User login
Leishmaniasis is a neglected parasitic disease with an estimated annual incidence of 1.3 million cases, the majority of which manifest as cutaneous leishmaniasis.1 The cutaneous and mucosal forms demonstrate substantial global burden with morbidity and socioeconomic repercussions, while the visceral form is responsible for up to 30,000 deaths annually.2 Despite increasing prevalence in the United States, awareness and diagnosis remain relatively low.3 We describe 2 cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis in New England, United States, in travelers returning from Central America, both successfully treated with miltefosine. We also review prevention, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Case Reports
Patient 1
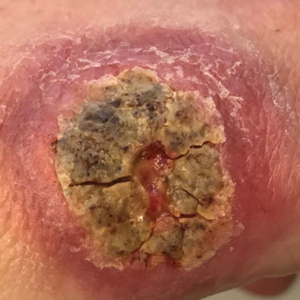
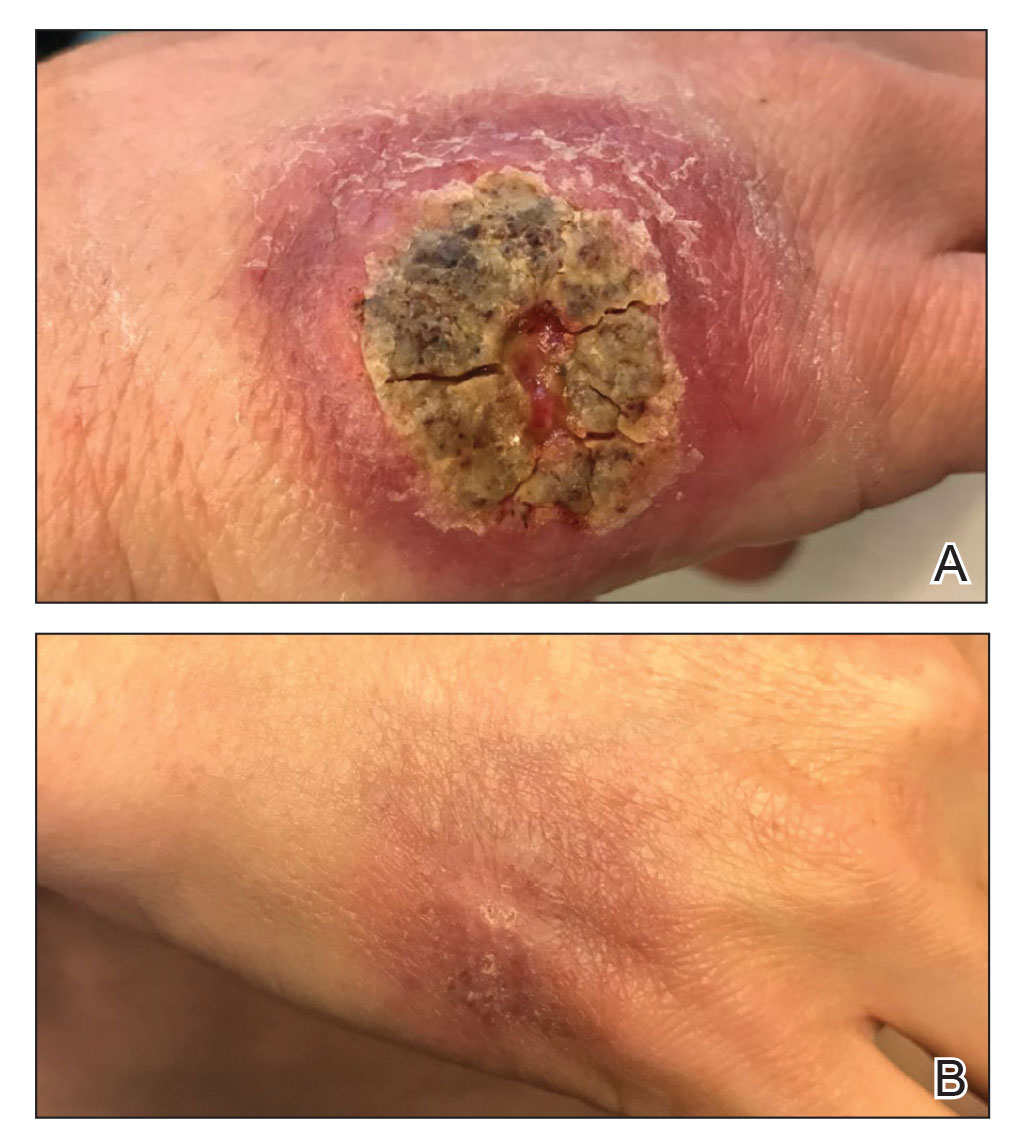
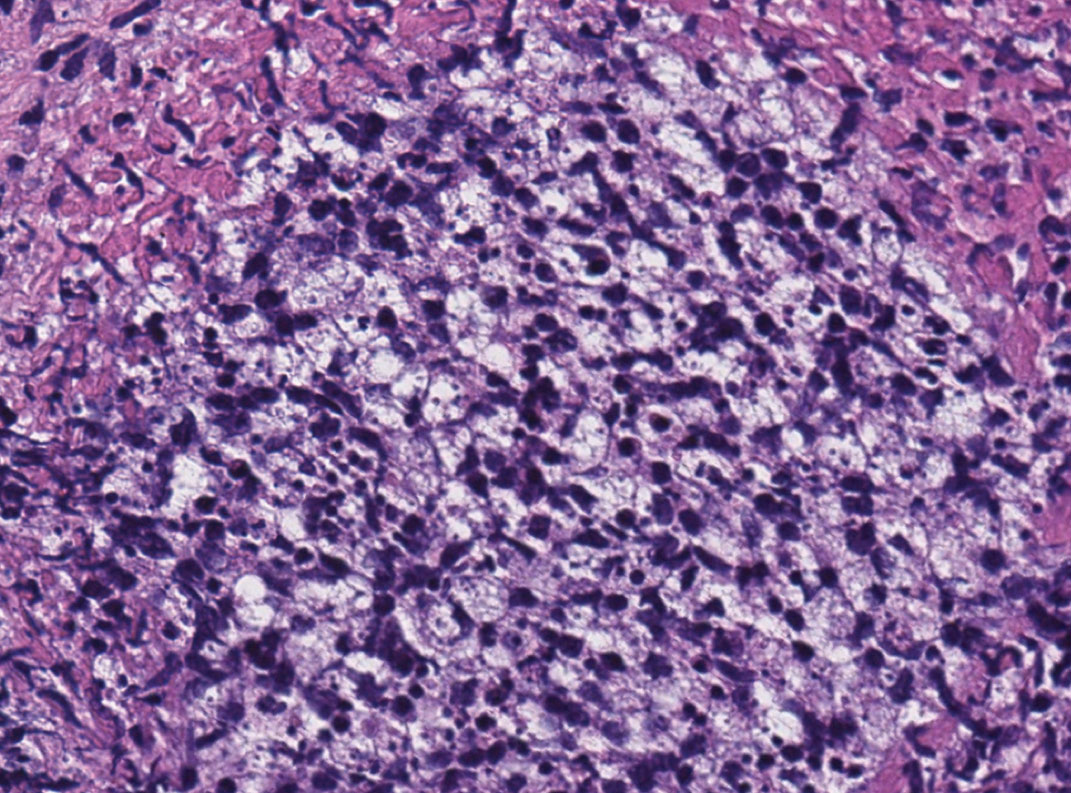
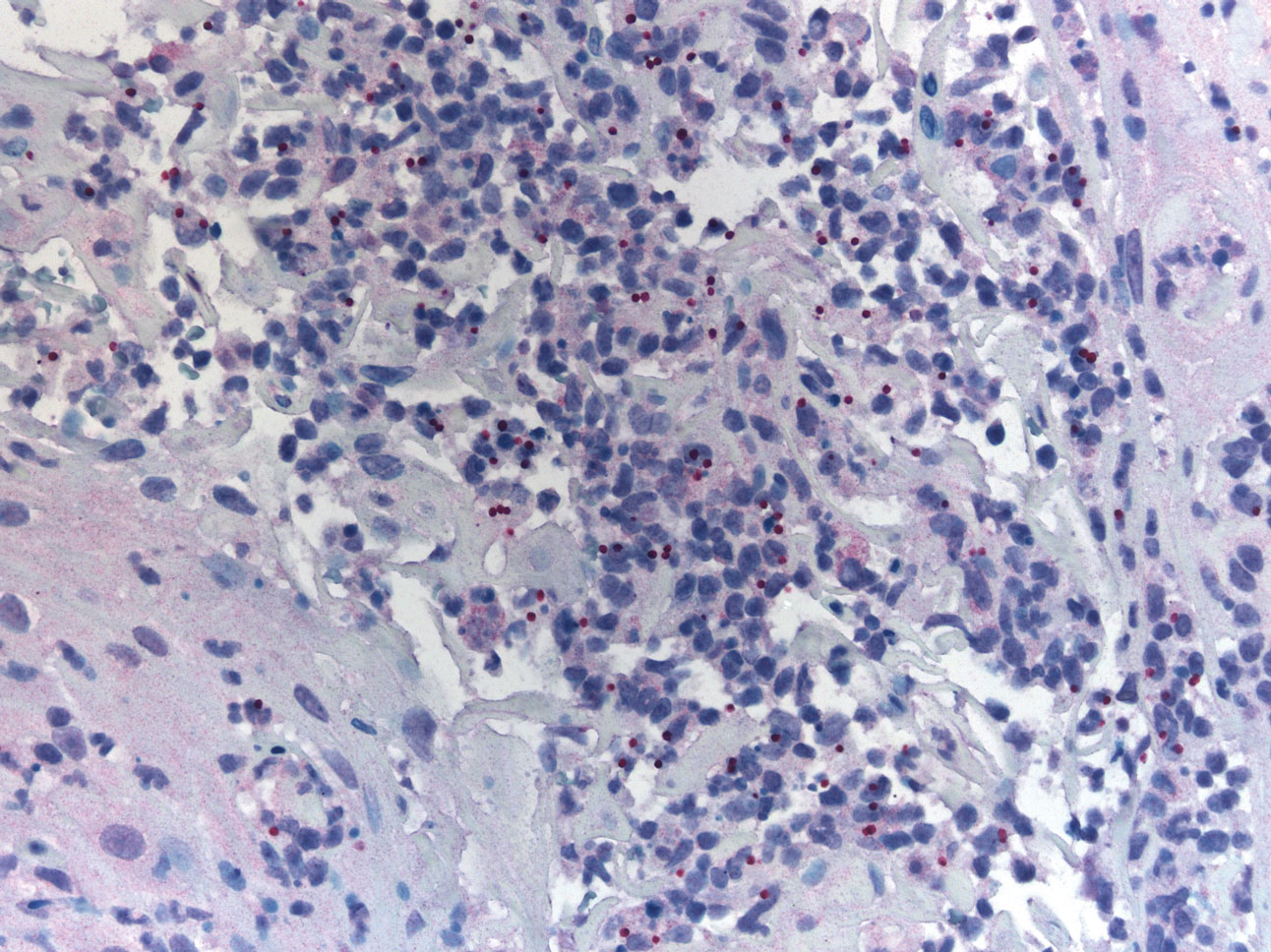
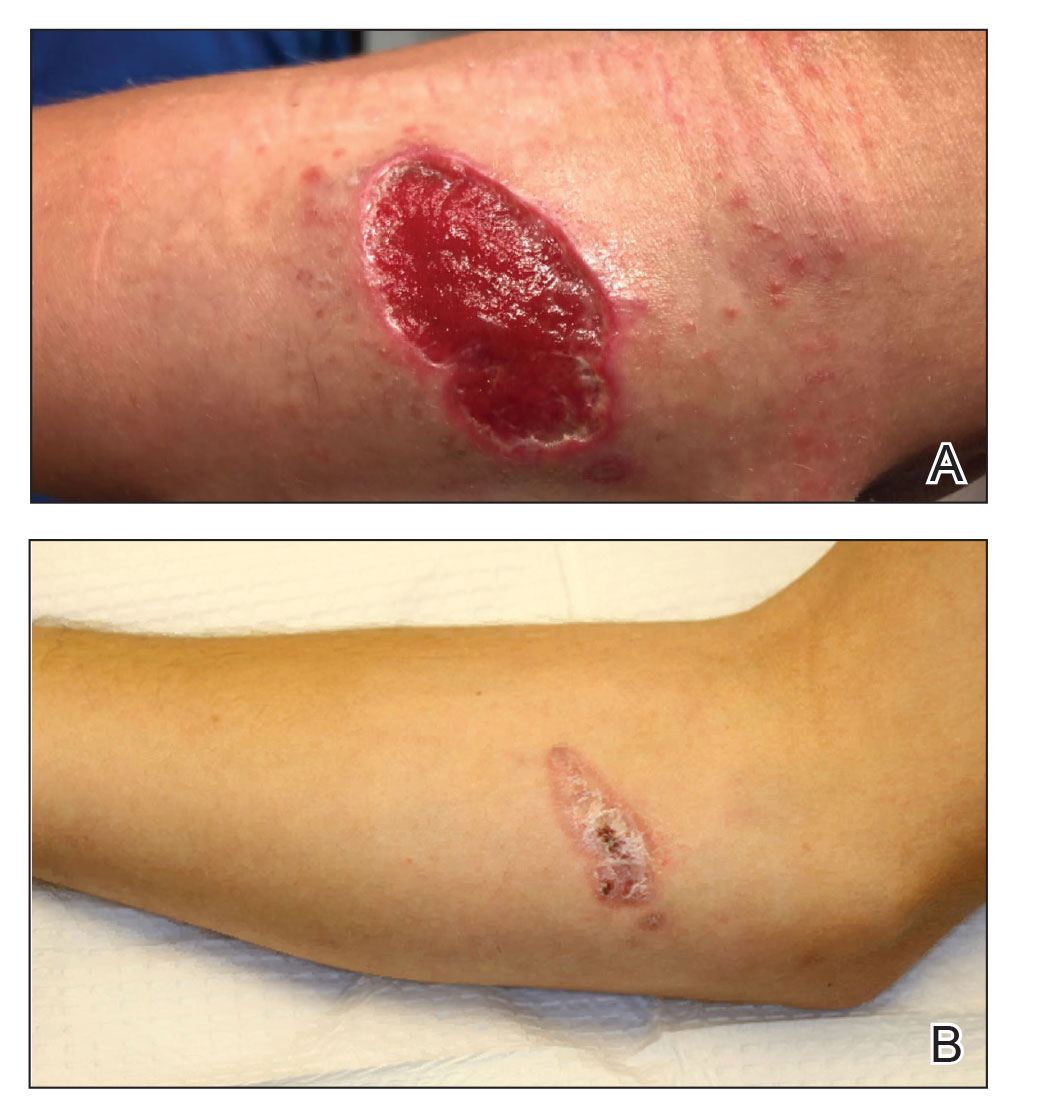
A 47-year-old woman presented with an enlarging, 2-cm, erythematous, ulcerated nodule on the right dorsal hand of 2 weeks’ duration with accompanying right epitrochlear lymphadenopathy (Figure 1A). She noticed the lesion 10 weeks after returning from Panama, where she had been photographing the jungle. Prior to the initial presentation to dermatology, salicylic acid wart remover, intramuscular ceftriaxone, and oral trimethoprim had failed to alleviate the lesion. Her laboratory results were notable for an elevated C-reactive protein level of 5.4 mg/L (reference range, ≤4.9 mg/L). A punch biopsy demonstrated pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with diffuse dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammation and small intracytoplasmic structures within histiocytes consistent with leishmaniasis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry was consistent with leishmaniasis (Figure 3), and polymerase chain reaction performed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) identified the pathogen as Leishmania braziliensis.
Patient 2
An 18-year-old man presented with an enlarging, well-delineated, tender ulcer of 6 weeks’ duration measuring 2.5×2 cm with an erythematous and edematous border on the right medial forearm with associated epitrochlear lymphadenopathy (Figure 4). Nine weeks prior to initial presentation, he had returned from a 3-month outdoor adventure trip to the Florida Keys, Costa Rica, and Panama. He had used bug repellent intermittently, slept under a bug net, and did not recall any trauma or bite at the ulcer site. Biopsy and tissue culture were obtained, and histopathology demonstrated an ulcer with a dense dermal lymphogranulomatous infiltrate and intracytoplasmic organisms consistent with leishmaniasis. Polymerase chain reaction by the CDC identified the pathogen as Leishmania panamensis.
Treatment
Both patients were prescribed oral miltefosine 50 mg twice daily for 28 days. Patient 1 initiated treatment 1 month after lesion onset, and patient 2 initiated treatment 2.5 months after initial presentation. Both patients had noticeable clinical improvement within 21 days of starting treatment, with lesions diminishing in size and lymphadenopathy resolving. Within 2 months of treatment, patient 1’s ulcer completely resolved with only postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 1B), while patient 2’s ulcer was noticeably smaller and shallower compared with its peak size of 4.2×2.4 cm (Figure 4B). Miltefosine was well tolerated by both patients; emesis resolved with ondansetron in patient 1 and spontaneously in patient 2, who had asymptomatic temporary hyperkalemia of 5.2 mmol/L (reference range, 3.5–5.0 mmol/L).
Comment
Epidemiology and Prevention
Risk factors for leishmaniasis include weak immunity, poverty, poor housing, poor sanitation, malnutrition, urbanization, climate change, and human migration.4 Our patients were most directly affected by travel to locations where leishmaniasis is endemic. Despite an increasing prevalence of endemic leishmaniasis and new animal hosts in the southern United States, most patients diagnosed in the United States are infected abroad by Leishmania mexicana and L braziliensis, both cutaneous New World species.3 Our patients were infected by species within the New World subgenus Viannia that have potential for mucocutaneous spread.4
Because there is no chemoprophylaxis or acquired active immunity such as vaccines that can mitigate the risk for leishmaniasis, public health efforts focus on preventive measures. Although difficult to achieve, avoidance of the phlebotomine sand fly species that transmit the obligate intracellular Leishmania parasite is a most effective measure.4 Travelers entering geographic regions with higher risk for leishmaniasis should be aware of the inherent risk and determine which methods of prevention, such as N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET) insecticides or permethrin-treated protective clothing, are most feasible. Although higher concentrations of DEET provide longer protection, the effectiveness tends to plateau at approximately 50%.5
Presentation and Prognosis
For patients who develop leishmaniasis, the disease course and prognosis depend greatly on the species and manifestation. The most common form of leishmaniasis is localized cutaneous leishmaniasis, which has an annual incidence of up to 1 million cases. It initially presents as macules, usually at the site of inoculation within several months to years of infection.6 The macules expand into papules and plaques that reach maximum size over at least 1 week4 and then progress into crusted ulcers up to 5 cm in diameter with raised edges. Although usually painless and self-limited, these lesions can take years to spontaneously heal, with the risk for atrophic scarring and altered pigmentation. Lymphatic involvement manifests as lymphadenitis or regional lymphadenopathy and is common with lesions caused by the subgenus Viannia.6
Leishmania braziliensis and L panamensis, the species that infected our patients, can uniquely cause cutaneous leishmaniasis that metastasizes into mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, which always affects the nasal mucosa. Risk factors for transformation include a primary lesion site above the waist, multiple or large primary lesions, and delayed healing of primary cutaneous leishmaniasis. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis can result in notable morbidity and even mortality from invasion and destruction of nasal and oropharyngeal mucosa, as well as intercurrent pneumonia, especially if treatment is insufficient or delayed.4
Diagnosis
Prompt treatment relies on accurate and timely diagnosis, which is complicated by the relative unfamiliarity with leishmaniasis in the United States. The differential diagnosis for cutaneous leishmaniasis is broad, including deep fungal infection, Mycobacterium infection, cutaneous granulomatous conditions, nonmelanoma cutaneous neoplasms, and trauma. Taking a thorough patient history, including potential exposures and travels; having high clinical suspicion; and being aware of classic presentation allows for identification of leishmaniasis and subsequent stratification by manifestation.7
Diagnosis is made by detecting Leishmania organisms or DNA using light microscopy and staining to visualize the kinetoplast in an amastigote, molecular methods, or specialized culturing.7 The CDC is a valuable diagnostic partner for confirmation and speciation. Specific instructions for specimen collection and transportation can be found by contacting the CDC or reading their guide.8 To provide prompt care and reassurance to patients, it is important to be aware of the coordination effort that may be needed to send samples, receive results, and otherwise correspond with a separate institution.
Treatment
Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis is indicated to decrease the risk for mucosal dissemination and clinical reactivation of lesions, accelerate healing of lesions, decrease local morbidity caused by large or persistent lesions, and decrease the reservoir of infection in places where infected humans serve as reservoir hosts. Oral treatments include ketoconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole, recommended at doses ranging from 200 to 600 mg daily for at least 28 days. For severe, refractory, or visceral leishmaniasis, parenteral choices include
Miltefosine is becoming a more common treatment of leishmaniasis because of its oral route, tolerability in nonpregnant patients, and commercial availability. It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for cutaneous leishmaniasis due to L braziliensis, L panamensis, and Leishmania guyanensis; mucosal leishmaniasis due to L braziliensis; and visceral leishmaniasis due to Leishmania donovani in patients at least 12 years of age. For cutaneous leishmaniasis, the standard dosage of 50 mg twice daily (for patients weighing 30–44 kg) or 3 times daily (for patients weighing 45 kg or more) for 28 consecutive days has cure rates of 48% to 85% by 6 months after therapy ends. Cure is defined as epithelialization of lesions, no enlargement greater than 50% in lesions, no appearance of new lesions, and/or negative parasitology. The antileishmanial mechanism of action is unknown and likely involves interaction with lipids, inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase, and apoptosislike cell death. Miltefosine is contraindicated in pregnancy. The most common adverse reactions in patients include nausea (35.9%–41.7%), motion sickness (29.2%), headache (28.1%), and emesis (4.5%–27.5%). With the exception of headache, these adverse reactions can decrease with administration of food, fluids, and antiemetics. Potentially more serious but rarer adverse reactions include elevated serum creatinine (5%–25%) and transaminases (5%). Although our patients had mild hyperkalemia, it is not an established adverse reaction. However, renal injury has been reported.10
Conclusion
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is increasing in prevalence in the United States due to increased foreign travel. Providers should be familiar with the cutaneous presentation of leishmaniasis, even in areas of low prevalence, to limit the risk for mucocutaneous dissemination from infection with the subgenus Viannia. Prompt treatment is vital to ensuring the best prognosis, and first-line treatment with miltefosine should be strongly considered given its efficacy and tolerability.
- Babuadze G, Alvar J, Argaw D, et al. Epidemiology of visceral leishmaniasis in Georgia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2725.
- Leishmaniasis. World Health Organization website. https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/Leishmaniasis. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- McIlwee BE, Weis SE, Hosler GA. Incidence of endemic human cutaneous leishmaniasis in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1032-1039.
- Leishmaniasis. World Health Organization website. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis. Update March 2, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for DEET insect repellent use. https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/toolkit/DEET.pdf. Accessed September 20, 2020.
- Buescher MD, Rutledge LC, Wirtz RA, et al. The dose-persistence relationship of DEET against Aedes aegypti. Mosq News. 1983;43:364-366.
- Aronson N, Herwaldt BL, Libman M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:e202-e264.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Practical guide for specimen collection and reference diagnosis of leishmaniasis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/leishmaniasis/resources/pdf/cdc_diagnosis_guide_leishmaniasis_2016.pdf. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Visceral leishmaniasis. Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative website. https://www.dndi.org/diseases-projects/leishmaniasis/. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Impavido Medication Guide. Food and Drug Administration Web site. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/204684s000lbl.pdf. Revised March 2014. Accessed May 18, 2020.
Leishmaniasis is a neglected parasitic disease with an estimated annual incidence of 1.3 million cases, the majority of which manifest as cutaneous leishmaniasis.1 The cutaneous and mucosal forms demonstrate substantial global burden with morbidity and socioeconomic repercussions, while the visceral form is responsible for up to 30,000 deaths annually.2 Despite increasing prevalence in the United States, awareness and diagnosis remain relatively low.3 We describe 2 cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis in New England, United States, in travelers returning from Central America, both successfully treated with miltefosine. We also review prevention, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Case Reports
Patient 1
A 47-year-old woman presented with an enlarging, 2-cm, erythematous, ulcerated nodule on the right dorsal hand of 2 weeks’ duration with accompanying right epitrochlear lymphadenopathy (Figure 1A). She noticed the lesion 10 weeks after returning from Panama, where she had been photographing the jungle. Prior to the initial presentation to dermatology, salicylic acid wart remover, intramuscular ceftriaxone, and oral trimethoprim had failed to alleviate the lesion. Her laboratory results were notable for an elevated C-reactive protein level of 5.4 mg/L (reference range, ≤4.9 mg/L). A punch biopsy demonstrated pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with diffuse dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammation and small intracytoplasmic structures within histiocytes consistent with leishmaniasis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry was consistent with leishmaniasis (Figure 3), and polymerase chain reaction performed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) identified the pathogen as Leishmania braziliensis.



Patient 2
An 18-year-old man presented with an enlarging, well-delineated, tender ulcer of 6 weeks’ duration measuring 2.5×2 cm with an erythematous and edematous border on the right medial forearm with associated epitrochlear lymphadenopathy (Figure 4). Nine weeks prior to initial presentation, he had returned from a 3-month outdoor adventure trip to the Florida Keys, Costa Rica, and Panama. He had used bug repellent intermittently, slept under a bug net, and did not recall any trauma or bite at the ulcer site. Biopsy and tissue culture were obtained, and histopathology demonstrated an ulcer with a dense dermal lymphogranulomatous infiltrate and intracytoplasmic organisms consistent with leishmaniasis. Polymerase chain reaction by the CDC identified the pathogen as Leishmania panamensis.

Treatment
Both patients were prescribed oral miltefosine 50 mg twice daily for 28 days. Patient 1 initiated treatment 1 month after lesion onset, and patient 2 initiated treatment 2.5 months after initial presentation. Both patients had noticeable clinical improvement within 21 days of starting treatment, with lesions diminishing in size and lymphadenopathy resolving. Within 2 months of treatment, patient 1’s ulcer completely resolved with only postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 1B), while patient 2’s ulcer was noticeably smaller and shallower compared with its peak size of 4.2×2.4 cm (Figure 4B). Miltefosine was well tolerated by both patients; emesis resolved with ondansetron in patient 1 and spontaneously in patient 2, who had asymptomatic temporary hyperkalemia of 5.2 mmol/L (reference range, 3.5–5.0 mmol/L).
Comment
Epidemiology and Prevention
Risk factors for leishmaniasis include weak immunity, poverty, poor housing, poor sanitation, malnutrition, urbanization, climate change, and human migration.4 Our patients were most directly affected by travel to locations where leishmaniasis is endemic. Despite an increasing prevalence of endemic leishmaniasis and new animal hosts in the southern United States, most patients diagnosed in the United States are infected abroad by Leishmania mexicana and L braziliensis, both cutaneous New World species.3 Our patients were infected by species within the New World subgenus Viannia that have potential for mucocutaneous spread.4
Because there is no chemoprophylaxis or acquired active immunity such as vaccines that can mitigate the risk for leishmaniasis, public health efforts focus on preventive measures. Although difficult to achieve, avoidance of the phlebotomine sand fly species that transmit the obligate intracellular Leishmania parasite is a most effective measure.4 Travelers entering geographic regions with higher risk for leishmaniasis should be aware of the inherent risk and determine which methods of prevention, such as N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET) insecticides or permethrin-treated protective clothing, are most feasible. Although higher concentrations of DEET provide longer protection, the effectiveness tends to plateau at approximately 50%.5
Presentation and Prognosis
For patients who develop leishmaniasis, the disease course and prognosis depend greatly on the species and manifestation. The most common form of leishmaniasis is localized cutaneous leishmaniasis, which has an annual incidence of up to 1 million cases. It initially presents as macules, usually at the site of inoculation within several months to years of infection.6 The macules expand into papules and plaques that reach maximum size over at least 1 week4 and then progress into crusted ulcers up to 5 cm in diameter with raised edges. Although usually painless and self-limited, these lesions can take years to spontaneously heal, with the risk for atrophic scarring and altered pigmentation. Lymphatic involvement manifests as lymphadenitis or regional lymphadenopathy and is common with lesions caused by the subgenus Viannia.6
Leishmania braziliensis and L panamensis, the species that infected our patients, can uniquely cause cutaneous leishmaniasis that metastasizes into mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, which always affects the nasal mucosa. Risk factors for transformation include a primary lesion site above the waist, multiple or large primary lesions, and delayed healing of primary cutaneous leishmaniasis. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis can result in notable morbidity and even mortality from invasion and destruction of nasal and oropharyngeal mucosa, as well as intercurrent pneumonia, especially if treatment is insufficient or delayed.4
Diagnosis
Prompt treatment relies on accurate and timely diagnosis, which is complicated by the relative unfamiliarity with leishmaniasis in the United States. The differential diagnosis for cutaneous leishmaniasis is broad, including deep fungal infection, Mycobacterium infection, cutaneous granulomatous conditions, nonmelanoma cutaneous neoplasms, and trauma. Taking a thorough patient history, including potential exposures and travels; having high clinical suspicion; and being aware of classic presentation allows for identification of leishmaniasis and subsequent stratification by manifestation.7
Diagnosis is made by detecting Leishmania organisms or DNA using light microscopy and staining to visualize the kinetoplast in an amastigote, molecular methods, or specialized culturing.7 The CDC is a valuable diagnostic partner for confirmation and speciation. Specific instructions for specimen collection and transportation can be found by contacting the CDC or reading their guide.8 To provide prompt care and reassurance to patients, it is important to be aware of the coordination effort that may be needed to send samples, receive results, and otherwise correspond with a separate institution.
Treatment
Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis is indicated to decrease the risk for mucosal dissemination and clinical reactivation of lesions, accelerate healing of lesions, decrease local morbidity caused by large or persistent lesions, and decrease the reservoir of infection in places where infected humans serve as reservoir hosts. Oral treatments include ketoconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole, recommended at doses ranging from 200 to 600 mg daily for at least 28 days. For severe, refractory, or visceral leishmaniasis, parenteral choices include
Miltefosine is becoming a more common treatment of leishmaniasis because of its oral route, tolerability in nonpregnant patients, and commercial availability. It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for cutaneous leishmaniasis due to L braziliensis, L panamensis, and Leishmania guyanensis; mucosal leishmaniasis due to L braziliensis; and visceral leishmaniasis due to Leishmania donovani in patients at least 12 years of age. For cutaneous leishmaniasis, the standard dosage of 50 mg twice daily (for patients weighing 30–44 kg) or 3 times daily (for patients weighing 45 kg or more) for 28 consecutive days has cure rates of 48% to 85% by 6 months after therapy ends. Cure is defined as epithelialization of lesions, no enlargement greater than 50% in lesions, no appearance of new lesions, and/or negative parasitology. The antileishmanial mechanism of action is unknown and likely involves interaction with lipids, inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase, and apoptosislike cell death. Miltefosine is contraindicated in pregnancy. The most common adverse reactions in patients include nausea (35.9%–41.7%), motion sickness (29.2%), headache (28.1%), and emesis (4.5%–27.5%). With the exception of headache, these adverse reactions can decrease with administration of food, fluids, and antiemetics. Potentially more serious but rarer adverse reactions include elevated serum creatinine (5%–25%) and transaminases (5%). Although our patients had mild hyperkalemia, it is not an established adverse reaction. However, renal injury has been reported.10
Conclusion
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is increasing in prevalence in the United States due to increased foreign travel. Providers should be familiar with the cutaneous presentation of leishmaniasis, even in areas of low prevalence, to limit the risk for mucocutaneous dissemination from infection with the subgenus Viannia. Prompt treatment is vital to ensuring the best prognosis, and first-line treatment with miltefosine should be strongly considered given its efficacy and tolerability.
Leishmaniasis is a neglected parasitic disease with an estimated annual incidence of 1.3 million cases, the majority of which manifest as cutaneous leishmaniasis.1 The cutaneous and mucosal forms demonstrate substantial global burden with morbidity and socioeconomic repercussions, while the visceral form is responsible for up to 30,000 deaths annually.2 Despite increasing prevalence in the United States, awareness and diagnosis remain relatively low.3 We describe 2 cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis in New England, United States, in travelers returning from Central America, both successfully treated with miltefosine. We also review prevention, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Case Reports
Patient 1
A 47-year-old woman presented with an enlarging, 2-cm, erythematous, ulcerated nodule on the right dorsal hand of 2 weeks’ duration with accompanying right epitrochlear lymphadenopathy (Figure 1A). She noticed the lesion 10 weeks after returning from Panama, where she had been photographing the jungle. Prior to the initial presentation to dermatology, salicylic acid wart remover, intramuscular ceftriaxone, and oral trimethoprim had failed to alleviate the lesion. Her laboratory results were notable for an elevated C-reactive protein level of 5.4 mg/L (reference range, ≤4.9 mg/L). A punch biopsy demonstrated pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with diffuse dermal lymphohistiocytic inflammation and small intracytoplasmic structures within histiocytes consistent with leishmaniasis (Figure 2). Immunohistochemistry was consistent with leishmaniasis (Figure 3), and polymerase chain reaction performed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) identified the pathogen as Leishmania braziliensis.



Patient 2
An 18-year-old man presented with an enlarging, well-delineated, tender ulcer of 6 weeks’ duration measuring 2.5×2 cm with an erythematous and edematous border on the right medial forearm with associated epitrochlear lymphadenopathy (Figure 4). Nine weeks prior to initial presentation, he had returned from a 3-month outdoor adventure trip to the Florida Keys, Costa Rica, and Panama. He had used bug repellent intermittently, slept under a bug net, and did not recall any trauma or bite at the ulcer site. Biopsy and tissue culture were obtained, and histopathology demonstrated an ulcer with a dense dermal lymphogranulomatous infiltrate and intracytoplasmic organisms consistent with leishmaniasis. Polymerase chain reaction by the CDC identified the pathogen as Leishmania panamensis.

Treatment
Both patients were prescribed oral miltefosine 50 mg twice daily for 28 days. Patient 1 initiated treatment 1 month after lesion onset, and patient 2 initiated treatment 2.5 months after initial presentation. Both patients had noticeable clinical improvement within 21 days of starting treatment, with lesions diminishing in size and lymphadenopathy resolving. Within 2 months of treatment, patient 1’s ulcer completely resolved with only postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (Figure 1B), while patient 2’s ulcer was noticeably smaller and shallower compared with its peak size of 4.2×2.4 cm (Figure 4B). Miltefosine was well tolerated by both patients; emesis resolved with ondansetron in patient 1 and spontaneously in patient 2, who had asymptomatic temporary hyperkalemia of 5.2 mmol/L (reference range, 3.5–5.0 mmol/L).
Comment
Epidemiology and Prevention
Risk factors for leishmaniasis include weak immunity, poverty, poor housing, poor sanitation, malnutrition, urbanization, climate change, and human migration.4 Our patients were most directly affected by travel to locations where leishmaniasis is endemic. Despite an increasing prevalence of endemic leishmaniasis and new animal hosts in the southern United States, most patients diagnosed in the United States are infected abroad by Leishmania mexicana and L braziliensis, both cutaneous New World species.3 Our patients were infected by species within the New World subgenus Viannia that have potential for mucocutaneous spread.4
Because there is no chemoprophylaxis or acquired active immunity such as vaccines that can mitigate the risk for leishmaniasis, public health efforts focus on preventive measures. Although difficult to achieve, avoidance of the phlebotomine sand fly species that transmit the obligate intracellular Leishmania parasite is a most effective measure.4 Travelers entering geographic regions with higher risk for leishmaniasis should be aware of the inherent risk and determine which methods of prevention, such as N,N-diethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET) insecticides or permethrin-treated protective clothing, are most feasible. Although higher concentrations of DEET provide longer protection, the effectiveness tends to plateau at approximately 50%.5
Presentation and Prognosis
For patients who develop leishmaniasis, the disease course and prognosis depend greatly on the species and manifestation. The most common form of leishmaniasis is localized cutaneous leishmaniasis, which has an annual incidence of up to 1 million cases. It initially presents as macules, usually at the site of inoculation within several months to years of infection.6 The macules expand into papules and plaques that reach maximum size over at least 1 week4 and then progress into crusted ulcers up to 5 cm in diameter with raised edges. Although usually painless and self-limited, these lesions can take years to spontaneously heal, with the risk for atrophic scarring and altered pigmentation. Lymphatic involvement manifests as lymphadenitis or regional lymphadenopathy and is common with lesions caused by the subgenus Viannia.6
Leishmania braziliensis and L panamensis, the species that infected our patients, can uniquely cause cutaneous leishmaniasis that metastasizes into mucocutaneous leishmaniasis, which always affects the nasal mucosa. Risk factors for transformation include a primary lesion site above the waist, multiple or large primary lesions, and delayed healing of primary cutaneous leishmaniasis. Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis can result in notable morbidity and even mortality from invasion and destruction of nasal and oropharyngeal mucosa, as well as intercurrent pneumonia, especially if treatment is insufficient or delayed.4
Diagnosis
Prompt treatment relies on accurate and timely diagnosis, which is complicated by the relative unfamiliarity with leishmaniasis in the United States. The differential diagnosis for cutaneous leishmaniasis is broad, including deep fungal infection, Mycobacterium infection, cutaneous granulomatous conditions, nonmelanoma cutaneous neoplasms, and trauma. Taking a thorough patient history, including potential exposures and travels; having high clinical suspicion; and being aware of classic presentation allows for identification of leishmaniasis and subsequent stratification by manifestation.7
Diagnosis is made by detecting Leishmania organisms or DNA using light microscopy and staining to visualize the kinetoplast in an amastigote, molecular methods, or specialized culturing.7 The CDC is a valuable diagnostic partner for confirmation and speciation. Specific instructions for specimen collection and transportation can be found by contacting the CDC or reading their guide.8 To provide prompt care and reassurance to patients, it is important to be aware of the coordination effort that may be needed to send samples, receive results, and otherwise correspond with a separate institution.
Treatment
Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis is indicated to decrease the risk for mucosal dissemination and clinical reactivation of lesions, accelerate healing of lesions, decrease local morbidity caused by large or persistent lesions, and decrease the reservoir of infection in places where infected humans serve as reservoir hosts. Oral treatments include ketoconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole, recommended at doses ranging from 200 to 600 mg daily for at least 28 days. For severe, refractory, or visceral leishmaniasis, parenteral choices include
Miltefosine is becoming a more common treatment of leishmaniasis because of its oral route, tolerability in nonpregnant patients, and commercial availability. It was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2014 for cutaneous leishmaniasis due to L braziliensis, L panamensis, and Leishmania guyanensis; mucosal leishmaniasis due to L braziliensis; and visceral leishmaniasis due to Leishmania donovani in patients at least 12 years of age. For cutaneous leishmaniasis, the standard dosage of 50 mg twice daily (for patients weighing 30–44 kg) or 3 times daily (for patients weighing 45 kg or more) for 28 consecutive days has cure rates of 48% to 85% by 6 months after therapy ends. Cure is defined as epithelialization of lesions, no enlargement greater than 50% in lesions, no appearance of new lesions, and/or negative parasitology. The antileishmanial mechanism of action is unknown and likely involves interaction with lipids, inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase, and apoptosislike cell death. Miltefosine is contraindicated in pregnancy. The most common adverse reactions in patients include nausea (35.9%–41.7%), motion sickness (29.2%), headache (28.1%), and emesis (4.5%–27.5%). With the exception of headache, these adverse reactions can decrease with administration of food, fluids, and antiemetics. Potentially more serious but rarer adverse reactions include elevated serum creatinine (5%–25%) and transaminases (5%). Although our patients had mild hyperkalemia, it is not an established adverse reaction. However, renal injury has been reported.10
Conclusion
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is increasing in prevalence in the United States due to increased foreign travel. Providers should be familiar with the cutaneous presentation of leishmaniasis, even in areas of low prevalence, to limit the risk for mucocutaneous dissemination from infection with the subgenus Viannia. Prompt treatment is vital to ensuring the best prognosis, and first-line treatment with miltefosine should be strongly considered given its efficacy and tolerability.
- Babuadze G, Alvar J, Argaw D, et al. Epidemiology of visceral leishmaniasis in Georgia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2725.
- Leishmaniasis. World Health Organization website. https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/Leishmaniasis. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- McIlwee BE, Weis SE, Hosler GA. Incidence of endemic human cutaneous leishmaniasis in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1032-1039.
- Leishmaniasis. World Health Organization website. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis. Update March 2, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for DEET insect repellent use. https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/toolkit/DEET.pdf. Accessed September 20, 2020.
- Buescher MD, Rutledge LC, Wirtz RA, et al. The dose-persistence relationship of DEET against Aedes aegypti. Mosq News. 1983;43:364-366.
- Aronson N, Herwaldt BL, Libman M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:e202-e264.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Practical guide for specimen collection and reference diagnosis of leishmaniasis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/leishmaniasis/resources/pdf/cdc_diagnosis_guide_leishmaniasis_2016.pdf. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Visceral leishmaniasis. Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative website. https://www.dndi.org/diseases-projects/leishmaniasis/. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Impavido Medication Guide. Food and Drug Administration Web site. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/204684s000lbl.pdf. Revised March 2014. Accessed May 18, 2020.
- Babuadze G, Alvar J, Argaw D, et al. Epidemiology of visceral leishmaniasis in Georgia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2725.
- Leishmaniasis. World Health Organization website. https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/Leishmaniasis. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- McIlwee BE, Weis SE, Hosler GA. Incidence of endemic human cutaneous leishmaniasis in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1032-1039.
- Leishmaniasis. World Health Organization website. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis. Update March 2, 2020. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidelines for DEET insect repellent use. https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/toolkit/DEET.pdf. Accessed September 20, 2020.
- Buescher MD, Rutledge LC, Wirtz RA, et al. The dose-persistence relationship of DEET against Aedes aegypti. Mosq News. 1983;43:364-366.
- Aronson N, Herwaldt BL, Libman M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of leishmaniasis: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (ASTMH). Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:e202-e264.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Practical guide for specimen collection and reference diagnosis of leishmaniasis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/leishmaniasis/resources/pdf/cdc_diagnosis_guide_leishmaniasis_2016.pdf. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Visceral leishmaniasis. Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative website. https://www.dndi.org/diseases-projects/leishmaniasis/. Accessed September 15, 2020.
- Impavido Medication Guide. Food and Drug Administration Web site. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/204684s000lbl.pdf. Revised March 2014. Accessed May 18, 2020.
Practice Points
- Avoiding phlebotomine sand fly vector bites is the most effective way to prevent leishmaniasis.
- Prompt diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania species that have potential for mucocutaneous spread are key to limiting morbidity and mortality.
- Partnering with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is critical for timely diagnosis.
- Miltefosine should be considered as a first-line agent for cutaneous leishmaniasis given its efficacy, tolerability, and ease of administration.