User login
In patients with myocardial infarction and anemia, a “liberal” red blood cell transfusion strategy did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrent MI or death within 30 days, compared with a “restrictive” transfusion strategy, in the 3,500-patient MINT trial.
Jeffrey L. Carson, MD, from Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in a press briefing.
He presented the study in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, and it was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Whether to transfuse is an everyday decision faced by clinicians caring for patients with acute MI,” Dr. Carson said.
“We cannot claim that a liberal transfusion strategy is definitively superior based on our primary outcome,” he said, but “the 95% confidence interval is consistent with treatment effects corresponding to no difference between the two transfusion strategies and to a clinically relevant benefit with the liberal strategy.”
“In contrast to other trials in other settings,” such as anemia and cardiac surgery, Dr. Carson said, “the results suggest that a liberal transfusion strategy has the potential for clinical benefit with an acceptable risk of harm.”
“A liberal transfusion strategy may be the most prudent approach to transfusion in anemic patients with MI,” he added.
Not a home run
Others agreed with this interpretation. Martin B. Leon, MD, from Columbia University, New York, the study discussant in the press briefing, said the study “addresses a question that is common” in clinical practice. It was well conducted, and international (although most patients were in the United States and Canada), in a very broad group of patients, designed to make the results more generalizable. The 98% follow-up was extremely good, Dr. Leon added, and the trialists achieved their goal in that they did show a difference between the two transfusion strategies.
The number needed to treat was 40 to see a benefit in the combined outcome of death or recurrent MI at 30 days, Dr. Leon said. The P value for this was .07, “right on the edge” of statistical significance.
This study is “not a home run,” for the primary outcome, he noted; however, many of the outcomes tended to be in favor of a liberal transfusion strategy. Notably, cardiovascular death, which was not a specified outcome, was significantly lower in the group who received a liberal transfusion strategy.
Although a liberal transfusion strategy was “not definitely superior” in these patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Carson said, he thinks the trial will be interpreted as favoring a liberal transfusion strategy.
C. Michael Gibson, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and CEO of Harvard’s Baim and PERFUSE institutes for clinical research, voiced similar views.
“Given the lack of acute harm associated with liberal transfusion and the preponderance of evidence favoring liberal transfusion in the largest trial to date,” concluded Dr. Gibson, the assigned discussant at the session, “liberal transfusion appears to be a viable management strategy, particularly among patients with non-STEMI type 1 MI and as clinical judgment dictates.”
Only three small randomized controlled trials have compared transfusion thresholds in a total of 820 patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Gibson said, a point that the trial investigators also made. The results were inconsistent between trials: the CRIT trial (n = 45) favored a restrictive strategy, the MINT pilot study (n = 110) favored a liberal one, and the REALITY trial (n = 668) showed noninferiority of a restrictive strategy, compared with a liberal strategy in 30-day MACE.
The MINT trial was four times larger than all prior studies combined. However, most outcomes were negative or of borderline significance for benefit.
Cardiac death was more common in the restrictive group at 5.5% than the liberal group at 3.2% (risk ratio, 1.74, 95% CI, 1.26-2.40), but this was nonadjudicated, and not designated as a primary, secondary, or tertiary outcome – which the researchers also noted. Fewer than half of the deaths were classified as cardiac, which was “odd,” Dr. Gibson observed.
A restrictive transfusion strategy was associated with increased events among participants with type 1 MI (RR, 1.32, 95% CI, 1.04-1.67), he noted.
Study strengths included that 45.5% of participants were women, Dr. Gibson said. Limitations included that the trial was “somewhat underpowered.” Also, even in the restrictive group, participants received a mean of 0.7 units of packed red blood cells.
Adherence to the 10 g/dL threshold in the liberal transfusion group was moderate (86.3% at hospital discharge), which the researchers acknowledged. They noted that this was frequently caused by clinical discretion, such as concern about fluid overload, and to the timing of hospital discharge. In addition, long-term potential for harm (microchimerism) is not known.
“There was a consistent nonsignificant acute benefit for liberal transfusion and a nominal reduction in CV mortality and improved outcomes in patients with type 1 MI in exploratory analyses, in a trial that ended up underpowered,” Dr. Gibson summarized. “Long-term follow up would be helpful to evaluate chronic outcomes.”
This is a very well-conducted, high-quality, important study that will be considered a landmark trial, C. David Mazer, MD, University of Toronto and St. Michael’s Hospital, also in Toronto, said in an interview.
Unfortunately, “it was not as definitive as hoped for,” Dr. Mazer lamented. Nevertheless, “I think people may interpret it as providing support for a liberal transfusion strategy” in patients with anemia and MI, he said.
Dr. Mazer, who was not involved with this research, was a principal investigator on the TRICS-3 trial, which disputed a liberal RBC transfusion strategy in patients with anemia undergoing cardiac surgery, as previously reported.
The “Red Blood Cell Transfusion: 2023 AABB International Guidelines,” led by Dr. Carson and published in JAMA, recommend a restrictive strategy in stable patients, although these guidelines did not include the current study, Dr. Mazer observed.
In the REALITY trial, there were fewer major adverse cardiac events (MACE) events in the restrictive strategy, he noted.
MINT can be viewed as comparing a high versus low hemoglobin threshold. “It is possible that the best is in between,” he said.
Dr. Mazer also noted that MINT may have achieved significance if it was designed with a larger enrollment and a higher power (for example, 90% instead of 80%) to detect between-group difference for the primary outcome.
Study rationale, design, and findings
Anemia, or low RBC count, is common in patients with MI, Dr. Carson noted. A normal hemoglobin is 13 g/dL in men and 12 g/dL in women. Administering a packed RBC transfusion only when a patient’s hemoglobin falls below 7 or 8 g/dL has been widely adopted, but it is unclear if patients with acute MI may benefit from a higher hemoglobin level.
“Blood transfusion may decrease ischemic injury by improving oxygen delivery to myocardial tissues and reduce the risk of reinfarction or death,” the researchers wrote. “Alternatively, administering more blood could result in more frequent heart failure from fluid overload, infection from immunosuppression, thrombosis from higher viscosity, and inflammation.”
From 2017 to 2023, investigators enrolled 3,504 adults aged 18 and older at 144 sites in the United States (2,157 patients), Canada (885), France (323), Brazil (105), New Zealand (25), and Australia (9).
The participants had ST-elevation or non–ST-elevation MI and hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL within 24 hours. Patients with type 1 (atherosclerotic plaque disruption), type 2 (supply-demand mismatch without atherothrombotic plaque disruption), type 4b, or type 4c MI were eligible.
They were randomly assigned to receive:
- A ‘restrictive’ transfusion strategy (1,749 patients): Transfusion was permitted but not required when a patient’s hemoglobin was less than 8 g/dL and was strongly recommended when it was less than 7 g/dL or when anginal symptoms were not controlled with medications.
- A ‘liberal’ transfusion strategy (1,755 patients): One unit of RBCs was administered after randomization, and RBCs were transfused to maintain hemoglobin 10 g/dL or higher until hospital discharge or 30 days.
The patients had a mean age of 72 years and 46% were women. More than three-quarters (78%) were White and 14% were Black. They had frequent coexisting illnesses, about a third had a history of MI, percutaneous coronary intervention, or heart failure; 14% were on a ventilator and 12% had renal dialysis. The median duration of hospitalization was 5 days in the two groups.
At baseline, the mean hemoglobin was 8.6 g/dL in both groups. At days 1, 2, and 3, the mean hemoglobin was 8.8, 8.9, and 8.9 g/dL, respectively, in the restrictive transfusion group, and 10.1, 10.4, and 10.5 g/dL, respectively, in the liberal transfusion group.
The mean number of transfused blood units was 0.7 units in the restrictive strategy group and 2.5 units in the liberal strategy group, roughly a 3.5-fold difference.
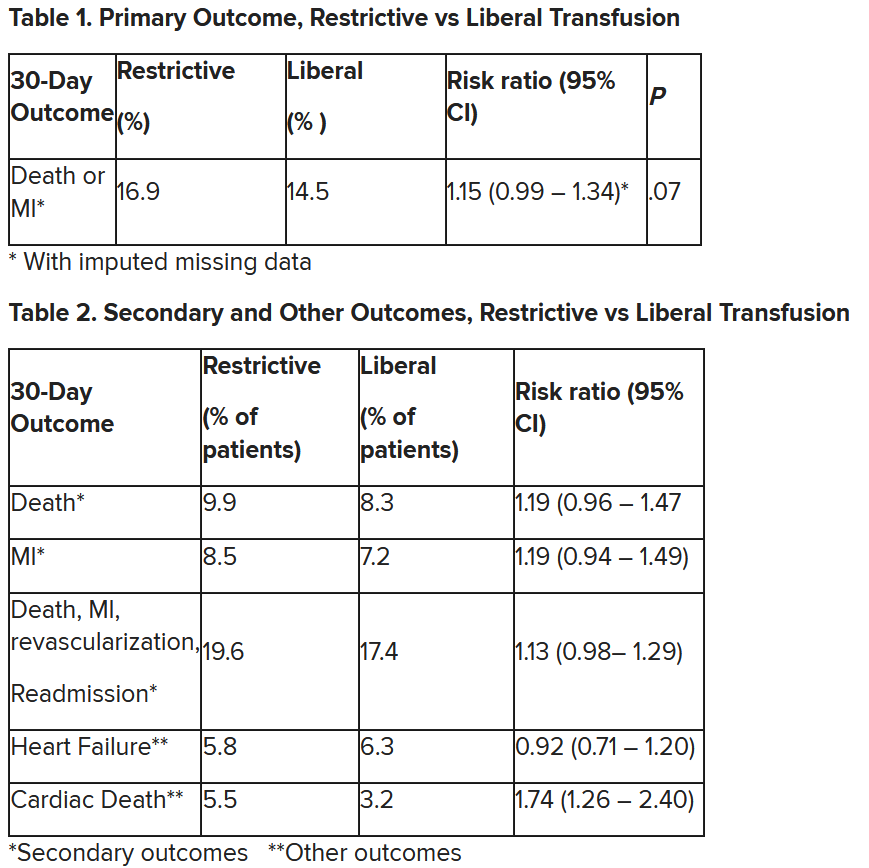
After adjustment for site and incomplete follow-up in 57 patients (20 with the restrictive strategy and 37 with the liberal strategy), the estimated RR for the primary outcome in the restrictive group versus the liberal group was 1.15 (P = .07).
“We observed that the 95% confidence interval contains values that suggest a clinical benefit for the liberal transfusion strategy and does not include values that suggest a benefit for the more restrictive transfusion strategy,” the researchers wrote. Heart failure and other safety outcomes were comparable in the two groups.
The trial was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the Canadian Blood Services and Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Circulatory and Respiratory Health. Dr. Carson, Dr. Leon, Dr. Gibson, and Dr. Mazer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients with myocardial infarction and anemia, a “liberal” red blood cell transfusion strategy did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrent MI or death within 30 days, compared with a “restrictive” transfusion strategy, in the 3,500-patient MINT trial.
Jeffrey L. Carson, MD, from Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in a press briefing.
He presented the study in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, and it was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Whether to transfuse is an everyday decision faced by clinicians caring for patients with acute MI,” Dr. Carson said.
“We cannot claim that a liberal transfusion strategy is definitively superior based on our primary outcome,” he said, but “the 95% confidence interval is consistent with treatment effects corresponding to no difference between the two transfusion strategies and to a clinically relevant benefit with the liberal strategy.”
“In contrast to other trials in other settings,” such as anemia and cardiac surgery, Dr. Carson said, “the results suggest that a liberal transfusion strategy has the potential for clinical benefit with an acceptable risk of harm.”
“A liberal transfusion strategy may be the most prudent approach to transfusion in anemic patients with MI,” he added.
Not a home run
Others agreed with this interpretation. Martin B. Leon, MD, from Columbia University, New York, the study discussant in the press briefing, said the study “addresses a question that is common” in clinical practice. It was well conducted, and international (although most patients were in the United States and Canada), in a very broad group of patients, designed to make the results more generalizable. The 98% follow-up was extremely good, Dr. Leon added, and the trialists achieved their goal in that they did show a difference between the two transfusion strategies.
The number needed to treat was 40 to see a benefit in the combined outcome of death or recurrent MI at 30 days, Dr. Leon said. The P value for this was .07, “right on the edge” of statistical significance.
This study is “not a home run,” for the primary outcome, he noted; however, many of the outcomes tended to be in favor of a liberal transfusion strategy. Notably, cardiovascular death, which was not a specified outcome, was significantly lower in the group who received a liberal transfusion strategy.
Although a liberal transfusion strategy was “not definitely superior” in these patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Carson said, he thinks the trial will be interpreted as favoring a liberal transfusion strategy.
C. Michael Gibson, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and CEO of Harvard’s Baim and PERFUSE institutes for clinical research, voiced similar views.
“Given the lack of acute harm associated with liberal transfusion and the preponderance of evidence favoring liberal transfusion in the largest trial to date,” concluded Dr. Gibson, the assigned discussant at the session, “liberal transfusion appears to be a viable management strategy, particularly among patients with non-STEMI type 1 MI and as clinical judgment dictates.”
Only three small randomized controlled trials have compared transfusion thresholds in a total of 820 patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Gibson said, a point that the trial investigators also made. The results were inconsistent between trials: the CRIT trial (n = 45) favored a restrictive strategy, the MINT pilot study (n = 110) favored a liberal one, and the REALITY trial (n = 668) showed noninferiority of a restrictive strategy, compared with a liberal strategy in 30-day MACE.
The MINT trial was four times larger than all prior studies combined. However, most outcomes were negative or of borderline significance for benefit.
Cardiac death was more common in the restrictive group at 5.5% than the liberal group at 3.2% (risk ratio, 1.74, 95% CI, 1.26-2.40), but this was nonadjudicated, and not designated as a primary, secondary, or tertiary outcome – which the researchers also noted. Fewer than half of the deaths were classified as cardiac, which was “odd,” Dr. Gibson observed.
A restrictive transfusion strategy was associated with increased events among participants with type 1 MI (RR, 1.32, 95% CI, 1.04-1.67), he noted.
Study strengths included that 45.5% of participants were women, Dr. Gibson said. Limitations included that the trial was “somewhat underpowered.” Also, even in the restrictive group, participants received a mean of 0.7 units of packed red blood cells.
Adherence to the 10 g/dL threshold in the liberal transfusion group was moderate (86.3% at hospital discharge), which the researchers acknowledged. They noted that this was frequently caused by clinical discretion, such as concern about fluid overload, and to the timing of hospital discharge. In addition, long-term potential for harm (microchimerism) is not known.
“There was a consistent nonsignificant acute benefit for liberal transfusion and a nominal reduction in CV mortality and improved outcomes in patients with type 1 MI in exploratory analyses, in a trial that ended up underpowered,” Dr. Gibson summarized. “Long-term follow up would be helpful to evaluate chronic outcomes.”
This is a very well-conducted, high-quality, important study that will be considered a landmark trial, C. David Mazer, MD, University of Toronto and St. Michael’s Hospital, also in Toronto, said in an interview.
Unfortunately, “it was not as definitive as hoped for,” Dr. Mazer lamented. Nevertheless, “I think people may interpret it as providing support for a liberal transfusion strategy” in patients with anemia and MI, he said.
Dr. Mazer, who was not involved with this research, was a principal investigator on the TRICS-3 trial, which disputed a liberal RBC transfusion strategy in patients with anemia undergoing cardiac surgery, as previously reported.
The “Red Blood Cell Transfusion: 2023 AABB International Guidelines,” led by Dr. Carson and published in JAMA, recommend a restrictive strategy in stable patients, although these guidelines did not include the current study, Dr. Mazer observed.
In the REALITY trial, there were fewer major adverse cardiac events (MACE) events in the restrictive strategy, he noted.
MINT can be viewed as comparing a high versus low hemoglobin threshold. “It is possible that the best is in between,” he said.
Dr. Mazer also noted that MINT may have achieved significance if it was designed with a larger enrollment and a higher power (for example, 90% instead of 80%) to detect between-group difference for the primary outcome.
Study rationale, design, and findings
Anemia, or low RBC count, is common in patients with MI, Dr. Carson noted. A normal hemoglobin is 13 g/dL in men and 12 g/dL in women. Administering a packed RBC transfusion only when a patient’s hemoglobin falls below 7 or 8 g/dL has been widely adopted, but it is unclear if patients with acute MI may benefit from a higher hemoglobin level.
“Blood transfusion may decrease ischemic injury by improving oxygen delivery to myocardial tissues and reduce the risk of reinfarction or death,” the researchers wrote. “Alternatively, administering more blood could result in more frequent heart failure from fluid overload, infection from immunosuppression, thrombosis from higher viscosity, and inflammation.”
From 2017 to 2023, investigators enrolled 3,504 adults aged 18 and older at 144 sites in the United States (2,157 patients), Canada (885), France (323), Brazil (105), New Zealand (25), and Australia (9).
The participants had ST-elevation or non–ST-elevation MI and hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL within 24 hours. Patients with type 1 (atherosclerotic plaque disruption), type 2 (supply-demand mismatch without atherothrombotic plaque disruption), type 4b, or type 4c MI were eligible.
They were randomly assigned to receive:
- A ‘restrictive’ transfusion strategy (1,749 patients): Transfusion was permitted but not required when a patient’s hemoglobin was less than 8 g/dL and was strongly recommended when it was less than 7 g/dL or when anginal symptoms were not controlled with medications.
- A ‘liberal’ transfusion strategy (1,755 patients): One unit of RBCs was administered after randomization, and RBCs were transfused to maintain hemoglobin 10 g/dL or higher until hospital discharge or 30 days.
The patients had a mean age of 72 years and 46% were women. More than three-quarters (78%) were White and 14% were Black. They had frequent coexisting illnesses, about a third had a history of MI, percutaneous coronary intervention, or heart failure; 14% were on a ventilator and 12% had renal dialysis. The median duration of hospitalization was 5 days in the two groups.
At baseline, the mean hemoglobin was 8.6 g/dL in both groups. At days 1, 2, and 3, the mean hemoglobin was 8.8, 8.9, and 8.9 g/dL, respectively, in the restrictive transfusion group, and 10.1, 10.4, and 10.5 g/dL, respectively, in the liberal transfusion group.
The mean number of transfused blood units was 0.7 units in the restrictive strategy group and 2.5 units in the liberal strategy group, roughly a 3.5-fold difference.
After adjustment for site and incomplete follow-up in 57 patients (20 with the restrictive strategy and 37 with the liberal strategy), the estimated RR for the primary outcome in the restrictive group versus the liberal group was 1.15 (P = .07).
“We observed that the 95% confidence interval contains values that suggest a clinical benefit for the liberal transfusion strategy and does not include values that suggest a benefit for the more restrictive transfusion strategy,” the researchers wrote. Heart failure and other safety outcomes were comparable in the two groups.
The trial was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the Canadian Blood Services and Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Circulatory and Respiratory Health. Dr. Carson, Dr. Leon, Dr. Gibson, and Dr. Mazer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In patients with myocardial infarction and anemia, a “liberal” red blood cell transfusion strategy did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrent MI or death within 30 days, compared with a “restrictive” transfusion strategy, in the 3,500-patient MINT trial.
Jeffrey L. Carson, MD, from Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J., said in a press briefing.
He presented the study in a late-breaking trial session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association, and it was simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Whether to transfuse is an everyday decision faced by clinicians caring for patients with acute MI,” Dr. Carson said.
“We cannot claim that a liberal transfusion strategy is definitively superior based on our primary outcome,” he said, but “the 95% confidence interval is consistent with treatment effects corresponding to no difference between the two transfusion strategies and to a clinically relevant benefit with the liberal strategy.”
“In contrast to other trials in other settings,” such as anemia and cardiac surgery, Dr. Carson said, “the results suggest that a liberal transfusion strategy has the potential for clinical benefit with an acceptable risk of harm.”
“A liberal transfusion strategy may be the most prudent approach to transfusion in anemic patients with MI,” he added.
Not a home run
Others agreed with this interpretation. Martin B. Leon, MD, from Columbia University, New York, the study discussant in the press briefing, said the study “addresses a question that is common” in clinical practice. It was well conducted, and international (although most patients were in the United States and Canada), in a very broad group of patients, designed to make the results more generalizable. The 98% follow-up was extremely good, Dr. Leon added, and the trialists achieved their goal in that they did show a difference between the two transfusion strategies.
The number needed to treat was 40 to see a benefit in the combined outcome of death or recurrent MI at 30 days, Dr. Leon said. The P value for this was .07, “right on the edge” of statistical significance.
This study is “not a home run,” for the primary outcome, he noted; however, many of the outcomes tended to be in favor of a liberal transfusion strategy. Notably, cardiovascular death, which was not a specified outcome, was significantly lower in the group who received a liberal transfusion strategy.
Although a liberal transfusion strategy was “not definitely superior” in these patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Carson said, he thinks the trial will be interpreted as favoring a liberal transfusion strategy.
C. Michael Gibson, MD, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and CEO of Harvard’s Baim and PERFUSE institutes for clinical research, voiced similar views.
“Given the lack of acute harm associated with liberal transfusion and the preponderance of evidence favoring liberal transfusion in the largest trial to date,” concluded Dr. Gibson, the assigned discussant at the session, “liberal transfusion appears to be a viable management strategy, particularly among patients with non-STEMI type 1 MI and as clinical judgment dictates.”
Only three small randomized controlled trials have compared transfusion thresholds in a total of 820 patients with MI and anemia, Dr. Gibson said, a point that the trial investigators also made. The results were inconsistent between trials: the CRIT trial (n = 45) favored a restrictive strategy, the MINT pilot study (n = 110) favored a liberal one, and the REALITY trial (n = 668) showed noninferiority of a restrictive strategy, compared with a liberal strategy in 30-day MACE.
The MINT trial was four times larger than all prior studies combined. However, most outcomes were negative or of borderline significance for benefit.
Cardiac death was more common in the restrictive group at 5.5% than the liberal group at 3.2% (risk ratio, 1.74, 95% CI, 1.26-2.40), but this was nonadjudicated, and not designated as a primary, secondary, or tertiary outcome – which the researchers also noted. Fewer than half of the deaths were classified as cardiac, which was “odd,” Dr. Gibson observed.
A restrictive transfusion strategy was associated with increased events among participants with type 1 MI (RR, 1.32, 95% CI, 1.04-1.67), he noted.
Study strengths included that 45.5% of participants were women, Dr. Gibson said. Limitations included that the trial was “somewhat underpowered.” Also, even in the restrictive group, participants received a mean of 0.7 units of packed red blood cells.
Adherence to the 10 g/dL threshold in the liberal transfusion group was moderate (86.3% at hospital discharge), which the researchers acknowledged. They noted that this was frequently caused by clinical discretion, such as concern about fluid overload, and to the timing of hospital discharge. In addition, long-term potential for harm (microchimerism) is not known.
“There was a consistent nonsignificant acute benefit for liberal transfusion and a nominal reduction in CV mortality and improved outcomes in patients with type 1 MI in exploratory analyses, in a trial that ended up underpowered,” Dr. Gibson summarized. “Long-term follow up would be helpful to evaluate chronic outcomes.”
This is a very well-conducted, high-quality, important study that will be considered a landmark trial, C. David Mazer, MD, University of Toronto and St. Michael’s Hospital, also in Toronto, said in an interview.
Unfortunately, “it was not as definitive as hoped for,” Dr. Mazer lamented. Nevertheless, “I think people may interpret it as providing support for a liberal transfusion strategy” in patients with anemia and MI, he said.
Dr. Mazer, who was not involved with this research, was a principal investigator on the TRICS-3 trial, which disputed a liberal RBC transfusion strategy in patients with anemia undergoing cardiac surgery, as previously reported.
The “Red Blood Cell Transfusion: 2023 AABB International Guidelines,” led by Dr. Carson and published in JAMA, recommend a restrictive strategy in stable patients, although these guidelines did not include the current study, Dr. Mazer observed.
In the REALITY trial, there were fewer major adverse cardiac events (MACE) events in the restrictive strategy, he noted.
MINT can be viewed as comparing a high versus low hemoglobin threshold. “It is possible that the best is in between,” he said.
Dr. Mazer also noted that MINT may have achieved significance if it was designed with a larger enrollment and a higher power (for example, 90% instead of 80%) to detect between-group difference for the primary outcome.
Study rationale, design, and findings
Anemia, or low RBC count, is common in patients with MI, Dr. Carson noted. A normal hemoglobin is 13 g/dL in men and 12 g/dL in women. Administering a packed RBC transfusion only when a patient’s hemoglobin falls below 7 or 8 g/dL has been widely adopted, but it is unclear if patients with acute MI may benefit from a higher hemoglobin level.
“Blood transfusion may decrease ischemic injury by improving oxygen delivery to myocardial tissues and reduce the risk of reinfarction or death,” the researchers wrote. “Alternatively, administering more blood could result in more frequent heart failure from fluid overload, infection from immunosuppression, thrombosis from higher viscosity, and inflammation.”
From 2017 to 2023, investigators enrolled 3,504 adults aged 18 and older at 144 sites in the United States (2,157 patients), Canada (885), France (323), Brazil (105), New Zealand (25), and Australia (9).
The participants had ST-elevation or non–ST-elevation MI and hemoglobin less than 10 g/dL within 24 hours. Patients with type 1 (atherosclerotic plaque disruption), type 2 (supply-demand mismatch without atherothrombotic plaque disruption), type 4b, or type 4c MI were eligible.
They were randomly assigned to receive:
- A ‘restrictive’ transfusion strategy (1,749 patients): Transfusion was permitted but not required when a patient’s hemoglobin was less than 8 g/dL and was strongly recommended when it was less than 7 g/dL or when anginal symptoms were not controlled with medications.
- A ‘liberal’ transfusion strategy (1,755 patients): One unit of RBCs was administered after randomization, and RBCs were transfused to maintain hemoglobin 10 g/dL or higher until hospital discharge or 30 days.
The patients had a mean age of 72 years and 46% were women. More than three-quarters (78%) were White and 14% were Black. They had frequent coexisting illnesses, about a third had a history of MI, percutaneous coronary intervention, or heart failure; 14% were on a ventilator and 12% had renal dialysis. The median duration of hospitalization was 5 days in the two groups.
At baseline, the mean hemoglobin was 8.6 g/dL in both groups. At days 1, 2, and 3, the mean hemoglobin was 8.8, 8.9, and 8.9 g/dL, respectively, in the restrictive transfusion group, and 10.1, 10.4, and 10.5 g/dL, respectively, in the liberal transfusion group.
The mean number of transfused blood units was 0.7 units in the restrictive strategy group and 2.5 units in the liberal strategy group, roughly a 3.5-fold difference.
After adjustment for site and incomplete follow-up in 57 patients (20 with the restrictive strategy and 37 with the liberal strategy), the estimated RR for the primary outcome in the restrictive group versus the liberal group was 1.15 (P = .07).
“We observed that the 95% confidence interval contains values that suggest a clinical benefit for the liberal transfusion strategy and does not include values that suggest a benefit for the more restrictive transfusion strategy,” the researchers wrote. Heart failure and other safety outcomes were comparable in the two groups.
The trial was supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and by the Canadian Blood Services and Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Circulatory and Respiratory Health. Dr. Carson, Dr. Leon, Dr. Gibson, and Dr. Mazer reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023