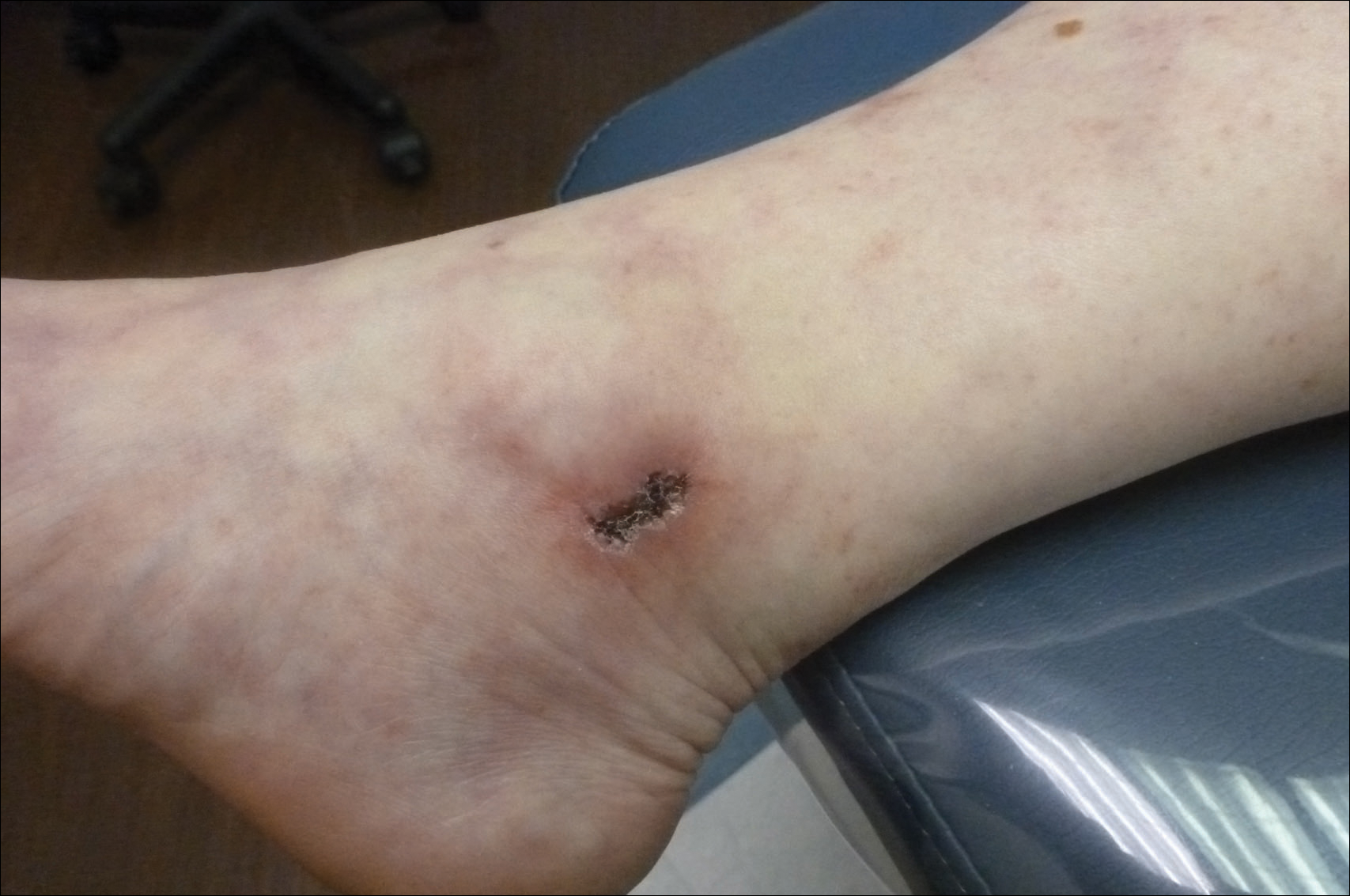
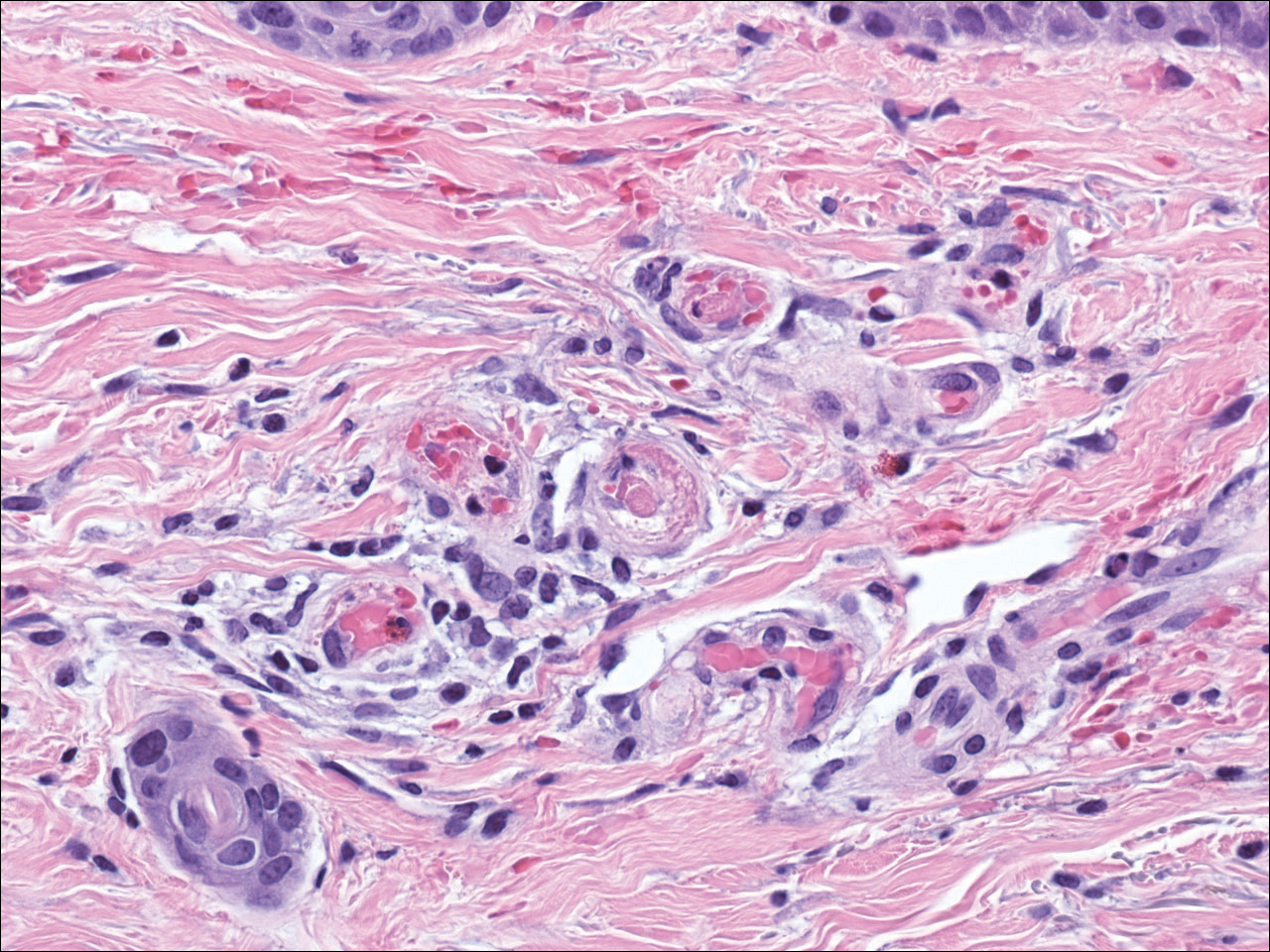
The Diagnosis: Livedoid Vasculopathy
Livedoid vasculopathy (LV) is a rare cutaneous disorder that most commonly affects the lower legs. It has an estimated incidence of 1 case per 100,000 per year and predominantly affects women.1 The disease pathogenesis is not fully understood but is thought to involve thrombosis and occlusion of dermal vessels resulting in tissue hypoxia.2 Both inherited and acquired thrombophilic conditions frequently are seen in patients with LV.3,4 Livedoid vasculopathy also has been described as idiopathic5 and is associated with immune complex deposition.6 However, the number of cases of idiopathic LV may be overestimated; as technological advancements to detect coagulation abnormalities improve, it is hypothesized that this entity will be identified less often.2,4
Livedoid vasculopathy has been described in the literature using the term PPURPLE (painful purpuric ulcers with reticular pattern of lower extremities).7 The triad of livedo racemosa, recurrent painful ulcerations, and residual healing with atrophie blanche characterizes the clinical manifestations of LV; however, all 3 characteristics do not need to appear simultaneously for a diagnosis to be made. The condition has a chronic course with spontaneous remissions and exacerbations. Episodic ulcerations occur, especially in the summertime, and heal slowly, leaving behind atrophic, porcelain white, stellate-shaped scars called atrophie blanche. Livedo racemosa also may be seen in Sneddon syndrome; however, these patients experience neurologic symptoms secondary to cerebrovascular occlusion. In contrast to livedo racemosa, acquired livedo reticularis represents a physiologic hypoperfusion pattern that occurs in response to cold exposure.8 A localized sharp pain, known as angina cutis, typically precedes the clinical symptom of painful ulcerations.9 Atrophie blanche once was thought to be specific to LV but has been seen in other diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and chronic venous insufficiency.2
The diagnosis of LV is based on identification of characteristic clinical features and skin biopsy. In almost all biopsy specimens, histopathology reveals fibrinoid occlusion of vessels in the superficial and mid dermis.4 Other findings may include epidermal necrosis and vessel wall hyalinization and infarction2 (Figure). Because LV is commonly misdiagnosed as vasculitis, the absence of hallmark features of vasculitis such as neutrophilic infiltrate of blood vessel walls and fibrinoid necrosis suggest the diagnosis. Extensive laboratory evaluation for inherited and acquired coagulation abnormalities should be performed.
Treatment of LV is difficult, as there is currently no consensus on optimal therapy. The mainstay of therapy is to reduce pain, prevent infection, and reduce ulceration and development of atrophie blanche. Underlying causes should be identified and appropriately treated. Because the primary pathogenesis of LV is considered to be a hypercoagulable state, first-line treatment often includes therapies to enhance blood flow and prevent thrombosis such as smoking cessation, antiplatelet therapy, and pentoxifylline. Vasodilating agents, anti-inflammatory agents, anticoagulation, and fibrinolytic therapy also have been used with varying degrees of success.7