Case Report
A 49-year-old man with a history of polysubstance abuse presented with intermittent fevers and painful swollen ears as well as joint pain of 3 weeks’ duration. One week after the lesions developed on the ears, similar lesions were seen on the legs, arms, and trunk. He admitted to cocaine use 3 weeks prior to presentation when the symptoms began.
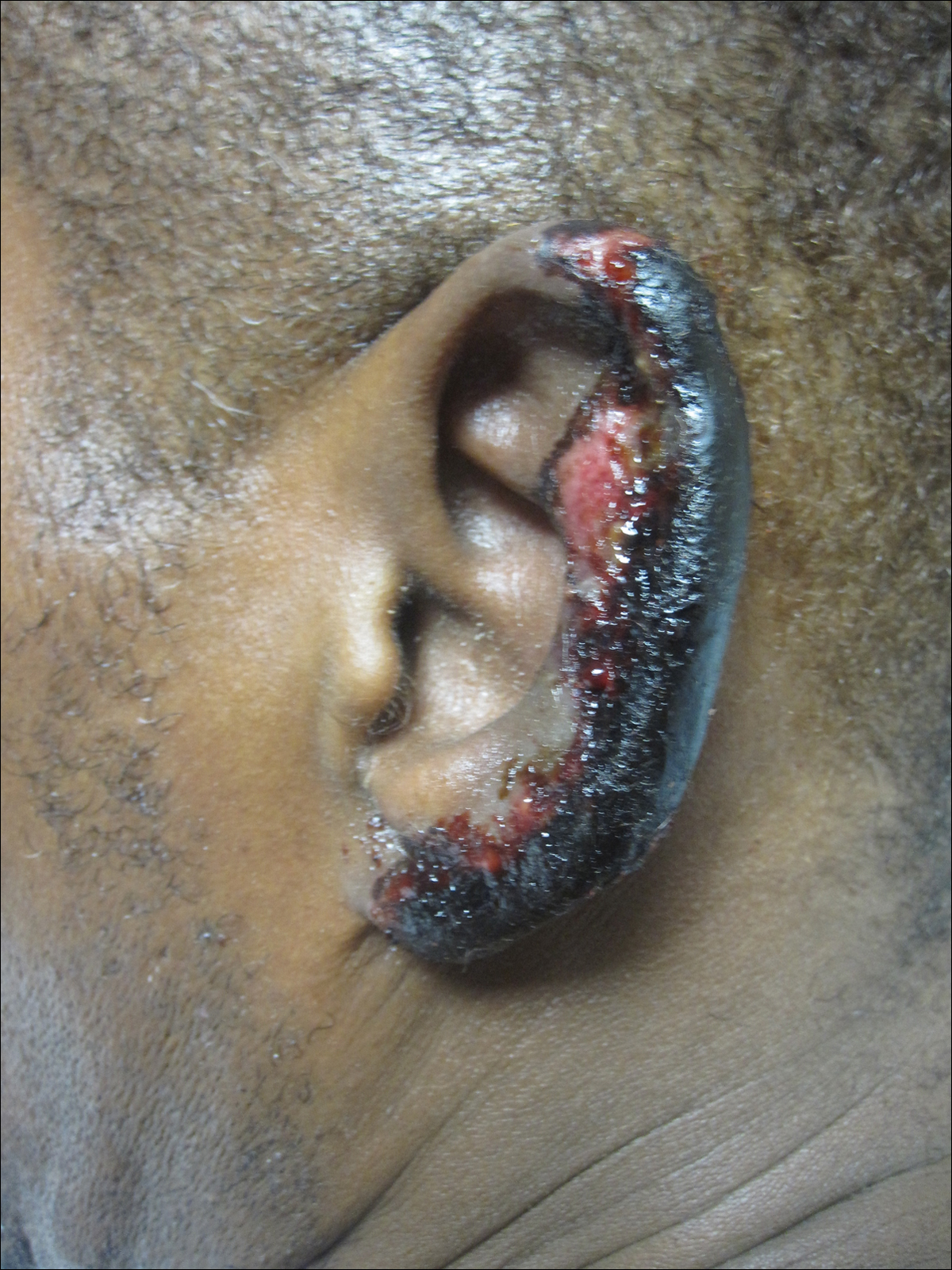
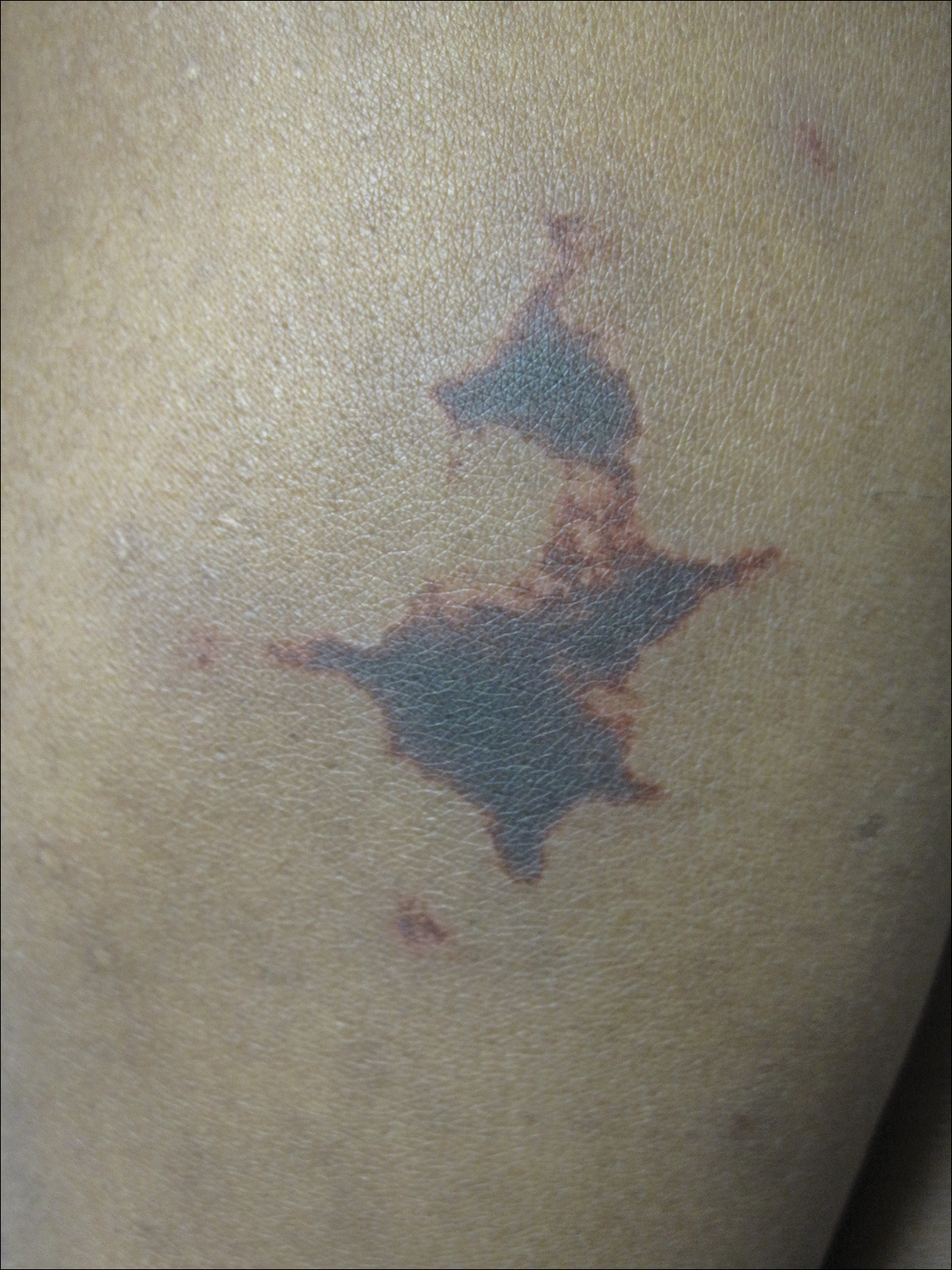
On physical examination, violaceous patches with necrotic bleeding edges and overlying black eschars were noted on the helices, antihelices, and ear lobules bilaterally (Figure 1). Retiform, purpuric to dark brown patches, some with signs of epidermal necrosis, were scattered on the arms, legs, and chest (Figure 2).
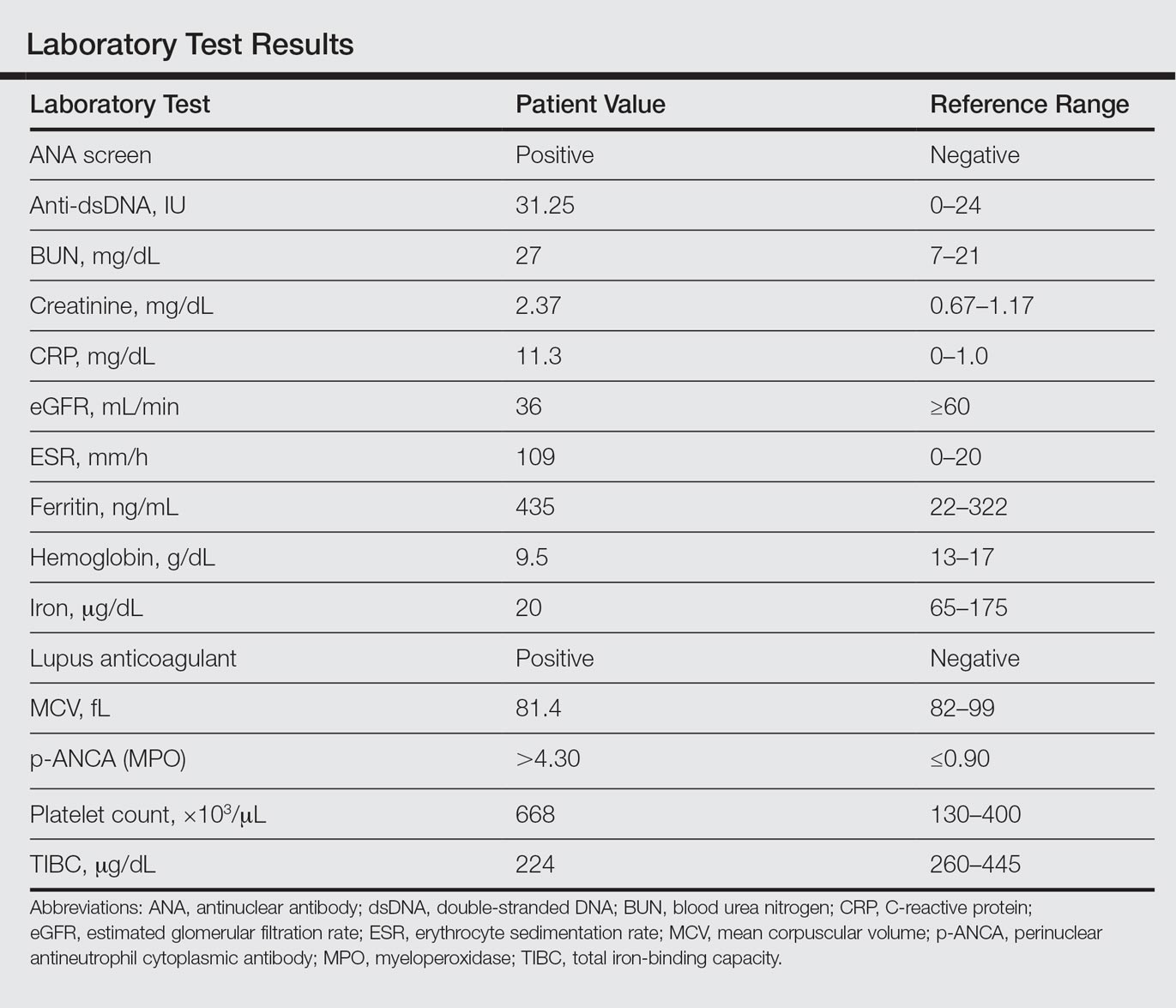
Laboratory examination revealed renal failure, anemia of chronic disease, and thrombocytosis (Table). The patient also screened positive for lupus anticoagulant and antinuclear antibodies and had elevated p-ANCA and anti–double-stranded DNA (Table). He also had an elevated sedimentation rate (109 mm/h [reference range, 0–20 mm/h]) and C-reactive protein level (11.3 mg/dL [reference range, 0–1.0 mg/dL])(Table). Urine toxicology was positive for cocaine.
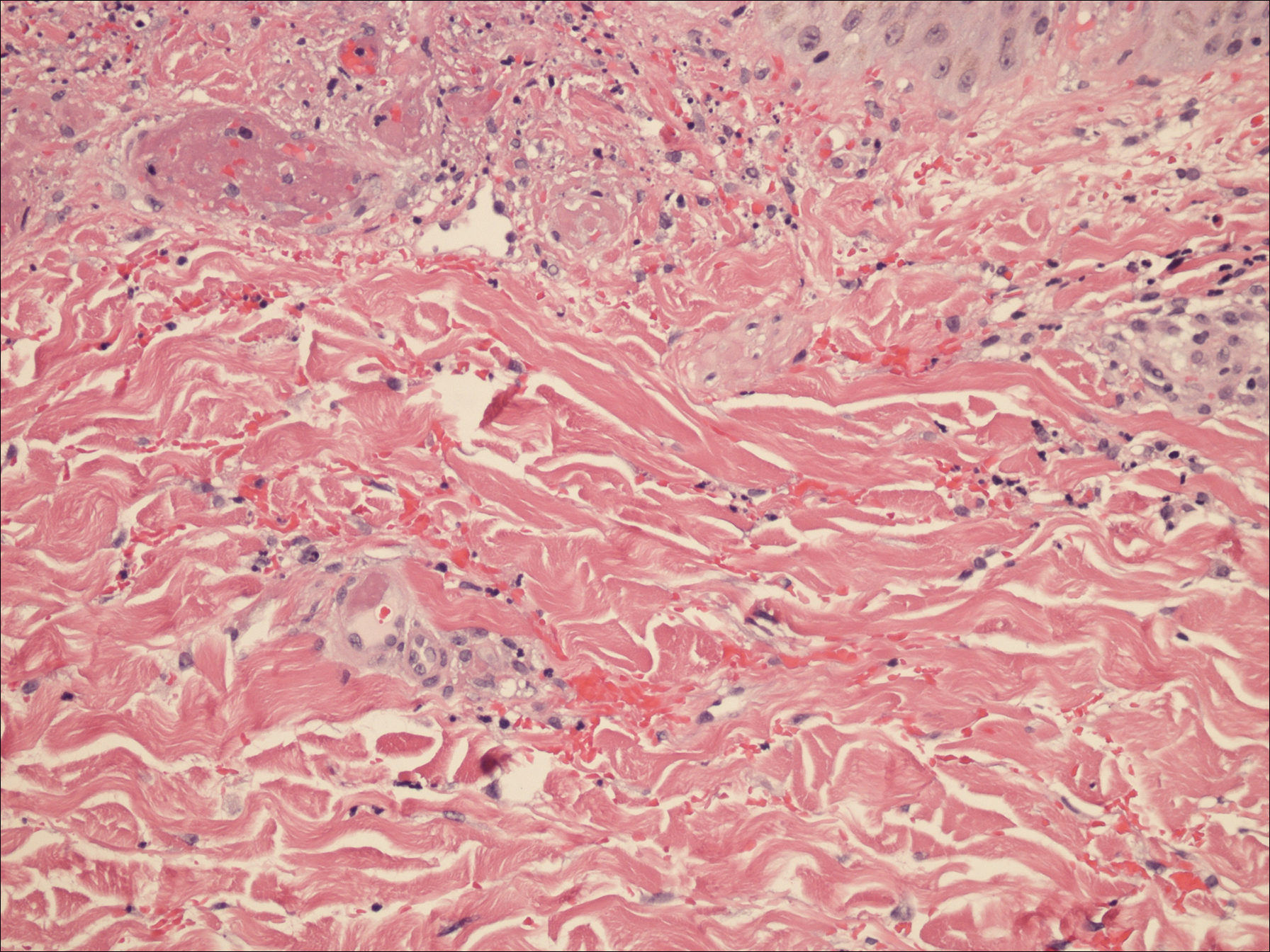
A punch biopsy of the left thigh was performed on the edge of a retiform purpuric patch. Histopathologic examination revealed epidermal necrosis with subjacent intraluminal vascular thrombi along with extravasated red blood cells and neutrophilic debris (leukocytoclasis) and fibrin in and around vessel walls, consistent with vasculitis (Figure 3).
The patient was admitted to the hospital for pain management and wound care. Despite cocaine cessation and oral prednisone taper, the lesions on the legs worsened over the next several weeks. His condition was further complicated by wound infections, nonhealing ulcers, and subjective fevers and chills requiring frequent hospitalization. The patient was managed by the dermatology department as an outpatient and in clinic between hospital visits. He was treated with antibiotics, ulcer debridement, compression wraps, and aspirin (81 mg once daily) with moderate improvement.
Ten weeks after the first visit, the patient returned with worsening and recurrent leg and ear lesions. He denied any cocaine use since the initial hospital admission; however, a toxicology screen was never obtained. It was decided that the patient would need additional treatment along with traditional trigger (cocaine) avoidance and wound care. Combined treatment with aspirin (81 mg once daily), oral prednisone (40 mg once daily), and vardenafil hydrochloride (20 mg twice weekly) was initiated. At the end of week 1, the patient began to exhibit signs of improvement, which continued over the next 4 weeks. He was then lost to follow-up.