User login
Doctor, doctor, gimme the news. I got a bad case of knowing better than you
Stop us if you’ve heard this before. One of your parents (let’s be honest, probably your ornery father) refuses to go to the doctor. You tell him it’s for the best, but in his words, “Doctors don’t know nothin’. I’m fine.” How many TV shows with grumpy fathers feature this exact plot in an episode as the frustrated child attempts increasingly convoluted traps to encourage the stubborn parent to get himself to the doctor?
As is so often the case, wacky sitcoms reflect reality, according to a new study from the Journal of the Economics of Aging. In a massive survey of 80,000 Europeans aged 50 years and older, the researchers found that individuals who were overconfident and rated their health as better than it actually was visited their doctor 17% less often than did those who correctly judge their own health. Fewer medical visits leaves them more vulnerable to chronic disease, since they’re not getting the preventive care they need to catch illnesses early.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, the inverse is also true: People who underestimate their health status visit the doctor 21% more often. On the one hand, regular visits to the doctor are a good thing, as is awareness of how healthy one really is. On the other hand, though, extra visits cost money and time, especially relevant in an aging society with high public health costs.
Nobody likes visiting the doctor, but it is kind of important, especially as we age and our bodies start to let us down. Confidence is fine, but don’t be overly confident. And if you do go, don’t be like a certain former president of the United States. Don’t pay a sycophant to look in your general direction and then declare that you are in very good (great!) condition on Twitter. That’s not how medicine is meant to work.
Your liver stays toddler age
Rapid cell regeneration might seem like something straight out of a sci-fi novel, but it happens to your liver all the time. So much so that the human liver is never a day over 3 years old.
How’s that possible? The liver deals with a lot of toxic substances in its job as the Brita filter of the human body, so it has a unique capacity among organs to regenerate itself after damage.
Dr. Olaf Bergmann and his team at Technical University Dresden’s (Germany) Center for Regenerative Therapies used retrospective radiocarbon birth dating to determine the age of the livers of a group of people who died at the ages of 20-84 years. The results were the same regardless of age.
This information could be a complete game changer for understanding cell regeneration. It’s important in determining cancer cell formation in the liver but also if new heart muscle cells can be generated in people with cardiovascular disease, which the researchers are looking into.
So sure, your liver may be totally capable of filtering those drinks at happy hour, but as old as it is, a juice box might be more appropriate.
To bee, or not to bee? That is the vacation
Sleeping is pretty important for humans, no doubt about that, so anything that improves sleep is worth considering, right? But how far would you go for a good night’s sleep? Would you be willing to travel to Italy to experience the ultimate white-noise generator?
For more on this exciting, yet also sleep-inducing, news story, let’s go to the village of Grottole in southern Italy, where we meet bee keeper and Airbnb host Rocco Filomeno. ”This is the first place in the world where you can sleep immersed in the distinctive sound and aroma of the bees, experiencing ‘bee-therapy’ in the most authentic and natural way,” he said in a written statement for Airbnb.
Mr. Filomeno worked with local NGO Wonder Grottole and a self-build specialist to take the next step in tiny-house evolution. The resulting structure cost just $17,000 – crowdfunded, of course, and built by 25 local bee-lievers (aka volunteers) – and consists of a single room surrounded by nine apiaries, which contain a combined total of 1 million working bees. It is now available to book on Airbnb, and guests “will receive their first lesson on bees and how to live with them,” Airbnb said.
The immersion in bee sound/scent is fully realized through the building’s most prominent interior feature, a screened box in the ceiling with a working hive that allows guests to see the bees and fall asleep to the “gently humming sound,” Airbnb explained. The sound from the hive is said to have a soothing effect that “acts as salve to day-to-day stressors,” according to the BBC.
This is just the start of a trend and we want in on it. Should our tiny house feature the sights/smells/sounds of angry rattlesnakes or a swarm of locusts?
Joysticks can make the world a better place
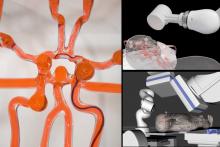
Someday, it might be possible for surgeons to treat a stroke or aneurysm during the “golden hour,” even if they’re not in the same hospital as the patient. MIT engineers have created a robotic system that can be controlled remotely with a modified joystick, so the patient can go to a closer, smaller hospital and be treated by a surgeon at a larger facility through live imaging.
Endovascular surgery seems difficult enough with the patient and doctor in the same hospital, “but having a robot twist with the same level of sophistication [as a surgeon] is challenging,” Yoonho Kim, lead author of a study in Science Robotics, said in a written statement. “Our system is based on a fundamentally different mechanism.”
It involves “a medical-grade robotic arm with a magnet attached to its wrist. With a joystick and live imaging, an operator can adjust the magnet’s orientation and manipulate the arm to guide a soft and thin magnetic wire through arteries and vessels,” MIT explained in the statement.
The system was tested using life-like models, and it took each surgeon about an hour of training to learn how to use the new joystick and other equipment. Another perk: No exposure to radiation from x-ray imaging.
If someone you know is obsessed with video games, stop thinking “slacker” and start thinking “neurosurgeon.”
Doctor, doctor, gimme the news. I got a bad case of knowing better than you
Stop us if you’ve heard this before. One of your parents (let’s be honest, probably your ornery father) refuses to go to the doctor. You tell him it’s for the best, but in his words, “Doctors don’t know nothin’. I’m fine.” How many TV shows with grumpy fathers feature this exact plot in an episode as the frustrated child attempts increasingly convoluted traps to encourage the stubborn parent to get himself to the doctor?
As is so often the case, wacky sitcoms reflect reality, according to a new study from the Journal of the Economics of Aging. In a massive survey of 80,000 Europeans aged 50 years and older, the researchers found that individuals who were overconfident and rated their health as better than it actually was visited their doctor 17% less often than did those who correctly judge their own health. Fewer medical visits leaves them more vulnerable to chronic disease, since they’re not getting the preventive care they need to catch illnesses early.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, the inverse is also true: People who underestimate their health status visit the doctor 21% more often. On the one hand, regular visits to the doctor are a good thing, as is awareness of how healthy one really is. On the other hand, though, extra visits cost money and time, especially relevant in an aging society with high public health costs.
Nobody likes visiting the doctor, but it is kind of important, especially as we age and our bodies start to let us down. Confidence is fine, but don’t be overly confident. And if you do go, don’t be like a certain former president of the United States. Don’t pay a sycophant to look in your general direction and then declare that you are in very good (great!) condition on Twitter. That’s not how medicine is meant to work.
Your liver stays toddler age
Rapid cell regeneration might seem like something straight out of a sci-fi novel, but it happens to your liver all the time. So much so that the human liver is never a day over 3 years old.
How’s that possible? The liver deals with a lot of toxic substances in its job as the Brita filter of the human body, so it has a unique capacity among organs to regenerate itself after damage.
Dr. Olaf Bergmann and his team at Technical University Dresden’s (Germany) Center for Regenerative Therapies used retrospective radiocarbon birth dating to determine the age of the livers of a group of people who died at the ages of 20-84 years. The results were the same regardless of age.
This information could be a complete game changer for understanding cell regeneration. It’s important in determining cancer cell formation in the liver but also if new heart muscle cells can be generated in people with cardiovascular disease, which the researchers are looking into.
So sure, your liver may be totally capable of filtering those drinks at happy hour, but as old as it is, a juice box might be more appropriate.
To bee, or not to bee? That is the vacation
Sleeping is pretty important for humans, no doubt about that, so anything that improves sleep is worth considering, right? But how far would you go for a good night’s sleep? Would you be willing to travel to Italy to experience the ultimate white-noise generator?
For more on this exciting, yet also sleep-inducing, news story, let’s go to the village of Grottole in southern Italy, where we meet bee keeper and Airbnb host Rocco Filomeno. ”This is the first place in the world where you can sleep immersed in the distinctive sound and aroma of the bees, experiencing ‘bee-therapy’ in the most authentic and natural way,” he said in a written statement for Airbnb.
Mr. Filomeno worked with local NGO Wonder Grottole and a self-build specialist to take the next step in tiny-house evolution. The resulting structure cost just $17,000 – crowdfunded, of course, and built by 25 local bee-lievers (aka volunteers) – and consists of a single room surrounded by nine apiaries, which contain a combined total of 1 million working bees. It is now available to book on Airbnb, and guests “will receive their first lesson on bees and how to live with them,” Airbnb said.
The immersion in bee sound/scent is fully realized through the building’s most prominent interior feature, a screened box in the ceiling with a working hive that allows guests to see the bees and fall asleep to the “gently humming sound,” Airbnb explained. The sound from the hive is said to have a soothing effect that “acts as salve to day-to-day stressors,” according to the BBC.
This is just the start of a trend and we want in on it. Should our tiny house feature the sights/smells/sounds of angry rattlesnakes or a swarm of locusts?
Joysticks can make the world a better place
Someday, it might be possible for surgeons to treat a stroke or aneurysm during the “golden hour,” even if they’re not in the same hospital as the patient. MIT engineers have created a robotic system that can be controlled remotely with a modified joystick, so the patient can go to a closer, smaller hospital and be treated by a surgeon at a larger facility through live imaging.
Endovascular surgery seems difficult enough with the patient and doctor in the same hospital, “but having a robot twist with the same level of sophistication [as a surgeon] is challenging,” Yoonho Kim, lead author of a study in Science Robotics, said in a written statement. “Our system is based on a fundamentally different mechanism.”
It involves “a medical-grade robotic arm with a magnet attached to its wrist. With a joystick and live imaging, an operator can adjust the magnet’s orientation and manipulate the arm to guide a soft and thin magnetic wire through arteries and vessels,” MIT explained in the statement.
The system was tested using life-like models, and it took each surgeon about an hour of training to learn how to use the new joystick and other equipment. Another perk: No exposure to radiation from x-ray imaging.
If someone you know is obsessed with video games, stop thinking “slacker” and start thinking “neurosurgeon.”
Doctor, doctor, gimme the news. I got a bad case of knowing better than you
Stop us if you’ve heard this before. One of your parents (let’s be honest, probably your ornery father) refuses to go to the doctor. You tell him it’s for the best, but in his words, “Doctors don’t know nothin’. I’m fine.” How many TV shows with grumpy fathers feature this exact plot in an episode as the frustrated child attempts increasingly convoluted traps to encourage the stubborn parent to get himself to the doctor?
As is so often the case, wacky sitcoms reflect reality, according to a new study from the Journal of the Economics of Aging. In a massive survey of 80,000 Europeans aged 50 years and older, the researchers found that individuals who were overconfident and rated their health as better than it actually was visited their doctor 17% less often than did those who correctly judge their own health. Fewer medical visits leaves them more vulnerable to chronic disease, since they’re not getting the preventive care they need to catch illnesses early.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, the inverse is also true: People who underestimate their health status visit the doctor 21% more often. On the one hand, regular visits to the doctor are a good thing, as is awareness of how healthy one really is. On the other hand, though, extra visits cost money and time, especially relevant in an aging society with high public health costs.
Nobody likes visiting the doctor, but it is kind of important, especially as we age and our bodies start to let us down. Confidence is fine, but don’t be overly confident. And if you do go, don’t be like a certain former president of the United States. Don’t pay a sycophant to look in your general direction and then declare that you are in very good (great!) condition on Twitter. That’s not how medicine is meant to work.
Your liver stays toddler age
Rapid cell regeneration might seem like something straight out of a sci-fi novel, but it happens to your liver all the time. So much so that the human liver is never a day over 3 years old.
How’s that possible? The liver deals with a lot of toxic substances in its job as the Brita filter of the human body, so it has a unique capacity among organs to regenerate itself after damage.
Dr. Olaf Bergmann and his team at Technical University Dresden’s (Germany) Center for Regenerative Therapies used retrospective radiocarbon birth dating to determine the age of the livers of a group of people who died at the ages of 20-84 years. The results were the same regardless of age.
This information could be a complete game changer for understanding cell regeneration. It’s important in determining cancer cell formation in the liver but also if new heart muscle cells can be generated in people with cardiovascular disease, which the researchers are looking into.
So sure, your liver may be totally capable of filtering those drinks at happy hour, but as old as it is, a juice box might be more appropriate.
To bee, or not to bee? That is the vacation
Sleeping is pretty important for humans, no doubt about that, so anything that improves sleep is worth considering, right? But how far would you go for a good night’s sleep? Would you be willing to travel to Italy to experience the ultimate white-noise generator?
For more on this exciting, yet also sleep-inducing, news story, let’s go to the village of Grottole in southern Italy, where we meet bee keeper and Airbnb host Rocco Filomeno. ”This is the first place in the world where you can sleep immersed in the distinctive sound and aroma of the bees, experiencing ‘bee-therapy’ in the most authentic and natural way,” he said in a written statement for Airbnb.
Mr. Filomeno worked with local NGO Wonder Grottole and a self-build specialist to take the next step in tiny-house evolution. The resulting structure cost just $17,000 – crowdfunded, of course, and built by 25 local bee-lievers (aka volunteers) – and consists of a single room surrounded by nine apiaries, which contain a combined total of 1 million working bees. It is now available to book on Airbnb, and guests “will receive their first lesson on bees and how to live with them,” Airbnb said.
The immersion in bee sound/scent is fully realized through the building’s most prominent interior feature, a screened box in the ceiling with a working hive that allows guests to see the bees and fall asleep to the “gently humming sound,” Airbnb explained. The sound from the hive is said to have a soothing effect that “acts as salve to day-to-day stressors,” according to the BBC.
This is just the start of a trend and we want in on it. Should our tiny house feature the sights/smells/sounds of angry rattlesnakes or a swarm of locusts?
Joysticks can make the world a better place
Someday, it might be possible for surgeons to treat a stroke or aneurysm during the “golden hour,” even if they’re not in the same hospital as the patient. MIT engineers have created a robotic system that can be controlled remotely with a modified joystick, so the patient can go to a closer, smaller hospital and be treated by a surgeon at a larger facility through live imaging.
Endovascular surgery seems difficult enough with the patient and doctor in the same hospital, “but having a robot twist with the same level of sophistication [as a surgeon] is challenging,” Yoonho Kim, lead author of a study in Science Robotics, said in a written statement. “Our system is based on a fundamentally different mechanism.”
It involves “a medical-grade robotic arm with a magnet attached to its wrist. With a joystick and live imaging, an operator can adjust the magnet’s orientation and manipulate the arm to guide a soft and thin magnetic wire through arteries and vessels,” MIT explained in the statement.
The system was tested using life-like models, and it took each surgeon about an hour of training to learn how to use the new joystick and other equipment. Another perk: No exposure to radiation from x-ray imaging.
If someone you know is obsessed with video games, stop thinking “slacker” and start thinking “neurosurgeon.”