User login
Case Report
A 19-year-old man first presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of a rash on the elbows and knees of 2 to 3 months’ duration. The lesions were asymptomatic. A review of symptoms including joint pain was largely negative. His medical history was remarkable for terminal ileitis, Crohn disease, anal fissure, rhabdomyolysis, and viral gastroenteritis. Physical examination revealed a well-nourished man with red, scaly, indurated papules and plaques involving approximately 0.5% of the body surface area. A diagnosis of plaque psoriasis was made, and he was treated with topical corticosteroids for 2 weeks and as needed thereafter.
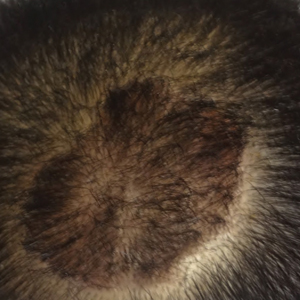
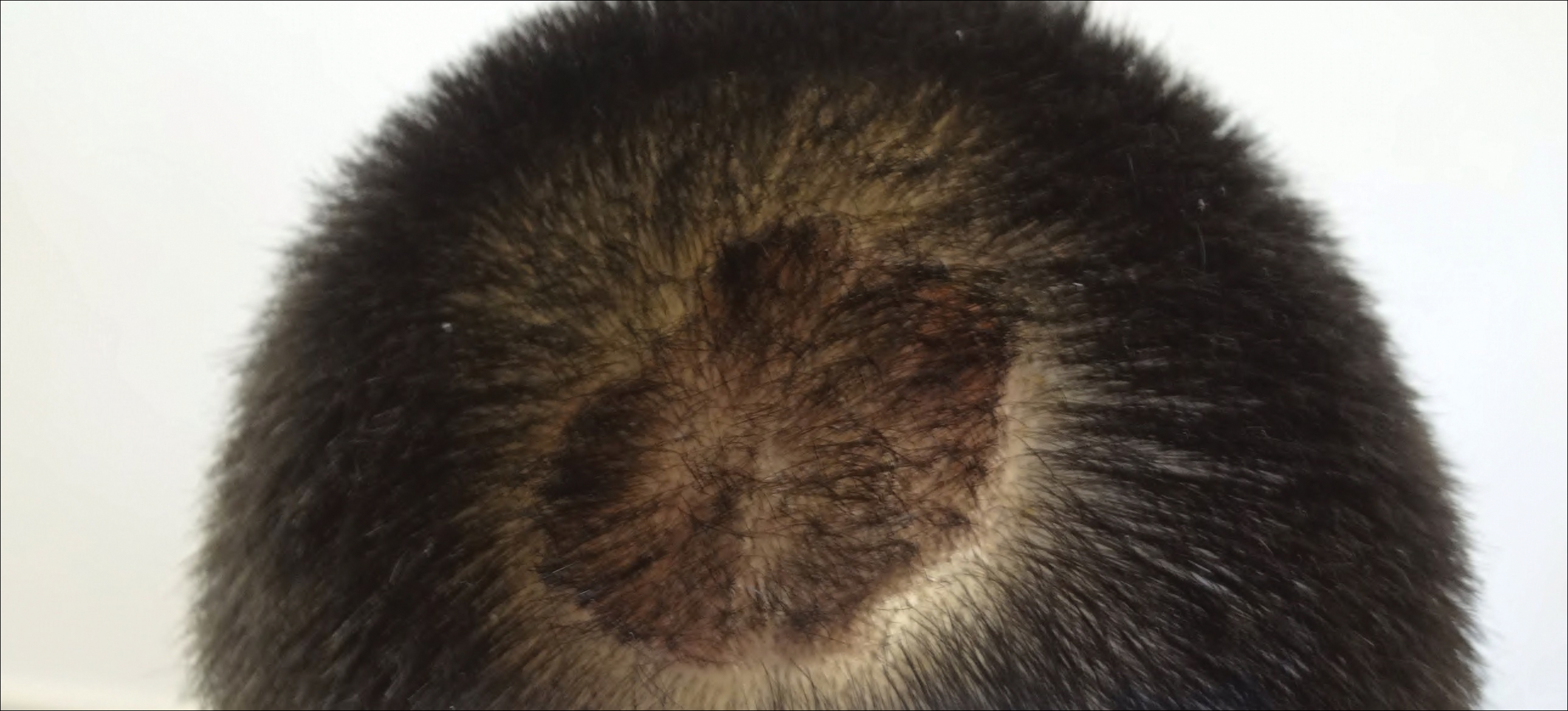
The patient remained stable for 5 years before presenting again to the dermatology clinic for psoriasis that had now spread to the scalp. Clinical examination revealed a very thin, faintly erythematous, scaly patch associated with increased hair density of the right frontal and parietal scalp (Figure). The patient denied any trauma or injury to the area or application of hair dye. We prescribed clobetasol solution 0.05% twice daily to the affected area of the scalp for 2 weeks, which resulted in minimal resolution of the psoriatic scalp lesion.
Comment
The scalp is a site of predilection in psoriasis, as approximately 80% of psoriasis patients report involvement of the scalp.1 Scalp involvement can dramatically affect a patient’s quality of life and often poses considerable therapeutic challenges for dermatologists.1 Alopecia in the setting of scalp psoriasis is common but is not well understood.2 First described by Shuster3 in 1972, psoriatic alopecia is associated with diminished hair density, follicular miniaturization, sebaceous gland atrophy, and an increased number of dystrophic bulbs in psoriatic plaques.4 It clinically presents as pink scaly plaques consistent with psoriasis with overlying alopecia. There are few instances of psoriatic alopecia reported as cicatricial hair loss and generalized telogen effluvium.2 It is known that a higher proportion of telogen and catagen hairs exist in patients with psoriatic alopecia.5 Additionally, psoriasis patients have more dystrophic hairs in affected and unaffected skin despite no differences in skin when compared to unaffected patients. Many patients achieve hair regrowth following treatment of psoriasis.2
We described a patient with scalp psoriasis who had increased and preserved hair density. Our case suggests that while most patients with scalp psoriasis experience psoriatic alopecia of the lesional skin, some may unconventionally experience increased hair density, which is contradictory to propositions that the friction associated with the application of topical treatments results in breakage of telogen hairs.2 Additionally, the presence of increased hair density in scalp psoriasis can further complicate antipsoriatic treatment by making the scalp inaccessible and topical therapies even more difficult to apply.
- Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
- George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
- Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
- Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
- Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
Case Report
A 19-year-old man first presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of a rash on the elbows and knees of 2 to 3 months’ duration. The lesions were asymptomatic. A review of symptoms including joint pain was largely negative. His medical history was remarkable for terminal ileitis, Crohn disease, anal fissure, rhabdomyolysis, and viral gastroenteritis. Physical examination revealed a well-nourished man with red, scaly, indurated papules and plaques involving approximately 0.5% of the body surface area. A diagnosis of plaque psoriasis was made, and he was treated with topical corticosteroids for 2 weeks and as needed thereafter.
The patient remained stable for 5 years before presenting again to the dermatology clinic for psoriasis that had now spread to the scalp. Clinical examination revealed a very thin, faintly erythematous, scaly patch associated with increased hair density of the right frontal and parietal scalp (Figure). The patient denied any trauma or injury to the area or application of hair dye. We prescribed clobetasol solution 0.05% twice daily to the affected area of the scalp for 2 weeks, which resulted in minimal resolution of the psoriatic scalp lesion.

Comment
The scalp is a site of predilection in psoriasis, as approximately 80% of psoriasis patients report involvement of the scalp.1 Scalp involvement can dramatically affect a patient’s quality of life and often poses considerable therapeutic challenges for dermatologists.1 Alopecia in the setting of scalp psoriasis is common but is not well understood.2 First described by Shuster3 in 1972, psoriatic alopecia is associated with diminished hair density, follicular miniaturization, sebaceous gland atrophy, and an increased number of dystrophic bulbs in psoriatic plaques.4 It clinically presents as pink scaly plaques consistent with psoriasis with overlying alopecia. There are few instances of psoriatic alopecia reported as cicatricial hair loss and generalized telogen effluvium.2 It is known that a higher proportion of telogen and catagen hairs exist in patients with psoriatic alopecia.5 Additionally, psoriasis patients have more dystrophic hairs in affected and unaffected skin despite no differences in skin when compared to unaffected patients. Many patients achieve hair regrowth following treatment of psoriasis.2
We described a patient with scalp psoriasis who had increased and preserved hair density. Our case suggests that while most patients with scalp psoriasis experience psoriatic alopecia of the lesional skin, some may unconventionally experience increased hair density, which is contradictory to propositions that the friction associated with the application of topical treatments results in breakage of telogen hairs.2 Additionally, the presence of increased hair density in scalp psoriasis can further complicate antipsoriatic treatment by making the scalp inaccessible and topical therapies even more difficult to apply.
Case Report
A 19-year-old man first presented to our outpatient dermatology clinic for evaluation of a rash on the elbows and knees of 2 to 3 months’ duration. The lesions were asymptomatic. A review of symptoms including joint pain was largely negative. His medical history was remarkable for terminal ileitis, Crohn disease, anal fissure, rhabdomyolysis, and viral gastroenteritis. Physical examination revealed a well-nourished man with red, scaly, indurated papules and plaques involving approximately 0.5% of the body surface area. A diagnosis of plaque psoriasis was made, and he was treated with topical corticosteroids for 2 weeks and as needed thereafter.
The patient remained stable for 5 years before presenting again to the dermatology clinic for psoriasis that had now spread to the scalp. Clinical examination revealed a very thin, faintly erythematous, scaly patch associated with increased hair density of the right frontal and parietal scalp (Figure). The patient denied any trauma or injury to the area or application of hair dye. We prescribed clobetasol solution 0.05% twice daily to the affected area of the scalp for 2 weeks, which resulted in minimal resolution of the psoriatic scalp lesion.

Comment
The scalp is a site of predilection in psoriasis, as approximately 80% of psoriasis patients report involvement of the scalp.1 Scalp involvement can dramatically affect a patient’s quality of life and often poses considerable therapeutic challenges for dermatologists.1 Alopecia in the setting of scalp psoriasis is common but is not well understood.2 First described by Shuster3 in 1972, psoriatic alopecia is associated with diminished hair density, follicular miniaturization, sebaceous gland atrophy, and an increased number of dystrophic bulbs in psoriatic plaques.4 It clinically presents as pink scaly plaques consistent with psoriasis with overlying alopecia. There are few instances of psoriatic alopecia reported as cicatricial hair loss and generalized telogen effluvium.2 It is known that a higher proportion of telogen and catagen hairs exist in patients with psoriatic alopecia.5 Additionally, psoriasis patients have more dystrophic hairs in affected and unaffected skin despite no differences in skin when compared to unaffected patients. Many patients achieve hair regrowth following treatment of psoriasis.2
We described a patient with scalp psoriasis who had increased and preserved hair density. Our case suggests that while most patients with scalp psoriasis experience psoriatic alopecia of the lesional skin, some may unconventionally experience increased hair density, which is contradictory to propositions that the friction associated with the application of topical treatments results in breakage of telogen hairs.2 Additionally, the presence of increased hair density in scalp psoriasis can further complicate antipsoriatic treatment by making the scalp inaccessible and topical therapies even more difficult to apply.
- Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
- George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
- Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
- Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
- Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
- Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:280-284.
- George SM, Taylor MR, Farrant PB. Psoriatic alopecia. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40:717-721.
- Shuster S. Psoriatic alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:73-77.
- Wyatt E, Bottoms E, Comaish S. Abnormal hair shafts in psoriasis on scanning electron microscopy. Br J Dermatol. 1972;87:368-373.
- Schoorl WJ, van Baar HJ, van de Kerkhof PC. The hair root pattern in psoriasis of the scalp. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992;72:141-142.
Practice Points
- Scalp psoriasis may present with hair loss or increased hair density.
- Psoriasis with increased hair density may make topical medications more difficult to apply.