Case Report
A 23-year-old woman presented with a horizontal split along the midline of the right great toenail associated with some tenderness of 2 to 3 months’ duration. Approximately 5 years prior, she noticed a bluish-colored area under the nail that had been steadily increasing in size. She denied a history of trauma, drainage, or bleeding. There was no history of other nail abnormalities. Her medications and personal, family, and social history were noncontributory.
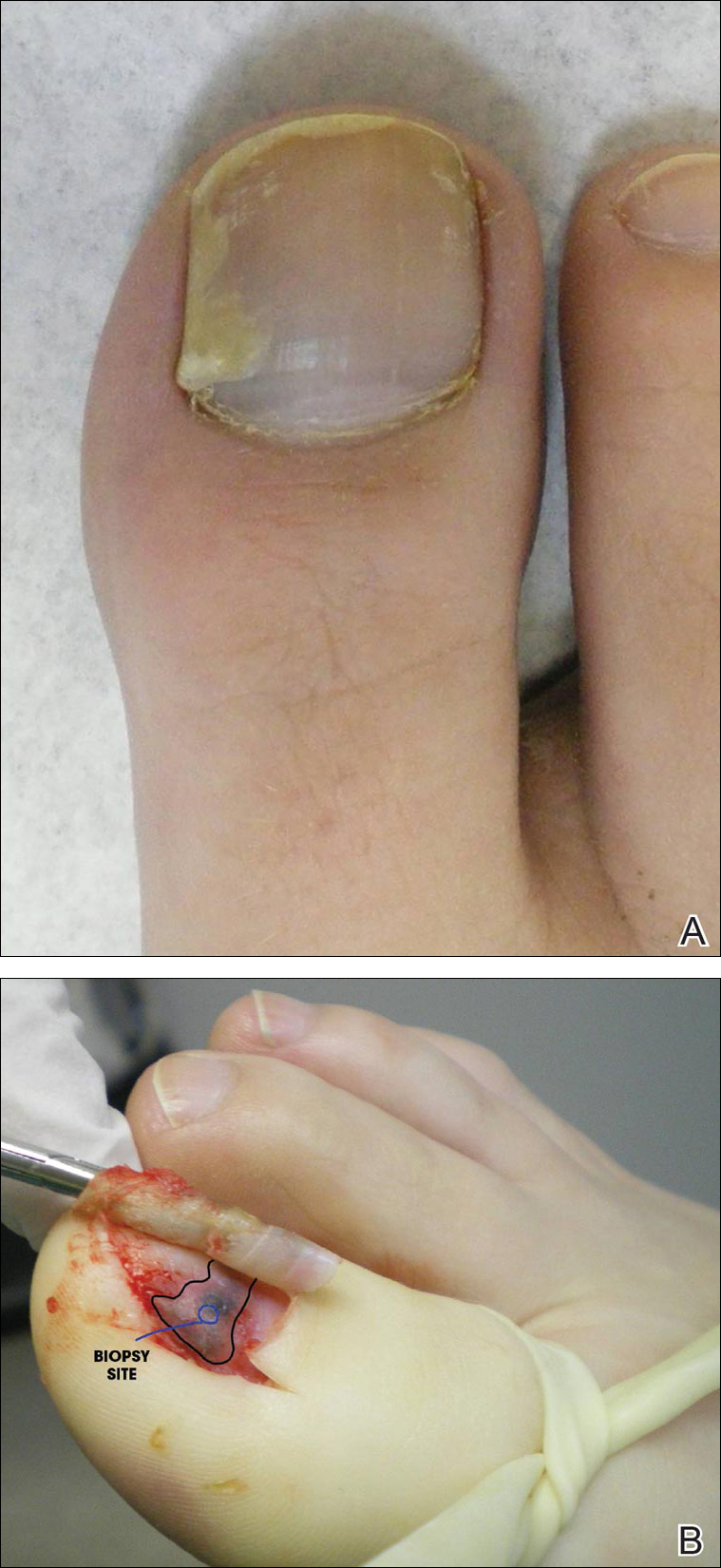
Physical examination of the right great toenail revealed a horizontal split of the nail plate with a bluish hue visible under the nail plate (Figure 1A). The remaining toenails and fingernails were normal. A punch biopsy of the nail bed was performed with a presumptive clinical diagnosis of subungual melanoma versus melanocytic nevus versus cyst (Figure 1B). Nail plate avulsion revealed a blackened nail bed dotted with areas of bluish color and a red friable nodule present focally. Upon further inspection, extension was apparent into the distal matrix.
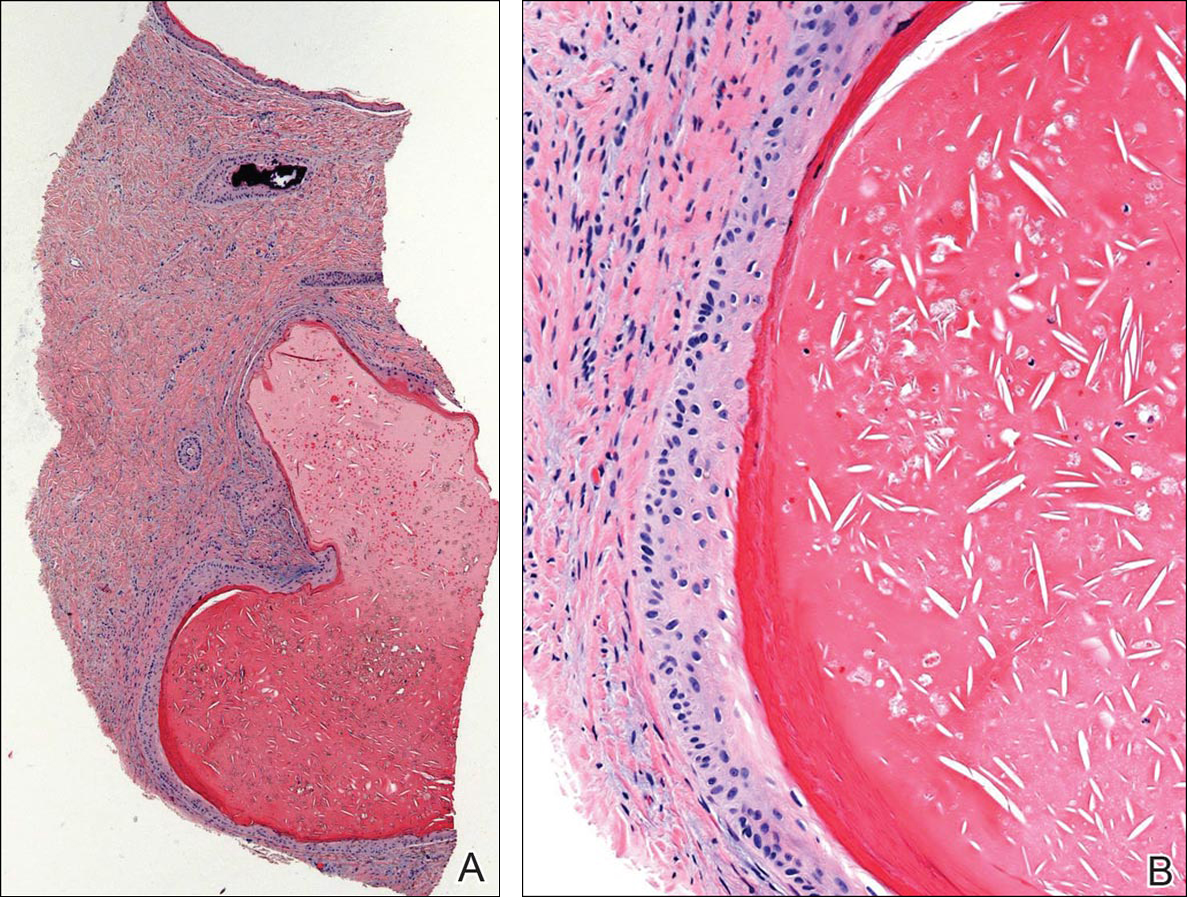
Histopathologic examination revealed a cystic structure with an epithelial lining mostly reminiscent of an isthmus catagen cyst admixed with the presence of both an intermittent focal granular layer and an eosinophilic cuticle surrounding pink laminated keratin, most consistent with a diagnosis of subungual onycholemmal cyst (SOC)(Figure 2). A reexcision was performed with removal of half of the nail bed, including a portion of the distal matrix extending inferiorly to the bone. Variably sized, epithelium-lined, keratin-filled cystic structures emanated from the nail bed epithelium. There were foci of hemorrhage and granulation tissue secondary to cyst rupture (Figure 3). The defect healed by secondary intention. No clinical evidence of recurrence was seen at 6-month follow-up.

Figure 3. The gross specimen after reexcision revealed multiple foci of hemorrhage and brown keratinaceous material (A). Scanning magnification revealed variably sized, epithelium-lined, keratin-filled cystic structures emanating from the nail bed epithelium containing foci of calcification. There was hemorrhage and granulation tissue secondary to cyst rupture (B)(H&E, original magnification ×20).
Subungual onycholemmal cysts, also known as subungual epidermoid cysts or subungual epidermoid inclusions, are rare and distinctive nail abnormalities occurring in the dermis of the nail bed. We present a case of an SOC in a toenail mimicking subungual malignant melanoma.
Originally described by Samman1 in 1959, SOCs were attributed to trauma to the nail with resultant implantation of the epidermis into the deeper tissue. Lewin2,3 examined 90 postmortem fingernail and nail bed samples and found 8 subungual epidermoid cysts associated with clubbing of the fingernails. He postulated that the early pathogenesis of clubbing involved dermal fibroblast proliferation in the nail bed, leading to sequestration of nail bed epithelium into the dermis with resultant cyst formation. Microscopic subungual cysts also were identified in normal-appearing nails without evidence of trauma, thought to have arisen from the tips of the nail bed rete ridges by a process of bulbous proliferation rather than sequestration. These findings in normal nails suggest that SOCs may represent a more common entity than previously recognized.