ECG Challenge
It Reminds Him of When His Heart “Got Very Sick”
An 84-year-old man is transferred to your facility from a skilled nursing facility (SNF). During the routine morning vital signs check, the...
Lyle W. Larson, PhD, PA-C, is clinical faculty in the Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Cardiac Electrophysiology, at the University of Washington, Seattle.
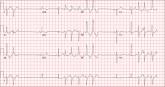
A 54-year-old man presents with a four-day history of productive cough, low-grade fever, and malaise. The patient, a long-haul trucker, has been on the road for the past 30 days, traveling from Florida to California, and then to New Jersey. He first noticed a change in his cough after leaving Chicago. He says he’s tried OTC cough syrups to no avail, and he wants you to prescribe antibiotics so he can get back to work. He denies blood in his sputum; the specimen he provides on request is yellow, mucoid, and malodorous. You know this patient well: He has been in your patient panel for the past five years. His active problem list includes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and heavy tobacco use. He is rarely compliant with any of the treatment regimens you prescribe, and he frequently misses scheduled appointments due to his job. The patient is divorced, with no children, and spends most of his time on the road. His family history is remarkable for diabetes and hypertension in both parents. He had a history of binge drinking in his early 20s but has never had a citation for driving under the influence. He denies current recreational drug use, but he admits to using amphetamines prior to his employer’s mandatory drug monitoring. He smokes 2 to 2.5 packs of cigarettes per day and always has one in his mouth. His surgical history includes appendectomy and cholecystectomy, as well as two laparoscopic procedures for abdominal adhesions. His current medication list includes an albuterol inhaler, hydrochlorothiazide, metoprolol, and metformin; however, he states he rarely takes any of them on a daily basis. He is allergic to tetracycline, which produces urticaria and a rash. Vital signs include a blood pressure of 168/114 mm Hg; pulse, 80 beats/min; respiratory rate, 14 breaths/min-1; O2 saturation, 92% on room air; and temperature, 101°F. The review of systems is positive for headaches, toothache in numbers 13 and 14, and bleeding hemorrhoids. The remainder of the review is noncontributory. The physical exam reveals a disheveled male who appears uncomfortable and diaphoretic. His weight is 314 lb and his height, 70 in. Pertinent physical findings include consolidation in the right lower chest that does not change with coughing. He has coarse respiratory sounds in all other lung fields. There are no murmurs or rubs; however, there is a fixed, split-second heart sound that you haven’t heard in previous exams. The patient’s abdomen is rotund and nontender, with wellhealed surgical scars. Two large, inflamed hemorrhoids are present, and a stool guaiac test is positive for blood. The peripheral exam reveals 2+ bilateral pitting edema. All pulses are full, and there are no focal neurologic abnormalities. Given your concern about the unfamiliar heart sound, you order an ECG in addition to laboratory bloodwork and chest x-ray. The white blood cell count measures 12.4 x 1,000 μL, and the chest xray is consistent with right lower lobe pneumonia. The ECG reveals a ventricular rate of 82 beats/min; PR interval, 148 ms; QRS duration, 82 ms; QT/QTc interval, 378/441 ms; P axis, 42°; R wave axis, 20°; and T axis, 96°. What is your interpretation of this ECG?
ANSWER
The correct interpretation of this ECG includes normal sinus rhythm, biatrial enlargement, nonspecific ST-T wave abnormality, and an RSR’ or QR pattern in V1, suggestive of right ventricular conduction delay.
Biatrial enlargement by definition encompasses right atrial enlargement (criteria include P waves in leads II, III, and aVF measuring 2.5 mm or more) and left atrial enlargement (evidenced by P waves in lead I ≥ 110 ms, and a biphasic, or “notched,” P wave with terminal negativity in lead V1).
Lead V1 may be interpreted as either an RSR’ or a QR pattern. However, the QRS duration of < 120 ms precludes this from meeting criteria for a right bundle branch block.
Finally, nonspecific ST-T wave changes were present in the precordial leads. These may be consistent with pulmonary disease.

An 84-year-old man is transferred to your facility from a skilled nursing facility (SNF). During the routine morning vital signs check, the...
An 82-year-old man is referred from a nearby Alzheimer care facility following an episode of postural hypotension. While trying to get out of bed...

A 47-year-old man presents with a five-day history of chest discomfort that he describes as vague and achy but not painful.
