User login
Summer officially began June 21, 2019, but many of your patients already may have departed or will soon be headed to international destinations. Reasons for travel are as variable as their destinations and include but are not limited to family vacations, mission trips, study abroad, parental job relocation, and visiting friends and relatives. The majority of the trips are planned at least 3 months in advance; however, for many travelers and their parents, they suddenly get an aha moment and realize there is/are specific vaccines required to obtain a visa or entry to their final destination. Unfortunately, too much emphasis is focused on required vaccines. The well-informed traveler knows that they may be exposed to multiple diseases and many are vaccine preventable.
The accompanying table lists vaccines traditionally considered to be travel vaccines. Several require multiple doses administered over 21-28 days to provide protection. Others such as cholera and yellow fever must be completed at least 10 days prior to departure to be effective. Typhoid has two formulations: The oral and injectable typhoid vaccines should be completed 1 and 2 weeks, respectively, prior to travel. Several vaccines have age limitations. Routine immunization of all infants against hepatitis A was recommended in 2006. Depending on your region, there may be adolescents who have not been immunized. Fortunately, hepatitis A vaccine works immediately.
One of the challenges you face is identifying someone in your area that provides travel medicine advice and immunizations to children and adolescents. Most children and teens travel with their parents, but today many adolescents travel independently with organized groups. Most of the vaccines listed are not routinely administered at your office, yet you most likely will be the first call a parent makes seeking travel advice.
Let me tell you about a few vaccines in particular.
Japanese encephalitis
This is most common cause of encephalitis in Asia and parts of the western Pacific. Risk generally is limited to rural agricultural areas where the causative virus is transmitted by a mosquito. Fatality rates are 20%-30%. Among survivors, 30%-50% have significant neurologic, cognitive, and psychiatric sequelae. Candidates for this vaccine are long-term travelers and short-term travelers with extensive outdoor rural activities.
Meningococcal conjugate vaccines (MCV4)
All travelers to the Hajj Pilgrimage (Aug. 9-14, 2019) and/or Umrah must show proof of immunization. Vaccine must be received at least 10 days prior to and no greater than 5 years prior to arrival to Saudi Arabia. Conjugate vaccine must clearly be documented for validity of 5 years. For all health entry requirements, go to www.moh.gov.sa/en/hajj/pages/healthregulations.aspx.
Measles
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends all infants 6-11 months old receive one dose of MMR prior to international travel regardless of the destination. This should be followed by two additional countable doses. All persons at least 12 months of age and born after 1956 should receive two doses of MMR at least 28 days apart prior to international travel.
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease endemic in more than 150 countries with approximately 60,000 fatal cases worldwide each year. Asia and Africa are the areas with the highest risk of exposure, and dogs are the principal hosts. Human rabies is almost always fatal once symptoms develop. Preexposure vaccine is recommended for persons with prolonged and/or remote travel to countries where rabies immunoglobulin is unavailable and the occurrence of animal rabies is high. Post exposure vaccination on days 0 and 3 still would be required.*
Typhoid
A bacterial infection caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi and Paratyphi manifests with fever, headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation. When bacteremia occurs, it usually is referred to as enteric fever. It is acquired by consumption of food/water contaminated with human feces. Highest risk areas include Africa, Southern Asia, and Southeast Asia
Yellow fever
Risk is limited to sub-Saharan Africa and the tropical areas of South America. It is transmitted by the bite of an infected mosquito. The vaccine is required for entry into at least 16 countries. In a country where yellow fever is present, persons transiting through for more than 12 hours to reach their final destination may actually cause a change in the entry requirements for the destination country. For example, travel from the United States to Tanzania requires no yellow fever vaccine while travel from the United States to Nairobi (more than 12 hours) to Tanzania requires yellow fever vaccine for entry into Tanzania. Travel sequence and duration is extremely important. Check the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention yellow fever site and/or the consulate for the most up-to-date yellow fever vaccine requirements.
YF-Vax (yellow fever vaccine) produced by Sanofi Pasteur in the United States currently is unavailable. The company is building a new facility, and vaccine will not be available for the remainder of 2019. To assure vaccine for U.S. travelers, Stamaril, a yellow fever vaccine produced by Sanofi Pasteur in France has been made available at more than 250 sites nationwide. Because Stamaril is offered at a limited number of locations, persons in need of vaccine should not delay seeking it. Because of increased demand related to summer travel, travelers in some areas have reported delays of several weeks in scheduling an appointment. To locate a Stamaril site in your area, go to wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/search-for-stamaril-clinics.
There are several other diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks including malaria, dengue, Zika and rickettsial diseases. Vigilant use of mosquito repellents is a must. Prophylactic medication is available for only malaria and should be initiated prior to exposure. Frequency and duration depends on the medication selected.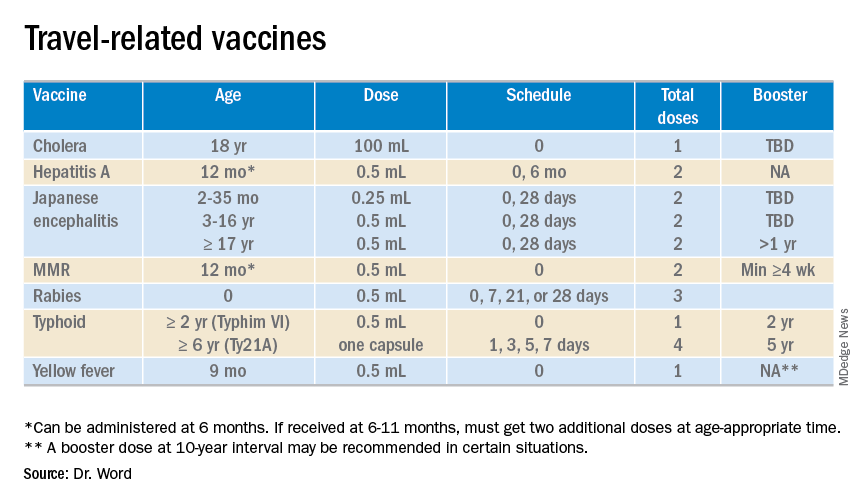
So how do you assist your patients?
Once you’ve identified a travel medicine facility in your area, encourage them to seek pretravel advice 4-6 weeks prior to international travel and make sure their routine immunizations are up to date. Generally, this is not an issue. One challenge is the early administration of MMR. While most practitioners know that early administration for international travel has been recommended for years, many office staff are accustomed to administration at only the 12 month and 4 year visit. When parents call requesting immunization, they often are informed that is it unnecessary and the appointment denied. This is a challenge, especially when coordination of administration of another live vaccine, such as yellow fever, is planned. Familiarizing all members of the health care team with current vaccine recommendations is critical.
For country-specific information, up-to-date travel alerts, and to locate a travel medicine clinic, visit www.cdc.gov/travel.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
*This article was updated 6/18/2019.
Summer officially began June 21, 2019, but many of your patients already may have departed or will soon be headed to international destinations. Reasons for travel are as variable as their destinations and include but are not limited to family vacations, mission trips, study abroad, parental job relocation, and visiting friends and relatives. The majority of the trips are planned at least 3 months in advance; however, for many travelers and their parents, they suddenly get an aha moment and realize there is/are specific vaccines required to obtain a visa or entry to their final destination. Unfortunately, too much emphasis is focused on required vaccines. The well-informed traveler knows that they may be exposed to multiple diseases and many are vaccine preventable.
The accompanying table lists vaccines traditionally considered to be travel vaccines. Several require multiple doses administered over 21-28 days to provide protection. Others such as cholera and yellow fever must be completed at least 10 days prior to departure to be effective. Typhoid has two formulations: The oral and injectable typhoid vaccines should be completed 1 and 2 weeks, respectively, prior to travel. Several vaccines have age limitations. Routine immunization of all infants against hepatitis A was recommended in 2006. Depending on your region, there may be adolescents who have not been immunized. Fortunately, hepatitis A vaccine works immediately.
One of the challenges you face is identifying someone in your area that provides travel medicine advice and immunizations to children and adolescents. Most children and teens travel with their parents, but today many adolescents travel independently with organized groups. Most of the vaccines listed are not routinely administered at your office, yet you most likely will be the first call a parent makes seeking travel advice.
Let me tell you about a few vaccines in particular.
Japanese encephalitis
This is most common cause of encephalitis in Asia and parts of the western Pacific. Risk generally is limited to rural agricultural areas where the causative virus is transmitted by a mosquito. Fatality rates are 20%-30%. Among survivors, 30%-50% have significant neurologic, cognitive, and psychiatric sequelae. Candidates for this vaccine are long-term travelers and short-term travelers with extensive outdoor rural activities.
Meningococcal conjugate vaccines (MCV4)
All travelers to the Hajj Pilgrimage (Aug. 9-14, 2019) and/or Umrah must show proof of immunization. Vaccine must be received at least 10 days prior to and no greater than 5 years prior to arrival to Saudi Arabia. Conjugate vaccine must clearly be documented for validity of 5 years. For all health entry requirements, go to www.moh.gov.sa/en/hajj/pages/healthregulations.aspx.
Measles
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends all infants 6-11 months old receive one dose of MMR prior to international travel regardless of the destination. This should be followed by two additional countable doses. All persons at least 12 months of age and born after 1956 should receive two doses of MMR at least 28 days apart prior to international travel.
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease endemic in more than 150 countries with approximately 60,000 fatal cases worldwide each year. Asia and Africa are the areas with the highest risk of exposure, and dogs are the principal hosts. Human rabies is almost always fatal once symptoms develop. Preexposure vaccine is recommended for persons with prolonged and/or remote travel to countries where rabies immunoglobulin is unavailable and the occurrence of animal rabies is high. Post exposure vaccination on days 0 and 3 still would be required.*
Typhoid
A bacterial infection caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi and Paratyphi manifests with fever, headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation. When bacteremia occurs, it usually is referred to as enteric fever. It is acquired by consumption of food/water contaminated with human feces. Highest risk areas include Africa, Southern Asia, and Southeast Asia
Yellow fever
Risk is limited to sub-Saharan Africa and the tropical areas of South America. It is transmitted by the bite of an infected mosquito. The vaccine is required for entry into at least 16 countries. In a country where yellow fever is present, persons transiting through for more than 12 hours to reach their final destination may actually cause a change in the entry requirements for the destination country. For example, travel from the United States to Tanzania requires no yellow fever vaccine while travel from the United States to Nairobi (more than 12 hours) to Tanzania requires yellow fever vaccine for entry into Tanzania. Travel sequence and duration is extremely important. Check the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention yellow fever site and/or the consulate for the most up-to-date yellow fever vaccine requirements.
YF-Vax (yellow fever vaccine) produced by Sanofi Pasteur in the United States currently is unavailable. The company is building a new facility, and vaccine will not be available for the remainder of 2019. To assure vaccine for U.S. travelers, Stamaril, a yellow fever vaccine produced by Sanofi Pasteur in France has been made available at more than 250 sites nationwide. Because Stamaril is offered at a limited number of locations, persons in need of vaccine should not delay seeking it. Because of increased demand related to summer travel, travelers in some areas have reported delays of several weeks in scheduling an appointment. To locate a Stamaril site in your area, go to wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/search-for-stamaril-clinics.
There are several other diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks including malaria, dengue, Zika and rickettsial diseases. Vigilant use of mosquito repellents is a must. Prophylactic medication is available for only malaria and should be initiated prior to exposure. Frequency and duration depends on the medication selected.
So how do you assist your patients?
Once you’ve identified a travel medicine facility in your area, encourage them to seek pretravel advice 4-6 weeks prior to international travel and make sure their routine immunizations are up to date. Generally, this is not an issue. One challenge is the early administration of MMR. While most practitioners know that early administration for international travel has been recommended for years, many office staff are accustomed to administration at only the 12 month and 4 year visit. When parents call requesting immunization, they often are informed that is it unnecessary and the appointment denied. This is a challenge, especially when coordination of administration of another live vaccine, such as yellow fever, is planned. Familiarizing all members of the health care team with current vaccine recommendations is critical.
For country-specific information, up-to-date travel alerts, and to locate a travel medicine clinic, visit www.cdc.gov/travel.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
*This article was updated 6/18/2019.
Summer officially began June 21, 2019, but many of your patients already may have departed or will soon be headed to international destinations. Reasons for travel are as variable as their destinations and include but are not limited to family vacations, mission trips, study abroad, parental job relocation, and visiting friends and relatives. The majority of the trips are planned at least 3 months in advance; however, for many travelers and their parents, they suddenly get an aha moment and realize there is/are specific vaccines required to obtain a visa or entry to their final destination. Unfortunately, too much emphasis is focused on required vaccines. The well-informed traveler knows that they may be exposed to multiple diseases and many are vaccine preventable.
The accompanying table lists vaccines traditionally considered to be travel vaccines. Several require multiple doses administered over 21-28 days to provide protection. Others such as cholera and yellow fever must be completed at least 10 days prior to departure to be effective. Typhoid has two formulations: The oral and injectable typhoid vaccines should be completed 1 and 2 weeks, respectively, prior to travel. Several vaccines have age limitations. Routine immunization of all infants against hepatitis A was recommended in 2006. Depending on your region, there may be adolescents who have not been immunized. Fortunately, hepatitis A vaccine works immediately.
One of the challenges you face is identifying someone in your area that provides travel medicine advice and immunizations to children and adolescents. Most children and teens travel with their parents, but today many adolescents travel independently with organized groups. Most of the vaccines listed are not routinely administered at your office, yet you most likely will be the first call a parent makes seeking travel advice.
Let me tell you about a few vaccines in particular.
Japanese encephalitis
This is most common cause of encephalitis in Asia and parts of the western Pacific. Risk generally is limited to rural agricultural areas where the causative virus is transmitted by a mosquito. Fatality rates are 20%-30%. Among survivors, 30%-50% have significant neurologic, cognitive, and psychiatric sequelae. Candidates for this vaccine are long-term travelers and short-term travelers with extensive outdoor rural activities.
Meningococcal conjugate vaccines (MCV4)
All travelers to the Hajj Pilgrimage (Aug. 9-14, 2019) and/or Umrah must show proof of immunization. Vaccine must be received at least 10 days prior to and no greater than 5 years prior to arrival to Saudi Arabia. Conjugate vaccine must clearly be documented for validity of 5 years. For all health entry requirements, go to www.moh.gov.sa/en/hajj/pages/healthregulations.aspx.
Measles
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends all infants 6-11 months old receive one dose of MMR prior to international travel regardless of the destination. This should be followed by two additional countable doses. All persons at least 12 months of age and born after 1956 should receive two doses of MMR at least 28 days apart prior to international travel.
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease endemic in more than 150 countries with approximately 60,000 fatal cases worldwide each year. Asia and Africa are the areas with the highest risk of exposure, and dogs are the principal hosts. Human rabies is almost always fatal once symptoms develop. Preexposure vaccine is recommended for persons with prolonged and/or remote travel to countries where rabies immunoglobulin is unavailable and the occurrence of animal rabies is high. Post exposure vaccination on days 0 and 3 still would be required.*
Typhoid
A bacterial infection caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi and Paratyphi manifests with fever, headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation. When bacteremia occurs, it usually is referred to as enteric fever. It is acquired by consumption of food/water contaminated with human feces. Highest risk areas include Africa, Southern Asia, and Southeast Asia
Yellow fever
Risk is limited to sub-Saharan Africa and the tropical areas of South America. It is transmitted by the bite of an infected mosquito. The vaccine is required for entry into at least 16 countries. In a country where yellow fever is present, persons transiting through for more than 12 hours to reach their final destination may actually cause a change in the entry requirements for the destination country. For example, travel from the United States to Tanzania requires no yellow fever vaccine while travel from the United States to Nairobi (more than 12 hours) to Tanzania requires yellow fever vaccine for entry into Tanzania. Travel sequence and duration is extremely important. Check the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention yellow fever site and/or the consulate for the most up-to-date yellow fever vaccine requirements.
YF-Vax (yellow fever vaccine) produced by Sanofi Pasteur in the United States currently is unavailable. The company is building a new facility, and vaccine will not be available for the remainder of 2019. To assure vaccine for U.S. travelers, Stamaril, a yellow fever vaccine produced by Sanofi Pasteur in France has been made available at more than 250 sites nationwide. Because Stamaril is offered at a limited number of locations, persons in need of vaccine should not delay seeking it. Because of increased demand related to summer travel, travelers in some areas have reported delays of several weeks in scheduling an appointment. To locate a Stamaril site in your area, go to wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/search-for-stamaril-clinics.
There are several other diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks including malaria, dengue, Zika and rickettsial diseases. Vigilant use of mosquito repellents is a must. Prophylactic medication is available for only malaria and should be initiated prior to exposure. Frequency and duration depends on the medication selected.
So how do you assist your patients?
Once you’ve identified a travel medicine facility in your area, encourage them to seek pretravel advice 4-6 weeks prior to international travel and make sure their routine immunizations are up to date. Generally, this is not an issue. One challenge is the early administration of MMR. While most practitioners know that early administration for international travel has been recommended for years, many office staff are accustomed to administration at only the 12 month and 4 year visit. When parents call requesting immunization, they often are informed that is it unnecessary and the appointment denied. This is a challenge, especially when coordination of administration of another live vaccine, such as yellow fever, is planned. Familiarizing all members of the health care team with current vaccine recommendations is critical.
For country-specific information, up-to-date travel alerts, and to locate a travel medicine clinic, visit www.cdc.gov/travel.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
*This article was updated 6/18/2019.


