User login
Lichenoid dermatoses are a heterogeneous group of diseases with varying clinical presentations. The term “lichenoid” refers to the popular lesions of certain skin disorders of which lichen planus (LP) is the prototype. The papules are shiny, flat topped, polygonal, of different sizes, and occur in clusters creating a pattern that resembles lichen growing on a rock. Lichenoid eruptions are quite common in children and can result from many different origins. In most instances the precise mechanism of disease is not known, although it is usually believed to be immunologic in nature. Certain disorders are common in children, whereas others more often affect the adult population.
Lichen striatus, lichen nitidus (LN), and lichen spinulosus are lichenoid lesions that are more common in children than adults.
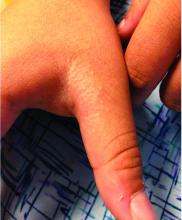
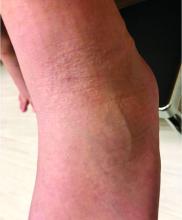
LN – as seen in the patient described here – is an uncommon benign inflammatory skin disease, primarily of children. Individual lesions are sharply demarcated, pinpoint to pinhead sized, round or polygonal, and strikingly monomorphous in nature. The papules are usually flesh colored, however, the color varies from yellow and brown to violet hues depending on the background color of the patient’s skin. This variation in color is in contrast with LP which is characteristically violaceous. The surfaces of the papules are flat, shiny, and slightly elevated. They may have a fine scale or a hyperkeratotic plug. The lesions tend to occur in groups, primarily on the abdomen, chest, glans penis, and upper extremities. The Koebner phenomenon is observed and is a hallmark for the disorder. LN is generally asymptomatic, unlike LP, which is exceedingly pruritic.
The cause of LN is unknown; however, it has been proposed that LN, in particular generalized LN, may be associated with immune alterations in the patient. The course of LN is slowly progressive with a tendency toward remission. The lesions can remain stationary for years; however, they sometimes disappear spontaneously and completely.
The differential diagnosis of LN beyond the entities discussed above includes frictional lichenoid eruption, lichenoid drug eruption, LP, and keratosis pilaris.
LP is the classic lichenoid eruption. It is rare in children and occurs most frequently in individuals aged 30-60 years. LP usually manifests as an extremely pruritic eruption of flat-topped polygonal and violaceous papules that often have fine linear white scales known as Wickham striae. The distribution is usually bilateral and symmetric with most of the papules and plaques located on the legs, flexor wrists, neck, and genitalia. The lesions may exhibit the Koebner phenomenon, appearing in a linear pattern along the site of a scratch. Generally, in childhood cases there is reported itching, and oral and nail lesions are less common.
Frictional lichenoid eruption occurs in childhood. The lesions consist of lichenoid papules with regular borders 1-2 mm in diameter that generally are asymptomatic, although they may be mildly pruritic. The papules are found in a very characteristic distribution with almost exclusive involvement of the backs of the hands, fingers, elbows, and knees with occasional involvement of the extensor forearms and cheeks. This disorder occurs in predisposed children who have been exposed to significant frictional force during play, and typically resolves spontaneously after removal of the stimulus.
Keratosis pilaris is a rash that usually is found on the outer areas of the upper arms, upper thighs, buttocks, and cheeks. It consists of small bumps that are flesh colored to red. The bumps generally don’t hurt or itch.
The lack of symptoms and spontaneous healing have rendered treatment unnecessary in most cases. LN generally is self-limiting, thus treatment may not be necessary. However, topical treatment with mid- to high-potency corticosteroids has hastened resolution of lesions in some children, as have topical dinitrochlorobenzene and systemic treatment with psoralens, astemizole, etretinate, and psoralen-UVA.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Eichenfield nor Dr. Bhatti has any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
Pickert A. Cutis. 2012 Sep;90(3):E1-3. https://mdedge-files-live.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/files/s3fs-public/Document/September-2017/0900300E1.pdf Tziotzios C et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Nov;79(5):789-804. Tilly JJ et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
Lichenoid dermatoses are a heterogeneous group of diseases with varying clinical presentations. The term “lichenoid” refers to the popular lesions of certain skin disorders of which lichen planus (LP) is the prototype. The papules are shiny, flat topped, polygonal, of different sizes, and occur in clusters creating a pattern that resembles lichen growing on a rock. Lichenoid eruptions are quite common in children and can result from many different origins. In most instances the precise mechanism of disease is not known, although it is usually believed to be immunologic in nature. Certain disorders are common in children, whereas others more often affect the adult population.
Lichen striatus, lichen nitidus (LN), and lichen spinulosus are lichenoid lesions that are more common in children than adults.
LN – as seen in the patient described here – is an uncommon benign inflammatory skin disease, primarily of children. Individual lesions are sharply demarcated, pinpoint to pinhead sized, round or polygonal, and strikingly monomorphous in nature. The papules are usually flesh colored, however, the color varies from yellow and brown to violet hues depending on the background color of the patient’s skin. This variation in color is in contrast with LP which is characteristically violaceous. The surfaces of the papules are flat, shiny, and slightly elevated. They may have a fine scale or a hyperkeratotic plug. The lesions tend to occur in groups, primarily on the abdomen, chest, glans penis, and upper extremities. The Koebner phenomenon is observed and is a hallmark for the disorder. LN is generally asymptomatic, unlike LP, which is exceedingly pruritic.
The cause of LN is unknown; however, it has been proposed that LN, in particular generalized LN, may be associated with immune alterations in the patient. The course of LN is slowly progressive with a tendency toward remission. The lesions can remain stationary for years; however, they sometimes disappear spontaneously and completely.
The differential diagnosis of LN beyond the entities discussed above includes frictional lichenoid eruption, lichenoid drug eruption, LP, and keratosis pilaris.
LP is the classic lichenoid eruption. It is rare in children and occurs most frequently in individuals aged 30-60 years. LP usually manifests as an extremely pruritic eruption of flat-topped polygonal and violaceous papules that often have fine linear white scales known as Wickham striae. The distribution is usually bilateral and symmetric with most of the papules and plaques located on the legs, flexor wrists, neck, and genitalia. The lesions may exhibit the Koebner phenomenon, appearing in a linear pattern along the site of a scratch. Generally, in childhood cases there is reported itching, and oral and nail lesions are less common.
Frictional lichenoid eruption occurs in childhood. The lesions consist of lichenoid papules with regular borders 1-2 mm in diameter that generally are asymptomatic, although they may be mildly pruritic. The papules are found in a very characteristic distribution with almost exclusive involvement of the backs of the hands, fingers, elbows, and knees with occasional involvement of the extensor forearms and cheeks. This disorder occurs in predisposed children who have been exposed to significant frictional force during play, and typically resolves spontaneously after removal of the stimulus.
Keratosis pilaris is a rash that usually is found on the outer areas of the upper arms, upper thighs, buttocks, and cheeks. It consists of small bumps that are flesh colored to red. The bumps generally don’t hurt or itch.
The lack of symptoms and spontaneous healing have rendered treatment unnecessary in most cases. LN generally is self-limiting, thus treatment may not be necessary. However, topical treatment with mid- to high-potency corticosteroids has hastened resolution of lesions in some children, as have topical dinitrochlorobenzene and systemic treatment with psoralens, astemizole, etretinate, and psoralen-UVA.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Eichenfield nor Dr. Bhatti has any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
Pickert A. Cutis. 2012 Sep;90(3):E1-3. https://mdedge-files-live.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/files/s3fs-public/Document/September-2017/0900300E1.pdf Tziotzios C et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Nov;79(5):789-804. Tilly JJ et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
Lichenoid dermatoses are a heterogeneous group of diseases with varying clinical presentations. The term “lichenoid” refers to the popular lesions of certain skin disorders of which lichen planus (LP) is the prototype. The papules are shiny, flat topped, polygonal, of different sizes, and occur in clusters creating a pattern that resembles lichen growing on a rock. Lichenoid eruptions are quite common in children and can result from many different origins. In most instances the precise mechanism of disease is not known, although it is usually believed to be immunologic in nature. Certain disorders are common in children, whereas others more often affect the adult population.
Lichen striatus, lichen nitidus (LN), and lichen spinulosus are lichenoid lesions that are more common in children than adults.
LN – as seen in the patient described here – is an uncommon benign inflammatory skin disease, primarily of children. Individual lesions are sharply demarcated, pinpoint to pinhead sized, round or polygonal, and strikingly monomorphous in nature. The papules are usually flesh colored, however, the color varies from yellow and brown to violet hues depending on the background color of the patient’s skin. This variation in color is in contrast with LP which is characteristically violaceous. The surfaces of the papules are flat, shiny, and slightly elevated. They may have a fine scale or a hyperkeratotic plug. The lesions tend to occur in groups, primarily on the abdomen, chest, glans penis, and upper extremities. The Koebner phenomenon is observed and is a hallmark for the disorder. LN is generally asymptomatic, unlike LP, which is exceedingly pruritic.
The cause of LN is unknown; however, it has been proposed that LN, in particular generalized LN, may be associated with immune alterations in the patient. The course of LN is slowly progressive with a tendency toward remission. The lesions can remain stationary for years; however, they sometimes disappear spontaneously and completely.
The differential diagnosis of LN beyond the entities discussed above includes frictional lichenoid eruption, lichenoid drug eruption, LP, and keratosis pilaris.
LP is the classic lichenoid eruption. It is rare in children and occurs most frequently in individuals aged 30-60 years. LP usually manifests as an extremely pruritic eruption of flat-topped polygonal and violaceous papules that often have fine linear white scales known as Wickham striae. The distribution is usually bilateral and symmetric with most of the papules and plaques located on the legs, flexor wrists, neck, and genitalia. The lesions may exhibit the Koebner phenomenon, appearing in a linear pattern along the site of a scratch. Generally, in childhood cases there is reported itching, and oral and nail lesions are less common.
Frictional lichenoid eruption occurs in childhood. The lesions consist of lichenoid papules with regular borders 1-2 mm in diameter that generally are asymptomatic, although they may be mildly pruritic. The papules are found in a very characteristic distribution with almost exclusive involvement of the backs of the hands, fingers, elbows, and knees with occasional involvement of the extensor forearms and cheeks. This disorder occurs in predisposed children who have been exposed to significant frictional force during play, and typically resolves spontaneously after removal of the stimulus.
Keratosis pilaris is a rash that usually is found on the outer areas of the upper arms, upper thighs, buttocks, and cheeks. It consists of small bumps that are flesh colored to red. The bumps generally don’t hurt or itch.
The lack of symptoms and spontaneous healing have rendered treatment unnecessary in most cases. LN generally is self-limiting, thus treatment may not be necessary. However, topical treatment with mid- to high-potency corticosteroids has hastened resolution of lesions in some children, as have topical dinitrochlorobenzene and systemic treatment with psoralens, astemizole, etretinate, and psoralen-UVA.
Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Bhatti is a research fellow in pediatric dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, San Diego. Neither Dr. Eichenfield nor Dr. Bhatti has any relevant financial disclosures. Email them at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
Pickert A. Cutis. 2012 Sep;90(3):E1-3. https://mdedge-files-live.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/files/s3fs-public/Document/September-2017/0900300E1.pdf Tziotzios C et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Nov;79(5):789-804. Tilly JJ et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
A 9-year-old healthy Kuwaiti male with no significant past medical history presents with a rash on his hands and feet that has been present for 3 years.
His mother reports that he has been seen by dermatologists in various countries and was last seen by a dermatologist in Kuwait 3 years ago. At that time, he was told that it was dryness and advised to not shower daily. Since then he has been taking showers three times weekly and using Cetaphil once weekly without improvement. He was seen by his pediatrician 6 months ago, diagnosed with xerosis, and was given hydrocortisone 2.5% to use twice daily, again without any improvement.
The rash is not itchy, and he has no oral lesions or nail involvement. Exam revealed lichenoid papules on bilateral dorsal hands and feet, bilateral upper arms, bilateral axilla, lower abdomen, and left upper chest.