve as long-term solutions.23 To contextualize our findings, a 2022 review by Chung et al42 examined the impact of various diets—low-caloric, gluten-free, Mediterranean, Western, and ketogenic—on psoriasis and reported insufficient evidence to suggest a benefit to the ketogenic diet for psoriasis patients, though the Mediterranean diet may be well suited for psoriasis patients because of improved cardiovascular health and reduced mortality.
Seborrheic Dermatitis—Sanders et al43 found that patients with a high-fruit diet had lower odds of having SD, while those on a Western diet had higher odds of having SD. Although the study did not measure glycemic load, it is conceivable that the high glycemic load characteristic of the Western diet contributed to these findings.43 However, no studies have investigated the direct link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and SD, leaving this area open for further study.
Atopic Dermatitis—It has been hypothesized that mitigating T cell–mediated inflammation via glucose control may contribute to the improvement in AD.35,36 However, in one study, 16.5% of AD patients self-identified sugar as a dietary trigger, ranking fourth among other dietary triggers.24 Thus, the connection between glucose levels and AD warrants further exploration.
Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Given the role of metabolic and hormonal influence in HS as well as the overlapping pathophysiology with acne, it is possible that low-glycemic and ketogenic diets may have a role in improving HS.38-40 However, there is a gap in observation and controlled studies investigating the link between low-glycemic or ketogenic diets and HS.
Conclusion
Our analysis focused on interventional and observational research exploring the effects of low-glycemic and ketogenic diets on associations and treatment of inflammatory skin conditions. There is sufficient evidence to counsel acne patients on the benefits of a low-glycemic diet as an adjunctive treatment for acne. Currently, there is insufficient evidence to recommend a low-glycemic or ketogenic diet as a treatment for patients with any other inflammatory skin disease. Prospective and controlled clinical trials are needed to clarify the utility of dietary interventions for treating inflammatory skin conditions.
- Pickett K, Loveman E, Kalita N, et al. Educational interventions to improve quality of life in people with chronic inflammatory skin diseases: systematic reviews of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2015;19:1-176, v-vi.
- Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:677-685.
- Dowlatshahi EA, van der Voort EA, Arends LR, et al. Markers of systemic inflammation in psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:266-282.
- Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015;21:263-269.
- Melnik BC. Acne vulgaris: the metabolic syndrome of the pilosebaceous follicle. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:29-40.
- Upala S, Sanguankeo A. Effect of lifestyle weight loss intervention on disease severity in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39:1197-1202.
- Heng AHS, Chew FT. Systematic review of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5754.
- Paoli A, Grimaldi K, Toniolo L, et al. Nutrition and acne: therapeutic potential of ketogenic diets. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:111-117.
- Masood W, Annamaraju P, Khan Suheb MZ, et al. Ketogenic diet. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Fomin DA, McDaniel B, Crane J. The promising potential role of ketones in inflammatory dermatologic disease: a new frontier in treatment research. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:484-487.
- Zhang D, Jin W, Wu R, et al. High glucose intake exacerbates autoimmunity through reactive-oxygen-species-mediated TGF-β cytokine activation. Immunity. 2019;51:671-681.e5.
- Cerman AA, Aktas E, Altunay IK, et al. Dietary glycemic factors, insulin resistance, and adiponectin levels in acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:155-162.
- Ferrere G, Tidjani Alou M, Liu P, et al. Ketogenic diet and ketone bodies enhance the anticancer effects of PD-1 blockade. JCI Insight. 2021;6:e145207.
- Burris J, Shikany JM, Rietkerk W, et al. A Low glycemic index and glycemic load diet decreases insulin-like growth factor-1 among adults with moderate and severe acne: a short-duration, 2-week randomized controlled trial. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118:1874-1885.
- Tan JKL, Stein Gold LF, Alexis AF, et al. Current concepts in acne pathogenesis: pathways to inflammation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018;37(3S):S60-S62.
- Kim J, Ochoa MT, Krutzik SR, et al. Activation of toll-like receptor 2 in acne triggers inflammatory cytokine responses. J Immunol. 2002;169:1535-1541.
- Bett DG, Morland J, Yudkin J. Sugar consumption in acne vulgaris and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Br Med J. 1967;3:153-155.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Rouhani P, Berman B, Rouhani G. Acne improves with a popular, low glycemic diet from South Beach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(Suppl 1):AB14.
- Aksu AE, Metintas S, Saracoglu ZN, et al. Acne: prevalence and relationship with dietary habits in Eskisehir, Turkey. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1503-1509.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Johnson JA, Ma C, Kanada KN, et al. Diet and nutrition in psoriasis: analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the United States. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:327-332.
- Barrea L, Macchia PE, Tarantino G, et al. Nutrition: a key environmental dietary factor in clinical severity and cardio-metabolic risk in psoriatic male patients evaluated by 7-day food-frequency questionnaire. J Transl Med. 2015;13:303.
- Nosrati A, Afifi L, Danesh MJ, et al. Dietary modifications in atopic dermatitis: patient-reported outcomes. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:523-538.
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017;7:227-242.
- Burris J, Rietkerk W, Shikany JM, et al. Differences in dietary glycemic load and hormones in New York City adults with no and moderate/severe acne. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017;117:1375-1383.
- Yamashita H, Morita T, Ito M, et al. Dietary habits in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: low intake of meat in psoriasis and high intake of vitamin A in psoriatic arthritis. J Dermatol. 2019;46:759-769.
- Marson J, Baldwin HE. 12761 Acne, twins, and glycemic index: a sweet pilot study of diet and dietary beliefs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(Suppl):AB110.
- Castaldo G, Rastrelli L, Galdo G, et al. Aggressive weight-loss program with a ketogenic induction phase for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a proof-of-concept, single-arm, open-label clinical trial. Nutrition. 2020;74:110757.
- Castaldo G, Pagano I, Grimaldi M, et al. Effect of very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on psoriasis patients: a nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic study. J Proteome Res. 2021;20:1509-1521.
- Ip W, Kirchhof MG. Glycemic control in the treatment of psoriasis. Dermatology. 2017;233:23-29.
- Vijaya Chandra SH, Srinivas R, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Cutaneous Malassezia: commensal, pathogen, or protector? Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:614446.
- David Boothe W, Tarbox JA, Tarbox MB. Atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1027:21-37.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Hanifin JM, Boguniewicz M, et al. The role of phosphodiesterase 4 in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis and the perspective for its inhibition. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:3-10.
- Furue K, Ito T, Tsuji G, et al. The IL-13–OVOL1–FLG axis in atopic dermatitis. Immunology. 2019;158:281-286.
- Renert-Yuval Y, Guttman-Yassky E. New treatments for atopic dermatitis targeting beyond IL-4/IL-13 cytokines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:28-35.
- Sellheyer K, Krahl D. “Hidradenitis suppurativa” is acne inversa! An appeal to (finally) abandon a misnomer. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:535-540.
- Danby FW, Margesson LJ. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:779-793.
- Fernandez JM, Marr KD, Hendricks AJ, et al. Alleviating and exacerbating foods in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14246.
- Yamanaka-Takaichi M, Revankar R, Shih T, et al. Expert consensus on priority research gaps in dietary and lifestyle factors in hidradenitis suppurativa: a Delphi consensus study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2129-2136.
- Meixiong J, Ricco C, Vasavda C, et al. Diet and acne: a systematic review. JAAD Int. 2022;7:95-112.
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckland). 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Sanders MGH, Pardo LM, Ginger RS, et al. Association between diet and seborrheic dermatitis: a cross-sectional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:108-114.
- Pickett K, Loveman E, Kalita N, et al. Educational interventions to improve quality of life in people with chronic inflammatory skin diseases: systematic reviews of clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2015;19:1-176, v-vi.
- Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation: emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:677-685.
- Dowlatshahi EA, van der Voort EA, Arends LR, et al. Markers of systemic inflammation in psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169:266-282.
- Youm YH, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite beta-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015;21:263-269.
- Melnik BC. Acne vulgaris: the metabolic syndrome of the pilosebaceous follicle. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:29-40.
- Upala S, Sanguankeo A. Effect of lifestyle weight loss intervention on disease severity in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39:1197-1202.
- Heng AHS, Chew FT. Systematic review of the epidemiology of acne vulgaris. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5754.
- Paoli A, Grimaldi K, Toniolo L, et al. Nutrition and acne: therapeutic potential of ketogenic diets. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2012;25:111-117.
- Masood W, Annamaraju P, Khan Suheb MZ, et al. Ketogenic diet. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Fomin DA, McDaniel B, Crane J. The promising potential role of ketones in inflammatory dermatologic disease: a new frontier in treatment research. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:484-487.
- Zhang D, Jin W, Wu R, et al. High glucose intake exacerbates autoimmunity through reactive-oxygen-species-mediated TGF-β cytokine activation. Immunity. 2019;51:671-681.e5.
- Cerman AA, Aktas E, Altunay IK, et al. Dietary glycemic factors, insulin resistance, and adiponectin levels in acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75:155-162.
- Ferrere G, Tidjani Alou M, Liu P, et al. Ketogenic diet and ketone bodies enhance the anticancer effects of PD-1 blockade. JCI Insight. 2021;6:e145207.
- Burris J, Shikany JM, Rietkerk W, et al. A Low glycemic index and glycemic load diet decreases insulin-like growth factor-1 among adults with moderate and severe acne: a short-duration, 2-week randomized controlled trial. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118:1874-1885.
- Tan JKL, Stein Gold LF, Alexis AF, et al. Current concepts in acne pathogenesis: pathways to inflammation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018;37(3S):S60-S62.
- Kim J, Ochoa MT, Krutzik SR, et al. Activation of toll-like receptor 2 in acne triggers inflammatory cytokine responses. J Immunol. 2002;169:1535-1541.
- Bett DG, Morland J, Yudkin J. Sugar consumption in acne vulgaris and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Br Med J. 1967;3:153-155.
- Smith RN, Mann NJ, Braue A, et al. A low-glycemic-load diet improves symptoms in acne vulgaris patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:107-115.
- Rouhani P, Berman B, Rouhani G. Acne improves with a popular, low glycemic diet from South Beach. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(Suppl 1):AB14.
- Aksu AE, Metintas S, Saracoglu ZN, et al. Acne: prevalence and relationship with dietary habits in Eskisehir, Turkey. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26:1503-1509.
- Kwon HH, Yoon JY, Hong JS, et al. Clinical and histological effect of a low glycaemic load diet in treatment of acne vulgaris in Korean patients: a randomized, controlled trial. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92:241-246.
- Johnson JA, Ma C, Kanada KN, et al. Diet and nutrition in psoriasis: analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the United States. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;28:327-332.
- Barrea L, Macchia PE, Tarantino G, et al. Nutrition: a key environmental dietary factor in clinical severity and cardio-metabolic risk in psoriatic male patients evaluated by 7-day food-frequency questionnaire. J Transl Med. 2015;13:303.
- Nosrati A, Afifi L, Danesh MJ, et al. Dietary modifications in atopic dermatitis: patient-reported outcomes. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28:523-538.
- Afifi L, Danesh MJ, Lee KM, et al. Dietary behaviors in psoriasis: patient-reported outcomes from a U.S. national survey. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2017;7:227-242.
- Burris J, Rietkerk W, Shikany JM, et al. Differences in dietary glycemic load and hormones in New York City adults with no and moderate/severe acne. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2017;117:1375-1383.
- Yamashita H, Morita T, Ito M, et al. Dietary habits in Japanese patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: low intake of meat in psoriasis and high intake of vitamin A in psoriatic arthritis. J Dermatol. 2019;46:759-769.
- Marson J, Baldwin HE. 12761 Acne, twins, and glycemic index: a sweet pilot study of diet and dietary beliefs. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83(Suppl):AB110.
- Castaldo G, Rastrelli L, Galdo G, et al. Aggressive weight-loss program with a ketogenic induction phase for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: a proof-of-concept, single-arm, open-label clinical trial. Nutrition. 2020;74:110757.
- Castaldo G, Pagano I, Grimaldi M, et al. Effect of very-low-calorie ketogenic diet on psoriasis patients: a nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic study. J Proteome Res. 2021;20:1509-1521.
- Ip W, Kirchhof MG. Glycemic control in the treatment of psoriasis. Dermatology. 2017;233:23-29.
- Vijaya Chandra SH, Srinivas R, Dawson TL Jr, et al. Cutaneous Malassezia: commensal, pathogen, or protector? Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:614446.
- David Boothe W, Tarbox JA, Tarbox MB. Atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1027:21-37.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Hanifin JM, Boguniewicz M, et al. The role of phosphodiesterase 4 in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis and the perspective for its inhibition. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:3-10.
- Furue K, Ito T, Tsuji G, et al. The IL-13–OVOL1–FLG axis in atopic dermatitis. Immunology. 2019;158:281-286.
- Renert-Yuval Y, Guttman-Yassky E. New treatments for atopic dermatitis targeting beyond IL-4/IL-13 cytokines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020;124:28-35.
- Sellheyer K, Krahl D. “Hidradenitis suppurativa” is acne inversa! An appeal to (finally) abandon a misnomer. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:535-540.
- Danby FW, Margesson LJ. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28:779-793.
- Fernandez JM, Marr KD, Hendricks AJ, et al. Alleviating and exacerbating foods in hidradenitis suppurativa. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E14246.
- Yamanaka-Takaichi M, Revankar R, Shih T, et al. Expert consensus on priority research gaps in dietary and lifestyle factors in hidradenitis suppurativa: a Delphi consensus study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2129-2136.
- Meixiong J, Ricco C, Vasavda C, et al. Diet and acne: a systematic review. JAAD Int. 2022;7:95-112.
- Chung M, Bartholomew E, Yeroushalmi S, et al. Dietary intervention and supplements in the management of psoriasis: current perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckland). 2022;12:151-176. doi:10.2147/PTT.S328581
- Sanders MGH, Pardo LM, Ginger RS, et al. Association between diet and seborrheic dermatitis: a cross-sectional study. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:108-114.
Practice Points
- As the ketogenic diet gains in popularity, dermatologists may inform patients that there is emerging evidence supporting the idea that low-glycemic diets may contribute to improvement in inflammatory skin conditions.
- Dermatologists may educate patients about the potential benefits of a low-glycemic diet as a supplementary treatment for acne based on existing evidence.
- Current evidence is insufficient to endorse a ketogenic diet as superior to other dietary approaches in treating inflammatory skin conditions.
Analysis of Nail Excision Practice Patterns in the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.
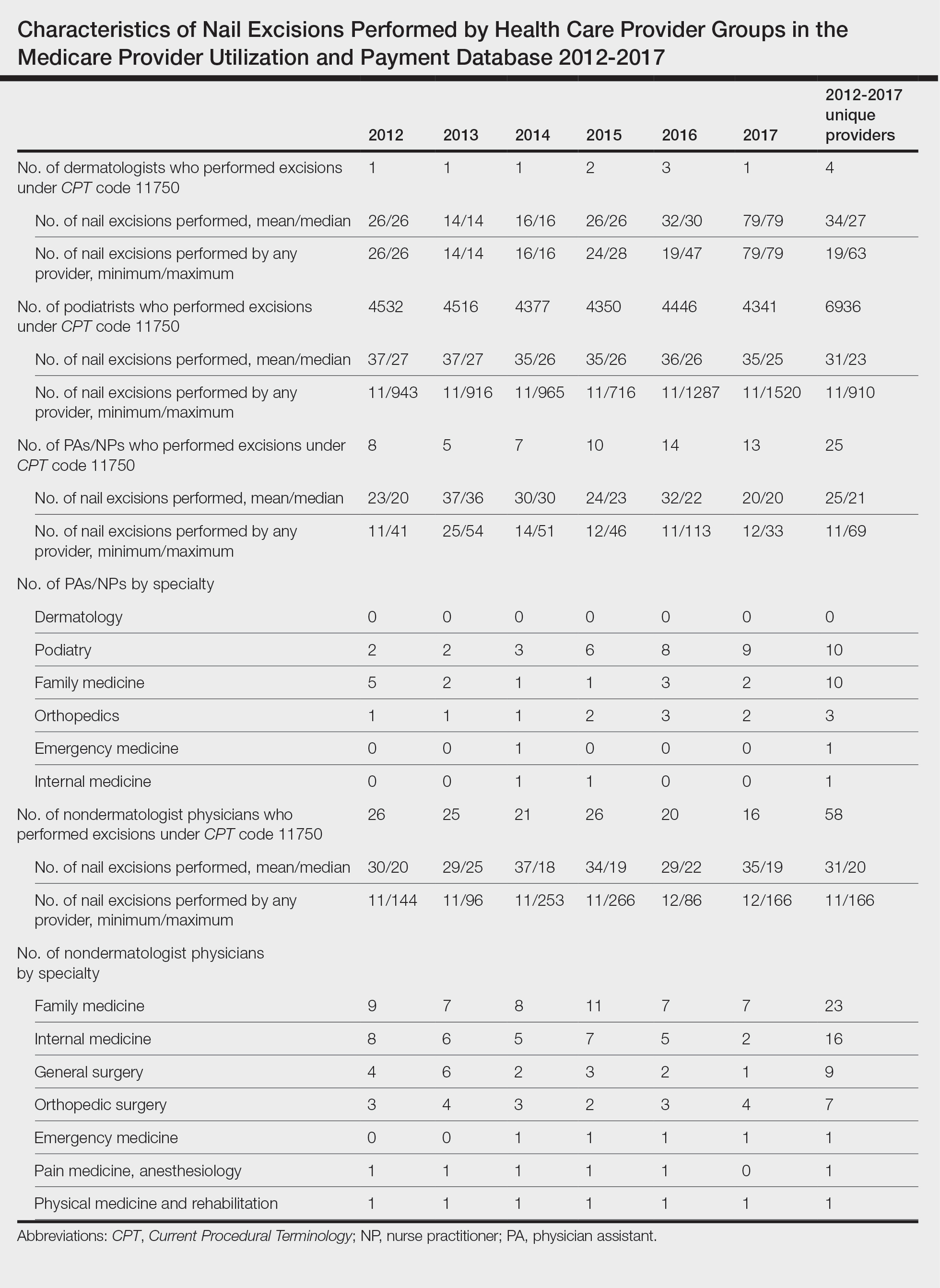
A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).
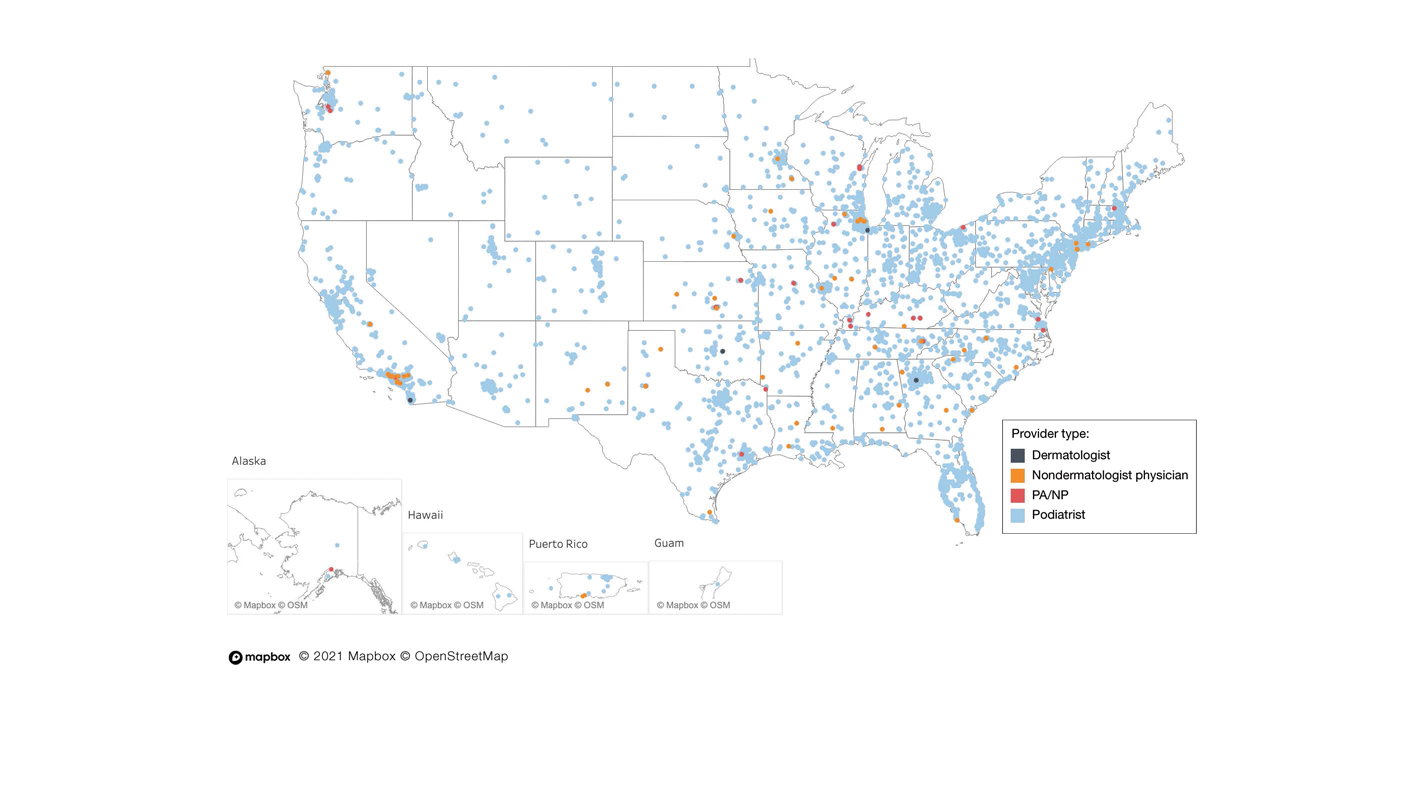
Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.

A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).

Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
To the Editor:
Partial or total nail plate excisions commonly are used for the treatment of onychocryptosis and nail spicules. Procedures involving the nail unit require advanced technical skills to achieve optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes, avoid complications, and minimize health care costs. Data on the frequency of nail plate excisions performed by dermatologists and their relative frequency compared to other medical providers are limited. The objective of our study was to analyze trends in nail excision practice patterns among medical providers in the United States.
A retrospective analysis on nail excisions using the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 11750 (excision of nail and nail matrix, partial or complete [eg, ingrown or deformed nail] for permanent removal), which is distinct from code 11755 (biopsy of nail unit [eg, plate, bed, matrix, hyponychium, proximal and lateral nail folds][separate procedure]), was performed using data from the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012-2017.1,2 This file also is used by Peck et al3 in an article submitted to the Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association and currently under consideration for publication. Procedures were recorded by year and provider type—dermatologist, podiatrist, physician assistant (PA)/nurse practitioner (NP), nondermatologist physician—and subcategorized by provider specialty (Table). Practice locations subcategorized by provider type were mapped using Tableau Software (Salesforce)(Figure). Descriptive statistics including number of providers, mean and median excisions per provider, and minimum/maximum nail excisions were calculated (Table). Practice types of PAs/NPs and specialization of nondermatologist physicians were determined using provider name, identification number, and practice address. This study did not require institutional review board review, as only publicly available data were utilized in our analysis.

A total of 6936 podiatrists, 58 nondermatologist physicians, 25 PAs/NPs, and 4 dermatologists performed 10 or more nail excisions annually under CPT code 11750 from January 2012 to December 2017 with annual means of 31, 31, 25, and 34, respectively (Table). No PAs/NPs included in the dataset worked in dermatology practices during the study period. Physician assistants and NPs most often practiced in podiatry and family medicine (FM) settings (both 40% [10/25]). Nondermatologist physicians most often specialized in FM (40% [23/58])(Table). The greatest number of providers practiced in 3 of the 4 most-populous states: California, Texas, and Florida; the fewest number practiced in 3 of the 10 least-populous states: Alaska, Hawaii, and Vermont. Vermont, Wyoming, and North Dakota—3 of the 5 least-populous states—had the fewest practitioners among the contiguous United States (Figure).

Our study showed that from January 2012 to December 2017, fewer dermatologists performed nail excisions than any other provider type (0.06%, 4 dermatologists of 7023 total providers), and dermatologists performed 1734-fold fewer nail excisions than podiatrists (99%, 6936 podiatrists of 7023 total providers). Only dermatologists practicing in California, Georgia, Indiana, and Oklahoma performed nail excisions. Conversely, podiatrists were more geographically distributed across the United States and other territories, with representation in all 50 states as well as the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Reasons for these large discrepancies in practice between dermatologists and other providers likely are multifactorial, encompassing a lack of emphasis on nail procedures in dermatology training, patient perception of the scope of dermatologic practice, and nail excision reimbursement patterns. Most dermatologists likely lack experience in performing nail procedures. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education requirements mandate that dermatology residents observe or perform 3 nail procedures over 3 years of residency, including 1 that may be performed on a human cadaver.4 In contrast, podiatry trainees must gain competency in toenail avulsion (both partial and complete), participate in anesthesia workshops, and become proficient in administering lower extremity blocks by the end of their training.5 Therefore, incorporating aspects of podiatric surgical training into dermatology residency requirements may increase the competency and comfort of dermatologists in performing nail excisions and practicing as nail experts as attending physicians.
It is likely that US patients do not perceive dermatologists as nail specialists and instead primarily consult podiatrists or FM and/or internal medicine physicians for treatment; for example, nail disease was one of the least common reasons for consulting a dermatologist (5%) in a German nationwide survey-based study (N=1015).6 Therefore, increased efforts are needed to educate the general public about the expertise of dermatologists in the diagnosis and management of nail conditions.
Reimbursement also may be a barrier to dermatologists performing nail procedures as part of their scope of practice; for example, in a retrospective study of nail biopsies using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, there was no statistically significant difference in reimbursements for nail biopsies vs skin biopsies from 2012 to 2017 (P=0.69).7 Similar to nail biopsies, nail excisions typically are much more time consuming and technically demanding than skin biopsies, which may discourage dermatologists from routinely performing nail excision procedures.
Our study is subject to a number of limitations. The data reflected only US-based practice patterns and may not be applicable to nail procedures globally. There also is the potential for miscoding of procedures in the Medicare database. The data included only Part B Medicare fee-for-service and excludes non-Medicare insured, uninsured, and self-pay patients, as well as aggregated records from 10 or fewer Medicare beneficiaries.
Dermatologists rarely perform nail excisions and perform fewer nail excisions than any other provider type in the United States. There currently is an unmet need for comprehensive nail surgery education in US-based dermatology residency programs. We hope that our study fosters interdisciplinary collegiality and training between podiatrists and dermatologists and promotes expanded access to care across the United States to serve patients with nail disorders.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-For-Service Provider Utilization & Payment Data Physician and Other Supplier Public Use File: A Methodological Overview . Updated September 22, 2020. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/research-statistics-data-and-systems/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-charge-data/downloads/medicare-physician-and-other-supplier-puf-methodology.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Billing and Coding: Surgical Treatment of Nails. Updated November 9, 2023. Accessed January 8, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/view/article.aspx?articleID=52998#:~:text=The%20description%20of%20CPT%20codes,date%20of%20service%20(DOS).
- Peck GM, Vlahovic TC, Hill R, et al. Senior podiatrists in solo practice are high performers of nail excisions. JAPMA. In press.
- Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. Case log minimums. review committee for dermatology. Published May 2019. Accessed January 5, 2024. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramResources/CaseLogMinimums.pdf?ver=2018-04-03-102751-650
- Council on Podiatric Medical Education. Standards and Requirements for Approval of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery Residencies. Published July 2023. Accessed January 17, 2024. https://www.cpme.org/files/320%20Council%20Approved%20October%202022%20-%20April%202023%20edits.pdf
- Augustin M, Eissing L, Elsner P, et al. Perception and image of dermatology in the German general population 2002-2014. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:2124-2130.
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare provider utilization and payment database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928.
Practice Points
- Dermatologists are considered nail experts but perform nail excisions less frequently than their podiatric counterparts and physicians in other specialties.
- Aspects of podiatric surgical training should be incorporated into dermatology residency to increase competency and comfort of dermatologists in nail excision procedures.
- Dermatologists may not be perceived as nail experts by the public, indicating a need for increased community education on the role of dermatologists in treating nail disease.
Knead a Hand? Use of a Portable Massager to Reduce Patient Pain and Anxiety During Nail Surgery
Practice Gap
Pain and anxiety are common in fully conscious patients undergoing dermatologic surgery with local anesthesia. Particularly during nail surgery, pain from anesthetic injection—caused by both needle insertion and fluid infiltration—occurs because the nail unit is highly vascularized and innervated.1 Current methods to improve patient comfort during infiltration include use of a buffered anesthetic solution, warming the anesthetic, slower technique, and direct cold application.2
Perioperative anxiety correlates with increased postoperative pain, analgesic use, and delayed recovery. Furthermore, increased perioperative anxiety reduces the pain threshold and elevates estimates of pain intensity.3 Therefore, reducing procedure-related anxiety and pain may improve quality of care and ease patient discomfort.
Distraction is a common and practical nonpharmacotherapeutic technique for reducing pain and anxiety during medical procedures. The refocusing method of distraction aims to divert attention away from pain to more pleasant stimuli to reduce pain perception.3 Several methods of distraction—using stress balls, engaging in conversation, hand-holding, applying virtual reality, and playing videos—can decrease perioperative anxiety and pain.3-6
Procedural pain and distraction techniques have been evaluated in the pediatric population more than in adults.4 Nail surgery–associated pain and distraction techniques for nail surgery have been inadequately studied.7
We offer a distraction technique utilizing a portable massager to ensure that patients are as comfortable as possible when the local anesthetic is injected prior to the first incision.
The Technique
A portable shiatsu massager that uses heat and deep-tissue kneading is placed on the upper thigh for toenail cases or lower arm for fingernail cases during injection of anesthetic to divert the patient’s attention from the surgical site (Figure). Kneading from the massage helps distract the patient from pain by introducing a competing, more pleasant, vibrating sensation that overrides pain signals; the relaxation component helps to diminish patient anxiety during injection.
Practice Implications
Use of a portable massager may reduce pain through both distraction and vibration. In a randomized clinical trial of 115 patients undergoing hand or facial surgery, patients who viewed a distraction video during the procedure reported a lower pain score compared to the control group (mean [SD] visual analog scale of pain score, 3.4 [2.6] vs 4.5 [2.6][P=.01]).4 In another randomized clinical trial of 25 patients undergoing lip augmentation, 92% of patients (23/25) in the vibration-assisted arm endorsed less pain during procedures compared to the arm without vibration (mean [SD] pain score, 3.82 [1.73] vs 5.6 [1.76][P<.001]).8
Utilization of a portable massager is a safe means of improving the patient experience; the distracting and relaxing effects and intense pulsations simultaneously reduce anxiety and pain during nail surgery. Controlled clinical trials are needed to evaluate its efficacy in diminishing both anxiety and pain during nail procedures compared to other analgesic methods.
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Hudson BF, Ogden J, Whiteley MS. Randomized controlled trial to compare the effect of simple distraction interventions on pain and anxiety experienced during conscious surgery. Eur J Pain. 2015;19:1447-1455. doi:10.1002/ejp.675
- Molleman J, Tielemans JF, Braam MJI, et al. Distraction as a simple and effective method to reduce pain during local anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019;72:1979-1985. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2019.07.023
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Guney K, Sezgin B, Yavuzer R. The efficacy of vibration anesthesia on reducing pain levels during lip augmentation: worth the buzz? Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37:1044-1048. doi:10.1093/asj/sjx073
Practice Gap
Pain and anxiety are common in fully conscious patients undergoing dermatologic surgery with local anesthesia. Particularly during nail surgery, pain from anesthetic injection—caused by both needle insertion and fluid infiltration—occurs because the nail unit is highly vascularized and innervated.1 Current methods to improve patient comfort during infiltration include use of a buffered anesthetic solution, warming the anesthetic, slower technique, and direct cold application.2
Perioperative anxiety correlates with increased postoperative pain, analgesic use, and delayed recovery. Furthermore, increased perioperative anxiety reduces the pain threshold and elevates estimates of pain intensity.3 Therefore, reducing procedure-related anxiety and pain may improve quality of care and ease patient discomfort.
Distraction is a common and practical nonpharmacotherapeutic technique for reducing pain and anxiety during medical procedures. The refocusing method of distraction aims to divert attention away from pain to more pleasant stimuli to reduce pain perception.3 Several methods of distraction—using stress balls, engaging in conversation, hand-holding, applying virtual reality, and playing videos—can decrease perioperative anxiety and pain.3-6
Procedural pain and distraction techniques have been evaluated in the pediatric population more than in adults.4 Nail surgery–associated pain and distraction techniques for nail surgery have been inadequately studied.7
We offer a distraction technique utilizing a portable massager to ensure that patients are as comfortable as possible when the local anesthetic is injected prior to the first incision.
The Technique
A portable shiatsu massager that uses heat and deep-tissue kneading is placed on the upper thigh for toenail cases or lower arm for fingernail cases during injection of anesthetic to divert the patient’s attention from the surgical site (Figure). Kneading from the massage helps distract the patient from pain by introducing a competing, more pleasant, vibrating sensation that overrides pain signals; the relaxation component helps to diminish patient anxiety during injection.

Practice Implications
Use of a portable massager may reduce pain through both distraction and vibration. In a randomized clinical trial of 115 patients undergoing hand or facial surgery, patients who viewed a distraction video during the procedure reported a lower pain score compared to the control group (mean [SD] visual analog scale of pain score, 3.4 [2.6] vs 4.5 [2.6][P=.01]).4 In another randomized clinical trial of 25 patients undergoing lip augmentation, 92% of patients (23/25) in the vibration-assisted arm endorsed less pain during procedures compared to the arm without vibration (mean [SD] pain score, 3.82 [1.73] vs 5.6 [1.76][P<.001]).8
Utilization of a portable massager is a safe means of improving the patient experience; the distracting and relaxing effects and intense pulsations simultaneously reduce anxiety and pain during nail surgery. Controlled clinical trials are needed to evaluate its efficacy in diminishing both anxiety and pain during nail procedures compared to other analgesic methods.
Practice Gap
Pain and anxiety are common in fully conscious patients undergoing dermatologic surgery with local anesthesia. Particularly during nail surgery, pain from anesthetic injection—caused by both needle insertion and fluid infiltration—occurs because the nail unit is highly vascularized and innervated.1 Current methods to improve patient comfort during infiltration include use of a buffered anesthetic solution, warming the anesthetic, slower technique, and direct cold application.2
Perioperative anxiety correlates with increased postoperative pain, analgesic use, and delayed recovery. Furthermore, increased perioperative anxiety reduces the pain threshold and elevates estimates of pain intensity.3 Therefore, reducing procedure-related anxiety and pain may improve quality of care and ease patient discomfort.
Distraction is a common and practical nonpharmacotherapeutic technique for reducing pain and anxiety during medical procedures. The refocusing method of distraction aims to divert attention away from pain to more pleasant stimuli to reduce pain perception.3 Several methods of distraction—using stress balls, engaging in conversation, hand-holding, applying virtual reality, and playing videos—can decrease perioperative anxiety and pain.3-6
Procedural pain and distraction techniques have been evaluated in the pediatric population more than in adults.4 Nail surgery–associated pain and distraction techniques for nail surgery have been inadequately studied.7
We offer a distraction technique utilizing a portable massager to ensure that patients are as comfortable as possible when the local anesthetic is injected prior to the first incision.
The Technique
A portable shiatsu massager that uses heat and deep-tissue kneading is placed on the upper thigh for toenail cases or lower arm for fingernail cases during injection of anesthetic to divert the patient’s attention from the surgical site (Figure). Kneading from the massage helps distract the patient from pain by introducing a competing, more pleasant, vibrating sensation that overrides pain signals; the relaxation component helps to diminish patient anxiety during injection.

Practice Implications
Use of a portable massager may reduce pain through both distraction and vibration. In a randomized clinical trial of 115 patients undergoing hand or facial surgery, patients who viewed a distraction video during the procedure reported a lower pain score compared to the control group (mean [SD] visual analog scale of pain score, 3.4 [2.6] vs 4.5 [2.6][P=.01]).4 In another randomized clinical trial of 25 patients undergoing lip augmentation, 92% of patients (23/25) in the vibration-assisted arm endorsed less pain during procedures compared to the arm without vibration (mean [SD] pain score, 3.82 [1.73] vs 5.6 [1.76][P<.001]).8
Utilization of a portable massager is a safe means of improving the patient experience; the distracting and relaxing effects and intense pulsations simultaneously reduce anxiety and pain during nail surgery. Controlled clinical trials are needed to evaluate its efficacy in diminishing both anxiety and pain during nail procedures compared to other analgesic methods.
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Hudson BF, Ogden J, Whiteley MS. Randomized controlled trial to compare the effect of simple distraction interventions on pain and anxiety experienced during conscious surgery. Eur J Pain. 2015;19:1447-1455. doi:10.1002/ejp.675
- Molleman J, Tielemans JF, Braam MJI, et al. Distraction as a simple and effective method to reduce pain during local anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019;72:1979-1985. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2019.07.023
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Guney K, Sezgin B, Yavuzer R. The efficacy of vibration anesthesia on reducing pain levels during lip augmentation: worth the buzz? Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37:1044-1048. doi:10.1093/asj/sjx073
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Hudson BF, Ogden J, Whiteley MS. Randomized controlled trial to compare the effect of simple distraction interventions on pain and anxiety experienced during conscious surgery. Eur J Pain. 2015;19:1447-1455. doi:10.1002/ejp.675
- Molleman J, Tielemans JF, Braam MJI, et al. Distraction as a simple and effective method to reduce pain during local anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019;72:1979-1985. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2019.07.023
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Guney K, Sezgin B, Yavuzer R. The efficacy of vibration anesthesia on reducing pain levels during lip augmentation: worth the buzz? Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37:1044-1048. doi:10.1093/asj/sjx073
Minimally Invasive Nail Surgery: Techniques to Improve the Patient Experience
Nail surgical procedures including biopsies, correction of onychocryptosis and other deformities, and excision of tumors are essential for diagnosing and treating nail disorders. Nail surgery often is perceived by dermatologists as a difficult-to-perform, high-risk procedure associated with patient anxiety, pain, and permanent scarring, which may limit implementation. Misconceptions about nail surgical techniques, aftercare, and patient outcomes are prevalent, and a paucity of nail surgery randomized clinical trials hinder formulation of standardized guidelines.1 In a survey-based study of 95 dermatology residency programs (240 total respondents), 58% of residents said they performed 10 or fewer nail procedures, 10% performed more than 10 procedures, 25% only observed nail procedures, 4% were exposed by lecture only, and 1% had no exposure; 30% said they felt incompetent performing nail biopsies.2 In a retrospective study of nail biopsies performed from 2012 to 2017 in the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, only 0.28% and 1.01% of all general dermatologists and Mohs surgeons, respectively, performed nail biopsies annually.3 A minimally invasive nail surgery technique is essential to alleviating dermatologist and patient apprehension, which may lead to greater adoption and improved outcomes.
Reduce Patient Anxiety During Nail Surgery
The prospect of undergoing nail surgery can be psychologically distressing to patients because the nail unit is highly sensitive, intraoperative and postoperative pain are common concerns, patient education materials generally are scarce and inaccurate,4 and procedures are performed under local anesthesia with the patient fully awake. In a prospective study of 48 patients undergoing nail surgery, the median preoperative Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory level was 42.00 (IQR, 6.50).5 Patient distress may be minimized by providing verbal and written educational materials, discussing expectations, and preoperatively using fast-acting benzodiazepines when necessary.6 Utilizing a sleep mask,7 stress ball,8 music,9 and/or virtual reality10 also may reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery.
Use Proper Anesthetic Techniques
Proper anesthetic technique is crucial to achieve the optimal patient experience during nail surgery. With a wing block, the anesthetic is injected into 3 points: (1) the proximal nail fold, (2) the medial/lateral fold, and (3) the hyponychium. The wing block is the preferred technique by many nail surgeons because the second and third injections are given in skin that is already anesthetized, reducing patient discomfort to a single pinprick11; additionally, there is lower postoperative paresthesia risk with the wing block compared with other digital nerve blocks.12 Ropivacaine, a fast-acting and long-acting anesthetic, is preferred over lidocaine to minimize immediate postoperative pain. Buffering the anesthetic solution to physiologic pH and slow infiltration can reduce pain during infiltration.12 Distraction12 provided by ethyl chloride refrigerant spray, an air-cooling device,13 or vibration also can reduce pain during anesthesia.
Punch Biopsy and Excision Tips
The punch biopsy is a minimally invasive method for diagnosing various neoplastic and inflammatory nail unit conditions, except for pigmented lesions.12 For polydactylous nail conditions requiring biopsy, a digit on the nondominant hand should be selected if possible. The punch is applied directly to the nail plate and twisted with downward pressure until the bone is reached, with the instrument withdrawn slowly to prevent surrounding nail plate detachment. Hemostasis is easily achieved with direct pressure and/or use of epinephrine or ropivacaine during anesthesia, and a digital tourniquet generally is not required. Applying microporous polysaccharide hemospheres powder14 or kaolin-impregnated gauze15 with direct pressure is helpful in managing continued bleeding following nail surgery. Punching through the proximal nail matrix should be avoided to prevent permanent onychodystrophy.
A tangential matrix shave biopsy requires a more practiced technique and is preferred for sampling longitudinal melanonychia. A partial proximal nail plate avulsion adequately exposes the origin of pigment and avoids complete avulsion, which may cause more onychodystrophy.16 For broad erythronychia, a total nail avulsion may be necessary. For narrow, well-defined erythronychia, a less-invasive approach such as trap-door avulsion, longitudinal nail strip, or lateral nail plate curl, depending on the etiology, often is sufficient. Tissue excision should be tailored to the specific etiology, with localized excision sufficient for glomus tumors; onychopapillomas require tangential excision of the distal matrix, entire nail bed, and hyperkeratotic papule at the hyponychium. Pushing the cuticle with an elevator/spatula instead of making 2 tangential incisions on the proximal nail fold has been suggested to decrease postoperative paronychia risk.12 A Teflon-coated blade is used to achieve a smooth cut with minimal drag, enabling collection of specimens less than 1 mm thick, which provides sufficient nail matrix epithelium and dermis for histologic examination.16 After obtaining the specimen, the avulsed nail plate may be sutured back to the nail bed using a rapidly absorbable suture such as polyglactin 910, serving as a temporary biological dressing and splint for the nail unit during healing.12 In a retrospective study of 30 patients with longitudinal melanonychia undergoing tangential matrix excision, 27% (8/30) developed postoperative onychodystrophy.17 Although this technique carries relatively lower risk of permanent onychodystrophy compared to other methods, it still is important to acknowledge during the preoperative consent process.12
The lateral longitudinal excision is a valuable technique for diagnosing nail unit inflammatory conditions. Classically, a longitudinal sample including the proximal nail fold, complete matrix, lateral plate, lateral nail fold, hyponychium, and distal tip skin is obtained, with a 10% narrowing of the nail plate expected. If the lateral horn of the nail matrix is missed, permanent lateral malalignment and spicule formation are potential risks. To minimize narrowing of the nail plate and postoperative paronychia, a longitudinal nail strip—where the proximal nail fold and matrix are left intact—is an alternative technique.18
Pain Management Approaches
Appropriate postoperative pain management is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes. In a prospective study of 20 patients undergoing nail biopsy, the mean pain score 6 to 12 hours postprocedure was 5.7 on a scale of 0 to 10. Patients with presurgery pain vs those without experienced significantly higher pain levels both during anesthesia and after surgery (both P<.05).19 Therefore, a personalized approach to pain management based on presence of presurgical pain is warranted. In a randomized clinical trial of 16 patients anesthetized with lidocaine 2% and intraoperative infiltration with a combination of ropivacaine 0.5 mL and triamcinolone (10 mg/mL [0.5 mL]) vs lidocaine 2% alone, the intraoperative mixture reduced postoperative pain (mean pain score, 2 of 10 at 48 hours postprocedure vs 7.88 of 10 in the control group [P<.001]).20
A Cochrane review of 4 unpublished dental and orthopedic surgery studies showed that gabapentin is superior to placebo in the treatment of acute postoperative pain. Therefore, a single dose of gabapentin (250 mg) may be considered in patients at risk for high postoperative pain.21 In a randomized double-blind trial of 210 Mohs micrographic surgery patients, those receiving acetaminophen and ibuprofen reported lower pain scores at 2, 4, 8, and 12 hours postprocedure compared with patients taking acetaminophen and codeine or acetaminophen alone.22 However, the role of opioids in pain management following nail surgery has not been adequately studied.
Wound Care
An efficient dressing protects the surgical wound, facilitates healing, and provides comfort. In our experience, an initial layer of petrolatum-impregnated gauze followed by a pressure-padded bandage consisting of folded dry gauze secured in place with longitudinally applied tape to avoid a tourniquet effect is effective for nail surgical wounds. As the last step, self-adherent elastic wrap is applied around the digit and extended proximally to prevent a tourniquet effect.23
Final Thoughts
Due to the intricate anatomy of the nail unit, nail surgeries are inherently more invasive than most dermatologic surgical procedures. It is crucial to adopt a minimally invasive approach to reduce tissue damage and potential complications in both the short-term and long-term. Adopting this approach may substantially improve patient outcomes and enhance diagnostic and treatment efficacy.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Nail surgery myths and truths. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:230-234.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.E4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Göktay F, Altan ZM, Talas A, et al. Anxiety among patients undergoing nail surgery and skin punch biopsy: effects of age, gender, educational status, and previous experience. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20:35-39. doi:10.1177/1203475415588645
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Vachiramon V, Sobanko JF, Rattanaumpawan P, et al. Music reduces patient anxiety during Mohs surgery: an open-label randomized controlled trial. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:298-305. doi:10.1111/dsu.12047
- Higgins S, Feinstein S, Hawkins M, et al. Virtual reality to improve the experience of the Mohs patient—a prospective interventional study. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:1009-1018. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001854
- Jellinek NJ, Vélez NF. Nail surgery: best way to obtain effective anesthesia. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:265-271. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.12.007
- Baltz JO, Jellinek NJ. Nail surgery: six essential techniques. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:305-318. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.015
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Microporous polysaccharide hemospheres powder for hemostasis following nail surgery [published online March 26, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.069
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Kaolin-impregnated gauze for hemostasis following nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:E13-E14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.008
- Jellinek N. Nail matrix biopsy of longitudinal melanonychia: diagnostic algorithm including the matrix shave biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:803-810. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.12.001
- Richert B, Theunis A, Norrenberg S, et al. Tangential excision of pigmented nail matrix lesions responsible for longitudinal melanonychia: evaluation of the technique on a series of 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:96-104. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.01.029
- Godse R, Jariwala N, Rubin AI. How we do it: the longitudinal nail strip biopsy for nail unit inflammatory dermatoses. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:311-313. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003707
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Di Chiacchio N, Ocampo-Garza J, Villarreal-Villarreal CD, et al. Post-nail procedure analgesia: a randomized control pilot study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:860-862. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.05.015
- Straube S, Derry S, Moore RA, et al. Single dose oral gabapentin for established acute postoperative pain in adults [published online May 12, 2010]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;2010:CD008183. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008183.pub2
- Sniezek PJ, Brodland DG, Zitelli JA. A randomized controlled trial comparing acetaminophen, acetaminophen and ibuprofen, and acetaminophen and codeine for postoperative pain relief after Mohs surgery and cutaneous reconstruction. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1007-1013. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02022.x
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. How we do it: pressure-padded dressing with self-adherent elastic wrap for wound care after nail surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:442-444. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002371
Nail surgical procedures including biopsies, correction of onychocryptosis and other deformities, and excision of tumors are essential for diagnosing and treating nail disorders. Nail surgery often is perceived by dermatologists as a difficult-to-perform, high-risk procedure associated with patient anxiety, pain, and permanent scarring, which may limit implementation. Misconceptions about nail surgical techniques, aftercare, and patient outcomes are prevalent, and a paucity of nail surgery randomized clinical trials hinder formulation of standardized guidelines.1 In a survey-based study of 95 dermatology residency programs (240 total respondents), 58% of residents said they performed 10 or fewer nail procedures, 10% performed more than 10 procedures, 25% only observed nail procedures, 4% were exposed by lecture only, and 1% had no exposure; 30% said they felt incompetent performing nail biopsies.2 In a retrospective study of nail biopsies performed from 2012 to 2017 in the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, only 0.28% and 1.01% of all general dermatologists and Mohs surgeons, respectively, performed nail biopsies annually.3 A minimally invasive nail surgery technique is essential to alleviating dermatologist and patient apprehension, which may lead to greater adoption and improved outcomes.
Reduce Patient Anxiety During Nail Surgery
The prospect of undergoing nail surgery can be psychologically distressing to patients because the nail unit is highly sensitive, intraoperative and postoperative pain are common concerns, patient education materials generally are scarce and inaccurate,4 and procedures are performed under local anesthesia with the patient fully awake. In a prospective study of 48 patients undergoing nail surgery, the median preoperative Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory level was 42.00 (IQR, 6.50).5 Patient distress may be minimized by providing verbal and written educational materials, discussing expectations, and preoperatively using fast-acting benzodiazepines when necessary.6 Utilizing a sleep mask,7 stress ball,8 music,9 and/or virtual reality10 also may reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery.
Use Proper Anesthetic Techniques
Proper anesthetic technique is crucial to achieve the optimal patient experience during nail surgery. With a wing block, the anesthetic is injected into 3 points: (1) the proximal nail fold, (2) the medial/lateral fold, and (3) the hyponychium. The wing block is the preferred technique by many nail surgeons because the second and third injections are given in skin that is already anesthetized, reducing patient discomfort to a single pinprick11; additionally, there is lower postoperative paresthesia risk with the wing block compared with other digital nerve blocks.12 Ropivacaine, a fast-acting and long-acting anesthetic, is preferred over lidocaine to minimize immediate postoperative pain. Buffering the anesthetic solution to physiologic pH and slow infiltration can reduce pain during infiltration.12 Distraction12 provided by ethyl chloride refrigerant spray, an air-cooling device,13 or vibration also can reduce pain during anesthesia.
Punch Biopsy and Excision Tips
The punch biopsy is a minimally invasive method for diagnosing various neoplastic and inflammatory nail unit conditions, except for pigmented lesions.12 For polydactylous nail conditions requiring biopsy, a digit on the nondominant hand should be selected if possible. The punch is applied directly to the nail plate and twisted with downward pressure until the bone is reached, with the instrument withdrawn slowly to prevent surrounding nail plate detachment. Hemostasis is easily achieved with direct pressure and/or use of epinephrine or ropivacaine during anesthesia, and a digital tourniquet generally is not required. Applying microporous polysaccharide hemospheres powder14 or kaolin-impregnated gauze15 with direct pressure is helpful in managing continued bleeding following nail surgery. Punching through the proximal nail matrix should be avoided to prevent permanent onychodystrophy.
A tangential matrix shave biopsy requires a more practiced technique and is preferred for sampling longitudinal melanonychia. A partial proximal nail plate avulsion adequately exposes the origin of pigment and avoids complete avulsion, which may cause more onychodystrophy.16 For broad erythronychia, a total nail avulsion may be necessary. For narrow, well-defined erythronychia, a less-invasive approach such as trap-door avulsion, longitudinal nail strip, or lateral nail plate curl, depending on the etiology, often is sufficient. Tissue excision should be tailored to the specific etiology, with localized excision sufficient for glomus tumors; onychopapillomas require tangential excision of the distal matrix, entire nail bed, and hyperkeratotic papule at the hyponychium. Pushing the cuticle with an elevator/spatula instead of making 2 tangential incisions on the proximal nail fold has been suggested to decrease postoperative paronychia risk.12 A Teflon-coated blade is used to achieve a smooth cut with minimal drag, enabling collection of specimens less than 1 mm thick, which provides sufficient nail matrix epithelium and dermis for histologic examination.16 After obtaining the specimen, the avulsed nail plate may be sutured back to the nail bed using a rapidly absorbable suture such as polyglactin 910, serving as a temporary biological dressing and splint for the nail unit during healing.12 In a retrospective study of 30 patients with longitudinal melanonychia undergoing tangential matrix excision, 27% (8/30) developed postoperative onychodystrophy.17 Although this technique carries relatively lower risk of permanent onychodystrophy compared to other methods, it still is important to acknowledge during the preoperative consent process.12
The lateral longitudinal excision is a valuable technique for diagnosing nail unit inflammatory conditions. Classically, a longitudinal sample including the proximal nail fold, complete matrix, lateral plate, lateral nail fold, hyponychium, and distal tip skin is obtained, with a 10% narrowing of the nail plate expected. If the lateral horn of the nail matrix is missed, permanent lateral malalignment and spicule formation are potential risks. To minimize narrowing of the nail plate and postoperative paronychia, a longitudinal nail strip—where the proximal nail fold and matrix are left intact—is an alternative technique.18
Pain Management Approaches
Appropriate postoperative pain management is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes. In a prospective study of 20 patients undergoing nail biopsy, the mean pain score 6 to 12 hours postprocedure was 5.7 on a scale of 0 to 10. Patients with presurgery pain vs those without experienced significantly higher pain levels both during anesthesia and after surgery (both P<.05).19 Therefore, a personalized approach to pain management based on presence of presurgical pain is warranted. In a randomized clinical trial of 16 patients anesthetized with lidocaine 2% and intraoperative infiltration with a combination of ropivacaine 0.5 mL and triamcinolone (10 mg/mL [0.5 mL]) vs lidocaine 2% alone, the intraoperative mixture reduced postoperative pain (mean pain score, 2 of 10 at 48 hours postprocedure vs 7.88 of 10 in the control group [P<.001]).20
A Cochrane review of 4 unpublished dental and orthopedic surgery studies showed that gabapentin is superior to placebo in the treatment of acute postoperative pain. Therefore, a single dose of gabapentin (250 mg) may be considered in patients at risk for high postoperative pain.21 In a randomized double-blind trial of 210 Mohs micrographic surgery patients, those receiving acetaminophen and ibuprofen reported lower pain scores at 2, 4, 8, and 12 hours postprocedure compared with patients taking acetaminophen and codeine or acetaminophen alone.22 However, the role of opioids in pain management following nail surgery has not been adequately studied.
Wound Care
An efficient dressing protects the surgical wound, facilitates healing, and provides comfort. In our experience, an initial layer of petrolatum-impregnated gauze followed by a pressure-padded bandage consisting of folded dry gauze secured in place with longitudinally applied tape to avoid a tourniquet effect is effective for nail surgical wounds. As the last step, self-adherent elastic wrap is applied around the digit and extended proximally to prevent a tourniquet effect.23
Final Thoughts
Due to the intricate anatomy of the nail unit, nail surgeries are inherently more invasive than most dermatologic surgical procedures. It is crucial to adopt a minimally invasive approach to reduce tissue damage and potential complications in both the short-term and long-term. Adopting this approach may substantially improve patient outcomes and enhance diagnostic and treatment efficacy.
Nail surgical procedures including biopsies, correction of onychocryptosis and other deformities, and excision of tumors are essential for diagnosing and treating nail disorders. Nail surgery often is perceived by dermatologists as a difficult-to-perform, high-risk procedure associated with patient anxiety, pain, and permanent scarring, which may limit implementation. Misconceptions about nail surgical techniques, aftercare, and patient outcomes are prevalent, and a paucity of nail surgery randomized clinical trials hinder formulation of standardized guidelines.1 In a survey-based study of 95 dermatology residency programs (240 total respondents), 58% of residents said they performed 10 or fewer nail procedures, 10% performed more than 10 procedures, 25% only observed nail procedures, 4% were exposed by lecture only, and 1% had no exposure; 30% said they felt incompetent performing nail biopsies.2 In a retrospective study of nail biopsies performed from 2012 to 2017 in the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database, only 0.28% and 1.01% of all general dermatologists and Mohs surgeons, respectively, performed nail biopsies annually.3 A minimally invasive nail surgery technique is essential to alleviating dermatologist and patient apprehension, which may lead to greater adoption and improved outcomes.
Reduce Patient Anxiety During Nail Surgery
The prospect of undergoing nail surgery can be psychologically distressing to patients because the nail unit is highly sensitive, intraoperative and postoperative pain are common concerns, patient education materials generally are scarce and inaccurate,4 and procedures are performed under local anesthesia with the patient fully awake. In a prospective study of 48 patients undergoing nail surgery, the median preoperative Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory level was 42.00 (IQR, 6.50).5 Patient distress may be minimized by providing verbal and written educational materials, discussing expectations, and preoperatively using fast-acting benzodiazepines when necessary.6 Utilizing a sleep mask,7 stress ball,8 music,9 and/or virtual reality10 also may reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery.
Use Proper Anesthetic Techniques
Proper anesthetic technique is crucial to achieve the optimal patient experience during nail surgery. With a wing block, the anesthetic is injected into 3 points: (1) the proximal nail fold, (2) the medial/lateral fold, and (3) the hyponychium. The wing block is the preferred technique by many nail surgeons because the second and third injections are given in skin that is already anesthetized, reducing patient discomfort to a single pinprick11; additionally, there is lower postoperative paresthesia risk with the wing block compared with other digital nerve blocks.12 Ropivacaine, a fast-acting and long-acting anesthetic, is preferred over lidocaine to minimize immediate postoperative pain. Buffering the anesthetic solution to physiologic pH and slow infiltration can reduce pain during infiltration.12 Distraction12 provided by ethyl chloride refrigerant spray, an air-cooling device,13 or vibration also can reduce pain during anesthesia.
Punch Biopsy and Excision Tips
The punch biopsy is a minimally invasive method for diagnosing various neoplastic and inflammatory nail unit conditions, except for pigmented lesions.12 For polydactylous nail conditions requiring biopsy, a digit on the nondominant hand should be selected if possible. The punch is applied directly to the nail plate and twisted with downward pressure until the bone is reached, with the instrument withdrawn slowly to prevent surrounding nail plate detachment. Hemostasis is easily achieved with direct pressure and/or use of epinephrine or ropivacaine during anesthesia, and a digital tourniquet generally is not required. Applying microporous polysaccharide hemospheres powder14 or kaolin-impregnated gauze15 with direct pressure is helpful in managing continued bleeding following nail surgery. Punching through the proximal nail matrix should be avoided to prevent permanent onychodystrophy.
A tangential matrix shave biopsy requires a more practiced technique and is preferred for sampling longitudinal melanonychia. A partial proximal nail plate avulsion adequately exposes the origin of pigment and avoids complete avulsion, which may cause more onychodystrophy.16 For broad erythronychia, a total nail avulsion may be necessary. For narrow, well-defined erythronychia, a less-invasive approach such as trap-door avulsion, longitudinal nail strip, or lateral nail plate curl, depending on the etiology, often is sufficient. Tissue excision should be tailored to the specific etiology, with localized excision sufficient for glomus tumors; onychopapillomas require tangential excision of the distal matrix, entire nail bed, and hyperkeratotic papule at the hyponychium. Pushing the cuticle with an elevator/spatula instead of making 2 tangential incisions on the proximal nail fold has been suggested to decrease postoperative paronychia risk.12 A Teflon-coated blade is used to achieve a smooth cut with minimal drag, enabling collection of specimens less than 1 mm thick, which provides sufficient nail matrix epithelium and dermis for histologic examination.16 After obtaining the specimen, the avulsed nail plate may be sutured back to the nail bed using a rapidly absorbable suture such as polyglactin 910, serving as a temporary biological dressing and splint for the nail unit during healing.12 In a retrospective study of 30 patients with longitudinal melanonychia undergoing tangential matrix excision, 27% (8/30) developed postoperative onychodystrophy.17 Although this technique carries relatively lower risk of permanent onychodystrophy compared to other methods, it still is important to acknowledge during the preoperative consent process.12
The lateral longitudinal excision is a valuable technique for diagnosing nail unit inflammatory conditions. Classically, a longitudinal sample including the proximal nail fold, complete matrix, lateral plate, lateral nail fold, hyponychium, and distal tip skin is obtained, with a 10% narrowing of the nail plate expected. If the lateral horn of the nail matrix is missed, permanent lateral malalignment and spicule formation are potential risks. To minimize narrowing of the nail plate and postoperative paronychia, a longitudinal nail strip—where the proximal nail fold and matrix are left intact—is an alternative technique.18
Pain Management Approaches
Appropriate postoperative pain management is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes. In a prospective study of 20 patients undergoing nail biopsy, the mean pain score 6 to 12 hours postprocedure was 5.7 on a scale of 0 to 10. Patients with presurgery pain vs those without experienced significantly higher pain levels both during anesthesia and after surgery (both P<.05).19 Therefore, a personalized approach to pain management based on presence of presurgical pain is warranted. In a randomized clinical trial of 16 patients anesthetized with lidocaine 2% and intraoperative infiltration with a combination of ropivacaine 0.5 mL and triamcinolone (10 mg/mL [0.5 mL]) vs lidocaine 2% alone, the intraoperative mixture reduced postoperative pain (mean pain score, 2 of 10 at 48 hours postprocedure vs 7.88 of 10 in the control group [P<.001]).20
A Cochrane review of 4 unpublished dental and orthopedic surgery studies showed that gabapentin is superior to placebo in the treatment of acute postoperative pain. Therefore, a single dose of gabapentin (250 mg) may be considered in patients at risk for high postoperative pain.21 In a randomized double-blind trial of 210 Mohs micrographic surgery patients, those receiving acetaminophen and ibuprofen reported lower pain scores at 2, 4, 8, and 12 hours postprocedure compared with patients taking acetaminophen and codeine or acetaminophen alone.22 However, the role of opioids in pain management following nail surgery has not been adequately studied.
Wound Care
An efficient dressing protects the surgical wound, facilitates healing, and provides comfort. In our experience, an initial layer of petrolatum-impregnated gauze followed by a pressure-padded bandage consisting of folded dry gauze secured in place with longitudinally applied tape to avoid a tourniquet effect is effective for nail surgical wounds. As the last step, self-adherent elastic wrap is applied around the digit and extended proximally to prevent a tourniquet effect.23
Final Thoughts
Due to the intricate anatomy of the nail unit, nail surgeries are inherently more invasive than most dermatologic surgical procedures. It is crucial to adopt a minimally invasive approach to reduce tissue damage and potential complications in both the short-term and long-term. Adopting this approach may substantially improve patient outcomes and enhance diagnostic and treatment efficacy.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Nail surgery myths and truths. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:230-234.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.E4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Göktay F, Altan ZM, Talas A, et al. Anxiety among patients undergoing nail surgery and skin punch biopsy: effects of age, gender, educational status, and previous experience. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20:35-39. doi:10.1177/1203475415588645
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Vachiramon V, Sobanko JF, Rattanaumpawan P, et al. Music reduces patient anxiety during Mohs surgery: an open-label randomized controlled trial. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:298-305. doi:10.1111/dsu.12047
- Higgins S, Feinstein S, Hawkins M, et al. Virtual reality to improve the experience of the Mohs patient—a prospective interventional study. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:1009-1018. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001854
- Jellinek NJ, Vélez NF. Nail surgery: best way to obtain effective anesthesia. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:265-271. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.12.007
- Baltz JO, Jellinek NJ. Nail surgery: six essential techniques. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:305-318. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.015
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Microporous polysaccharide hemospheres powder for hemostasis following nail surgery [published online March 26, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.069
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Kaolin-impregnated gauze for hemostasis following nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:E13-E14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.008
- Jellinek N. Nail matrix biopsy of longitudinal melanonychia: diagnostic algorithm including the matrix shave biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:803-810. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.12.001
- Richert B, Theunis A, Norrenberg S, et al. Tangential excision of pigmented nail matrix lesions responsible for longitudinal melanonychia: evaluation of the technique on a series of 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:96-104. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.01.029
- Godse R, Jariwala N, Rubin AI. How we do it: the longitudinal nail strip biopsy for nail unit inflammatory dermatoses. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:311-313. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003707
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Di Chiacchio N, Ocampo-Garza J, Villarreal-Villarreal CD, et al. Post-nail procedure analgesia: a randomized control pilot study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:860-862. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.05.015
- Straube S, Derry S, Moore RA, et al. Single dose oral gabapentin for established acute postoperative pain in adults [published online May 12, 2010]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;2010:CD008183. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008183.pub2
- Sniezek PJ, Brodland DG, Zitelli JA. A randomized controlled trial comparing acetaminophen, acetaminophen and ibuprofen, and acetaminophen and codeine for postoperative pain relief after Mohs surgery and cutaneous reconstruction. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1007-1013. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02022.x
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. How we do it: pressure-padded dressing with self-adherent elastic wrap for wound care after nail surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:442-444. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002371
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Nail surgery myths and truths. J Drugs Dermatol. 2020;19:230-234.
- Lee EH, Nehal KS, Dusza SW, et al. Procedural dermatology training during dermatology residency: a survey of third-year dermatology residents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:475-483.E4835. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.05.044
- Wang Y, Lipner SR. Retrospective analysis of nail biopsies performed using the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Database 2012 to 2017. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:E14928. doi:10.1111/dth.14928
- Ishack S, Lipner SR. Evaluating the impact and educational value of YouTube videos on nail biopsy procedures. Cutis. 2020;105:148-149, E1.
- Göktay F, Altan ZM, Talas A, et al. Anxiety among patients undergoing nail surgery and skin punch biopsy: effects of age, gender, educational status, and previous experience. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20:35-39. doi:10.1177/1203475415588645
- Lipner SR. Pain-minimizing strategies for nail surgery. Cutis. 2018;101:76-77.
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilizing a sleep mask to reduce patient anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2021;108:36. doi:10.12788/cutis.0285
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Utilization of a stress ball to diminish anxiety during nail surgery. Cutis. 2020;105:294.
- Vachiramon V, Sobanko JF, Rattanaumpawan P, et al. Music reduces patient anxiety during Mohs surgery: an open-label randomized controlled trial. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39:298-305. doi:10.1111/dsu.12047
- Higgins S, Feinstein S, Hawkins M, et al. Virtual reality to improve the experience of the Mohs patient—a prospective interventional study. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45:1009-1018. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001854
- Jellinek NJ, Vélez NF. Nail surgery: best way to obtain effective anesthesia. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33:265-271. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.12.007
- Baltz JO, Jellinek NJ. Nail surgery: six essential techniques. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39:305-318. doi:10.1016/j.det.2020.12.015
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Air cooling for improved analgesia during local anesthetic infiltration for nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:E231-E232. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.11.032
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Microporous polysaccharide hemospheres powder for hemostasis following nail surgery [published online March 26, 2021]. J Am Acad Dermatol. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.03.069
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. Kaolin-impregnated gauze for hemostasis following nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:E13-E14. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.02.008
- Jellinek N. Nail matrix biopsy of longitudinal melanonychia: diagnostic algorithm including the matrix shave biopsy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:803-810. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.12.001
- Richert B, Theunis A, Norrenberg S, et al. Tangential excision of pigmented nail matrix lesions responsible for longitudinal melanonychia: evaluation of the technique on a series of 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69:96-104. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.01.029
- Godse R, Jariwala N, Rubin AI. How we do it: the longitudinal nail strip biopsy for nail unit inflammatory dermatoses. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:311-313. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003707
- Ricardo JW, Qiu Y, Lipner SR. Longitudinal perioperative pain assessment in nail surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87:874-876. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.11.042
- Di Chiacchio N, Ocampo-Garza J, Villarreal-Villarreal CD, et al. Post-nail procedure analgesia: a randomized control pilot study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;81:860-862. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.05.015
- Straube S, Derry S, Moore RA, et al. Single dose oral gabapentin for established acute postoperative pain in adults [published online May 12, 2010]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;2010:CD008183. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008183.pub2
- Sniezek PJ, Brodland DG, Zitelli JA. A randomized controlled trial comparing acetaminophen, acetaminophen and ibuprofen, and acetaminophen and codeine for postoperative pain relief after Mohs surgery and cutaneous reconstruction. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1007-1013. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02022.x
- Ricardo JW, Lipner SR. How we do it: pressure-padded dressing with self-adherent elastic wrap for wound care after nail surgery. Dermatol Surg. 2021;47:442-444. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000002371