User login
The vaping lung disease outbreak continues, but according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, it may have peaked and the number of new hospitalized cases reported to the CDC may be decreasing.
In the Dec. 6, 2019, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, the CDC has updated information about cases of e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI): As of Dec. 3, there have been 2,291 cases reported from all 50 states, Washington, D.C., and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). A total of 48 deaths have been confirmed in 25 states and Washington, D.C., the CDC reported.
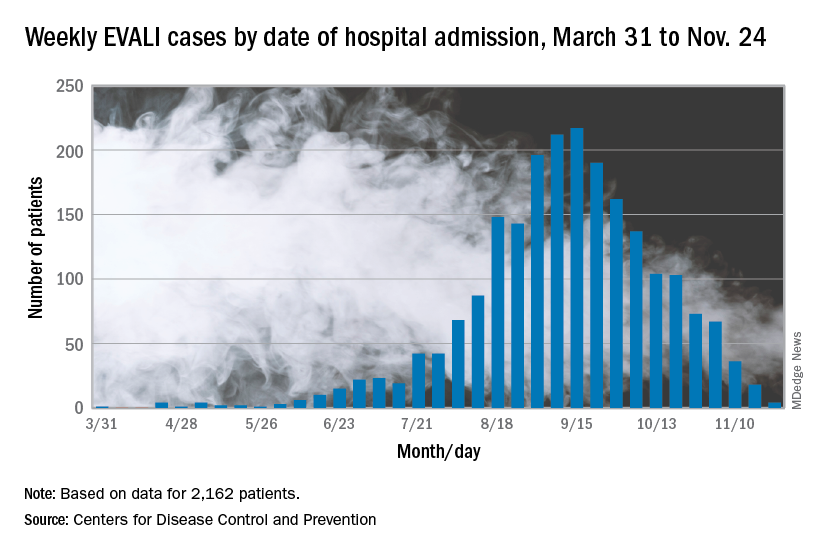
The largest number of weekly hospitalized cases occurred during the week of Sept. 15, 2019; since then, hospitalized cases have steadily declined. “Among all hospitalized EVALI patients reported to CDC weekly, the percentage of recent cases (patients hospitalized within the preceding 3 weeks) declined from 58% reported November 12 to 30% reported December 3,” the report stated.
About 80%of hospitalized EVALI patients reported using tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)–containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products. “Dank Vapes,” counterfeit THC-containing products of unknown origin, were the most commonly reported THC-containing branded products used. Dank Vapes were used by 56% of hospitalized EVALI patients nationwide, followed by TKO brand (15%), Smart Cart (13%), and Rove (12%).
Of EVALI patients for whom data were available, 67% were male, and the median age was 24 years (range, 13-77 years); 78% were aged under 35 years and 16% were under 18 years. About 75% of EVALI patients were non-Hispanic white and 16% were Hispanic. Among the 48 deaths, 54% of patients were male, and the median age was 52 years (range, 17-75 years).
CDC research on EVALI continues to be limited by the self-reported data, lack of data on substances used, missing data, loss to follow-up, and reporting lags, but the intensive investigation and data collection is ongoing.
The report concludes: “While the investigation continues, persons should consider refraining from the use of all e-cigarette, or vaping, products. Adults using e-cigarette, or vaping, products to quit smoking should not return to smoking cigarettes; they should weigh all risks and benefits and consider using [Food and Drug Administration]–approved cessation medications. Adults who continue to use e-cigarette, or vaping, products should carefully monitor themselves for symptoms and see a health care provider immediately if they develop symptoms similar to those reported in this outbreak. Irrespective of the ongoing investigation, e-cigarette, or vaping, products should never be used by youths, young adults or pregnant women.”
Information on the current investigation, reporting of cases, and other resources can be found on the CDC website.
SOURCE: Lozier MJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Dec 6. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6849e1.
The vaping lung disease outbreak continues, but according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, it may have peaked and the number of new hospitalized cases reported to the CDC may be decreasing.
In the Dec. 6, 2019, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, the CDC has updated information about cases of e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI): As of Dec. 3, there have been 2,291 cases reported from all 50 states, Washington, D.C., and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). A total of 48 deaths have been confirmed in 25 states and Washington, D.C., the CDC reported.
The largest number of weekly hospitalized cases occurred during the week of Sept. 15, 2019; since then, hospitalized cases have steadily declined. “Among all hospitalized EVALI patients reported to CDC weekly, the percentage of recent cases (patients hospitalized within the preceding 3 weeks) declined from 58% reported November 12 to 30% reported December 3,” the report stated.
About 80%of hospitalized EVALI patients reported using tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)–containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products. “Dank Vapes,” counterfeit THC-containing products of unknown origin, were the most commonly reported THC-containing branded products used. Dank Vapes were used by 56% of hospitalized EVALI patients nationwide, followed by TKO brand (15%), Smart Cart (13%), and Rove (12%).
Of EVALI patients for whom data were available, 67% were male, and the median age was 24 years (range, 13-77 years); 78% were aged under 35 years and 16% were under 18 years. About 75% of EVALI patients were non-Hispanic white and 16% were Hispanic. Among the 48 deaths, 54% of patients were male, and the median age was 52 years (range, 17-75 years).

CDC research on EVALI continues to be limited by the self-reported data, lack of data on substances used, missing data, loss to follow-up, and reporting lags, but the intensive investigation and data collection is ongoing.
The report concludes: “While the investigation continues, persons should consider refraining from the use of all e-cigarette, or vaping, products. Adults using e-cigarette, or vaping, products to quit smoking should not return to smoking cigarettes; they should weigh all risks and benefits and consider using [Food and Drug Administration]–approved cessation medications. Adults who continue to use e-cigarette, or vaping, products should carefully monitor themselves for symptoms and see a health care provider immediately if they develop symptoms similar to those reported in this outbreak. Irrespective of the ongoing investigation, e-cigarette, or vaping, products should never be used by youths, young adults or pregnant women.”
Information on the current investigation, reporting of cases, and other resources can be found on the CDC website.
SOURCE: Lozier MJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Dec 6. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6849e1.
The vaping lung disease outbreak continues, but according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, it may have peaked and the number of new hospitalized cases reported to the CDC may be decreasing.
In the Dec. 6, 2019, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, the CDC has updated information about cases of e-cigarette, or vaping, product use–associated lung injury (EVALI): As of Dec. 3, there have been 2,291 cases reported from all 50 states, Washington, D.C., and two U.S. territories (Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands). A total of 48 deaths have been confirmed in 25 states and Washington, D.C., the CDC reported.
The largest number of weekly hospitalized cases occurred during the week of Sept. 15, 2019; since then, hospitalized cases have steadily declined. “Among all hospitalized EVALI patients reported to CDC weekly, the percentage of recent cases (patients hospitalized within the preceding 3 weeks) declined from 58% reported November 12 to 30% reported December 3,” the report stated.
About 80%of hospitalized EVALI patients reported using tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)–containing e-cigarette, or vaping, products. “Dank Vapes,” counterfeit THC-containing products of unknown origin, were the most commonly reported THC-containing branded products used. Dank Vapes were used by 56% of hospitalized EVALI patients nationwide, followed by TKO brand (15%), Smart Cart (13%), and Rove (12%).
Of EVALI patients for whom data were available, 67% were male, and the median age was 24 years (range, 13-77 years); 78% were aged under 35 years and 16% were under 18 years. About 75% of EVALI patients were non-Hispanic white and 16% were Hispanic. Among the 48 deaths, 54% of patients were male, and the median age was 52 years (range, 17-75 years).

CDC research on EVALI continues to be limited by the self-reported data, lack of data on substances used, missing data, loss to follow-up, and reporting lags, but the intensive investigation and data collection is ongoing.
The report concludes: “While the investigation continues, persons should consider refraining from the use of all e-cigarette, or vaping, products. Adults using e-cigarette, or vaping, products to quit smoking should not return to smoking cigarettes; they should weigh all risks and benefits and consider using [Food and Drug Administration]–approved cessation medications. Adults who continue to use e-cigarette, or vaping, products should carefully monitor themselves for symptoms and see a health care provider immediately if they develop symptoms similar to those reported in this outbreak. Irrespective of the ongoing investigation, e-cigarette, or vaping, products should never be used by youths, young adults or pregnant women.”
Information on the current investigation, reporting of cases, and other resources can be found on the CDC website.
SOURCE: Lozier MJ et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019 Dec 6. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6849e1.
FROM THE MMWR

